UNIT 2 EXAM REVIEW
1/335
Earn XP
Description and Tags
REVIEW THE ENTIRE MUSCULAR SYSTEM (HEAD/NECK, TRUNK, ARMS AND LEGS COMBINED)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
336 Terms
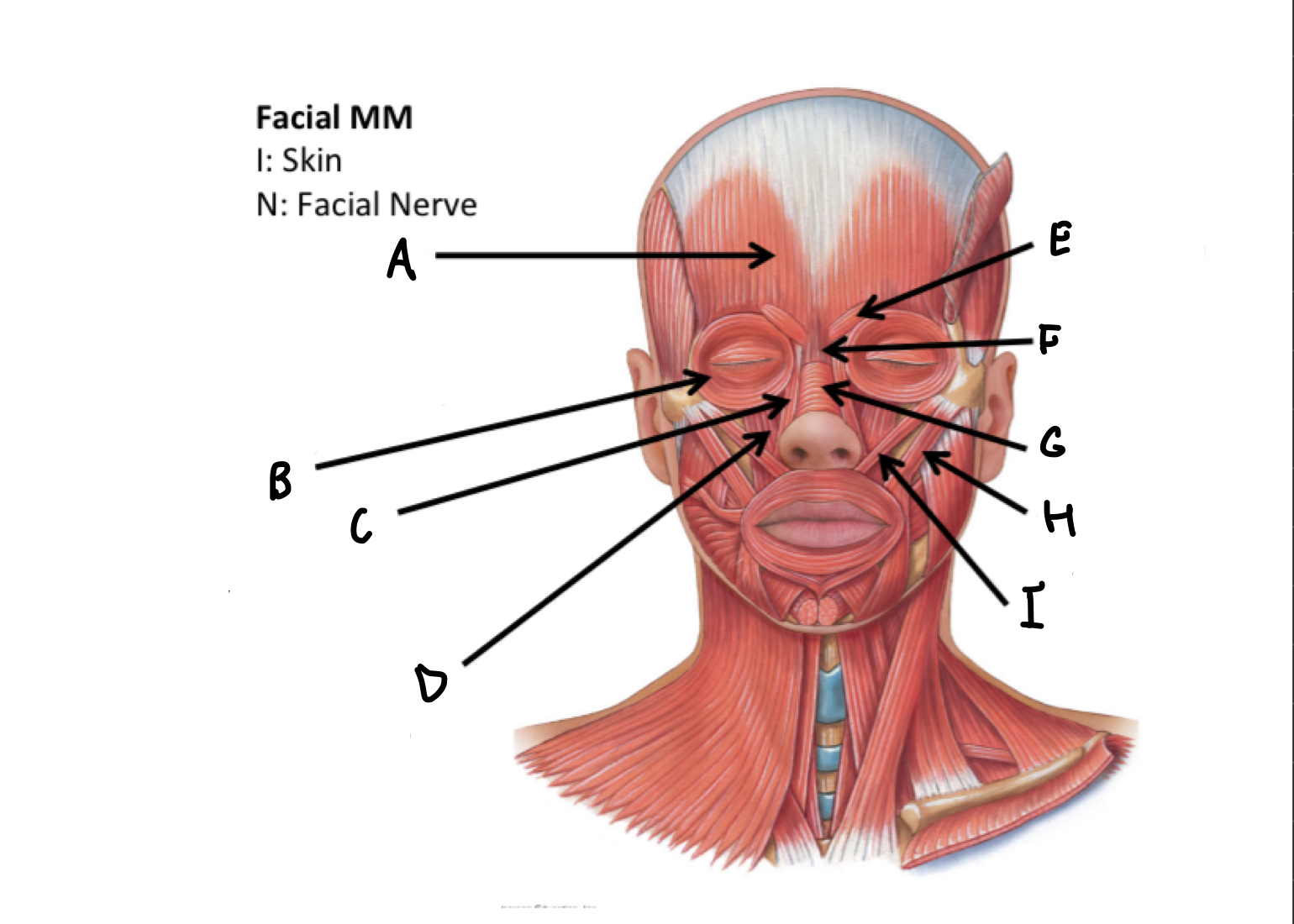
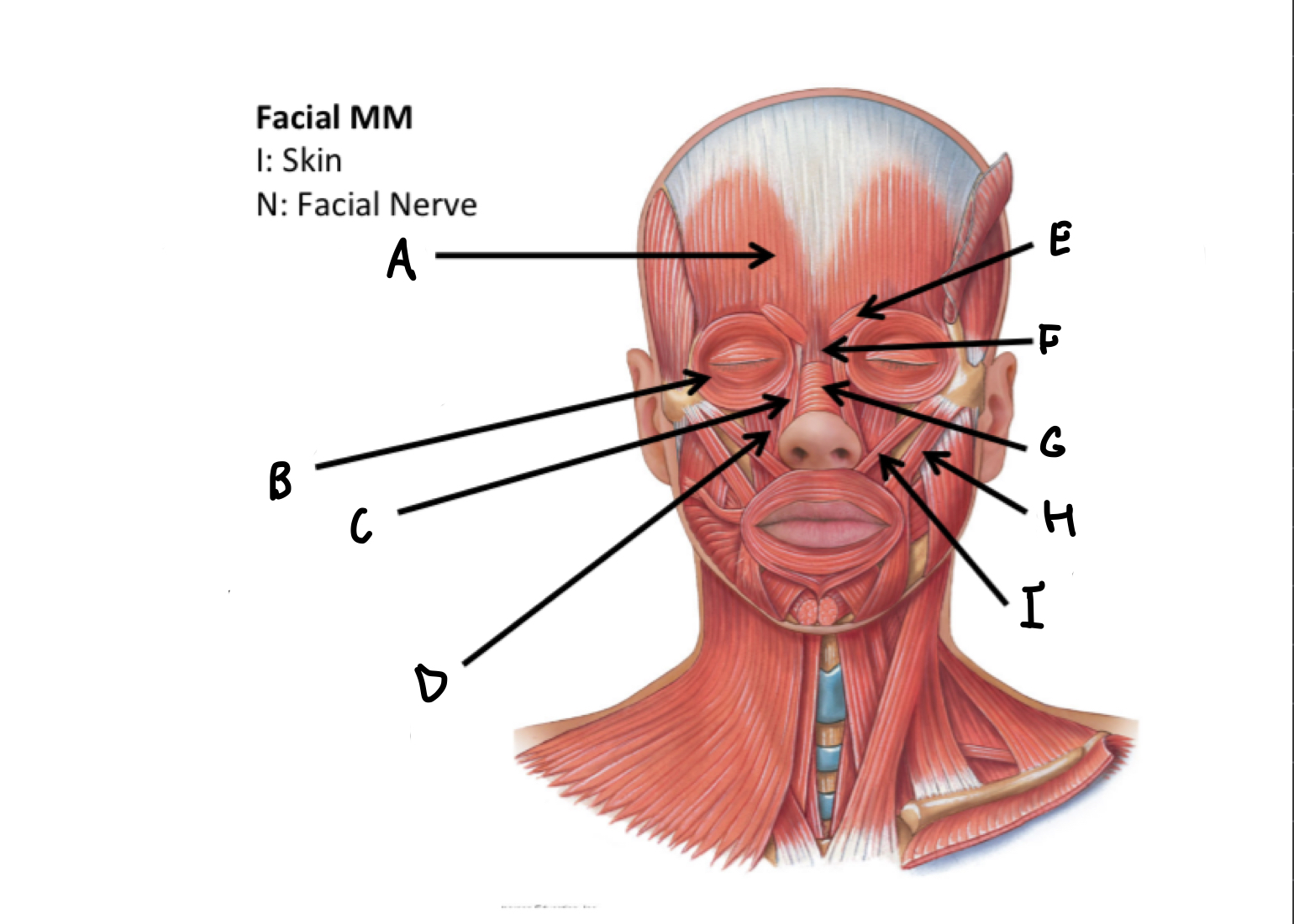
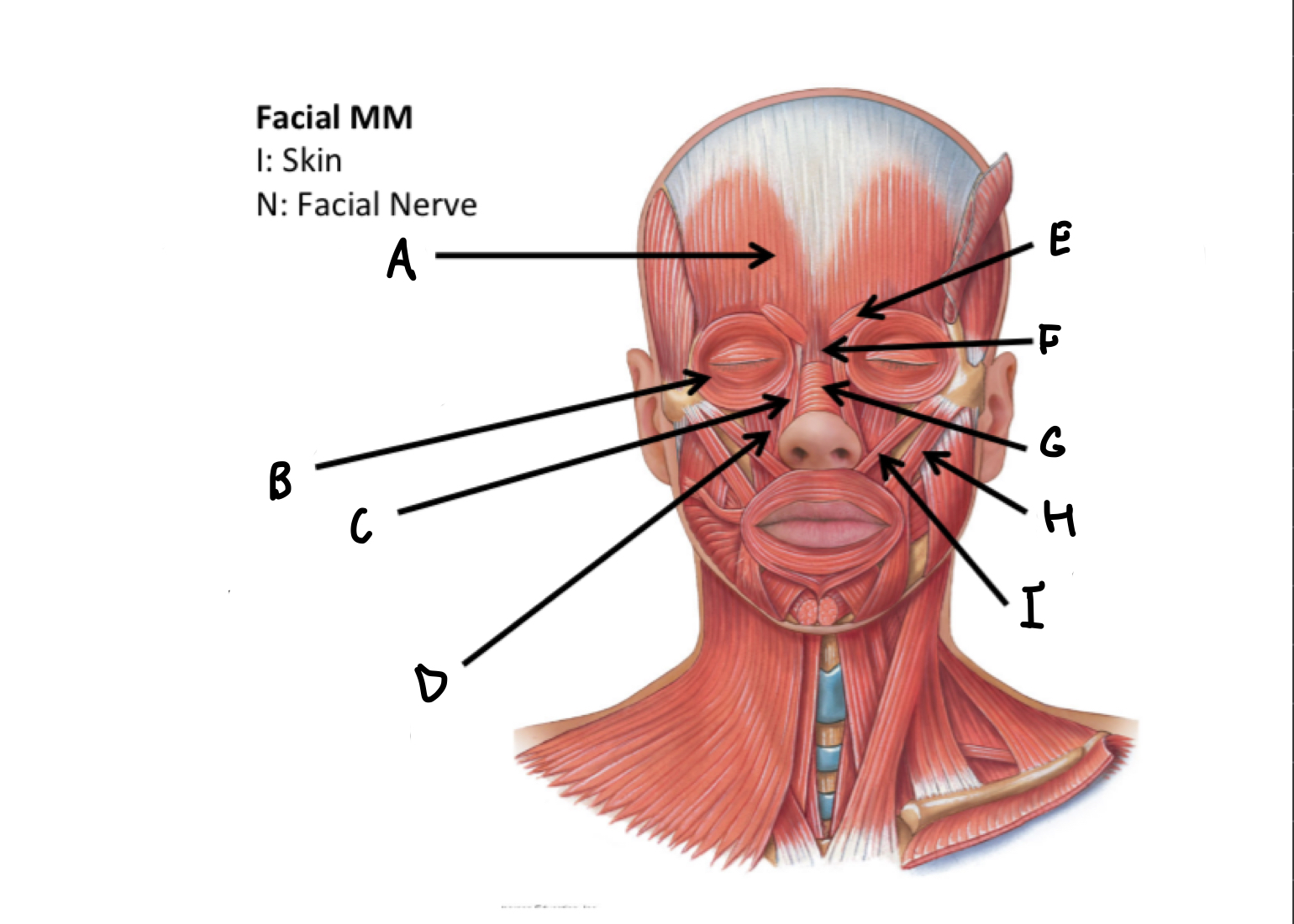
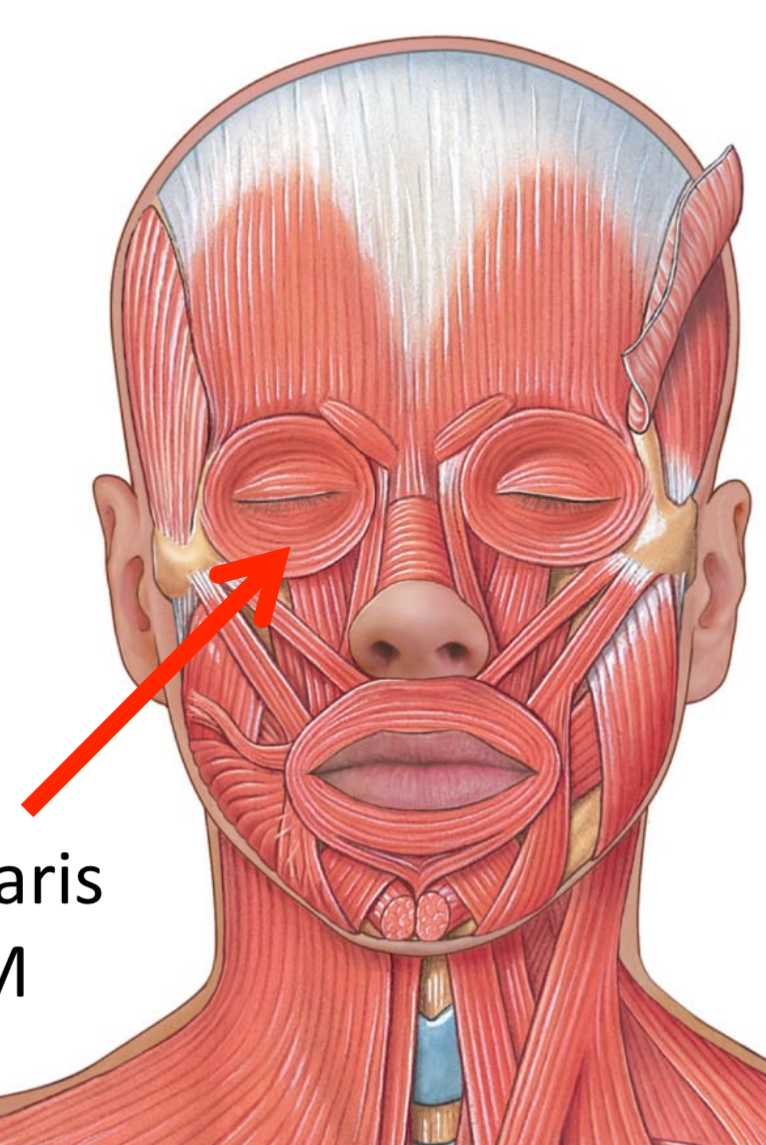
What muscles are these?
Facial muscles
What muscle contains the Epicranial aponeurosis, Frontal belly, and the Occipital belly?
Occipitofrontalis M
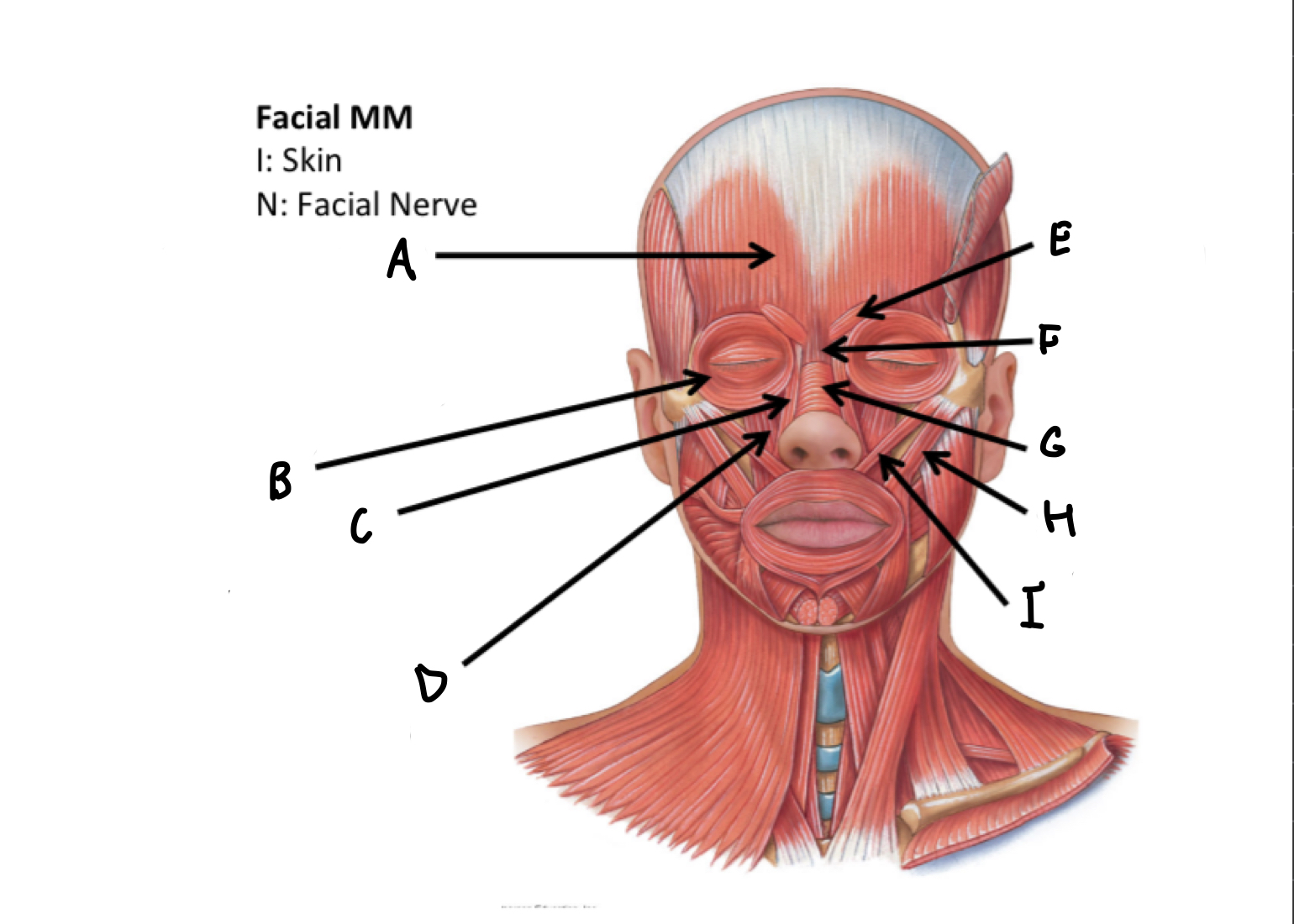
A
frontal belly of Occipitofrontalis M
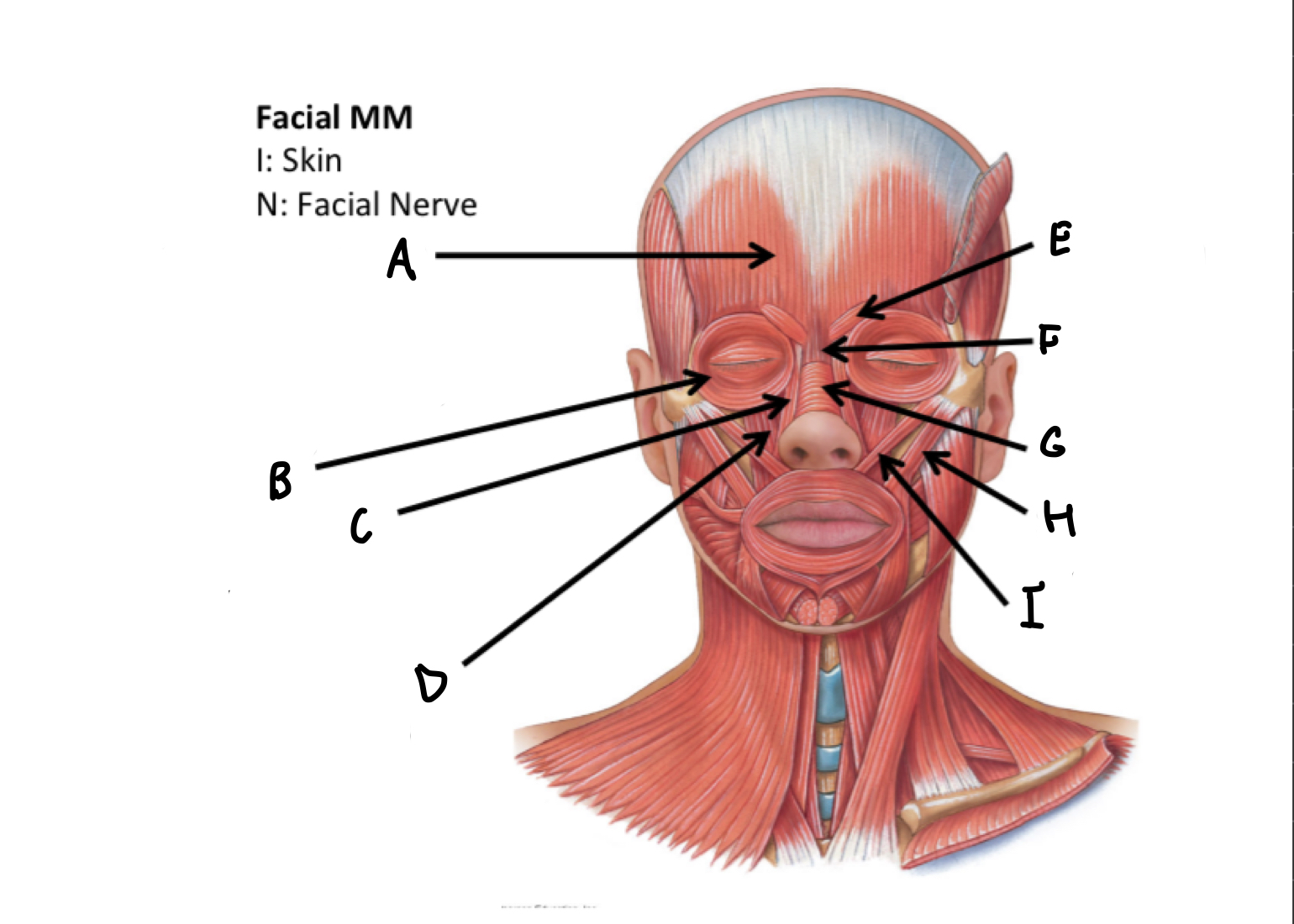
B
Orbicularis occuli M
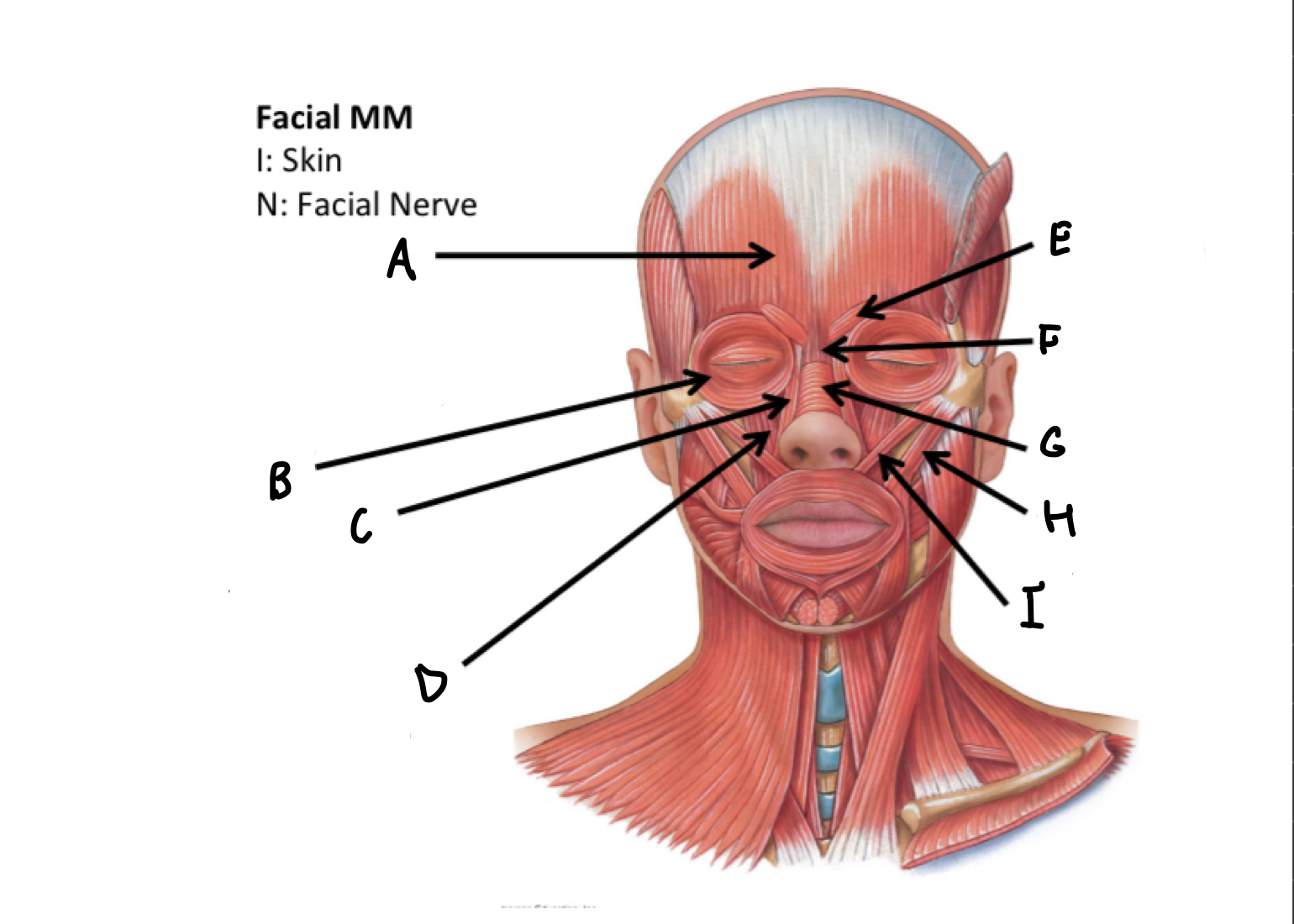
C
Levator labii alaeque nasi superioris M
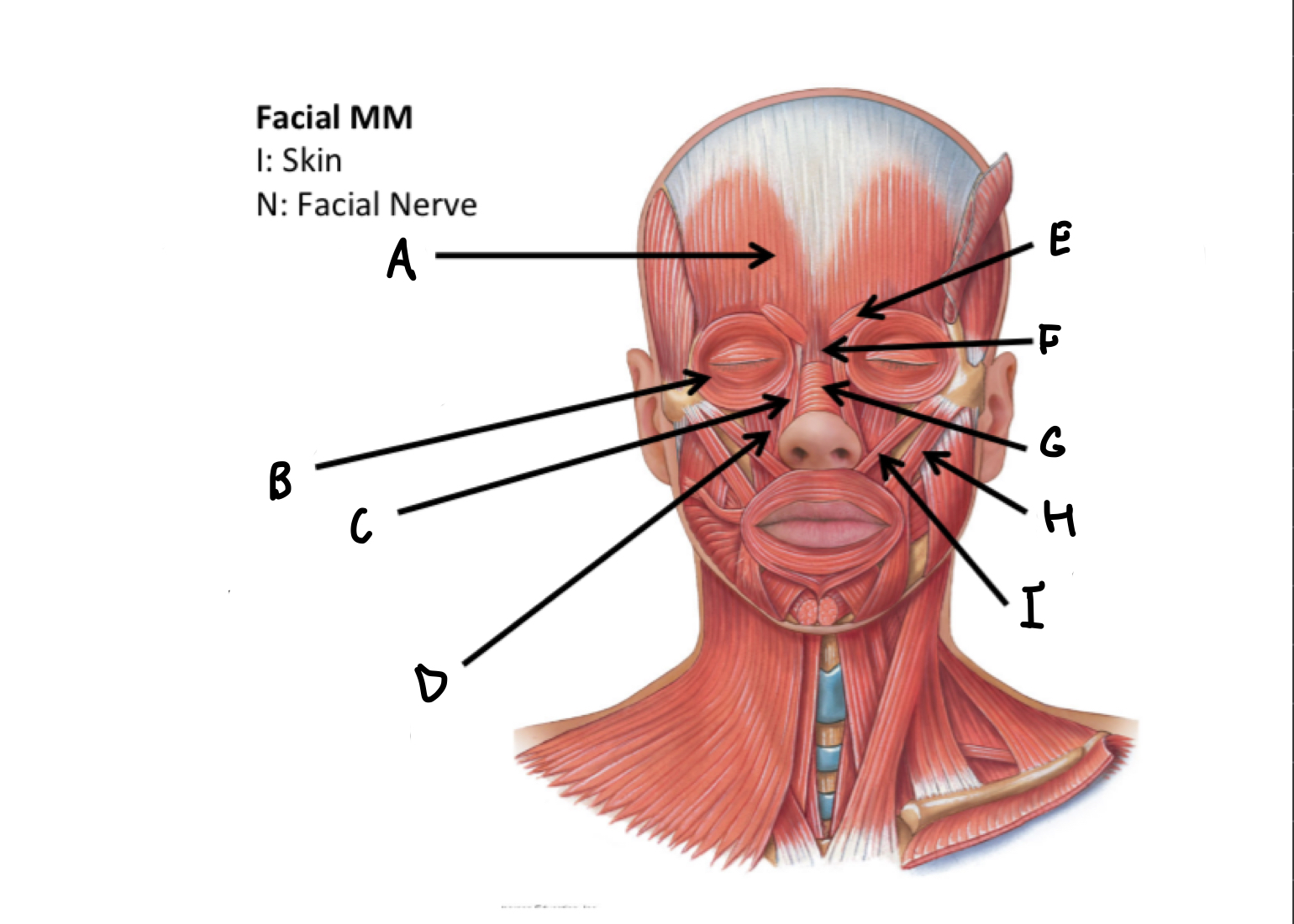
D
Levator labii superioris M
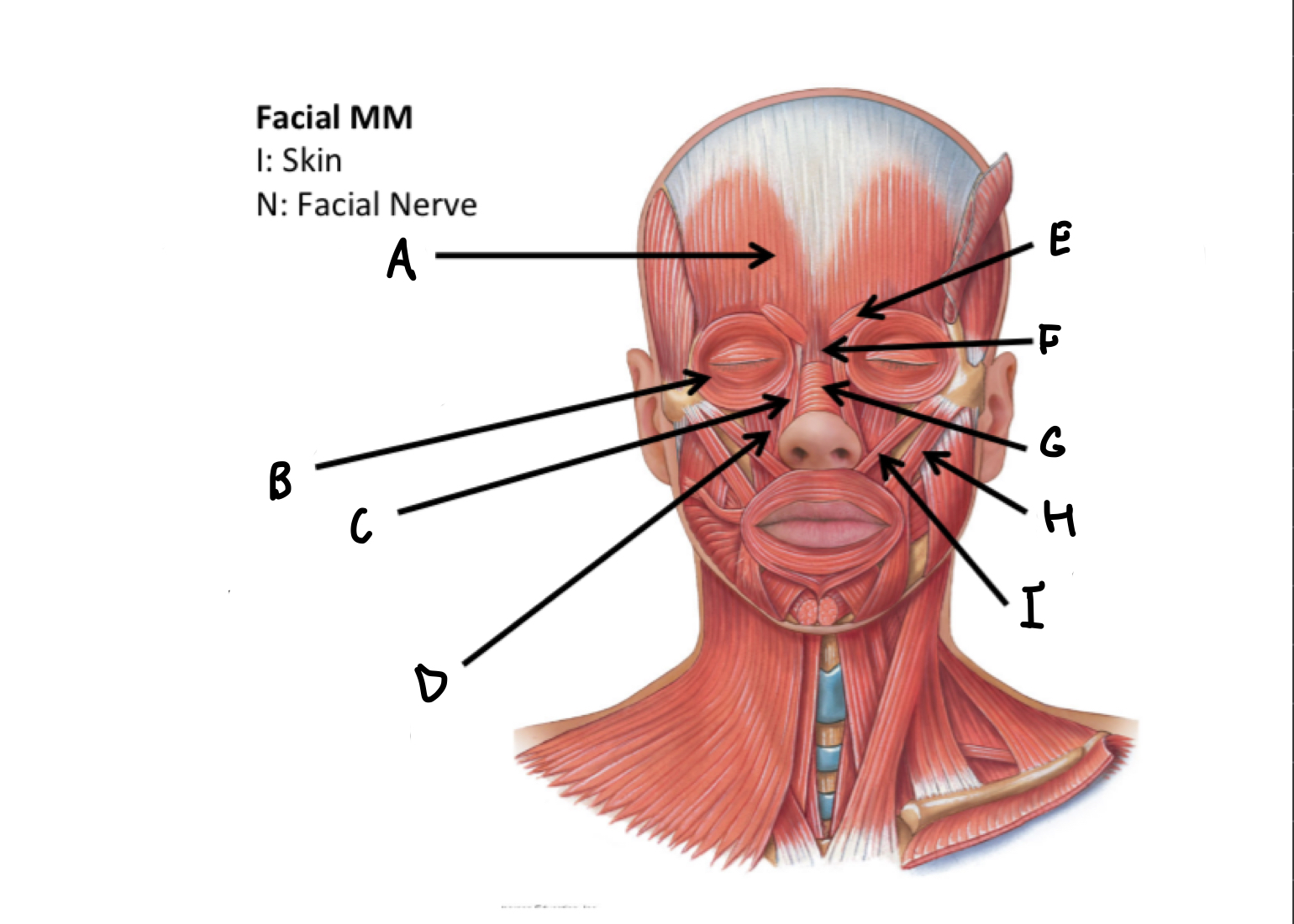
E
Corrugatorsupercilii M
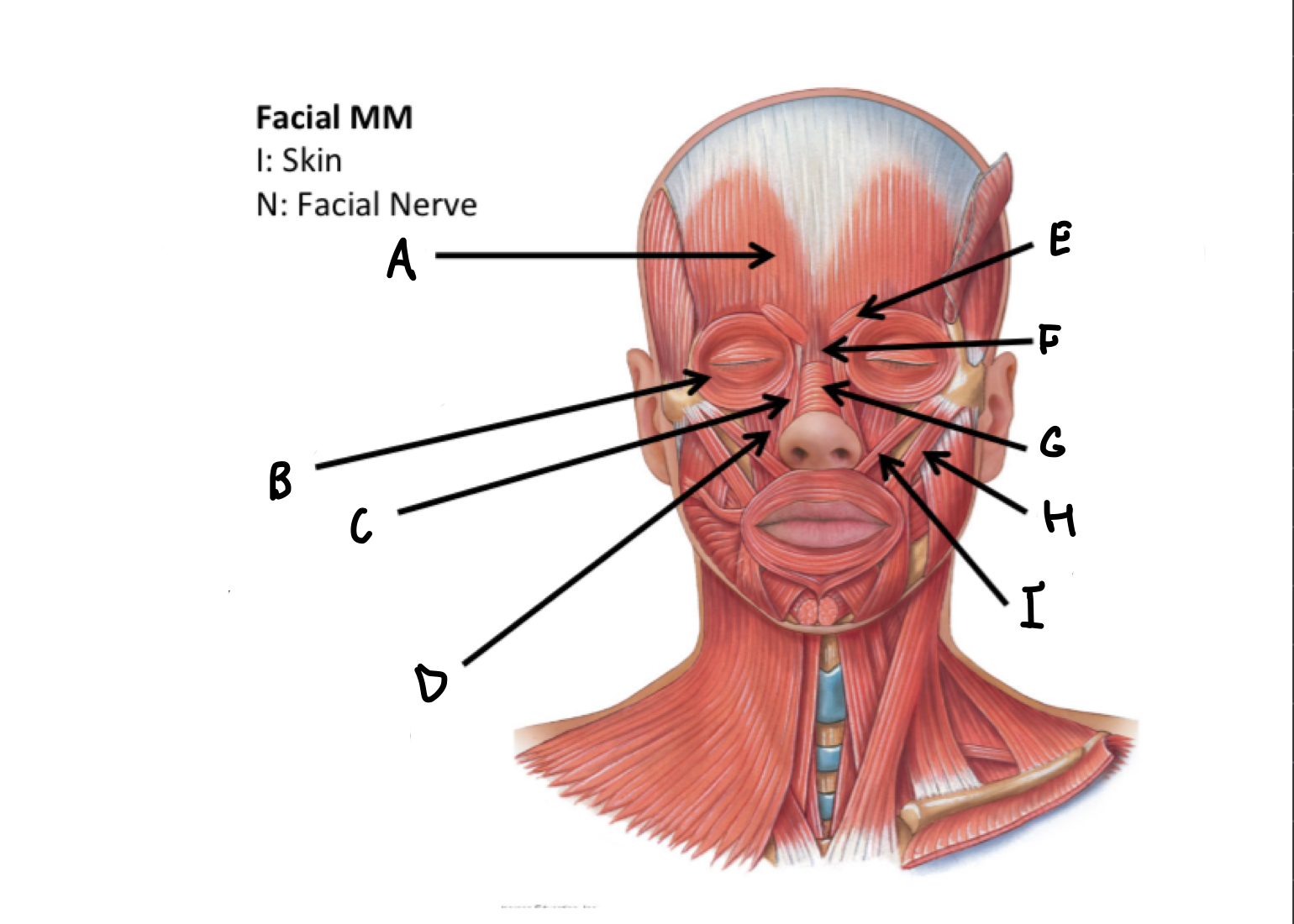
F
Procerus M
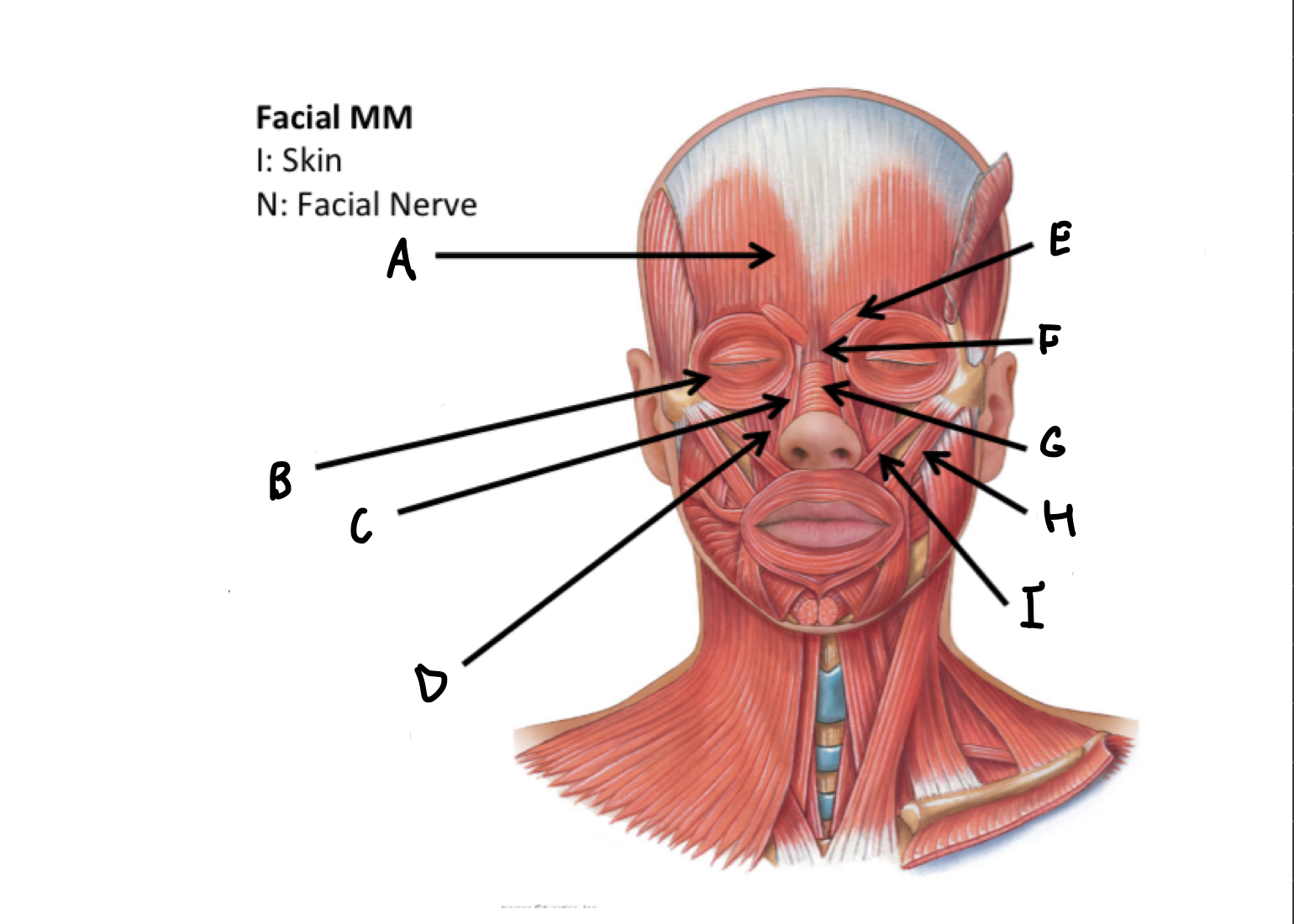
G
Nasalis M
H
Zygomaticus major M
I
Zygomaticus minor M
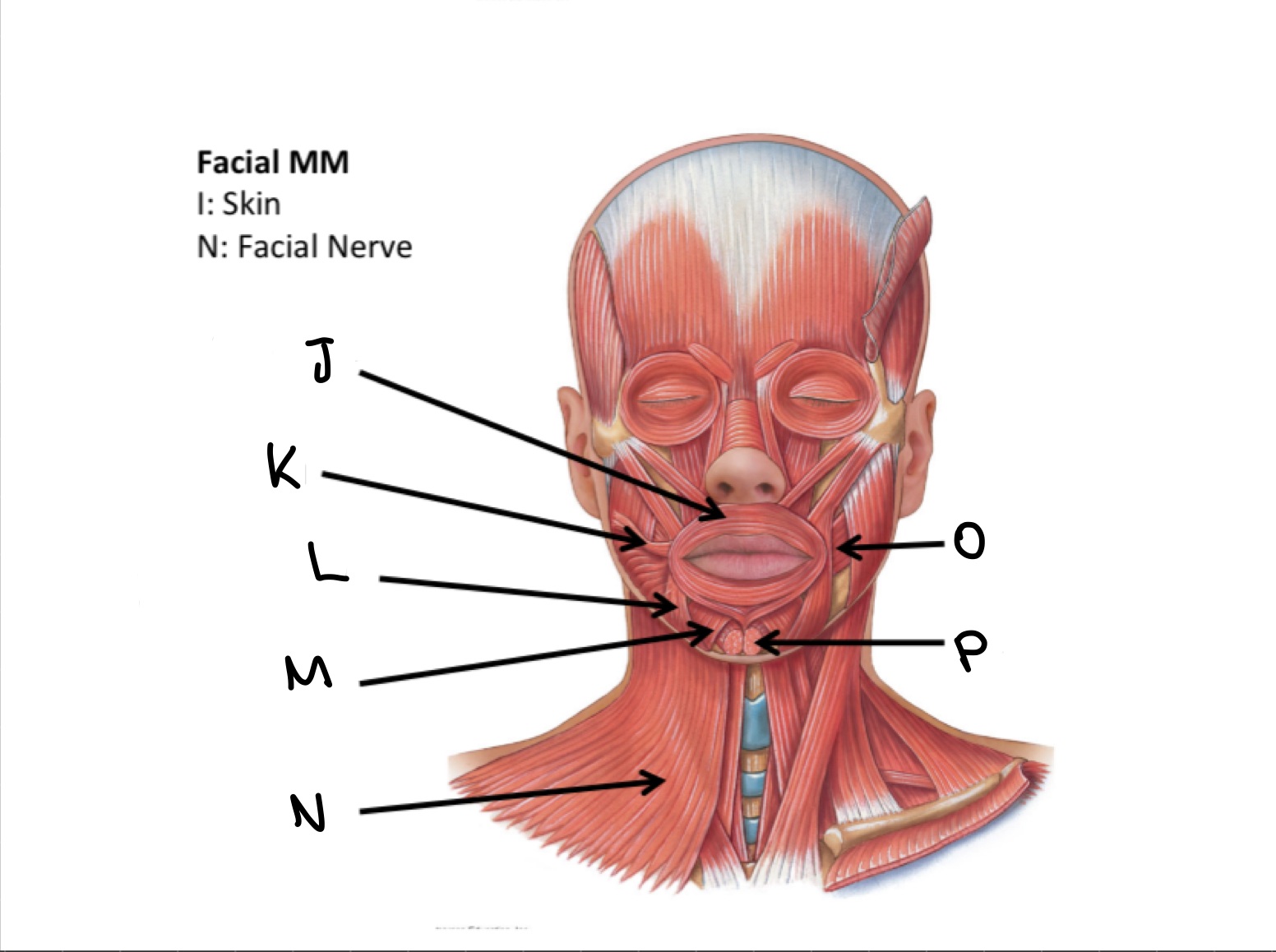
J
Orbicularis oris M
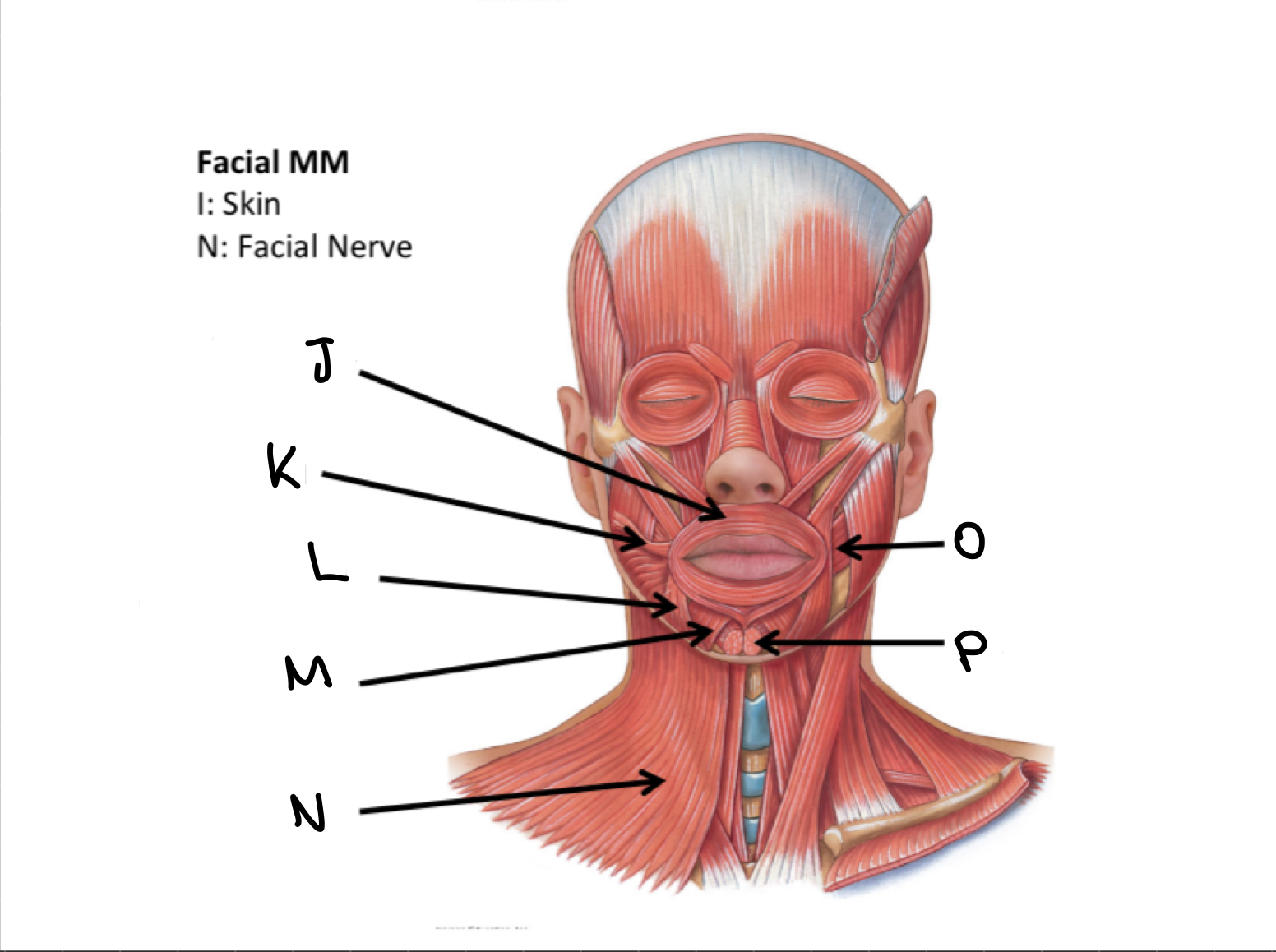
K
Risorius M
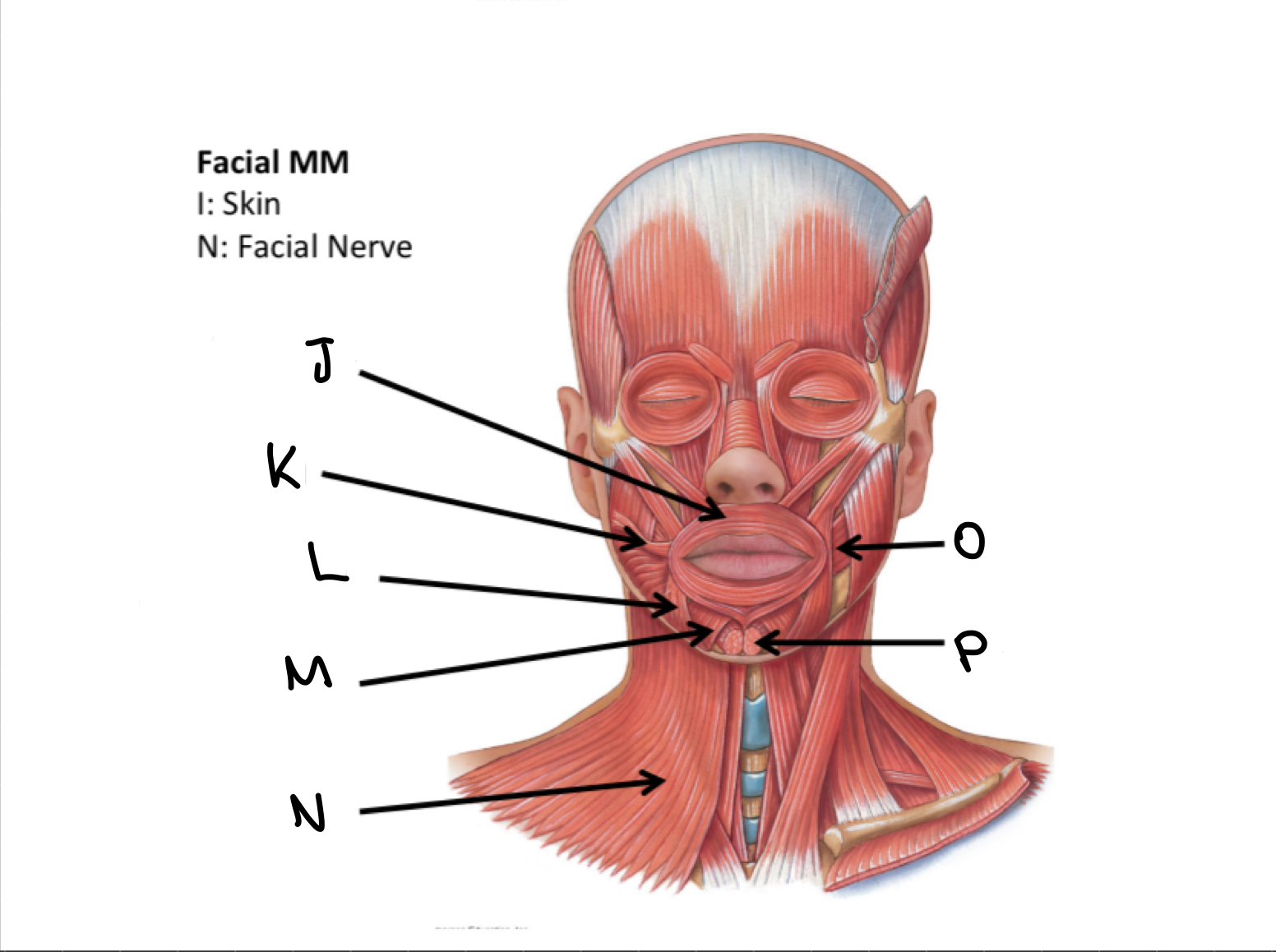
L
Depressor anguli oris M
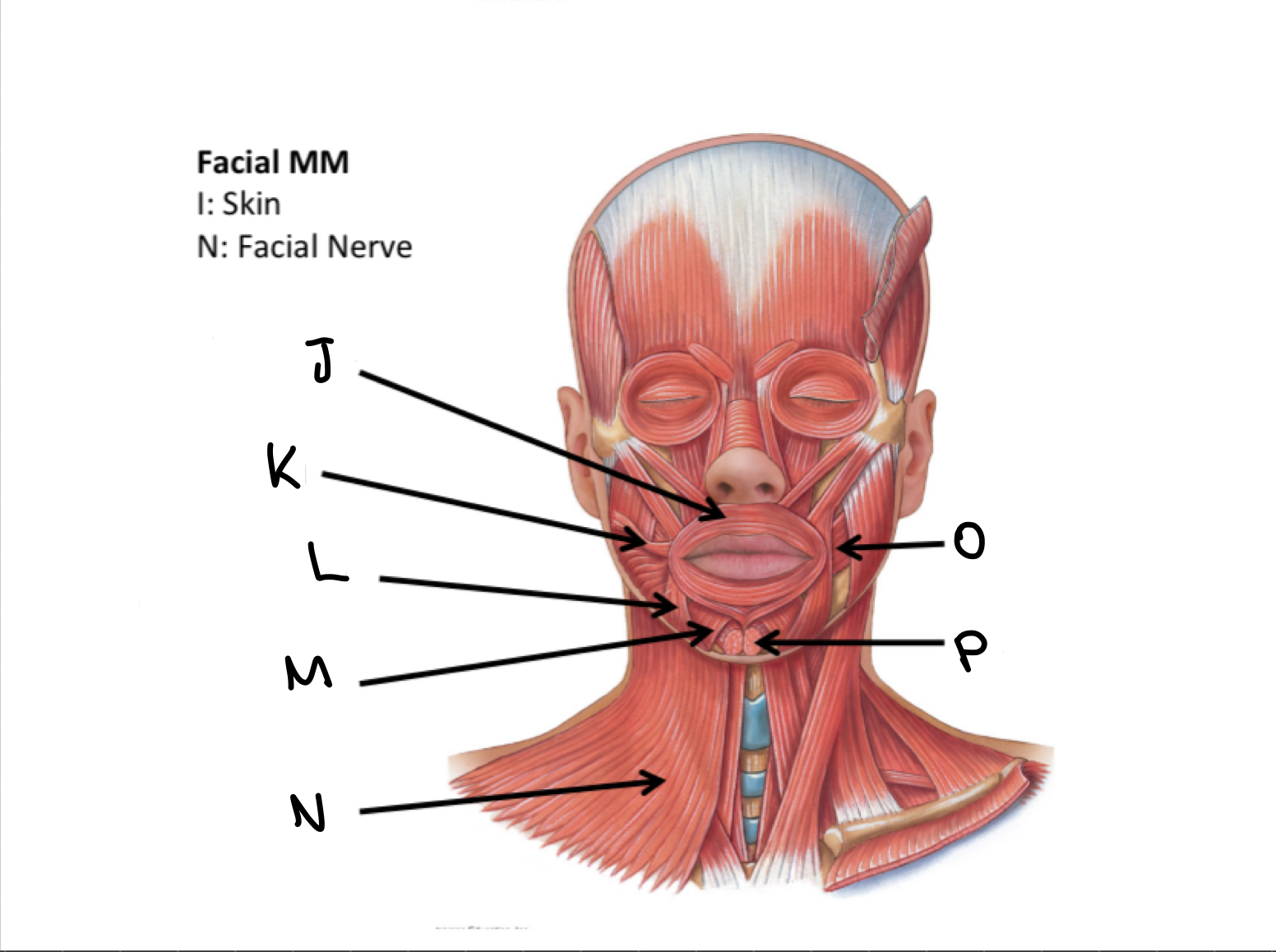
M
Depressor labii inferioris M
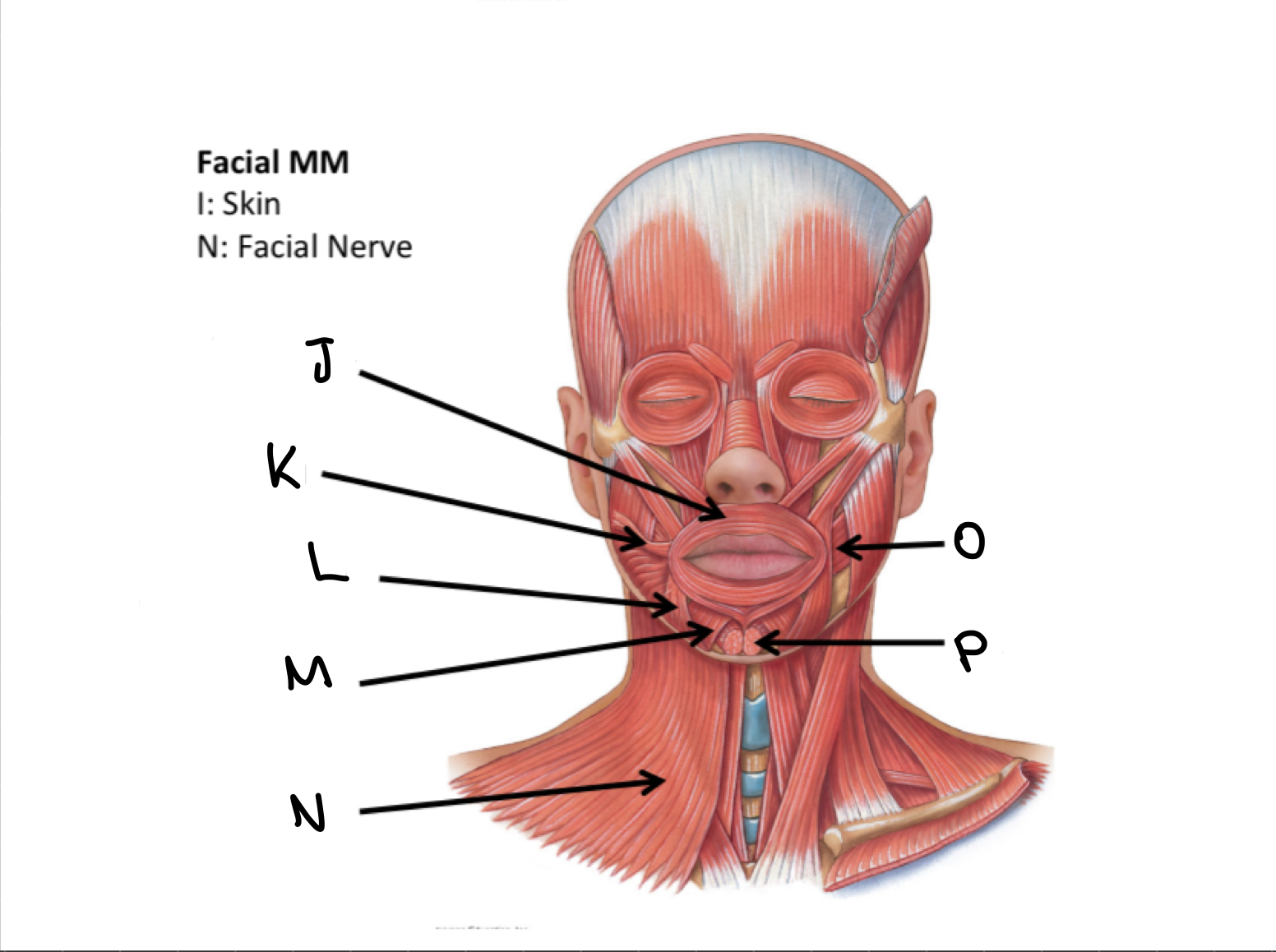
N
Platysma M
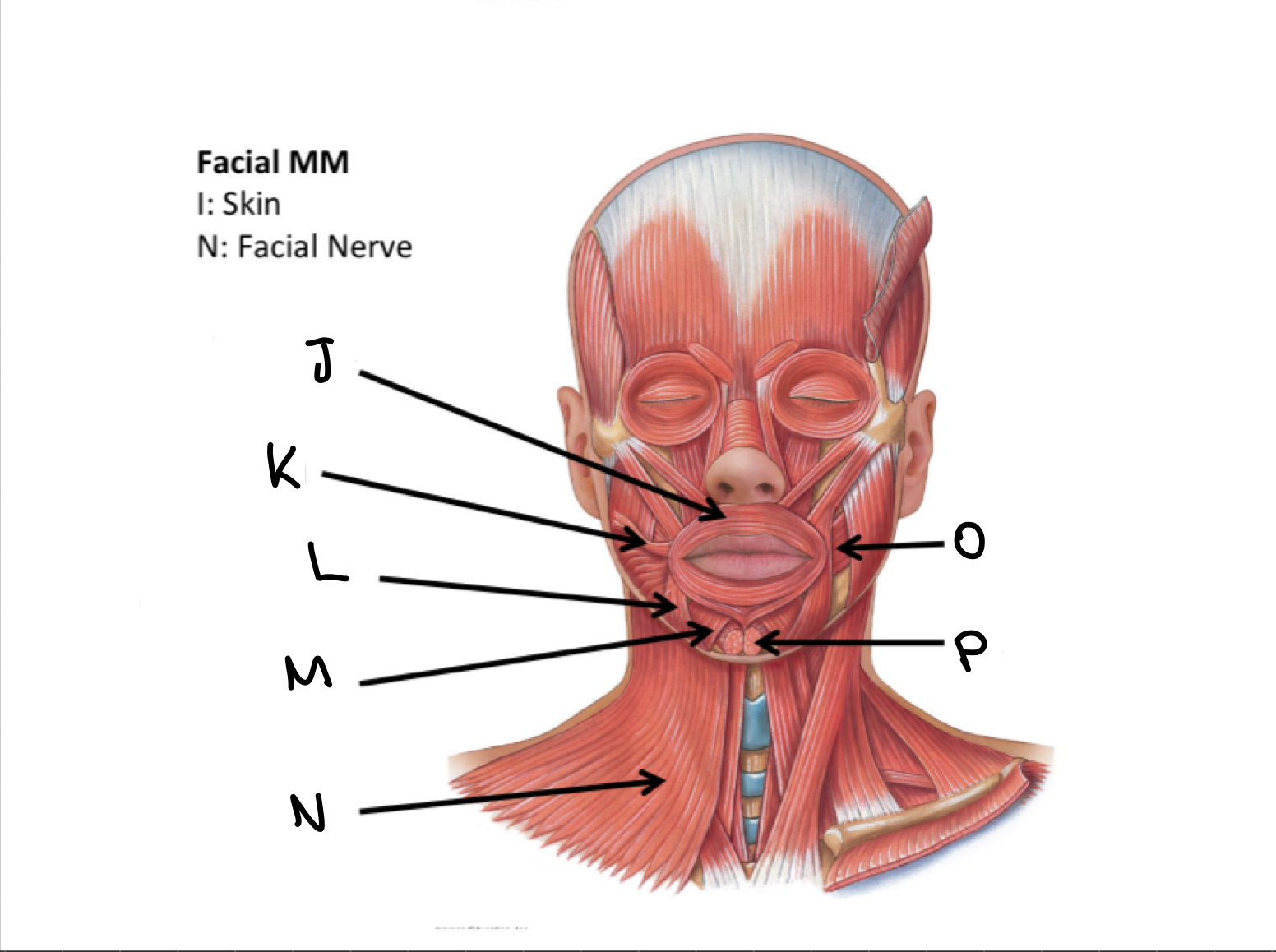
O
Buccinator M
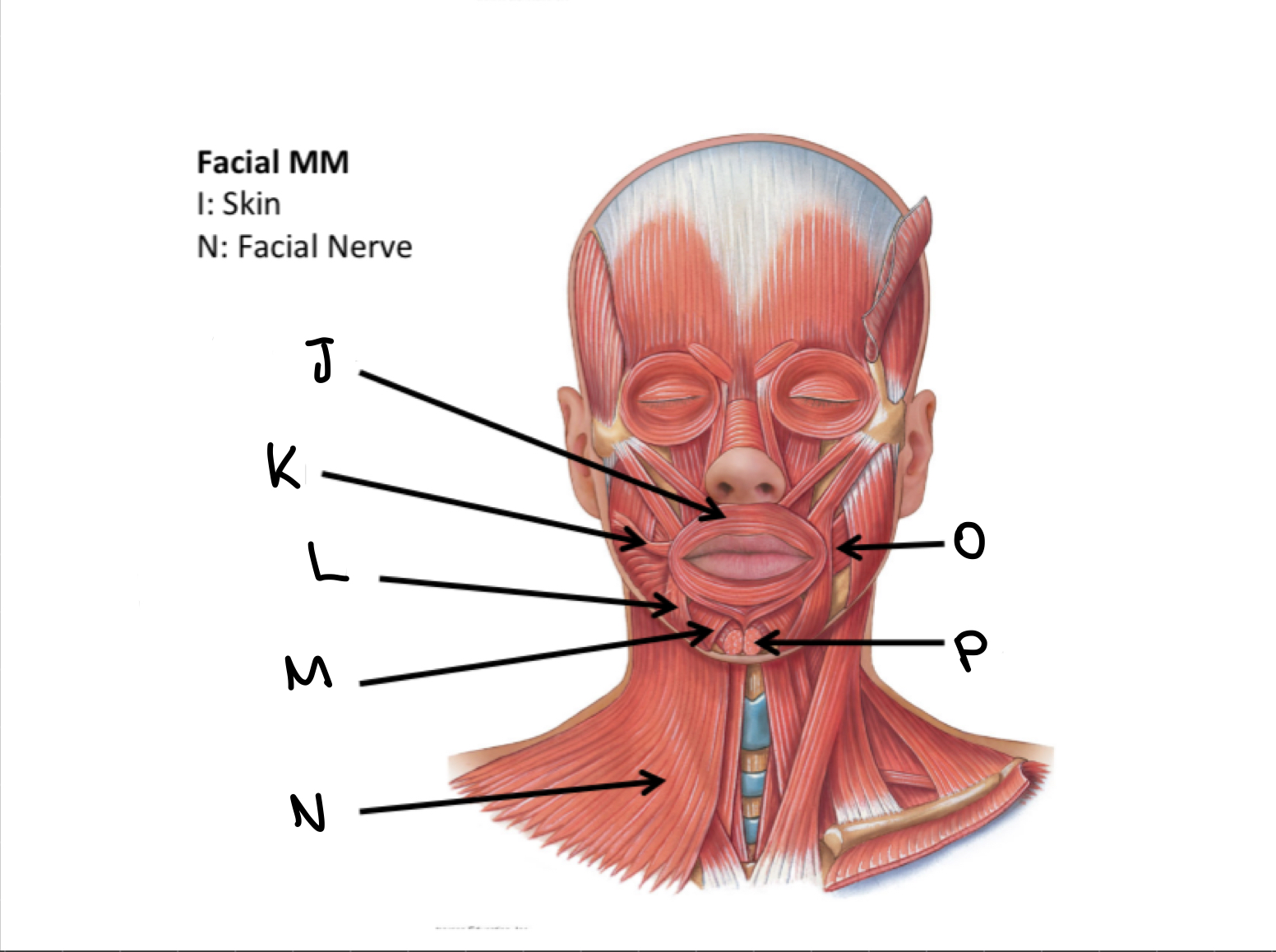
P
Mentalis M
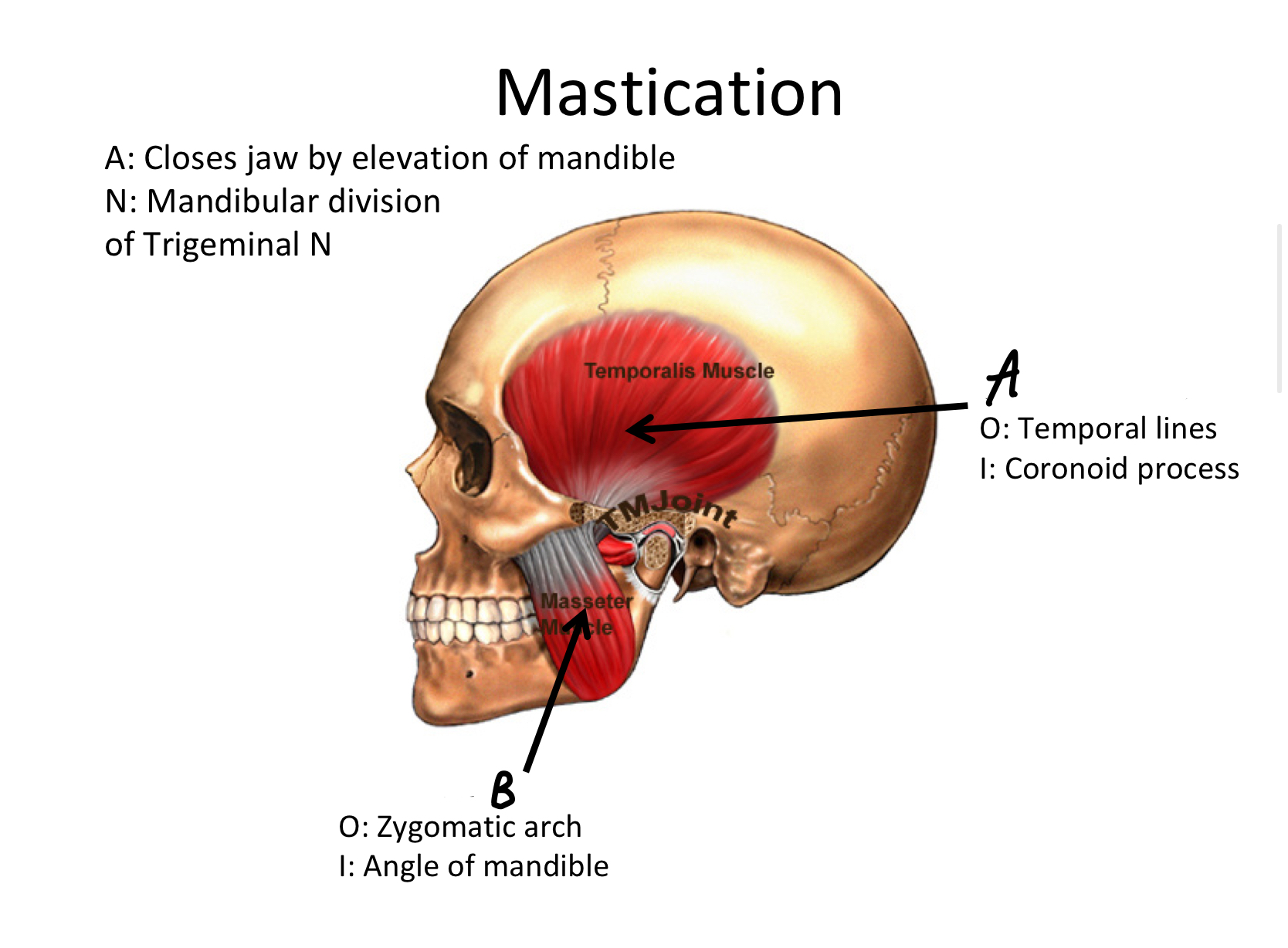
A
Temporalis M
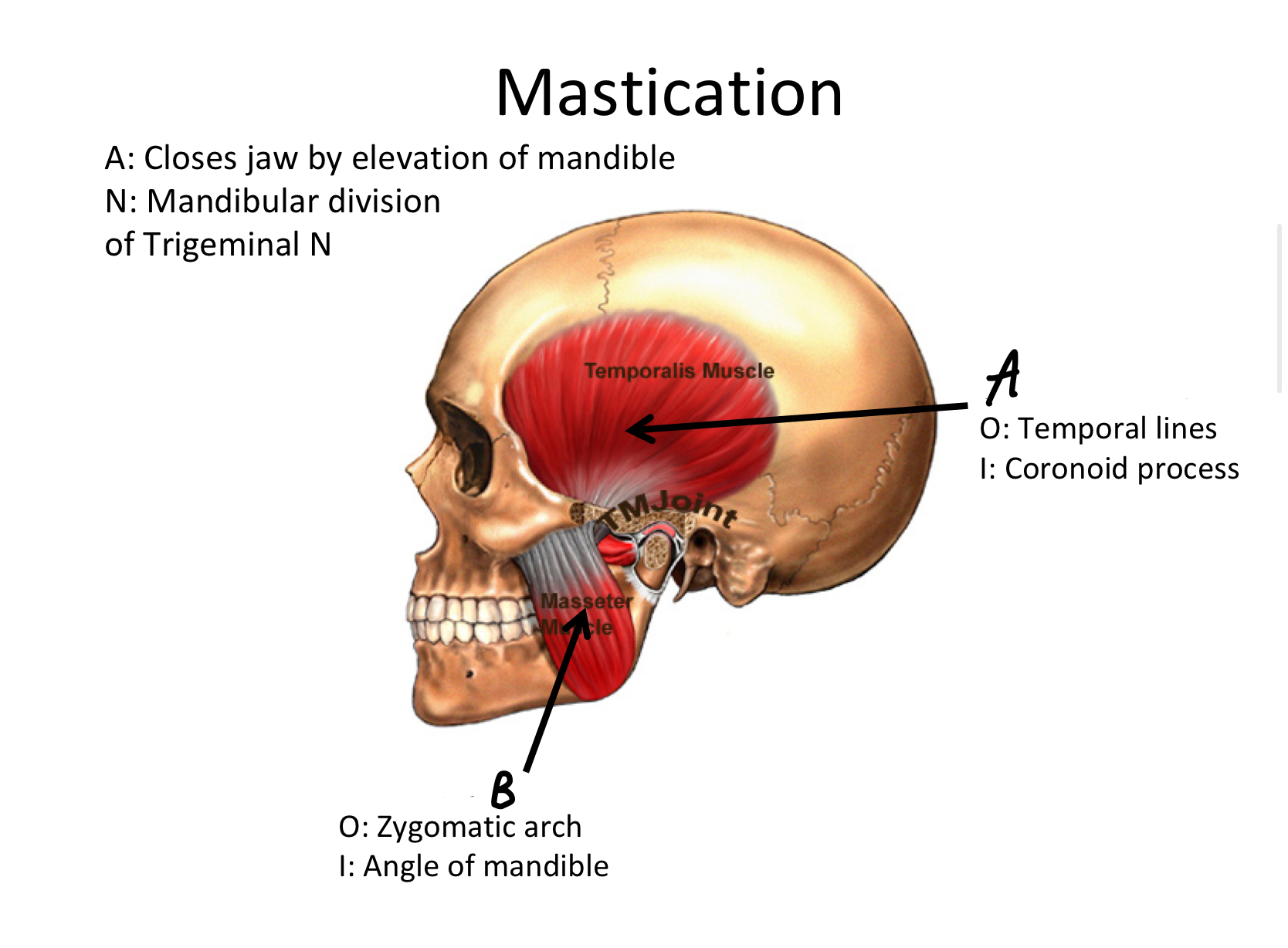
B
Masseter M
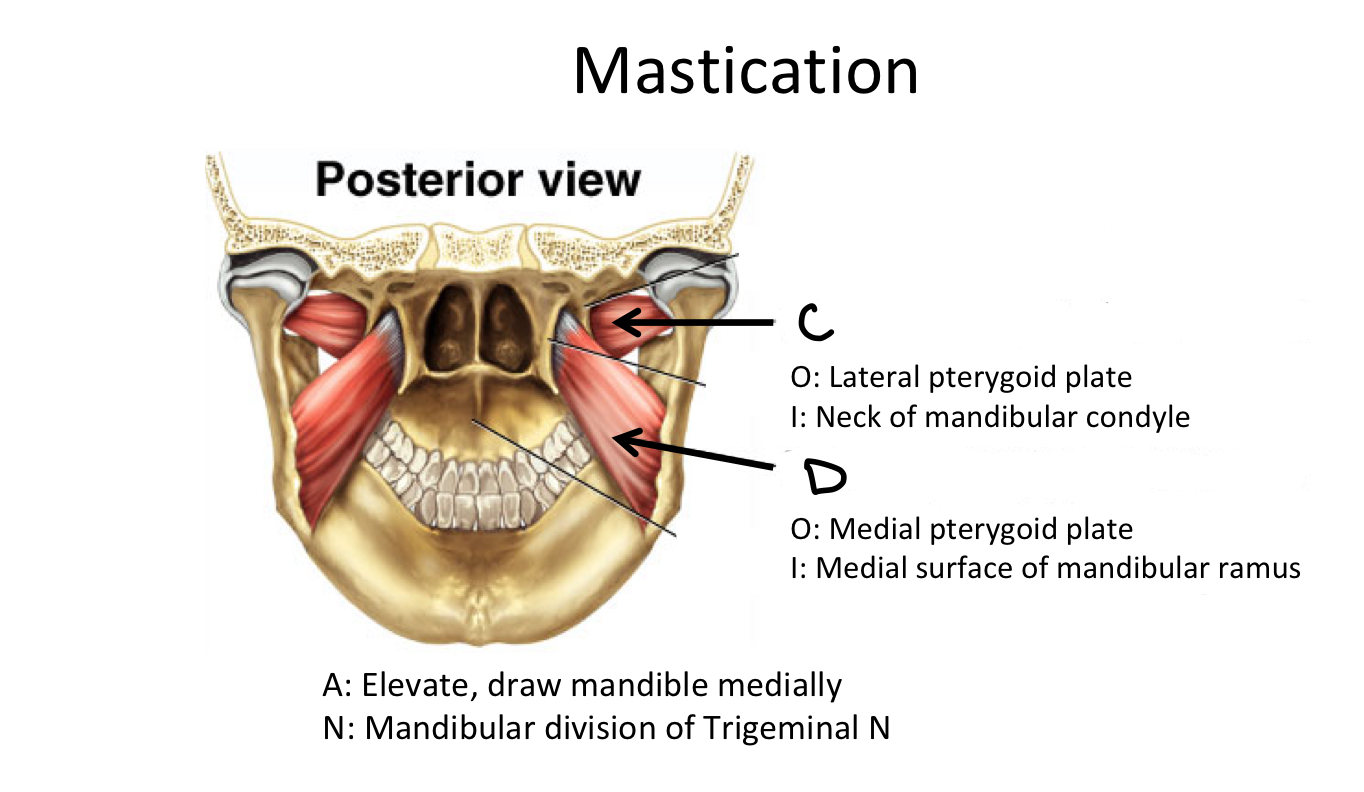
C
Lateral Pterygoid Plate M
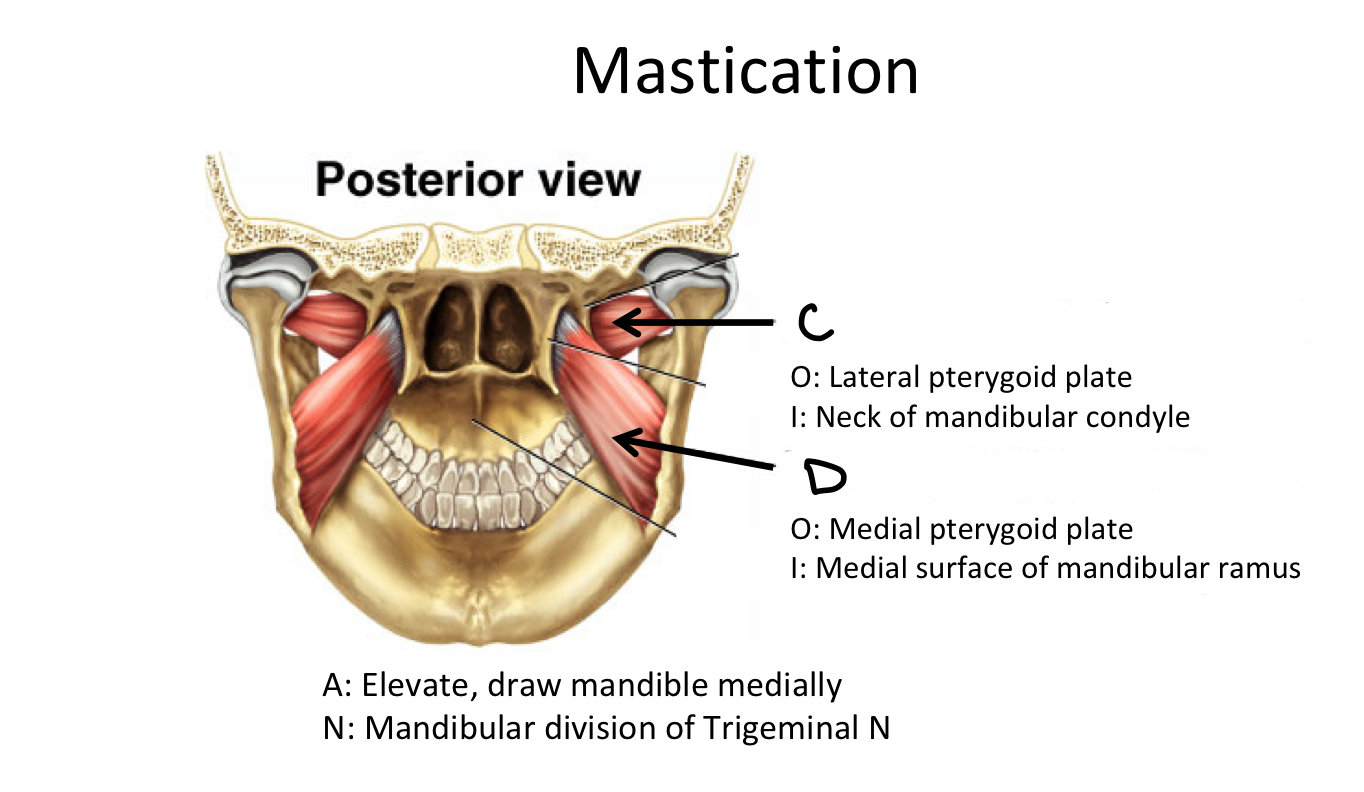
D
Medial Pterygoid Plate M
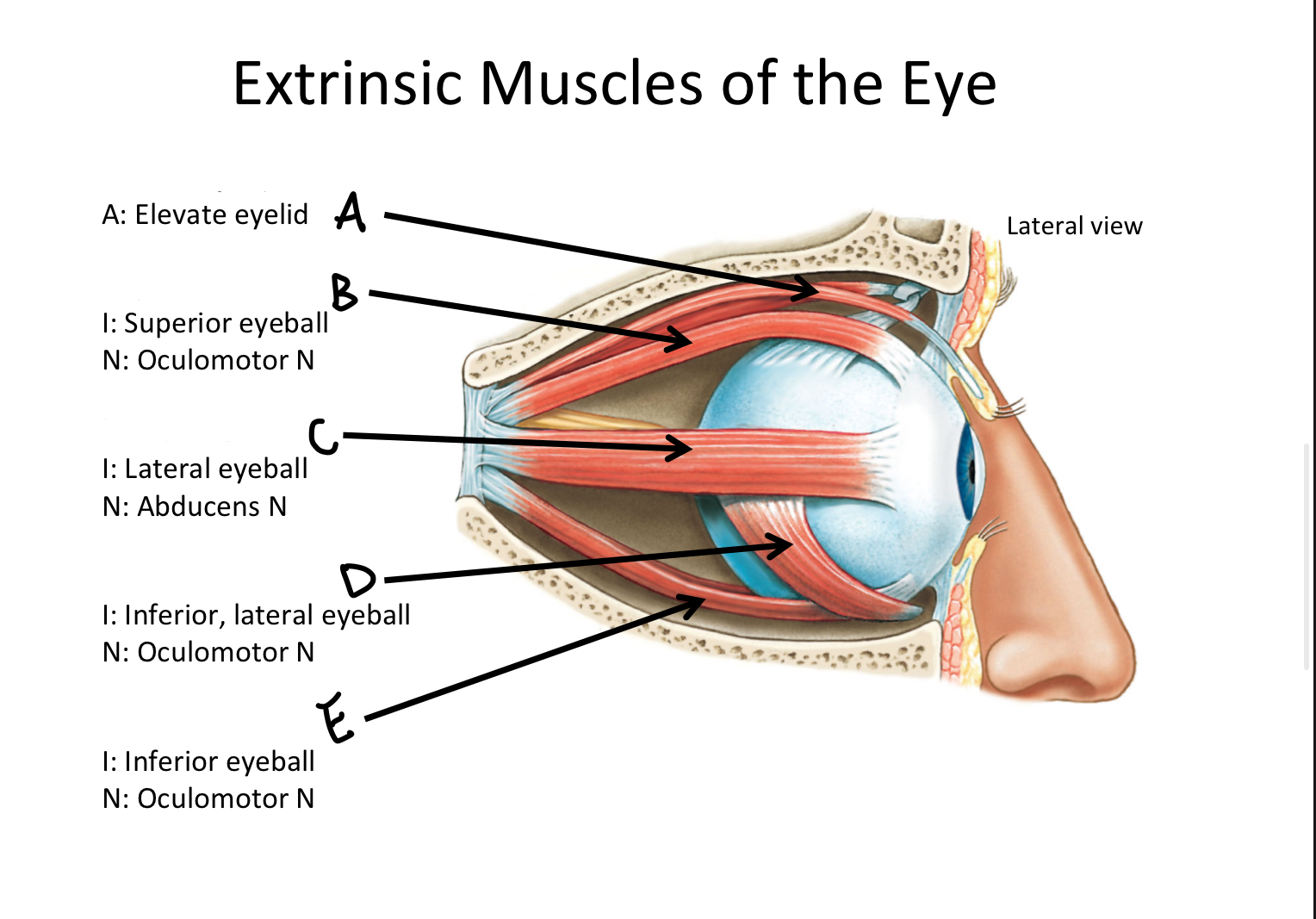
A
levator palpebrae superioris M
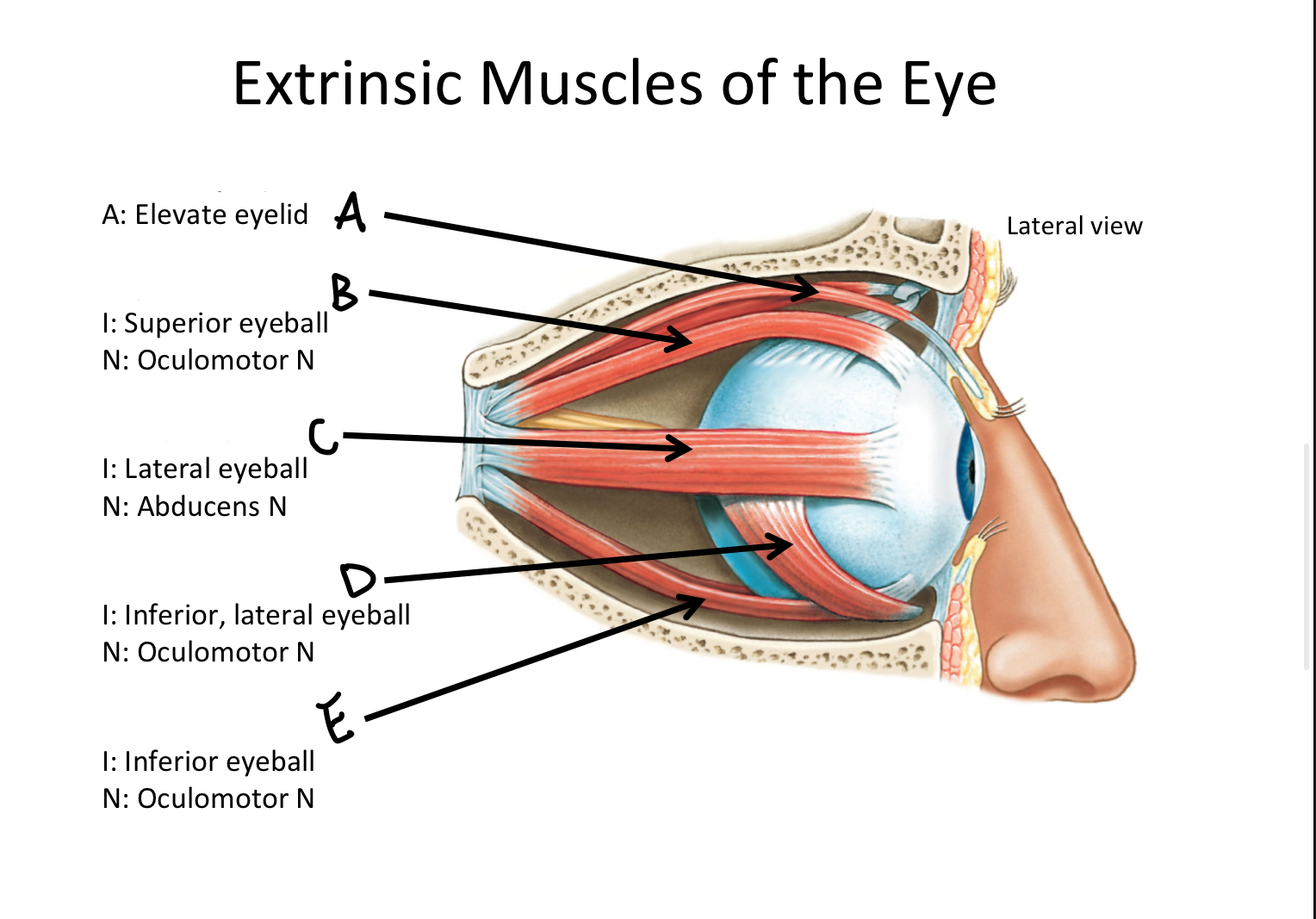
B
Superior rectus M
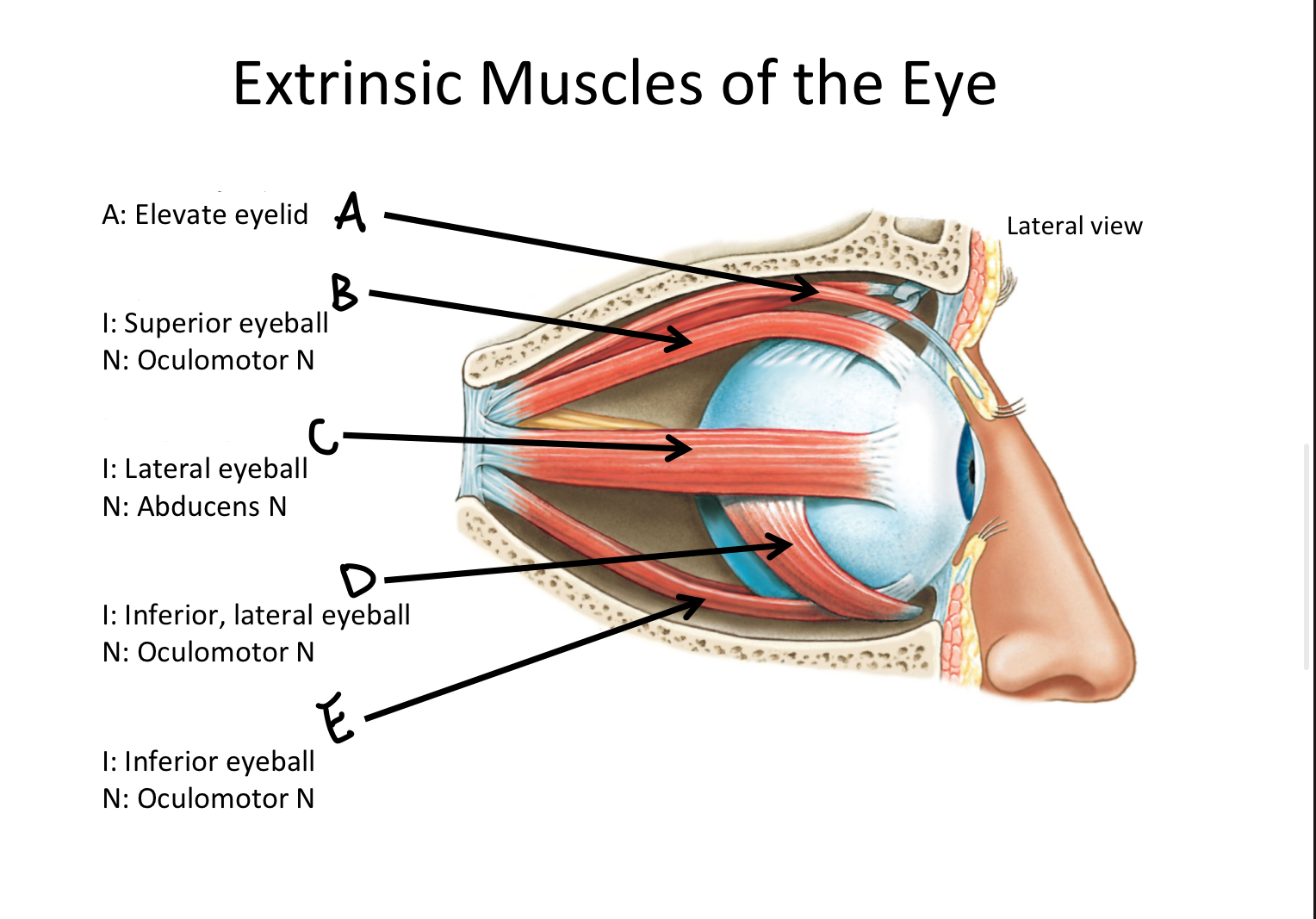
C
Lateral rectus M
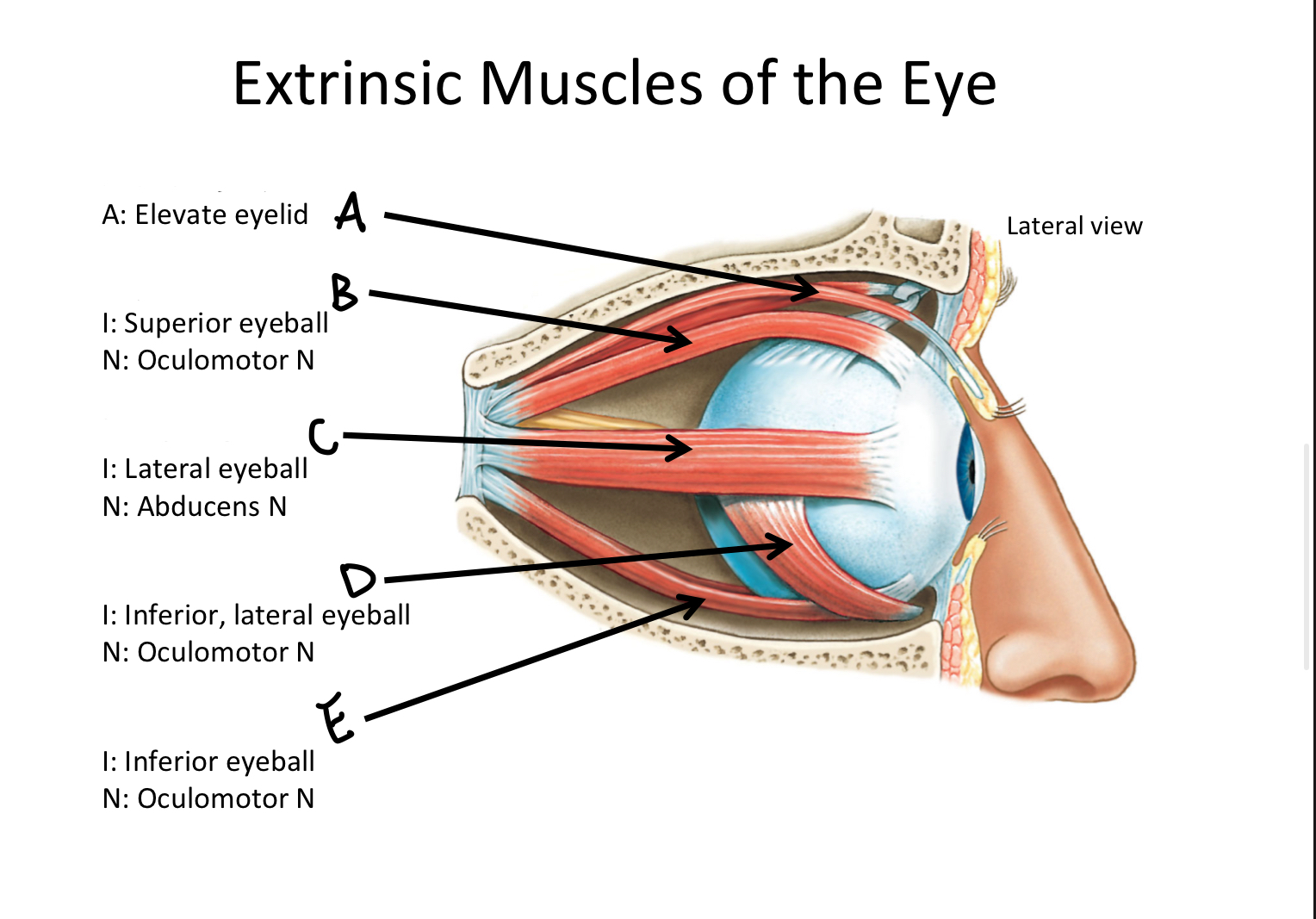
D
Inferior oblique M
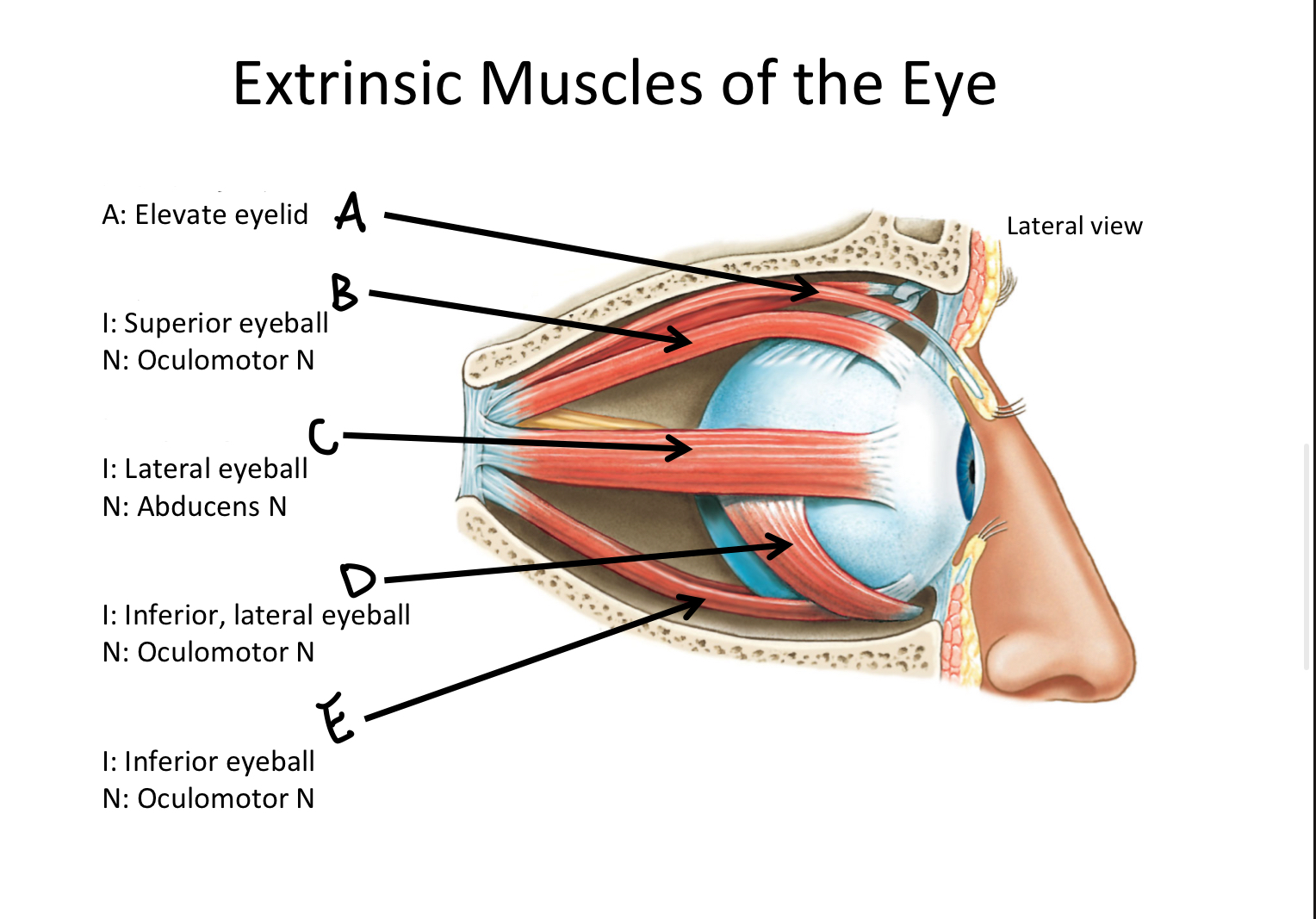
E
Inferior rectus M
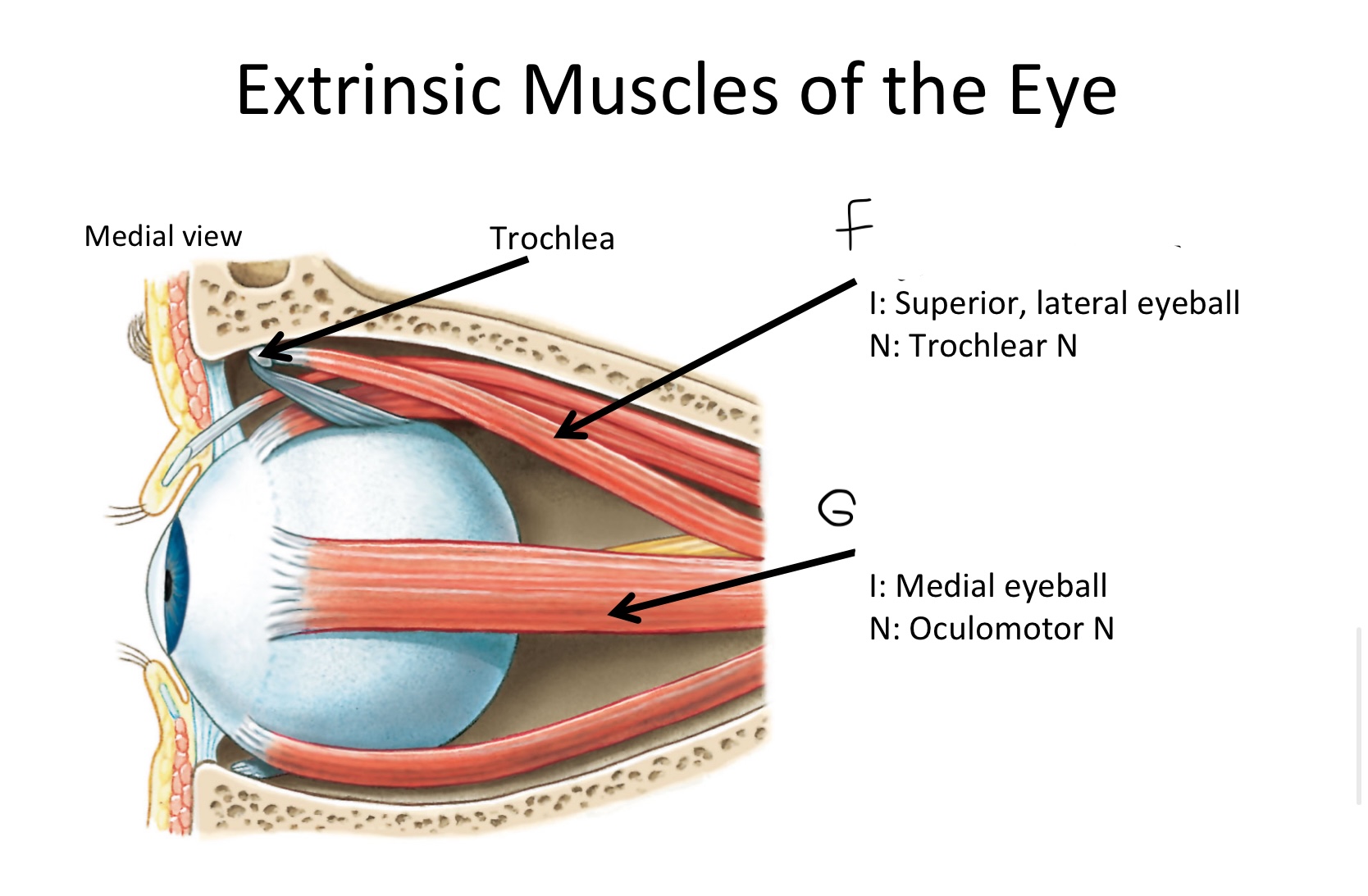
F
Superior oblique M
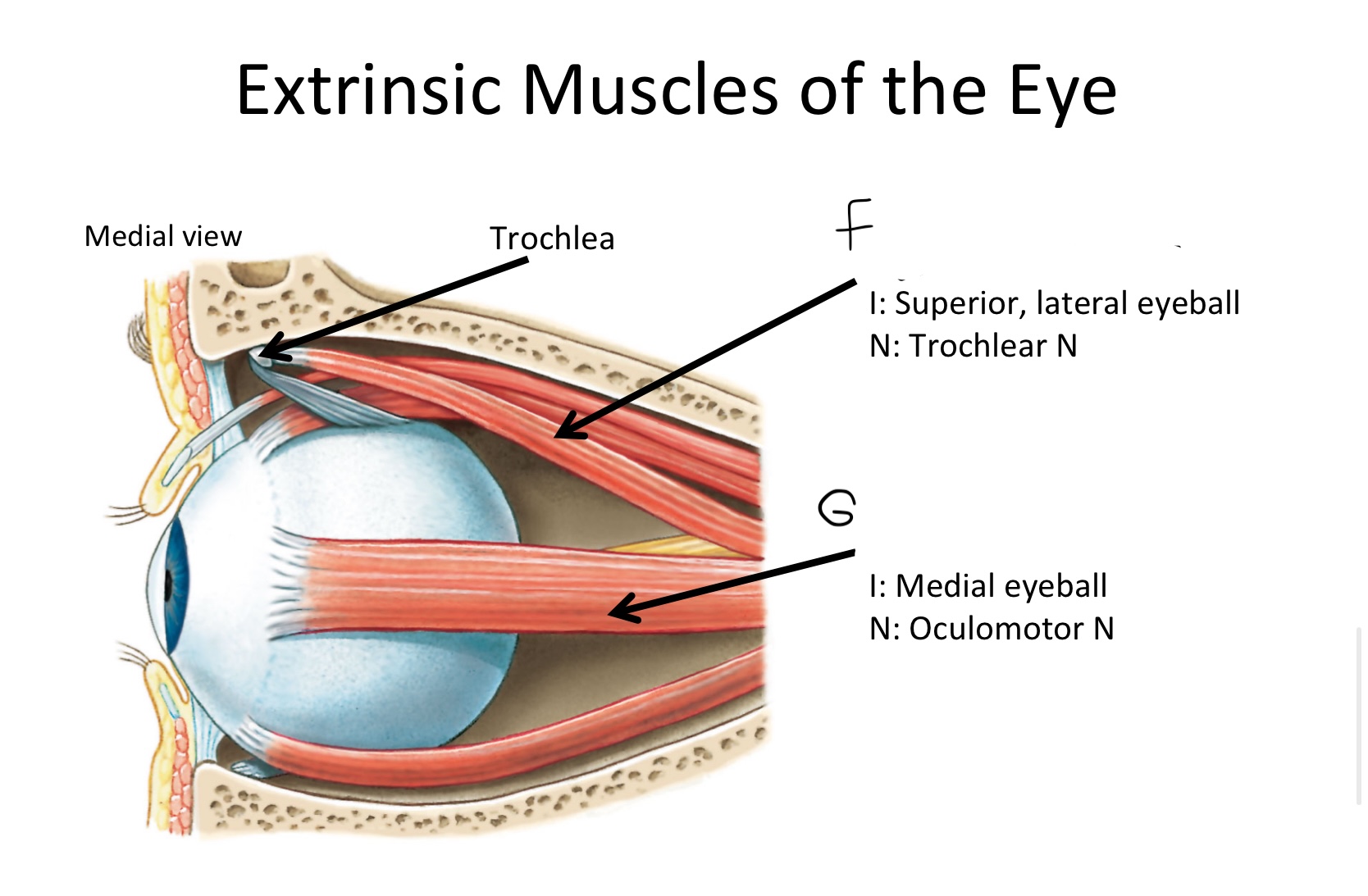
G
Medial rectus M
What muscle contains the anterior and posterior bellies?
Digastric M
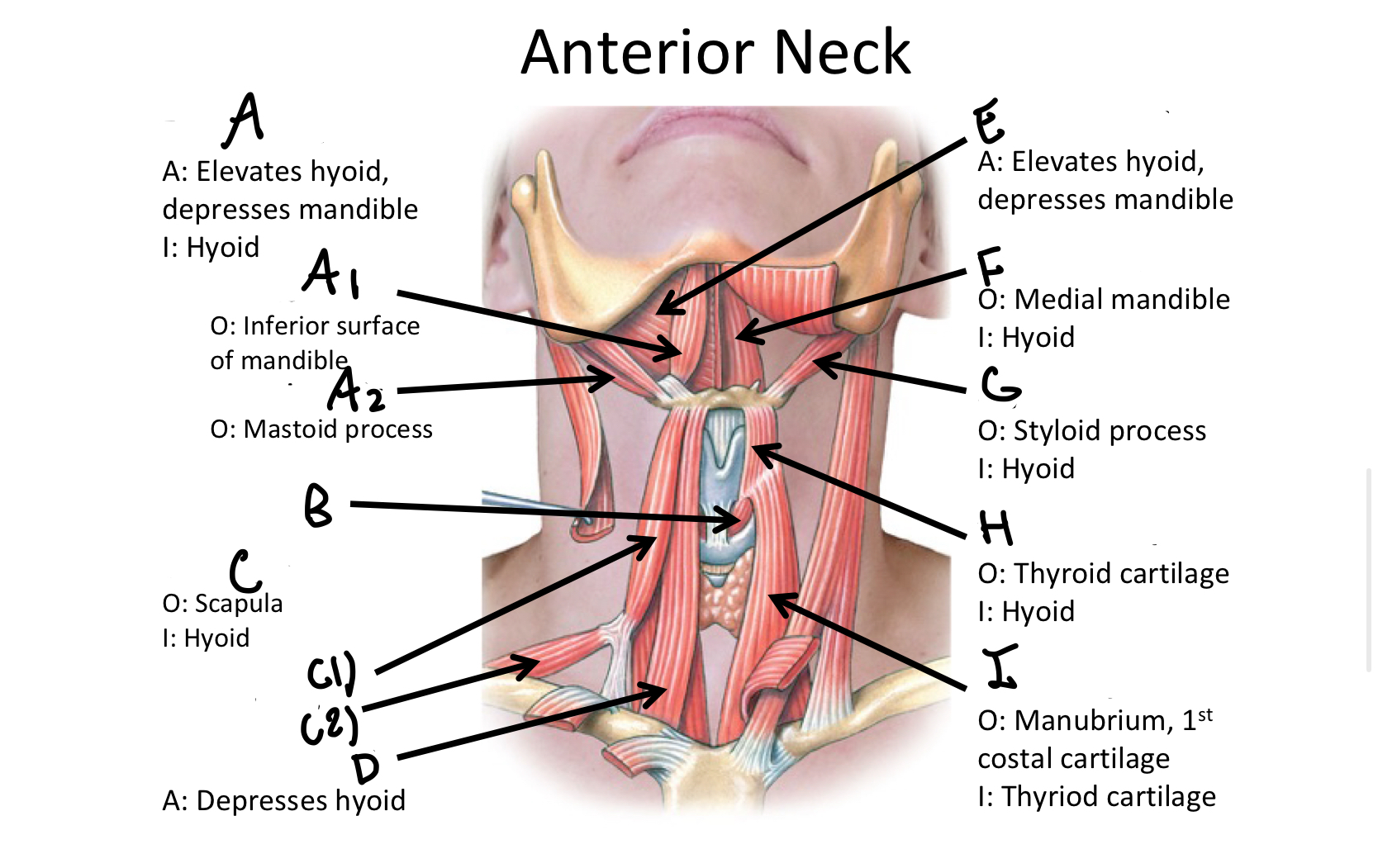
A1
anterior belly of digastric muscle
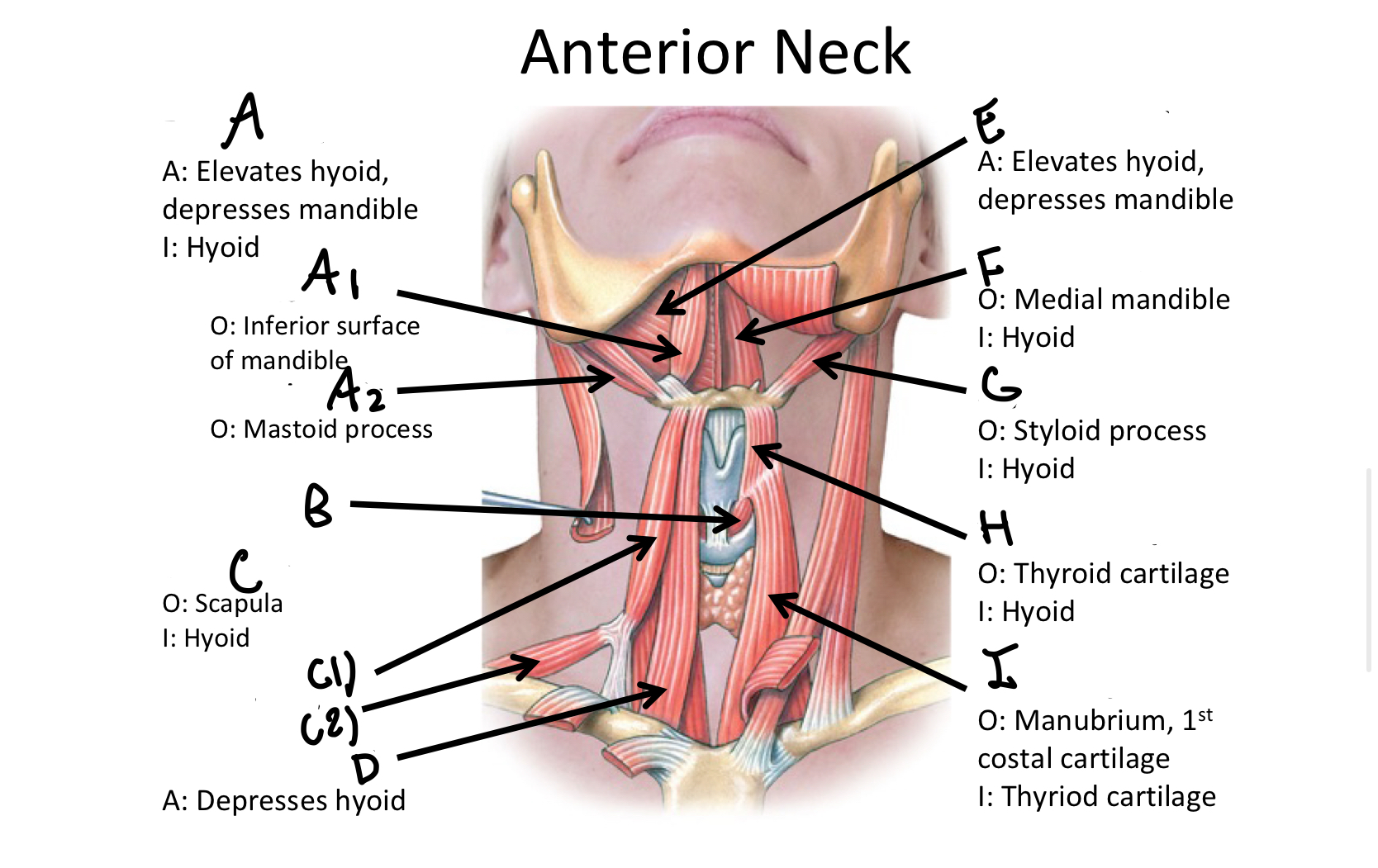
A2
posterior belly of digastric m
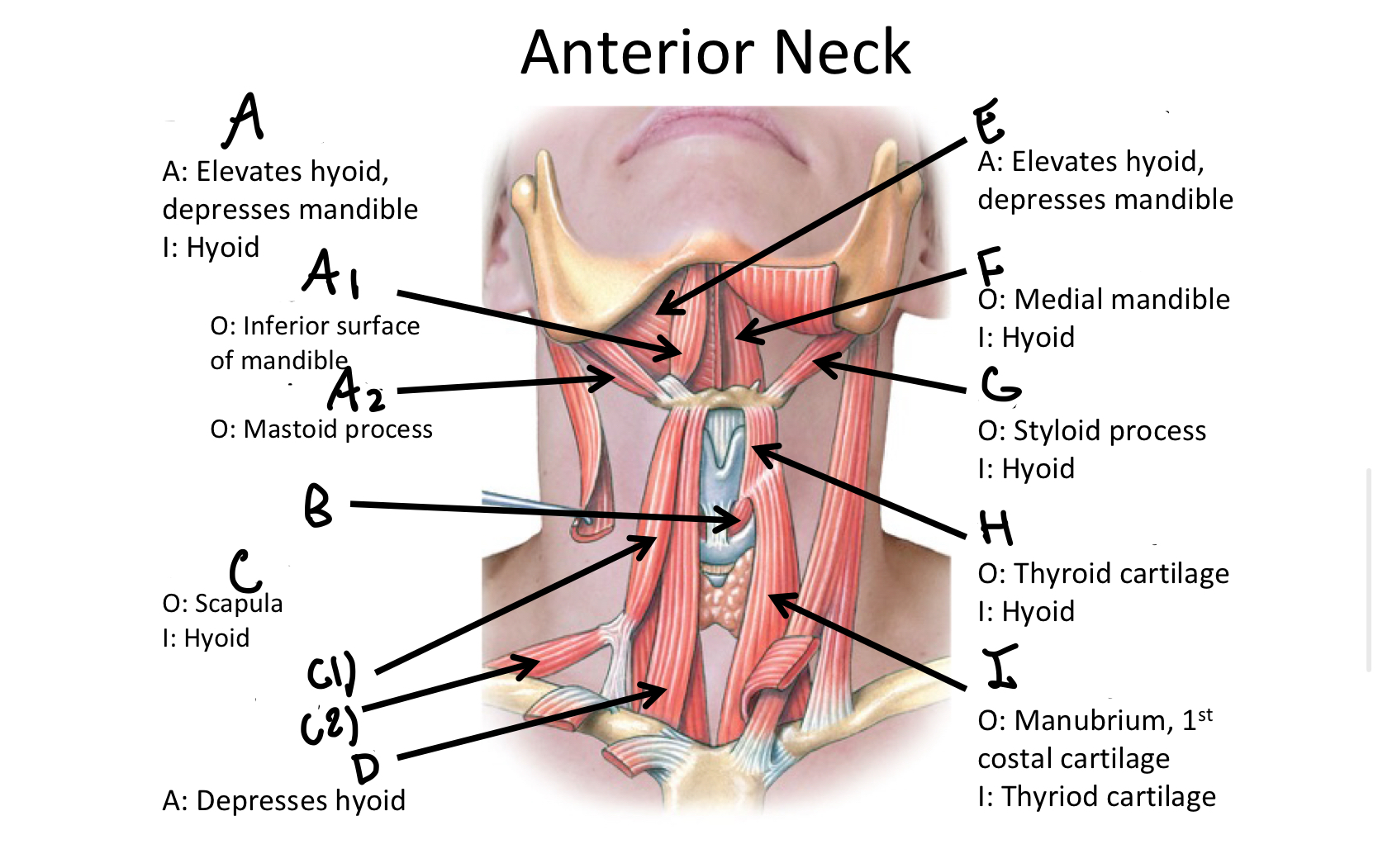
B
Cricothyroid
Which muscle contains both the superior and inferior belly in the neck region?
Omohyoid
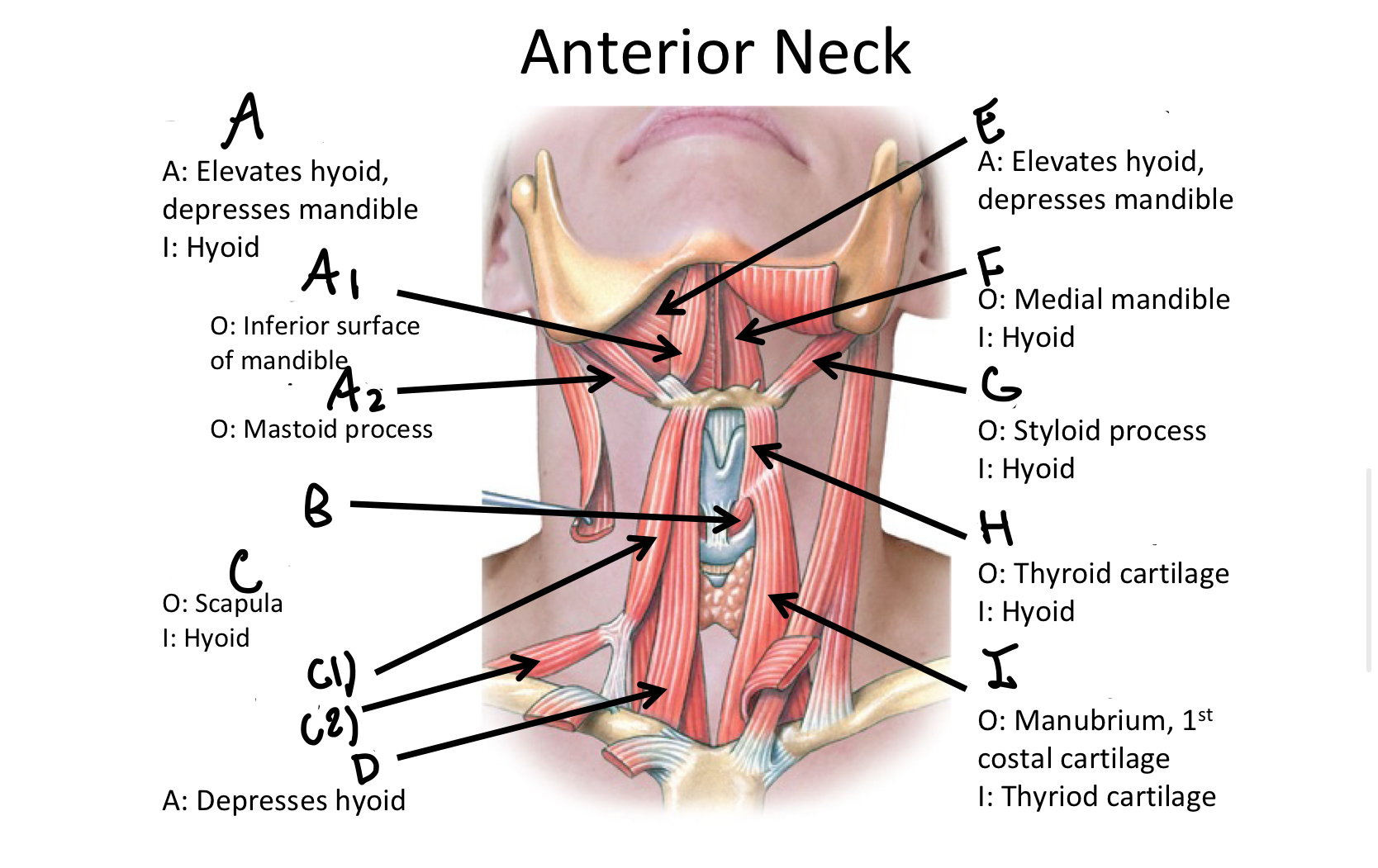
C1
Superior Belly of omohyoid m
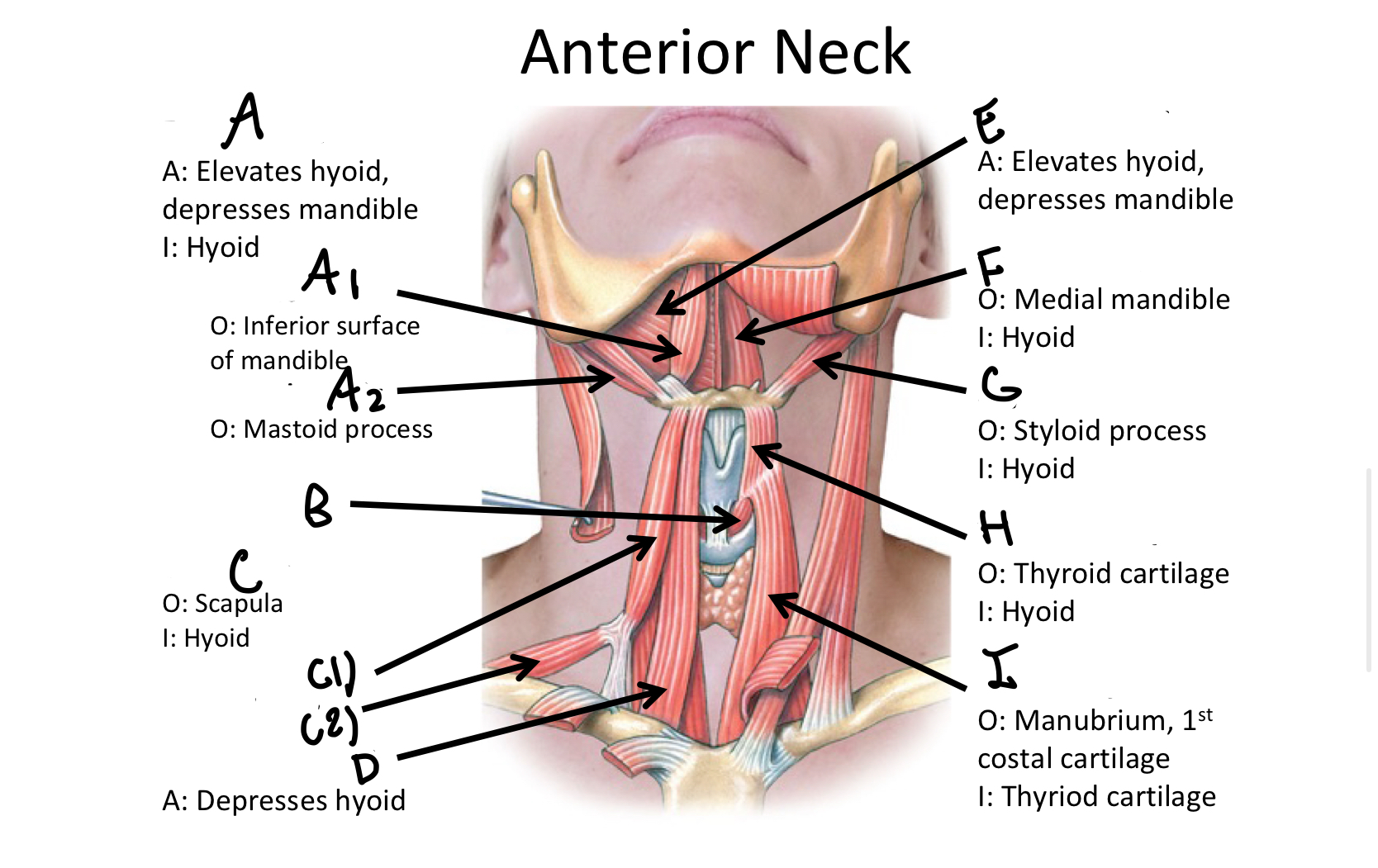
C2
Inferior Belly of omohyoid m
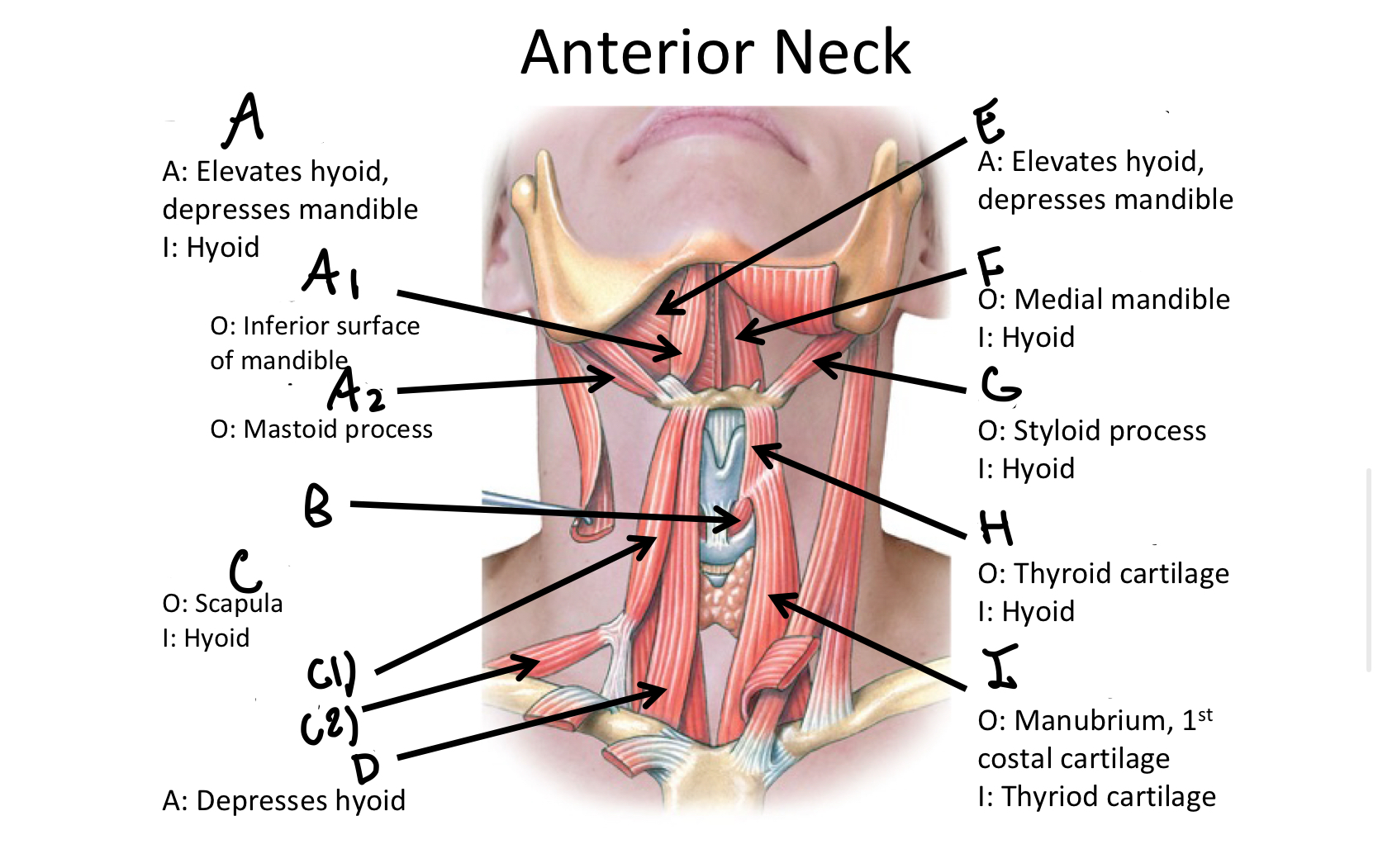
D
Sternohyoid M
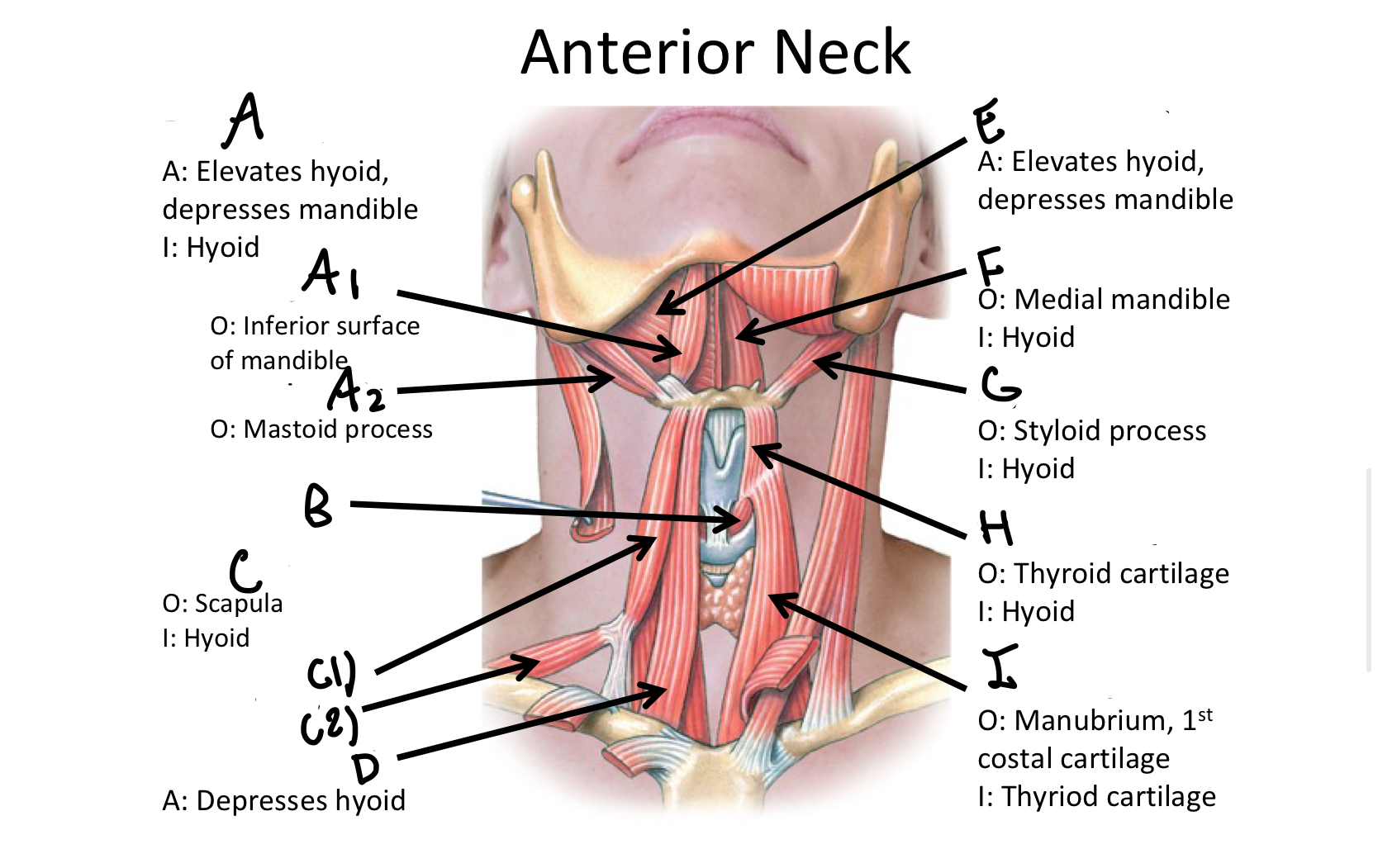
E
Mylohyoid M
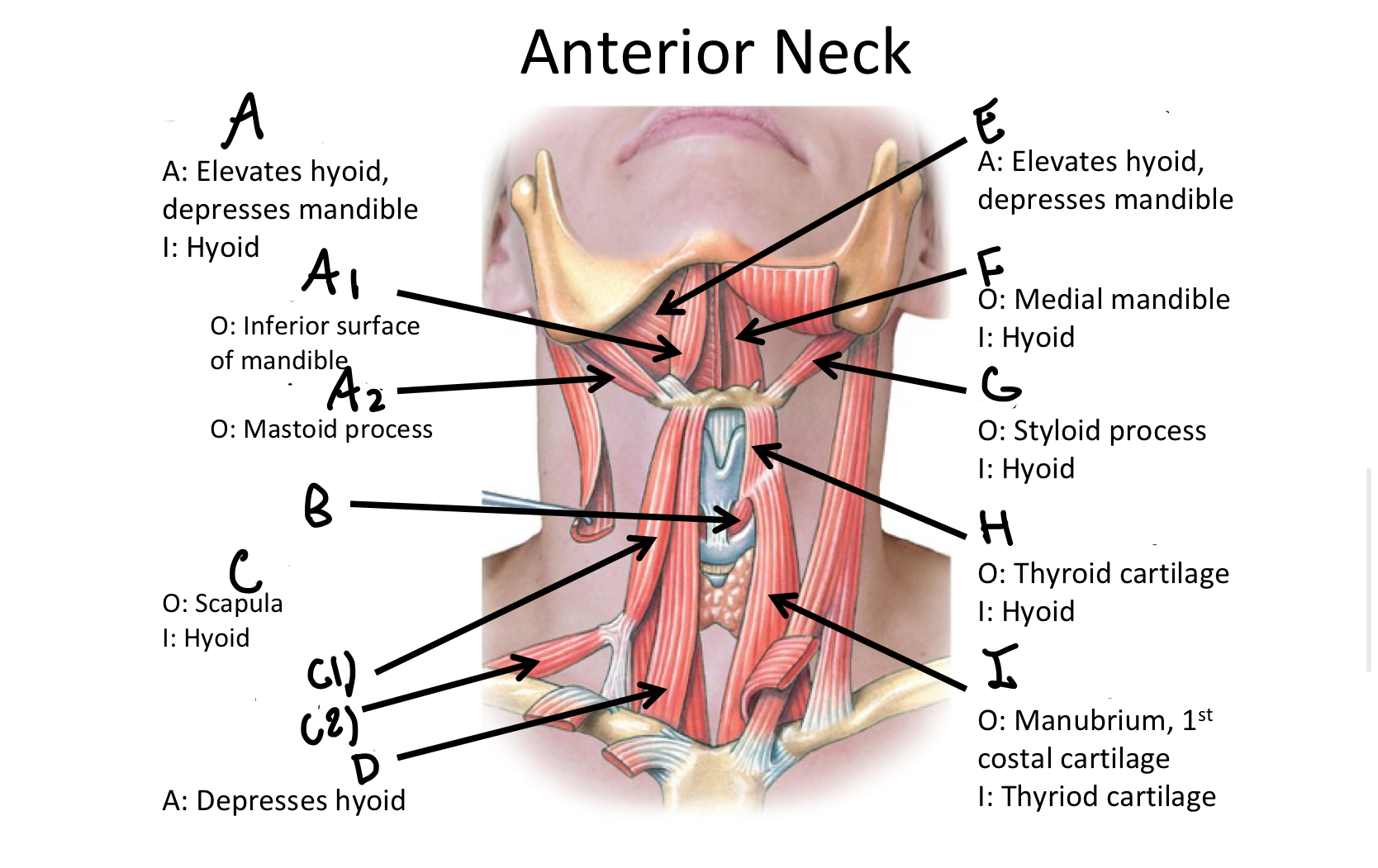
F
Geniohyoid
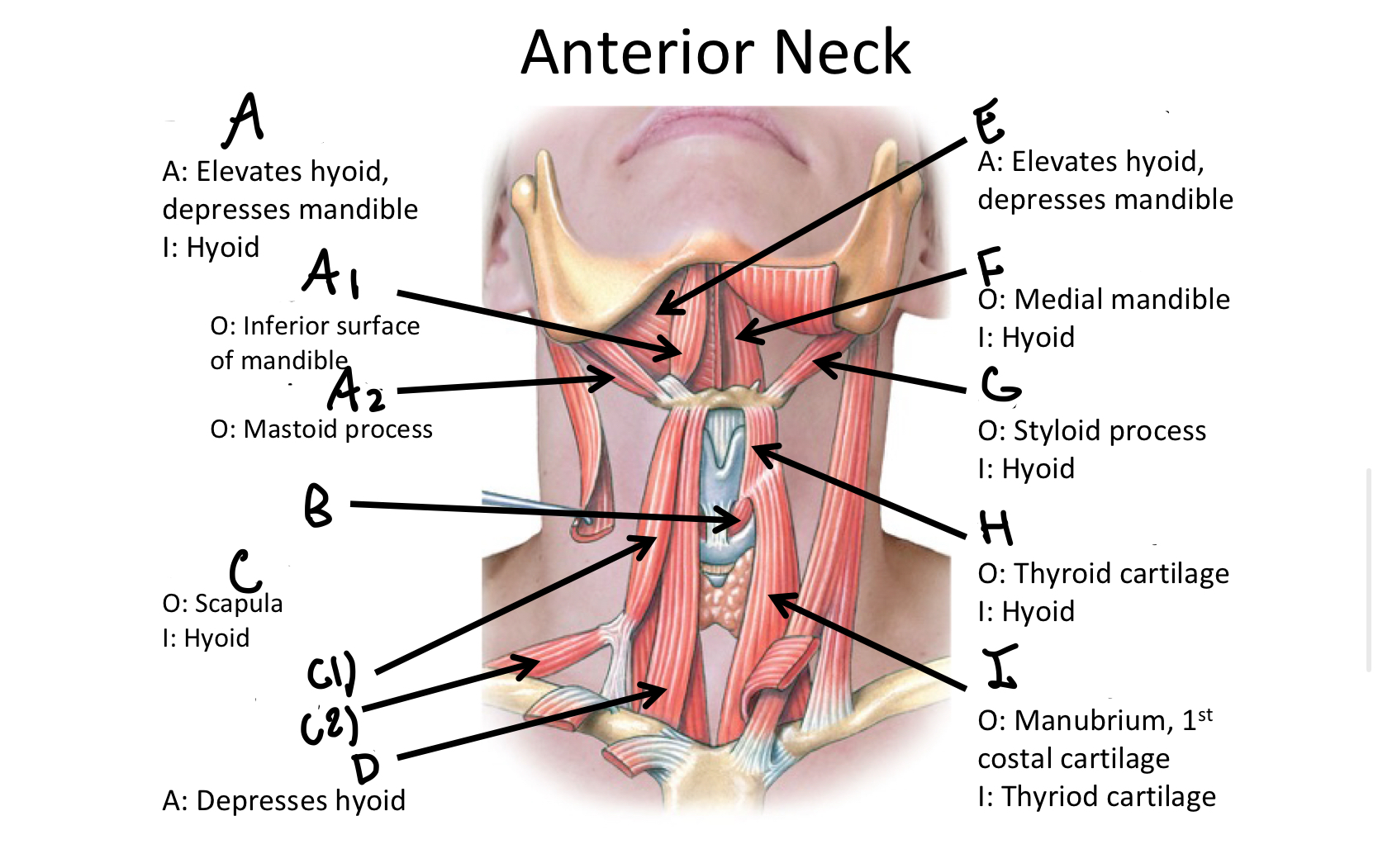
G
Stylohyoid M
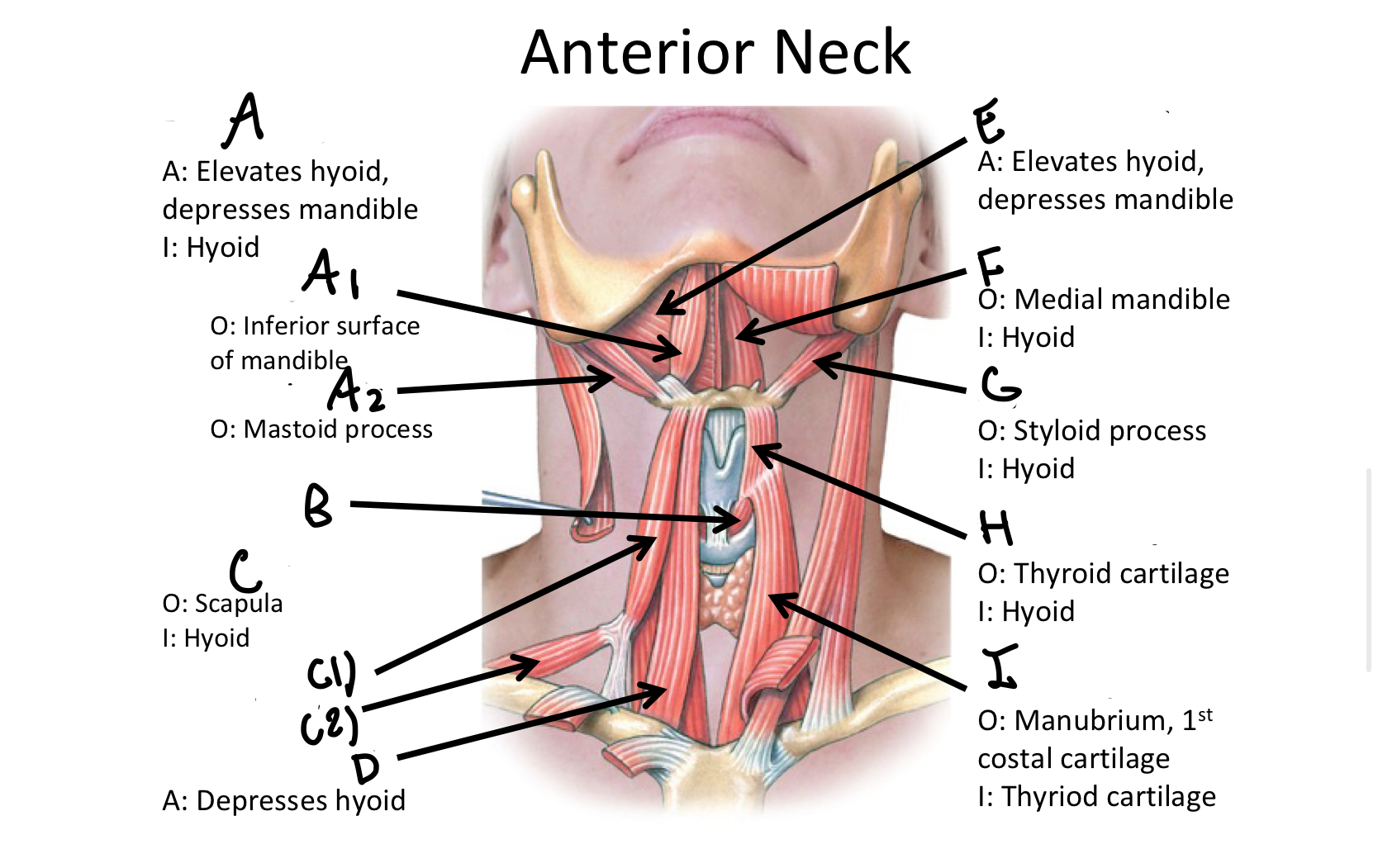
H
Thyrohyoid M
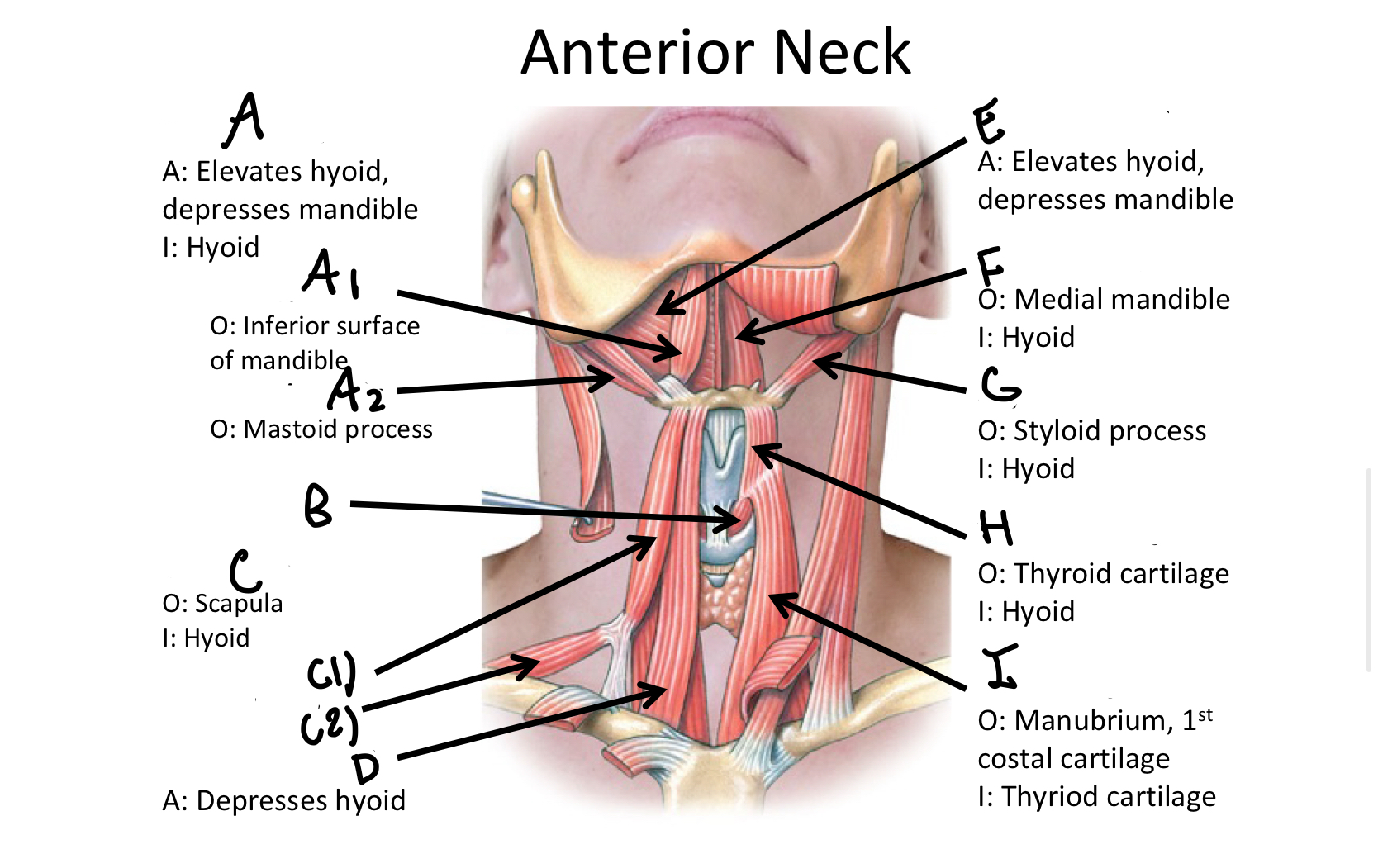
I
Sternothyroid M
Which muscle includes the sternal and clavicular head muscles?
Sternocleidomastoid M
J1
Clavicular Head of the sternocleidomastoid m
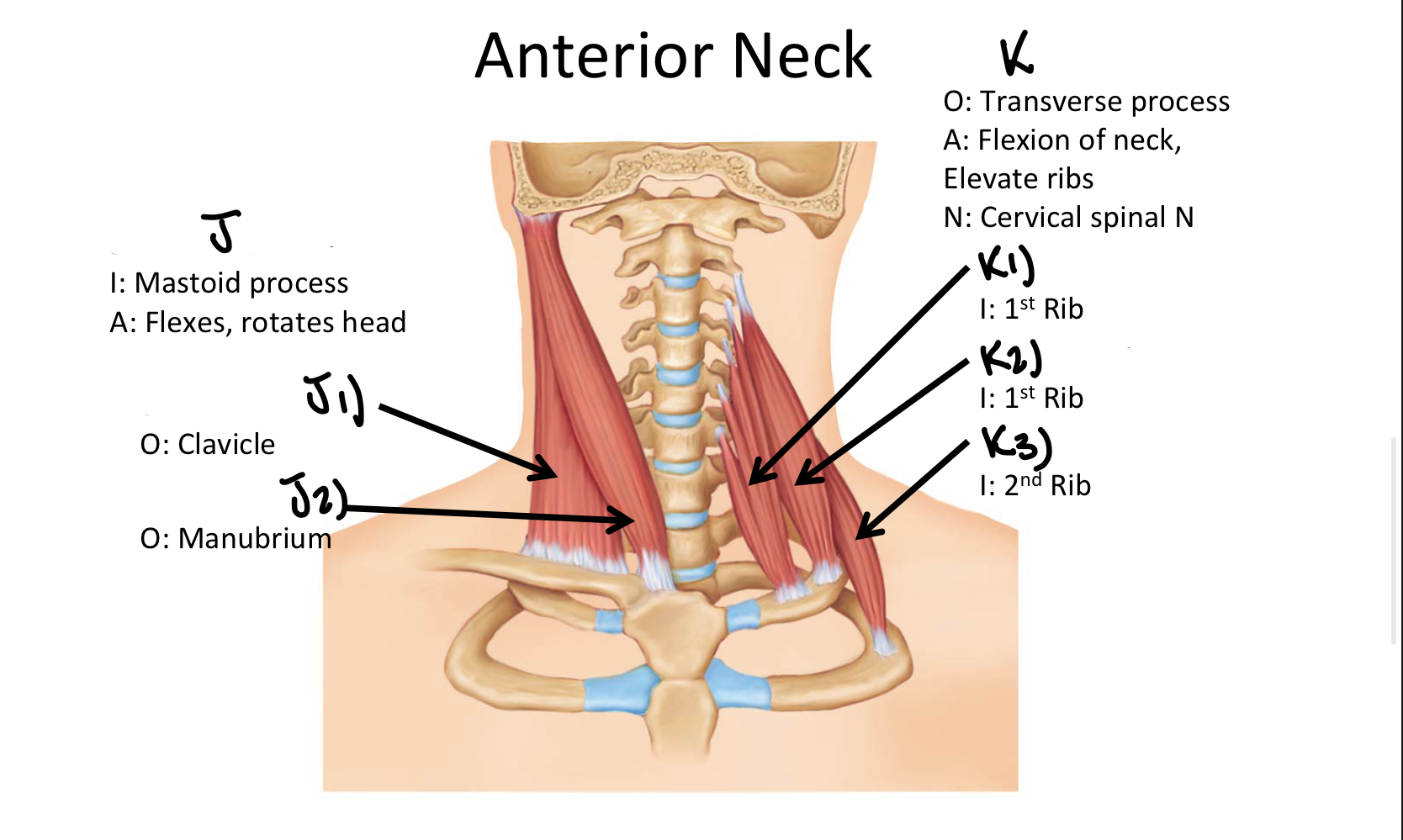
J2
Sternal Head of the Sternocleidomastoid M
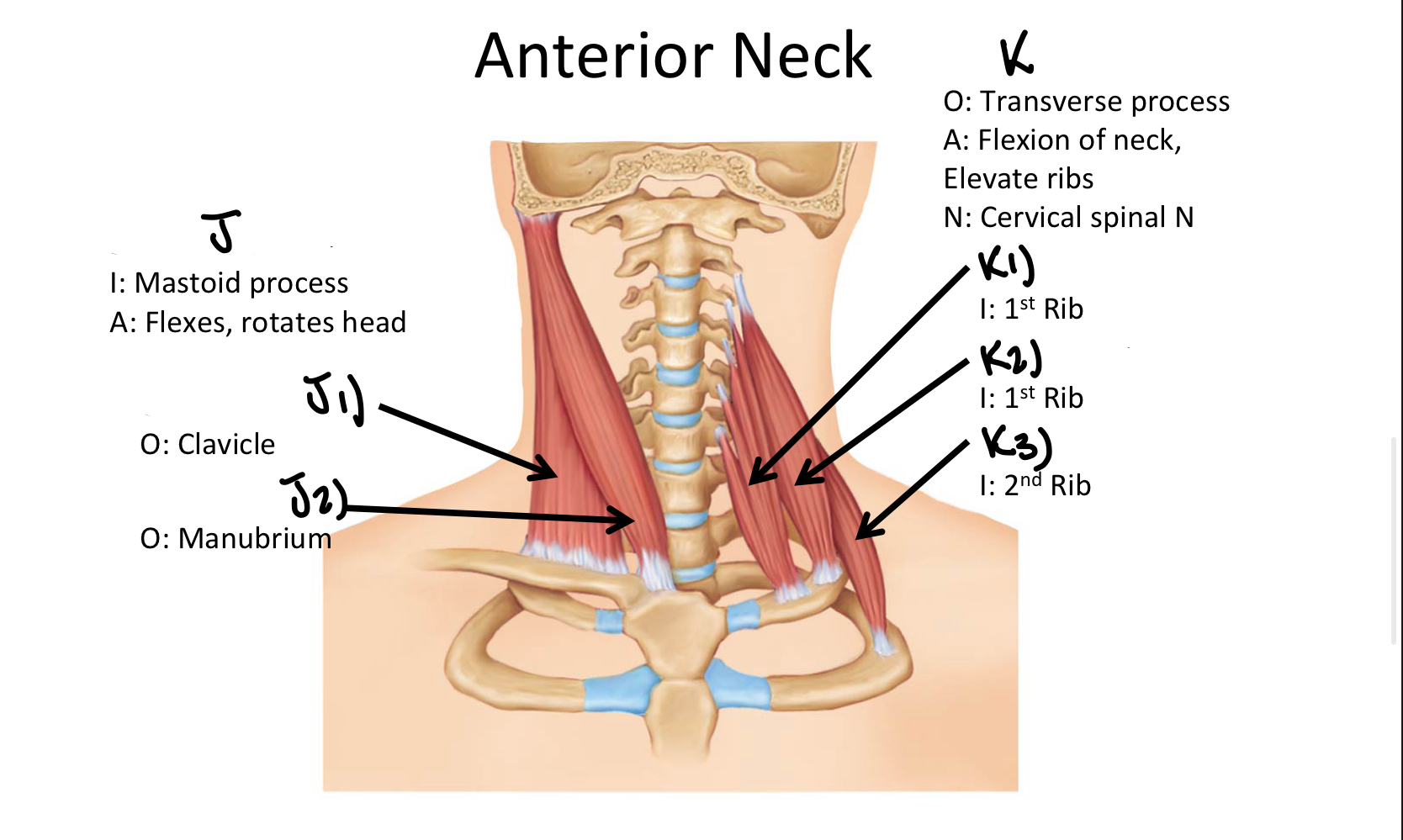
Which muscle includes the Anterior, Middle, and Posterior Scalene muscles?
Scalene MM
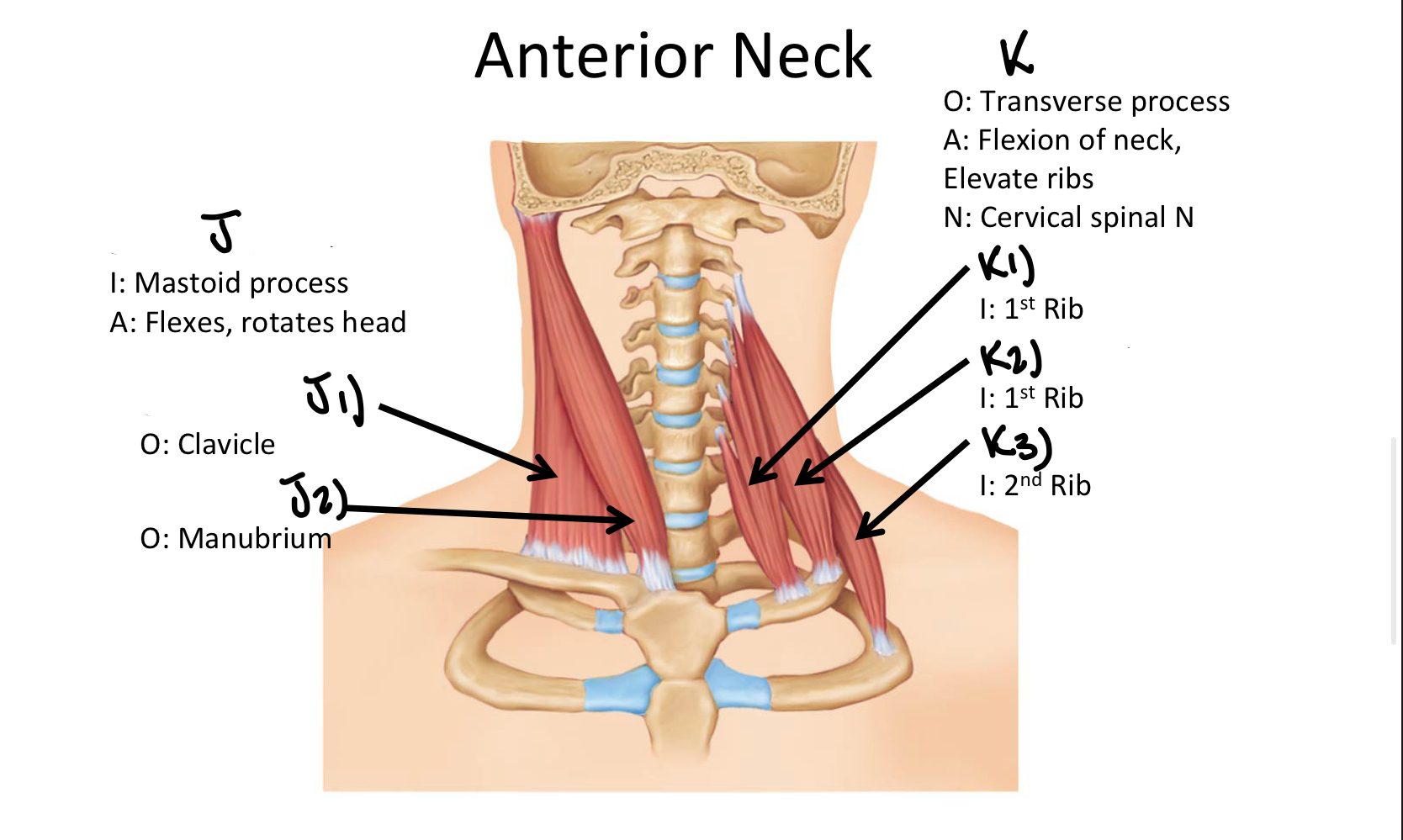
K1
Anterior Scalene M
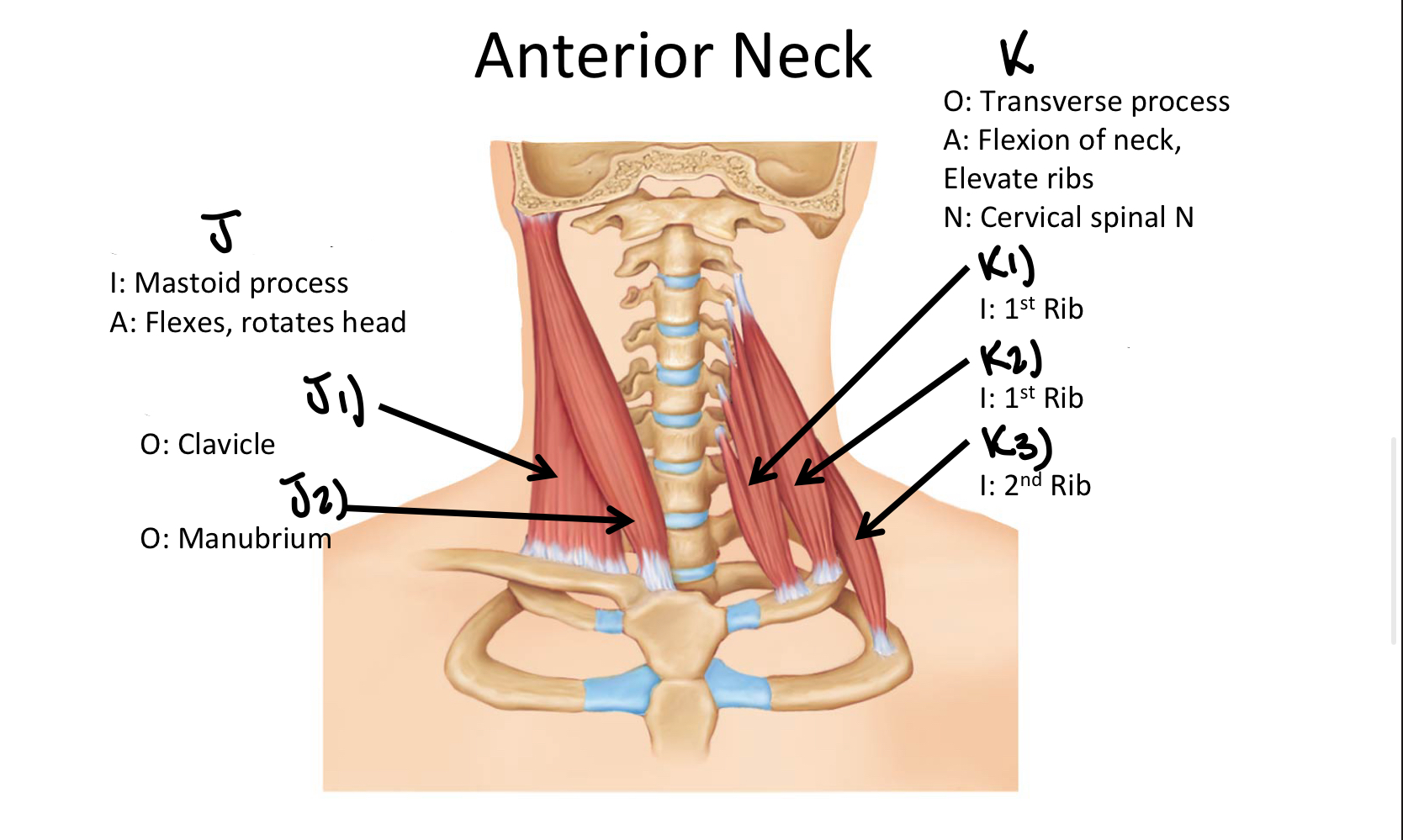
K2
Middle Scalene M
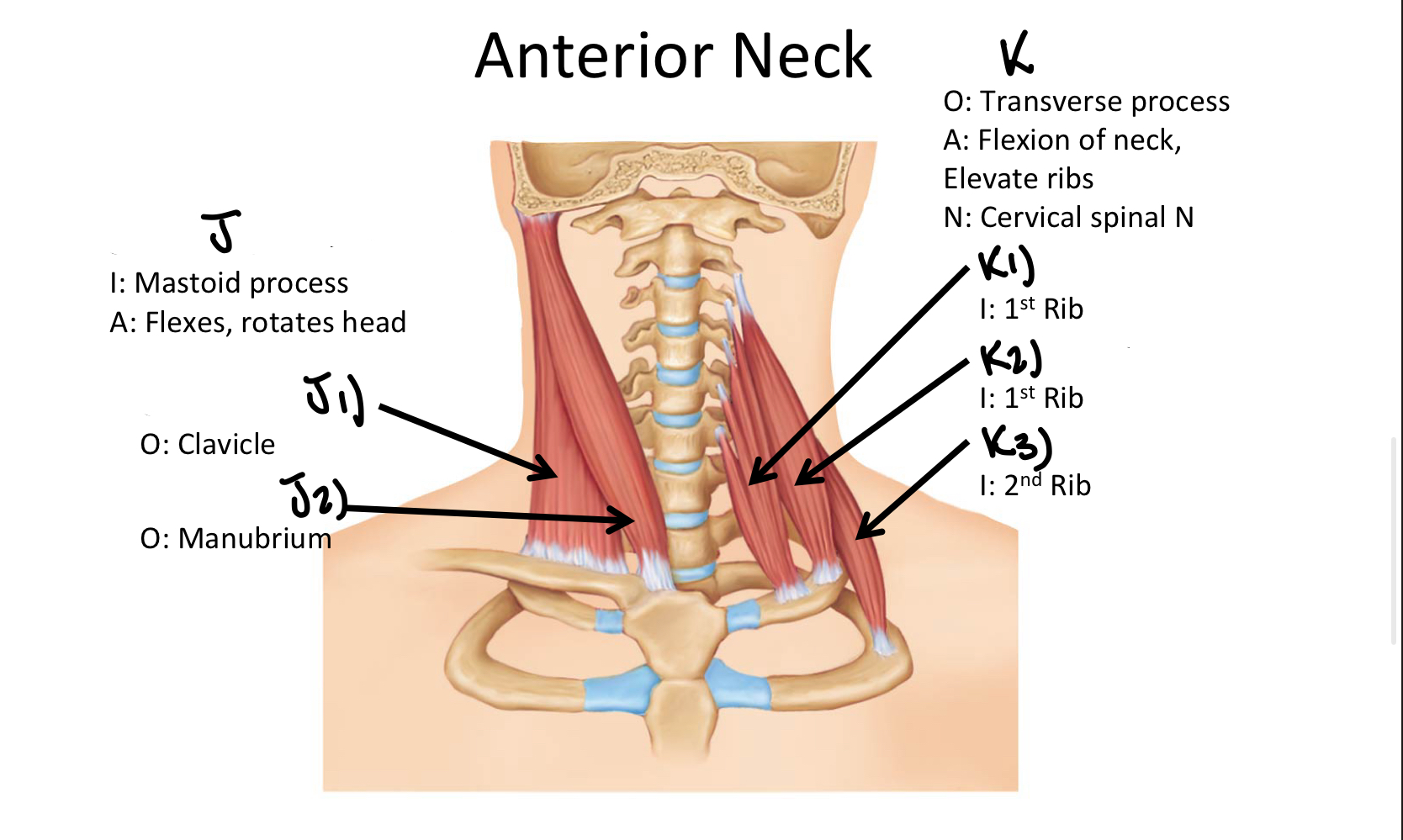
K3
Posterior Scalene M
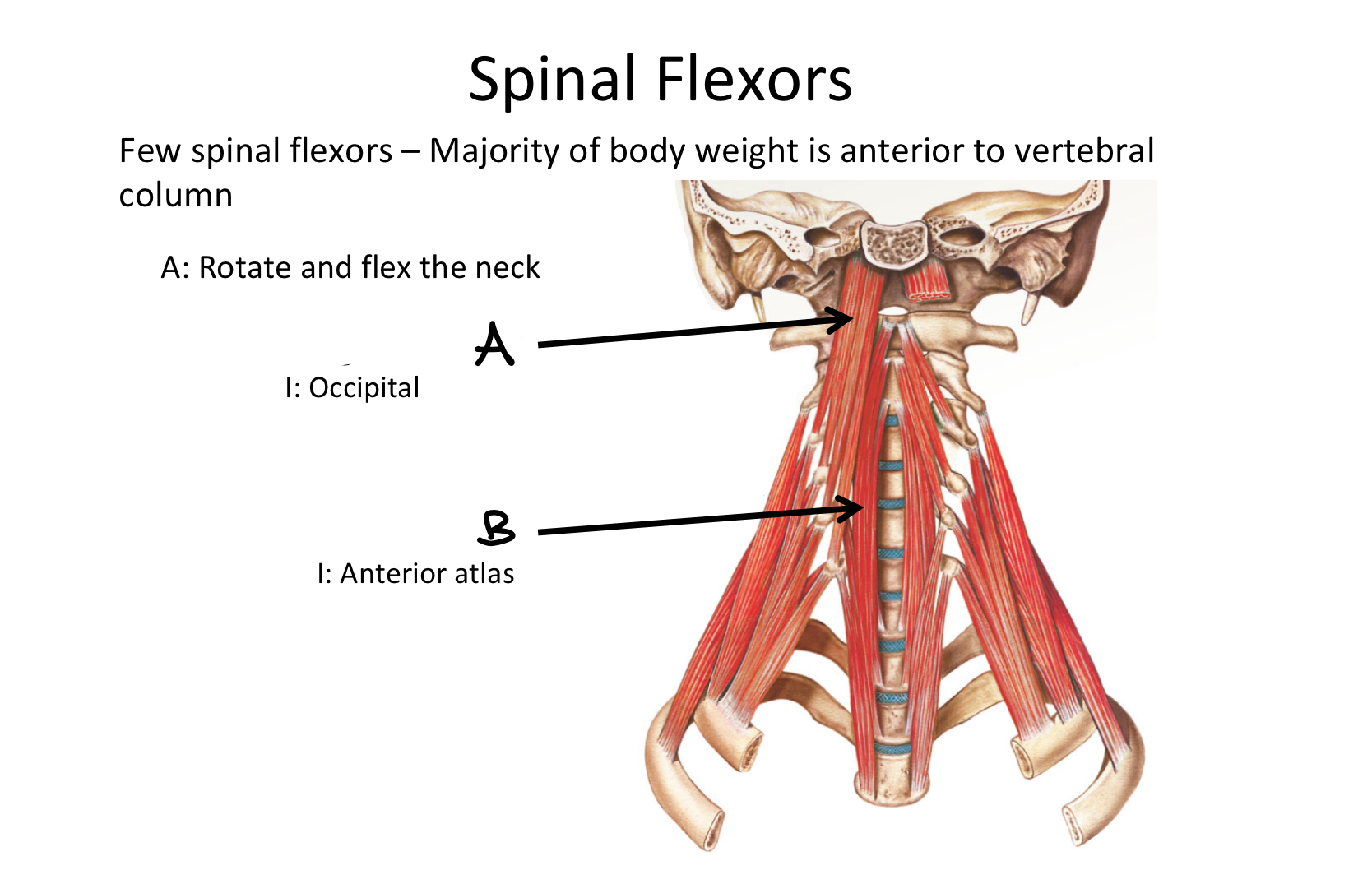
A
Longus Capitis M
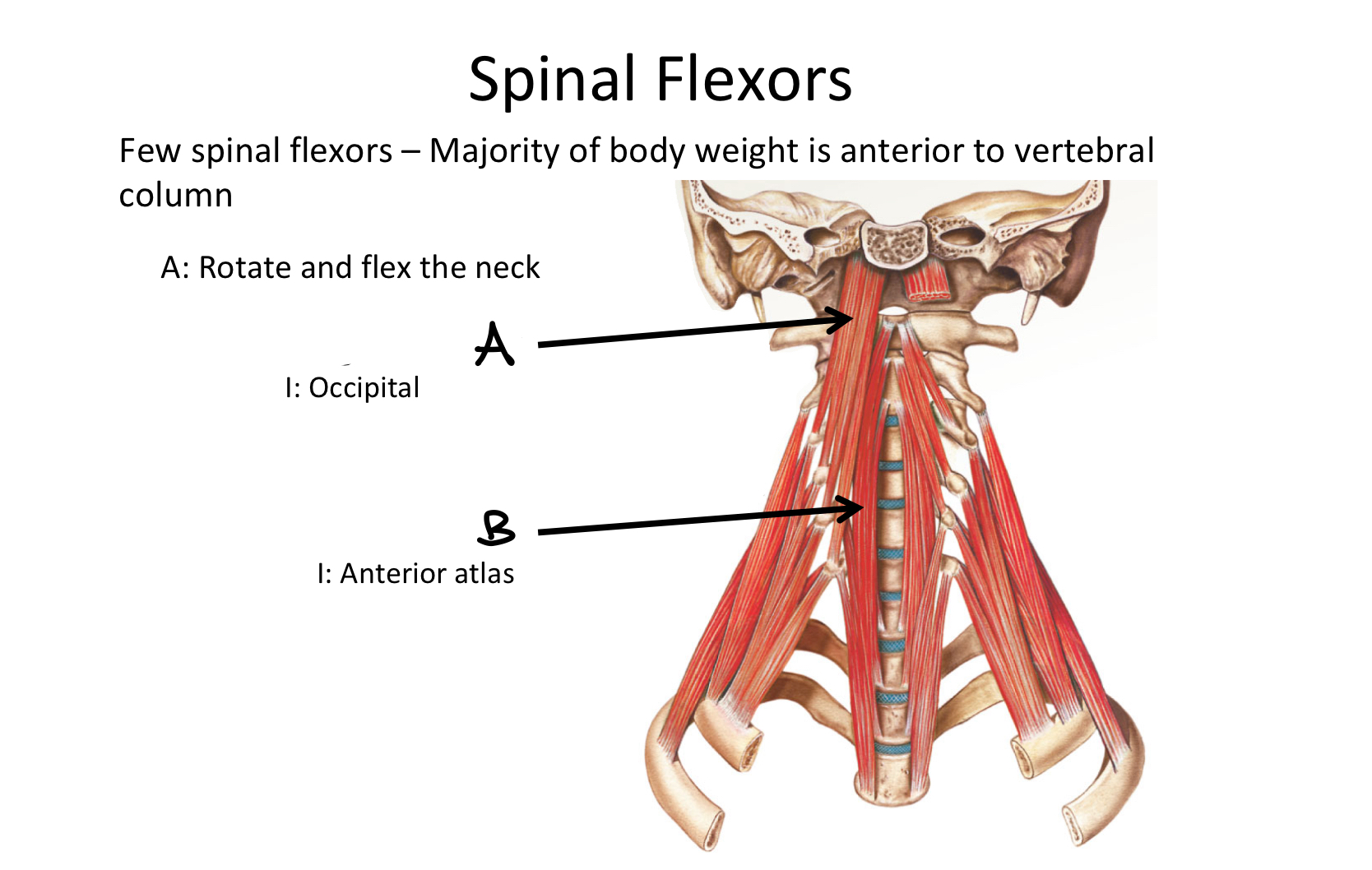
B
Longus Colli M
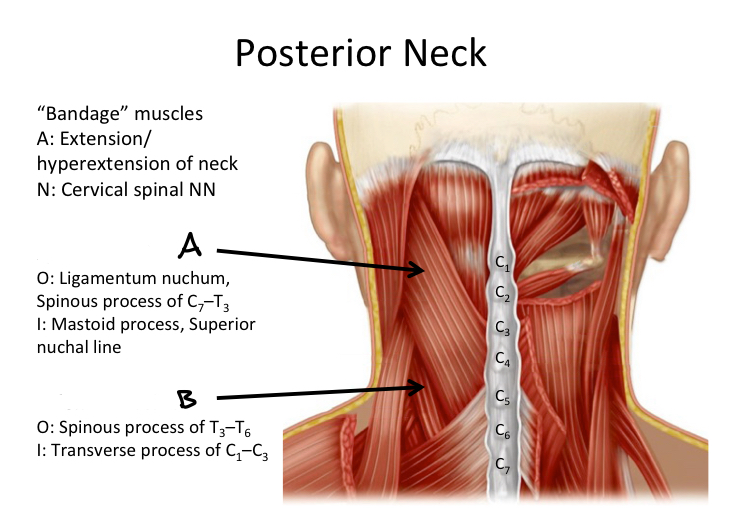
A
Splenius capitis M
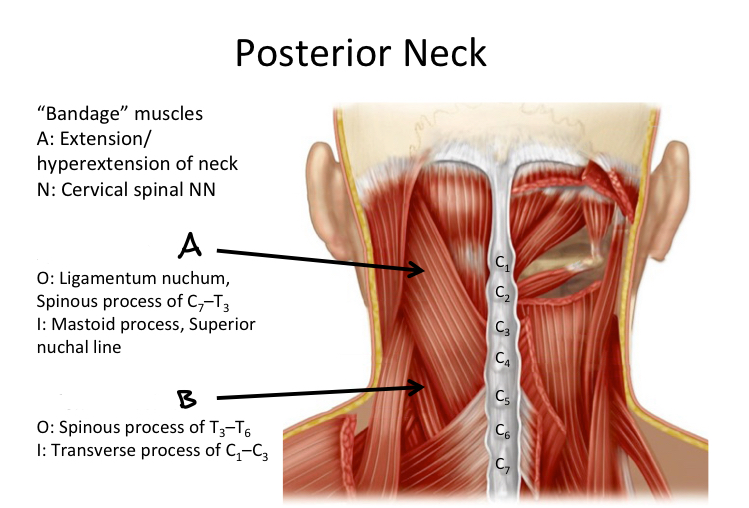
B
Splenius cervicis M
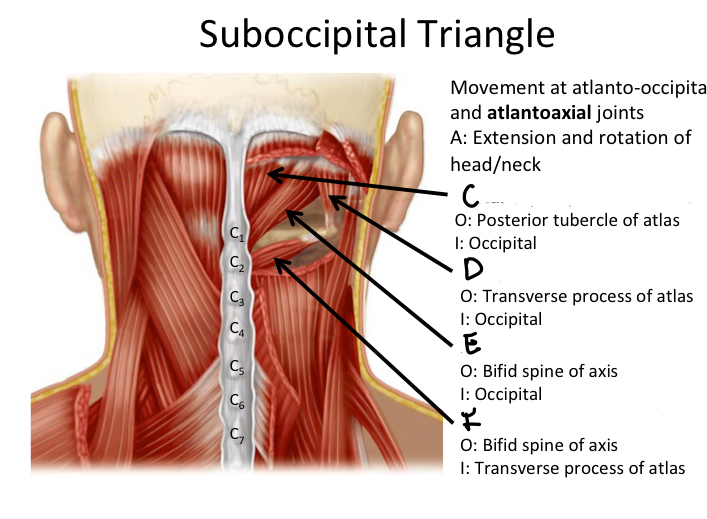
C
Rectus capitis posterior minor M
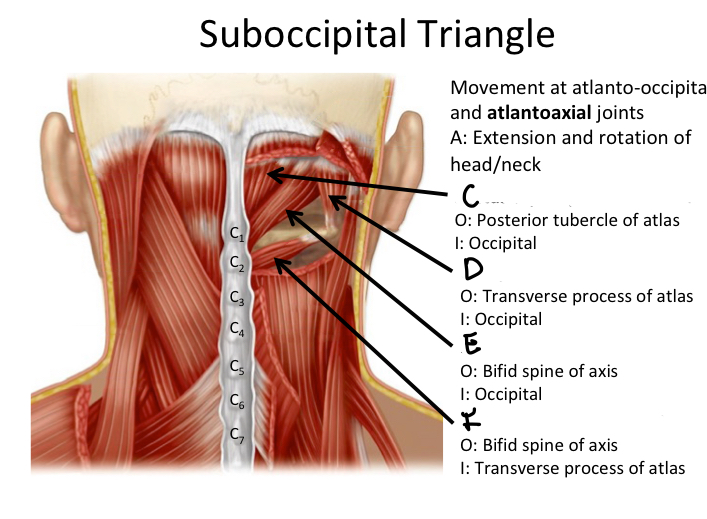
D
Oblique capitis superior M
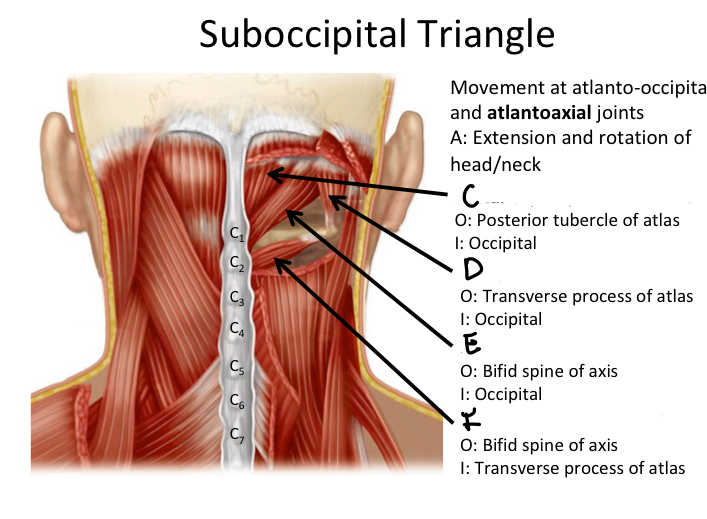
E
Rectus capitis posterior major M
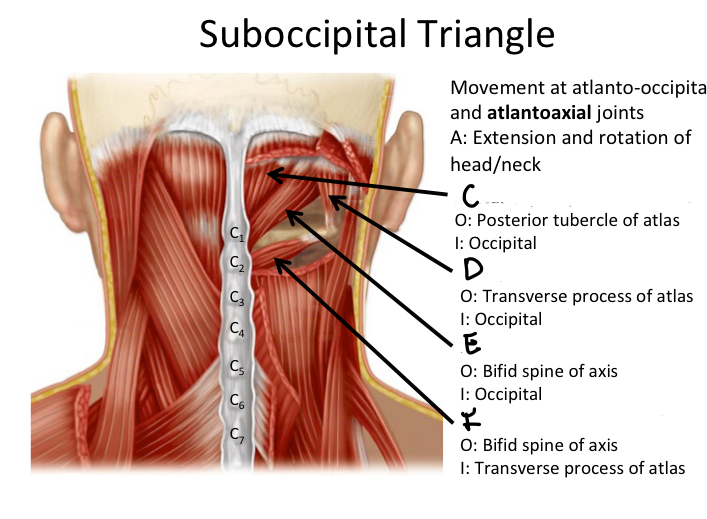
F
Oblique capitis inferior M
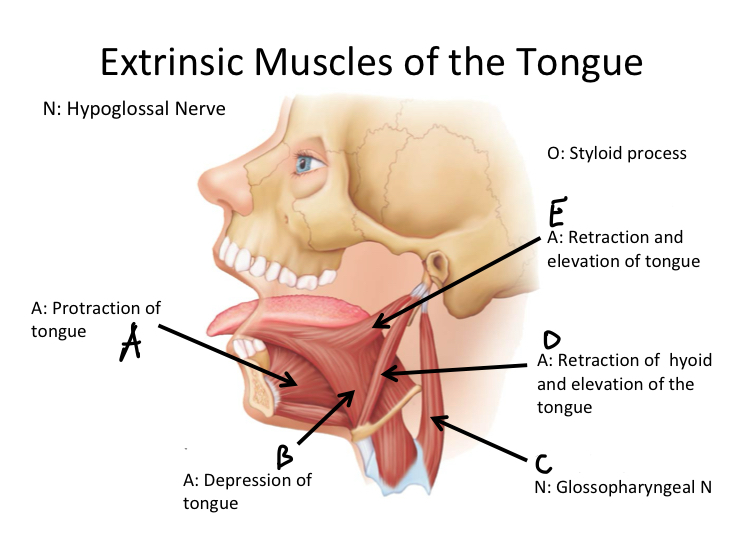
A
Genioglossus M
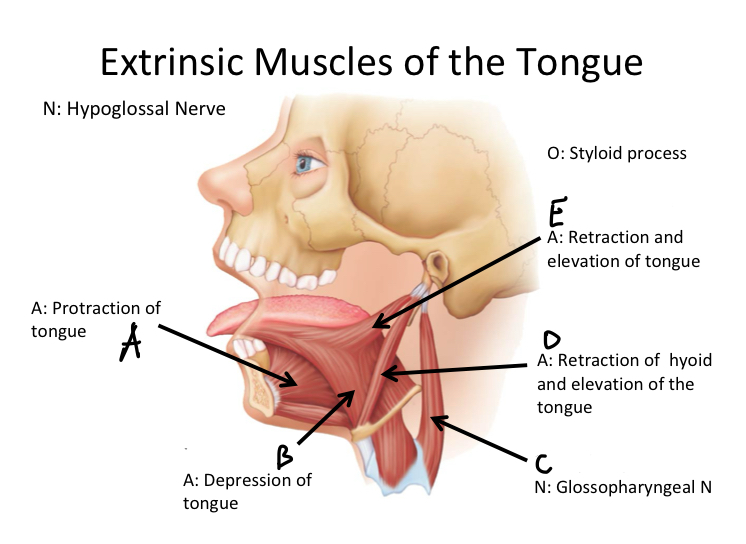
B
Hyoglossus M
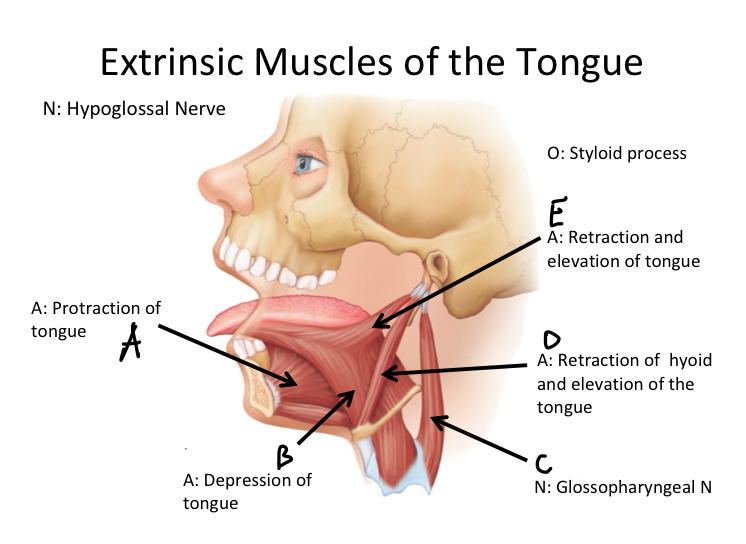
C
Stylopharyngeus M
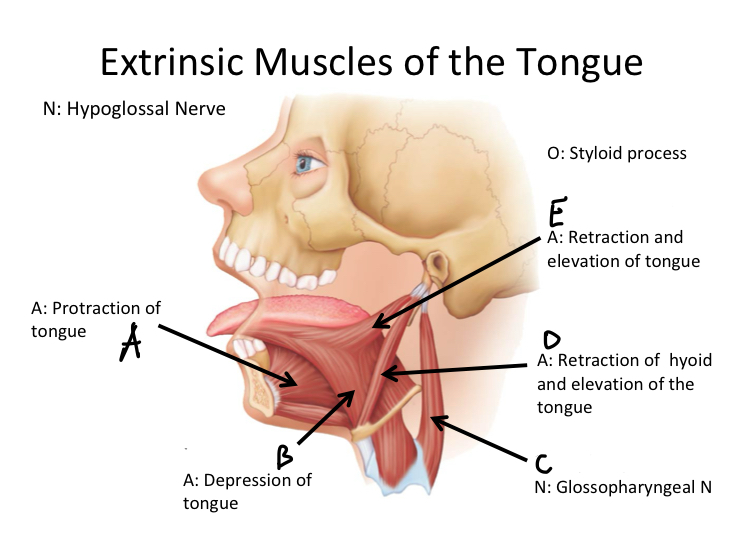
D
Stylohyoid M
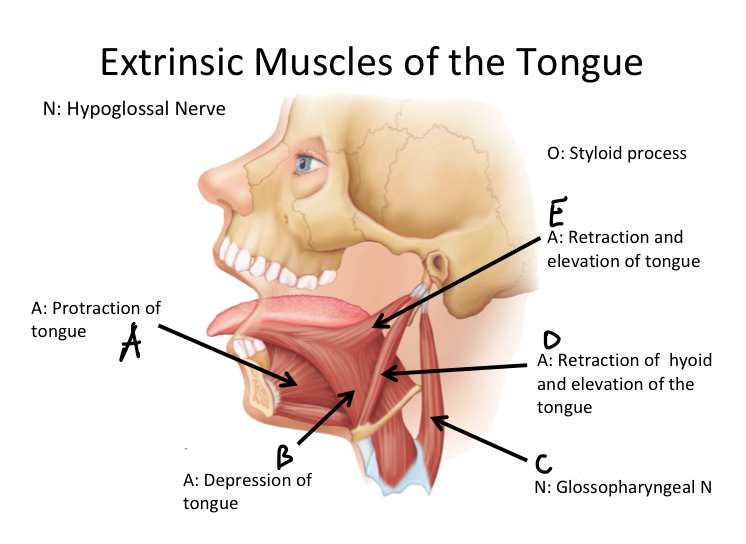
E
Styloglossus M
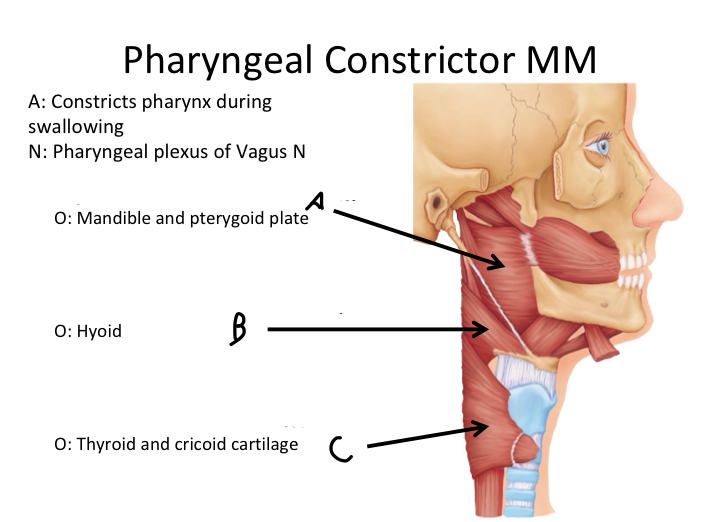
A
Superior pharyngeal constrictor M
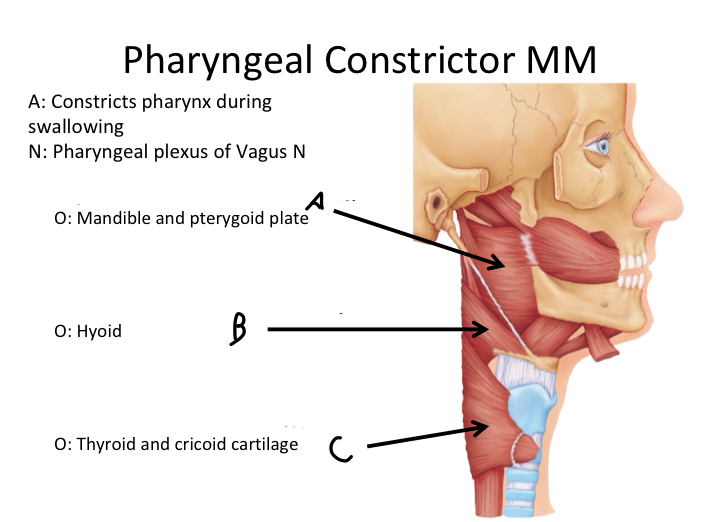
B
Middle pharyngeal constrictor M
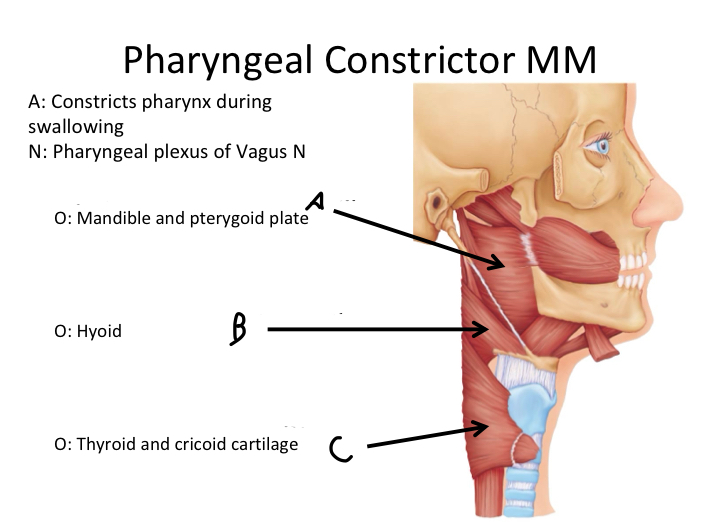
C
Inferior pharyngeal constrictor M
Which muscle contains Superior, Middle and Inferior Pharyngeal constrictor muscles?
Pharyngeal Constrictor MM
Skeletal Muscle
A type of muscle tissue that is under voluntary control and is responsible for movement and posture.
Muscle Function
producing movement, maintaining posture, regulating material entry/exit, and generating body heat.
Fascicle
A bundle of muscle fibers within a muscle.
Myofibril
Structure within a muscle fiber that contains bundles of sarcomeres, helps contract muscle
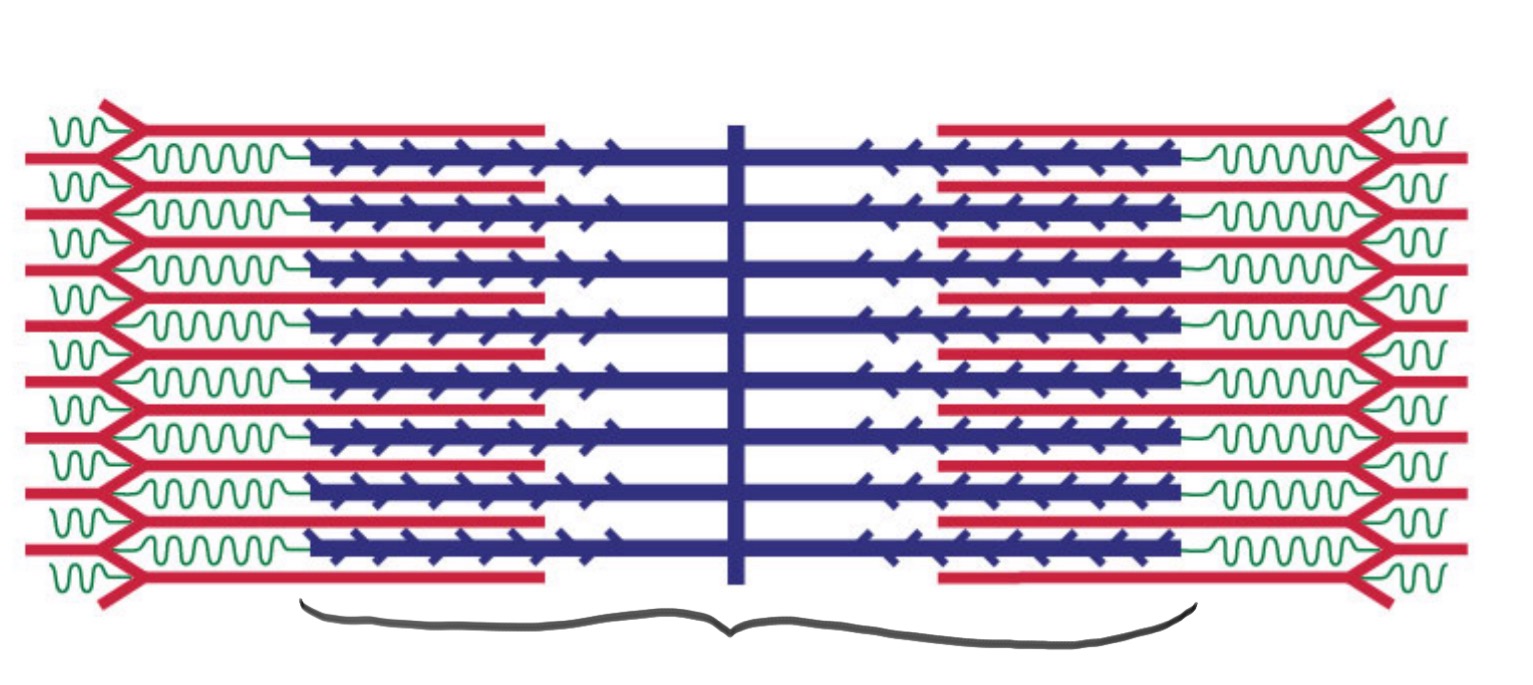
Sarcomere
The basic functional unit of a muscle fiber, is responsible for muscle contraction. (layers)
Myosin
A thick filament protein that interacts with actin to produce muscle contraction.
Actin
A thin filament protein that interacts with myosin during muscle contraction.
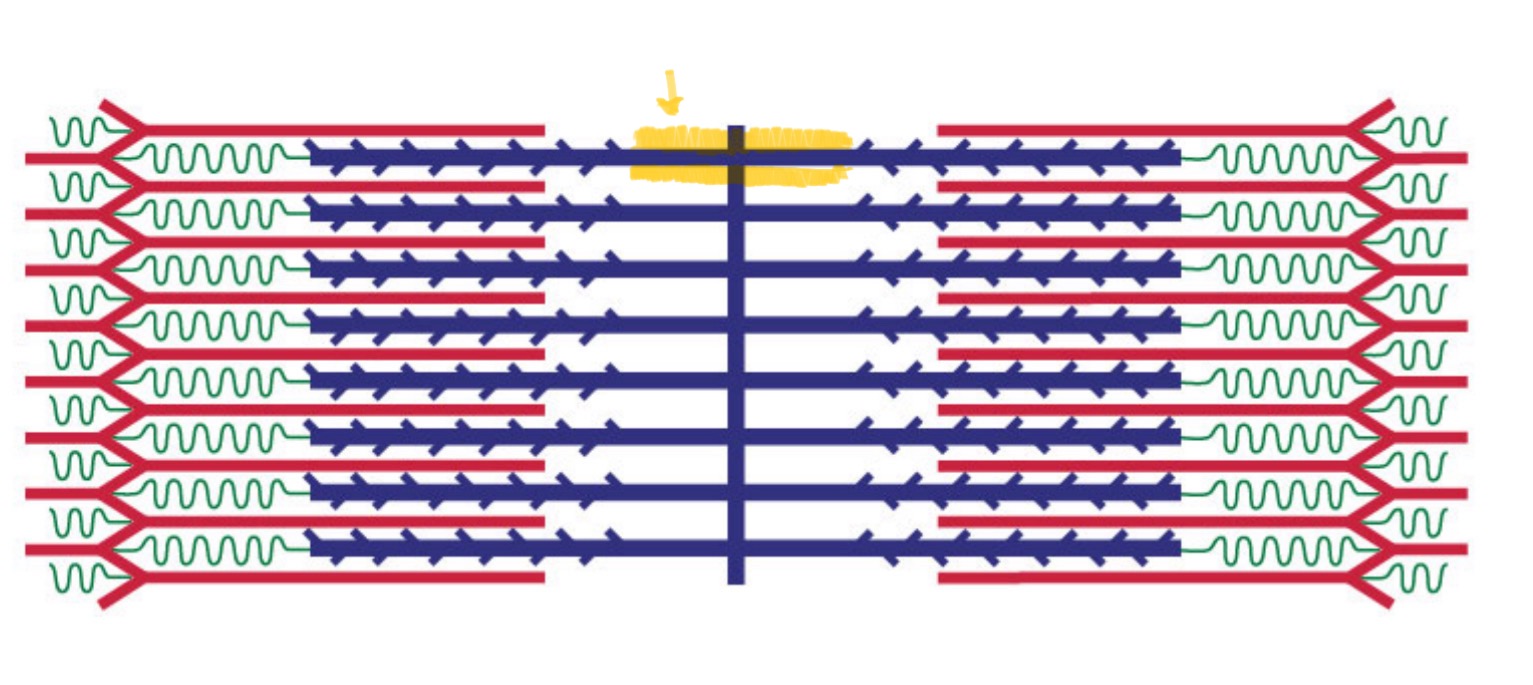
I Band
The light band in a sarcomere where only thin filaments (actin) are present.
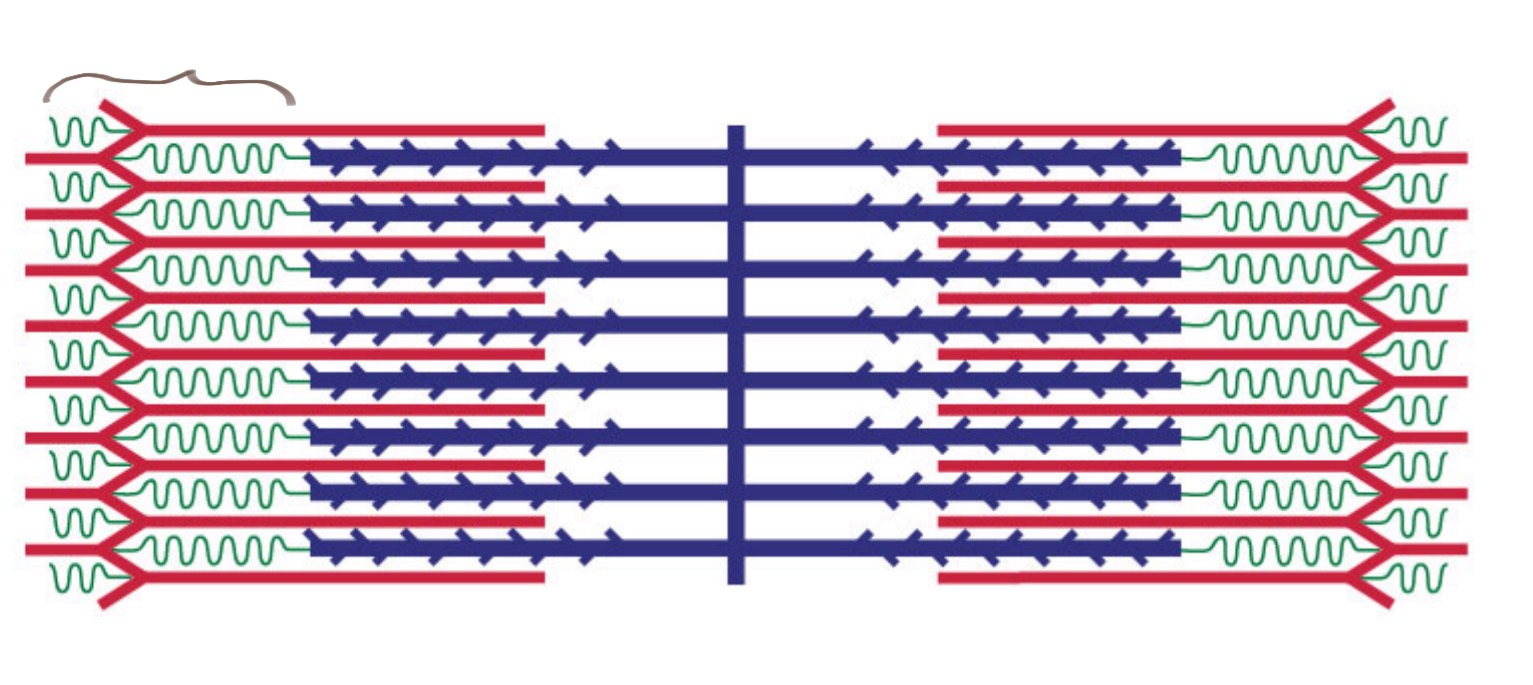
A Band
The dark band in a sarcomere that contains both thick (myosin) and thin (actin) filaments.
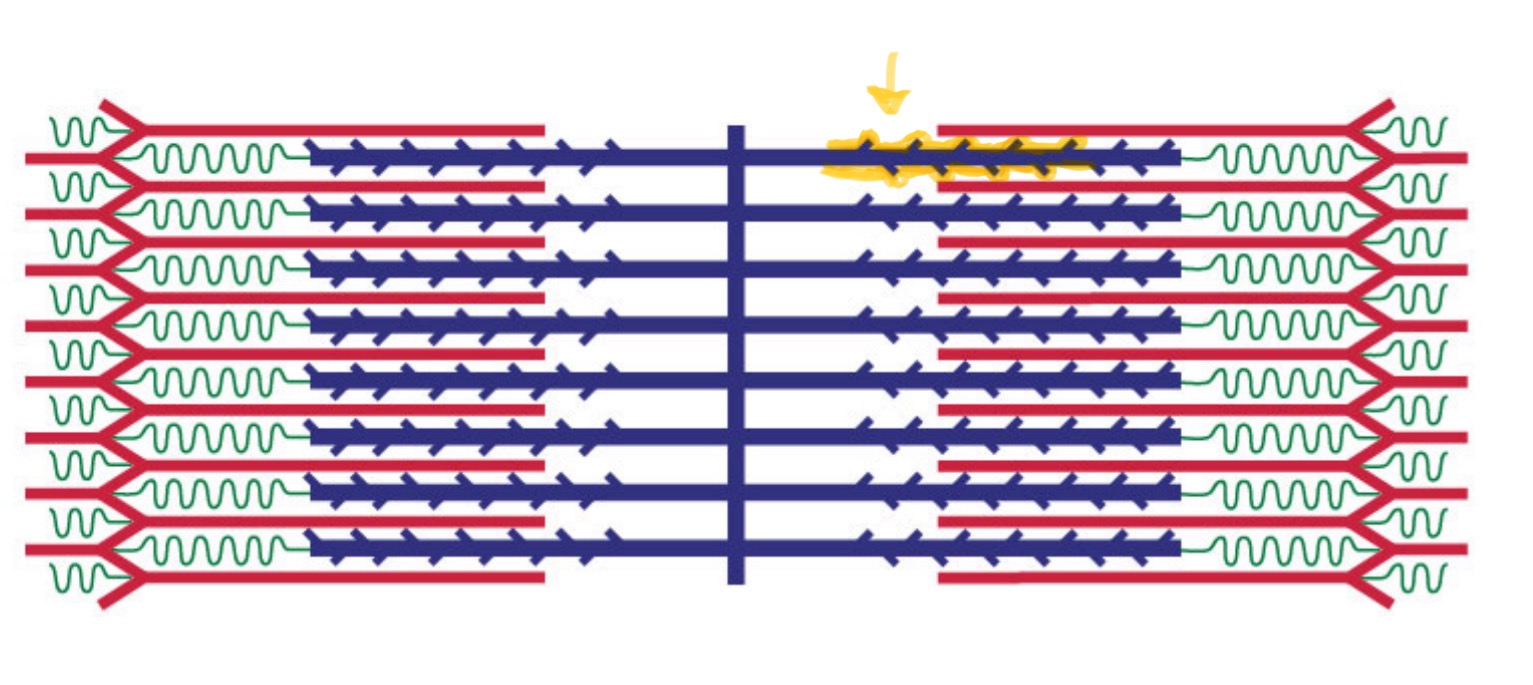
Zone of Overlap
The area in a sarcomere where thick and thin filaments overlap during contraction.
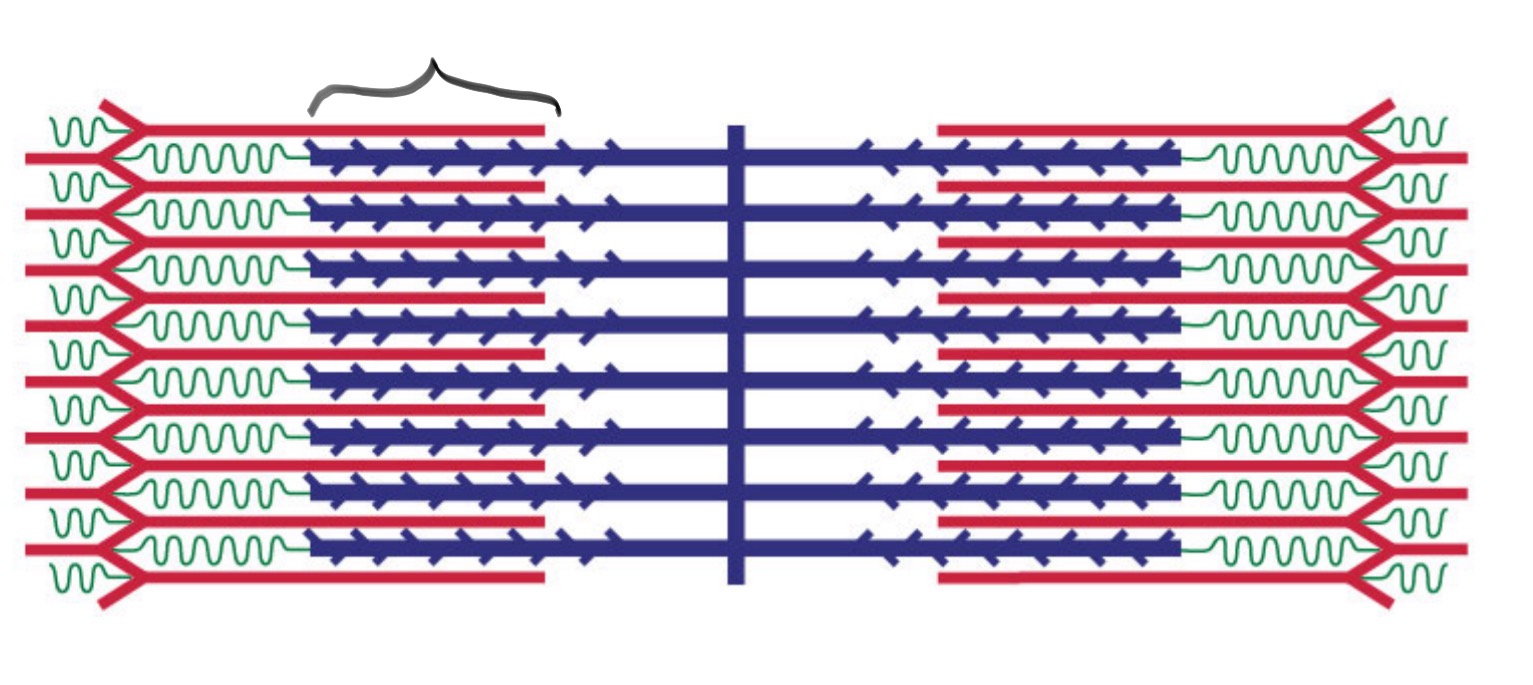
Lever System
The arrangement of bones and muscles that allows for movement at joints.
Origin
The fixed attachment point of a muscle that does not move during contraction.
Insertion
The movable attachment point of a muscle that moves during contraction.
Agonist
The primary muscle responsible for a specific movement.
Antagonist
A muscle that opposes the action of another muscle.
Synergist
A muscle that assists the agonist in performing a movement.
Fixator
A muscle that stabilizes a joint or origin during movement.
Pennate Muscle
A muscle with fascicles that are arranged at an angle to the tendon, increasing strength.
Circular Muscle
A muscle that encircles an opening, such as the sphincters.
Facial Muscles
Muscles responsible for facial expressions, innervated by the facial nerve.
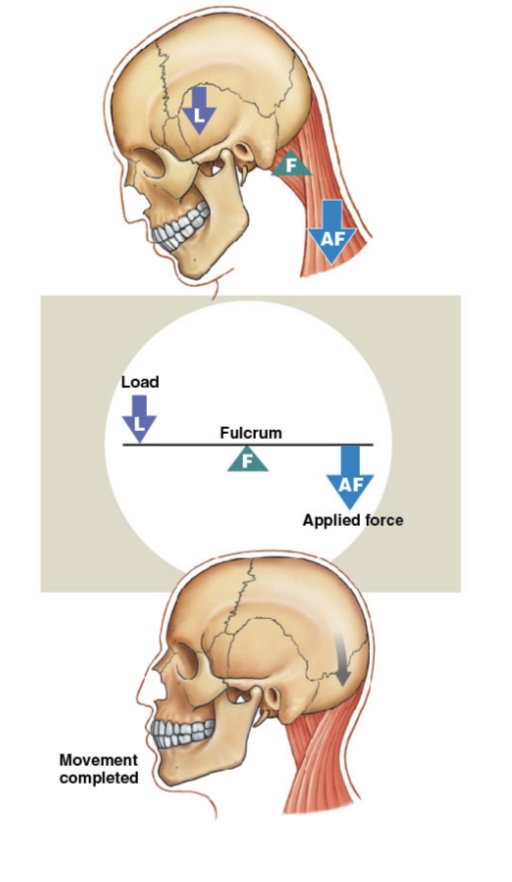
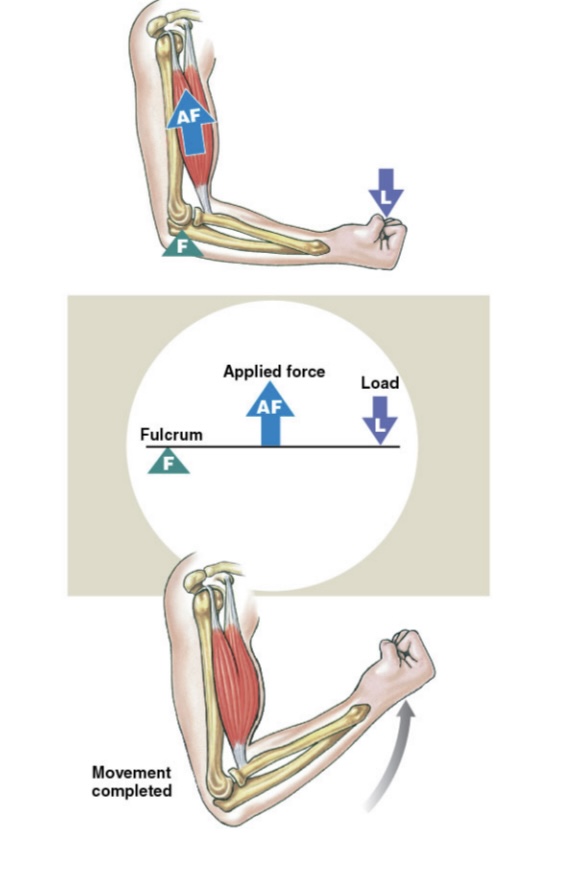
First Class Lever
The Joint is located between force and load. “Seesaw”: Load, Fulcrum, Force
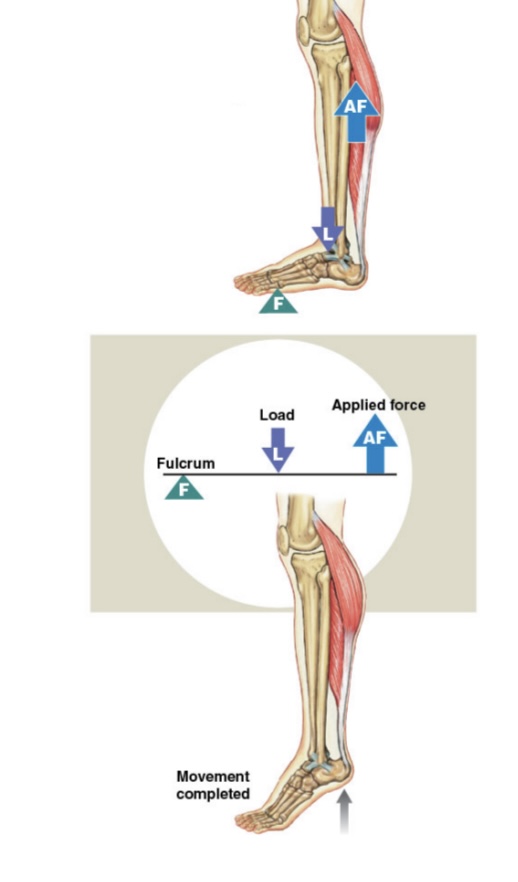
Second Class Lever
Load and force are located on the same side of the fulcrum: Fulcrum, load, force
Third Class Lever
fulcrum, force, load
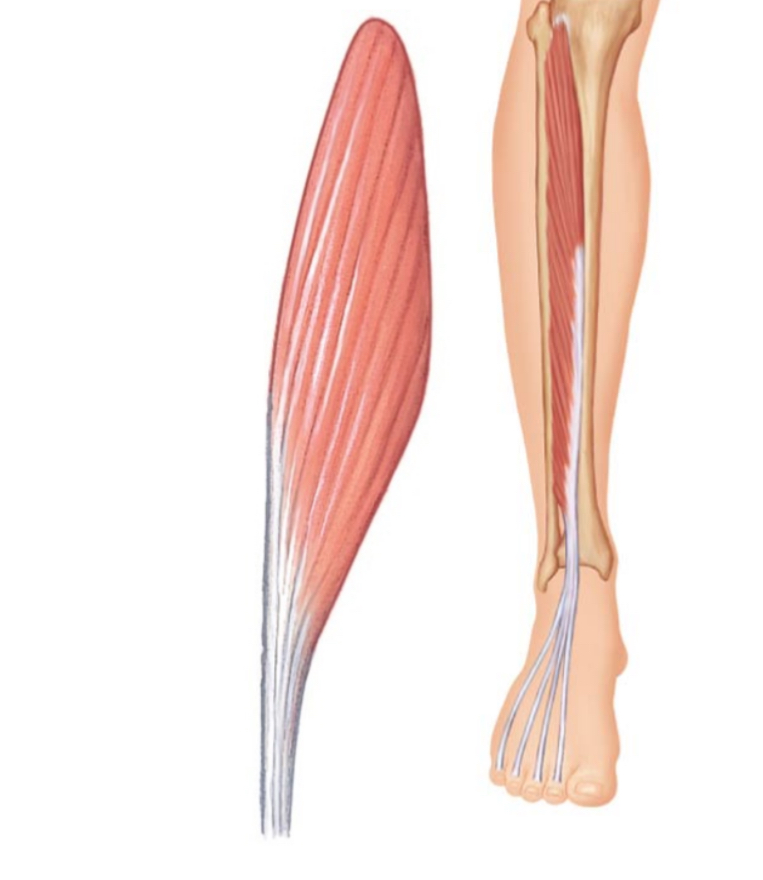
Unipennate
A muscle arranged at one common angle to the tendon
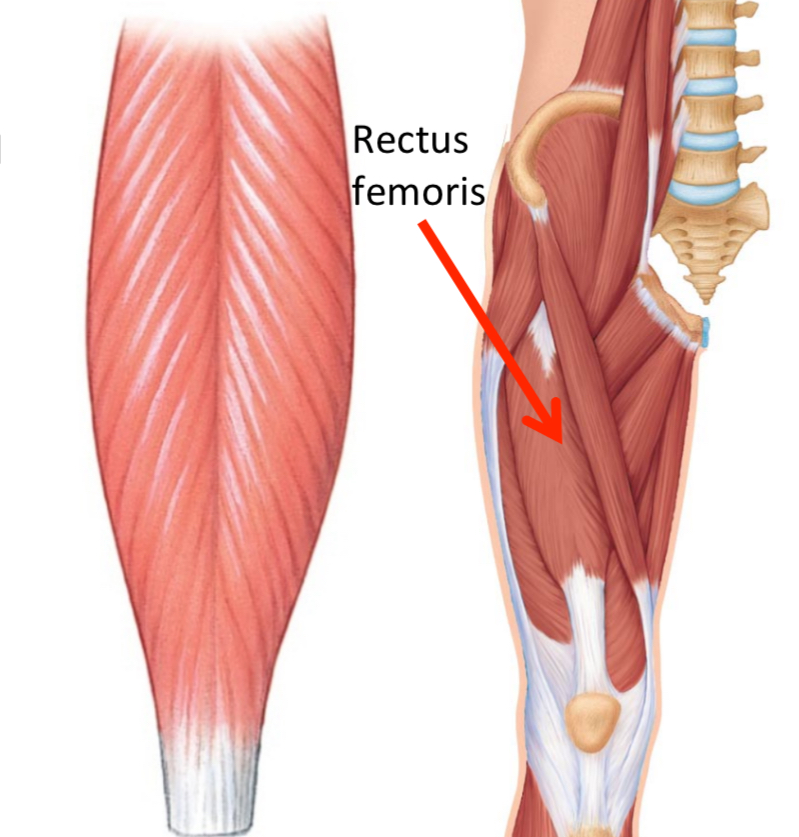
bipennate
2 muscles arranged at two common angles that converge to a tendon
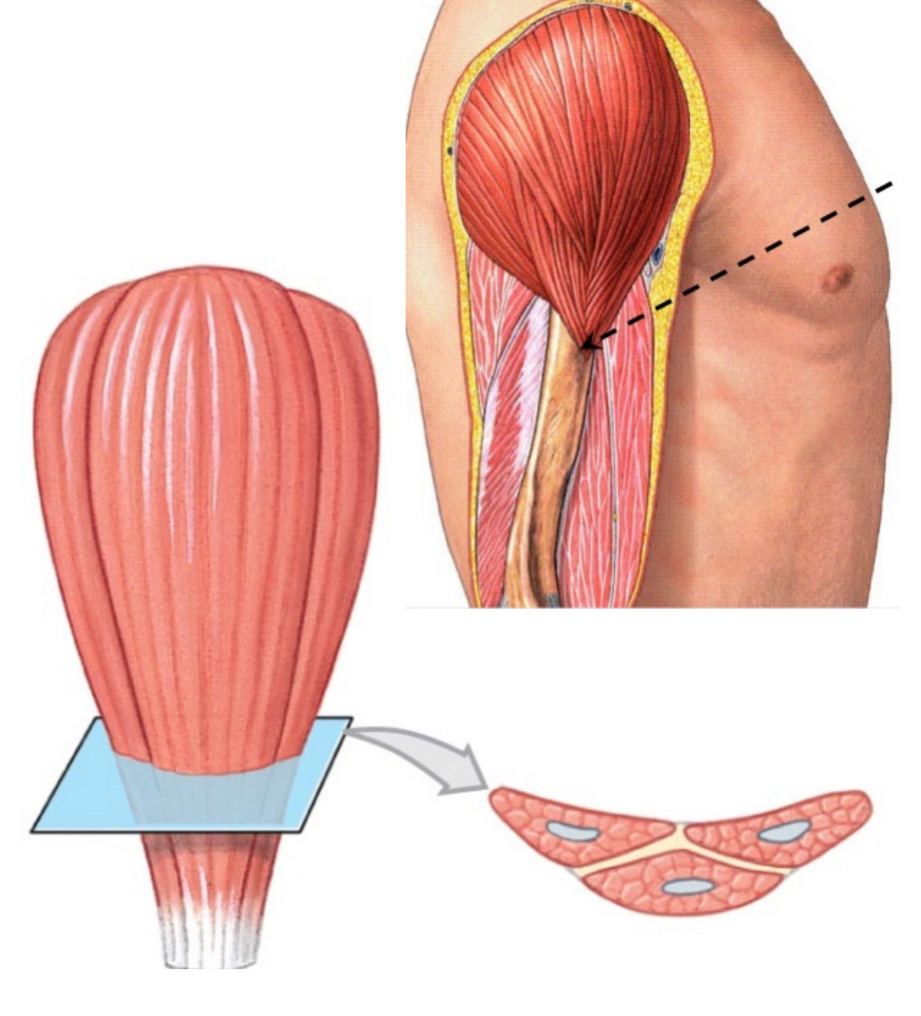
multipennate
Usually, the strongest muscles that are arranged at three or more common angles that converge to a tendon.
Endomysium
connective tissue that holds fascicles and muscle fibers together
Perimysium
connective tissue that holds myofibrils and sarcomeres together
Epimysium
thick connective tissue that surrounds entire muscle
What forms tendons that anchor muscles to bone and skin.
Fascicles, Muscle fibers, sarcomeres
muscle fiber
cell in a fascicle
Muscle cells
multi-nucleated and contain mitochondria
T-tubules
action potential to stimulate muscle contraction
sarcoplasmic reticulum
filled with calcium ions to control contraction, surrounds myofibril, releases calcium from muscle