anat2
5.0(1)Studied by 12 people
Card Sorting
1/62
Last updated 12:46 AM on 11/30/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
1
New cards
cells
2
New cards
robert hooke
English scientist - Mid 1600s, cut a piece of cork and viewed it under
lenses; coined the term “cell”
lenses; coined the term “cell”
3
New cards
anton van leeuwenhoek
dutch fabric salesman; making microscopes was his hobby; first person to observe bacteria, blood cells, and organisms in pond water in 1675
4
New cards
cell theory
Schleidan, Schwann, and Virchow observed and concluded three basic facts about cells:
1. All living things are composed of one or more cells.
2. Cells are an organisms’ basic unit of structure and function.
3. Cells come from other cells
1. All living things are composed of one or more cells.
2. Cells are an organisms’ basic unit of structure and function.
3. Cells come from other cells
5
New cards
selectively preamble
Only allow certain molecules in the cell. Only allows a certain amount of molecules in the cell.
6
New cards
fluid - mosaic model
the lipids and proteins are free to move about
7
New cards
organelles & functions
“little organ,” part of a cell that performed a specific function
8
New cards
passive transport
is movement of molecules into/out of a cell without using energy. Moves molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
9
New cards
diffusion
is the process where molecules move from an area of higher consternation to an area of lower concentration
10
New cards
osmosis
is the diffusion of water. Water is moving from an area of high concentration (of water) to an area of low concentration (of water). Water is the solvent in our cells.
11
New cards
active trasport
includes: sodium-potassium pump, endocytosis, phagocytosis, pinocytosis, exocytosis. All require use of ATP (cellular energy)
12
New cards
concentration gradient
the difference in concentration of molecules across an area
13
New cards
endocytosis
how cells engulf large substances. Phagocytosis- ingesting solid particles. Pinocytosis- ingesting liquids. The cell membrane moves around the material and then makes it a vesicle that pinches off into the cell membrane
14
New cards
cell cycle
the cell cycle is made of 2 parts: interphase and division. Cell division also involves two parts: mitosis- division of the nucleus. Cytokinesis- division of the cytoplasm. It does not change the amount of DNA in a cell. For some organisms, it is a means of reproduction
15
New cards
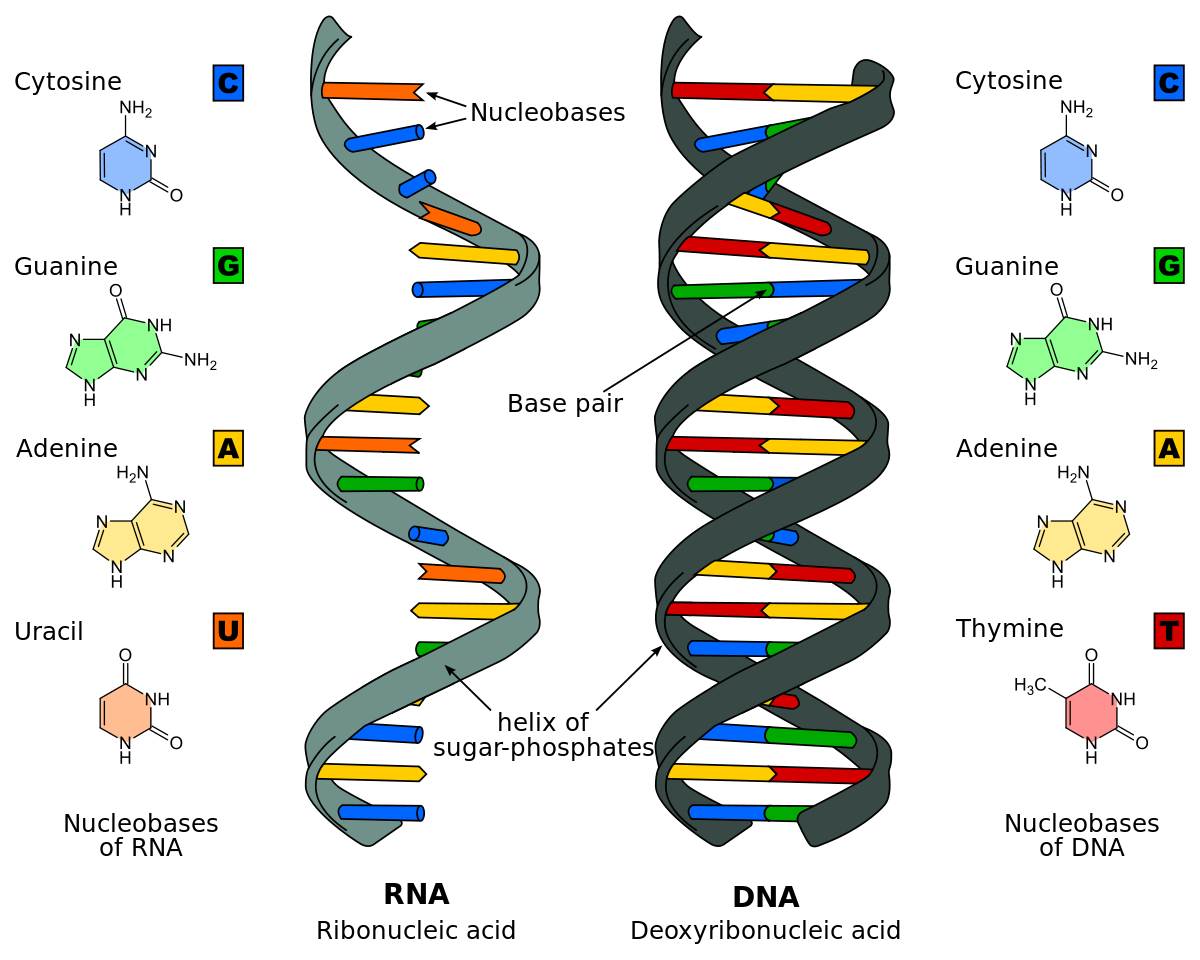
nucleic acid
naturally occurring chemical compounds that serve as the primary information-carrying molecules in cells DNA and RNA
16
New cards
nitrogenous bases
Purines- Adenine and Guanine - Contain a double ring of carbon and
nitrogen; Pyridamines- Thymine and Cytosine Contain a single ring of
carbon and nitrogen
nitrogen; Pyridamines- Thymine and Cytosine Contain a single ring of
carbon and nitrogen
17
New cards
Adenine and Guanine
purines; double ring of carbon and nitrogen
18
New cards
Thymine and Cytosine
pyridamines; contain a single ring of carbon and nitrogen
19
New cards
complementary bases (AT)
Adenine always bonds with Thymine
20
New cards
complementary bases (CG)
Cytosine always bonds with Guanine
21
New cards
complementary bases
When two nucleotides pair together
22
New cards
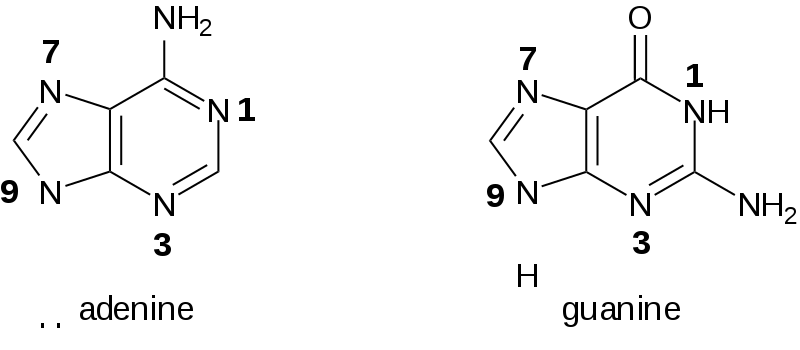
purines
Adenine and Guanine
23
New cards
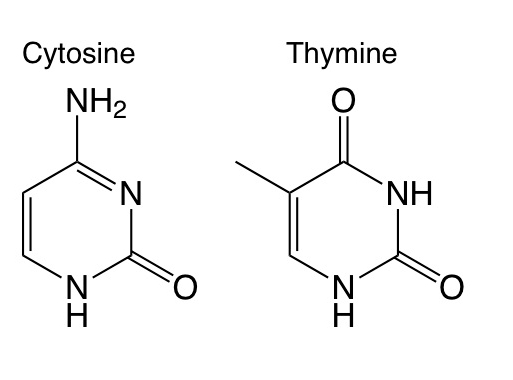
Pyrimadines
Thymine and Cytosine
24
New cards
chromatin
When cell is not dividing, DNA is in an uncoiled form
25
New cards
chromosomes
condensed strand of DNA
26
New cards
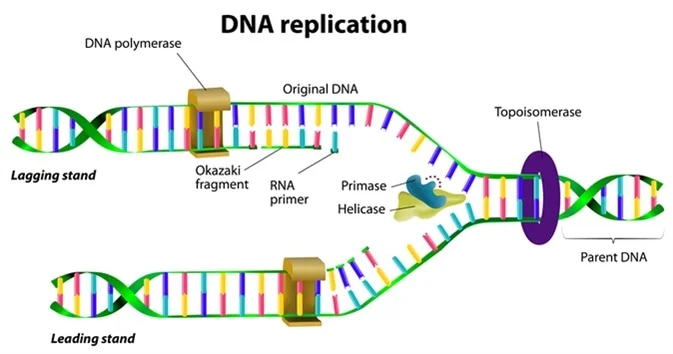
dna replication
the process by which the genome's DNA is copied in cells
27
New cards
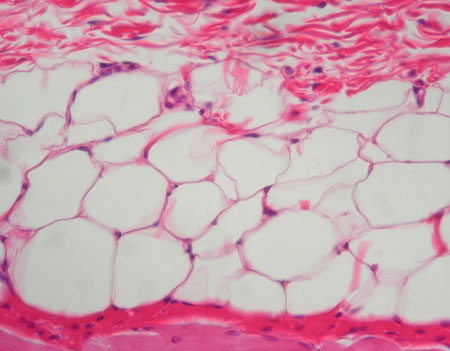
adipose
form - large storage cells
function - stores lipids
found in - organs, yellow bone marrow
function - stores lipids
found in - organs, yellow bone marrow
28
New cards
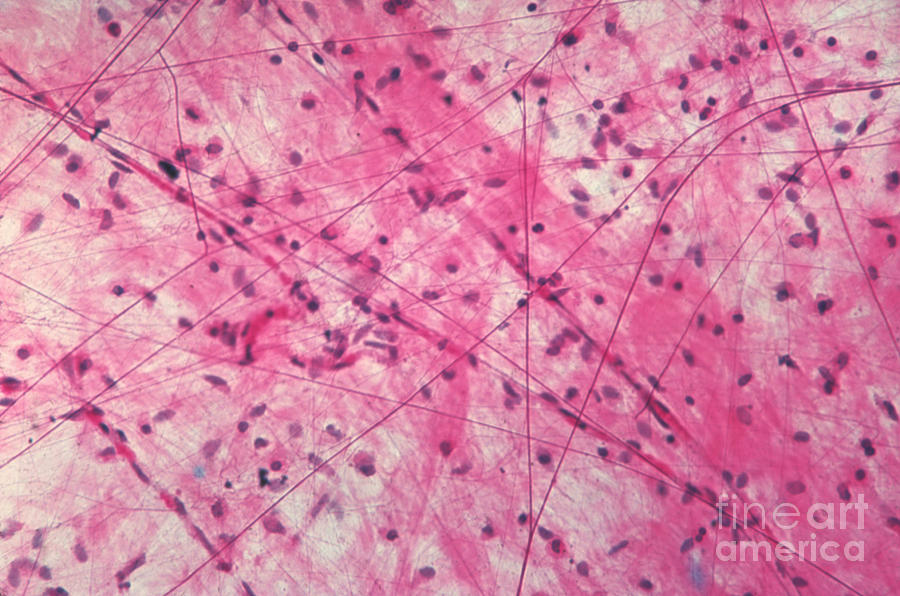
areolar
form - delicate webs of fibers and cells
function - 'glue' that gives form to internal organs, provides strength, support, and elasticity
found in - Most widely distributed. Found around blood vessels, nerves, organs; in mucus membrane; subcutaneous layer
function - 'glue' that gives form to internal organs, provides strength, support, and elasticity
found in - Most widely distributed. Found around blood vessels, nerves, organs; in mucus membrane; subcutaneous layer
29
New cards
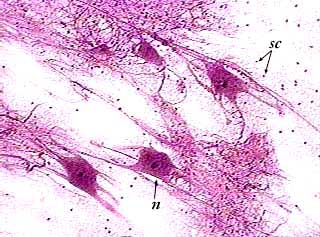
nervous
form (2) - neurons (nerve cells) glial cells (connect and support cells)
function - rapid communications, control of body structures
found in - brain, spinal cord, and nerves
function - rapid communications, control of body structures
found in - brain, spinal cord, and nerves
30
New cards
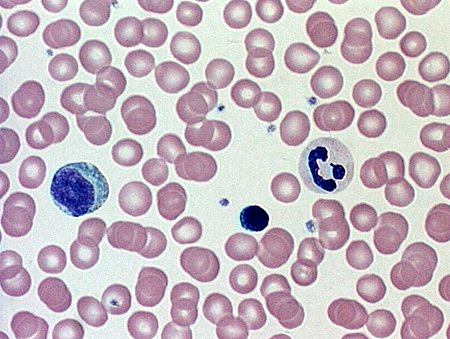
blood
form - blood cells suspended in a liquid matrix
function - transport / protection and immune functions
function - transport / protection and immune functions
31
New cards
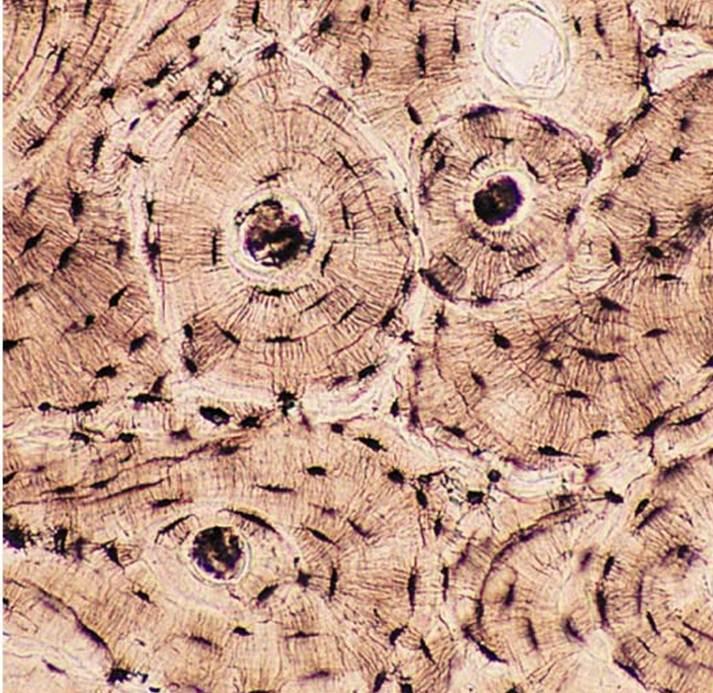
bone
form - matrix is hard and calcified. Made up of osteocytes.
function - support, protections, and storage for calcium
function - support, protections, and storage for calcium
32
New cards
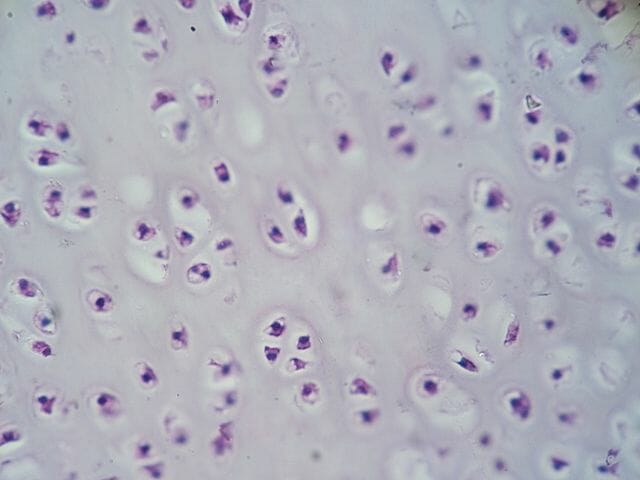
cartilage
form - area between cells is gel-like with white collagen and elastin fibers in it
function - Cushioning between bones. Support surrounding structures and provide shape
function - Cushioning between bones. Support surrounding structures and provide shape
33
New cards
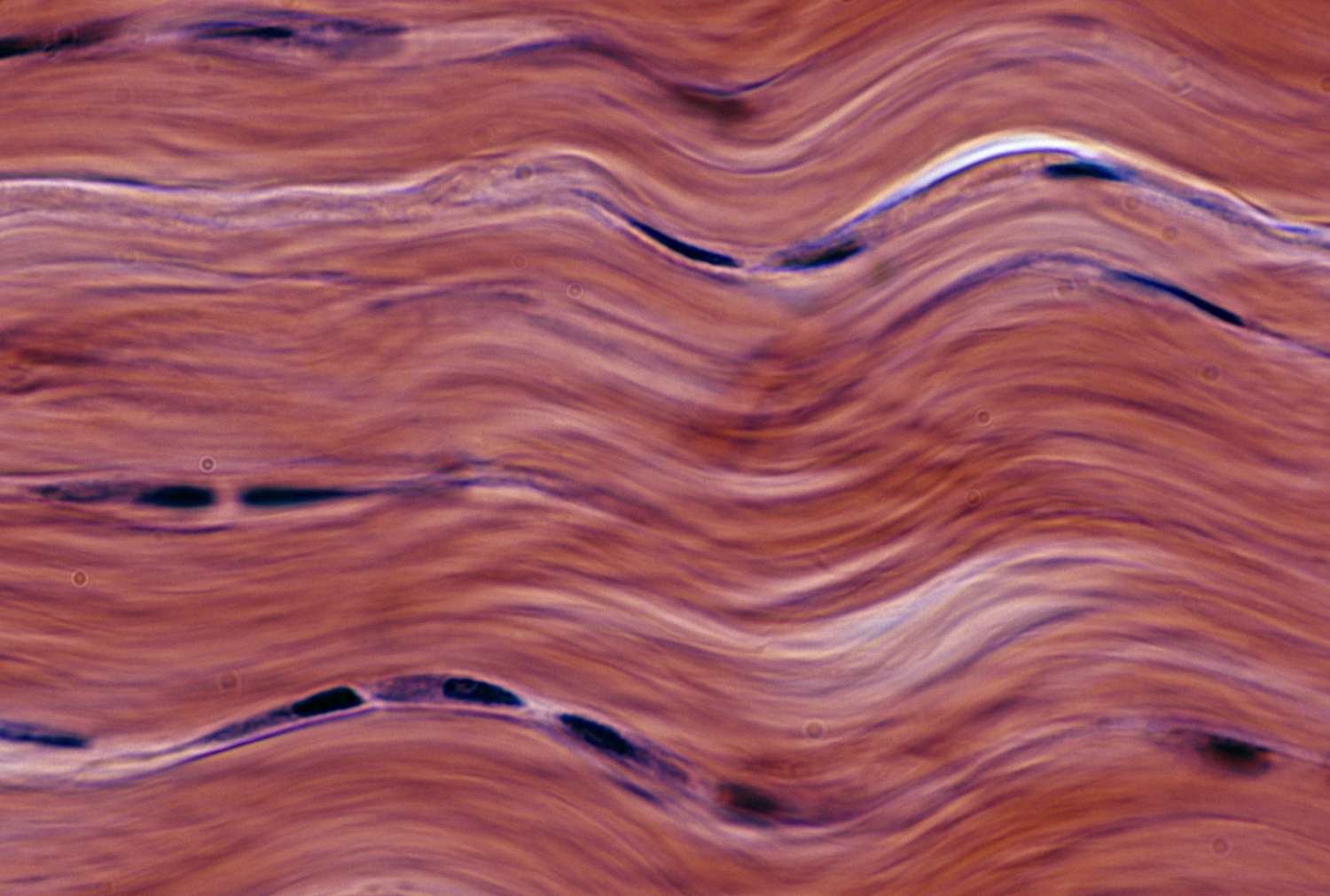
dense fibrous
form - bundles of strong, white collagen fibers in parallel rows
function - flexible and strong connections
found in - Makes up tendons, ligaments, scar tissue
*no white spacing*
function - flexible and strong connections
found in - Makes up tendons, ligaments, scar tissue
*no white spacing*
34
New cards
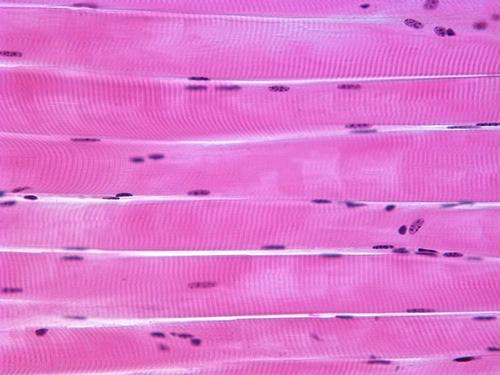
skeletal
form - parallel
function - control body movements and moves bones
found in - attached to bones
function - control body movements and moves bones
found in - attached to bones
35
New cards
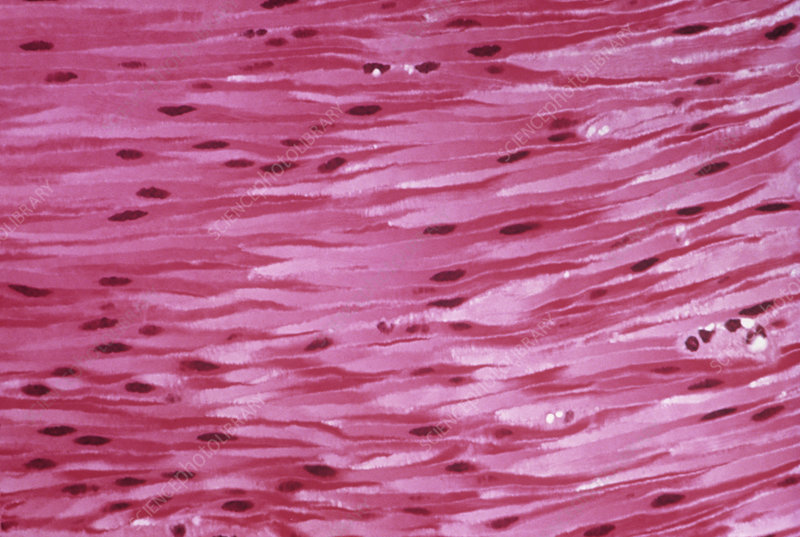
smooth
form - white spaces, ovals
function - contraction of digestive tract, changes diameter of blood vessels, pupils, bronchioles in lungs, digestive tract, shapes of lenses
function - contraction of digestive tract, changes diameter of blood vessels, pupils, bronchioles in lungs, digestive tract, shapes of lenses
36
New cards
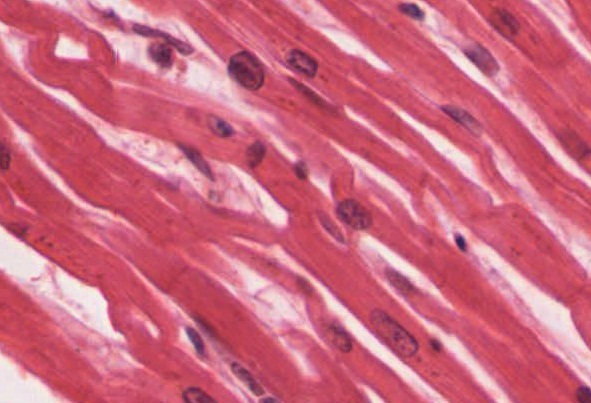
cardiac
form - branched, long, and skinny
function - regular in voluntary contractions of the heart to pump blood
found - the heart muscle
function - regular in voluntary contractions of the heart to pump blood
found - the heart muscle
37
New cards
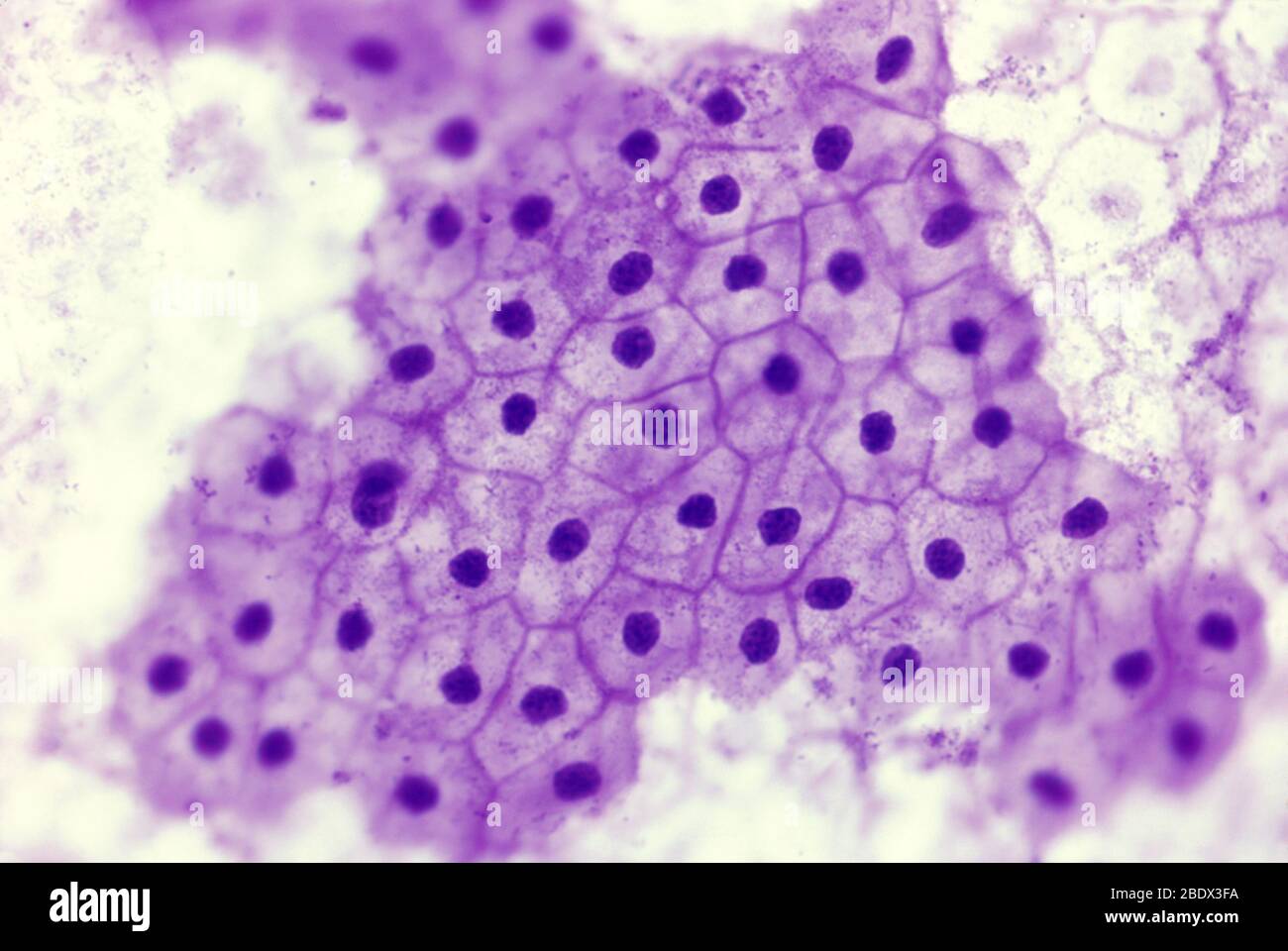
simple squamos
form - several layers of closely packed scale like cells
function - absorption absorbed from lungs into blood
function - absorption absorbed from lungs into blood
38
New cards
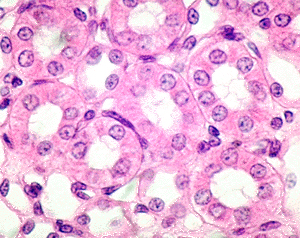
simple cubodial
form - single layer of cube shaped cells
function - allows for secretions
found in - saliva, sweat
function - allows for secretions
found in - saliva, sweat
39
New cards
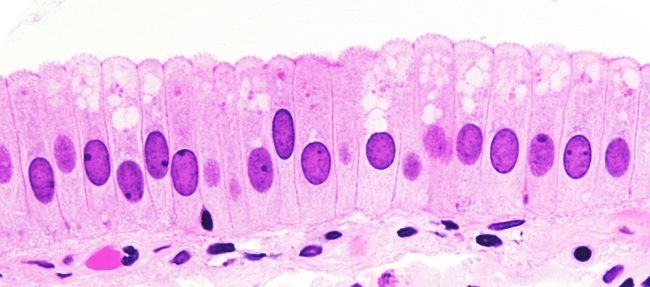
simple columnar
form - single layer of cells that are higher than wide
function - absorption
found in - lining of stomach, intestines
function - absorption
found in - lining of stomach, intestines
40
New cards
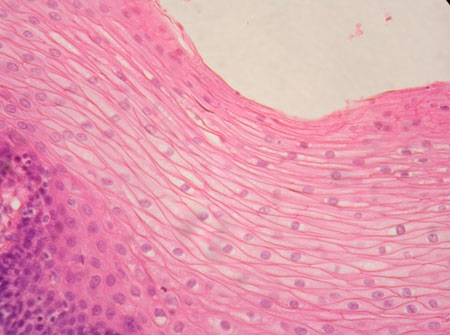
stratified squamos
form - several layers of closely packed scale like cells
function - protection
found in - skin
function - protection
found in - skin
41
New cards
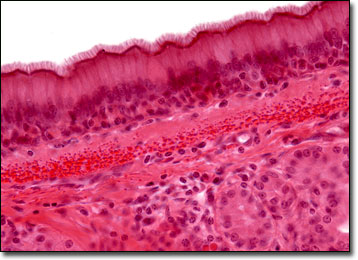
pseudo - stratified
form - 2 layers thick
function - protects lungs against dust, etc
found in - lining of trachea
*always has hairs *
function - protects lungs against dust, etc
found in - lining of trachea
*always has hairs *
42
New cards
body tissues
Tissues differ from each other in size, shape and the kind of material between their cells
43
New cards
body tissues (Epithelial)
covers/lines body
44
New cards
body tissues (connective)
most abundant - connects body part
45
New cards
body tissues (muscle)
responsible for movement
46
New cards
body tissues (nervous)
responsible for sending quick messages
47
New cards
shapes of cells (squamos)
flat and scalelike
48
New cards
shapes of cells (cubodial)
cube shaped
49
New cards
shapes of cells (columnar)
higher than they are wide
50
New cards
arrangement of cells (simple)
single layer of cells of the same shape
51
New cards
arrangement of cells (stratified)
many layers of cells of the same shape
52
New cards
arrangement of cells (transitional)
several layers of cells of different shape
53
New cards
Integumentary system
function - made up of skin; sweat, protection, helps with body temp
SKIN - helps with body temp regulation and protection
SKIN - helps with body temp regulation and protection
54
New cards
Skeletal System
function - allows movement, bones create blood and cells, protects internal organs
BONES - skull, spine, sternum, ribs, collarbone, protects internal organs
BONES - skull, spine, sternum, ribs, collarbone, protects internal organs
55
New cards
Muscular System
function - movement
Muscles - movement, smooth, skeletal, and cardiac tissue
Muscles - movement, smooth, skeletal, and cardiac tissue
56
New cards
Nervous System
function - sends electrical signals that allow for the body to control muscle movements and maintain homeostasis by activating glands and muscles
SPINAL CORD - sends commands to the body that were sent from the brain
BRAIN - command center of the body, controls motor skills, memory, and vision, regulates the body
SPINAL CORD - sends commands to the body that were sent from the brain
BRAIN - command center of the body, controls motor skills, memory, and vision, regulates the body
57
New cards
Endocrine System
function - creation of hormones that get sent around the body to maintain homeostasis, helps control moos and the way our organs work
PITUITARY GLAND - regulates growth, metabolism, and reproduction
ADRENAL GLAND - release hormones to maintain multiple bodily functions
THYROID - releases hormones to keep bodys metabolism under control
PITUITARY GLAND - regulates growth, metabolism, and reproduction
ADRENAL GLAND - release hormones to maintain multiple bodily functions
THYROID - releases hormones to keep bodys metabolism under control
58
New cards
Reproductive System
function - making babies
OVARIES - eggs, estrogen
TESTES - sperm, testosterones
OVARIES - eggs, estrogen
TESTES - sperm, testosterones
59
New cards
Lymphatic System
function - defends against infections and other diseases, protect body from invading pathos, transport lymph, white blood cells, fats, proteins, IMMUNE
SPLEEN - stores and filters blood, takes things out that are dead
THYMUS - produces and trains lymphocytes, immune cannot live without it
*T cells - white blood cells *
SPLEEN - stores and filters blood, takes things out that are dead
THYMUS - produces and trains lymphocytes, immune cannot live without it
*T cells - white blood cells *
60
New cards
Cardiovascular System
function - move nutrients and oxygen through the body
HEART - pumps blood so you can deliver the oxygen and nutrients throughout the body
ARTERIES - separates the oxygen and nutrients through your body
VEINS - bring the use of oxygen and nutrients to the heart so the heart can do its job
HEART - pumps blood so you can deliver the oxygen and nutrients throughout the body
ARTERIES - separates the oxygen and nutrients through your body
VEINS - bring the use of oxygen and nutrients to the heart so the heart can do its job
61
New cards
Respiratory System
function - transport fresh air into your body while disposing waste gas (co2)
LARYNX- hollow tube that transports air from throat to trachea to your lungs
BRONCHI - carry oxygen to and from your lungs
LUNGS - bring air from the atmosphere and move oxygen into the blood stream
LARYNX- hollow tube that transports air from throat to trachea to your lungs
BRONCHI - carry oxygen to and from your lungs
LUNGS - bring air from the atmosphere and move oxygen into the blood stream
62
New cards
Digestive System
function - digest food
ESOPHAGUS - contracts as it moves food into stomach
STOMACH - holds food, enzymes and acid break down food into a liquid/goo
LIVER - process the blood, breaks down, balances and creates nutrients
SMALL INTESTINES - helps to further digest food coming from the stomach, nutrient absorption
GALLBLADDER - small pouch under liver, stores bile produced by liver
LARGE INTESTINES - absorbs water and changes the waste from liquid into stool
PANCREAS - enzymes that releases hormones insuline and glucagon into the blood stream
ESOPHAGUS - contracts as it moves food into stomach
STOMACH - holds food, enzymes and acid break down food into a liquid/goo
LIVER - process the blood, breaks down, balances and creates nutrients
SMALL INTESTINES - helps to further digest food coming from the stomach, nutrient absorption
GALLBLADDER - small pouch under liver, stores bile produced by liver
LARGE INTESTINES - absorbs water and changes the waste from liquid into stool
PANCREAS - enzymes that releases hormones insuline and glucagon into the blood stream
63
New cards
Urinary System
function - main blood filter, makes urine
KIDNEYS - main filter, filters blood
BLADDER - stores urine
URETERS - transports urine from kidney to bladder
URETHRA - takes out of body; bladder ----- > out of body
KIDNEYS - main filter, filters blood
BLADDER - stores urine
URETERS - transports urine from kidney to bladder
URETHRA - takes out of body; bladder ----- > out of body