Personal Financial Planning: Goals, Economy, and Time Value of Money
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
Personal financial planning
The process of managing your money to achieve personal economic satisfaction.
Financial literacy
The use of knowledge and skills for earning, saving, spending, and investing money to achieve personal, family, and community goals.
Financial plan
A formalized report that summarizes your current financial situation, analyzes your financial needs, and recommends future financial activities.
Adult life cycle
The stages in the family situation and financial needs of an adult.
Personal factors influencing spending and saving patterns
Include age, income, household size, and personal beliefs.
Societal changes influencing financial needs
Examples include delaying marriage, dual-income households, single parent households, and caring for both children and elderly parents.
Values
The ideas and principles that a person considers correct, desirable, and important.
Economics
The study of how wealth is created and distributed.
Economic environment
Includes business, labor, and government working together to satisfy needs and wants.
Federal Reserve System (The Fed)
Attempts to maintain an adequate money supply to encourage consumer spending, business growth, and job creation.
Inflation
A rise in the general level of prices.
Buying power of the dollar
Decreases in times of inflation.
Consumer price index (CPI)
Computed and published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics; measures average change in the prices urban consumers pay for a fixed 'basket' of goods and services.
Hidden inflation
A situation where consumers face inflation that is not immediately apparent.
Level of imports/exports
Affects the available supply of dollars; when exports are lower than imports, more U.S. dollars leave the country than the dollar value of foreign currency coming into the U.S.
Level of foreign investment
Affects domestic money supply.
Money supply
Affects consumer interest rates.
Increased effectiveness in financial literacy
Achieved through obtaining, using, and protecting financial resources throughout your life.
Expanded control of finances
Achieved by avoiding excessive debt and dependence on others.
Improved personal relationships
Resulting from well-planned financial decisions.
Sense of freedom from worries
Results from looking to the future, anticipating expenses, and achieving goals.
Deflation
A decline in prices.
Rule of 72
A formula to estimate how fast prices or savings will double by dividing 72 by the annual inflation or interest rate.
Interest Rates
The cost of money, influenced by the forces of supply and demand.
Short-term Goals
Financial objectives to be achieved within the next year.
Intermediate Goals
Financial objectives with a time frame of two to five years.
Long-term Goals
Financial plans that are more than five years off.
Consumable-product Goals
Goals that involve items used up relatively quickly, such as food and clothing.
Durable-product Goals
Goals that involve infrequently purchased, expensive items such as appliances and cars.
Intangible-purchase Goals
Goals related to personal relationships, health, education, and community service.
SMART Goals
Goals that are Specific, Measurable, Action-oriented, Realistic, and Time-based.
Opportunity Cost
What you give up when making a choice, often referred to as a trade-off.
Personal Opportunity Costs
Costs that include time, energy, health, abilities, and knowledge.
Financial Opportunity Costs
Costs associated with the choice of receiving money now versus in the future.
Time Value of Money
The increase in an amount of money as a result of interest earned.
Earnings
The income received as a saver or investor, reflecting current interest rates and risk premiums.
Saving
Setting aside money for future use, which can earn interest.
Borrowing
Taking money from others with the promise to pay it back, usually with interest.
Spending
Using money to purchase goods and services.
Managing Risk
The process of identifying and mitigating potential financial losses.
Investing
Allocating money in order to generate a return or profit.
Retirement Planning
The process of determining retirement income goals and the actions necessary to achieve those goals.
Estate Planning
The process of arranging for the disposal of a person's estate.
Principal
The amount of the savings used in calculating the time value of money.
Annual Interest Rate
The percentage at which interest is earned on the principal over a year.
Time Period
The length of time the money is on deposit.
Simple Interest
Calculated as Amount in savings × Annual interest rate × Time period.
Future Value
The amount that will be available at a later date based on current savings and interest.
Present Value
The current value of an amount desired in the future based on a certain interest rate.
Calculation Methods
Methods used to calculate time value of money including formula calculation, T V M tables, financial calculator, spreadsheet software, and websites/apps.
Compounding
The process where interest is earned on previously earned interest.
Annuity
A series of equal deposits or payments made over time.
Future Value of a Series of Deposits
The total amount accumulated from a series of equal deposits made at a constant interest rate.
Present Value of a Series of Deposits
The current amount needed to be deposited to achieve a desired future amount based on a certain interest rate.
Discounting
The process of determining the present value of a future amount.
$1,000 at 4% for six months
An example of interest calculation where the interest earned is determined based on the principal, rate, and time.
$100 deposited in a 3% account for one year
An example illustrating compounding where the amount grows to $103.
$50 a year at 7% for six years
An example of an annuity where total savings at the end of the period amounts to $357.65.
$1,000 five years from now at 5%
An example of present value calculation where $784 needs to be deposited now.
$400 out of an investment account each year for nine years at 8%
An example showing that a current deposit of $2,498.80 is needed to withdraw the specified amount.
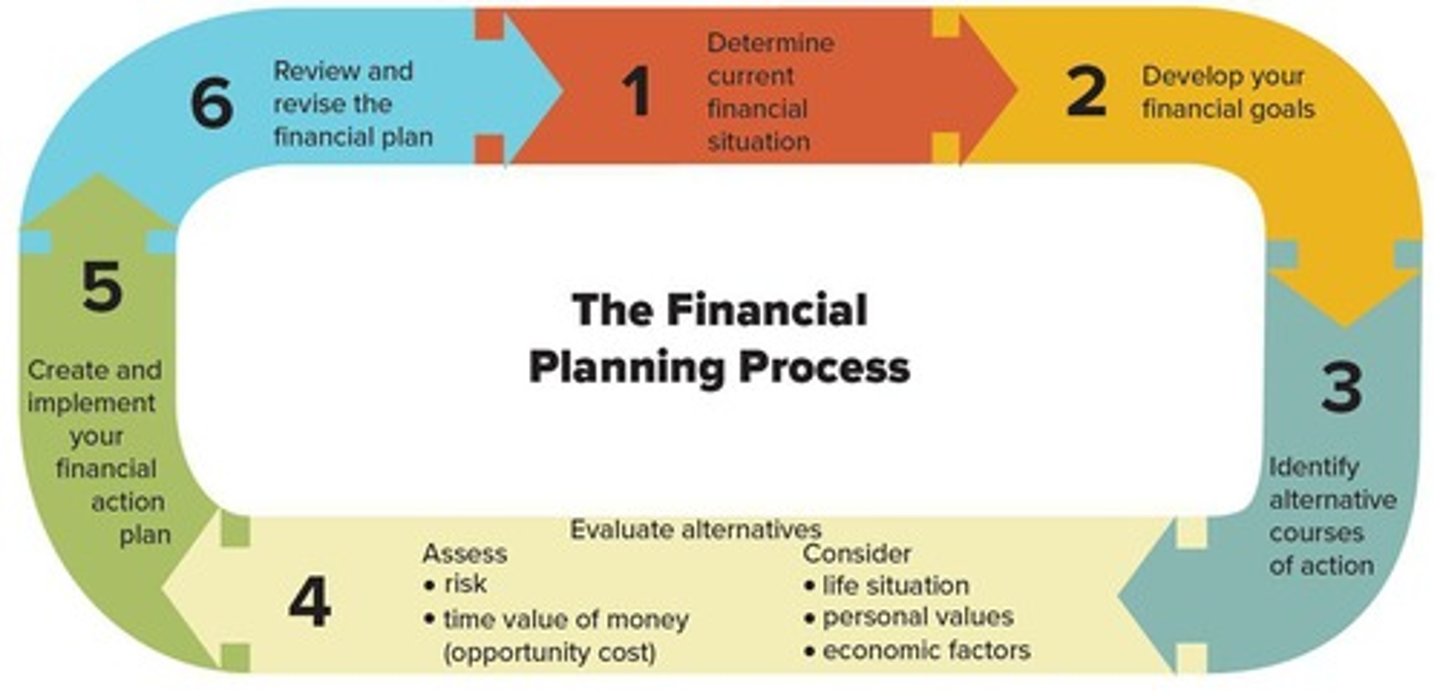
Financial Planning Process
A structured approach to managing finances that includes determining current financial situation, developing financial goals, and identifying alternative courses of action.
Specific Financial Goals
Clear objectives that are vital to effective financial planning.
Evaluate your alternatives
Take into consideration your life situation, personal values, and current economic conditions.
Create and implement your financial action plan
You may need assistance from others, such as an insurance agent or an investment broker.
Review and revise your plan
Financial planning is an ongoing process.
Financial Planning Information Sources
Useful sources include online sources and apps, experiences of friends, family, and social media, media sources, financial institutions, and financial specialists.
Career Choice and Financial Planning
Career selection requires planning and education can be a significant investment with future career and financial benefits.
Alternatives to fund school costs
Grants, financial aid and work-study programs, scholarships, education loans, tax credits, personal savings, lower-cost living locations, and tuition reimbursement programs.
Major elements of financial planning
Financial decisions are affected by obtaining, life situation, planning, personal values, saving, borrowing, spending, managing risk, investing, and retirement and estate planning.
SMART financial goals
Financial goals should be Specific, Measurable, Action-oriented, Realistic, and Time-based.
Future value and present value calculations
Enable you to measure the increased value (or lost interest) that results from a saving, investing, borrowing, or purchasing decision.
Personal financial planning steps
Determine your current financial situation, develop financial goals, identify alternative courses of action, evaluate alternatives, create and implement a financial action plan, and review and revise the financial plan.
S.M.A.R.T method
A method to develop financial goals that are Specific, Measurable, Action-oriented, Realistic, and Time-based.
Economic factors
Include prices, interest rates, and employment opportunities.
Life situation
Factors such as income, age, household size, and health that affect financial decisions.
Financial specialists
Include financial planners, insurance agents, investment advisers, credit counsellors, and tax preparers.
Financial institutions
Include apps, websites, credit unions, banks, and investment companies.
Media sources
Include newspapers, magazines, television, radio, podcasts, and online videos.
Trade-off
Every decision involves a trade-off.
Financial planning
An ongoing process that requires regular review and adjustment.
Financial action plan
A plan created to achieve specific financial goals.
Ongoing process
Financial planning requires continuous evaluation and adjustment.
Step 1
Determine current financial situation.
Step 2
Develop your financial goals.
Step 3
Identify alternative courses of action.
Step 4
Evaluate alternatives by assessing risk, time value of money (opportunity cost), life situation, personal values, and economic factors.
Step 5
Create and implement your financial action plan.
Step 6
Review and revise the financial plan.
Financial Intermediaries
Financial intermediaries include banks, credit unions, insurance companies, investment companies, and other financial institutions.
Users
Users refer to borrowers and spenders of funds, including individuals, businesses, governments, and foreign entities.
Financial Markets
Financial markets include stock markets, bond markets, money markets, and commodity markets.
Providers
Providers refer to savers and investors of funds, including individuals, businesses, governments, and foreign entities.
Financial Regulators
Financial regulators include the Federal Reserve System, Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, National Credit Union Administration, Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, Securities and Exchange Commission, and state banking and insurance agencies.
Income or Sources of Funds
Income or sources of funds lead to spending, saving, and sharing.
Sharing
Sharing refers to providing local and global assistance to those in need.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment involves evaluating potential risks associated with financial decisions.
Personal Values
Personal values are individual beliefs that influence financial decisions.
Review and Revise
Review and revise involves regularly assessing and updating the financial plan as needed.
Now
Refers to assessing your current situation, developing financial goals, and selecting appropriate plans of action.
Within a Year
Means making Short-Term Financial Strategies, including creating and implementing a budget, paying off credit card debts, obtaining adequate insurance, establishing a regular savings program, investing in safe income-producing financial instruments, and using rental housing to save for home purchase.