Hygiene principles (neurological and sensory deficits *stroke, Parkinson’s, dementia, and alzheimers*
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Stroke
This is a generic term used to refer to a cerebrovascular accident. This is a serious often fatal neurological event. The cause: sudden interruption of oxygenated blood to the brain. The result: focal necrosis of brain tissue and possibly death. A survivor often is, to some degree, debilitated in motor function, speech, or mentation. This is the leading cause of long term disability in the US; 5% of the population older than 65 have had this.
6 months
How long is it recommended that stroke survivors do not undergo selective procedures.
Cerebrovascular disease
This is the primary factor associated with strokes. Causes increased risk of thrombolic and embolic strokes associated with atherosclerosis and cardiac pathosis (myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation). Hypertension is the most important risk factor for intracerebral hemorrhagic stroke. Approx 10% of persons who have had an MI will have a stroke within 6 years.
TIA (transient ischemic attack)
This is sometimes referred to as a "mini stroke". Caused by a temporary disturbance in blood supply to a localized area of the brain. these often cause numbness of the face, arm, or leg on one side of the body (hemiplegia), weakness, tingling, numbness, or speech disturbances that usually last less than 10 min. Most commonly, a major stroke is preceded by 1 or 2 of these within several days of the first attack.
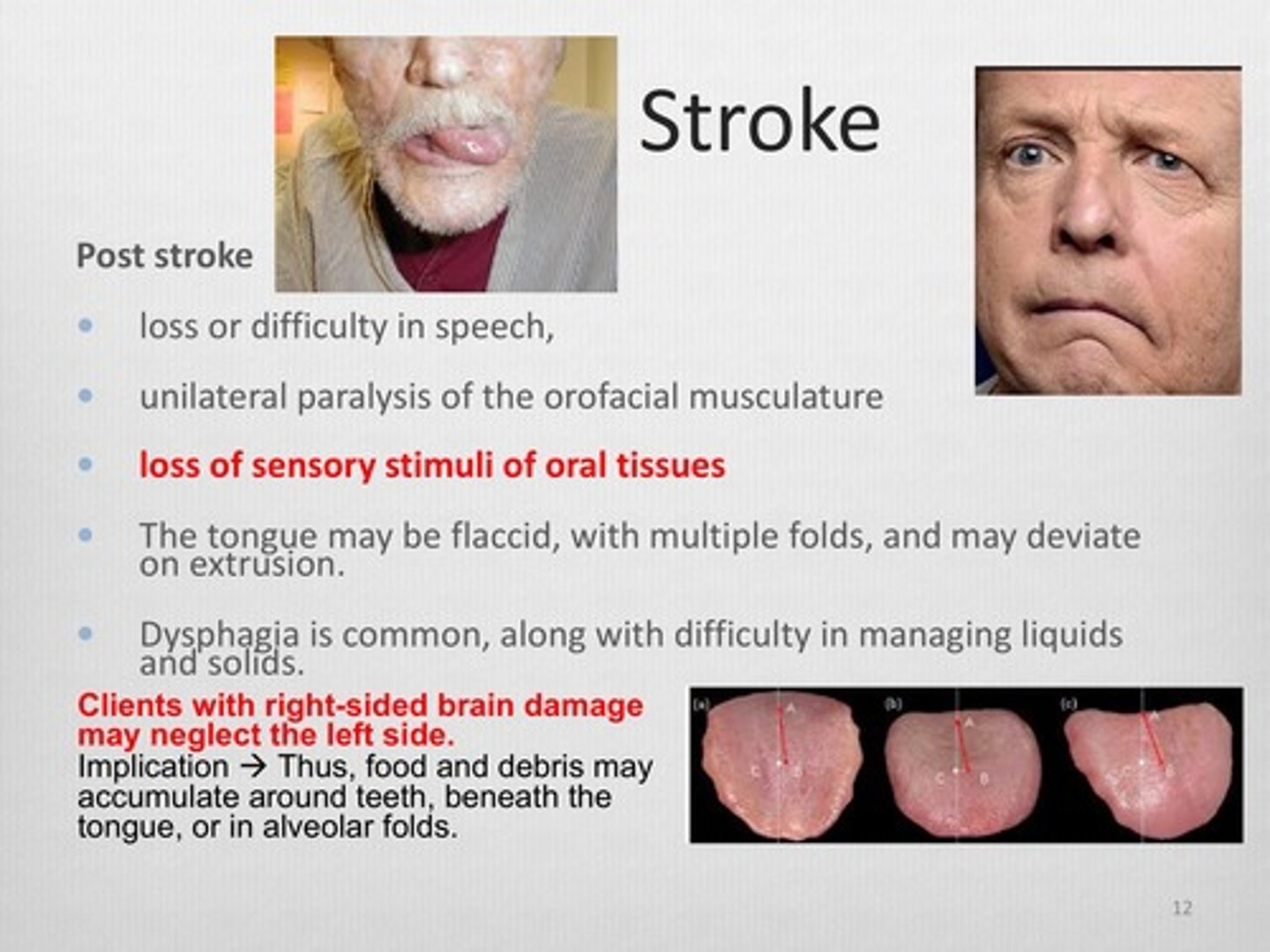
Right sided brain damage
Paralyzed left side, spacial or perceptual deficits, impaired thought, quick impulsive behaviour, pt cannot use mirror, difficulty performing tasks (toothbrushing), and neglect of the left side are all results of brain damage on what side?
Left sided brain damage
Paralyzed right side, language and speech problems, decreased auditory memory (cannot remember long instructions), slow, cautious disorganized behavior, memory deficits— language based, and anxiety are all results of brain damage on what side?
3.5
After a stroke there is a risk for abnormal bleeding associated with Coumadin or anti platelet drugs. An INR level of —.— or less is acceptable for performance of most invasive and non invasive dental procedures.
3months
What should the recare interval be for clients who suffered a stroke?
Central post-stroke pain (CPSP)
This is also known as thalamic syndrome or thalamic pain syndrome. Constant, moderate or severe pain caused by damage to the brain. The brain no longer understands normal messages sent from the body in response to touch, warmth, cold, and other stimuli. The brain registers even slight sensations in the skin as painful. Happens after a stroke. Not common.
Parkinson's disease
This disease was first described by James Parkinson in 1817. It's a progressive and chronic neurodegenerative disorder of neurons that produce dopamine. Approximately 80% of the dopamine in these neurons must be depleted before symptoms of the disease arise. Neuron loss results in characteristic motor disturbances (resting tremor, muscular rigidity, bradykinesia, postural instability). The peak of age of onset is between 55-66 years.
1 in 300
Parkinson's disease in a common disease of the CNS that affects about 1 million Americans, or — in ——— persons.
carbidopa/levodopa (Sinemet)
This is a drug used in the management of Parkinson's disease. Immediate precursor of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Generally reserved for later in the course of the disease. Its activity wanes after about 5-10 years. Long term effect: produces complicating adverse effects (dyskinesia—rapid involuntary flowing movements of the limbs, trunk, or head).
Depression
This has been described as the major psychological complication, with a prevalence of 2%-70% in those suffering from Parkinson's Disease.
Orthostatic hypotension and rigidity
This is a common adverse effect associated with Parkinson's medications. The client requires assistance when rising from the dental chair. At the end of the appointment, the chair should be inclined slowly to allow for reequilibriation.
Parkinson's disease
Staring, excessive salivation and drooling, decreased frequency of blinking and swallowing, muscle rigidity which interferes with good OH, and drugs used to treat the disease resulting in xerostomia, nausea, and tardive dyskinesia are all complications and manifestations of what disease?
Cerebral palsy
This is a chronic disorder caused by damage to motor areas of the immature brain, primarily affecting the ability to control posture and movement. Second most common neurological disorder among children. Most oral findings in these clients are related to disturbances of the oral musculature. Characteristics: from mild (awkwardness of movement or difficulty with fine motor skills) to severe (complete incapacitation of the child). Some associated conditions are hearing and vision problems, communication problems, impairment of other senses, epilepsy, and mental deficiencies.
Monoplegia (1), diplegia (2), triplegial (3), and quadriplegia (4)
There are 4 categories classified according to the dupe of movement disorder and do divided according to the number of limbs involved. What are the 4 categories?
Hemiplegia
This is when a CP client has diplegia but it affects both limbs on one side.
Spastic
This is type 1 cerebral palsy. ————— is characterized by spasticity in the muscles which leads to stiffness and resistance to movements and contractures. Spasms: sudden involuntary contractions of muscles.
Athetoid or dyskinetic
This is type 2 cerebral palsy. Characterized by: slow writhing uncontrolled movements, usually affect hands, feet, arms, legs, and sometimes the face causing drooling and grimacing. Movements may increase with emotional stress and may disappear during sleep.
Dysarthria
This is the term for difficulties with speech muscles.
Ataxic
This is type 3 cerebral palsy. Presents with problems associated with balance, coordination, and depth perception caused by damage to the cerebellum.
Mixed form
This is type 4 cerebral palsy. It is a combination of symptoms such as spastic-athetoid.
Bguifjoespdkmnjfhoaijkpwmnsjikoq
Hreuhjwkdfnbhruefsiojwpokdjn budfhoiajsedpwoifnb how