ARCH 2311: Exam 3
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
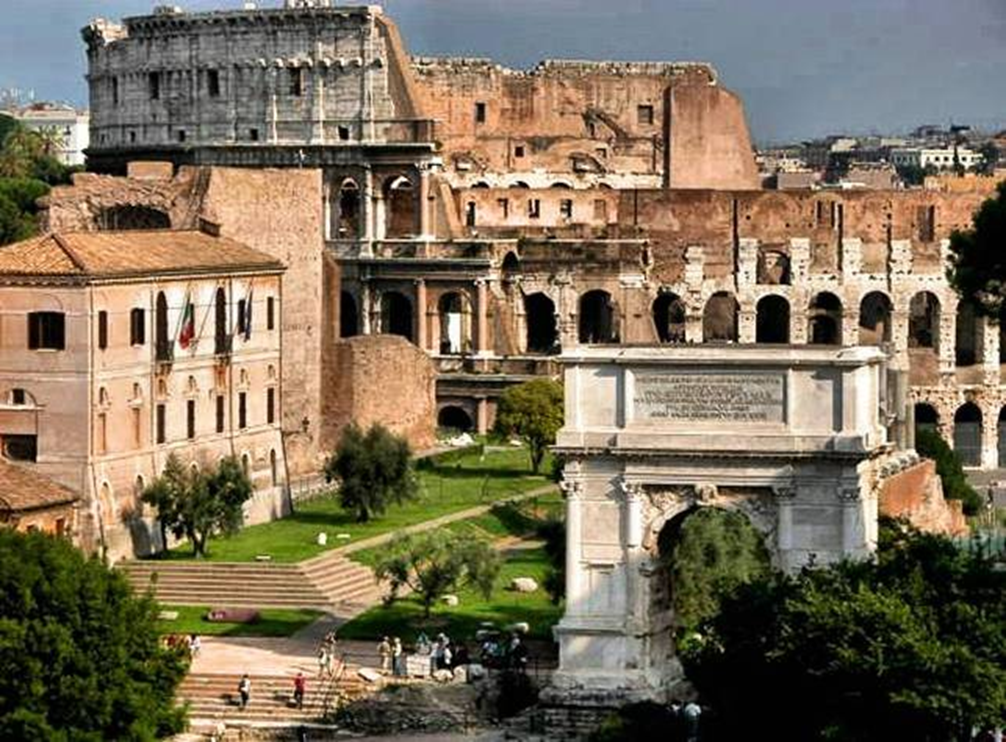
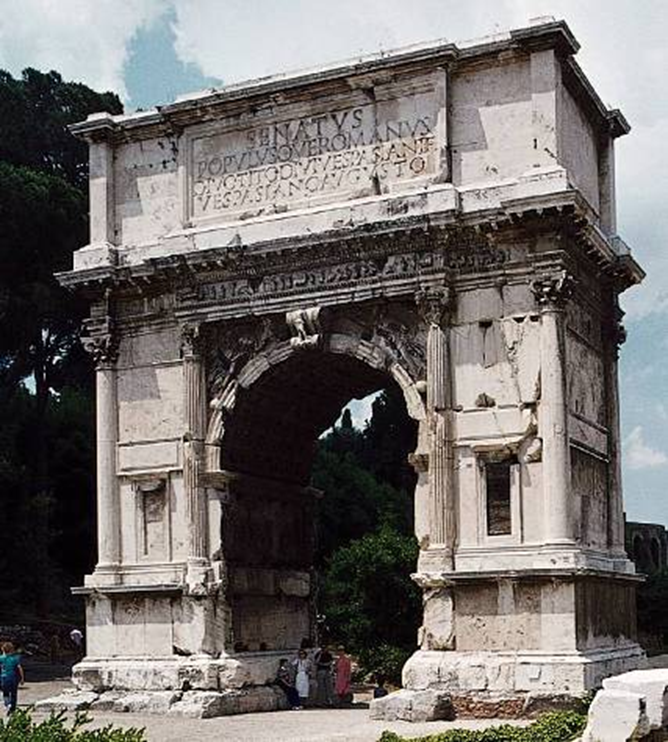
arch of titus: forum romanum, rome (after 81 ad)
imperial rome
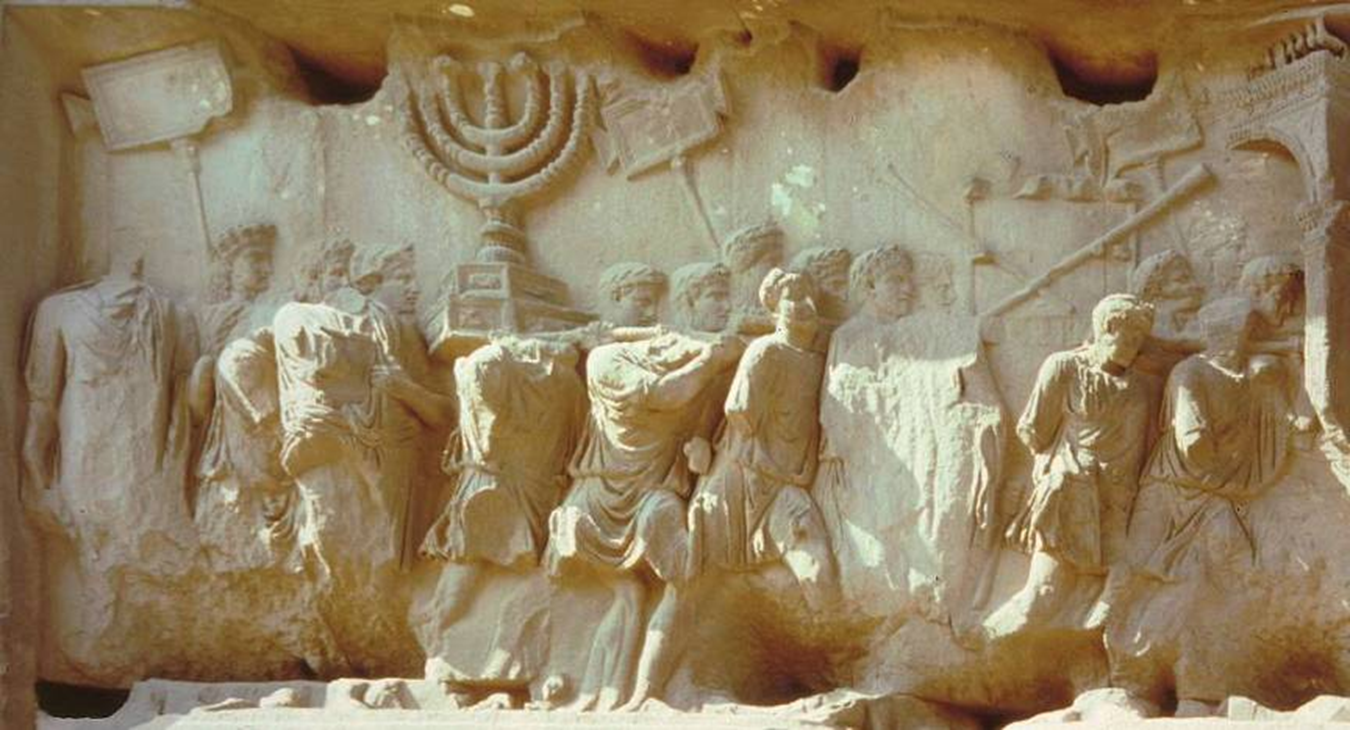



spoils of jerusalem: relief panel (marble)
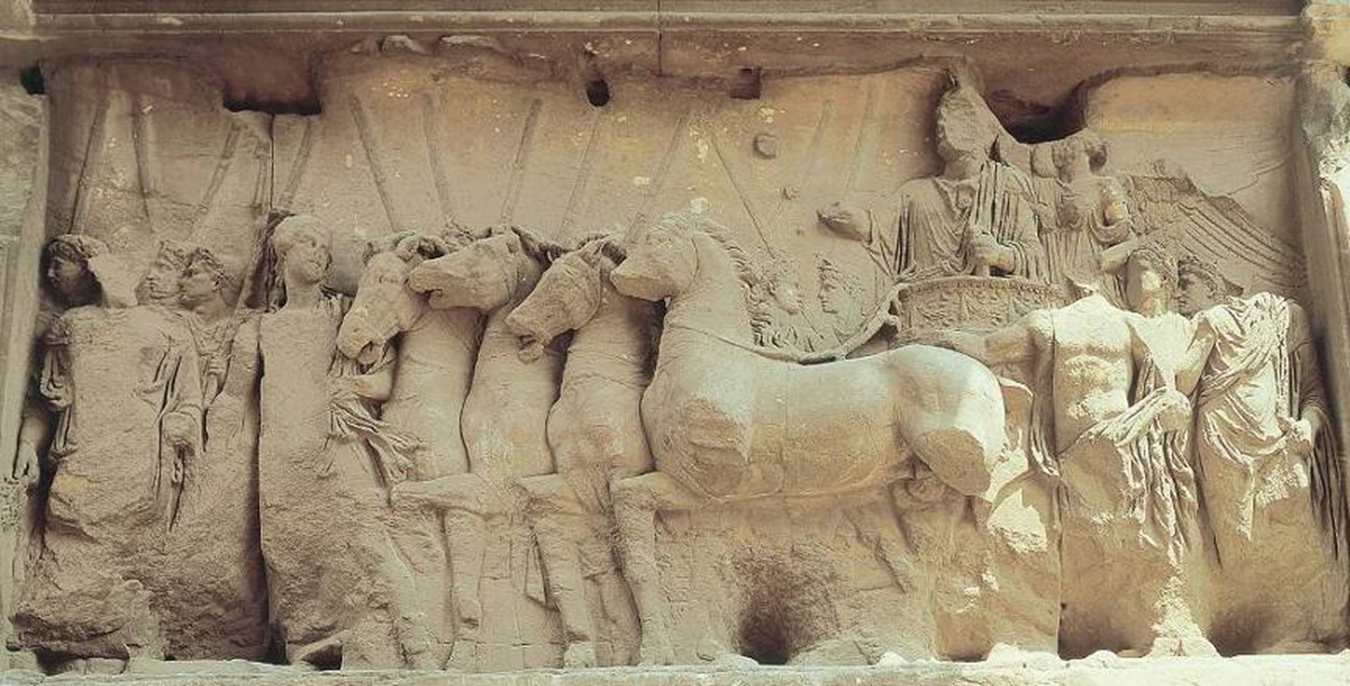

triumph of titus: relief panel (marble)
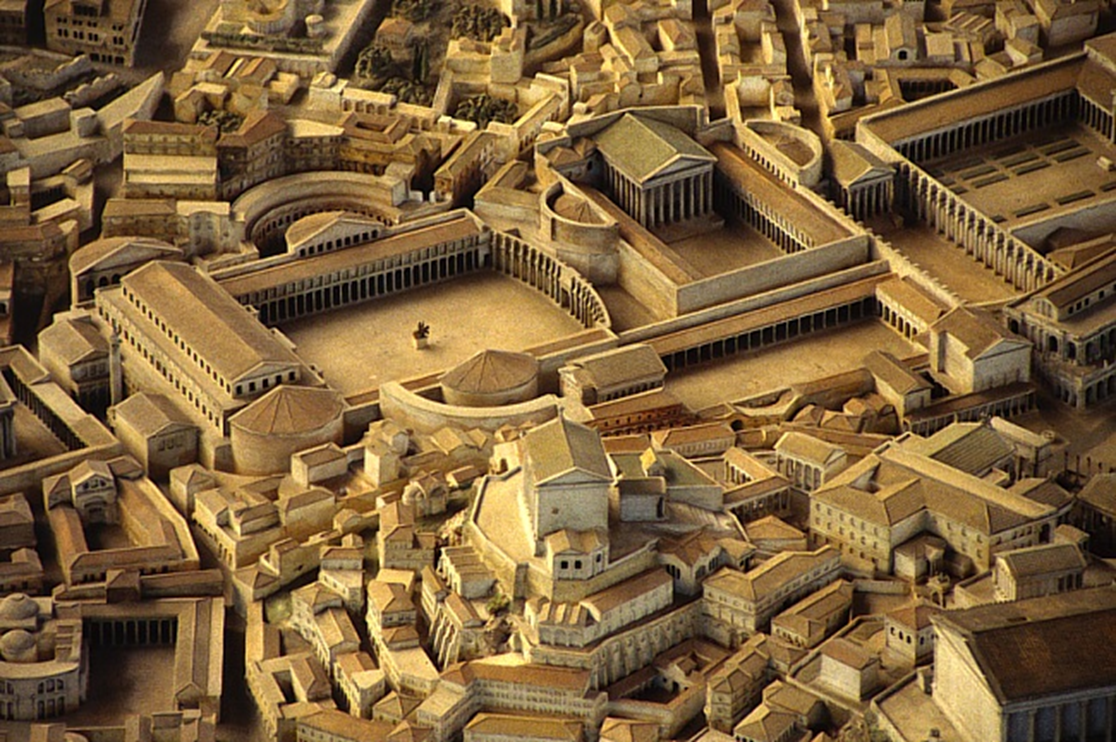
apollodorus of damascus: trajans forum, rome
imperial rome
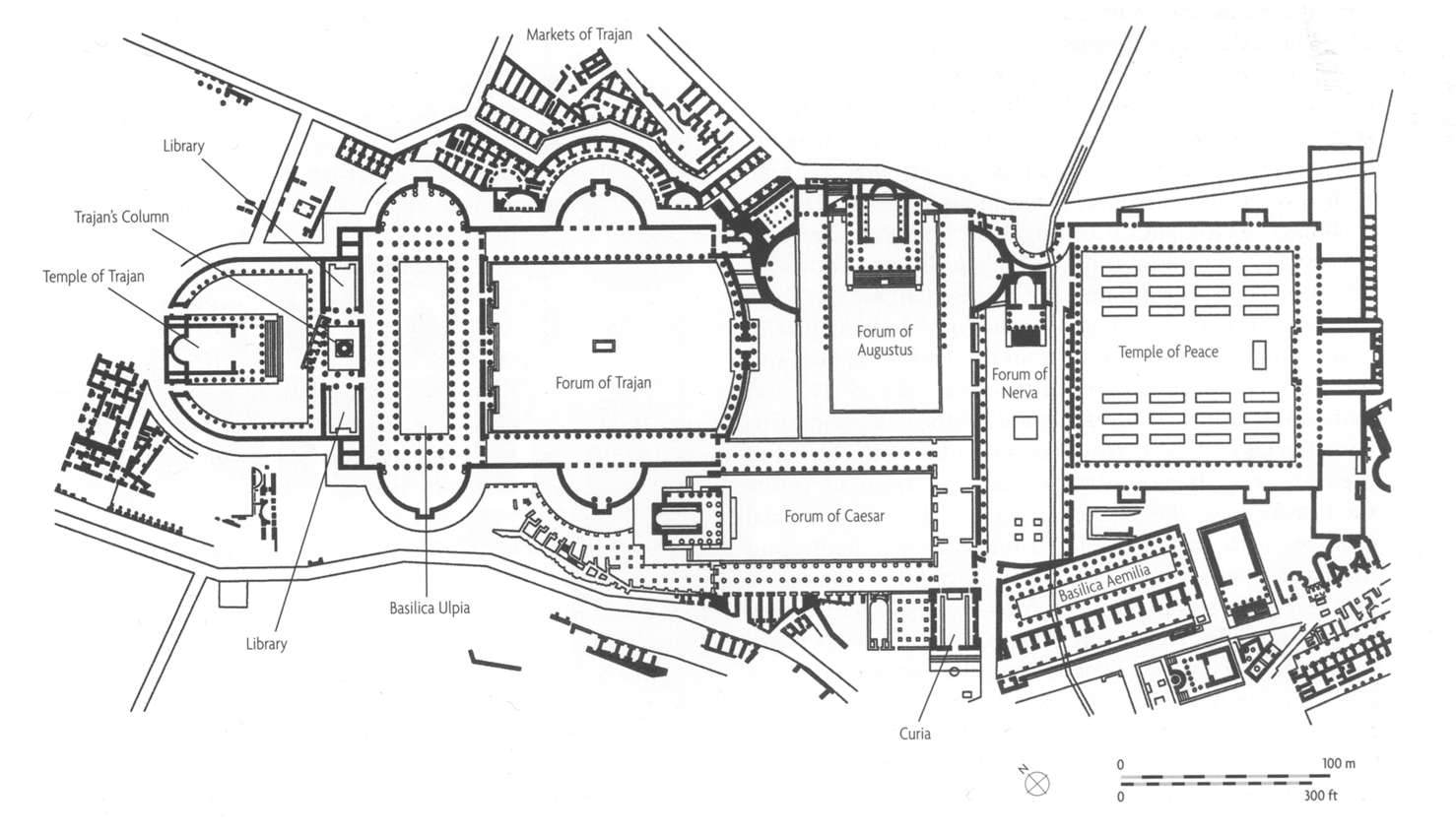
forum of trajan was the largest and the grandest of imperial forums
built using monies from the conquest of dacia

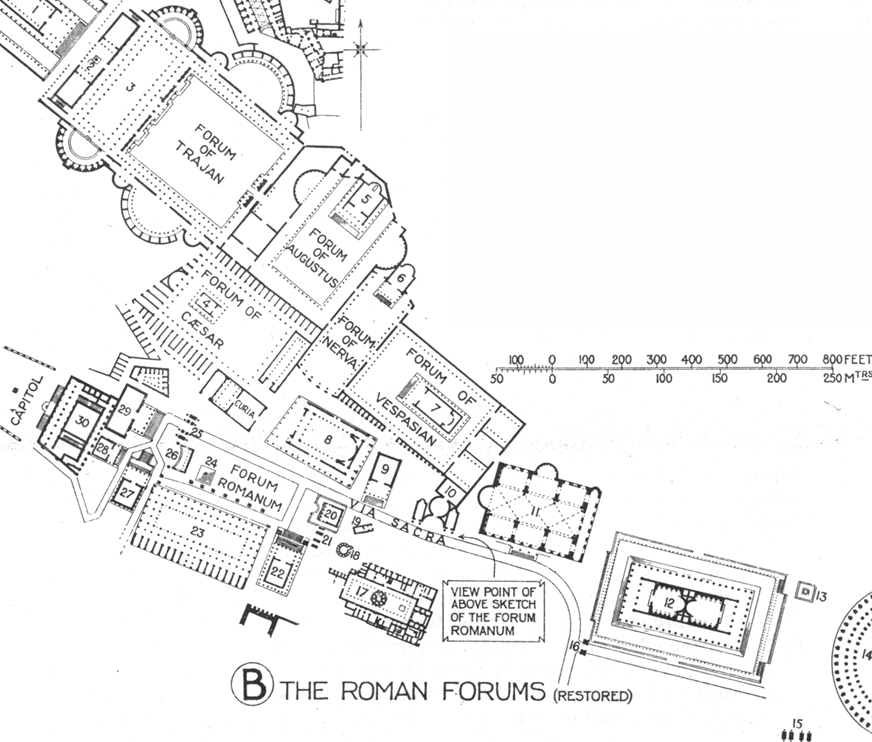
apollodorous of damascus, basilica ulpia (98-117 ad)
things found in basilicas: business dealings, contracts, courts
ulpia: family name
oriented transversely
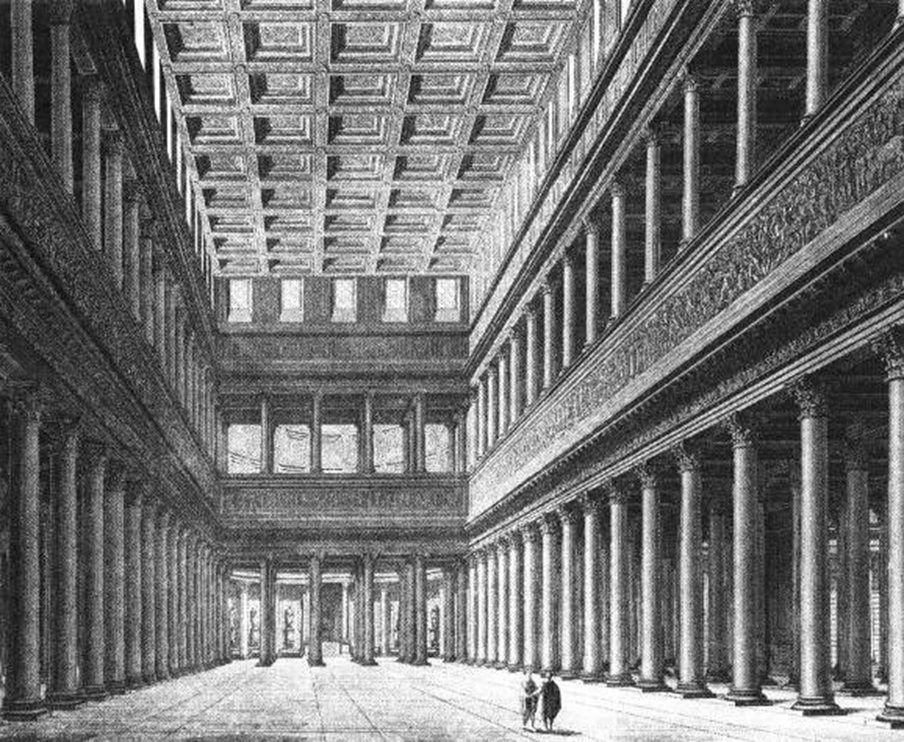
corinthian columns
nave: central space of basilica
screened off with columns
aps: half circle dome shape in back
basilicas have flat wooden roof structure (waffle like)
trajans column (106-113 ad)
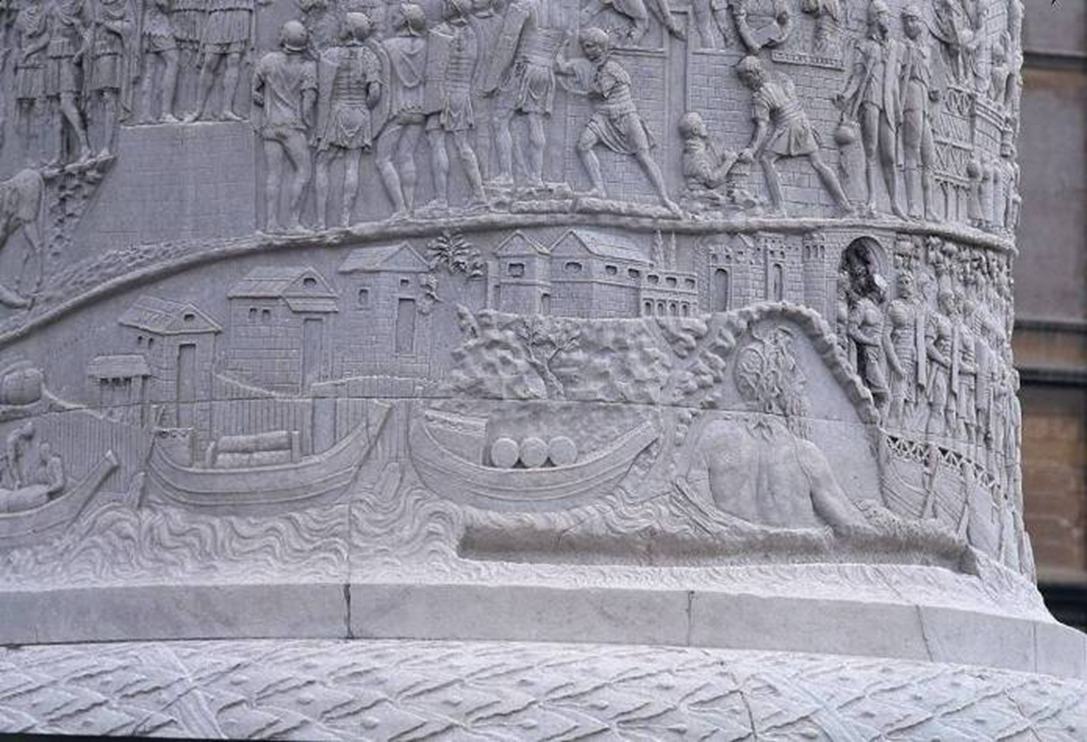


continuous seam around the shaft
625 ft of relief carvings
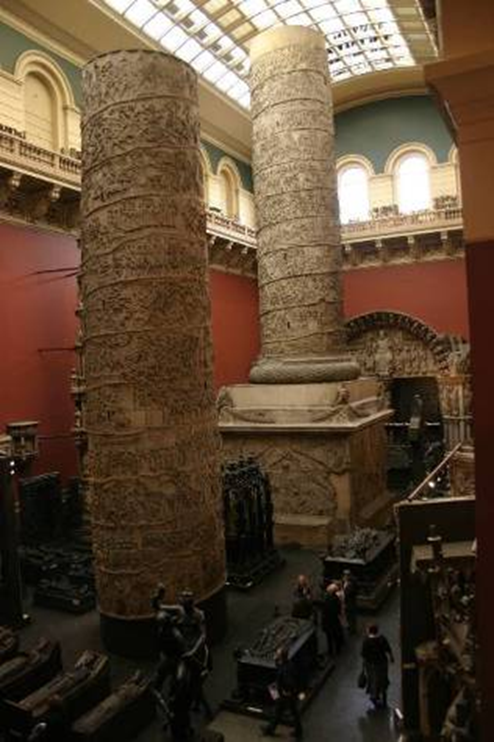

cast copy of trajan’s column in victoria and albert museum (london)
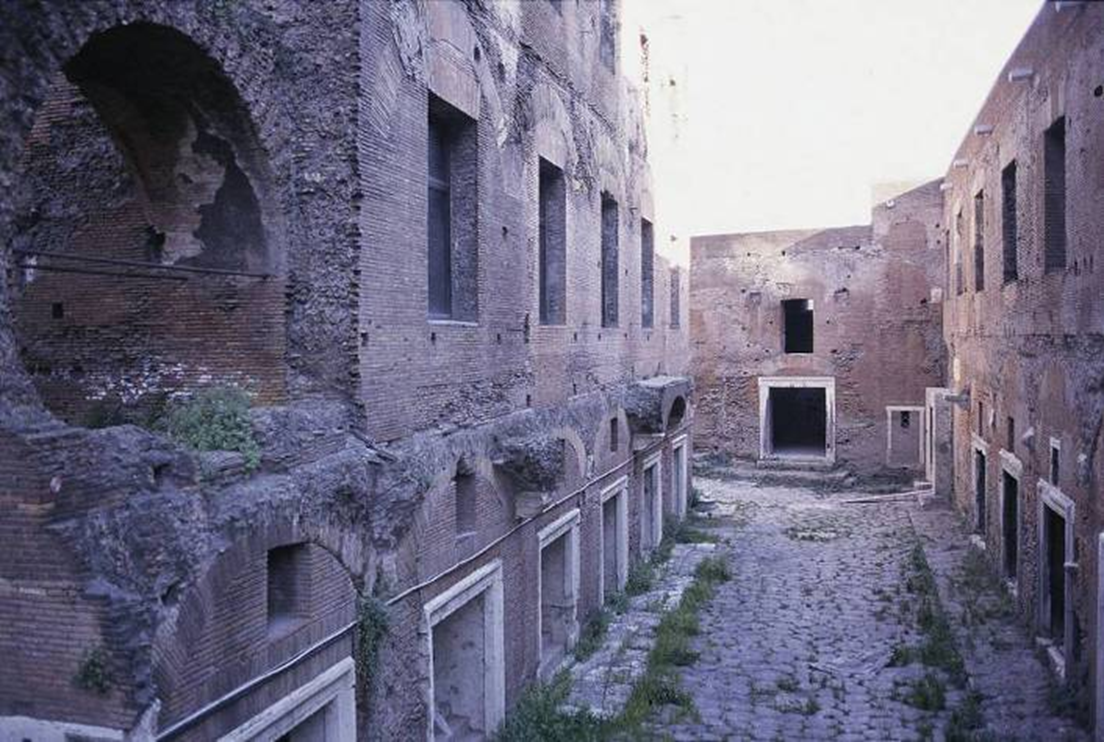
apollodorous of damascus, markets of trajan (100-112 ad)
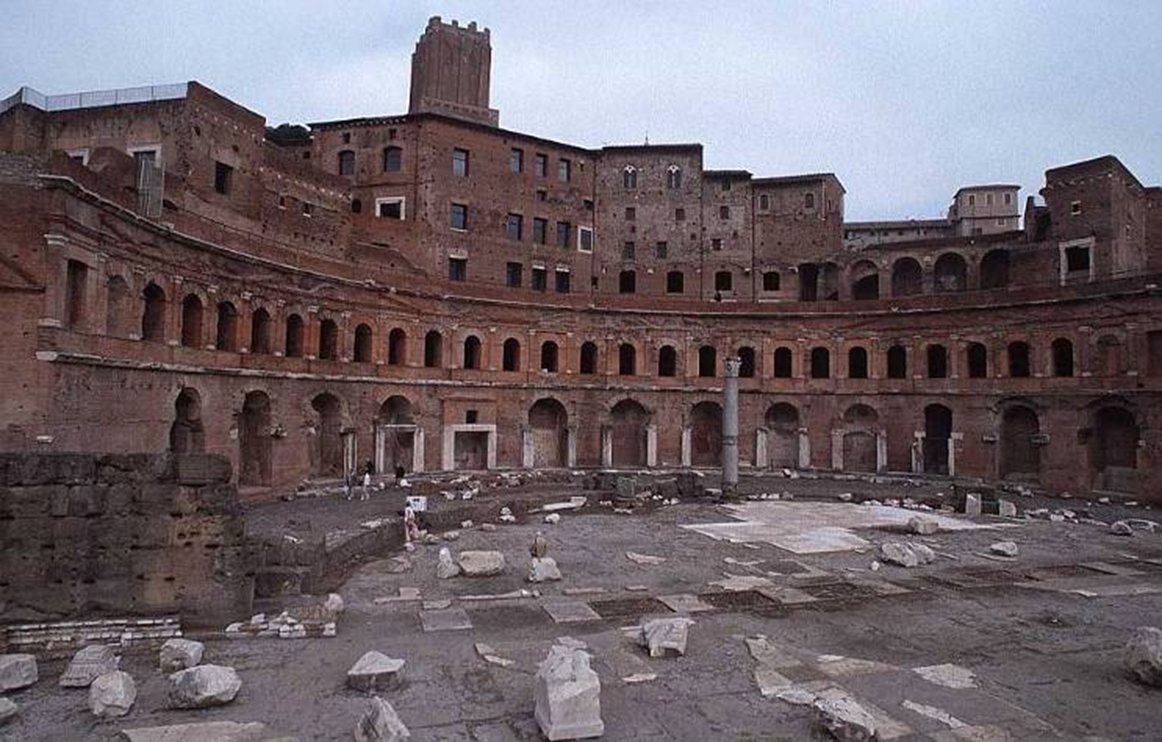

arculation arches
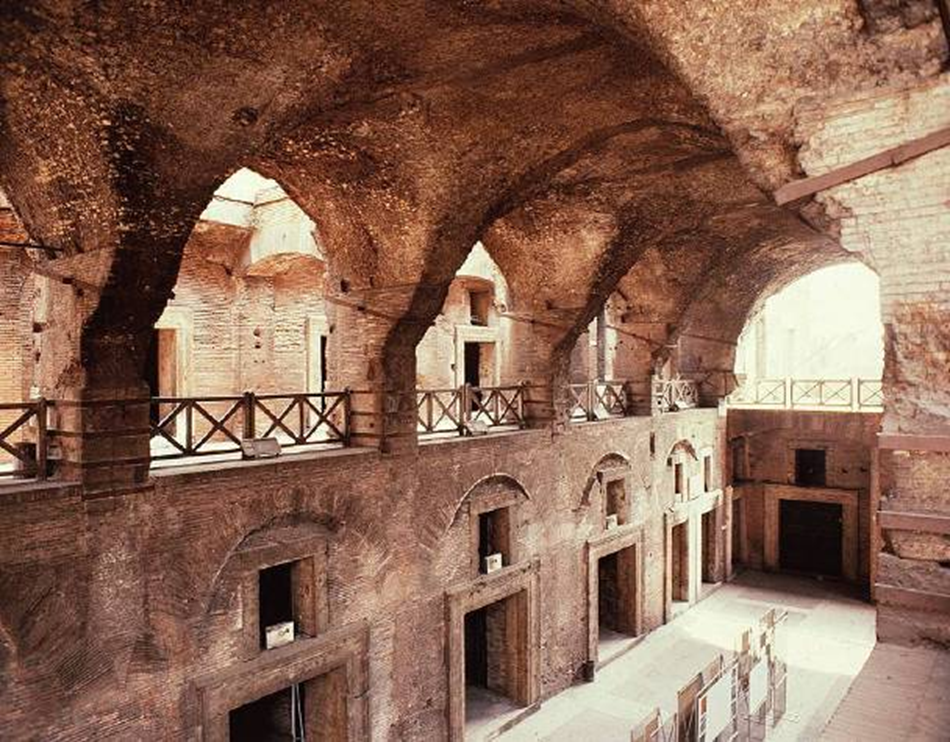


interior of great hall: groin vaults (intersected barrel vaults)
flavian amphitheater (the colosseum): rome (72-80 ad)
imperial rome
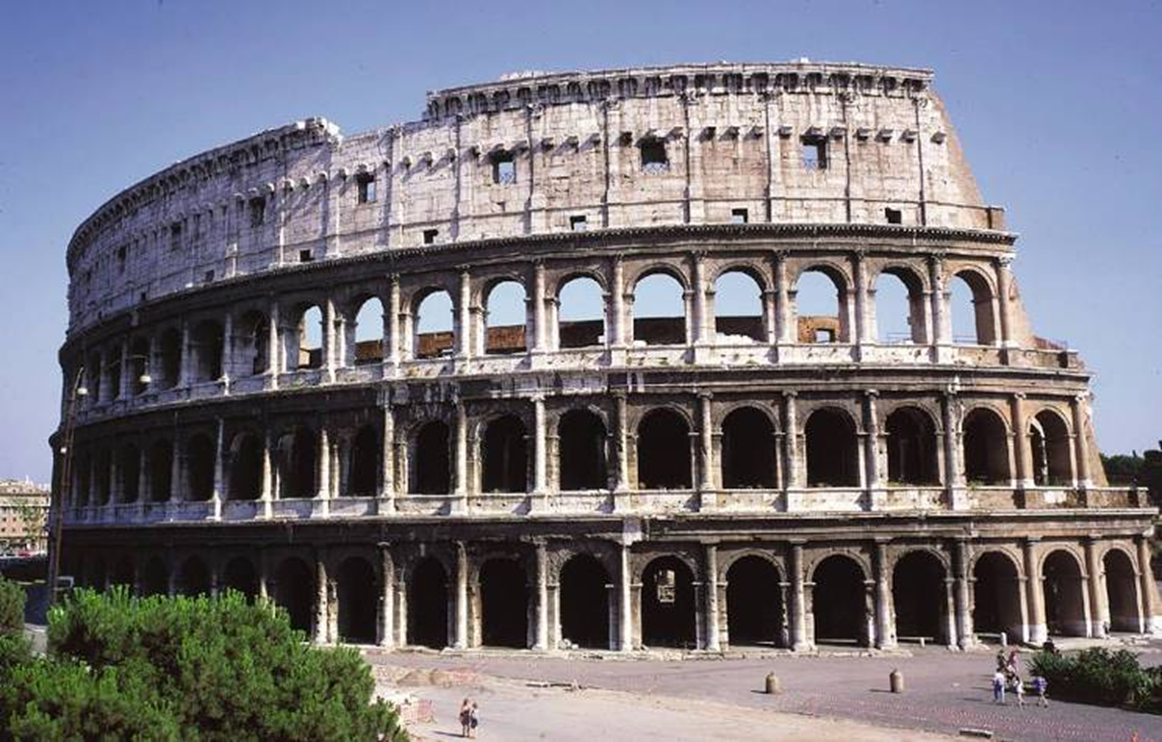

called colosseum because next to a colossal statue (colossal statue of nero)
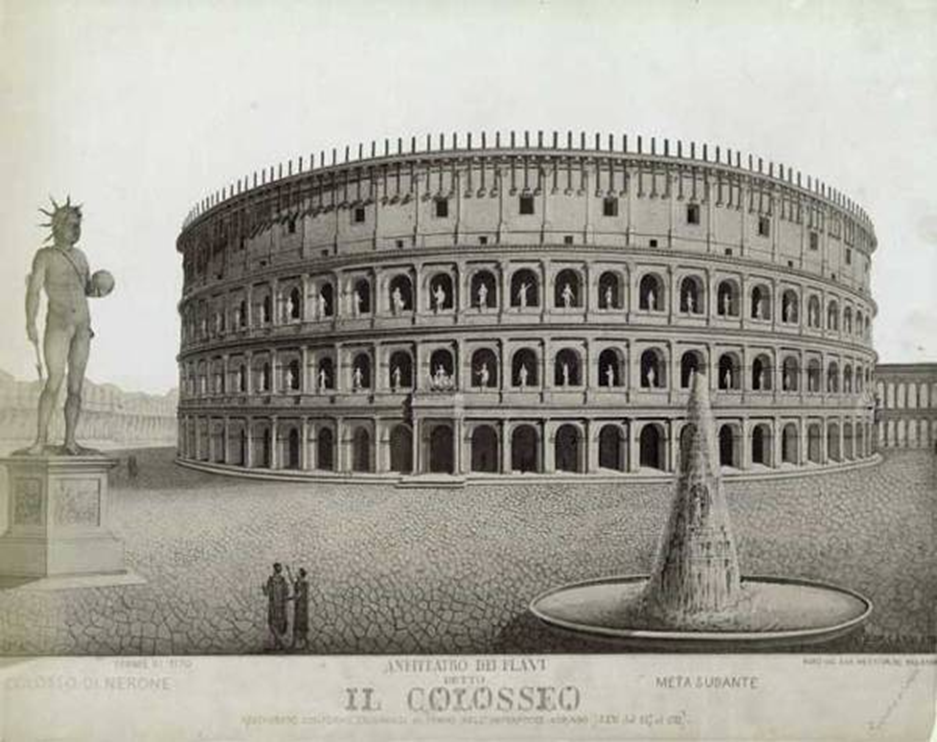

reconstruction showing colossal statue of nero modified as a sun god
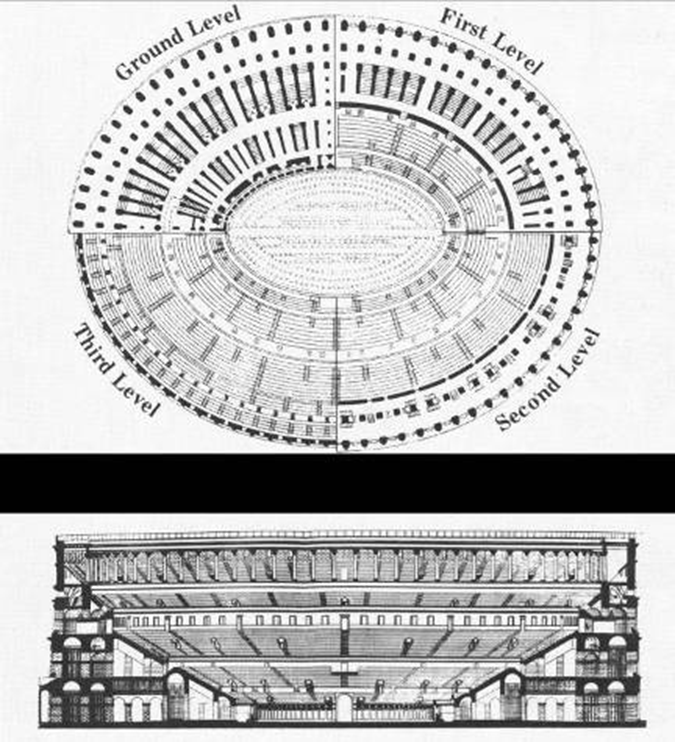
could fit 50,000 people
barrel vaults and radial barrel vaults
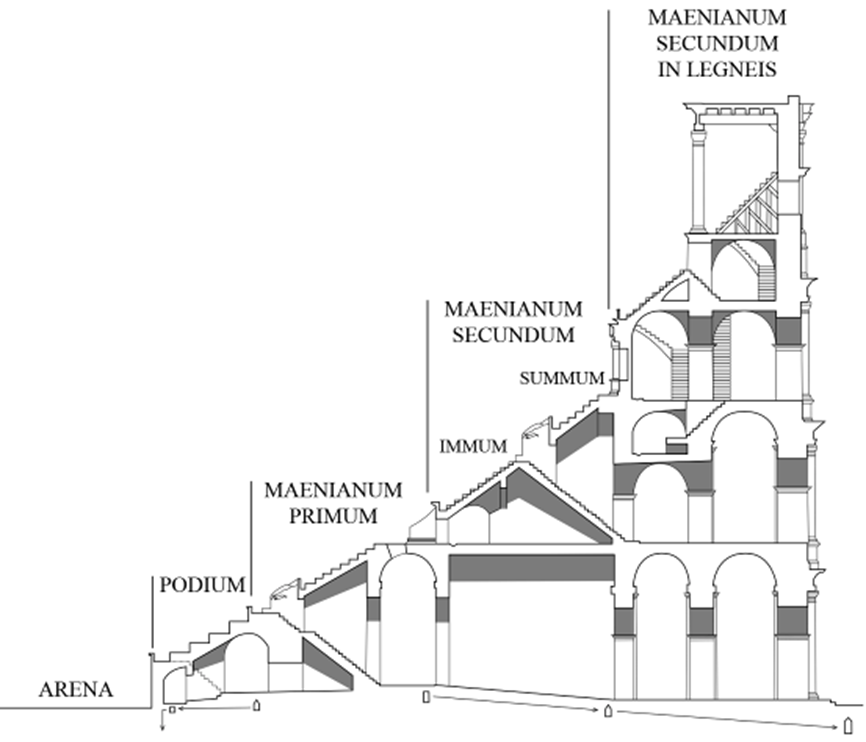
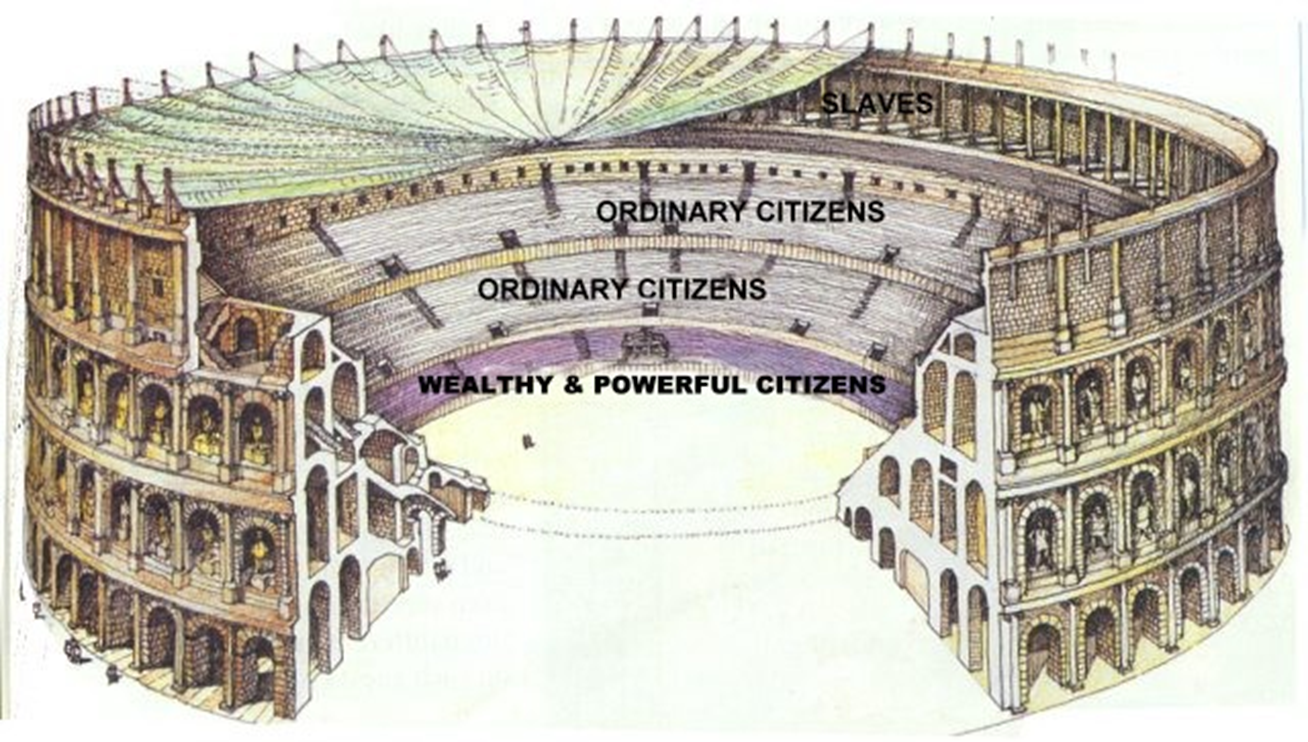
seating sections by class and tarp covering
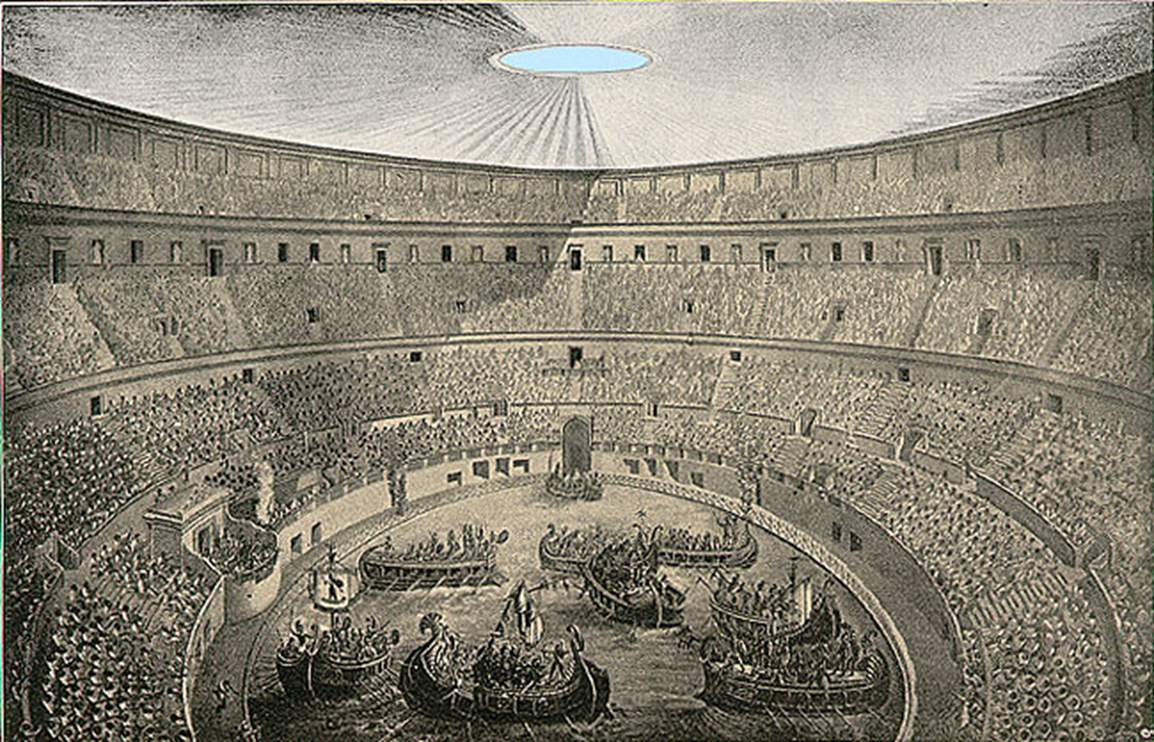
reenactment of roman naval battles
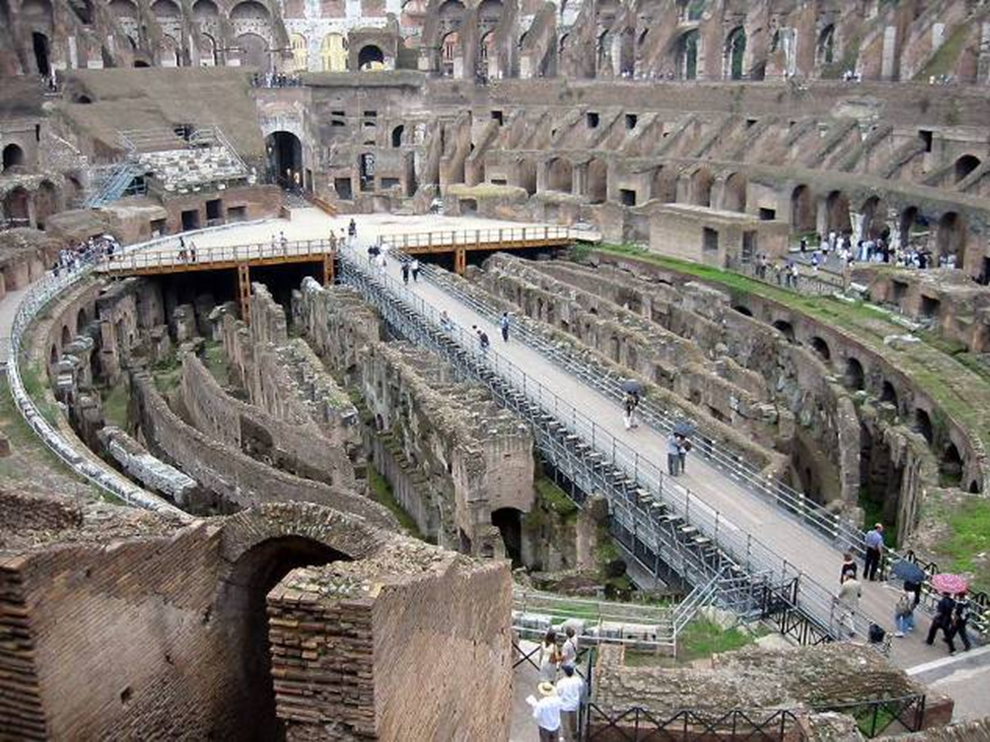

chambers under central floor (hypogeum)
hypogeum (hypo = under)
behind the scenes section (dressing rooms, animal cages, etc)
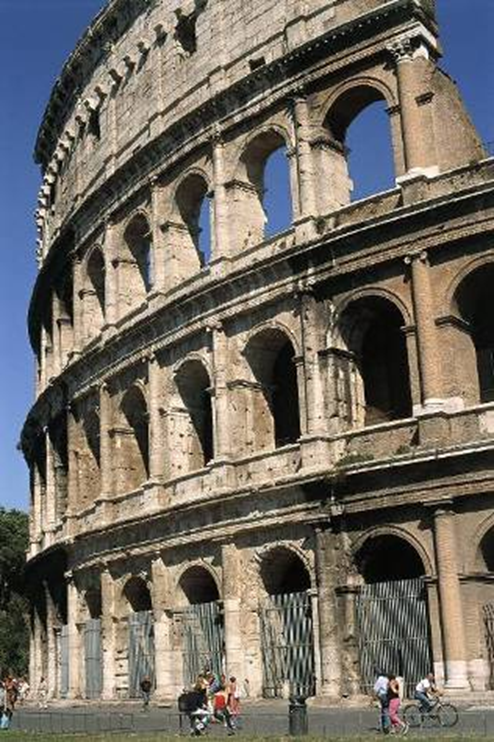

graduated orders: low orders to decorative orders (top to bottom: corinthian, ionic, tuscan)
(the very very top = corinthian pilasters)
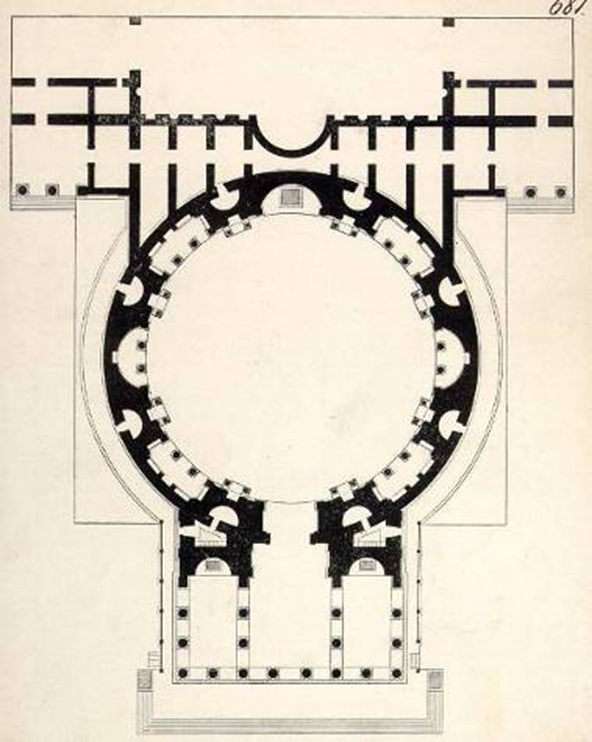
pantheon: apollodorous of damascus (architect) rome (118-128 ad)
imperial rome

octastyle

like other roman temples, is placed within temple enclosures
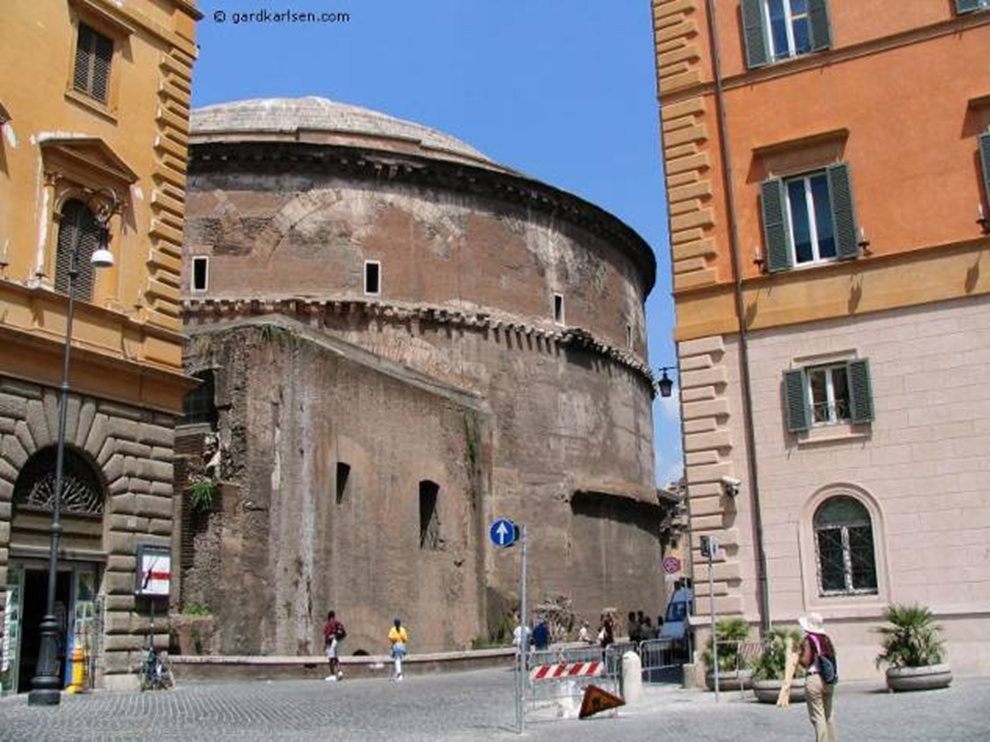

relieving arches in upper wall
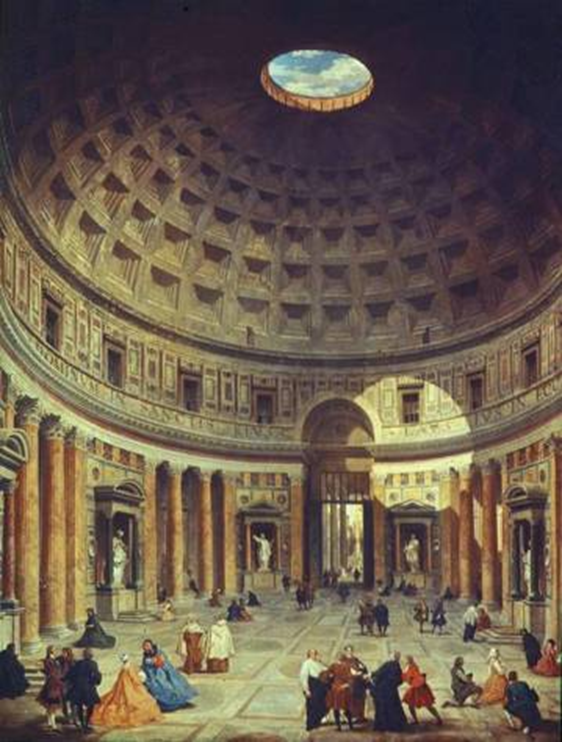

giovanni paolo, oil on canvas
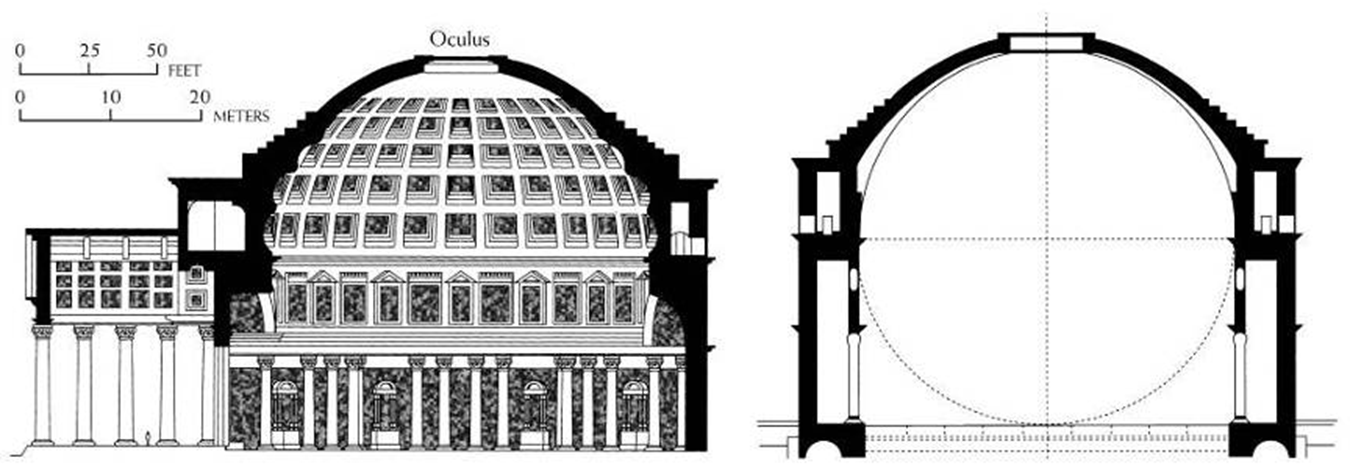
dome span & height = 142 ft
oculus = 28 ft wide
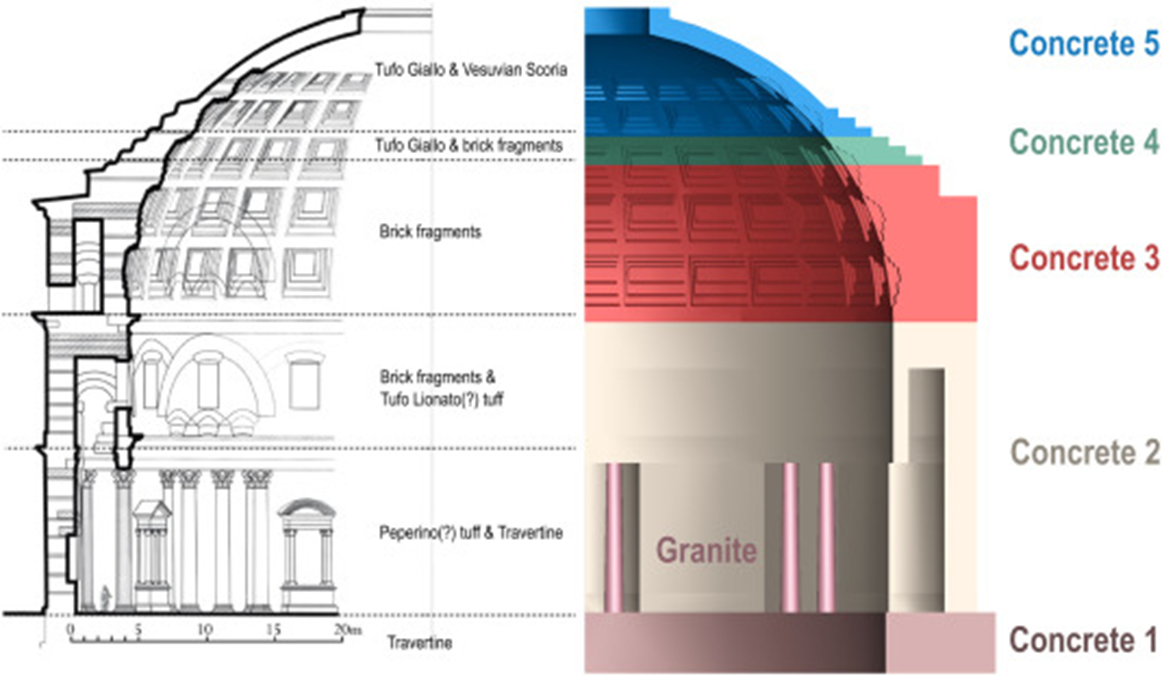
lighter aggregate (stone material?) is used in the concrete as the height increases
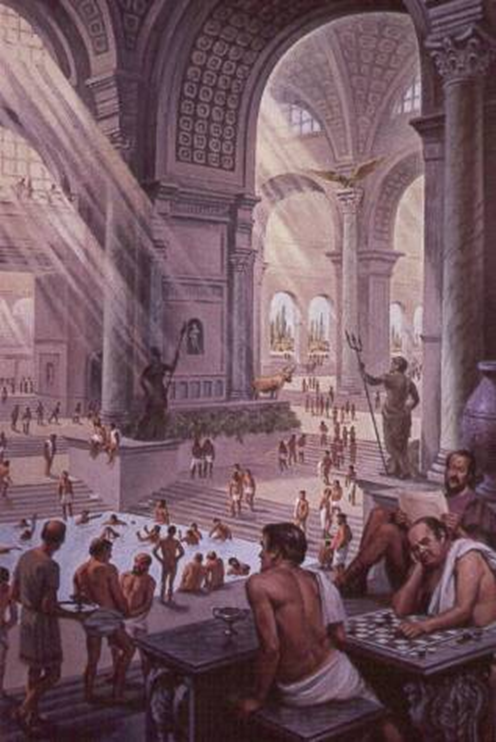
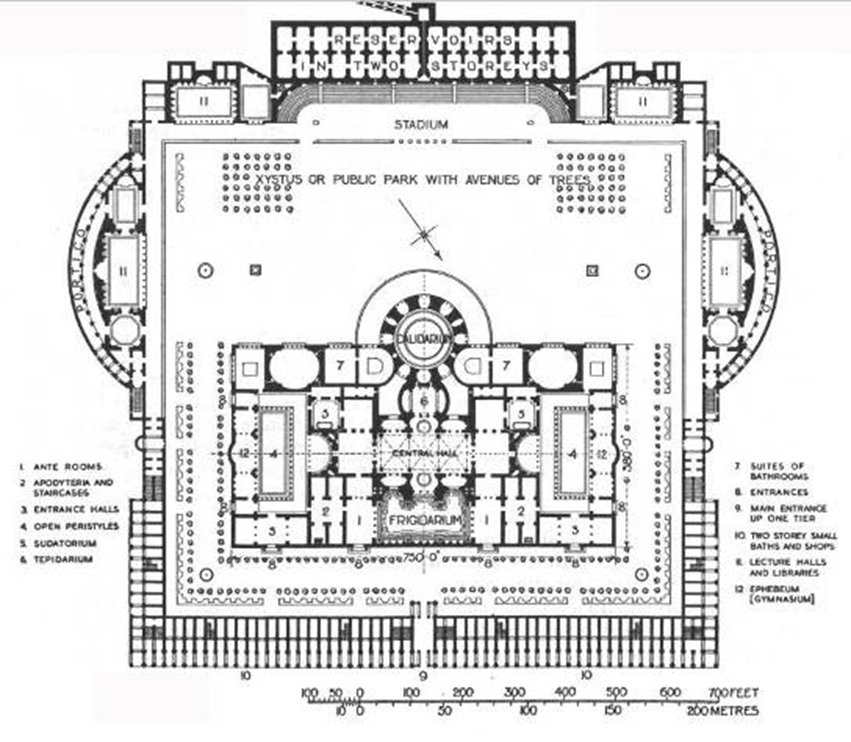
caracalla thermae, rome (211-217 ad)
imperial rome
bath house



aula palatina, at the palace of constantine, trier, germany (early 14th century)
late antiquity / early christianity
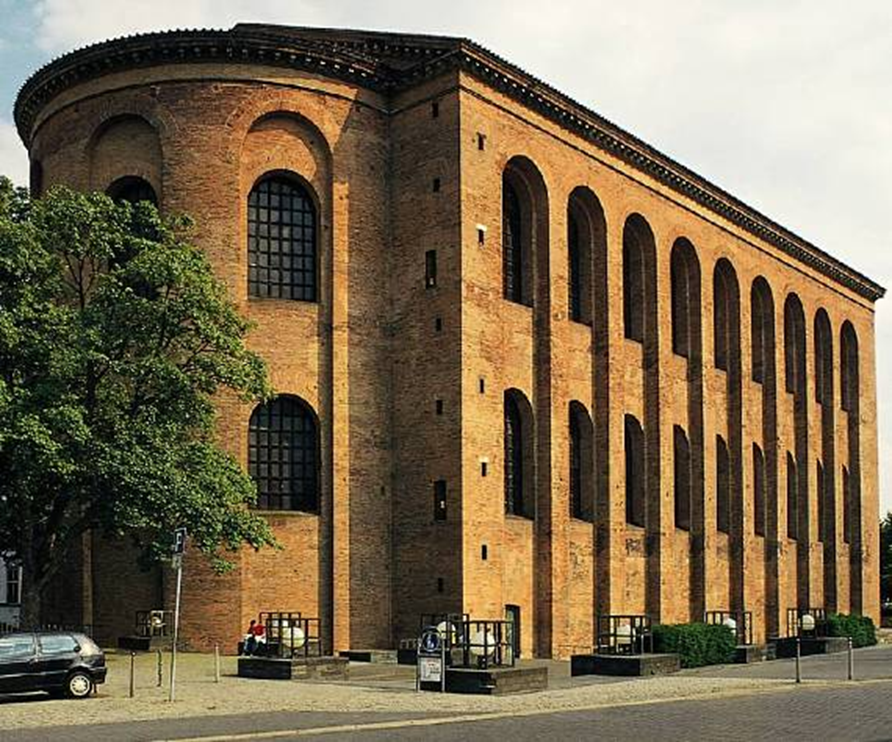
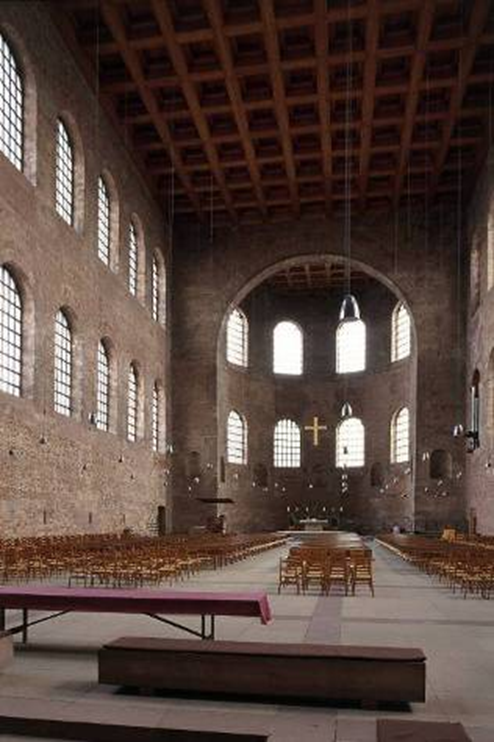

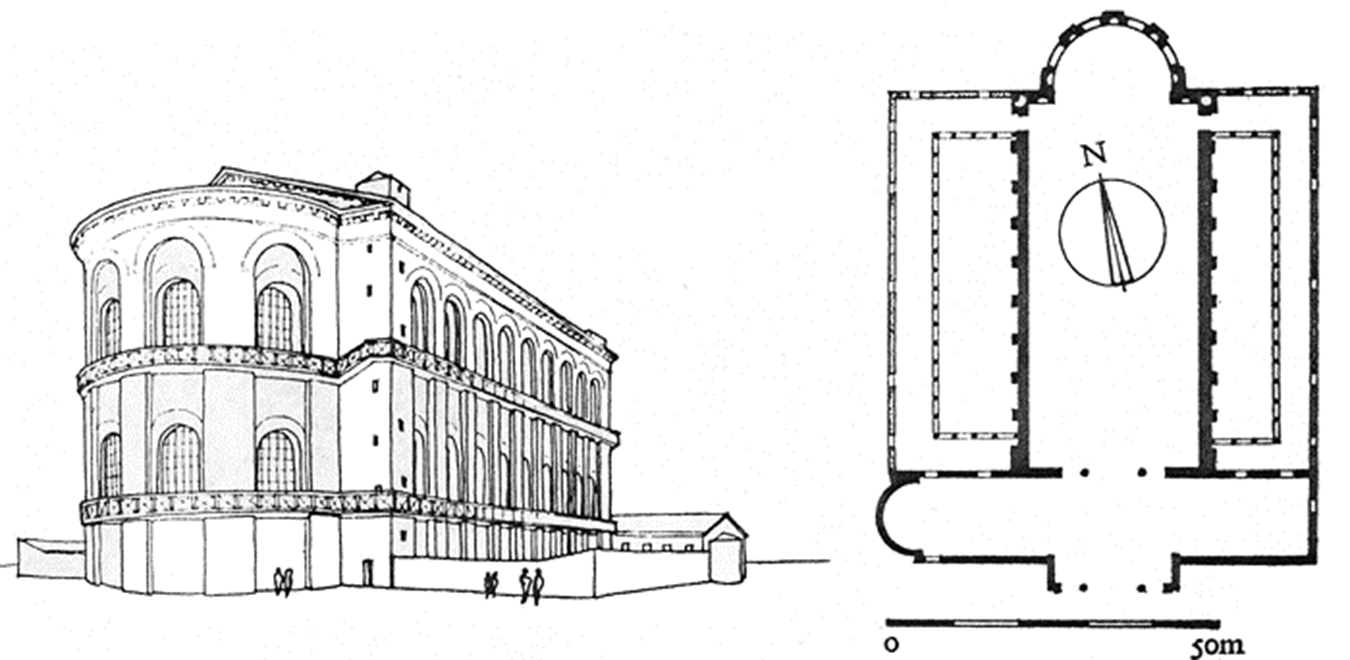

arch of constantine, rome (312-15)
late antiquity / early christianity
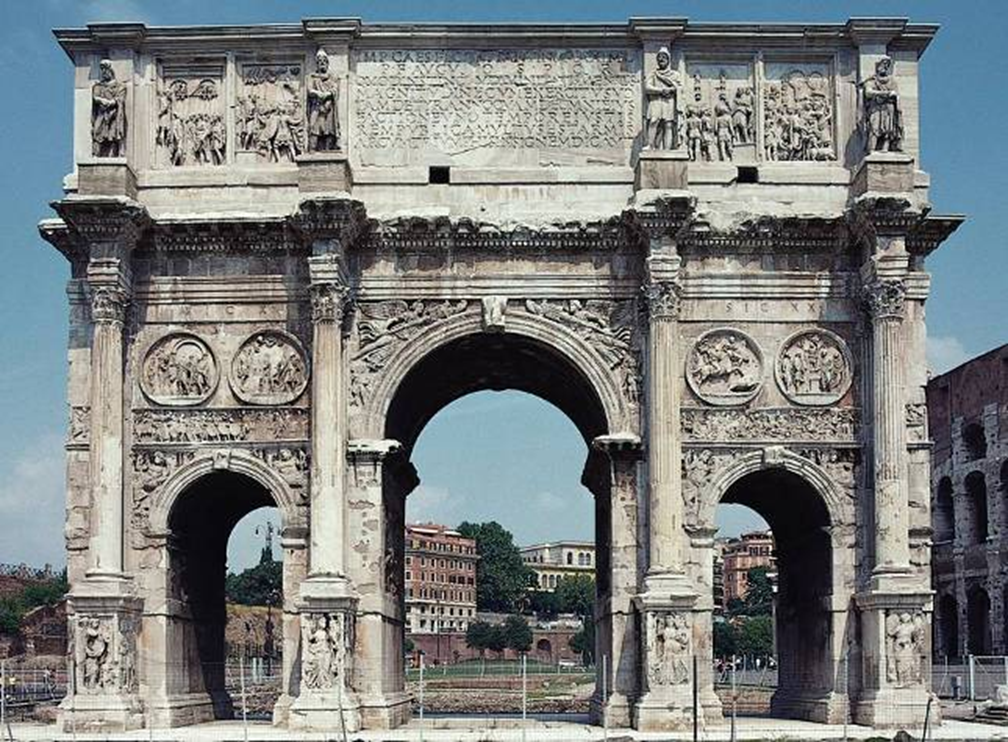
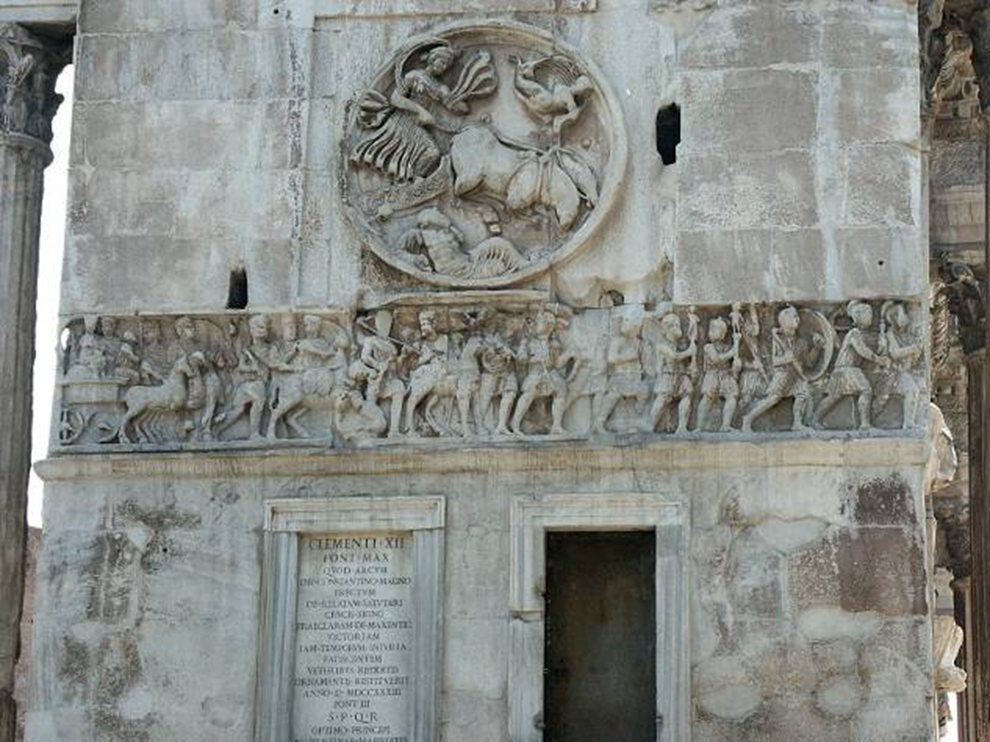


luna, rounded on west end
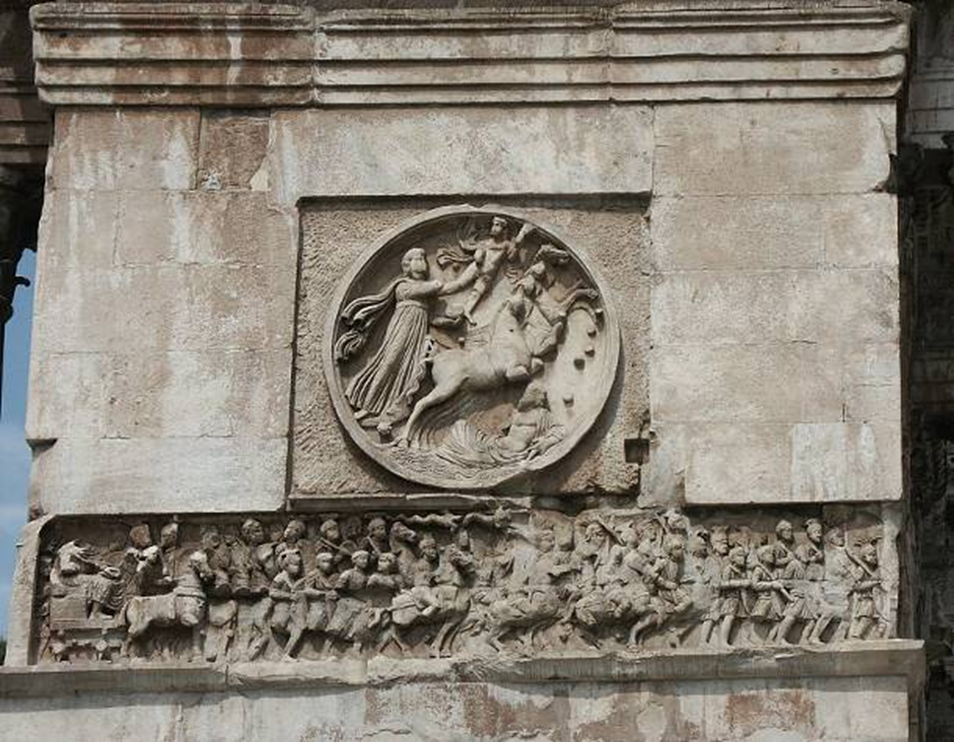

“constantine as sol invictus” rounded on east end
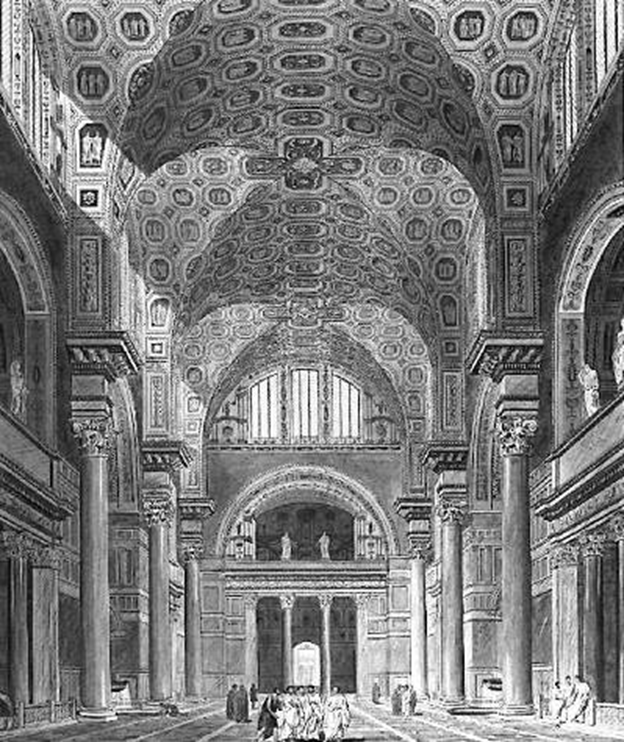
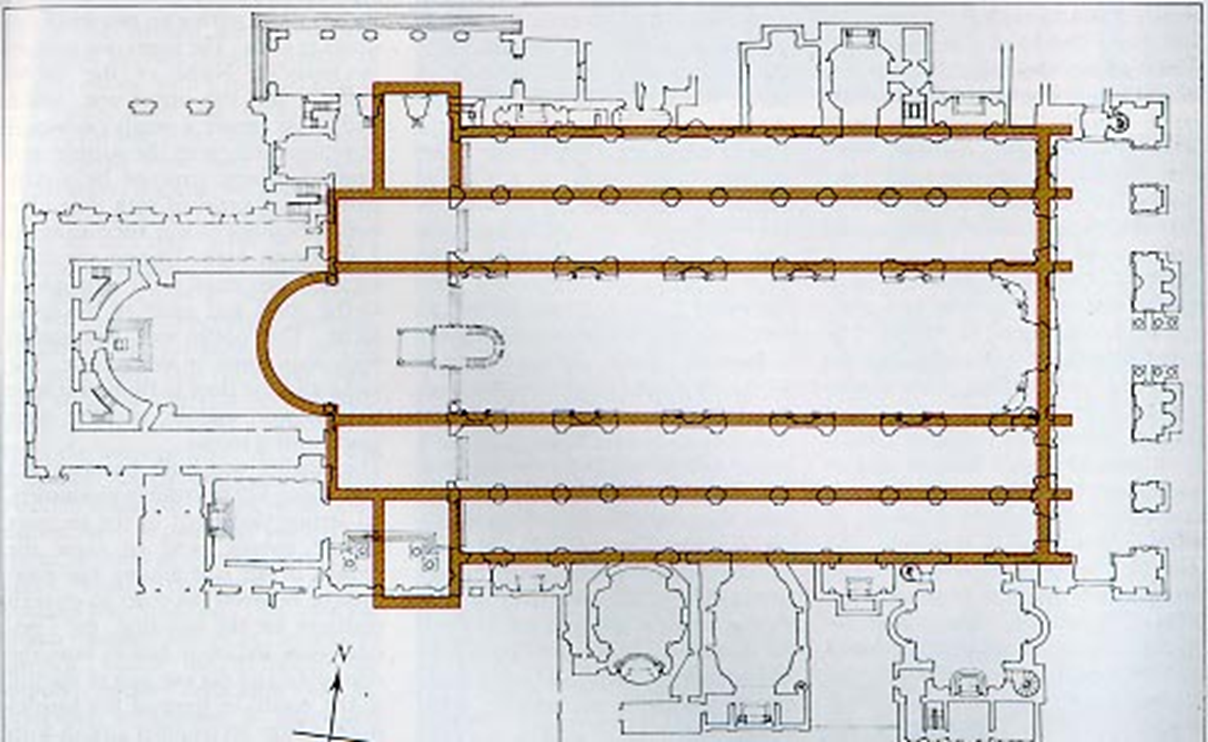
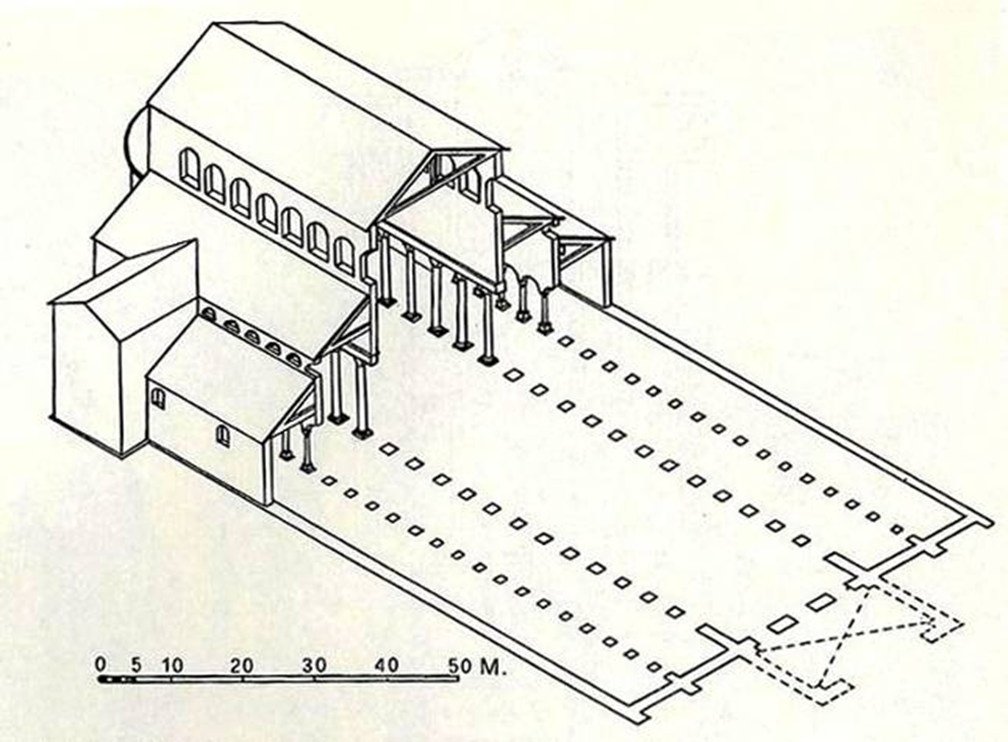
old st. peter’s, vatican hill, rome (bagan 320)
late antiquity / early christianity
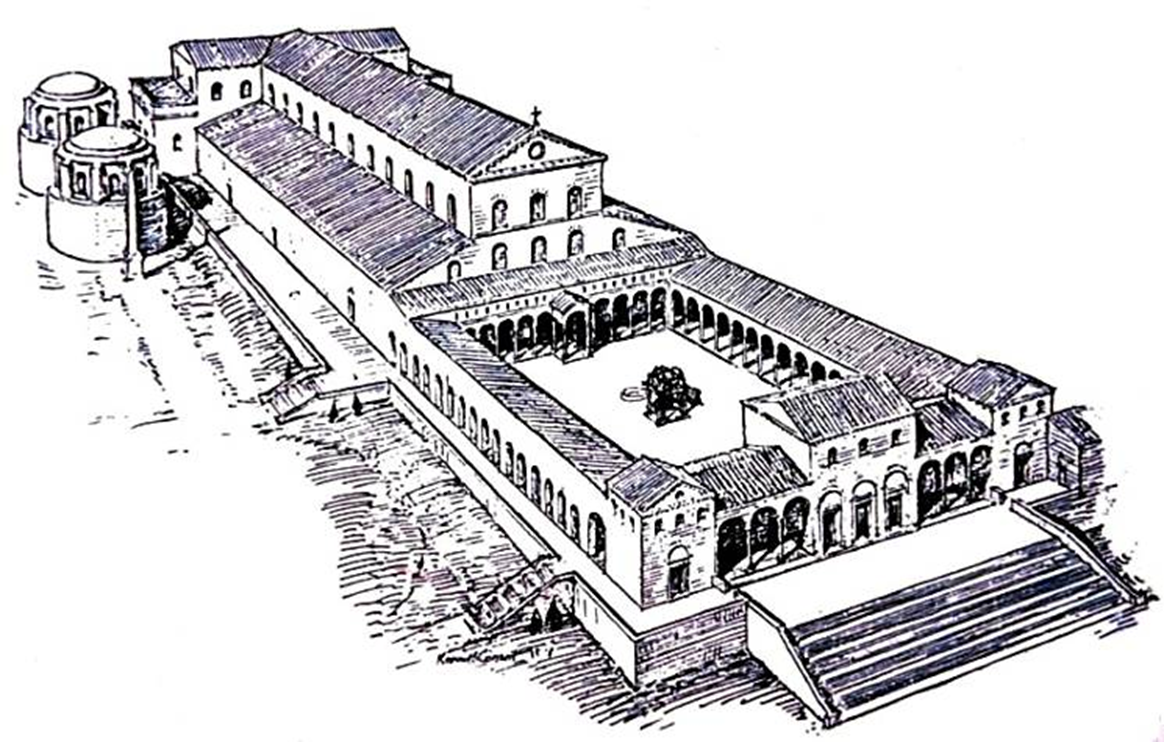
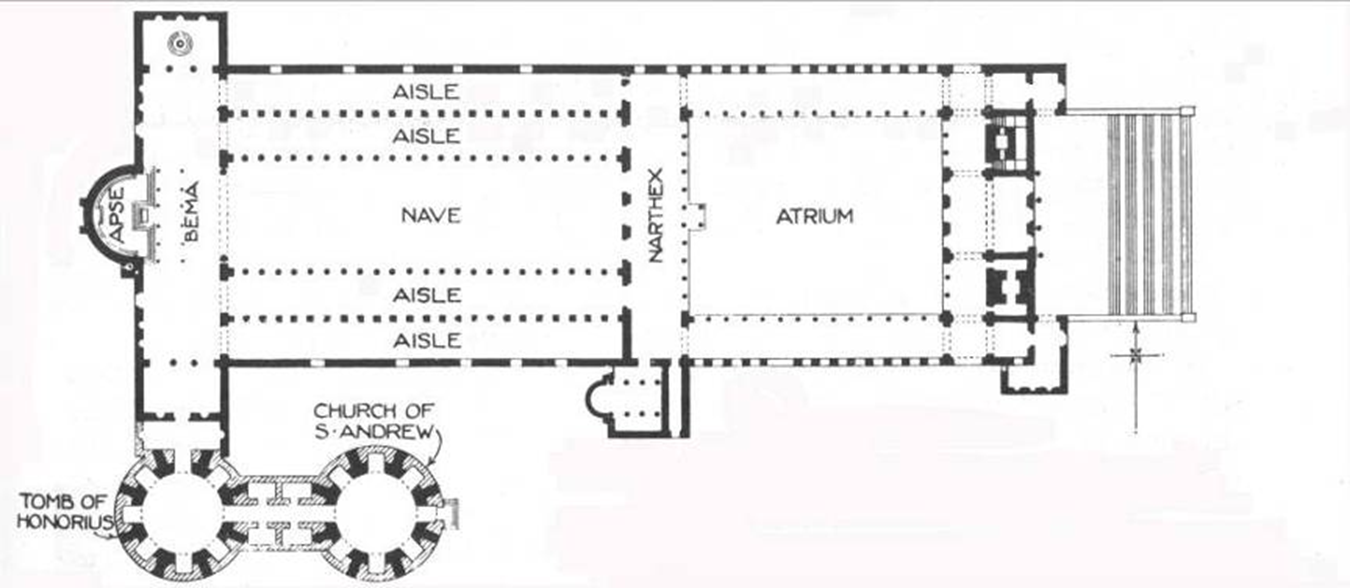
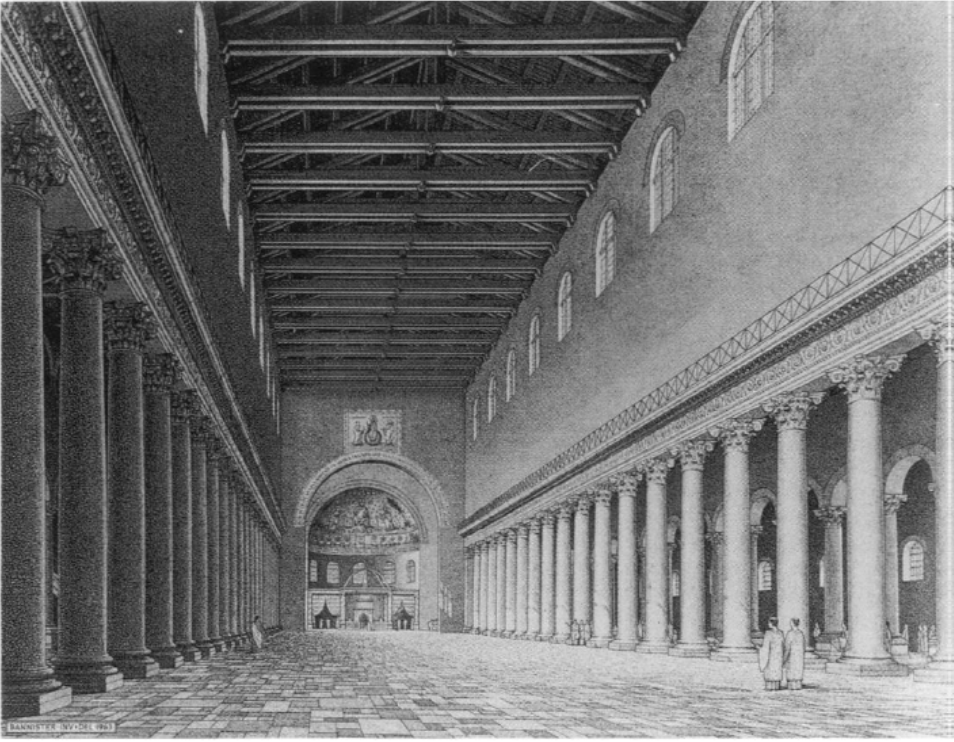
view of nave towards apse
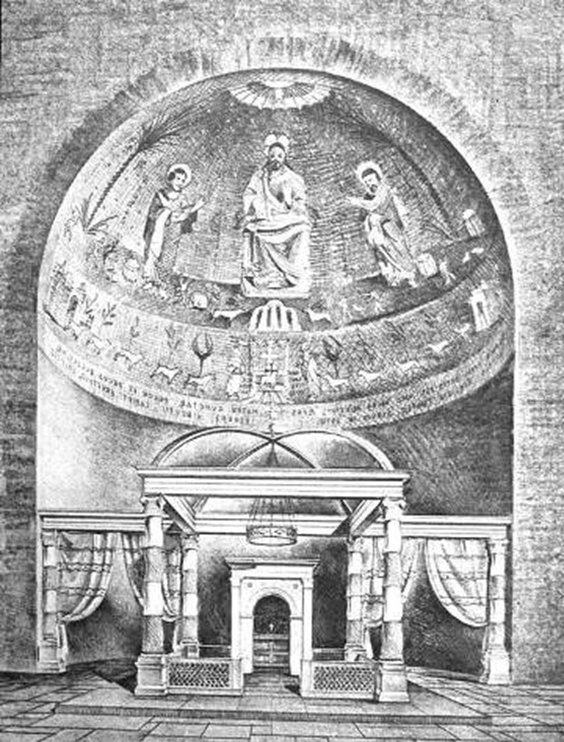
view of apse with baldacchino
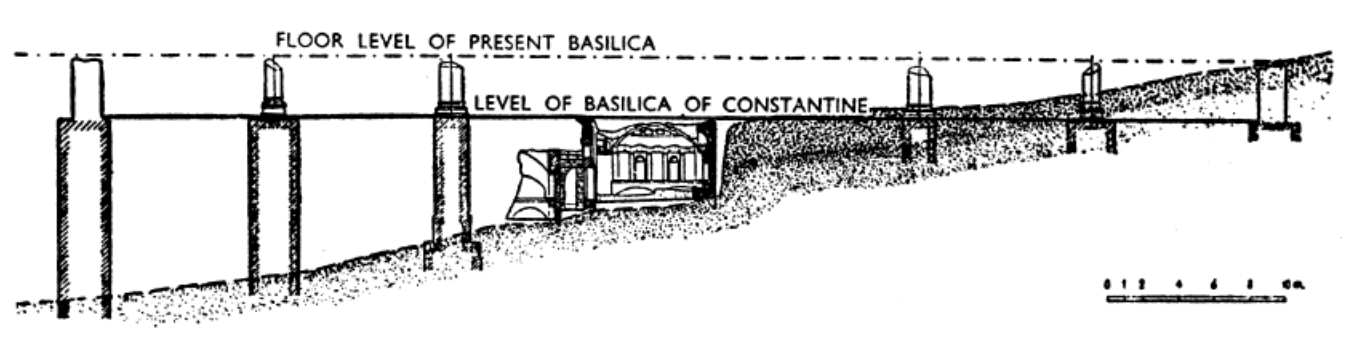
section of vatician hill showing relation of saint peters tomb to the floor level of the old and new saint peters basilica
sta. costanza, rome (337-351)
late antiquity / early christianity
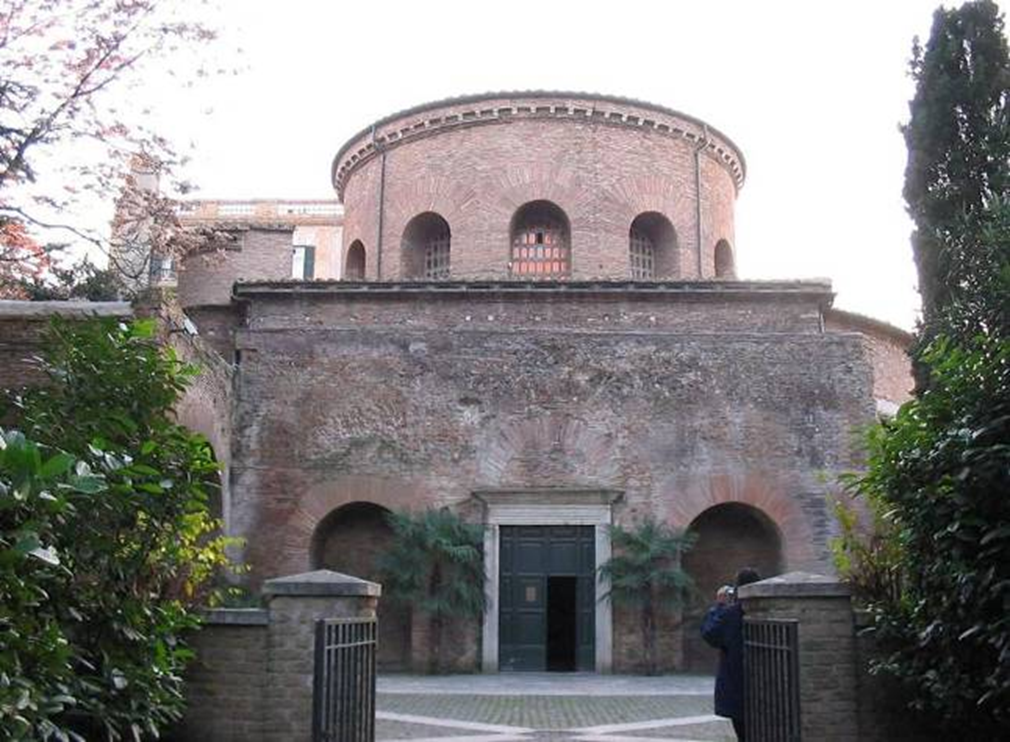
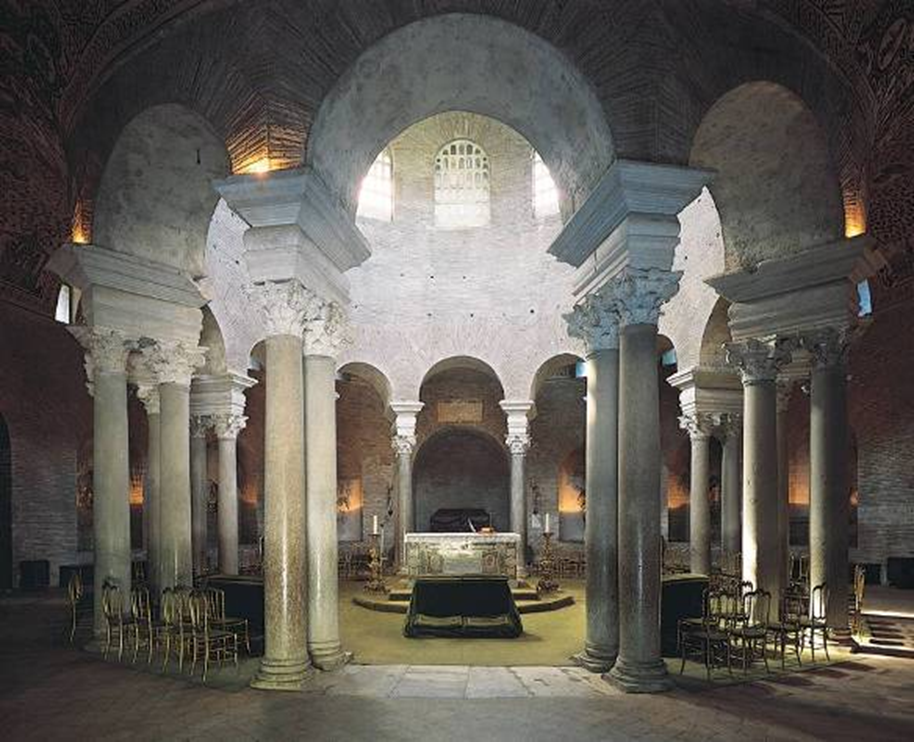
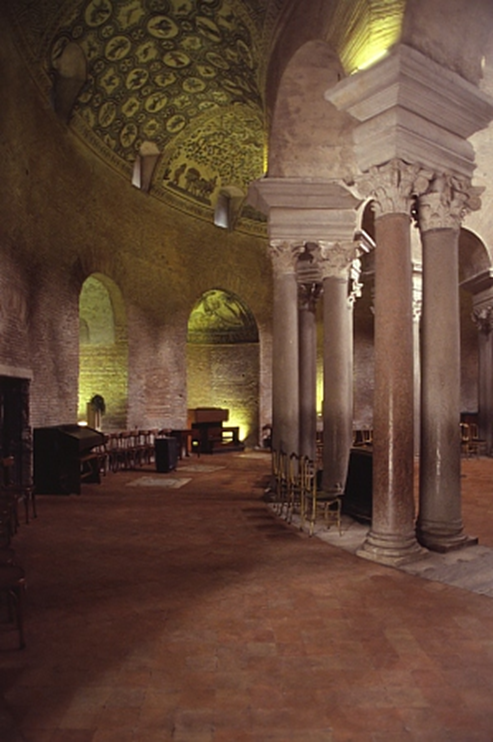


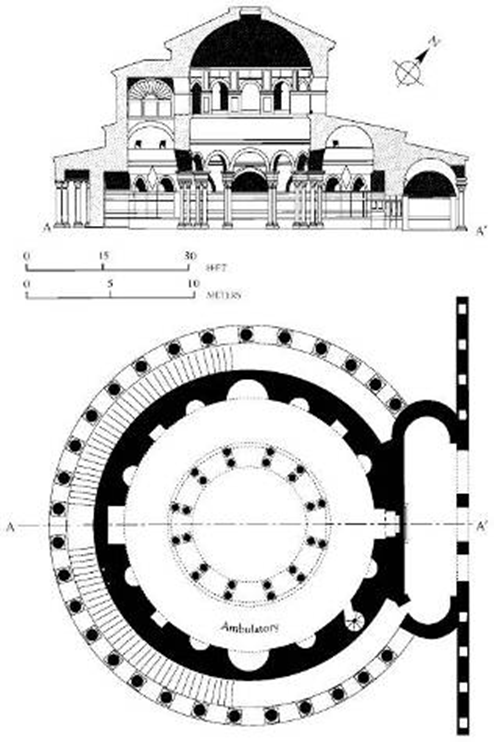

ambulatory (walkway around the apse)
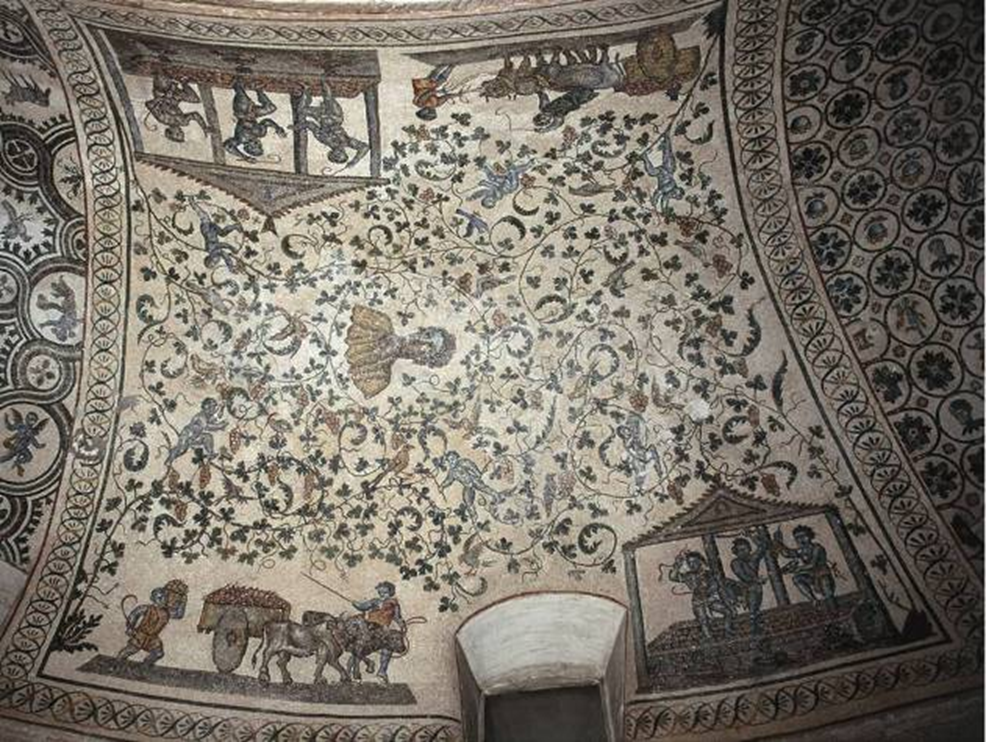

detail of vault mosaic in the ambulatory
baptistery, at san giovanni in laterano, rome (14th century)
late antiquity / early christianity
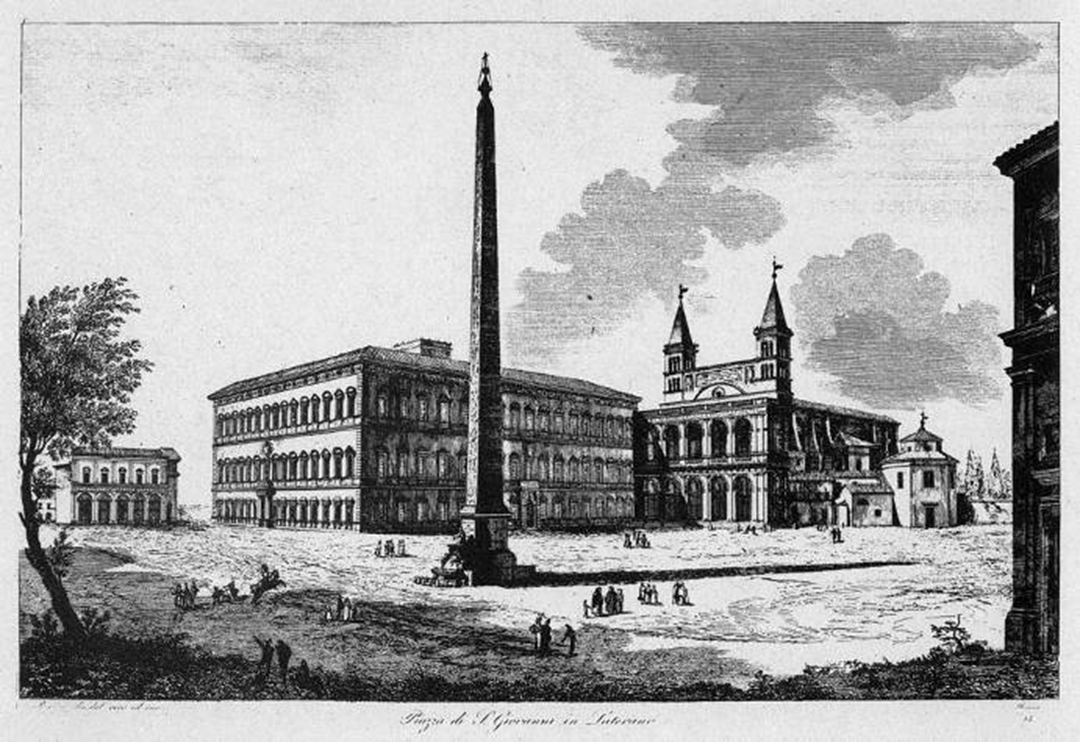
st john lateran is the cathedral of the bishop of rome (pope)
basilica has its own feast day in the roman catholic calendar (november 9)
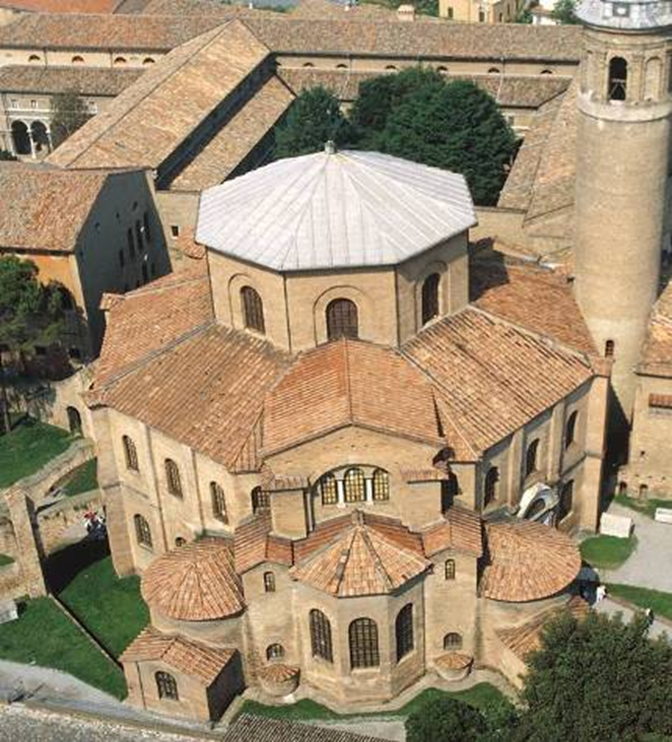
san vitale, ravenna (526 - 547)
byzantium
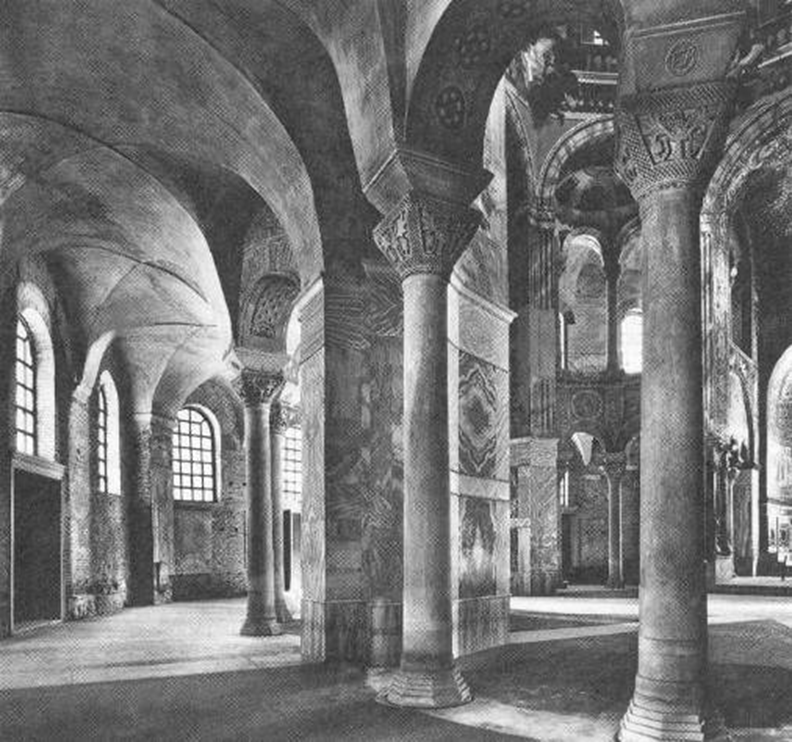

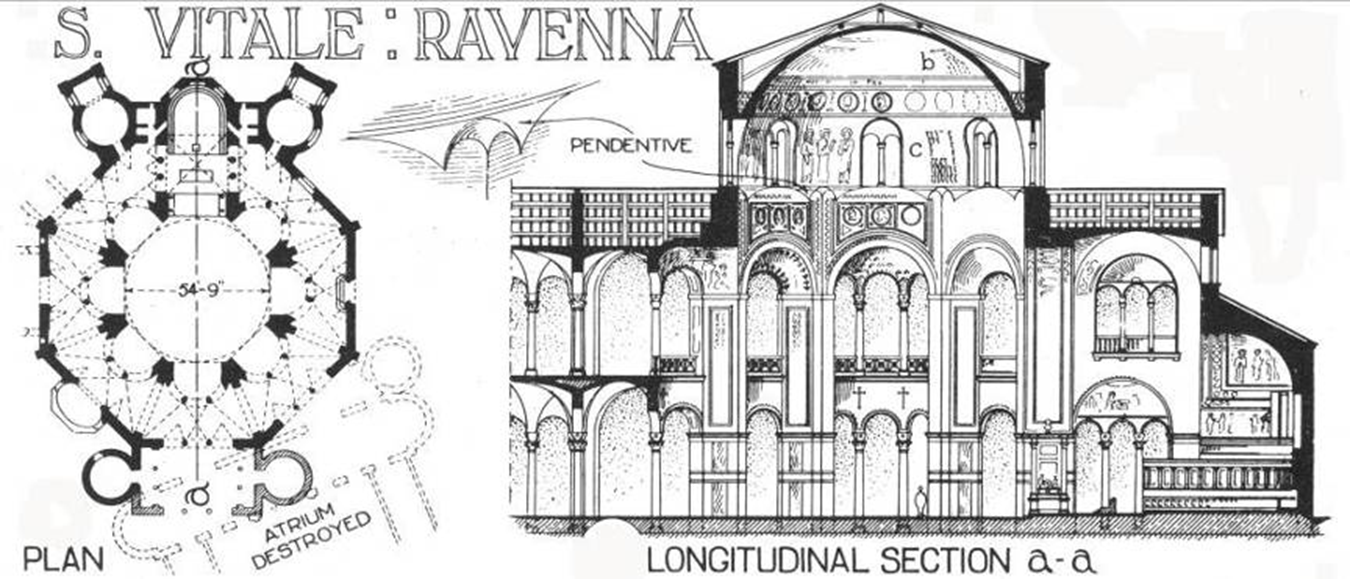

ambulatory

apse mosiacs of christ between two angels
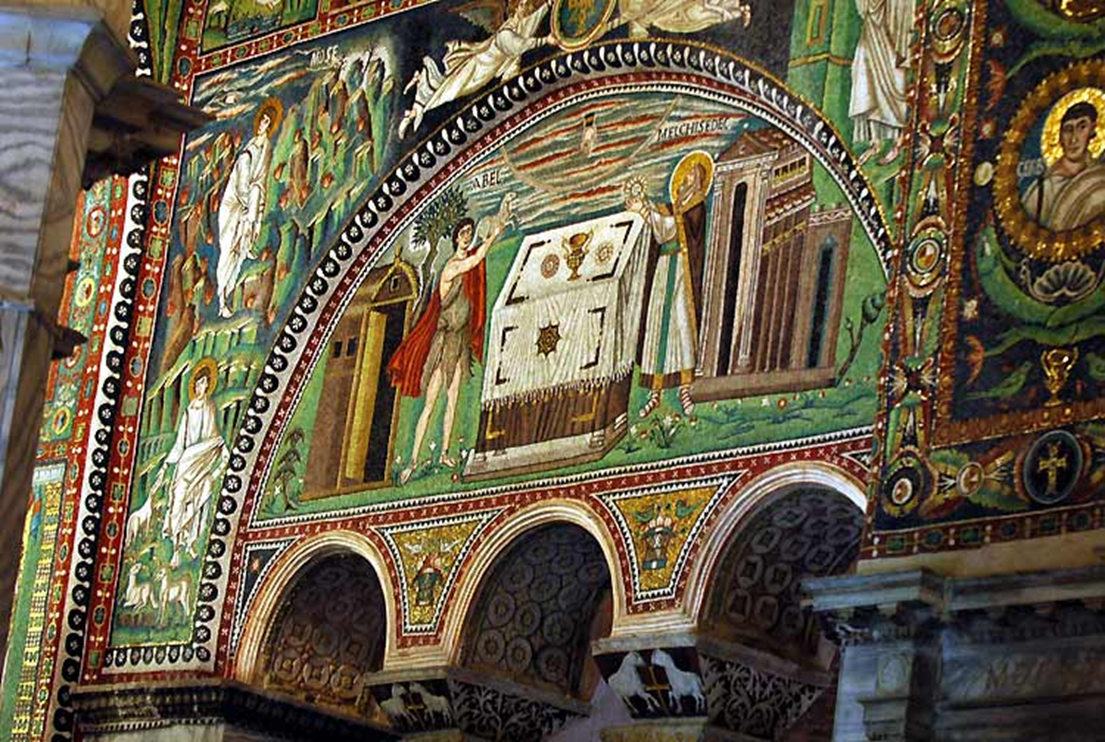
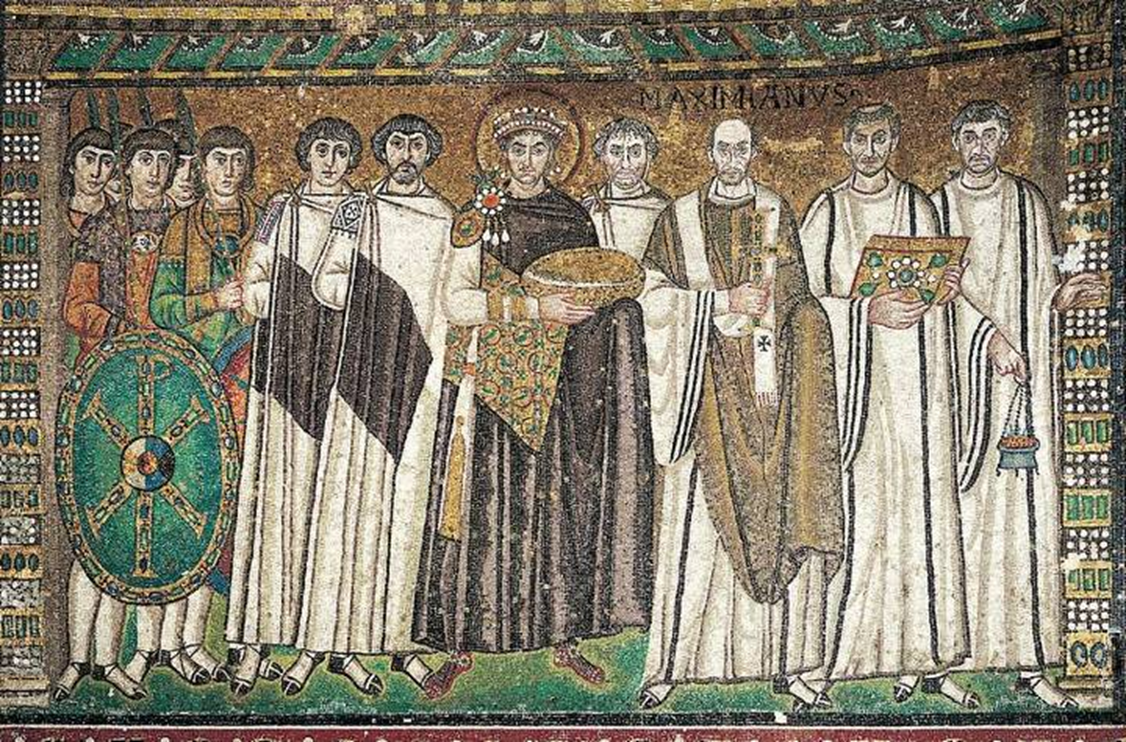


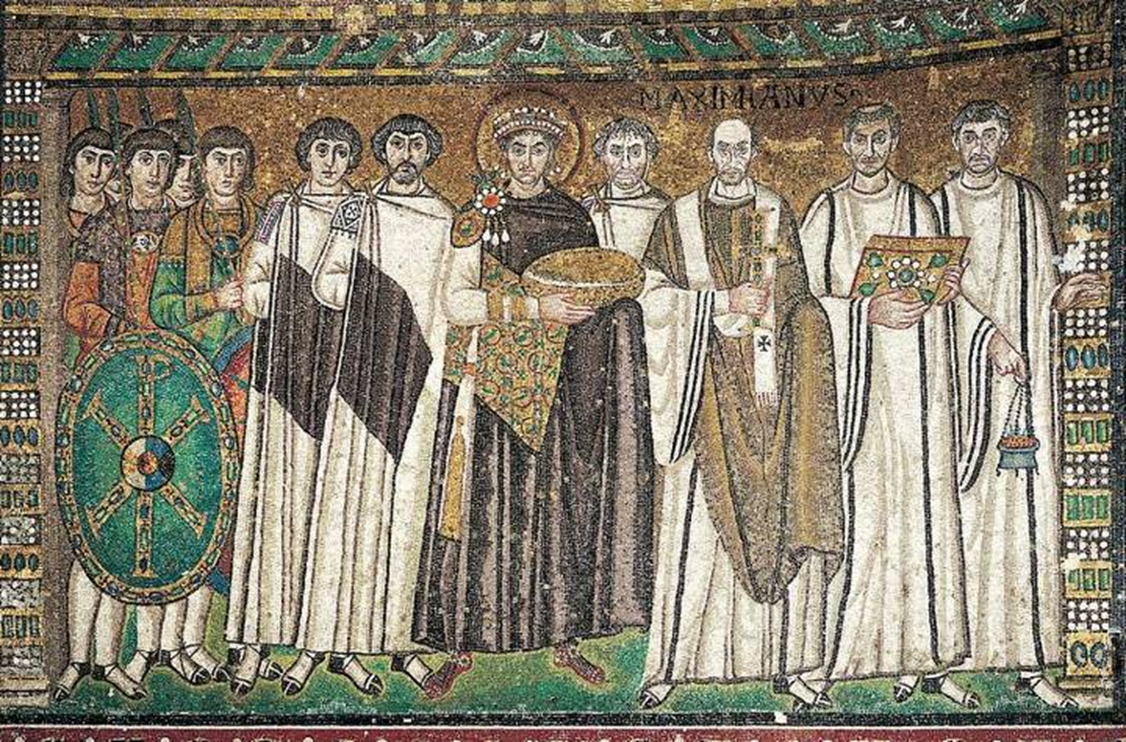
mosaics of justinian, bishop maximianus, and attendants

mosiac of theodore and attendants
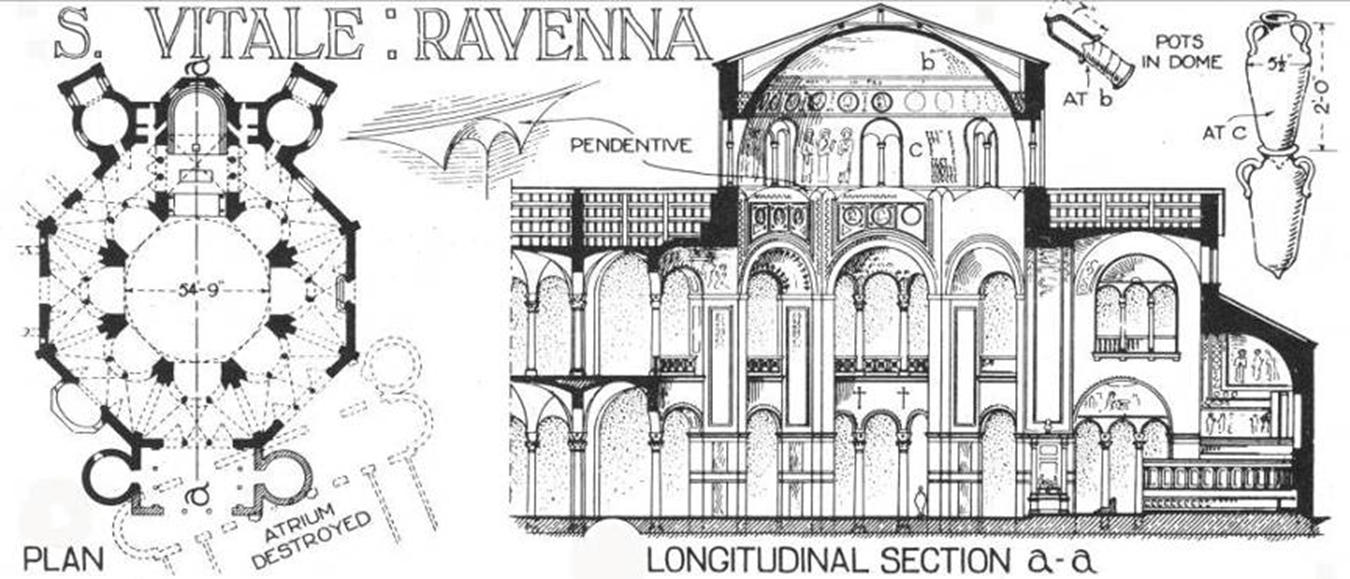
justian’s architects build the dome out of hollow clay pots
justinian and his retinue, mosaic in apse, church of san vitale, ravenna (547)
byzantium

anthemius of tralles and isodorous of miletus, hagia sophia, constantinople (532-537)
byzantium
sutton hoo burial ship and mounds, suffolk, england (early 7th century)
early medieval: carolingian and ottonian
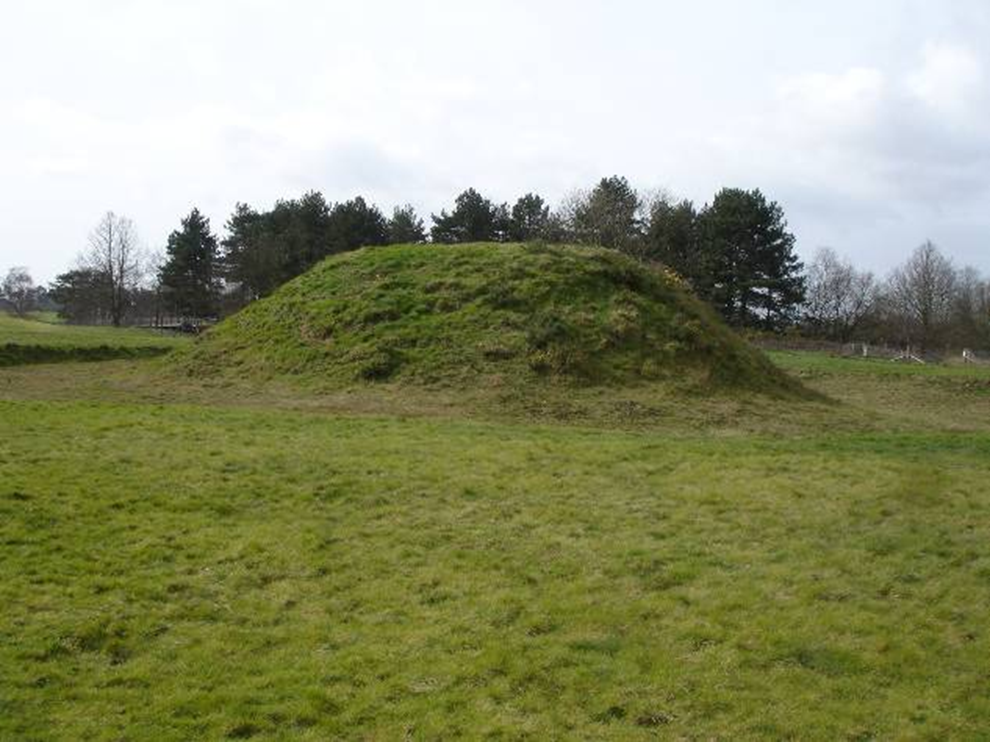

restored mound
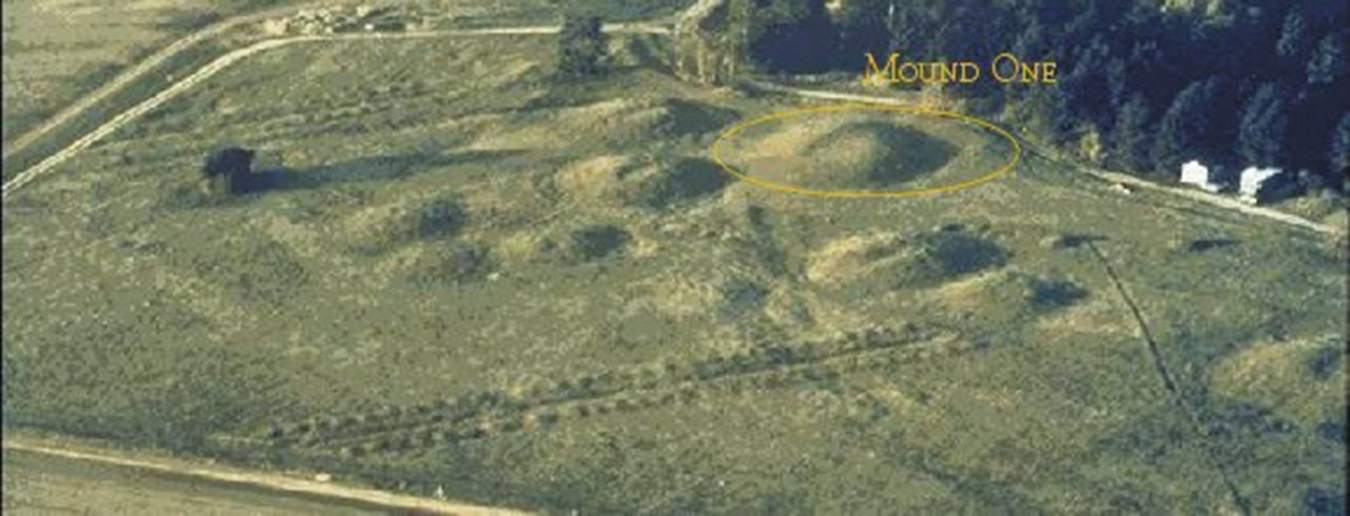

where burial ship was located
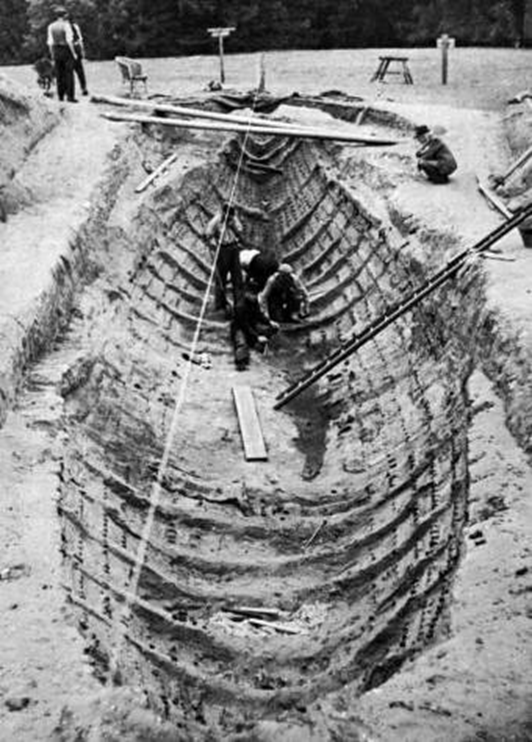

excavation of burial ship
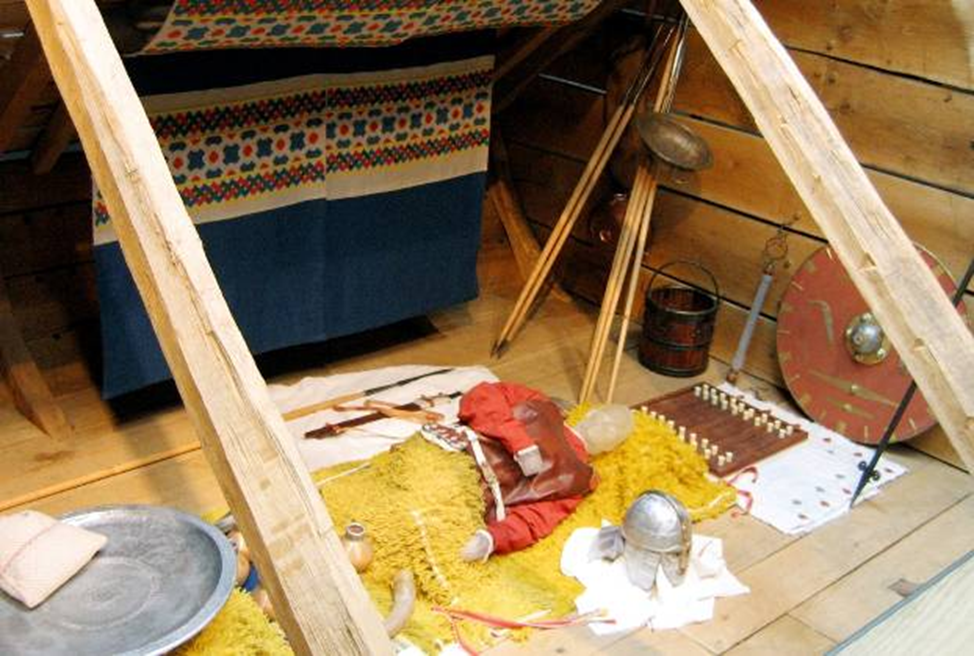


arrangement of objects around body
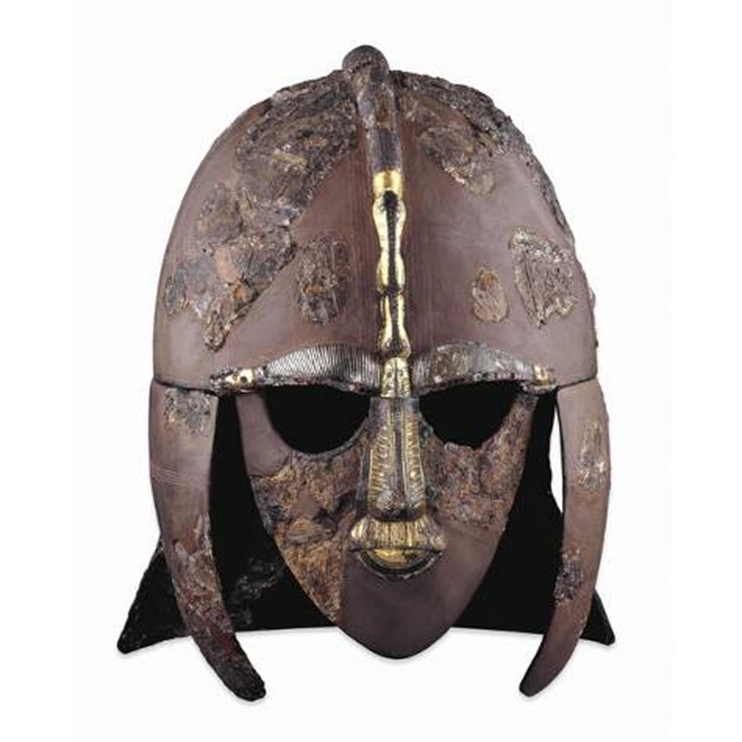

helmet
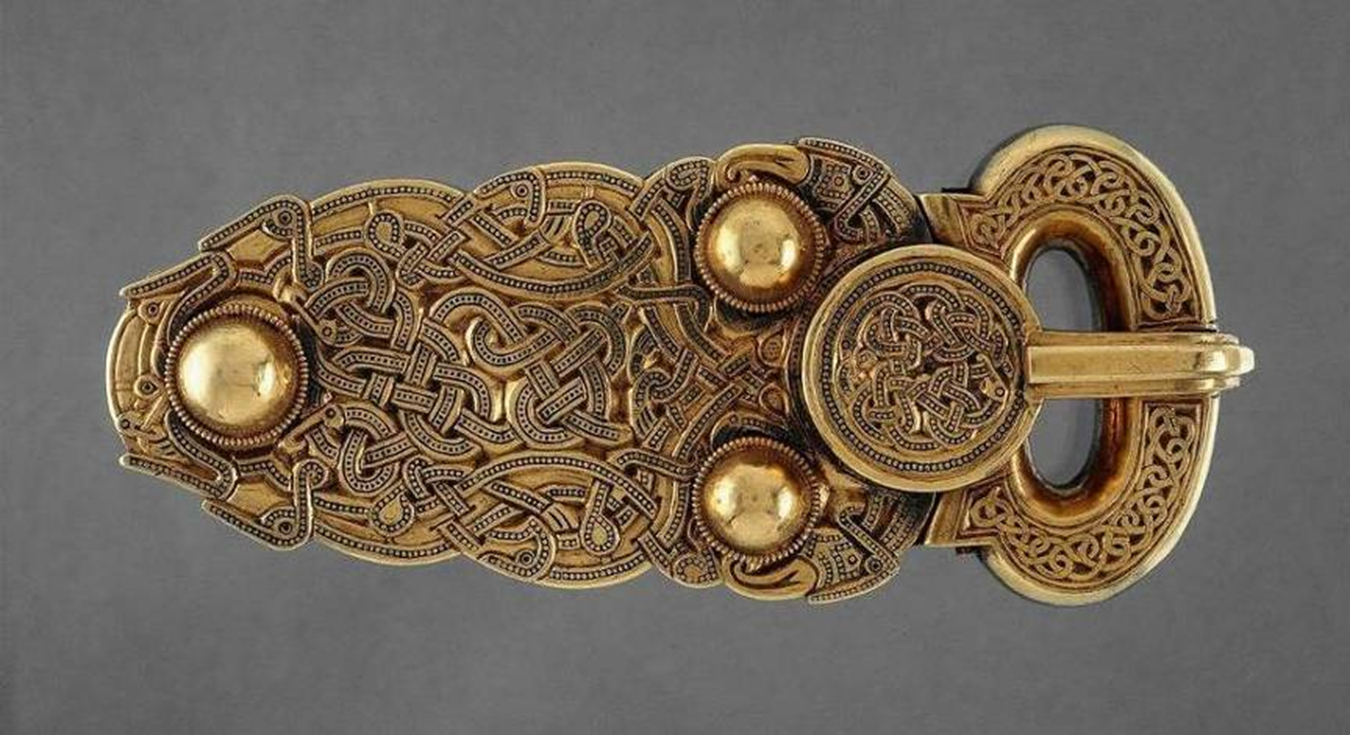

belt buckle
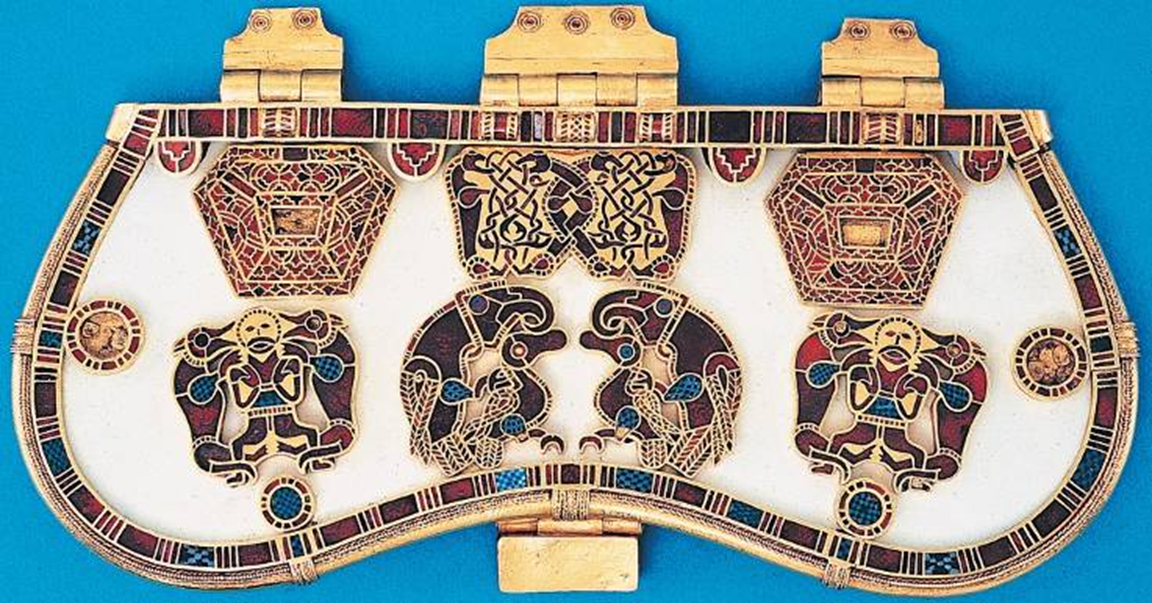

purse cover
odo of metz (architect), palatine chapel, at palace of charlemagne, aachen (aix la chapelle), germany (792 - 805)
early medieval: carolingian and ottonian
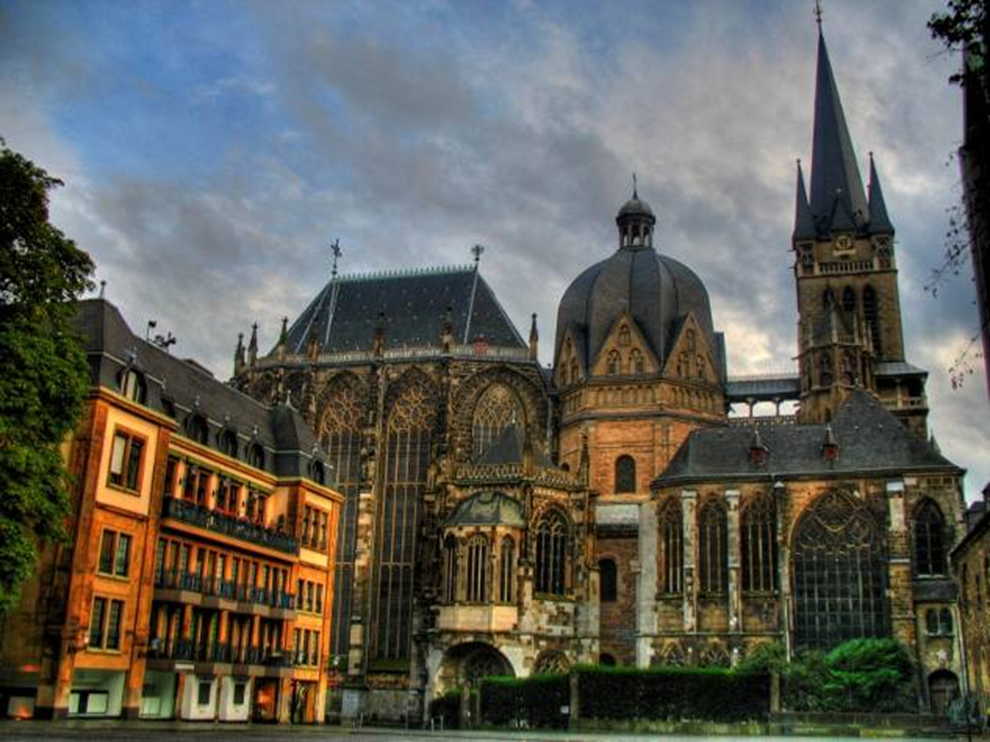
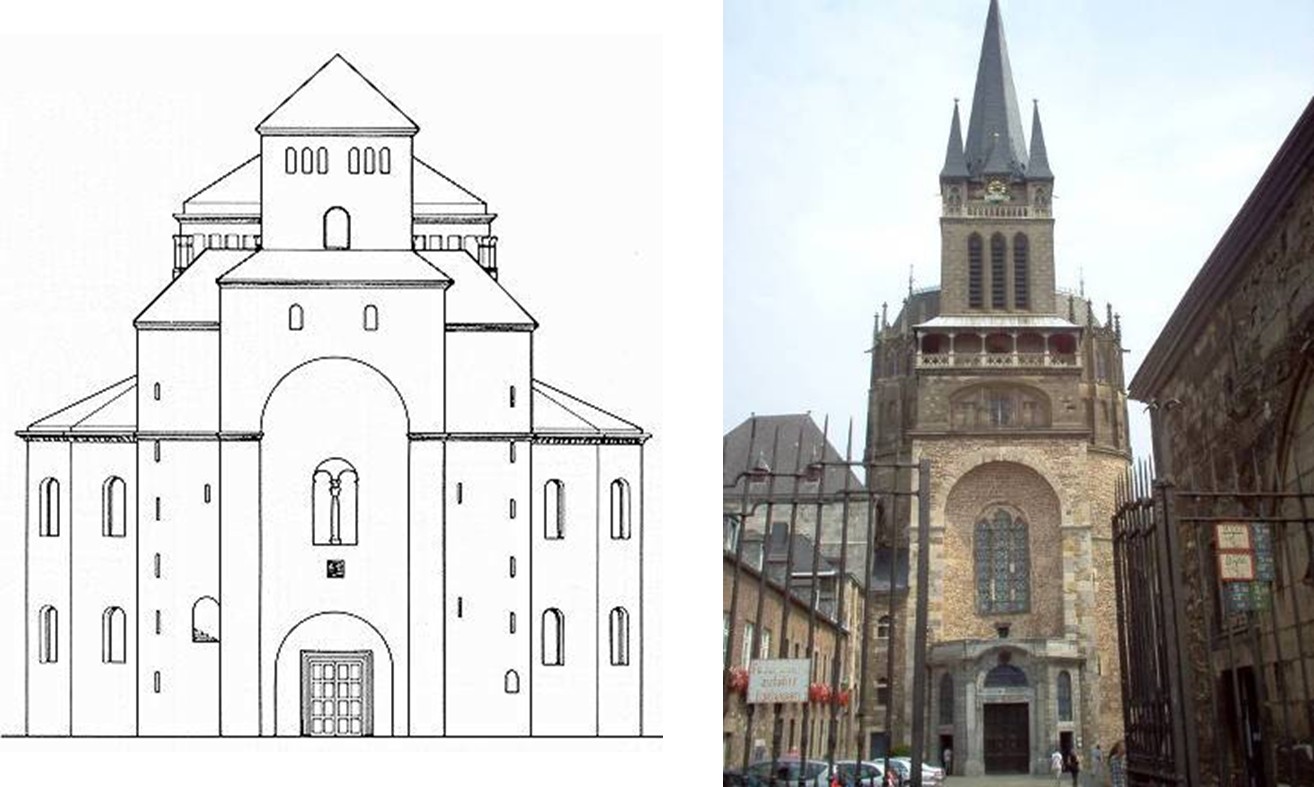

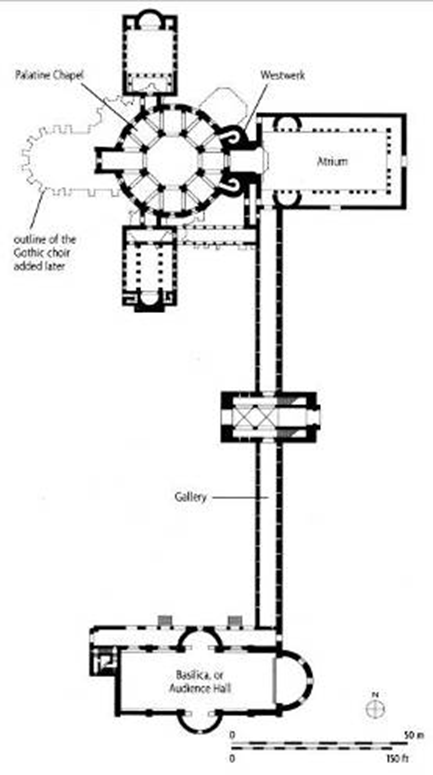
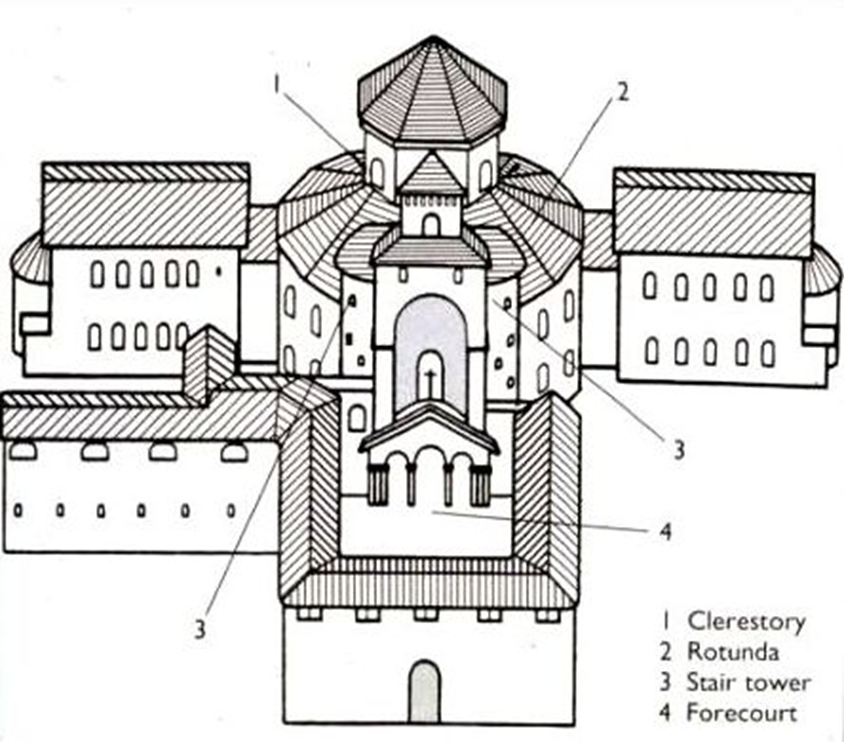

west work: tower-like western-entrance to a church with a chapel over it
charlemagne’s throne located here
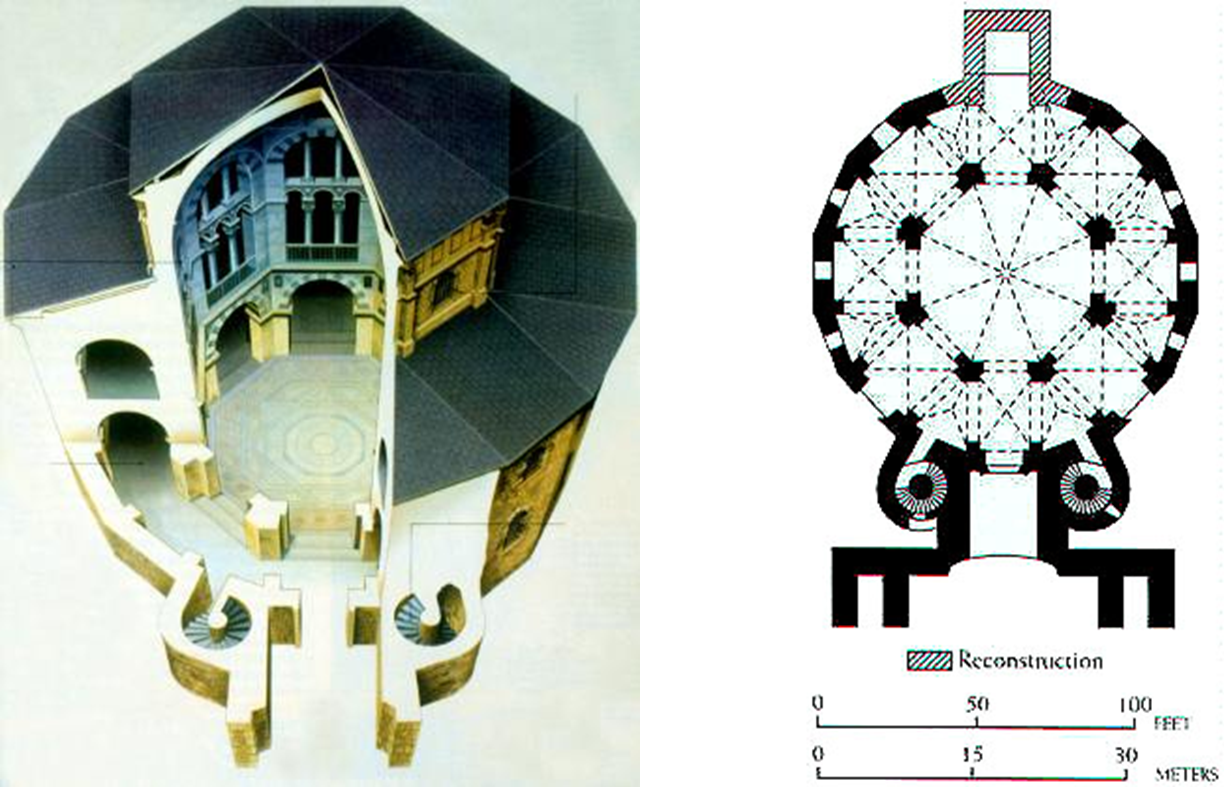
8 sided to 12 sided
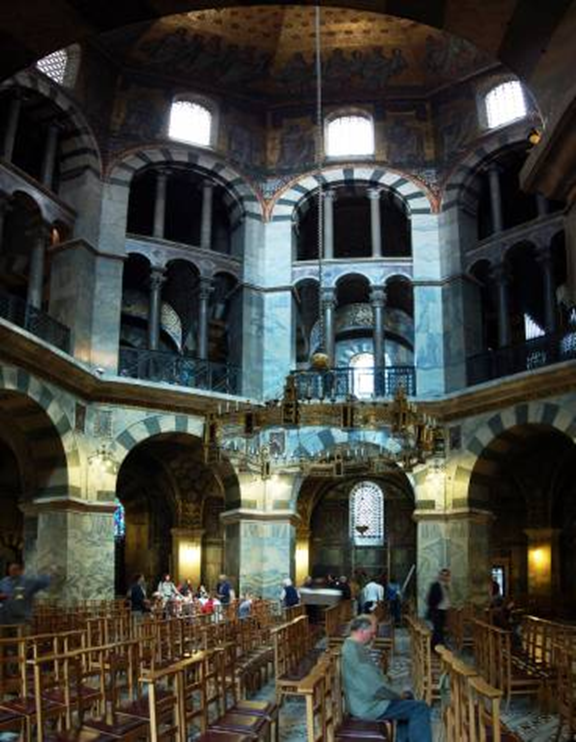

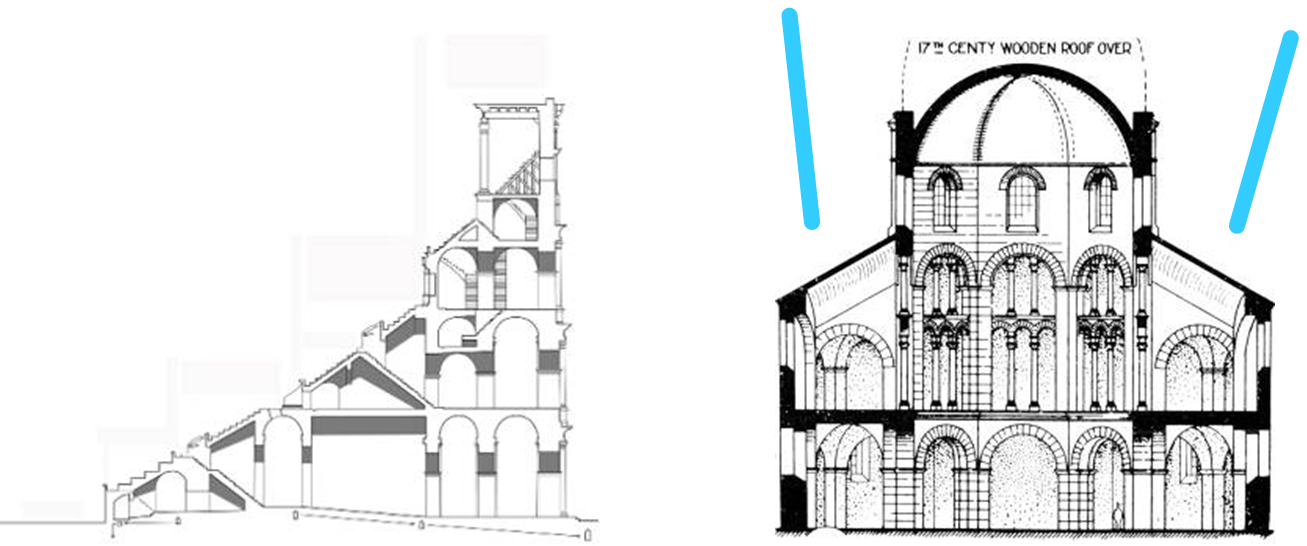
odo of metz utilized the (now visible) predominant structural solution at the colosseum for the chapel the barrel vault
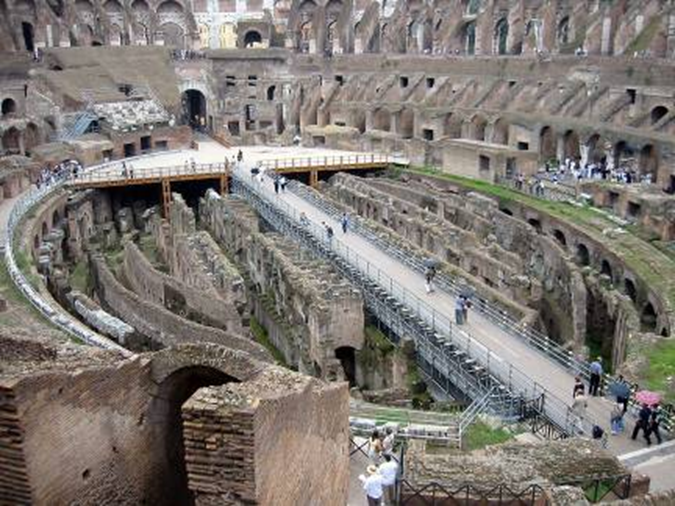


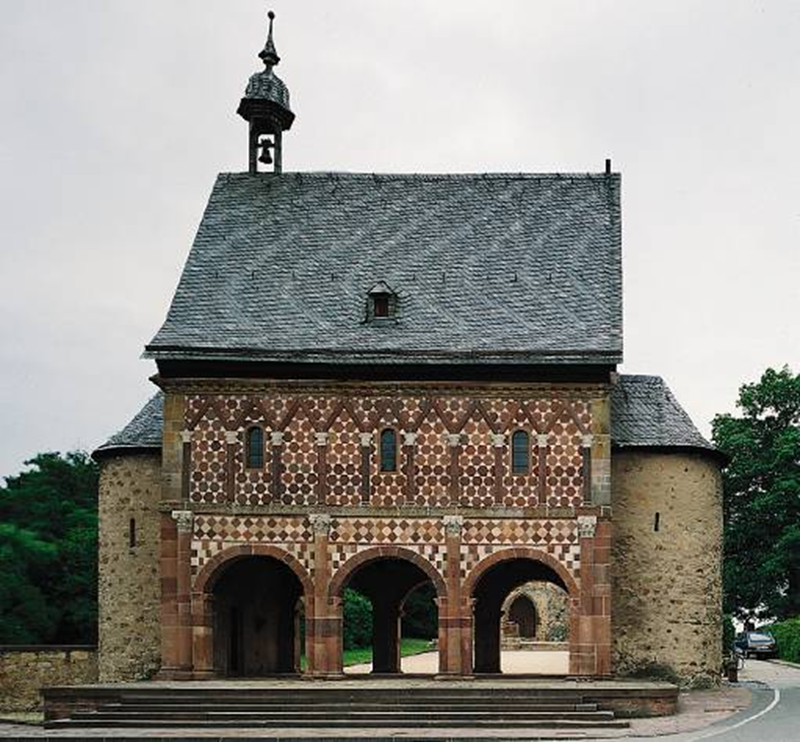
torhalle (gatehouse), monastery at lorsch, germany (767-74)
early medieval: carolingian and ottonian

restricted access
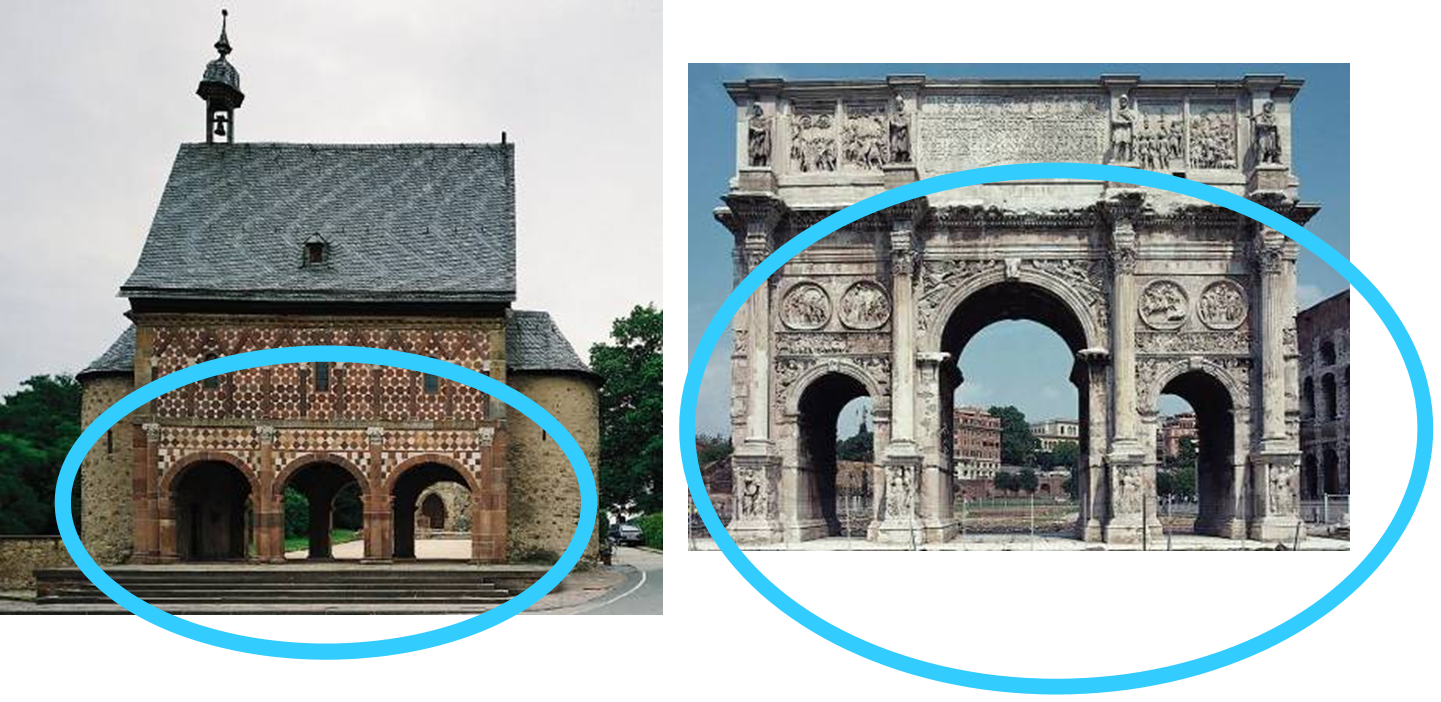

triple arch opening
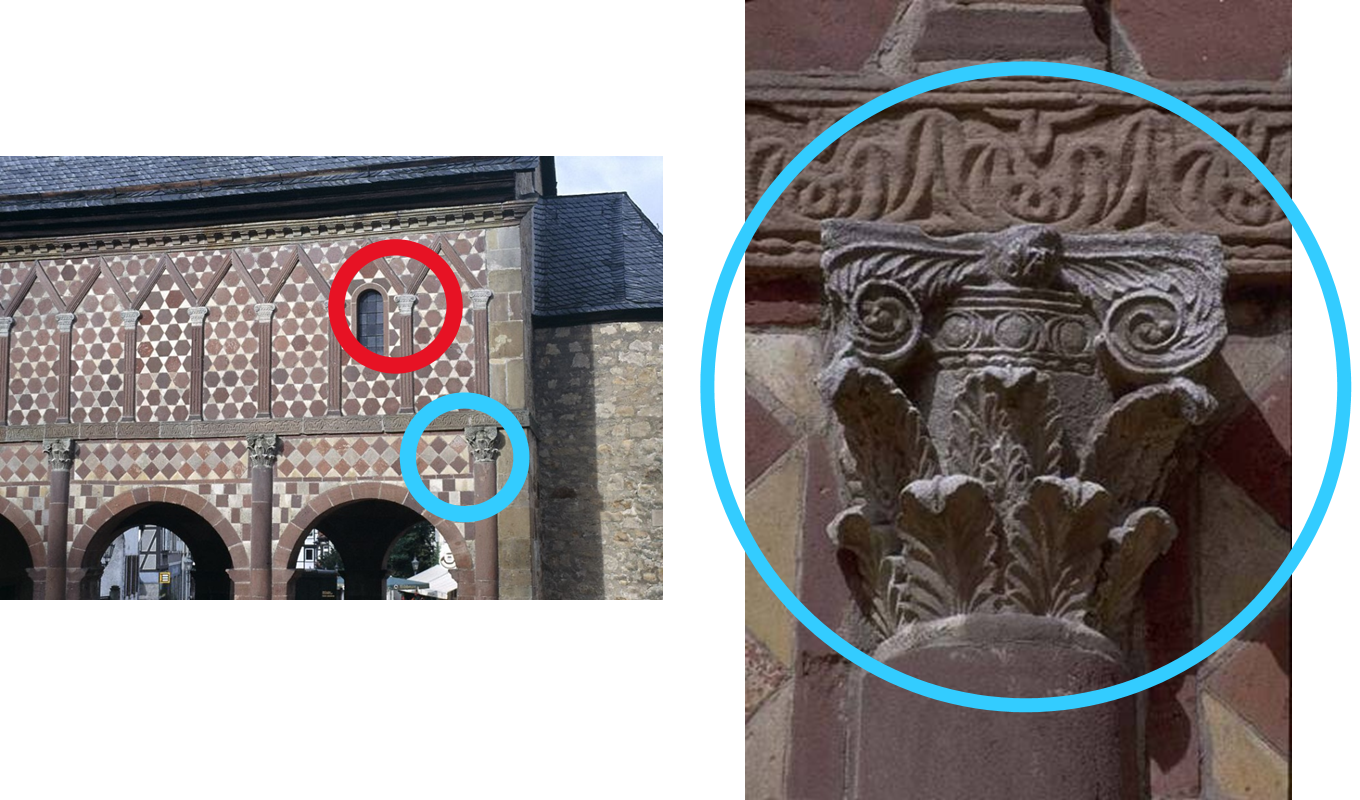

detail of stonework
engaged columns: reference to roman composite capitals
pilasters are in pattern from composite capital on the bottom floor and ionic on the second floor
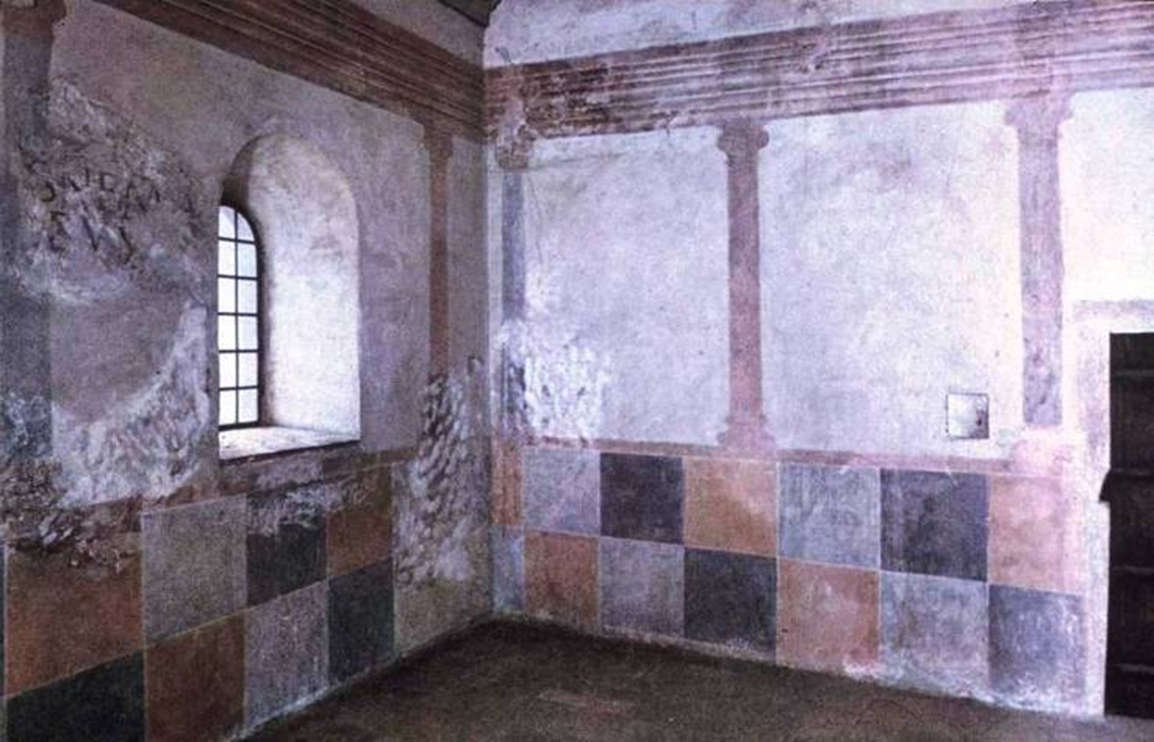

second floor room with roman-like fresco painting (painting on plaster)

ideal plan for a monastery, from st. gall, switzerland (820)
early medieval: carolingian and ottonian
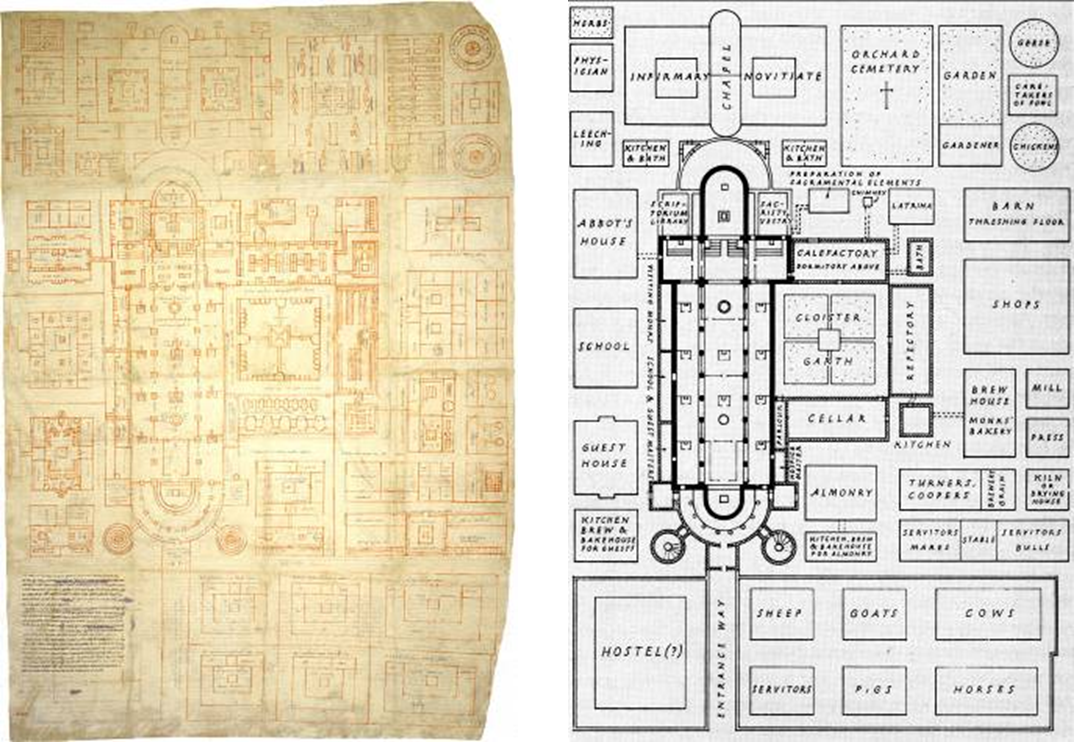
charlemagne reintroduces monumental planning in the west
manuscripts of how to organize and function a monastery
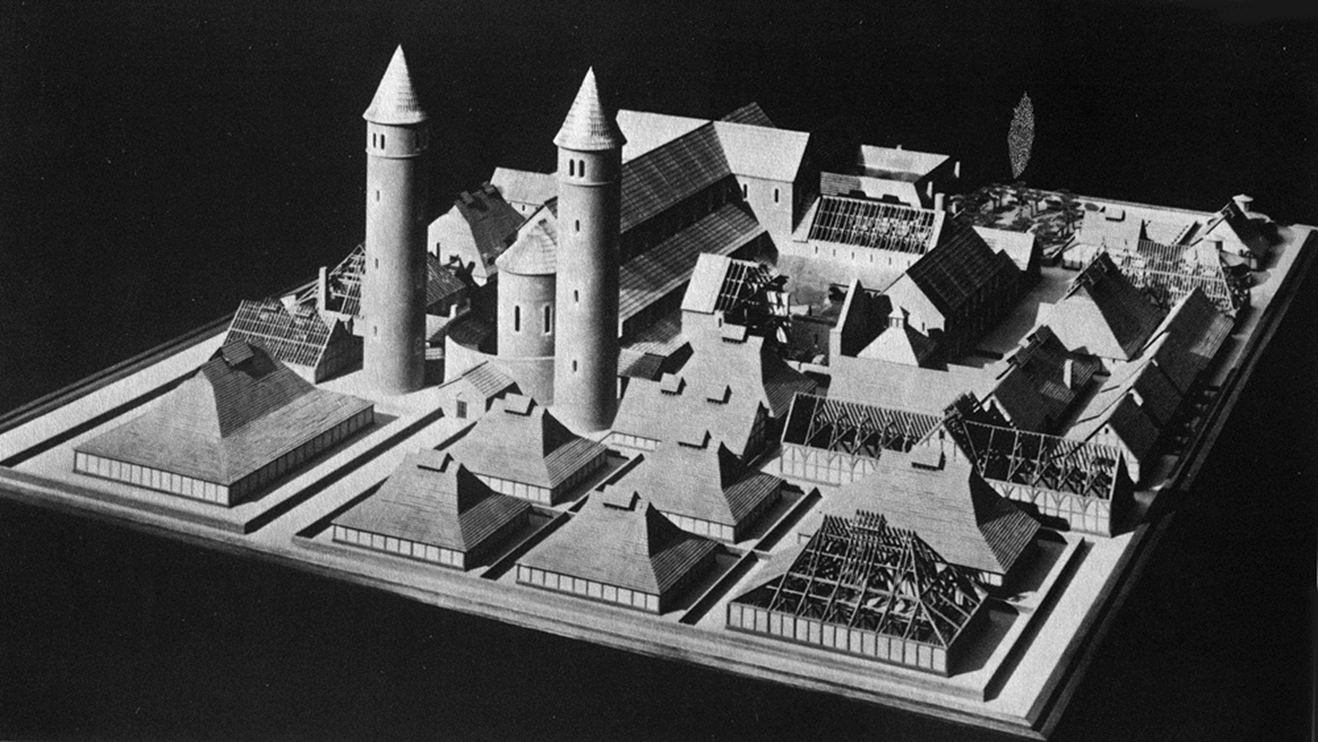
towers at western end of abbey church
brought scholars all over from europe and different religious leaders to work on certain areas of the monasteries
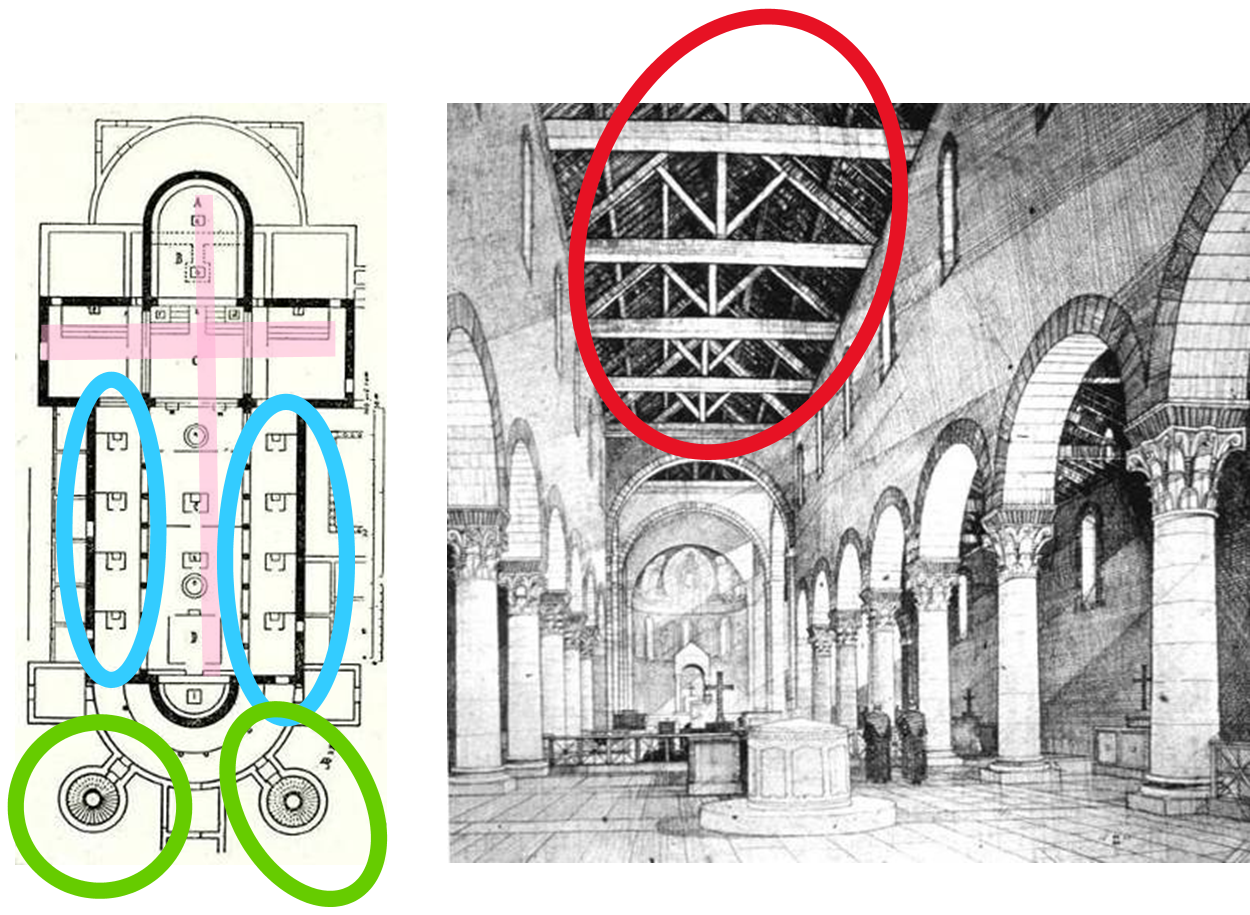
pink: cross-like plan
blue: alters surrounding
red: wooden roof structures
green: towers
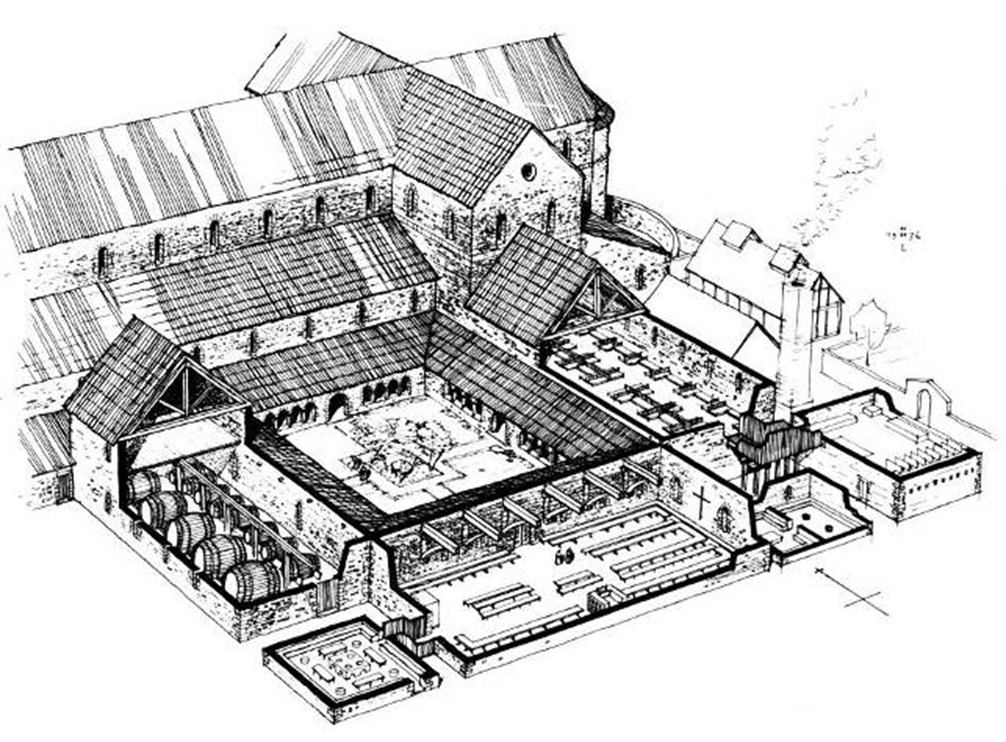
cloister: center of life revolved around the church and the cloister
open garden space like a courtyard because the important buildings that people went to in their daily lives surrounded it
st. michaels church, hildesheim, germany (1001-31)
early medieval: carolingian and ottonian
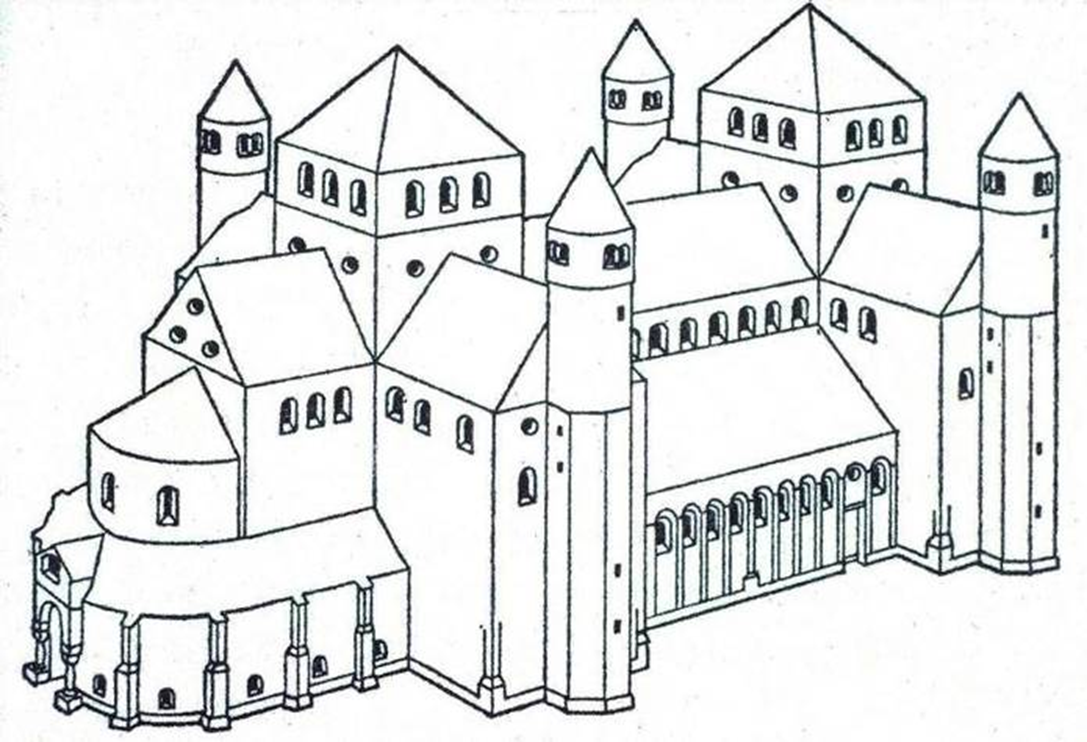

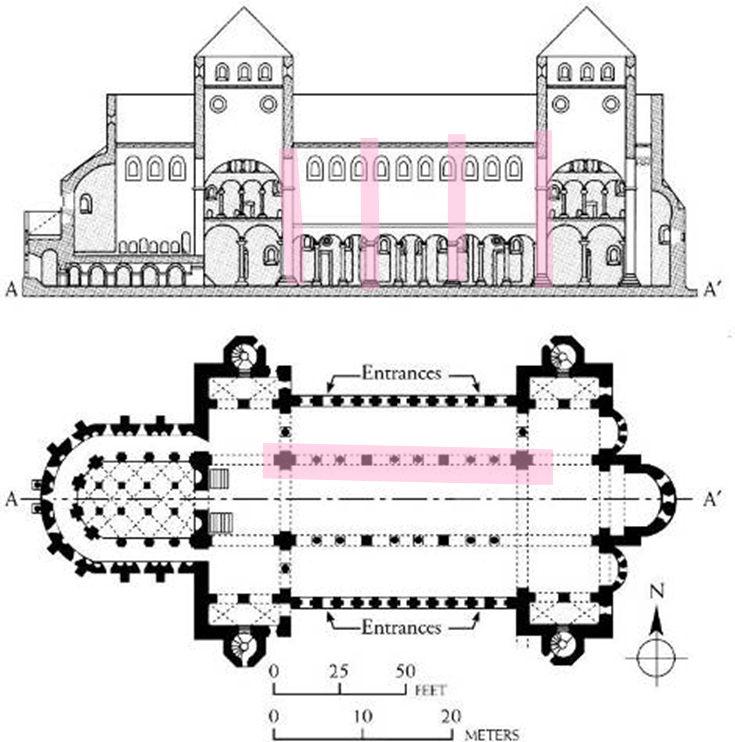
introduction of rhythm in architecture elements
a - b - b - a (rhythm of the nave) pier - column - column - pier
bays: vertical divisions marked by architectural elements

door with relief panels of genesis and the life of christ (bishop bernward)
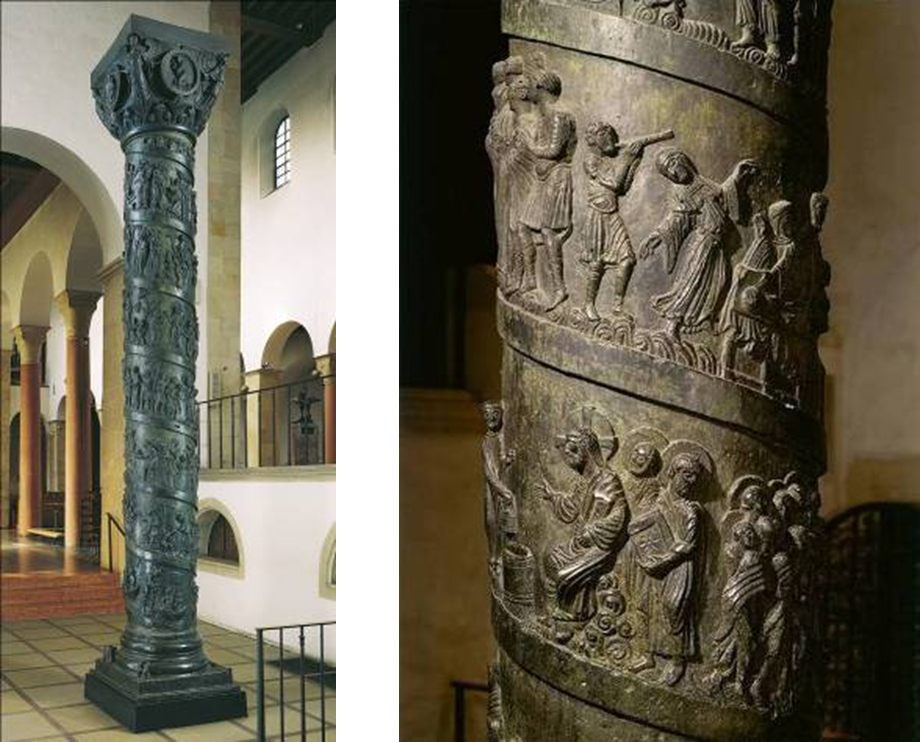

columns too
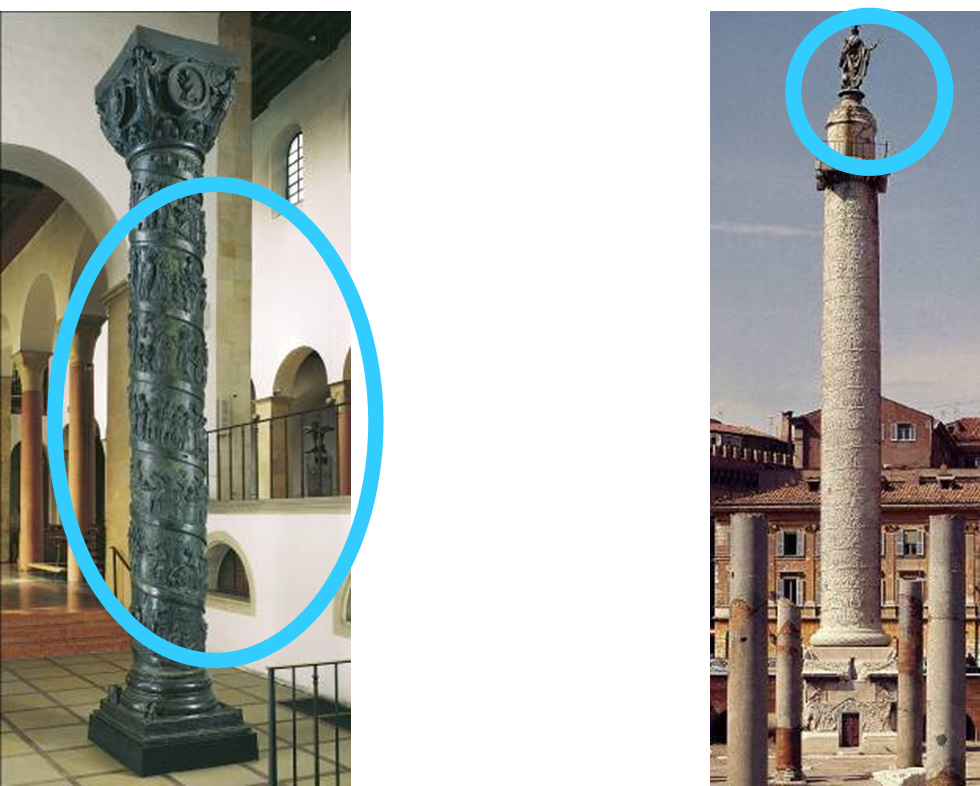

inspiration and correlation

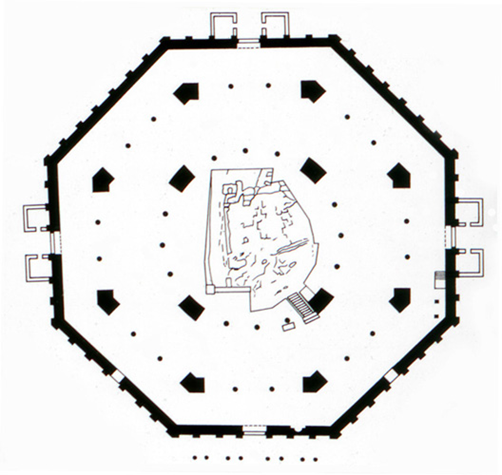
dome of the rock, jerusalem (687-692)
islam
close proximity to the jewish temple of soloman (destroyed by titus in 70 ad)
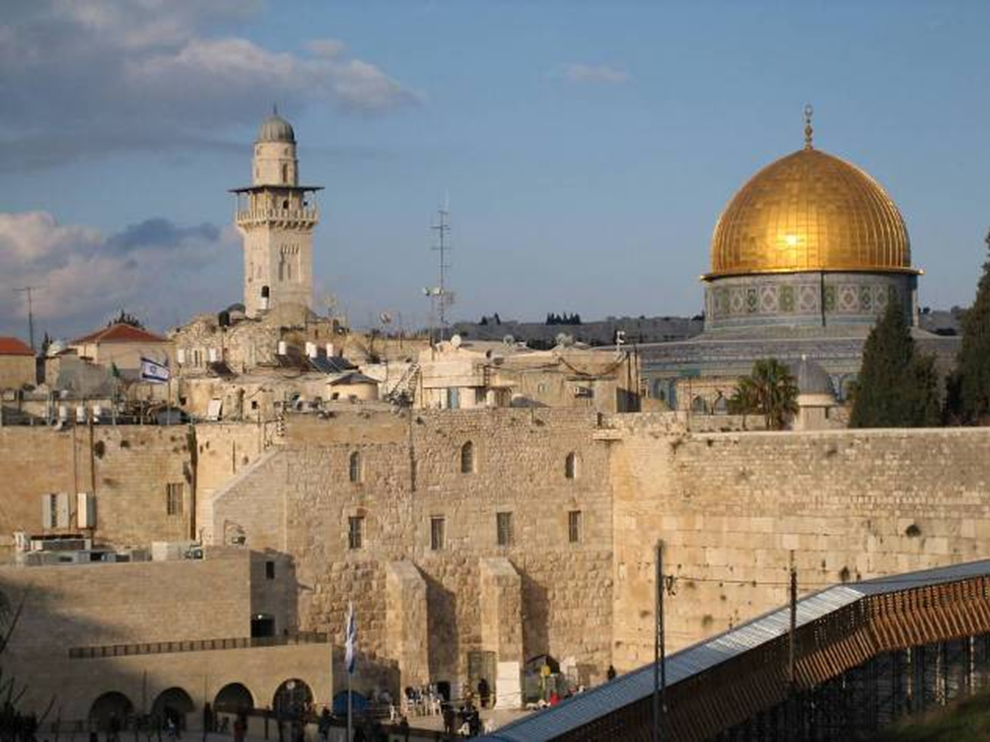

close proximity to the wailing wall (part of temple of soloman)
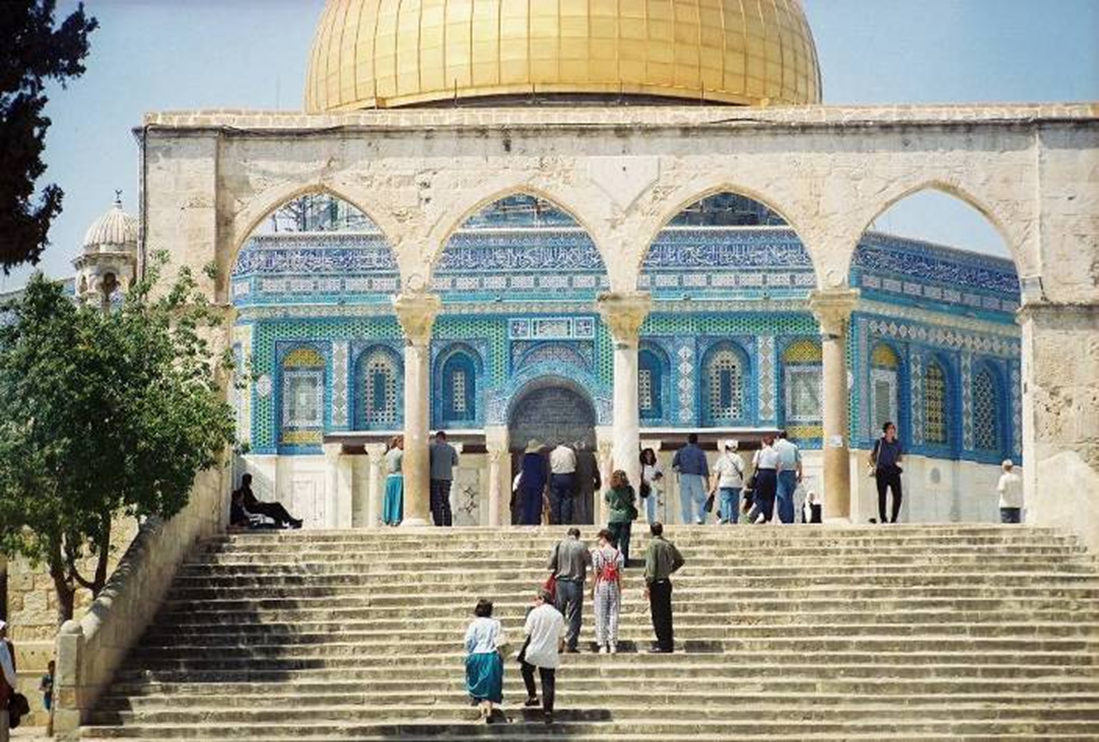

arched screens
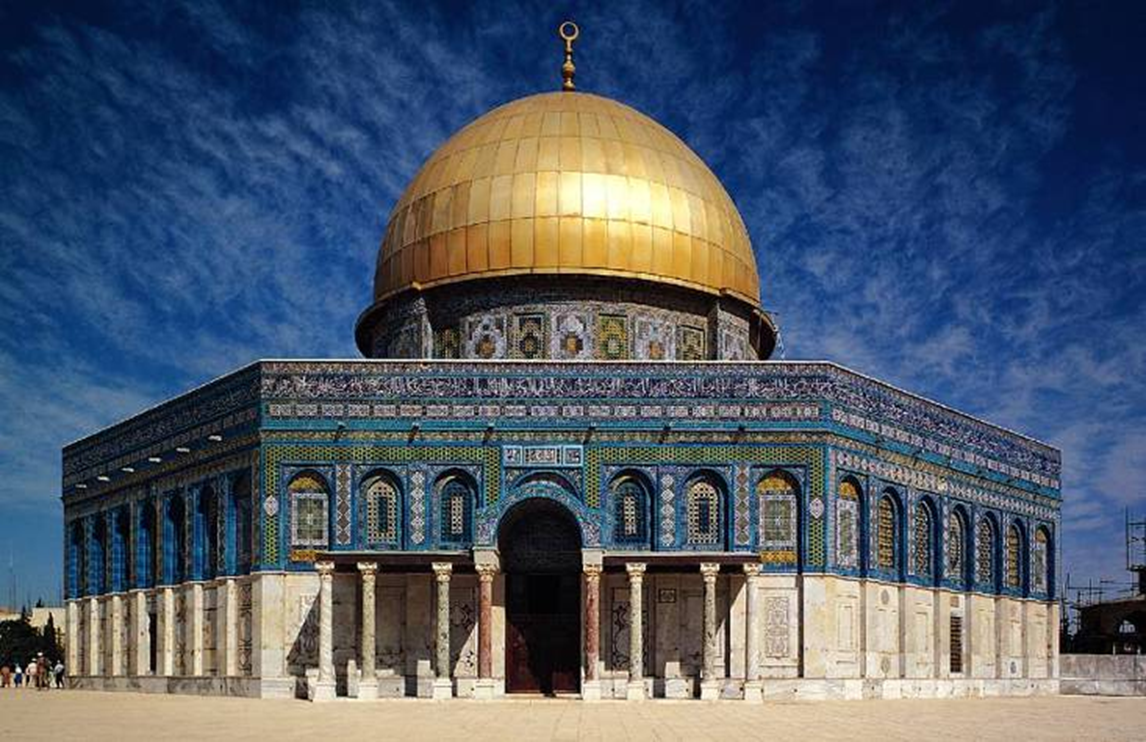

oldest extant islamic structure
shrine not a mosque for mohammad that resurrected

tile work
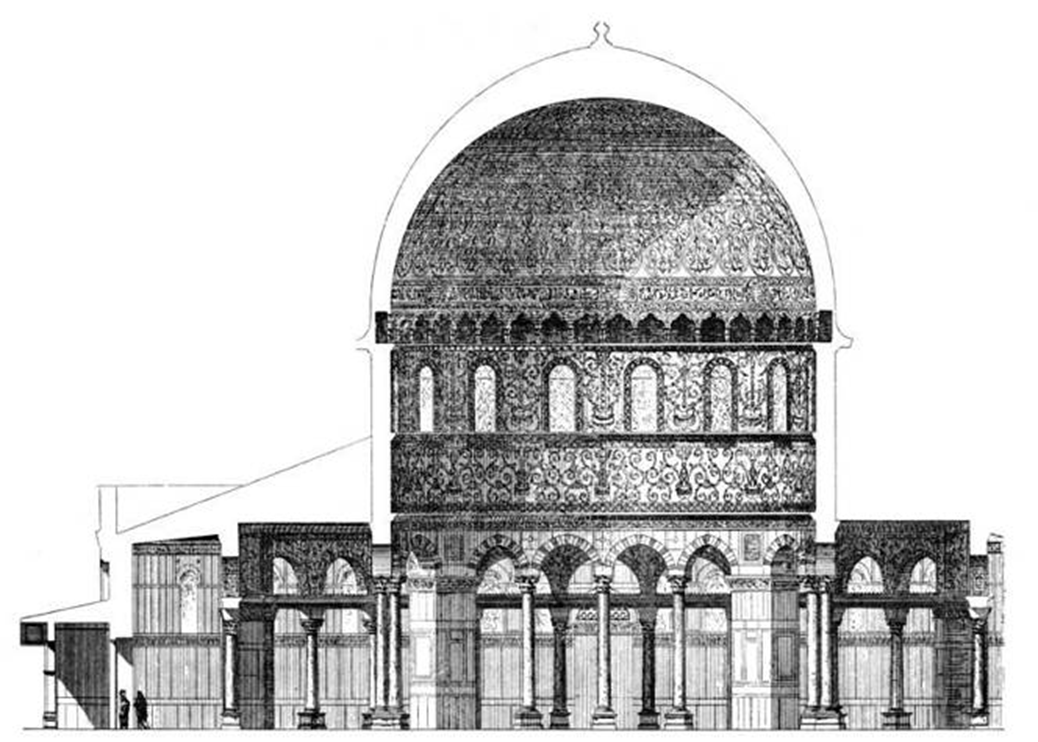
dome is 75 ft high and spans of 67 ft
interior feels like byzantine architecture

dome decor
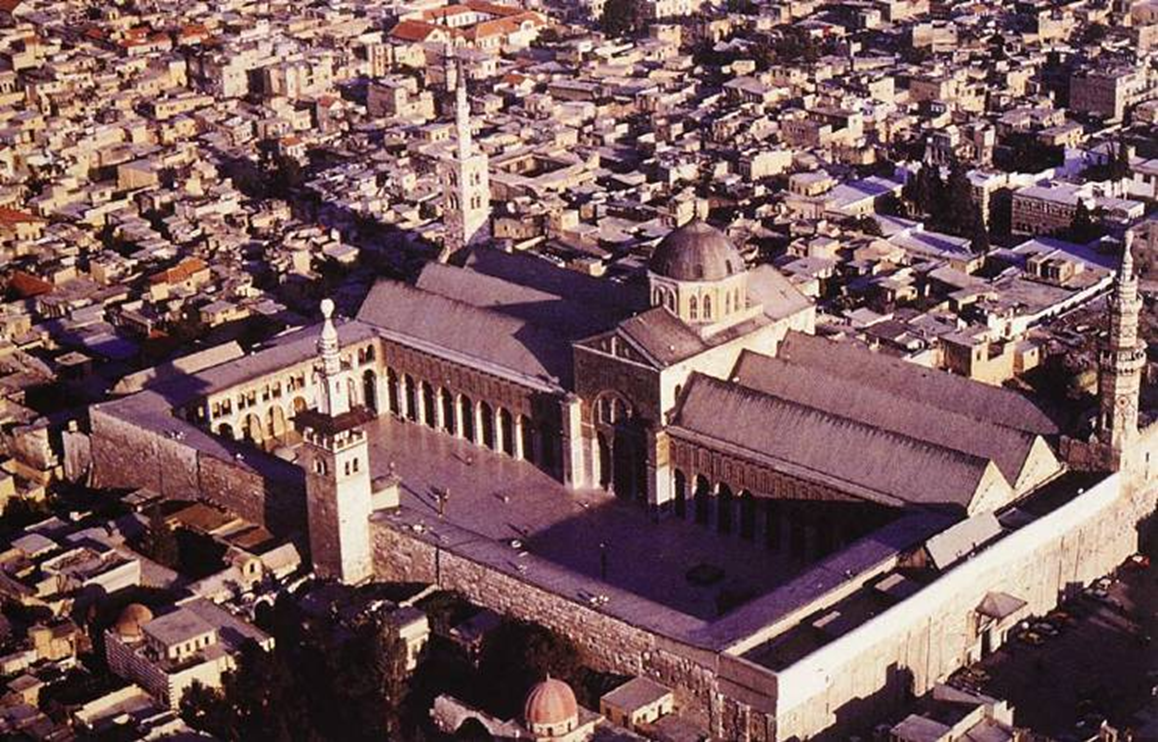
great mosque, damascus, syria (706 - 715)
islam
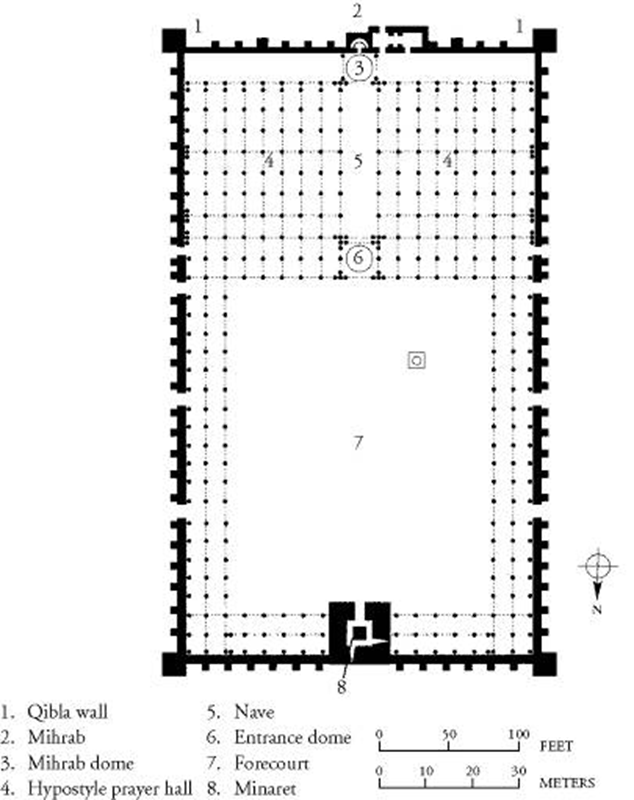
large prayer hall with hypostyle: meant to gather large groups of gatherings for prayer
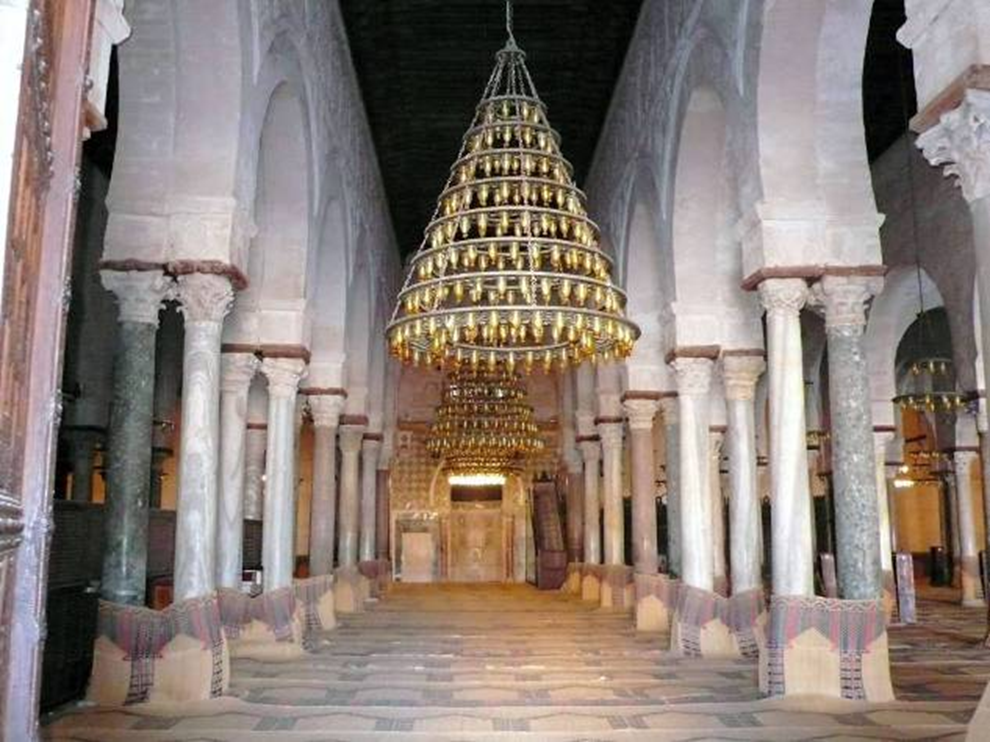

layout is like a basilica church
utilized roman building elements: capital of columns
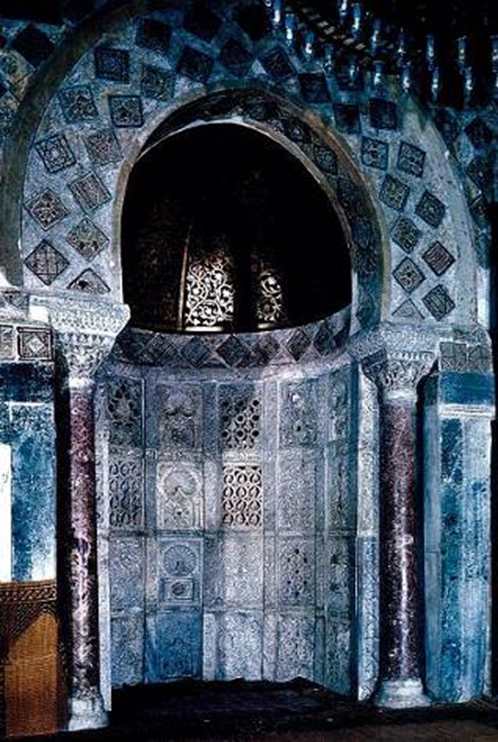

mihrab: a semicircle niche in the wall for people to pray
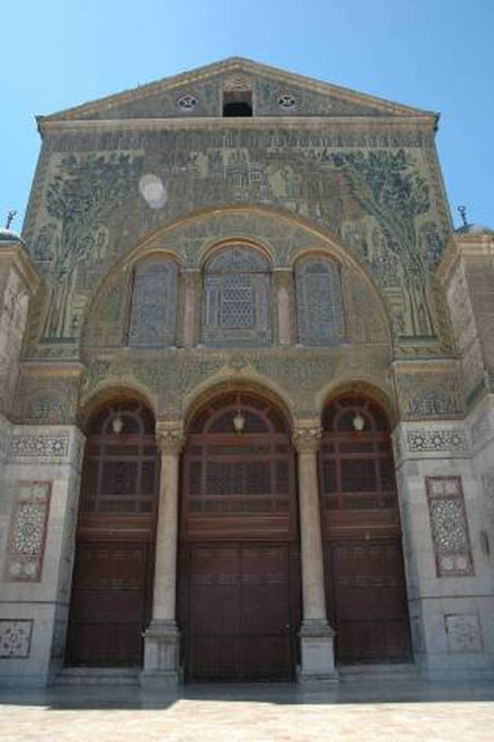


entry to prayer hall with elaborate byzantine mosaics
great mosque, cordoba, spain (786, 833 - 988)
islam
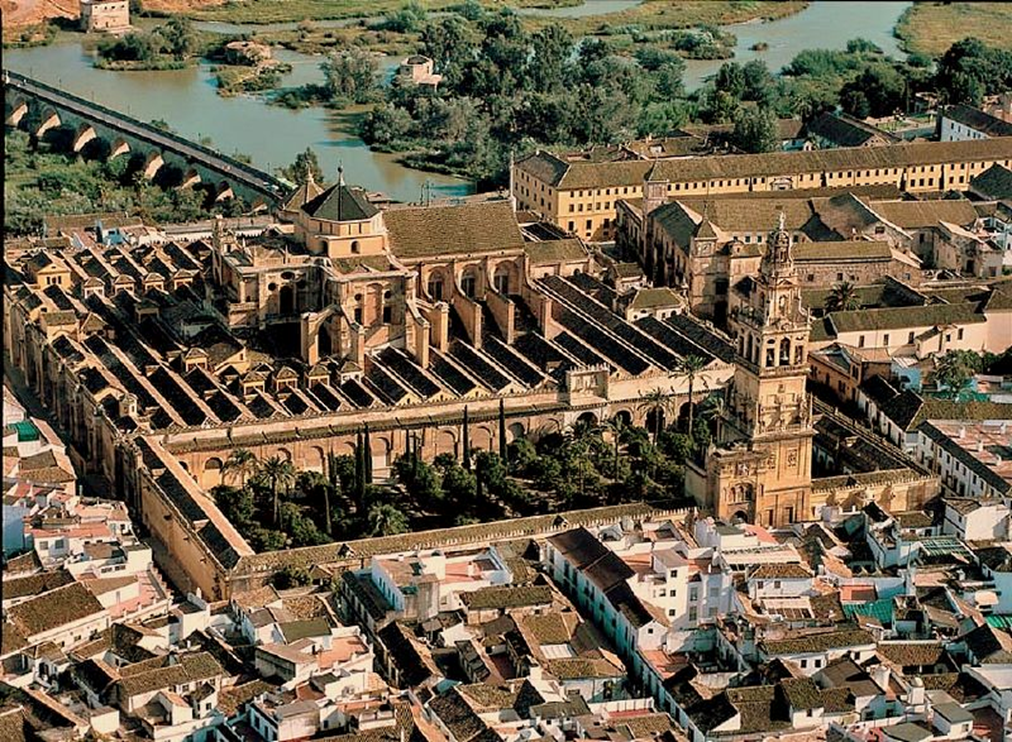
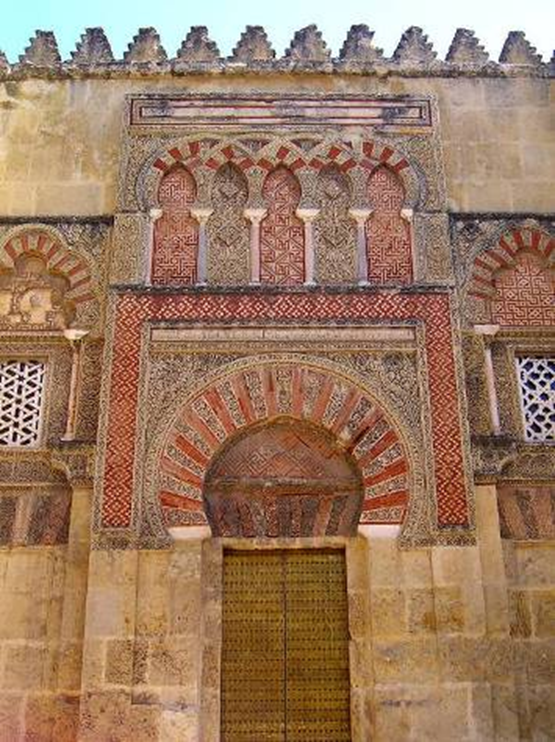

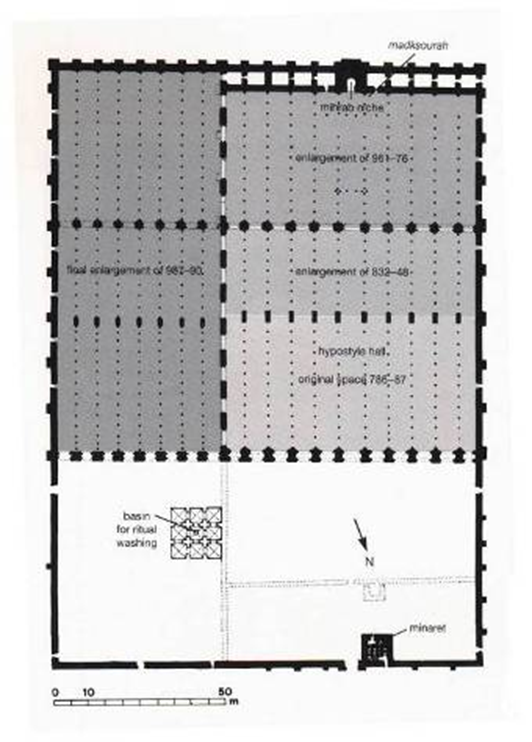

horseshow arch entry
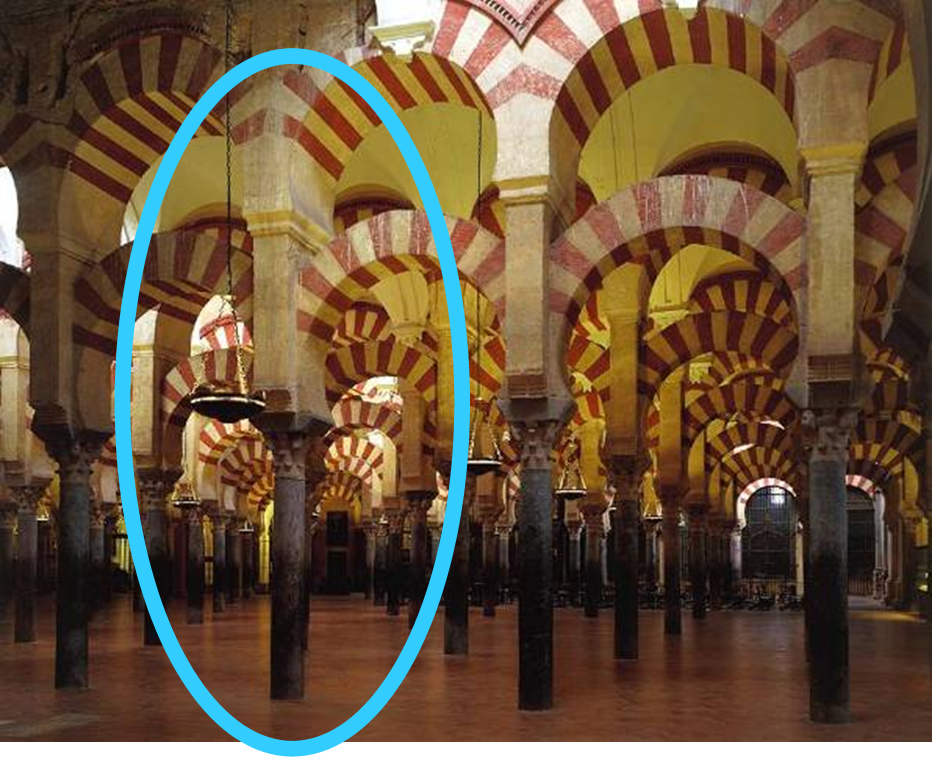

hypostyle prayer hall
double colonnade hypostyle
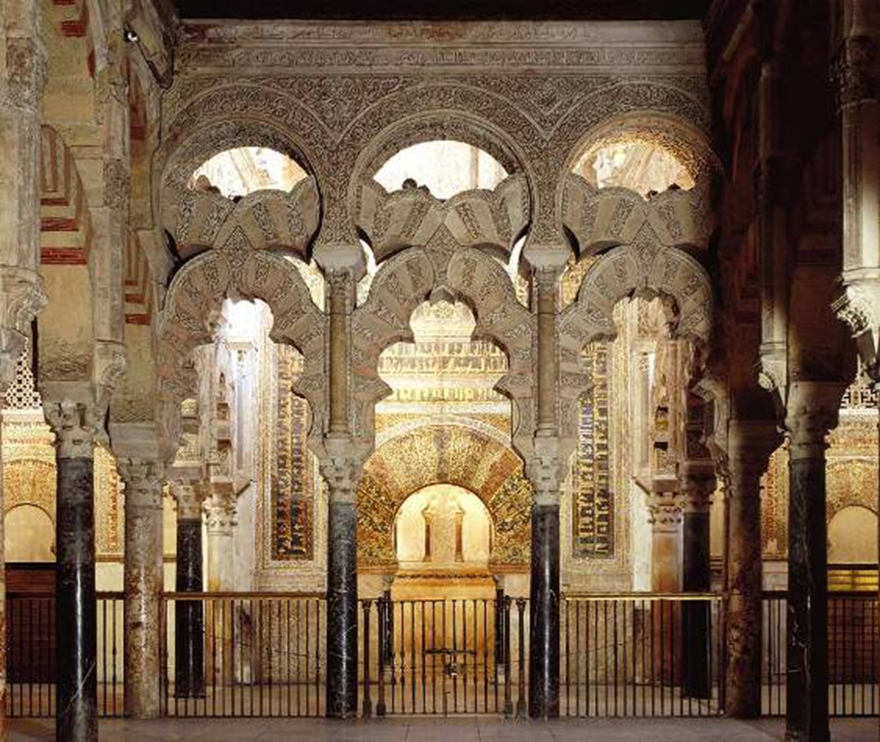

scalloped arches separate the prayer hall and private section for the caliph

dome
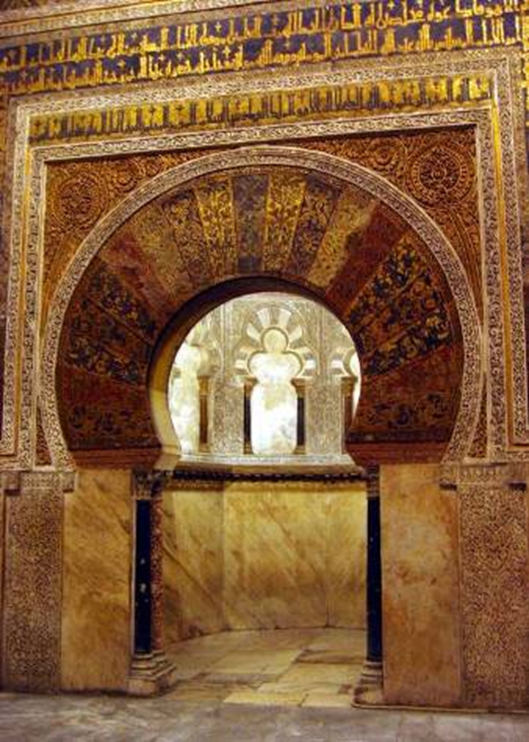

mihrab
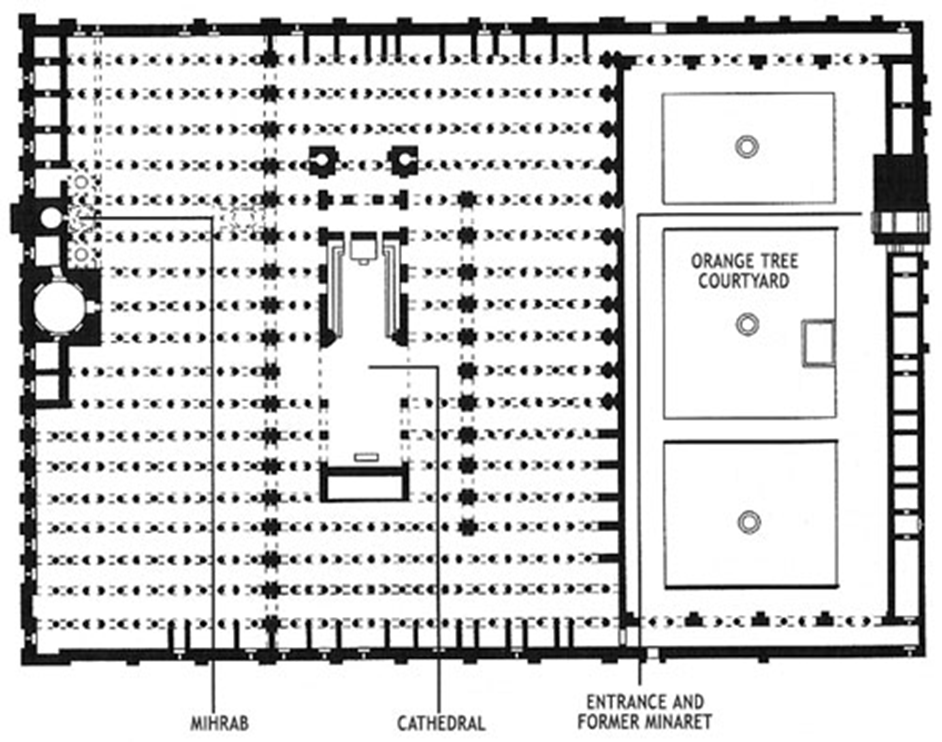
catholic cathedral of cordoba is placed in the middle of the prayer hall
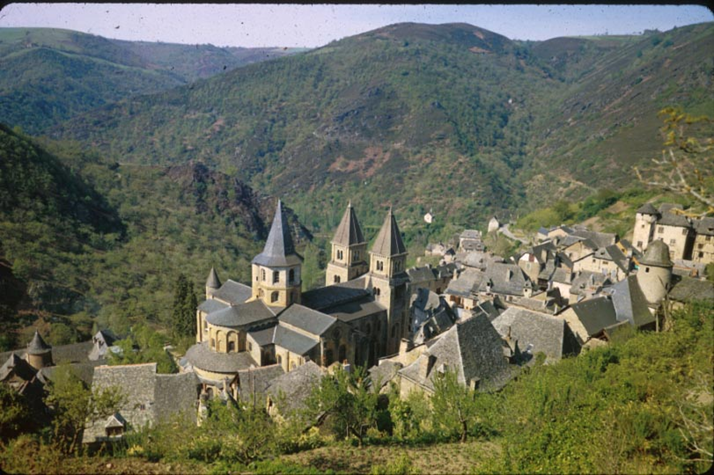
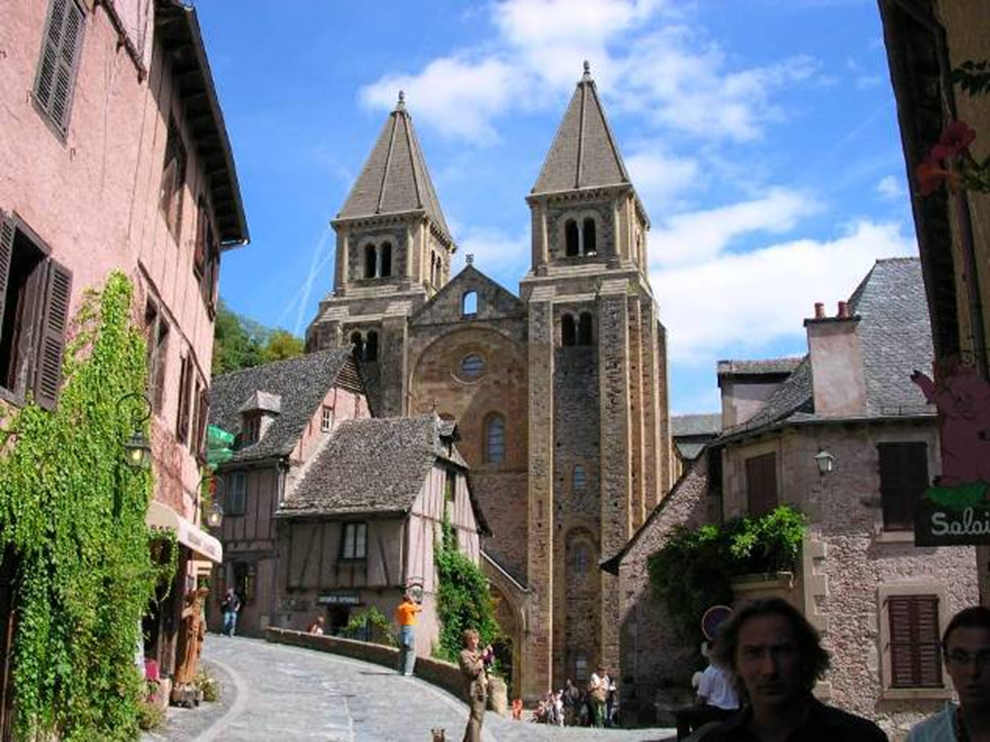
sainte-foy, conques, france (1050 - 1130)
romanesque
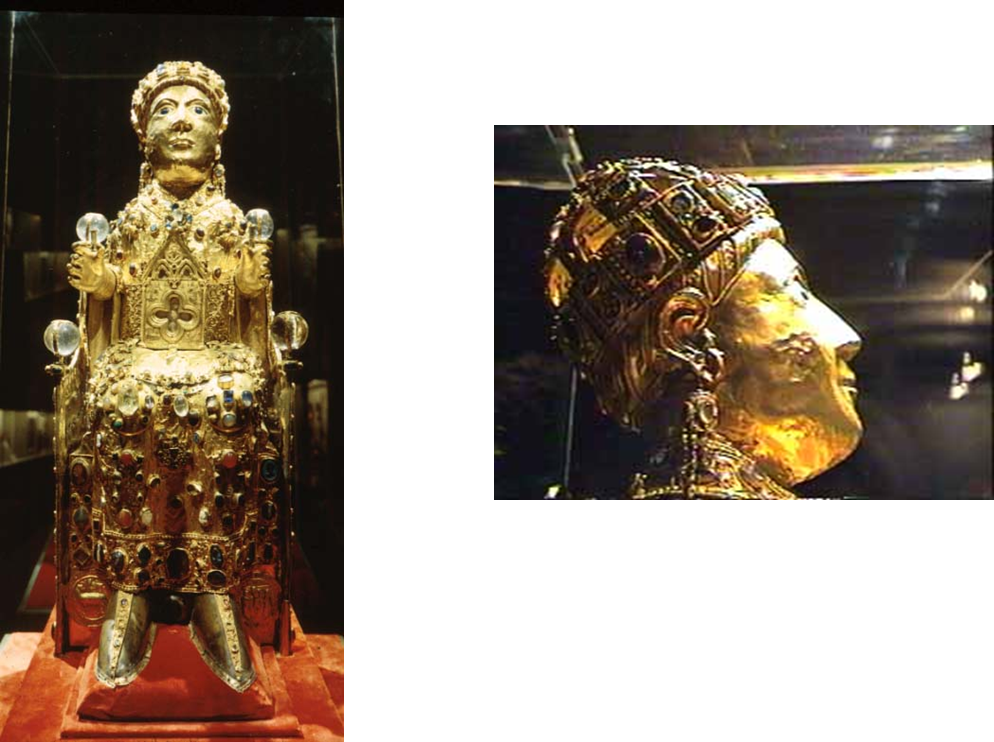


relic statue of ste foye
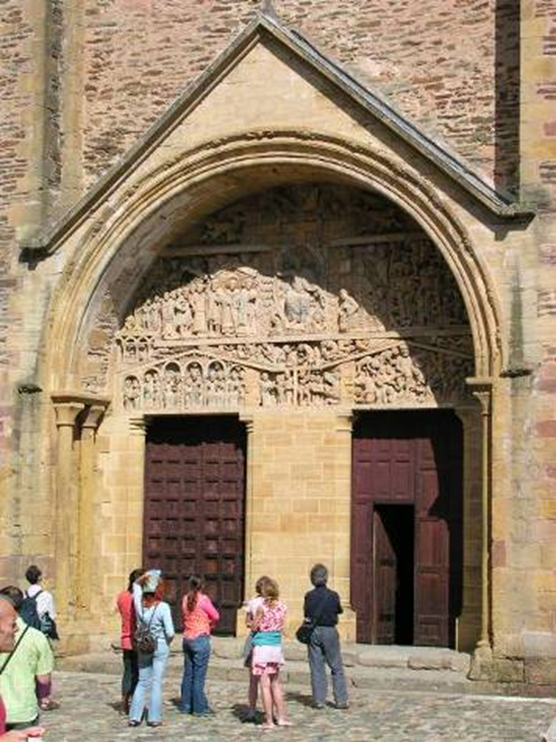

entry portal with tympanum sculpture of the last judgement
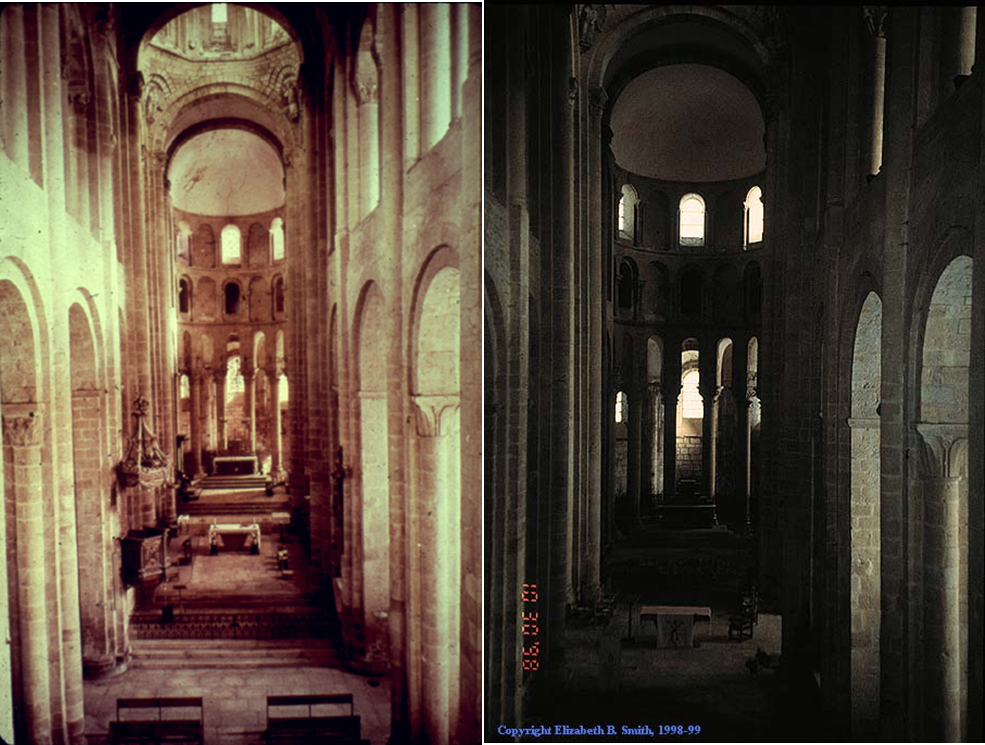
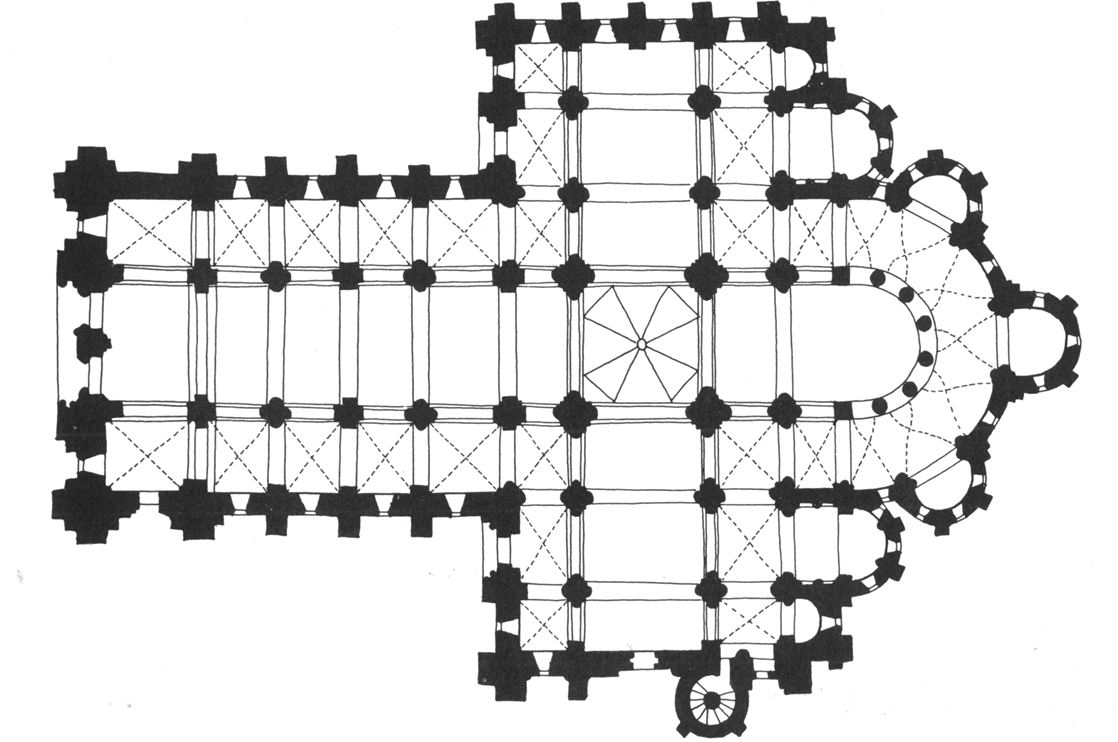

naves were typically dark in romanesque with light only from windows
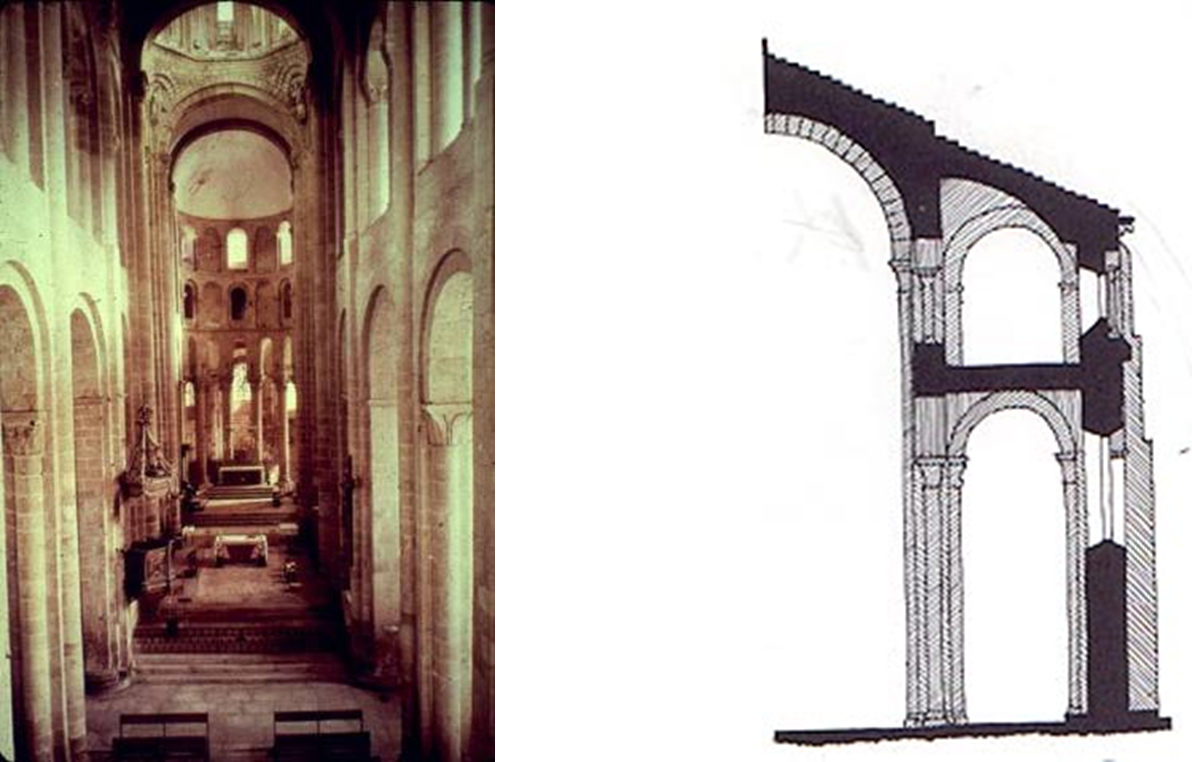
needed butressing for barrel vaults
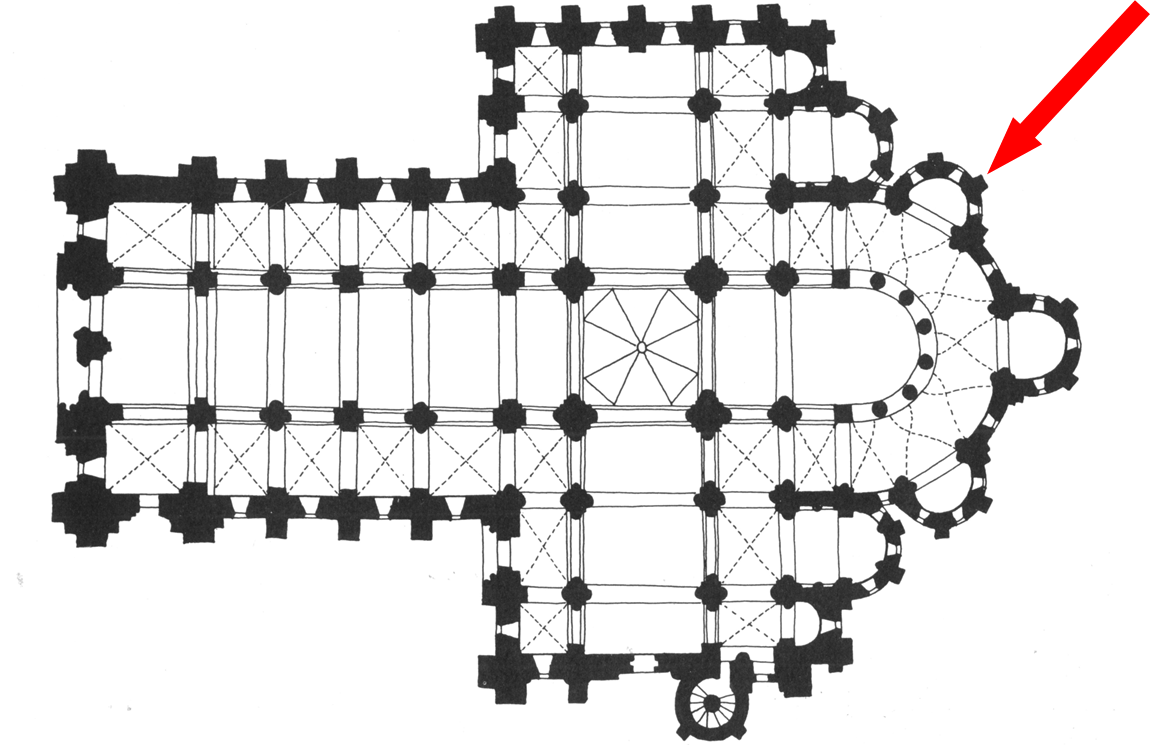
relics were displayed here
