Path: Regeneration and Repair
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
serous fluid
fibrinous inflammation
purulent/suppurative inflammation
ulcers
what are 4 patterns of acute inflammation ?
serous fluid
watery fluid containing very little protein triggered by agents causing mild damage to blood vessel walls and cytokines associated with increased vascular permeability
fibrinous inflammation
if macrophages fail to completely remove fibrin (lack of resolution), it will organize into granulation tissue with newly formed blood vessels subsequently resulting in scar formation
fibrinous adhesions
fibrinous exudate is present in the pleural cavity causing formation of dense scar tissue that bridges and obliterates the pleural cavity
purulent (suppurative) inflammation
result of severe inflammatory insult in which the exudate composed mainly of dead neutrophils that release lysosomal granules and cause tissue necrosis
empyema
pus in pleural space
ulcer
results from necrosis caused by an acute inflammatory episode involving the mucosal lining or surface of an organ, followed by sloughing of the necrotic tissue and the formation of a crater
resolution/regeneration - injurious stimulus cleared, mediators clear, replacement of injured cells and return to original state
scarring (fibrosis)/repair - extensive tissue damaged and filled in with CT
chronic inflammation - injured stimulus not cleared
what are outcomes of acute inflammation (3)
labile (GI, skin, respiratory, reproductive, urinary, hematopoietic)
tissues that are in a constant state of renewal, allowing replacement of dead cells with newly formed cells
stable/quiescent tissue (liver, kidney, and pancreas parenchymal cells; endothelial cells)
limited replication under normal homeostasis, few percentage of cells are undergoing mitosis; may replicate in response to stimuli
permanent/non-dividing tissue (neurons, skeletal and cardiac muscle)
no physiologically significant mitotic activity; injured cells are replaced by supportive elements or scarring
embryonic
stem cells that are pluripotent, or can differentiate into all cells of the adult organism up to the stage of the preimplantation blastocyst
adult (somatic)
stem cells that are multipotent, but lineage-restricted (e.g. hematopoietic stem cells) and allow regeneration (and homeostasis) in labile tissues; reside in special microenvironments
CD34 and CD90
markers expressed on hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow that are not lineage-committed
stem cell transplantation in the treatment of leukemia and lymphoma
what is the most important clinical use of hematopoietic stem cells?
epidermal growth factor (EGF)
growth factor involved in mitosis and migration of keratinocytes and formation of granulation tissue after injury; stimulates epidermal cell growth
transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-alpha)
growth factor involved with proliferation of hepatocytes and other cells
fibroblast growth factor
stimulates proliferation of endothelial cells and stimulates angiogenesis; recruits fibroblasts for ECM protein synthesis
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
growth factors involved with endothelial cell proliferation and stimulates angiogenesis
platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
growth factor that recruits inflammatory cells and enhances ECM synthesis
transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta)
stimulates ECM protein synthesis; suppresses acute inflammation, endothelial cell proliferation and migration; inhibits metalloproteinases
keratinocyte growth factor (KGF)
growth factor that stimulates keratinocyte migration, proliferation, and differentiation
receptor with kinase activity
receptors that reside on the cell surface; ligand binding induces receptor dimerization and activation which phosphorylates downstream effector molecules that transmit the signal to the cell nucleus
receptor with kinase activity
which type of receptors are most growth factors?
receptors without kinase activity which recruit extrinsic kinase
which type of signaling is used by interleukins, interferons, and growth hormone (regulates self-renewal of HSCs)?
receptors without kinase activity which recruits kinase
type of signaling that involves JAK binding to receptors that activates STAT through phosphorylation which enters the nucleus and activates gene transcription by directly binding DNA (in signal transduction)
receptors with extrinsic tyrosine kinase activity
receptors lacking intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity that recruit extrinsic kinases
G protein-couple receptors
steroid hormone receptors
what are the 4 types of cellular receptors that determine the mechanisms of signal transduction?
G protein-couple receptors
composed of seven transmembrane alpha-helices that are activated by GDP→GTP from ligand binding in signal transduction
G protein-coupled receptors
largest family of plasma membrane receptors in signal transduction including histamine receptor and epinephrine
steroid hormone receptors
receptors that reside in a cell cytoplasm or nucleus; once ligand-activated, will bind to specific DNA sequences in target genes or interact with other transcription factors
steroid hormone receptors
estrogen, thyroid hormone, vitamin D bind to what type of receptor?
transcription factors
growth factors induce activity of _________ which binds to DNA
type IV
type of collagen forms highly organized sheets instead of fibrils and is a component of the basement membrane
vitamin C
required for the cross-linking of collagen fibrils
synthesis of pro-alpha-chains with Gly-X-Y (usually proline or lysine)
hydroxylation of pro/lys (requires vitamin C)
glycosylation of hydroxylysine
formation of triple helical procollagen via hydrogen and disulfide bonds
exocytosis to extracellular space
endoproteinase activity to cleave to tropocollagen
cross-linkage of tropocollagen by lysyl oxidase to stable collagen
describe collagen synthesis (7)
collagen
ehlers-danlos, osteogenesis imperfecta, and alport syndrome are associated with deficiencies in ?
fibrillin
elastin consists of a central core with cross-linked network of ?
marfan syndrome
disorder associated with inherited defects in fibrillin resulting in weakness of vessels walls and skeletal system
integrins
transmembrane heterodimeric glycoprotein composed of alpha and beta subunits that bind to adhesive proteins allowing cell-cell and cell-ECM adhesion which maintains cell shape and stimulates cellular motility, proliferation, and differentiation
RGD-motif (tripeptide arginine-glycine-aspartic acid)
how do integrins bind to ECM components?
laminin
most abundant glycoprotein in the BM that forms tight networks with collagen IV; binds to integrins and other cell surface receptors
fibronectin
large disulfide linked heterodimer in tissue and plasma forms that binds integrins, collagen, heparin, and fibrin; synthesized by fibroblasts, monocytes and endothelium and provides scaffolding in healing wounds for ECM deposition, angiogenesis and re-epithelization
selectins
cell adhesion molecules that are single chain transmembrane glycoproteins and are involved in leukocyte recruitment to the site of injury
p-selectin
single chain transmembrane glycoprotein that is expressed on platelets and leukocytes
e-selectin
single chain transmembrane glycoproteins that are expressed on endothelial cells
l-selectin
single chain transmembrane glycoproteins that are expressed on leukocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, and eosinophils
cadherins
calcium-dependent adherence protein that connects the membranes of adjacent cells; regulate cell motility, proliferation, and differentiation
E-cadherin
loss of ________ is thought to enable metastasis by disrupting intercellular contacts in human carcinomas (breast and gastric)
laminin
________ mutations result in epidermolysis bullosa, or separation of basement membrane and epidermis
inflammation - clot formation to stop bleeding and contain damage, promote ECM deposition and angiogenesis
granulation tissue - fibroblasts, new leaky blood vessels, macrophages replace neutrophils; edema
scar formation - maturation of granulation into dense fibrous
remodeling of CT
describe the steps of tissue repair (4)
VEGF, FGF (fibroblast growth factor), Ang1 and 2 (angiopoietins)
what growth factors are involved in angiogenesis?
attract and entrap water which gives the ability of tissue to resist compression
what is the function of proteoglycans and GAGs?
inflammatory cells release cytokines and growth factors that stimulate proliferation of endothelial cells and fibroblasts that form granulation tissue
how is granulation tissue formed?
debridement/removal of injured tissue and debris (phagocytosis, collagenase, elastase)
antimicrobial activity (nitric acid, ROS)
chemotaxis and proliferation of fibroblasts and keratinocytes (PDGF, TGF-beta, TNF, IL-1, KGF-7)
angiogenesis (VEGF, FGF-2, PDGF)
deposition and remodeling of ECM (TGF-beta, PDGF, TNF, OPN, IL-1, collagenase, MMPs)
what are key roles of macrophages in repair (5)?
leukocytic infiltrate, edema, and vascularity decreases secondary to continuous collagen deposition
what occurs in week 2 of scar formation and wound contraction?
type III, then replaced by type I
what type of collagen is laid down during scar formation?
spindle-shaped fibroblasts, dense collagen, fragments of elastic tissue, and other ECM components
what are the components of a scar?
matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)
proteinases produced by fibroblasts, macrophages, neutrophils, synovial cells, and some epithelial cells that degrade the ECM during CT remodeling
TIMPs
inhibit MMPs to prevent uncontrolled degrading of ECM during tissue remodeling?
primary intention
clean, uninfected cutaneous wound with adjacent borders that has minimal tissue damage and allows for epithelial regeneration and minimal scarring
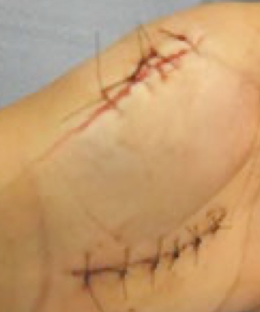
secondary intention
large wound with inflammation/infection/ischemia and distant borders that results in extensive scarring and wound contraction (repair)
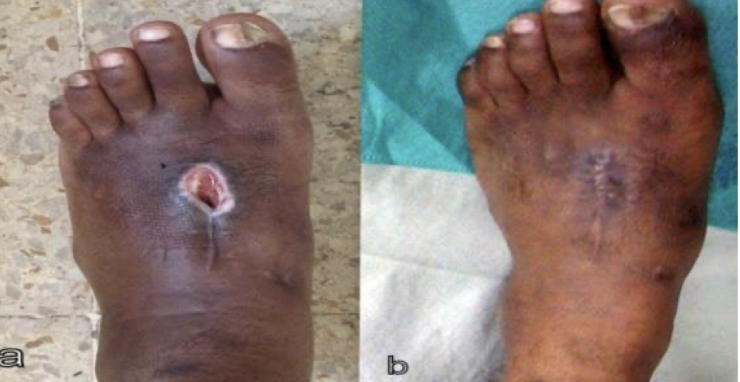
dehiscence
rupture of wound, typically after abdominal surgery due to increased pressure
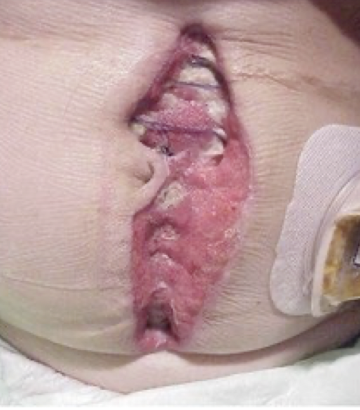
proud flesh
excessive granulation tissue protruding above the level of the surrounding skin that blocks re-epithelization
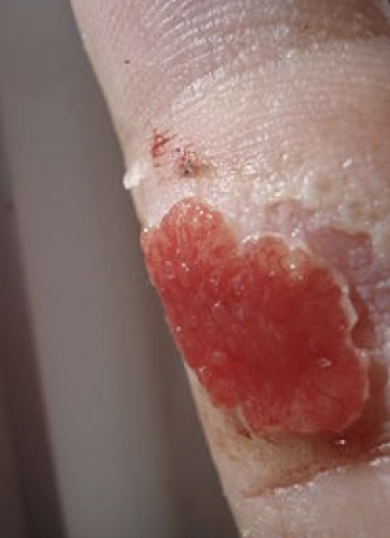
contracture
exaggerated contraction of wound that can compromise joint movement; commonly seen after serious burns
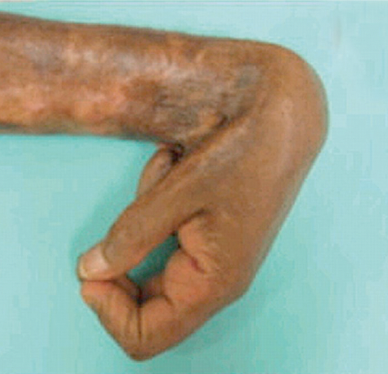
keloid
excessive scar tissue due to insufficient remodeling and collagen degradation with increased deposition of disorganized type I and III collagen
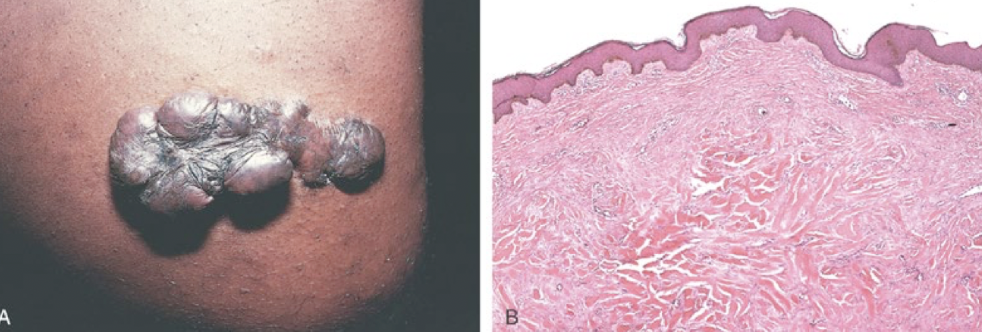
fibrosis
excessive deposition of collagen and ECM components (excessive scarring) following a prolonged or chronic injury
elastic fibers
