FAM exam 6 - cows and mini goats
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Goat intestinal parasites
MOA: GI nematodes, flukes, lungworms, barber pole worm
CS: Weight loss, poor growth, anemia, poor hair coat, submandibular edema/ bottle jaw, diarrhea.
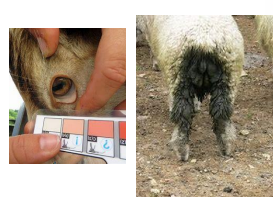
ID: Fecal examination, Fecal egg count, FAMACHA
TX: Albendazole + Levamisole, Albendazole + COWPs, Levamisole + COWPs
Only when CS appear
Prevention:
Young: 4-6w, 8-12w of age
Adults: q 6-12m dewormed
Fecal egg counts (FEC)
Avoid over grazing
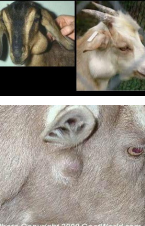
Goat Mange
Psoroptic: Ear lesions, pruritic→ head shaking/rubbing, alopecia, redness, crust
non burrowing
Chorioptic: leg/abdomen lesions, pruritic→ restlessness, alopecia, redness, crust
non burrowing
Demodectic: facial lesions, non pruritic→ papules/nodules: gray waxy material(mites found here)
TX:
Ivermectin, moxidectin, eprinomectin
Topical Dips: Coumaphos/ Toxaphene/ Lime sulfur/ Phosmet
q 2x 5-7 days apart
secondary pyoderma: antibiotic therapy
Lice Infestation In Goats
Lice Infestation (Pediculosis)→ sucking/chewing
CS: Pruritus, alopecia, skin damage, anemia, loss of condition
TX: improve BCS/housing, late summer or fall, whole herd, repeat 2× 5-7 days apart
Biting Type: Synthetic pyrethroids (methrin), Coumaphos, Malathionor
Sucking Type: Ivermectin(systemic), doramectin

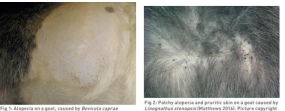
Dermatophilosis
AKA: Streptothricosis, Lumpy Wool Disease, Rain Scald, Rain Rot
MOA: Dermatophilus congolensis, contact, biting insects, skin abrasions, moisture
CS: Papules, pustules,"paintbrush" crusts, not pruritic, but painful
ID: Gram stain, morphology(branching filaments), culture, histopath
TX: Oxytetracycline, Topical iodine/ chlorhexidine, Vax, keep dry, good diet
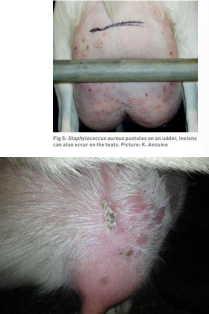
Staphylococcal Dermatitis in Goats
CS: Nonpruritic lesions on head and face, alopecia, papules, crusts, ulcers, erythema, exudation, hyperpigmentation, skin thickening
ID: Culture, histopath
TX: Pen G, Oxytetracycline, enrofloxacin, lincomycin-spectinomycin, topical iodine/ chlorhexidine
Prevention: control flies, isolate affected
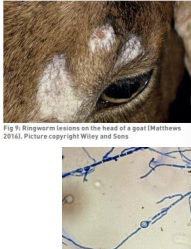
Dermatophytosis (Ringworm) in Goats
MOA: Trichophyton verrucosum
Zoonotic, direct contact
CS: Circular areas of hair loss, scaling, crusting
ID: CS, Fungal culture
TX: isolation, griseofulvin, Enilconazole, Lime sulfur, iodine, sodium hypochlorite (bleach), Sun exposure
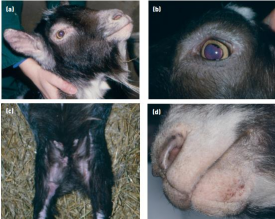
Seborrhoeic Dermatitis in Goats
MOA: unknown
CS: Non-pruritic scaling and crusting: around the eyes, ears, nose and head, and in the axilla, groin and perineal region
TX: antibiotics, methylprednisolone acetate, corticosteroid
Bacti Pneumonia in Goats
MOA: Pasteurella multocida, Mannheamia haemolytica, Mycoplasma
CS: Fever(>104), Coughing, Nasal discharge, Difficulty breathing, Weakness
ID: Auscultation(crackling/wheezing), X-ray, tracheal wash(culture)
TX: Antibiotics, NSAIDs, Supportive care, Vax, Ventilation
Viral Pneumonia in Goats
MOA: Parainfluenza 3(PI3), Adenovirus, Respiratory Syncytial Virus(RSV), Caprine Herpesvirus
CS: coughing, nasal discharge, anorexia, fever, conjunctivitis, tachypnea, tachycardia
ID: virus isolation, serology
TX: supportive, intranasal vax
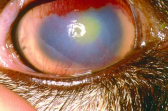
Keratoconjunctivitis in Goats
MOA: Chlamydophila, Mycoplasma
Highly contagious
CS: Epiphora (tearing), redness, mucopurulent discharge, keratitis
Herd wide Mastitis, Polyarthritis, Pleuropneumonia
ID: Cytology, IFA, Culture
TX: Oxytetracycline + Polymyxin B(eye meds), NSAIDs (Flunixin/Meloxicam), eye patch
Prevention: fly control, vax
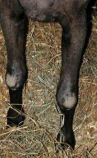
Caprine Arthritis Encephalitis (CAE)
MOA: Lentivirus
CS:
Kids 2-6m →1y: Progressive weakness, leukoencephalomalacia!
Adults: chronic arthritis carpal joints, hard bag, pneumonia
ID: ELISA, AGID, PCR
TX: Aspirin, Flunixin meglumine, Euth,
Prevention: isolate @ birth, pasteurized colostrum
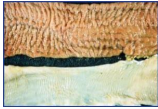
Paratuberculosis (Johne's Disease) in Goats
MOA: Mycobacterium avium
CS: Weight loss, rough hair coat, submandibular edema, weakness, anemia
don’t appear until 2-4 years of age
ID: Fecal PCR testing, necropsy, thickened intestine/large lymph nodes
TX: none, pasteurize colostrum, test/cull
Caseous Lymphadenitis in Goats (CL)
AKA: Cheesy Gland
MOA: Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
Via Skin breaks
CS: chronic weight loss, external abscesses
ID: Culture, serology
TX: Pen G, Oxytetracycline drain w/ iodine lavage, isolate, clean shearing equipment
Mycoplasma in Goats
MOA: Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. capri (highly pathogenic) , M. putrefaciens(less common)
Lifelong intermittent shedding
Shed after stress
CS: Mastitis, arthritis, pneumonia, meningitis, abortion
ID: Culture milk/joint fluid
TX: none
Prevention: test/cull/replacement herd
Tetanus in Goats
Clostridium Tetani
MOA: Wound infection
CS: Lockjaw, muscle spasms, especially in neck, limbs, and back, difficulty breathing, seizures, death
ID: History of injury.
TX: Tetanus antitoxin, antibiotics, muscle relaxants, sedatives,
Prevention: vax
Poor prognosis
Mastitis in Goats
MOA:
Staphylococcus aureus(severe)/agalactiae/uberis(mild)
Mycoplasma(systemic)
Escherichia coli(severe)
Coagulase-negative Staphylococci(mild/chronic)
CS: Heat, pain, swelling, abnormal milk
ID: Clinical signs, CMT
TX: antibiotics, frequent stripping out, oxytocin injections, NSAIDs,
Prevention: pre/post teat dip, clean udders/hands
Acute Rumen Acidosis in Goats
MOA: drastic diet change, too much grain/corn
CS: Bloat, abdominal distension, dehydration, tachycardia, tachypnea, lethargy, recumbency and death
TX: Rumenotomy(early), transfaunation, antibiotics, vit B, IV/oral fluids

Pregnancy Toxemia in Goats
MOA: High energy demand late in pregnancy
especially w/ multi kids
CS: Depression, teeth grinding, star-gazing, incoordination, recumbency, and death
ID: detect ketone in urine or milk
TX: propylene glycol, vit B, calcium borogluconate, transfaunation, C-section/induction/abortion → 30-36h later
Polio in Goats
MOA:
Primary: Thiamine deficiency, sulfur toxicity
Secondary: Excessive grain, rumen acidosis
CS: Stargazing, circling, head pressing, blindness, nystagmus, convulsions, death
TX: Thiamine, probiotics, brewer’s yeast
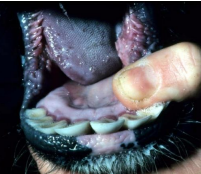
Diarrhea in Neonatal Goats
MOA: E. coli, Rotavirus, Cryptosporidium, Salmonella, Giardia, Nutritional
CS: Dehydration, liquid stools, Fever, Depression, Tenesmus
ID: Fecal, culture, serotyping, Histopath, IFA
TX: IV Fluids, Trimethoprim-Sulfonamide, Oxytetracycline, Metronidazole, Neomycin sulfate, NSAIDs, Probiotics, Vax
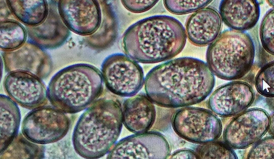
Coccidiosis in Neonatal Goats
CS: Thin kids, diarrhea , anemia, rough hair coat, weakness, dehydration, stunted growth, death
ID: fecal flotat
TX: Amprolium, Decoquinate, Benzeacetonitrile (-azurill), sulfadimethoxine, sulfadimidin
Navel ill and Septic joints in Neonatal Goats
MOA: Infection of the umbilicus.
CS: Swollen umbilicus, swollen joints, reluctance to move, failure to gain weight.
TX: antibiotics, joint lavage, surgical removal of the umbilicus,
Prevention: navel dip

Contagious Ecthyma in Neonatal Goats
AKA: Sore mouth
MOA: Orf virus
CS: Painful lesions around mouths/teats, anorexia
TX: antibiotics, NSAIDs,
Prevention: Vax (live) → only if dz is present
Septic Meningitis
MOA: Bacti sepsis, Failure of passive transfer, umbilical infections, poor hygiene
(E. coli, Pasteurella spp., Salmonella spp)
CS: Depression, fever, inappetence, Stiff neck, opisthotonos (arched back), Ataxia, tremors, seizures, Blindness, altered mentation
ID: Culture, CSF Analysis
TX: Antibiotics, NSAIDs, Fluids, Plasma transfusion, Vax
Dystocia in Goats
Difficulty in delivery, requiring assistance
MOA: Fetal malpositioning, fetal disproportion, multi fetuses, incomplete cervical dilation (ringwomb), uterine inertia, and uterine torsion.
TX: C-sections(common), manual correction→ cervical dilation(<30%), manipulation, Oxytocin(careful with close cervix’s), NSAIDs, Antibiotics
Urolithiasis in Goats
MOA: Goats normally have alkaline urine
Phosphatic calculi (struvite): grain diets
MOST COMMON
Calcium carbonate: legume diets
More prominent if neutered b4 3m
Common sites: Urethral process; sigmoid flexure
CS: Straining to urinate, tail pumping, blood/crystals on preputial hairs, anorexia, lethargy, urethral rupture leading to potbelly appearance, bladder rupture
ID(rupture): xray, abdominocentesis, US, creatine ratio: blood/fluid
TX: Med management(not enough), Urethral process amputation, urethrostomy, cystostomy, bladder marsupialization(ruptured urethra), increase salt in the diet, ammonium chloride
Urethral process amputation, cystostomy: good kidney function, bladder/urethra is intact → good long term prognosis
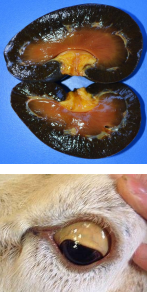
Copper Toxicosis in Goats
CS: Anorexia, depression, diarrhea, weakness, hemoglobinuria, icterus.
ID: Serum copper concentrations, liver and kidney copper levels.
TX: Supportive care, fluid therapy, ammonium, sodium thiosulfate
Foot Rot in Goats
MOA: Fusobacterium necrophorum, Dichelobacter nodosus, wet enviro, overgrown hooves
CS: Lameness, necrotic lesions in the interdigital space w/ foul odor.
TX: penicillin, oxytetracycline, formalin/zinc sulfate foot bath, farrier work, dry enviro
Degenerative Joint Disease in Goats
Common in geriatric goats
CS: Stiff gait, reluctance to walk, overgrown hooves, progressive lameness
TX: Polysulfated glycosaminoglycan, Phenylbutazone, Aspirin, Hoof trimming, weight management

Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
MOA: #1 congenital heart defect of ruminants
Herefords, Limousins, Jersey cattle
CS: Calves: ocular anomalies, tail anomalies, resp distress, poor growth, right side murmur
Some VSDs can be large with significant shunting of blood (Mostly L to R)
ID: US, necropsy
TX: euth (grave)
Tetralogy of fallot
MOA: Right to left shunt
CS: cyanosis, exercise intolerance, dyspnea, Polycythemia
MOA: euth (grave)
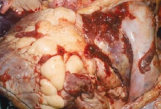
Neoplasia of the Bovine Heart
MOA: lymphosarcoma involving the 1) right atrium in cows 3-4y
2) abomasum, 3) uterus, 4) CNS
CS: Tachycardia, Atrial fibrillation, murmurs, heart failure, distended jug v. ,brisket edema/bottle jaw(ventral)
White nodules or streaks within the myocardium
ID: AGID, US, necropsy
TX: euth (grave)
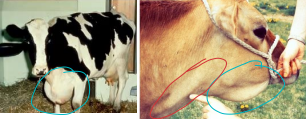
Cardiomyopathies
MOA:
Primary: Genetic -RARE
Red Holstein, Ayrshire cattle
Secondary: toxicity- MOST COMMON
oleander, Monensin, lasolacid, cottonseed
CS: CHF, brisket edema/bottle jaw
abnormal jugular vein
TX: digoxin, fluids, rumenotomy (6-12hr if toxic)
poor-grave prognosis

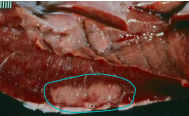
Vitamin E/selenium Deficiency
MOA: Acute muscle degen of rapidly growing calves
CS: Resp distress, arrhythmias, sudden death, Elevated cTnI
TX: Selenium w/ vit E injections, supplement
fair to good prognosis
Infectious Myocarditis
MOA: Histophilus somnus - vasculitits
CS: Sudden death, depression, pyrexia, foaming at mouth, dyspnea
ID: Histopath - see colonies in tissue
TX: Tulathromycin/ tetracyclines/ enrofloxacin (antibiotics), NSAIDs, fluids
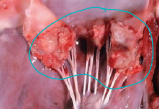
Endocarditis
More common the myocarditis
MOA: tricuspid valve of Dairy Cattle than any other species
bacti infection
CS: intermittent fever, tachycardia, systolic heart murmur for a long time, pounding heart sounds
ID: Anemia(non-regen), Neutrophilia(mature), High Gb + fibrinogen, US, Bld culture
TX: >3w of ceftiofur (antibiotics), Furosemide, NSAIDs
Guarded to poor prognosis
w/ ventral edema, right heart failure

Pericarditis
MOA: traumatic reticulopericarditis
CS: Jugular vein distention, tachycardia, splashing heart sound, fever, painful stance, brisket edema/bottle jaw
ID: Withers pinch test (x3), bar test, grunt test, X-ray, US, culture
Pericardiocentesis: smells, high TP(>8.5) + fibrinogen(>850) + SG + WBC
5-6 ICS right side
TX: antibiotics, NSAIDs, magnets (give @ 4-8m old), SX (Rumenotomy/ Thoracotomy/ pericardiectomy) - not practical
Prognosis is poor

SR Pericardial Effusion (Heartwater)
MOA: Ambyloma ticks
CS: fever, resp distress, edema
TX: Tetracycline - if given early
difficult to control
Brisket edema; Mountain Sickness; High Mountain Dx
right ventricular hypertrophy
MOA: only "herd" cardio dx
COR pulmonale (R ventricular hypertrophy), genetic, grazing Astragalus/Oxytropis (locoweed)
CS: dyspnea, tachycardia, ventral edema, jugular pulsations
ID: US, TTW, X-ray, measure PA pressure
DDX: other ‘carditis’, pneumonia
TX: lower elevation, TX lung dx, Breed the low PA pressure bulls
Arrhythmias
Dairy cattle
MOA: atrial fibrillation
GI problems w/ high vagal tone, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, metabolic alkalosis, lymphoma
ID: irregularly irregular rhythm, high HR, ECG
TX: correct GI support, fluids, Ca solutions, KCl
Most likely a 2ndary heart problem
arrhythmia associated with high electrolytes
hypercalcemia
MOA: Rapid IV Ca for milk fever TX
careful with IV calcium - issues
CS: Bradycardia, Ectopic beats, Death
TX: atropine
hyperkalemia
MOA: Calves w/ acute diarrhea
CS: arrest of ventricular rhythm
ID: No P waves
TX: bicarbonate, dextrose solutions to drive potassium intracellularly
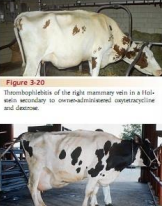
Thrombosis and Phlebitis
Dairy cattle
MOA: Traumatic venipuncture by owner
Ca, dextrose, phynelbutazone, oxytocin, tetracycline, IV NaI
CS: Local swelling, Fever, Abscess, Skin sloughing, Anorexia, Tachycardia, Edema
TX: compress, inject site w/ NS, Antibiotics, NSAIDs
Prognosis is guarded


Anemia
MOA:
Bld loss: Ruptured uterine a., SR parasites
shock = >30% loss
IV hemolysis: see hemoglobinuria, Heinz body(methemoglobinemia)
Onion , Allium, Brassica, lepto
EV hemolysis: no hemoglobinuria
Anaplasmosis, mycoplasmas
CS: Fever, icrurus, weakness, polypnea, tachycardia, anxiety, MM pallor, hemorrhagic shocks
TX: transfusion
no cross match: no alloantibodies ab
indicated PCV < 15%
Donor: BSC >4, dry, >1m post calving, BLV/anaplasmosis neg
give 12g of Na citrate in 300 mL saline, 5L of blood
Recipt: 5L cow; 500ml SR
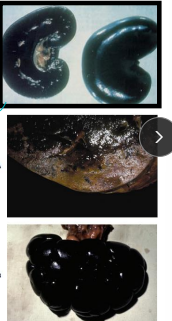
Copper Toxicity
MOA: sheep/SAC, molybdemum
cow/goats resistant
copper stored in liver
Under stressful situations copper released into blood
Hepatic necrosis and intravascular hemolysis
CS: peracute hemolytic shock, sudden death, lethargy, weakness, icteric sclera, pale MM, Hemoglobenuria, arched back from kidney pain
gun meatal kidney
ID: liver Cu > 150 ppm, kidney Cu > 15 ppm
TX: Penicillamine(orally), Vit C, Ammonium molybdate (3w)
prevention: correct diet, supplement (copper)
Bacillary Hemoglobinuria
Gram +, dairy/meat cows
MOA: Clostridium hemolyticum, liver fluke
intravascular
CS: anemia, hemoglobinuria, sudden death
ID: liver necrosis, anemic infarct in liver, discolored kidney
TX: Antitoxin, Penicillin, transfusion, Vax, prevent flukes
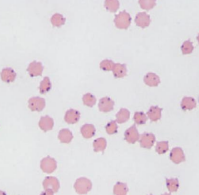
Anaplasmosis
AKA: Yellow fever
MOA: only cattle tick dx in USA
anaplasma marginale, centrale, bovis, ovis
common in S-E/N-W states
extravascular hemolysis
CS: sudden death, abortions, anemia, pale MM, anorexia, incoordination, breathlessness, rapid bounding pulse
ID: bld smears, PCR
TX: Oxytetracylcine, tick prevention
lifelong carriers
No vax
Mycoplasma haemolamae (Hemoplasmas)
MOA: Unique to SACs, goats
Transmitted by ticks
Extravascular hemolysis
CS: Fever, anemia, depression, icterus, infertility, edema, poor growth
TX: Oxytetracycline suppresses infection, but doesn’t eliminate it, Bld transfusion
Babesiosis,Texas cattle fever, Tick fever, piroplasmosis
MOA: Ticks, Mexico, zoonotic
transmitted by the cattle fever tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus)
CS: anorexia, depression, fever, anemia, red urine
TX: Diminazene, imidocarb(not in the usa), NSAIDs, IV fluids, transfusion
notifiable
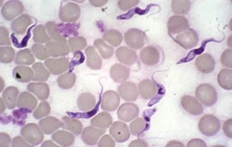
Trypanosomiasis
MOA: Tsetse/biting flies
sleeping sickness - zoonotic
CS: Fever, anemia, weight loss, lymphadenopathy
ID: Bld smear, PCR.
TX: Diminazene injections, vector control(prevention), genetics
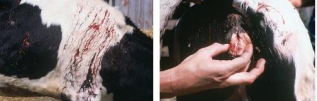
Vit K Deficiency
MOA: diet issues, microbial rumen disruption, dicumarol poisoning, rodenticides!! (warfarin, brodifacoum), moldy sweet clover
CS: Hemorrhage, Weakness, Pallor
ID: clotting profile w/ prolonged PT+PTT
loss of clotting factors (factor II, VII, IX and X, proteins C, S and Z)
TX: Vit K1, Blood transfusion
Lameness
Location: lateral claw, hind limb > forelimb
DX: sole ulceration, hoof overgrowth, interdigital hyperplasia, digital dermatitis
Scoring:
1 = sound
2 = uneven gait
3 = obvious lameness
4 = difficulty turning
5 = extreme difficulty rising & non-weight bearing
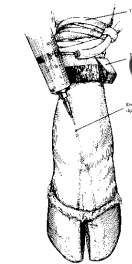
Anesthesia of the Lower Limb (Bier Block)
Tourniquet
Lidocaine
Adequate analgesia for 1 hour
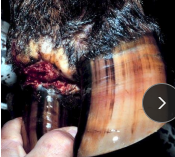
Foot Rot (Interdigital dermatitis)
# 1 disease in food animals
MOA: Trauma, wet/muddy enviro, bacti
Fusobacterium necrophorum
Bacteroides melaninogenicus
CS: Acute lameness, foul odor, swollen tissues between toes - wet seasons
sudden 3-5 lameness score
TX: clean, debride, antibiotics, NSAIDs, farrier work, soaks, dry enviro, ZiSO4 under bandage
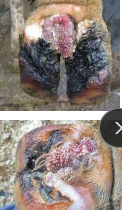
Digital Dermatitis
AKA: Hairy heel warts, Papillomatous DD, strawberry foot, verrucous dermatitis, digital warts
MOA: wet/muddy enviro, bacti, older heifers
Treponema spp.
CS: Chronic lameness, lesions above interdigital cleft
TX: ELDU Oxytetracycline/SA under bandage, foot bath, dry enviro, Vax
not curable
Regular foot baths
WASH feet
Footbath Guidelines
Frequency: 1–5 days/week
Change solution after 150–200 cows pass through
Design:
Pre footbath: gross contaminants
Bath: wide and long, 5’ of solution, in alleys
Solutions: Formalin (pH 3), Copper sulfate, Zinc sulfate
Avoid Antibiotics

Acute Laminitis (Founder)
MOA: sensitive laminae inflam
rumen acidosis, peripartum metabolic stress
CS: Acute lameness, "Cross-legged" stance, chronic hoof deformities
Prognosis: Increased risk of white line, ulcers, abscesses, false sole
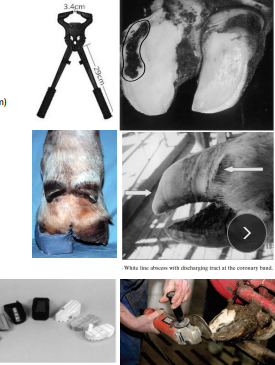
White Line Disease
MOA: Separation of the sole + hoof wall
sequelae of laminitis
CS: Acute lameness of outer claw (hindlimb) or medial claw (forelimb)
TX: hoof trim, debride, oxytetracycline, bandage, wooden block on healthy claw, NSAIDs, dry enviro
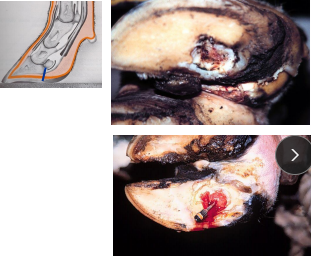
Sole Ulcer (Pododermatitis Circumscripta)
MOA: Subclinical laminitis and rumen acidosis
CS: lamness, leasion of lateral hind claws
TX: remove sole, CuSO4 under bandage, hoof block on sound leg
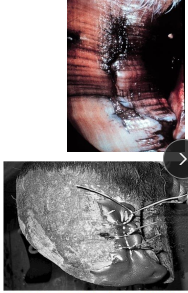
Interdigital Fibroma
MOA: Hypertrophy of interdigital space skin
(dairy) late lactation, Herford bulls
CS: Chronic skin irritation, lameness
TX: SX, wire stabilization
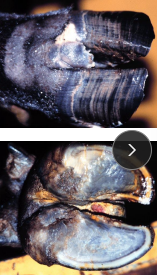
Hoof cracks
Vertical (Sand Cracks)
CS: crack originating @ hairline
TX: trim, suture with wires, apply acrylic, apply wooden block
Horizontal (Thimbles)
MOA: disruption of hoof growth
Laminitis, Rumen acidosis, dry enviro
CS: crack parallel to coronary band, severe lameness
TX: trim, remove affected horn
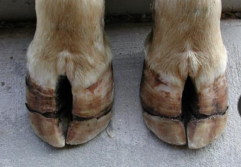

Corkscrew Claw
MOA: older cows, heritable
CS: twist of lateral claws of hind leg
TX: cull, frequent trims
No Cure

Pickup Bumper Syndrome
MOA: Gastrocnemius m. rupture
trama
CS: severe lameness, swelling
Swelling in the affected area, "dropped hock“
TX: rest, bandage, splint, NSAIDs
Poor prognosis

Blackleg (Clostridium chauvoei)
MOA: ingested bacti
CS: sudden death in healthy animals, acute severe lameness, crepitant muscle swellings
ID: gas-filled swellings, dark muscles/emphysema
TX: vax
Malignant Edema (Clostridium septicum)
MOA: Wounds from castration, docking, parturition, shearing, fighting
CS: Depression, fever, anorexia, sudden death, edematous, dark, cold swellings
TX: high-dose antibiotics, NSAIDs, IV fluids, wound debridement, vax, wound hygiene
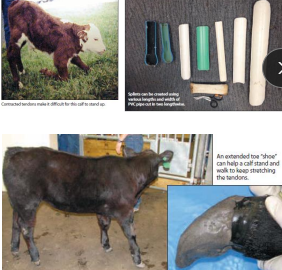
Contracted Tendons
MOA: young
TX: splint, tenotomy of SDFT, DDFT and suspensory lig.
Good prognosis

Arthrogryposis and Acorn Calves
MOA: Genetic (Charolais), toxins (lupines @ 40-70d), intrauterine infection
CS: dystocia, severe contracted tendons
TX: cull

Spider Lamb Syndrome
AKA: Corkscrew lambs, Monkey lambs, Crooked lambs, Bent lambs
MOA: Hereditary chondrodysplasia in sheep
Suffolk, Suffolk crossbred, Hampshire
CS: Kyphosis, Scoliosis, Angular limb deformities
TX: Cull
Myotonia Congenita in Goats
MOA: genetic mutation of Cl channels
Tennessee fainting goat <6w
CS: stiff/fall w/ stimulation, not painful, remains conscious,
ID: EMG, genetic testing
Capture Myopathy
MOA: Stress-induced muscle damage
CS: Muscle stiffness, weakness, tachypnea, tachycardia, hyperthermia, sudden death
TX: IV fluids, NSAIDs, calm handling

Tarsal Cellulitis (Hygroma)
MOA: Repeated trauma or pressure on bony prominences
Welfare indicator in housed livestock
CS: Firm, fluid-filled swelling over lateral hock, not painful
TX: clean enviro, drain abscess, bedding
Osteoarthritis (DJD)
MOA: Progressive joint degeneration
CS: Lameness, stiffness, joint swelling
ID: xray
TX: NSAIDs, PT, glucosamine, chondroitin, SX, avoid overcrowding
Osteochondrosis
MOA: defective endochondral ossification in rapidly growing males
CS: Lameness, peri-articular swelling
ID: ‘cyst’ like lesion on X-ray
TX: NSAIDs, arthroscopy, arthrotomy
Stifle Injuries in Cattle
MOA: Trauma
CS: upper hind-limb lameness, stifle joint effusion, pain, crepitus, patellar luxation
TX: confinement + prolonged NSAIDs, good footing
Guarded to poor prognosis
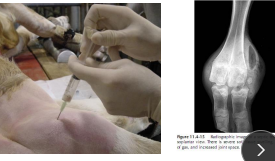
Septic Arthritis
Neonates
MOA: <1m old, FPT
CS: Hot, painful, swollen joints, Fever, depression
ID: Arthrocentesis, Xray
TX: Antibiotics, NSAIDs, joint lavage, Colostrum, hygiene, naval dip
Good prognosis unless FPT
Adult
MOA: trauma, sepsis, hematogenous
CS: Lameness, joint swelling, pain, heat, fever, lethargy
ID: Arthrocentesis, Xray
TX: Antibiotics, NSAIDs, joint lavage,
Prognosis is Guarded
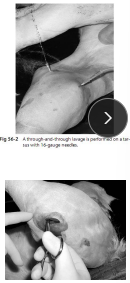
Joint Lavage
Use: septic arthritis
Steps: 1L of Sterile balanced polyionic solution pushed into joint space, through and through method
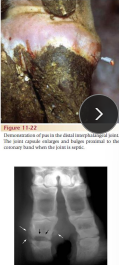
Sepsis of the Distal Interphalangeal Joint (DIP)
MOA: Untreated/advanced foot rot/sole ulcer/white line/punctures
CS: Severe non-weight-bearing lameness
ID: Arthrocentesis, Xray
TX: euth, antibiotics, NSAIDs, SX
Joint arthrodesis: Aggressive ($$) tx for valuable/young
drill + lavage w/ wooden block on healthy foot
Digit amputation: Salvage tx for older/invaluable
immediate pain relief but breakdown over time
P3, PIP, DIP, sperate P1+P2
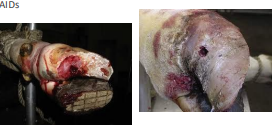
Fractures
Tx: good ortho patients!
Dynamic Compression Plating: Humerus, femur, tibia
not for heavy animals
Intramedullary Pinning: Humerus, femur, tibia
watch for implant migration, not for heavy animals
Transfixation Pin-Cast: comminuted/unstable fractures, proximal limb fractures
good for heavy animals
Thomas Splint-Cast: distal to the elbow or stifle
Short-limb Cast: distal to the carpus and tarsal joints
easy, cheap, common
Full limb cast: distal physis of the radius or distal physis of the tibia
Splint: distal to the carpus and tarsal joints, pediatrics, simple breaks
easy, cheap, common
Complications: Osteomyelitis, delayed healing, sequestration, lameness, compartment syndrome
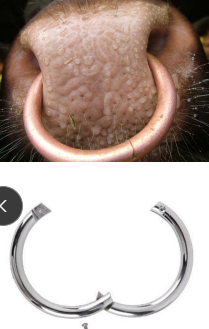
Nose Ring
Why: control bulls
Use: self-piercing, non-rusting metal ring
Steps: 9 - 12m old, local analgesia, through the nasal septum about one inch from the tip of the nose
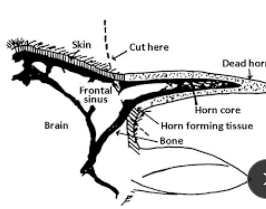
Dehorning/Disbudding cows
Why: safety for cattle and staff, reduce carcuss bruising
When: Perform as early as possible
Buds not attached to the skull <2m of age
How:
Caustic chemicals: <1w of age
Paste: NaOH, KOH, or CaOH
Injectable: CaCl
Hot iron: <2m of age
Butane-powered, rechargeable, or corded for 5–10 sec
Barnes dehorner: 3m-1y
Remove 1–1.5 cm skin at base, control bld, remove bone frag
Keystone dehorner: adult
Horn tipping: adult
Removes distal 1/3 of horn w/ saw
Meds: w/ local block (Cornual or ring), NSAIDs.
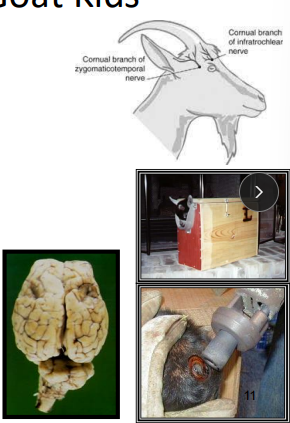
Dehorning/Disbudding goats
Why: safety
When: Perform as early as possible
How:
Hot iron: <2w of age
Meds: NSAIDs, tetanus antitoxin, ring/cornual block
Complications: Thermal meningitis, Scurs and ingrown horns
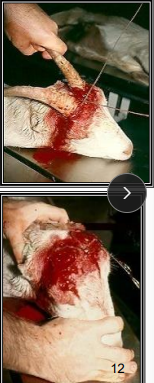
Descenting Goats
Sedation: Gen anesthesia
Tool: cautery
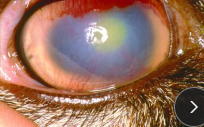
Keratoconjuctivitis (pink eye)
MOA: summer, flies
SR: Chlamydophila pecorum (#1), Mycoplasma
Cow: Moraxella bovis, Mycoplasma
Herefords + young @ risk
CS: Epiphora, hyperemia, mucopurulent discharge, keratitis, mastitis, polyarthritis, pleuropneumonia
ID: cytology, IFA, culture
TX: Topical antibiotics, systemic oxytetracycline, NSAIDs, eye patch, Subconjunctival penicillin, vax
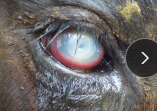
Ocular Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
MOA: Locally invasive tumor of limbus, third eyelid, upper/lower eyelid margins
sunlight, age, no pigment, Herefords, Simmentals, Holstein-Friesians
TX: cryosurgery, eyelid wedge resection, third eyelid resection, enucleation (Lg), culling (invasive)
high recurrence

Enucleation
Why: Panophthalmitis, Intra-ocular neoplasia, Severe infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis, Trauma of globe
Restraint: Standing or recumbent
Analgesia: xylazine, locals
Postop: Systemic antibiotics, NSAIDs, remove sutures
Complications: Incomplete removal of neoplastic tissue, hemorrhage, abscess formation
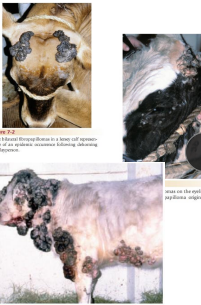
Papillomatosis (Fibropapillomas, “Warts”)
MOA: BPV (#1), benign, self-limiting
6-24m old, associated with skin trama
CS: cauliflower-like, flat, gray, rough, crusty on the head, neck, brisket, teats, eyelids
TX: Spontaneous, Sx, cauterized, crush, vax

Dermatophytosis (Ringworm)
AKA: Club lamb fungus
MOA: Trichophyton verrucosum
zoonotic, contact, winter
TX: iodine solution, chlorine bleach, sunlight
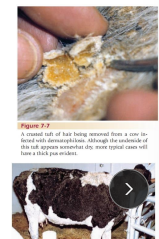
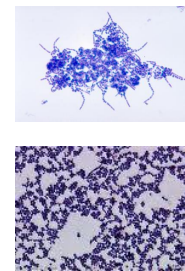
Dermatophilosis (Rain rot; Rain Scald)
AKA: Streptothricosis, Lumpy wool
MOA: Dermatophilus congolensis, actinomycete
Moist enviro, zoonotic
CS: matted tufts of hair
ID: smear, diff-quick, railroad tracks or tramcar line
TX: antibiotics, lime sulfur, keep dry
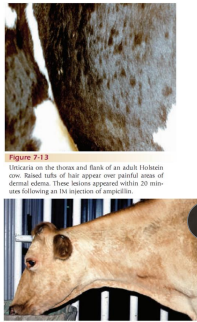
Urticaria and Angioedema
MOA: Type 1 hypersensitivity rxn
bites, vax, milk allergy
CS: rapid hives, skin wheals, lg edema plaques
ID: rxn to tx
TX: Antihistamines, NSAIDs
Photosensitization
MOA:
Primary: photodynamic agent is directly ingested, injected
Hypericin (St. John’s wort), Fagopyrin (buckwheat)
Congenital: abnormal pigment synthesis
Bovine erythropoietic protoporphyria and bovine erythropoietic porphyria
Secondary (#1): impaired hepatic excretion of phylloerythrin
pyrrolizidine alkaloids, Blue-green algae
Cs: erythema, edema, crusting, and necrosis of non-pigmented, hairless skin
ID: high SDH, GGT, ALP, bilirubin
TX: Remove from pasture, shade, NSAIDs, corticosteroids
poor prognosis
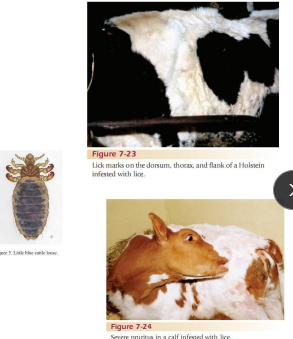
Lice
CS: pruritus, restlessness, and excessive licking, anemia
TX: Organochlorine, organophosphurus, pyrethroid, Coumaphos, Diazinon and permethrin, Ivermectin (sucking lice but not biting)
Ticks
MOA: Cattle fever tick (babesia-reportable), Dermacentor (anaplasmosis)
CS: Inflam, itching, and swelling, disease, anemia, death, secondary infections
Mange
MOA: colder months, housed animals with close contact
Psoroptes ovis: Eradicated in sheep, found in cattle,highly pruritic
Psoroptes cuniculi: SA Ear mite
Scabies: Burrowing mite, severe pruritus
*Chorioptes bovis: "tail mange," "foot mange," "red mange“, #1 cause of cattle mange
*Demodex: non-pruritic, cigar-shaped mites
CS: skin irritation, hide damage, reduced weight gain
ID: deep skin scrape
TX: macrocyclic lactones, topical hot lime sulfur
Obligatory or Primary Myiasis
MOA: Cochliomyia hominivorax, the New World screwworm
must live on living tissue for life cycle
TX: lindane, ronnel, nitenpyram
Reportable disease

Facultative or Cutaneous Myiasis (Flystrike, Blow fly strike or Maggots)
MOA: fly stike, contaminated wounds, sheep
tail docking, sx
CS: begin feeding on the sheep's skin and flesh, causing irritation, tissue damage, secondary bacti infections
TX: Shear, ivermectin, organophosphates, wound care, Crutching
Hypodermiasis (Warbles, Grubs)
MOA:
H. lineatum: migrate to caudal esophagus submucosa
H. bovis: migrate to epidural fat of thoracolumbar vertebrae
CS: bloat, paralysis, salivation, anaphylaxis
TX: ivermectin, moxidectin, OP
July and Oct
watch for anaphalaxis

Sheep ked
MOA: direct contact, fall/winter, long wool
zoonotic
CS: Loss of condition, anemia, irritation, biting, rubbing, damaged skin and poor fleece quality
ID: wingless flies
TX: ivermectin, moxidectin, OP