Sensation Fundamentals
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Sensation
sensory & nervous system reiche and represent stimulus energies from our enviornment
Perception
process of organizing & interpreting sensory info to make sense of the world around us; involves brains interpretation of sensory inputs
Transduction
conversion of sensory stimuli into neural impulses that can be understood by the brain
Absolute Threshold
minimum amount of stimulation required ti detect a stimuli 50% of the time
Subliminal
below ones absolute threshold for conscious awareness
Just-Noticeable Difference (JND)
the smallest change in stimuli that can be detected by an individual; the minimal difference needed for a person to perceive that change
Weber’s Law
the perceived difference in a stimulus must be proportional to the original intensity; the bigger something is the more change needed
Sensory Adaptation
the process by which sensory receptors become less responsive to constant stimuli over time
Synesthesia
stimulation of one sensory pathway leads to automatic, involuntary experiences in another sensory pathway
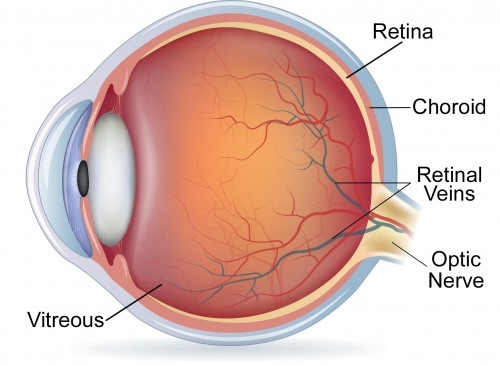
Retina
the light sensitive inner surface of the eye, contains photoreceptor cells that convert light into neural signals
Rods
photoreceptor cells in retina; responsible for vision in low light
provides black and white vision and his highly sensitive to light allowing vision in dim environments
Cones
photoreceptor cells in the retina; responsible for color and detail in bright light
enables us to perceive colors and fine visual details
Fovea
central area of retina responsible for sharp central vision
high concentration of cone cells (no rods)
Blind Spot
area on retina where optic nerve exits the eye; lacks photo receptor cells
spot where vision is absent
Ganglion Cells
neurons in retina that receives visual info from bipolar cells & transmits to the brain by the optic nerve
role in processing visual signals & relays them to the brain for interpretation
Lens
transparent structure in the eye that focuses
adjusts its shape to help the eye let in light
Accommodation
the process by the lens of the eye changes its shape to focus on objects at different distances
allows for clear vision of nearby & distant objects
Nearsightedness
close objects appear clear, distant objects appear blurry
Farsightedness
distant objects are seen more clearly than close ones
Trichromatic Theory