Cortex and Blood Supply
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Localisation of function of the brain
Idea that different functions are localised to a specific lobe in the cortex of the brain
Frontal lobe
Higher cognitive functions - decision making, consciousness, problem solving, emotions, behaviour, personality, intelligence
Broca’s area - speech production (only present in left hemisphere)
Parietal lobe
Integrating body’s sensory information, body perception, integrate somatosensory information, coordination of senses in relation to the environment
Temporal lobe
Parts of memory, hearing, emotion, some aspects of language, hearing, auditory cortex
Wernicke’s area - language processing/understanding (only in left hemisphere)
Occipital lobe
Visual processing, object and face recognition. assessing depth and distance, mapping visual world
Sensory homunculus
Description of how each body part is mapped to a specific area of the cerebral cortex in the primary somatosensory area (post central gyrus is parietal lobe)

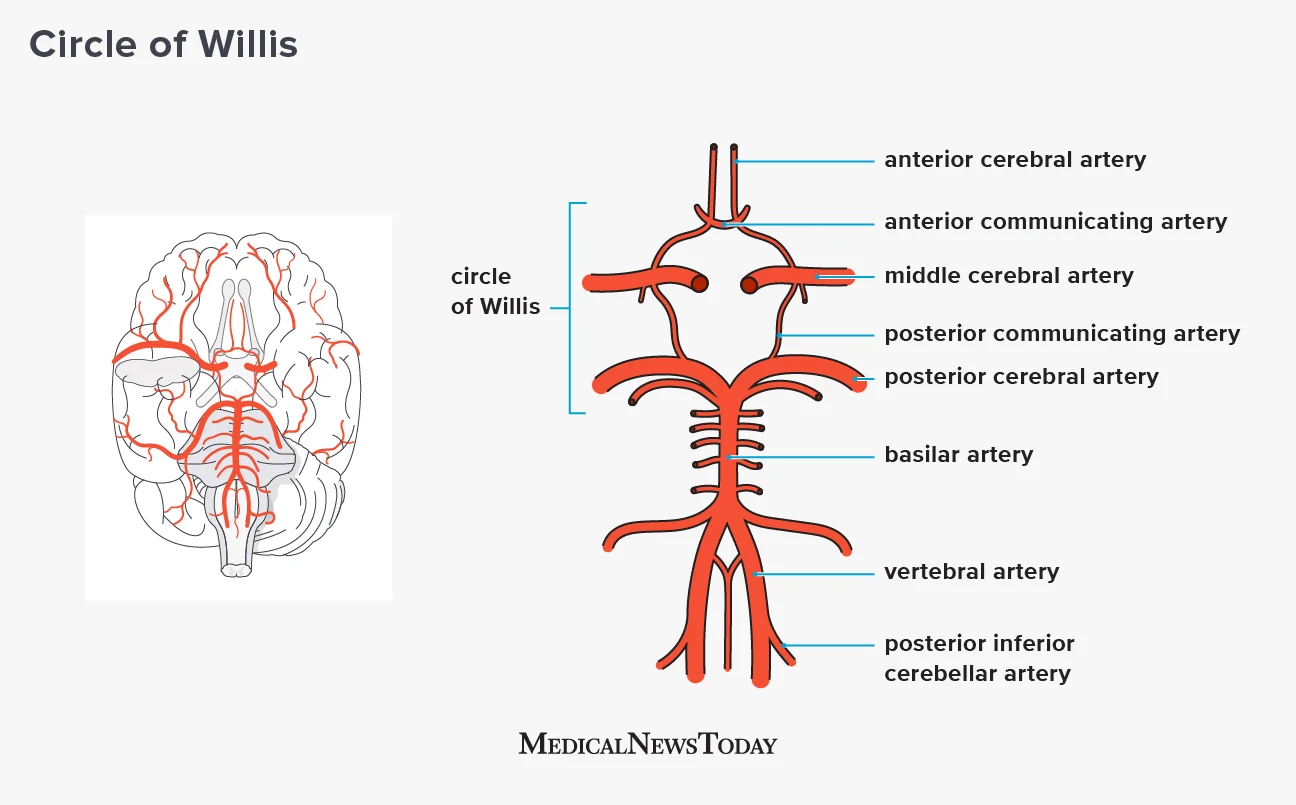
Blood supply of the brain
Blood enters cranial cavity through two pairs of arteries
Internal carotid arteries anteriorly and the vertebral arteries posteriorly
Vertebral come to form the Basilar artery
These anastomose at the base of the brain as the Circle of Willis
Internal carotid arteries join into the middle cerebral artery
Posterior communicating artery connects anterior and posterior circulation
Left and right circulation are connected by the anterior communicating artery
Circle of Willis
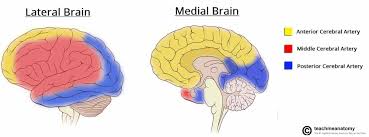
Blood supply of cerebral cortex
Yellow by anterior cerebral
Red by middle cerebral
Blue by posterior cerebral
How impaired blood supply affects function
Reduced O2 to area means nerve tissue will die
Brain has high metabolic rate so requires high O2
Stroke
Blockage of blood supply to the brain
When brain is starved of oxygen
Brisk reflex
Reduced descending inhibition of reflex
Reduced sensation
Sensory pathways damaged
Weakness
Damage to motor pathways
Speech deficits
Damage to Broca’s area
Altered muscle tone
Damage to reticulospinal tract
Anterior cerebral artery
Supply anteromedial portion of cerebrum
Medial and superior parts of the frontal lobe and anterior parietal lobe
Middle cerebral artery
Supply majority of lateral part of brain
Lateral areas of the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes, Wernicke’s area and Broca’s area
Posterior cerebral artery
Supply medial and lateral parts of the posterior cerebrum
Occipital lobe, medial and inferior parts of temporal lobe
Midbrain, thalamus and choroid plexus