Monomers Polymers and Carbohydrates
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Which isomer of glucose is glycogen, amylose, amylopectin and celluose made from
all made from the monosaccharide alpha-glucose except cellulose which is made from beta glucose
What is an isomer?
An isomer is a molecule with the same molecular formula as another molecule but with a different arrangement of atoms.
What are the two isomers of glucose?
Alpha glucose and beta glucose.
What distinguishes beta glucose from alpha glucose?
In beta glucose, the hydroxyl group is at the top and the hydrogen is at the bottom on the carbon 1
Draw alpha glucose and beta glucose
.
What are polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are formed by the condensation of many glucose units, bonded by glycosidic bonds.
Name examples of polysaccharides
Starch, cellulose, and glycogen.
What are the two forms of starch?
Amylose and amylopectin.
Describe the structure of amylose.
Amylose is an unbranched, long chain of alpha- glucose monomers which are joined via 1-4 glycosidic bonds, the angles of the glycosidc bond gives it a helical shape, which means it has a colied-spiral structure
Describe the structure of amylopectin.
Amylopectin is a branched, long chain of alpha-glucose monomers which are bonded via 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
What is the main function of starch?
To store glucose in plants
How does the structure of starch support its function?
Starch is insoluble → it will not affect the water balance of cells so doesn't lead to osmosis
Starch is large→ won't easily diffuse out of cells
Amylose is coiled: allowing compact storage,allowing plants to store a lot of glucose into a small space
Amylopectin has a lot of side branches: which makes it easy for enzymes to hydrolyse the glycosidic bonds and break apart glucose for respiration
What is the structure of glycogen?
Glycogen is branched like amylopectin and made up of alpha-glucose monomers that are joined via 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
What is the main function of glycogen?
To store glucose in animals
How does the structure of glycogen support its function?
Glycogen is insoluble → it will not affect the water balance of cells so doesn't lead to osmosis
Glycogen is large→ so it will not easily diffuse in and out of cells
Glycogen is more branched than starch → this extra branching is important for animals because animals are more active than plants so they need to access energy stores more quickly/ faster hydrolysis
Glycogen is a glucose polymer so provides respiratory substrate for energy release
Glycogen is also coiled so is more compact storing more glucose in less space
Why is it significant that that glycogen has more branches?
More branches means that there are more ends to the molecule which makes it easier to break of glucose molecules for respiration and then to release that stored energy
What is the structure of cellulose?
Cellulose is made from beta-glucose monomers that are joined via 1-4 glycosidic bonds and that form long, unbranched chains, with every other beta-glucose monomer being flipped.
Why is every other beta-glucose monomer flipped in cellulose
This is because when two beta-glucose monomers are next to each other the hydroxyl groups are too far from each other. Therefore one beta-glucose monomer will flip (inverted beta glucose) so that the condensation reaction can take place
How are cellulose chains held together?
Cellulose chains are cross-linked by hydrogen bonds, forming strong bundles called microfibral and several microfibrils make a macrofibral
What is the main function of cellulose?
To provide structural support in plant cell walls.
How does the structure of cellulose support its function?
Its long unbranched chains provide rigidity, and hydrogen bonds give tensile strength.
What is the difference between reducing and non-reducing sugars?
Al sugars can be classified into two categories, reducing and non-reducing sugars
Reducing sugars include all monosaccharides and some dissaccharides such as maltose and lactose
Non-reducing sugars include some disaccharides such as sucrose and all polysaccharides
How do you test for reducing sugars?
Place 2 cm3 of your food sample into a test tube.
Add an equal volume of Benedict's reagent.
Heat the mixture in a gently boiling water bath for 5 minutes.
How do you know if reducing sugar is present?
the mixture will change from a blue solution to a brick red precipitate.
How can you determine the concentration of reducing sugar?
precipitate.
The concentration of reducing sugar determines the colour of this mixture:
Blue - This indicates no reducing sugar is present.
Green - This indicates a low concentration.
Orange - This indicates a medium concentration.
Brick-red - This indicates a high concentration.
This allows you to compare the concentration of reducing sugar between different samples.
What are quantitative methods to determine concentration of reducing sugars?
More accurate methods for comparison:
Use a colorimeter to measure the absorbance of each solution.
Filter the solution and weigh the precipitate
How do you know you need to test for non-reducing sugars?
Non-reducing sugars give a negative result (blue solution) for the normal reducing sugars test.
How do you test for non-reducing sugars?
Carry out the test for reducing sugars, and if the result is negative (turns blue), continue with the next steps.
Add 2 cm3 of the food sample to 2 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid.
Heat the mixture in a gently boiling water bath for 5 minutes (the acid will hydrolyse disaccharides into monosaccharides).
Neutralise the mixture by adding sodium hydrogencarbonate solution.
Retest this mixture using the test for reducing sugars.
If non-reducing sugars were present at the start, the mixture will now change from a blue solution to a brick red precipitate.
How do you test for starch and what is a positive result?
Place 2 cm3 of your food sample into a test tube.
Add a couple of drops of iodine solution and shake.
If starch is present, the solution will turn from orange to blue-black.
What type of bond connects monosaccharides in polysaccharides?
Glycosidic bonds.
What process forms polysaccharides from monosaccharides?
Condensation reaction.
What process breaks down polysaccharides into monosaccharides?
Hydrolysis.
What are monomers of polysaccharides called?
Monosaccharides.
What is the significance of the helical shape of amylose?
It allows for compact storage of glucose in plants.
Create a table with the all the difference and similarities of the four polysaccharides: include the source, the monomer it is made from, the bonding, the branches and the shape
.
What are the bonds of cellulose, amylose, amylopectin and glycogen?
Cellulose: 1-4
Amylose: 1-4
Amylopectin: 1-4 and 1-6
Glycogen: 1-4 and 1-6
What does the evidence of evolution show us the monomers and polymers of life?
The theory of eveolution is that organisms have changed and diversified over time, however the biochemical basis of life is similar for all living things. They all contain the same groups of carbon-based compounds that interact in similar ways.
Monomer
The smaller units from which large molecules are made.
Examples of monomers
Glucose
amino acids
nucleotides
glucose
Polymer
Molecules made from a large number of the same or similar monomers which are joined together.
Examples of polymers
starch
protein
polynucleotides
What is a condensation reaction?
A reaction that joins two molecules together with the formation of a chemical bond and involves the elimination of a molecule of water.
What is a monosaccharide?
The monomers from which larger carbohydrates are made.
Give the common monosaccharides
Glucose, fructose, and galactose.
Process of bonding two monosaccharides
Carry out a condensation reaction:
get your two monosaccharides (this could be alpha glucose and alpha glucose or alpha glucose with fructose etc. it just has to be two monomers from which larger carbohydrates can be made)
2. find where there is a OH on one and OH on the other
3. Remove one hydrogen (H) and one OH to produce the water
4. bond the two monosaccharides together with the oxygen (O) that was left behind
5. Your result is a disaccharide which is bonded together by a glycosidic bond.
What does the condensation of monosaccharides lead to
leads to the formation of disaccharides with a glycosidic bond
What are disaccharides?
Formed by the condensation of two monosaccharides.
Glycosidic bond
The bond that connects two monosaccharides in a disaccharide.
Draw the condensation reaction between alpha glucose and alpha glucose (must know alpah glucose structure)
.
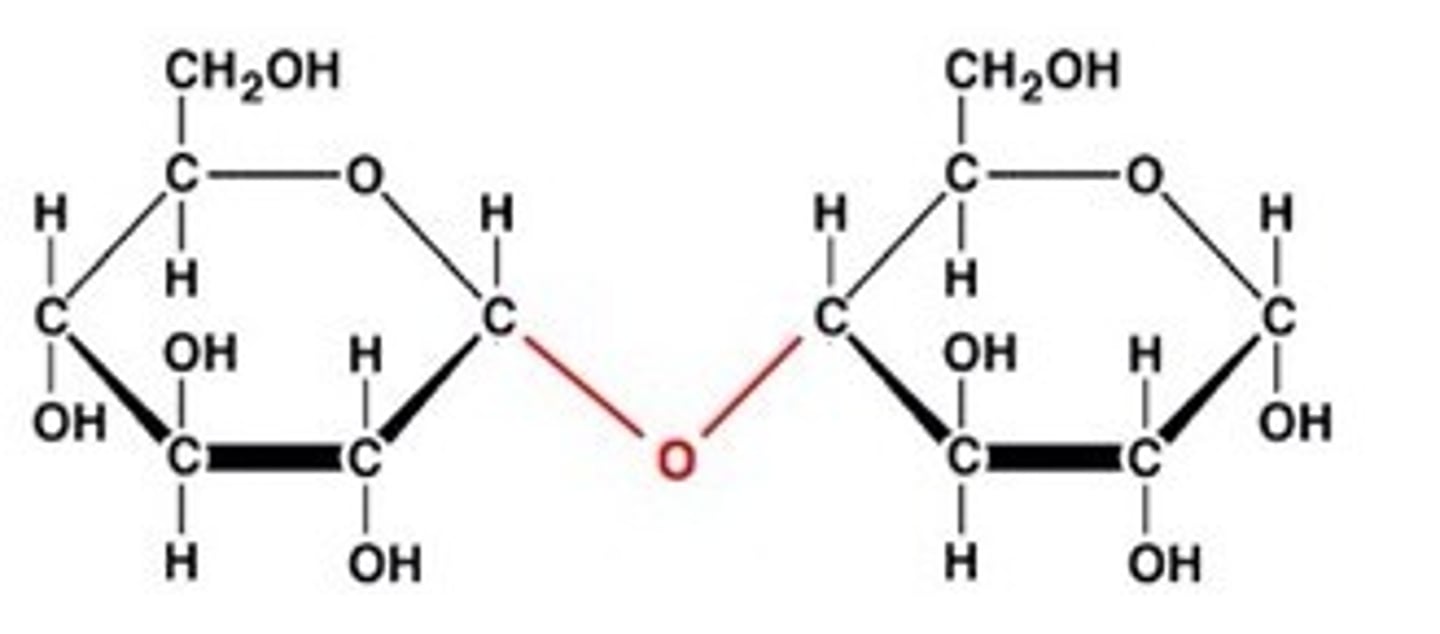
Draw the condensation reaction between alpha glucose and fructose (don't need to know fructose)
.
Draw the condesation reaction of alpha glucose with galactose (don't need to know galactose)
.
What is a hydrolysis reaction?
A reaction that breaks a chemical bond between two molecules and involves the use of a water molecule.
What is maltose composed of?
A disaccharide formed by the condensation of two alpha glucose molecules.
What is sucrose composed of?
A disaccharide formed by the condensation of an alpha glucose molecule and a fructose molecule.
What is lactose composed of?
A disaccharide formed by the condensation of an alpha glucose molecule and a galactose molecule.
How are disaccharides formed?
Occurs through the condensation of two monosaccharides.
Alpha glucose
One of the isomers of glucose
What reaction needs to take place to return the disaccharides into monosaccharides?
hydrolysis reaction
Process of breaking a disaccharide
1.add water to the glycosidic bond
2.onehydrogen (H) will go to the oxygen (O) of one monosaccharide and the OH that is left will join with the other monosaccharide
3. you are then left with the two monosacchardies separated
Result of hydrolysis
Two separate monosaccharides are produced.