1 - Multi store model / coding, capacity, duration
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is the MSM (describe)
Describes how info flows through memory system
Coding definition
Info stored in memory in diff forms depending on memory store.
Process of converting info between diff forms = coding
Outline MSM model structure
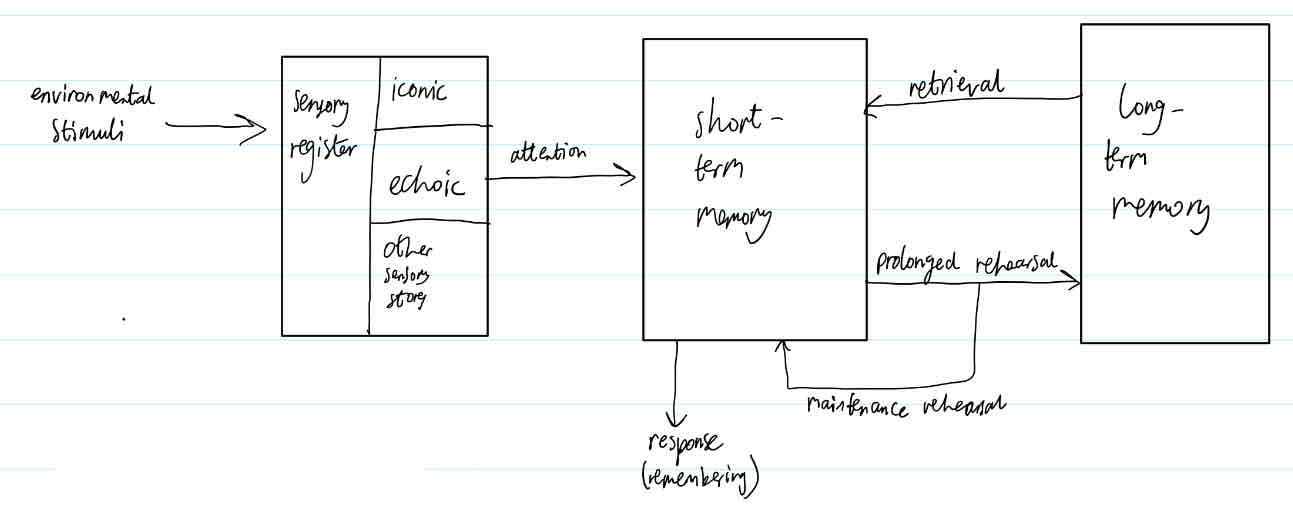
Sensory register
coding
Capacity
Duration
Coding - modality specific (depends on the sense)
Eg iconic codes visual, echoing codes acoustic
Capacity - large
due to millions of sensory receptors
Duration - Limited, less than half a second
Sperling 1960’
Sperling 1960
Shown grid of letters and asked to recall them
Despite only seeing grid for short time, can recall a lot of it,
shows high capacity nature of SR (high capacity)
Recall significantly declined as interval between seeing grid and recall increased. After a second it was virtually impossible
shows fleeting nature (low duration)
STM
coding
Capacity
Duration
Coding - acoustic
baddeley 1966
Capacity
Jacobs 1887
digit span = 9.3
Letter span = 7.3
Miller 1956
About 7 items +- 2
Duration - 18s
Peterson + Peterson 1959
Jacob’s 1887
Start with 4 numbers, researcher adds a number and participant must recall the full list
Until participant can’t recall correctly
Digit span = 9.3
Letter span = 7.3
Strength of Jacob’s 1887
Study has been replicated in 2005 by Bopp and Verhaeghan
Tf increasing external validity
Miller 1956
Observations of everyday practice
Noted that things come in 7s (eg 7 days of week), tf STM capacity = 7 items
Chunking (grouping sets of digits/letters into chunks)
Miller limitation
Overestimated STM capacity
Nelson Cowan 2001 concluded capacity only 4+-1 chunks
Baddeley 1966
Given initial list
Gave second list. 4 diff types of lists to 4 diff groups
Acoustically similar/dissimilar, Semantically similar/dissimilar
Recall original list
Recalling from STM - did worse acoustically similar words - tf STM coded acoustically
Recalling from LTM - did worse with semantically similar words - tf LTM coded semantically
Baddeley 1966 limitations
Low mundane realism = low ecological validity bc in highly controlled lab setting. Participants may not act ass they would irl
Use of artificial stimuli lowers external validity and real life application (comes up later)
Peterson + Peterson (1959)
Participants given consonant syllable (eg YCG)
given 3 digit number to count back from
Would be stopped at varying periods of time
After 18 seconds recall fell to 3%
tf STM duration around 18s
Peterson + Peterson 1959 limitation
Use of artificial stimuli
Doesn’t reflect everyday life
Tf lacks external validity + real life application
LTM
coding
Capacity
Duration
Coding - semantic
Baddeley 1966
Capacity - unlimited
Duration - lifetime
Bahrick 1975
Bahrick 1975
Participants of varying age + yearbook
Various tests = Photo recognition test, free recall test(recalling names)
Recall was better for younger but still present in older
Shows LTM may last up to a lifetime for some material
Strength of Bahrick 1975
High external validity + real life application
Bc investigated meaningful memories
Recall rates lower w/ meaningless pictures
More real estimate of of LTM duration
MSM strengths (2)
Support from case studies showing that LTM and STM are different
Baddeley
COUNTER = not everything is related to words (word lists = artificial stimuli) (eg faces, places)
Tf not valid model of how memory works irl, tf limited application + lacks external validity
Real life application
Prolonged rehearsal + active recall helps w/ revision
MSM limitations (1)
Evidence of more than 1 STM
Shallice + Warrington Studied client w/ amnesia (KF)
Could only recall info when read, not verbal said
Tf only visual store was damaged
Tf model must be more complicated than MSM