QCE Biology
4.0(1)
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
1
New cards
Prokaryote (prokaryotic)
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles.
2
New cards
Eukaryote (eukaryotic)
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles.
3
New cards
What is ATP?
Adenosine Triphosphate, the main energy source that cells use for most of their work.
4
New cards
Autotroph (autotrophic)
Organisms that make their own food from carbon dioxide.
5
New cards
Heterotroph (heterotrophic)
an organism that cannot make its own food and instead relies on consuming other organisms; all animals, fungi and protozoans are heterotrophic, as well as most bacteria.
6
New cards
Unicellular
An organism made up of one type of cell.
7
New cards
Multicellular
An organism made up of more than one type of cell.
8
New cards
Animals (Anamalia)
eukaryotic; multicellular; heterotroph; consumers; complex organ systems.
9
New cards
Plants (Plantae)
Eukaryotic, multicellular organisms with cell walls and chloroplasts. Photosynthesis for energy.
10
New cards
Fungus (Fungi)
Saprophytic and parasitic spore-producing eukaryotic organisms that lack chlorophyll and include molds, rusts, mildews, smuts, mushrooms, and yeasts.
11
New cards
Protists
single-celled or simple multicellular eukaryotic organisms that generally do not fit in any other kingdom. Which Domain?
12
New cards
Bacteria (Bactae)
single-celled, prokaryotic, micro-organisms that reproduce by cell division and may cause infection by invading body tissue of animals.
13
New cards
MRS GREN
Movement, Respiration, Sensitivity, Growth, Reproduction, Excretion, Nutrition.
14
New cards
total magnification \= ?
objective lens x ocular lens.
15
New cards
Objective Lenses
lenses that are found on the nosepiece of a microscope and range from low to high power.
16
New cards
Ocular Lense
The eye piece of the microscope that has a lens generally between the ranges of 10x to 15x magnification.
17
New cards
Eubacteria
Kingdom of unicellular prokaryotic bacteria, generally involved in causing sickness,. Examples include E-Coli and Salmonella (A branch of the bacteria kingdom)
18
New cards
Archbacteria
kingdom of unicellular prokaryotes bacteria, are known to live in more extreme and harsh conditions and therefore not coming into contact with other organisms as much (A branch of the bacteria kingdom)
19
New cards
Cellular Resperation Formula \= ?
6O2 + C6H12O6 \= 6CO2 + 6H2O + C10H16N5O13P3
20
New cards
Carlos Linnaeus
A swedish naturalist, devised a system for grouping organisms into hierarchical categories. This system is now called the Linnaeus System.
21
New cards
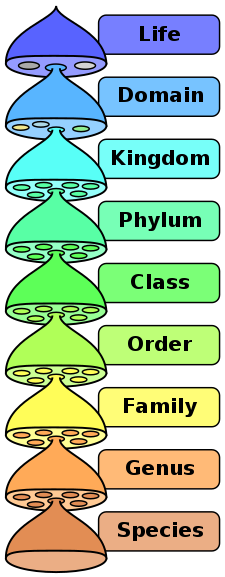
Hierarchy of classification (in order).
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
22
New cards
Dichotomus Key
series of questions that leads to choices that leads to the scientific name of an organism. Almost like a flow chart leading allowing you to quickly determine a species or other classification form.
23
New cards
Anaerobic Respiration
A variation of respiration that does not require oxygen
24
New cards
Aerobic Respiration
A variation of respiration that requires oxygen
25
New cards
length of cell formula
FOV. Diameter ÷ Approx. occurrence of cells inside FOV
26
New cards
FOV
Field of view
27
New cards
1MM \= ?μm
1 MM \= 1000μm
28
New cards
Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid
DNA (Expanded Name)
29
New cards
Chromosome
a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and proteins found in the nucleus of most living cells; it carries genetic information in the form of genes.
30
New cards
Double Helix
two strands of nucleotides wound about each other; the structure of DNA.
31
New cards
Nucleotites
The smallest building blocks of DNA; is made of phosphate (PO4), deoxyribose and a base.
32
New cards
Gene
A segment of DNA ( apart of a chromosome) that codes for a specific genetic trait.
33
New cards
Proteins
Chains of amino acids.
34
New cards
Amino acids
building blocks of proteins.
35
New cards
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome.
36
New cards
Transcription
the organic process where a DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA
37
New cards
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
38
New cards
Coriolis Effect
Movement caused by the rotation of earth on its axis.
39
New cards
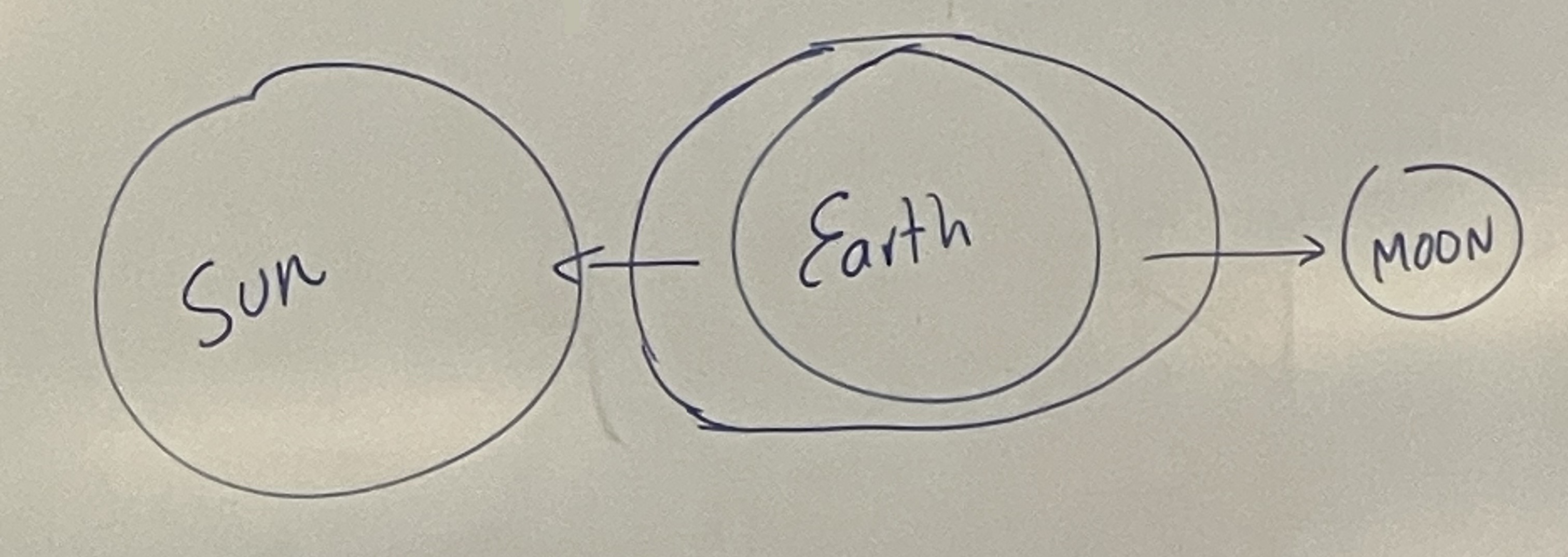
Spring Tide
The highest tide setting, it is made when the moon and sun are on opposite sides of the earth.
40
New cards
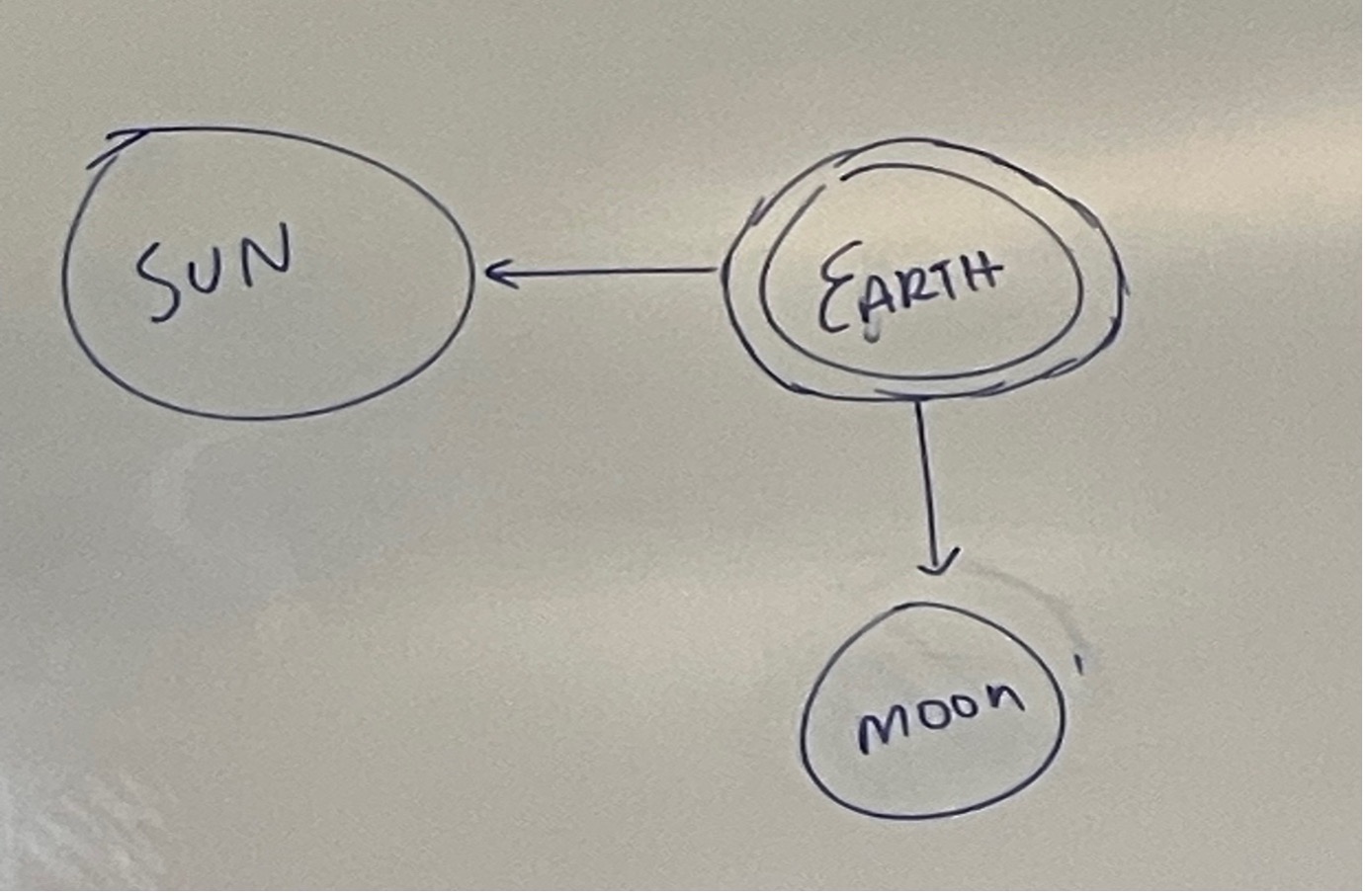
Neap Tide
The lowest tide setting, it is made when the moon and sun are 90° to each other.
41
New cards
Surface Currents
ocean currents on the surface (top 10%) that are driven by wind.
42
New cards
Deep Sea Currents
Currents that are caused by the differences in the density of ocean water (thermohaline circulation).
43
New cards
Coriolis effect
The effect of Earth's rotation on the direction of winds and currents.
44
New cards
Gyres
Huge circular moving current systems dominate the surfaces of the oceans.
45
New cards
Nucleus
contains the dna of a cell; something of a cells brain.
46
New cards
Mitochondria
supplies cell with energy, by preforming resperation.
47
New cards
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
48
New cards
cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
49
New cards
Lysosomes
Breaks down waste, food, etc.
50
New cards
cell wall
A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to the cell
51
New cards
Vacuole
A sac inside a cell that acts as a storage area for fluids
52
New cards
Prophase
The nuclear membrane starts to break up into two identical sides
53
New cards
Metaphase
The chromosomes align at the equatorial plane or center of the cell
54
New cards
Anaphase
Spindle fibers shorten and as a result chromosomes are pulled towards the poles - sister chromatids are separated at the centromere
55
New cards
Telophase
Chromosomes uncoil once they have reached the poles
56
New cards
Chromosomes
Structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
57
New cards
Chromotid
One copy of a newly copied chromosome which is still joined to the other copy by a single centromere.
58
New cards
Sister chromatid
Two identical copies of a chromatid
59
New cards
Cytokinesis
The cytoplasmic division of a cell at the end of mitosis or meiosis, bringing about the separation into two daughter cells
60
New cards
Asexual reproduction
A type of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single organism
61
New cards
Sexual reproduction
The production of new living organisms by combining genetic information from two individuals of different types
62
New cards
Gamete
A mature haploid male or female germ cell that is able to unite with another of the opposite sex in sexual reproduction to form a zygote.
63
New cards
Diploid
Containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
64
New cards
Haploid
Having a single set of unpaired chromosomes
65
New cards
Meiosis
A type of cell division that results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell, as in the production of gametes and plant spores
66
New cards
Anaphase 1
Homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite ends of the cell
67
New cards
Prophase 1
homologous chromosomes pair up
68
New cards
Metaphase 1
Homologous chromosomes line up at the equator
69
New cards
Point of meiosis
To reproduce gamates in order to preserve a species.