Advanced Old Age: Over 75
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Advanced Age
People over the age of 75.
Senescence
Early-Old
Middle-Old
Late-Old

Early-Old
60 to 75
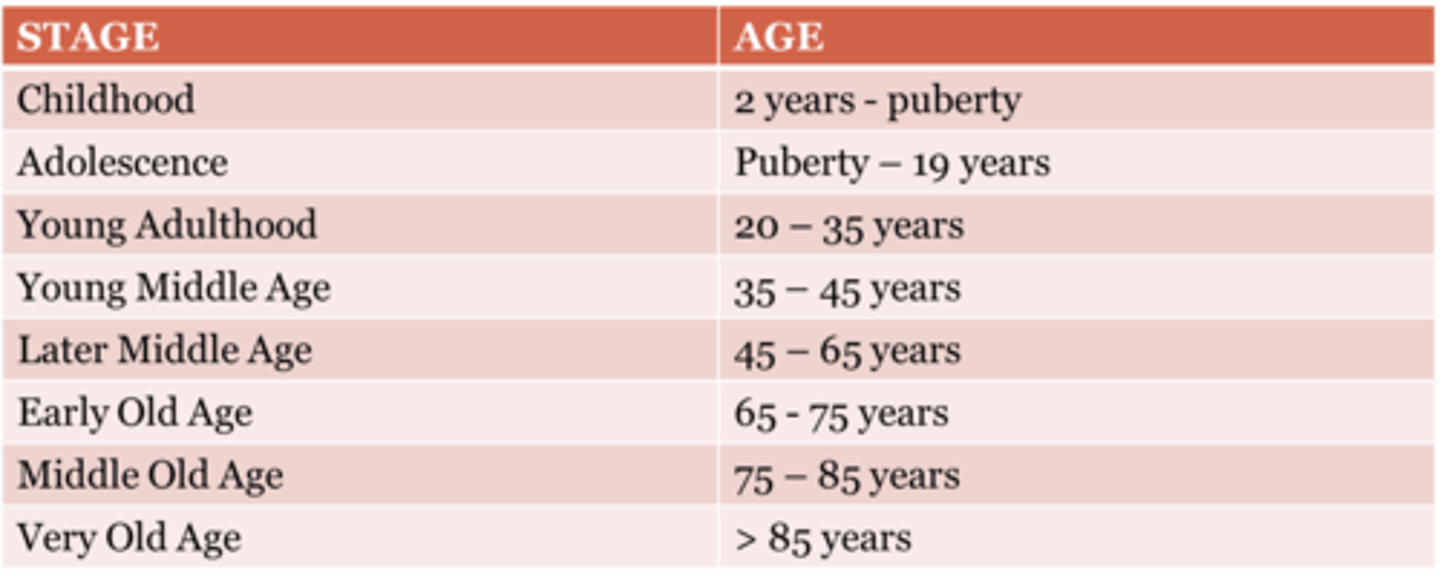
Middle-Old
76 to 90
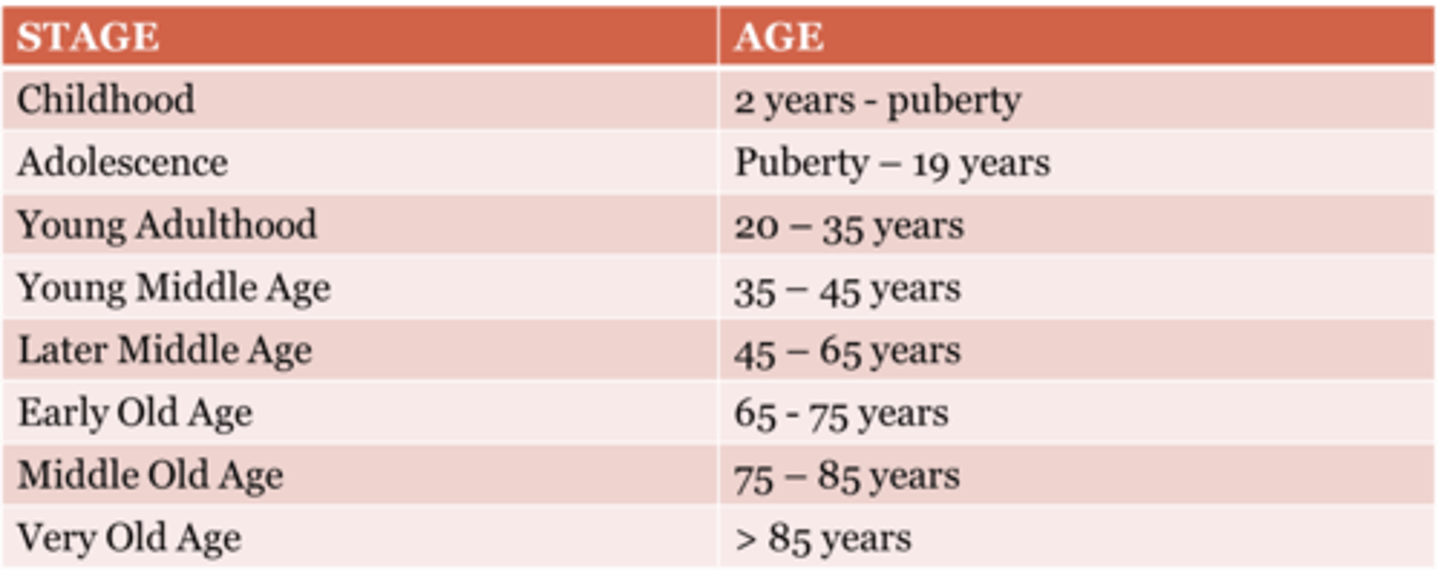
Late-Old
90+
What is senescence?
A period in an older adult's life in which the body begins to age and weaken.
What does senescence signal in terms of lifespan?
It is considered a signal of the final stage or end of the lifespan.
Is senescence a gradual process?
Yes, senescence is a gradual process.
Do people age at the same rate during senescence?
No, people age in different ways and at different rates.
What do older adults seek to achieve for a sense of integrity beyond their death?
Immortality through legacy, family, spirituality, or accomplishments.
What can failure to achieve a sense of immortality lead to in older adults?
Despair and fear of extinction.
What practices can promote ego integrity in older adults?
Supporting life review, legacy building, and meaning.
What is the wear-and-tear theory of aging?
Aging results from accumulated damage to cells/tissues due to use, environmental assaults, and mechanical wear, reducing organism function over time.

Wear and Tear Theory (Biological/Cellular)
Deterioration over time due to continued use.
Human body wears down

Immune Theory (Biological)
Aging is a programmed accumulation of damage and decline in immune function
What is the immune theory of aging
Age-related decline in immune function reduces ability to detect/destroy abnormal cells and pathogens; increased infections, cancers, and autoimmune responses result.

Free Radical Theory or Oxidative Stress (Biological/Cellular)
Errors are a result of random damage from free radicals; they are unpaired unstable ions
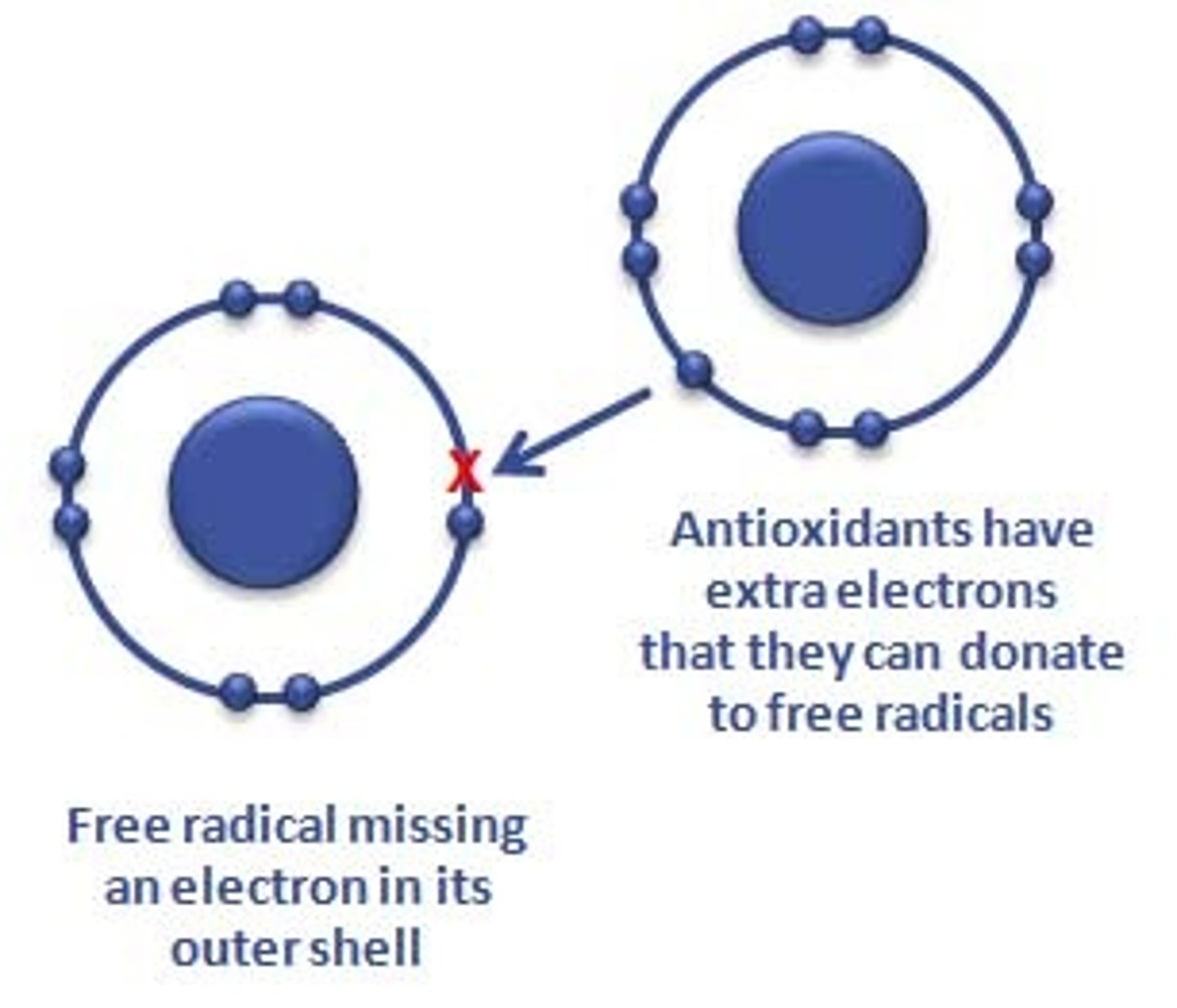
What is the free radical theory of aging?
Free radicals (unstable oxygen molecules) produced in metabolism damage DNA/proteins/membranes over time; cumulative oxidative damage contributes to aging and disease. (Slides/text list free radical theory among biologic theories).
Healthy People 2030 Goals
Attain healthy, thriving lives and well-being, free of preventable disease, disability, injury and premature death.
Eliminate health disparities, achieve health equity, and attain health literacy to improve the health and well-being of all.
Create social, physical, and economic environments that promote attaining full potential for health and well-being for all.
Promote healthy development, healthy behaviors and well-being across all life stages.
Engage leadership, key constituents, and the public across multiple sectors to take action and design policies that improve the health and well-being of all.
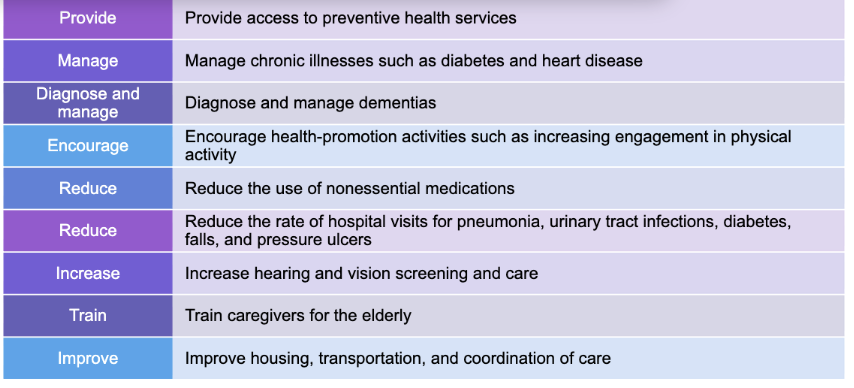
What Healthy People 2030 goals relate to older adults?
Increase healthy lifespan and quality of life; focus on illness prevention, early diagnosis/management of dementia, promoting mobility and independence, increase physical activity among those with physical/cognitive problems, reduce hip fractures and pressure ulcer-related admissions, and reduce hospitalizations for diabetes.
Physiological Changes
Bones and cartilage
Height
Blood vessels
Lungs
Kidneys and bladder
Metabolism
Nervous system
Digestion
Senses
Teeth
Skin
Eyes
Ears
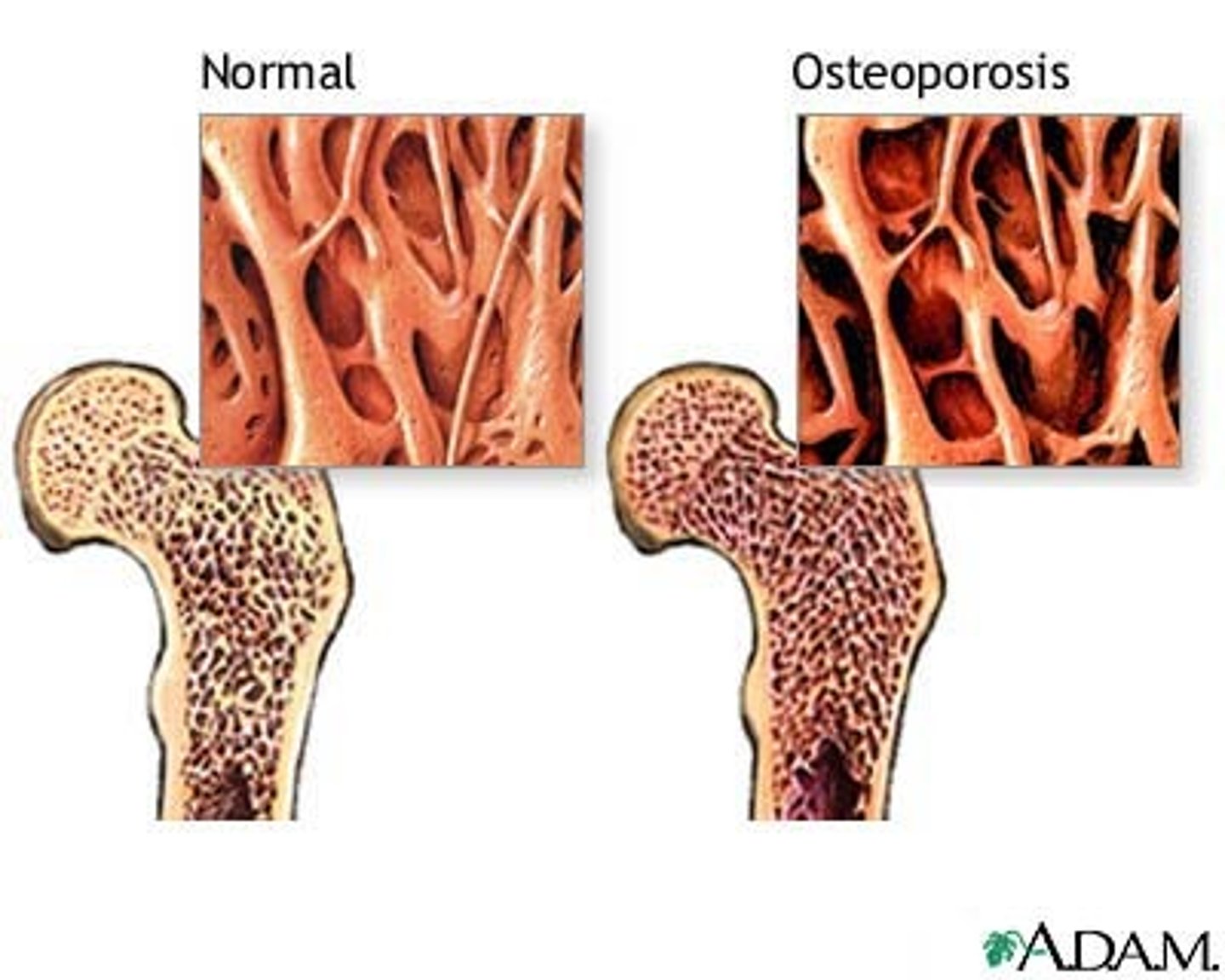
Bones and Cartilage
Loses density
Greater risk for fractures
Cartilage wears down
Joint stiffness common
Osteoporosis risk increases with age
Decreased bone mass
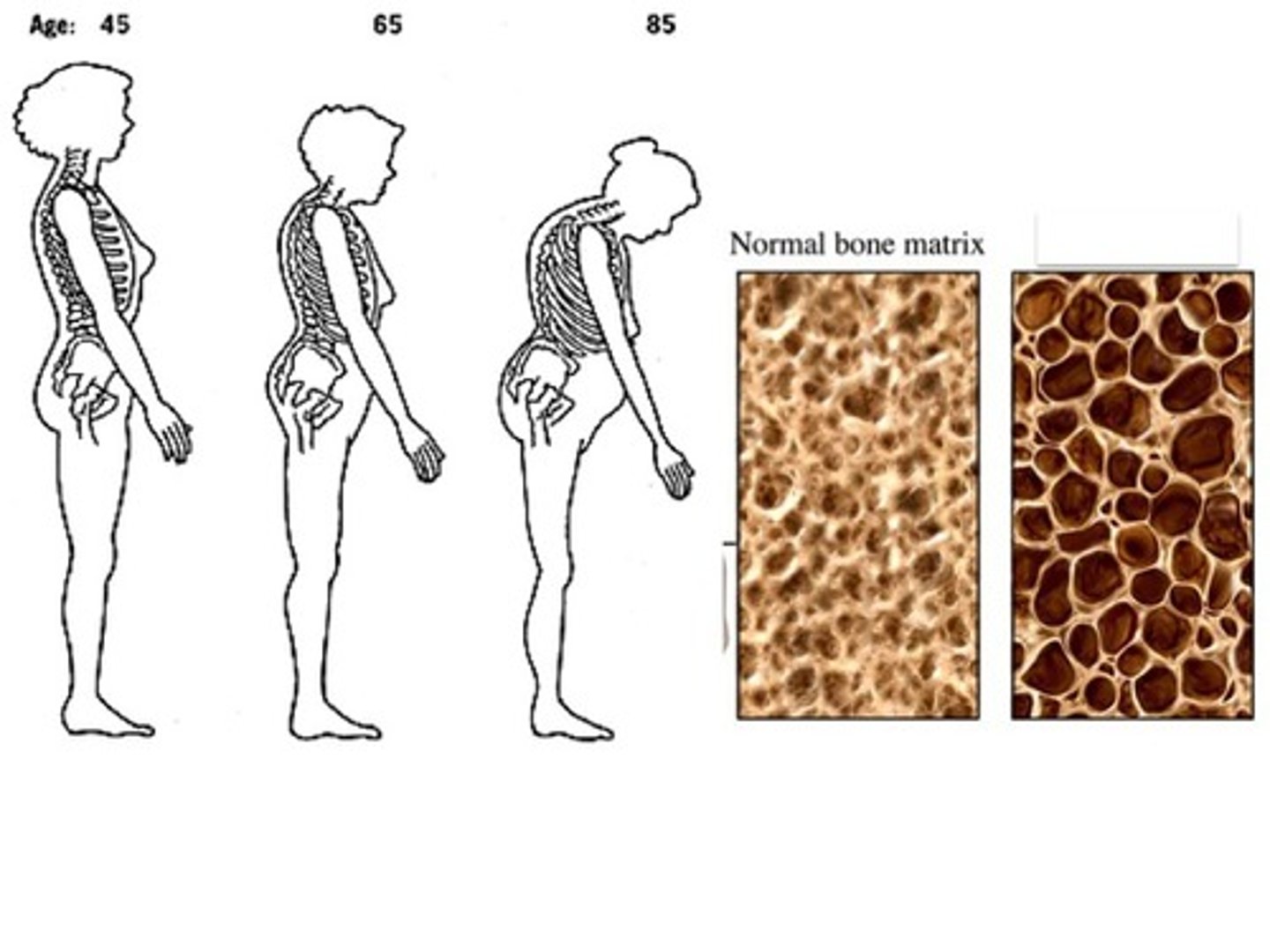
Height
Decreases due to vertebral compression and postural changes.
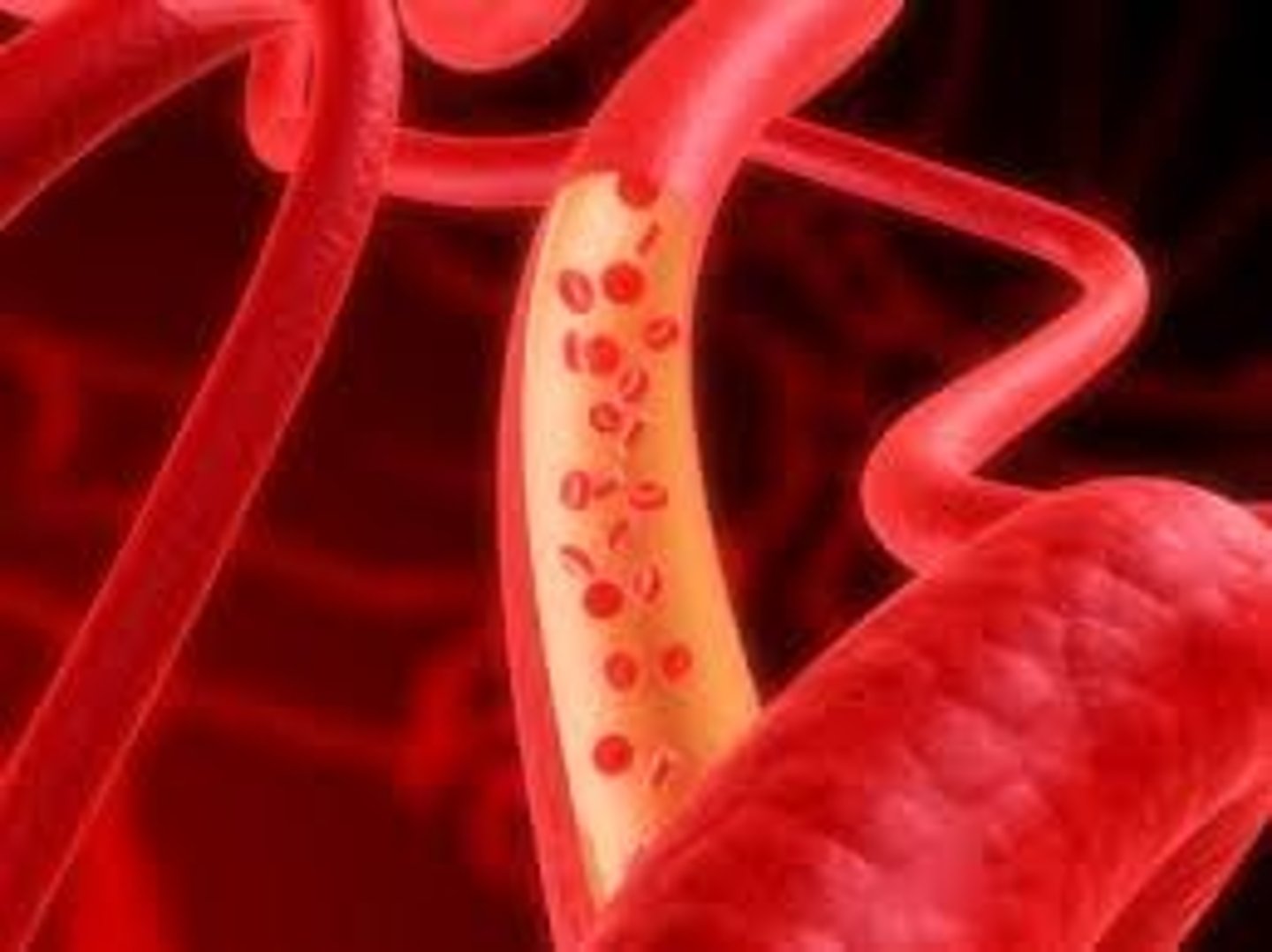
Blood Vessels
Loses elasticity.
Increased peripheral resistance
Blood pressure rises with age.
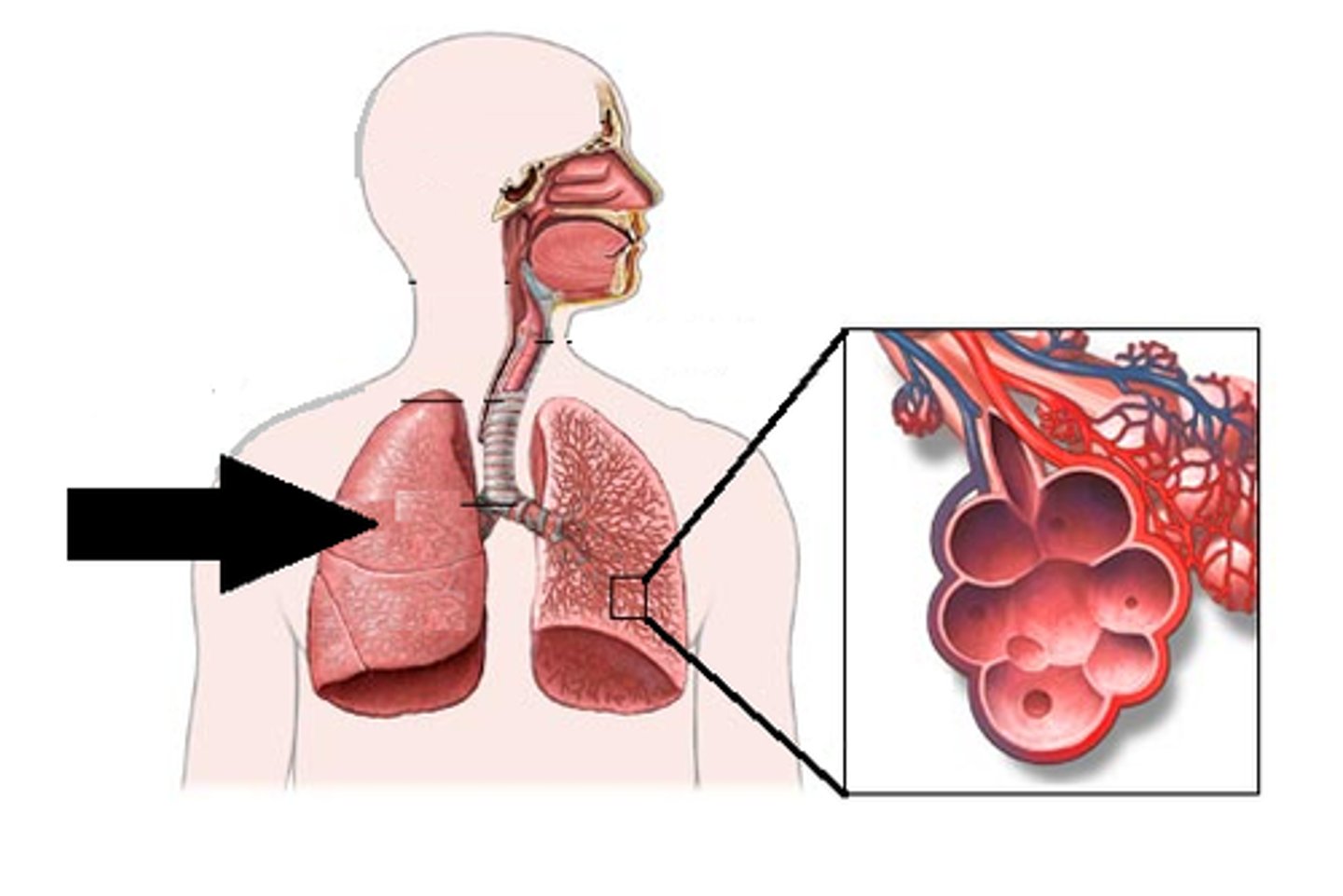
Lungs
Decreased expansion
Decreased vital capacity
Reduced efficiency of gas exchange
Kidneys and Bladder
Kidneys decrease in size.
Reduced renal blood flow.
Decreased filtration rate.
Bladder capacity decreases.
More frequent urination.
Metabolism
Slows with age
Decreased caloric needs
Nervous system
Forgetfulness
Inattentiveness
Disorganized thinking
Altered level of consciousness
Perceptual disturbances
Psychomotor disturbances
Sleep-wake disorder
Digestion/GI System
Saliva production decreases → difficulty swallowing dry foods.
Decreased digestive secretions.
Constipation is common.
Vision
Decreased tear production
Decreased visual acuity, color discrimination, pupil size
Safety concerns—driving (esp night)
Annual eye examinations needed
Presbyopia
age-related loss of accommodation—need for reading glasses almost universal

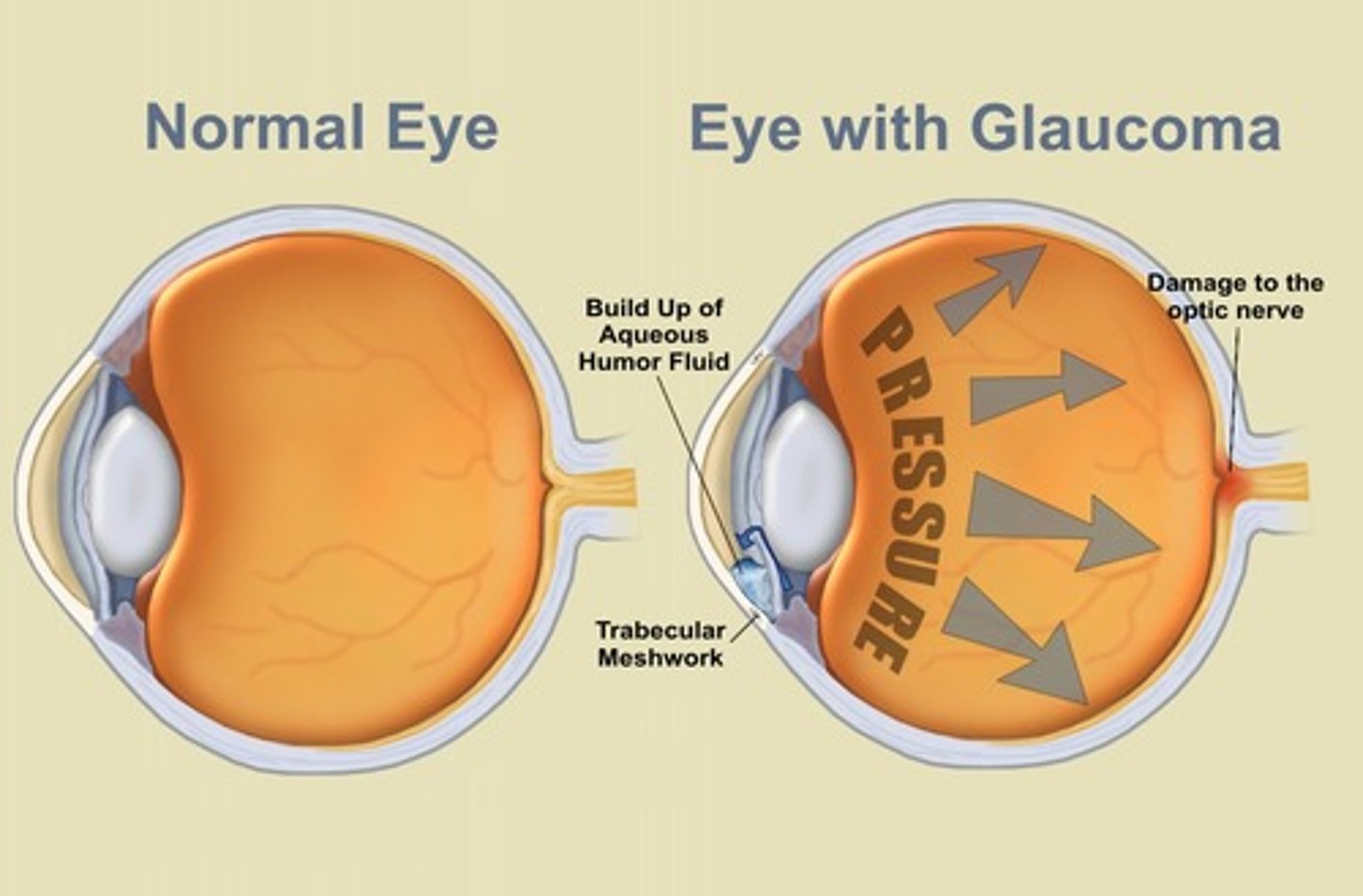
Glaucoma
intraocular pressure
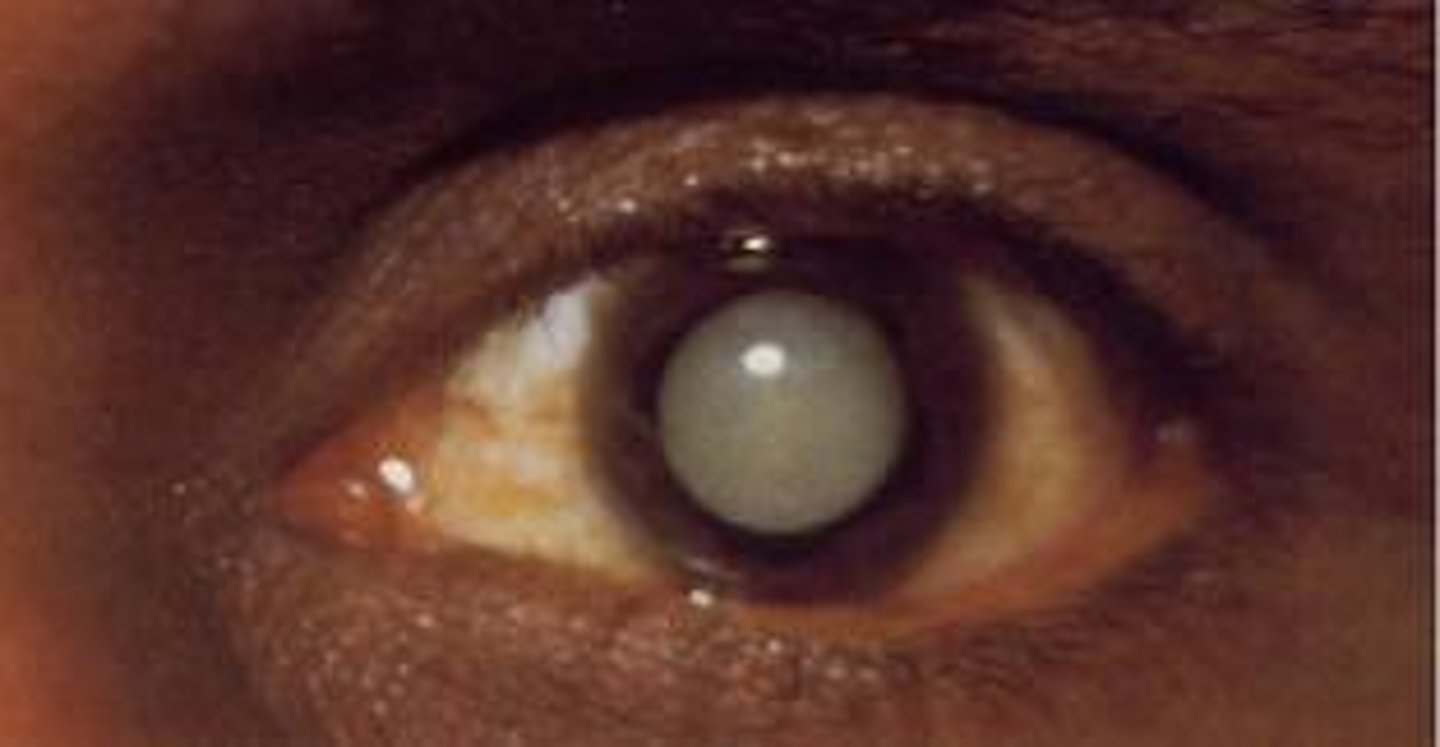
Cataracts
opacity and yellowing of lens
What is inner-ear atrophy?
A condition characterized by the degeneration of cells in the inner ear.
What causes loss of hearing hair cells?
Damage or degeneration of the hair cells in the inner ear.
Why is annual audiology testing important?
To monitor hearing loss and detect changes in hearing ability.
What is tympanic membrane atrophy/sclerosis?
A condition where the eardrum becomes thin or hard, affecting hearing.
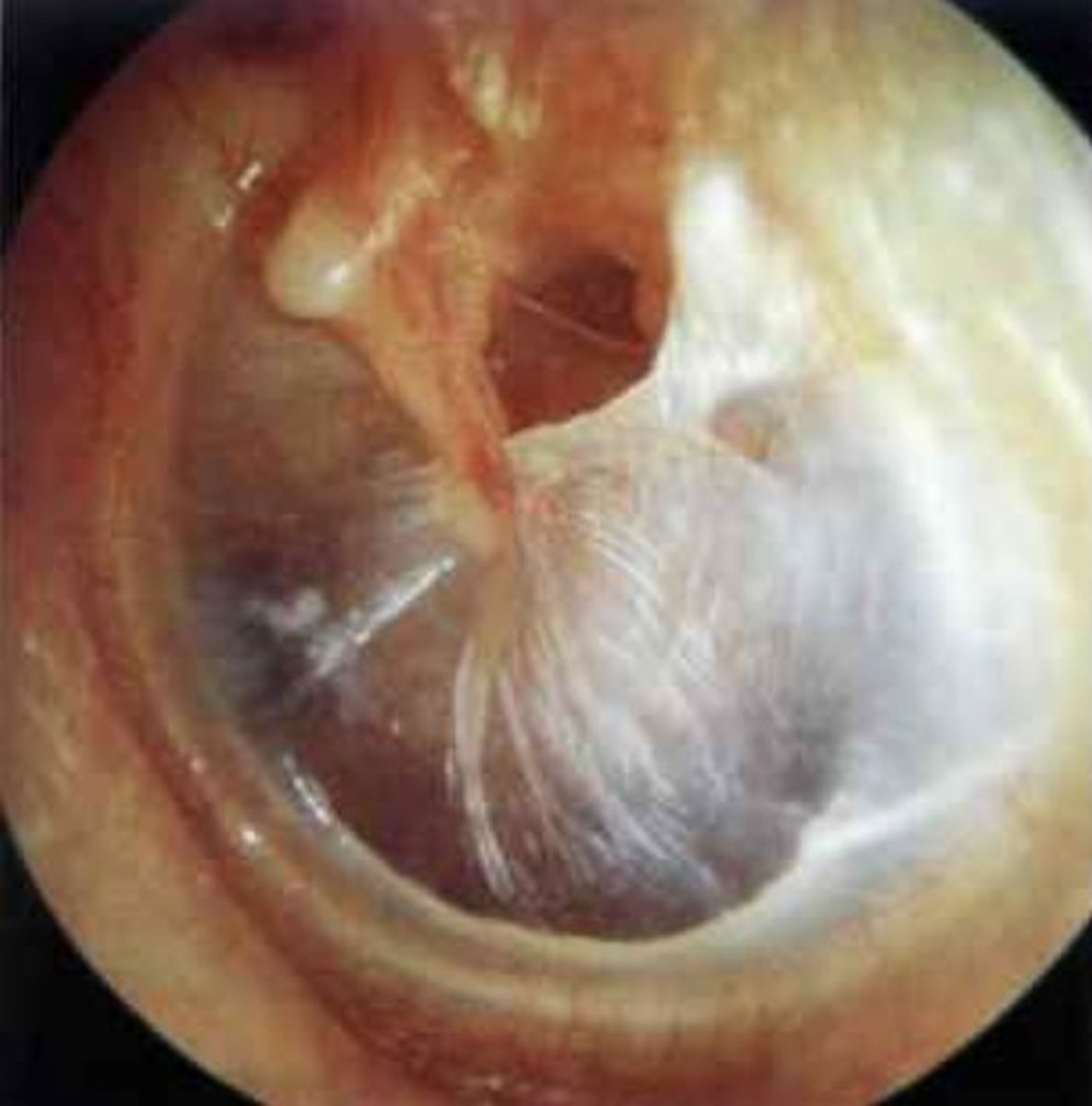
What is presbycusis?
Progressive sensorineural hearing loss associated with aging.

How does hearing loss affect quality of life?
It can lead to miscommunication, loss of self-esteem, depression, falls, safety risks, and cognitive decline.
Skin
Becomes more thinner, wrinkled, and fragile
Safety issues from decreased sensation: burns from cooking, bathing; motor skill consideration
Decreased function of sweat glands: Difficulty with temperature regulation
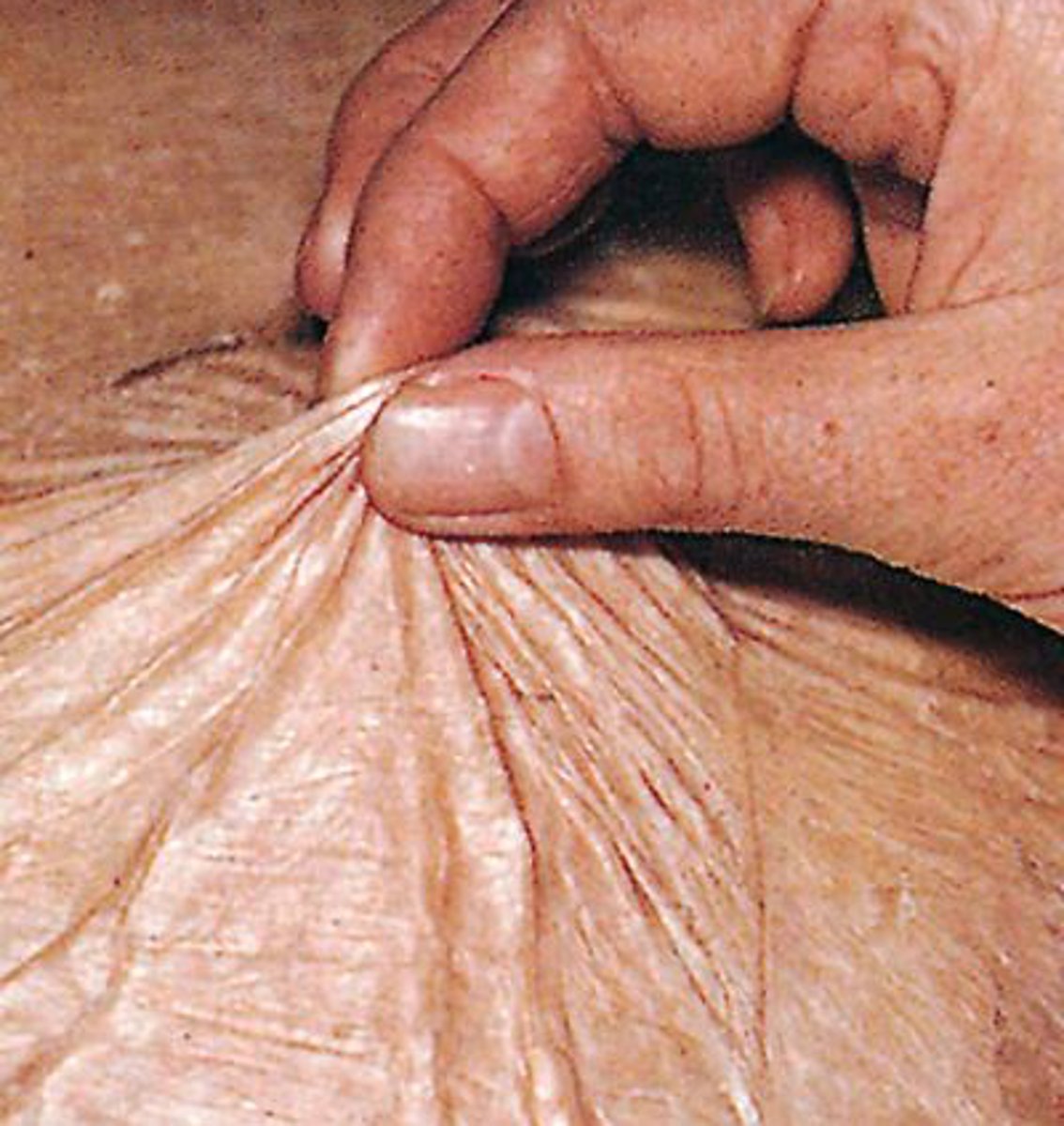
Skin with age comes with risk of decubitus Ulcer
localized tissue necrosis (from compression against bone)
Hazard of chronic disease esp CVA• Proper nutrition will help prevent
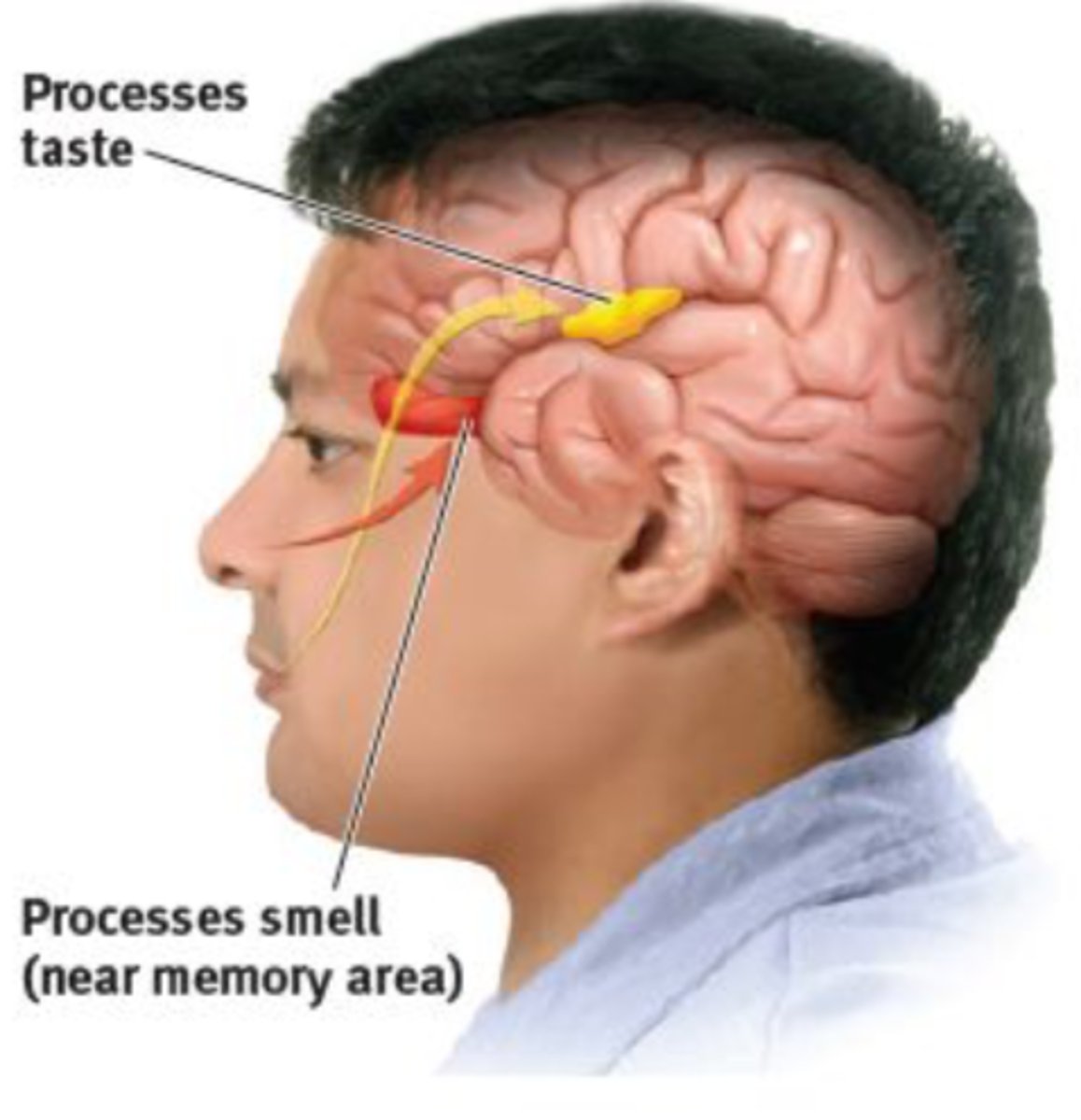
Taste/Smell
Loss of taste buds
Changes result in large amount of salt/sugar in food
Dental health important—semiannual dental visits
Loss of teeth, caries, periodontitis, gingivitis
Decreased acuity of olfactory nerve
Food safety issues with loss of smell
Concerns related to living arrangements include:
Safety
Accessibility
Social isolation
Health-care access
Financial considerations
Living Modifications
Majority of older people prefer to stay in their own home, best to alter:
•Widened doorways
•Door levers
•Ramps
•Lighting
•Smart home devices
•Bathtub with walk-in shower or bathtub w/bench or bath chair & safety bars

Concerns Related to Living Arrangements
Access to health care and assessment
Individual's perception of move as "dumping" or as assistance
Control of patient's finances
Personal space allowed
Accommodation of special needs
Privacy or shared room
Providing pet care, allowing plants in room
Peer-group activity
Rehabilitation and therapies available
Living Placements
Assisted living in a residential setting - Adult needs minimal or moderatesupervision & careNursing home or long-term care facility - Higher level of care
Assisted living in a residential setting
Adult needs minimal or moderate supervision & care

Nursing home or long-term care facility
Higher level of care

High Prevalence of Sleep Disorders
Decrease in total hours required
Increase in nocturnal awakenings, shorter periods of sleep, decrease in slow-wave activity
Nursing Interventions for Sleep
• Teach re: normal changes in sleep
• Encourage sleep routine
• Increase daytime physical activity
• Pain management
• Environmental adjustments(lights/sound)
• Sleep medications: short-term use
Sleep-related issues are listed as symptoms within cognitive decline and dementia:
Sleep-wake disorder
Sleep-wake disturbance
Sleep promotion strategies
Maintain routines and structure
Address causes contributing to sleep changes (e.g., medication effects, environmental factors)
Monitor sleep as part of dementia management
Dementia Definition
An abnormal condition marked by multiple cognitive defects that include memory impairment.
2 Types of Dementia
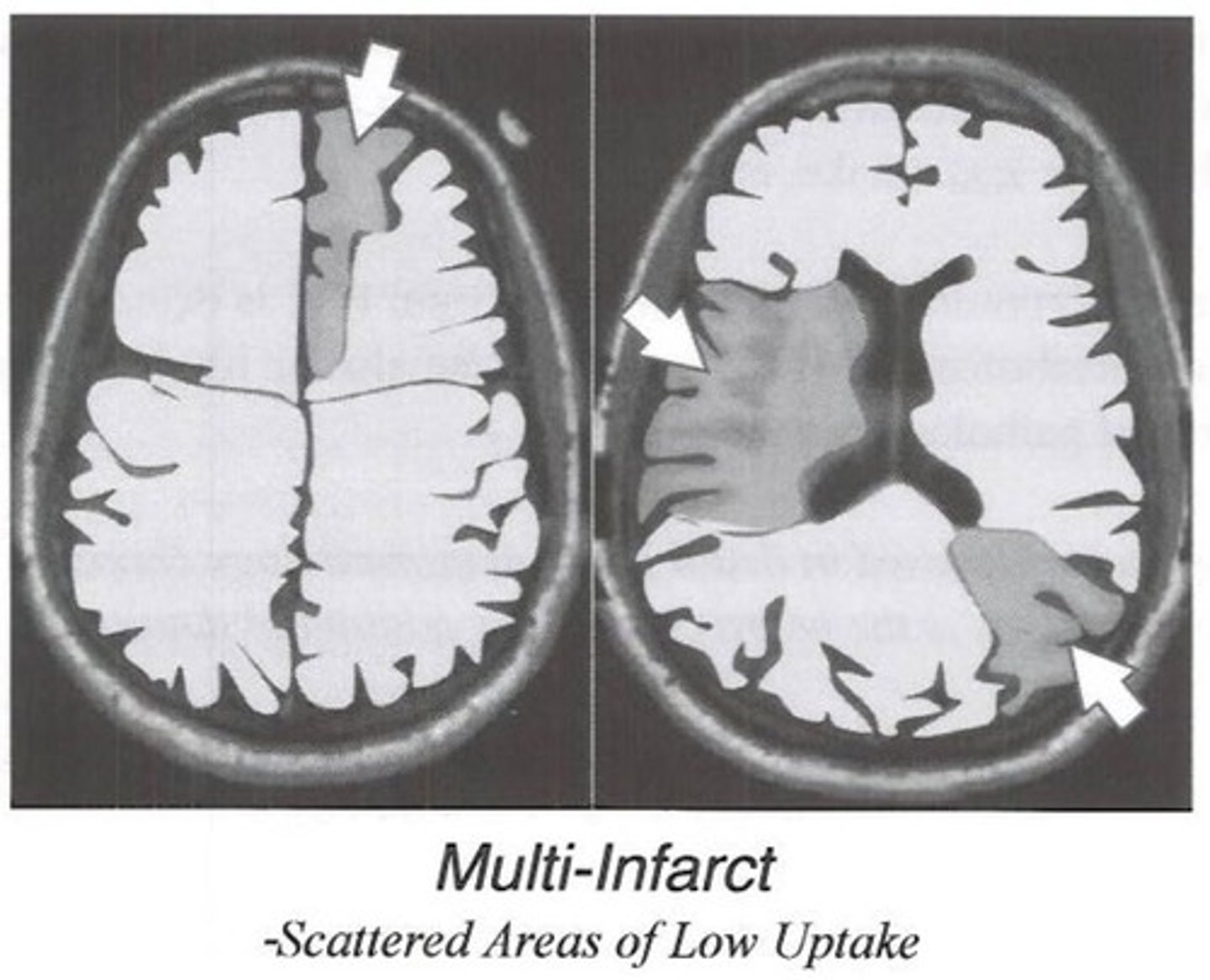
Multi-infarct Dementia
Alzhemier's Disease
Dementia
Not inevitable outcome of aging

Multi-Infarct Dementia
Death of brain tissue
Treatment for Dementia
Medications, encourage self-care, routines, and stimulation, safety interventions (falls, wandering)

Alzheimer's Disease
Most common form of dementia
Causes not fully understood
No cure
Symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease
Forgetfulness
Inattentiveness
Disorganized thinking
Altered level of consciousness
Perceptual disturbances
Sleep-wake disorders
Psychomotor disturbances
Disorientation
Treatment for Alzheimer's
"No cure."
Medications for memory, behaviors, sleep
Nonpharmacologic:
Routine
Structure
Safety modifications
Encourage self-care
Nursing role in Alzheimer's
Provide structure
Environmental safety
Support for family/caregivers
Monitor reversible causes of cognitive decline
Who is at the highest risk for depression?
Older adults

What are some factors that contribute to depression?
Isolation, loss, change in environment, low self-esteem, medical conditions, medications
Chronic illness
Social isolation
Hearing loss (linked in sensory loss slide)
Cognitive decline
What are common treatments for depression?
Counseling, social support, pleasurable activities
Which age group has the highest rate of suicide?
Elderly
What are some factors contributing to suicide in the elderly?
Serious illnesses, social isolation, alcohol abuse, bereavement
What is physician-assisted suicide also known as?
Euthanasia
What is a challenge related to suicide prevention?
Promote value in life and alleviate suffering
Memory Change Warning Signs:
Memory loss that affects job functioning
Difficulty performing familiar tasks
Disorientation
Losing track of time/place/date
Decreased abstract thinking
Personality, mood, or language changes

Reversible / Preventable Causes of Memory Issues:
Drug toxicity
Depression
Metabolic problems (kidney or liver dysfunction, hypoglycemia)
Sensory problems (hearing, vision)
Nutritional deficiencies (Dehydration, B12 deficiency, Iron deficiency)
Illnesses
Pneumonia
Infections
What is a key aspect of coping with immortality versus extinction?
Reminiscing about the past; focus on activities that bring pleasure.
What should individuals identify to adjust to retirement?
Hobbies and activities that bring fulfillment.
What is important for adjusting to aging?
Accepting the frailties of aging and changes in physical appearance and lifestyles.