Ruggeri Science Olympiad Dynamic Planet: Glaciers
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Cirque glacier
glacier formed in a bowl shaped depression in mountains
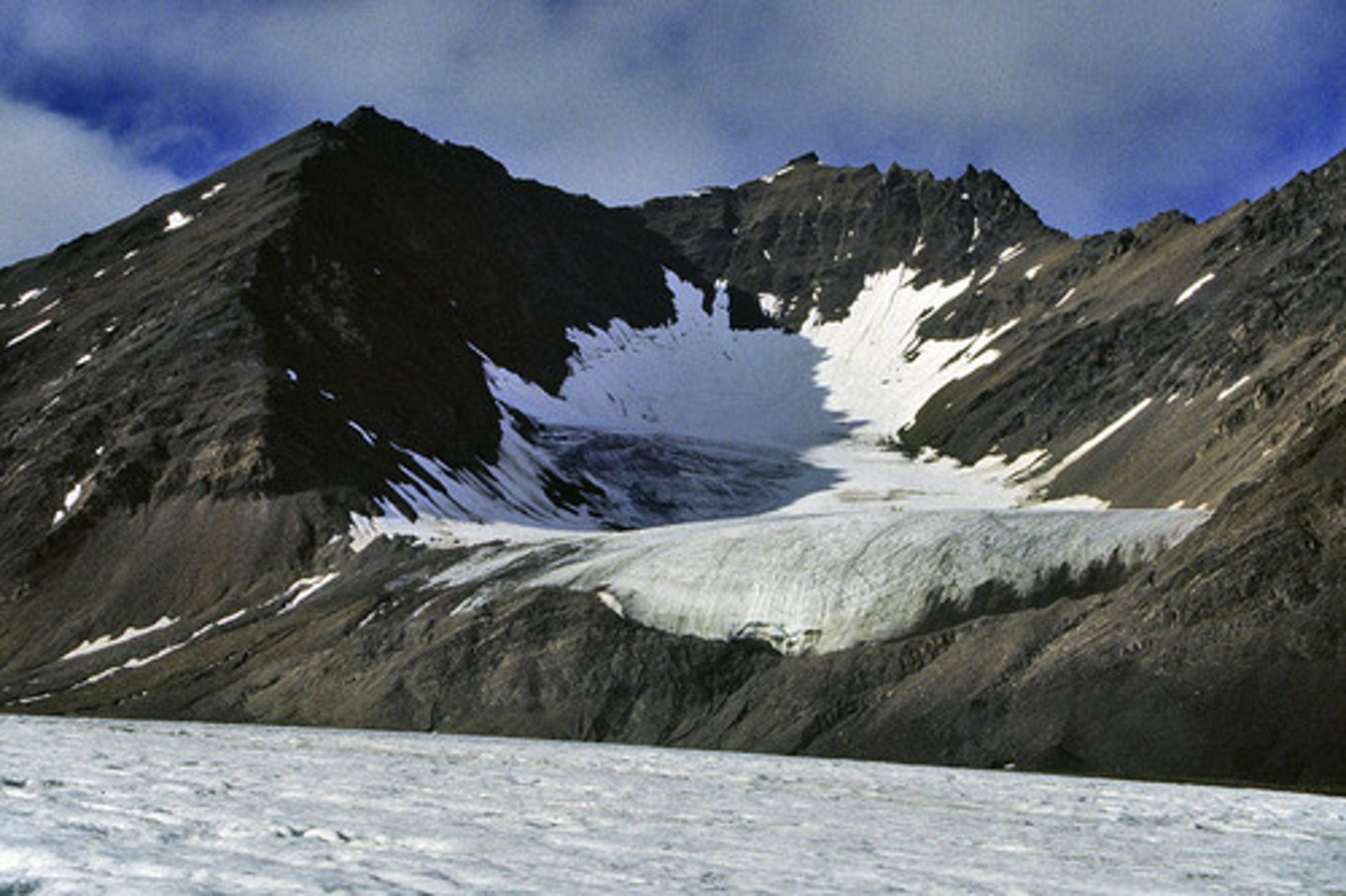

valley glacier
glaciers that flow through valleys in mountains, these are sometimes cirque glaciers that escaped their depression.
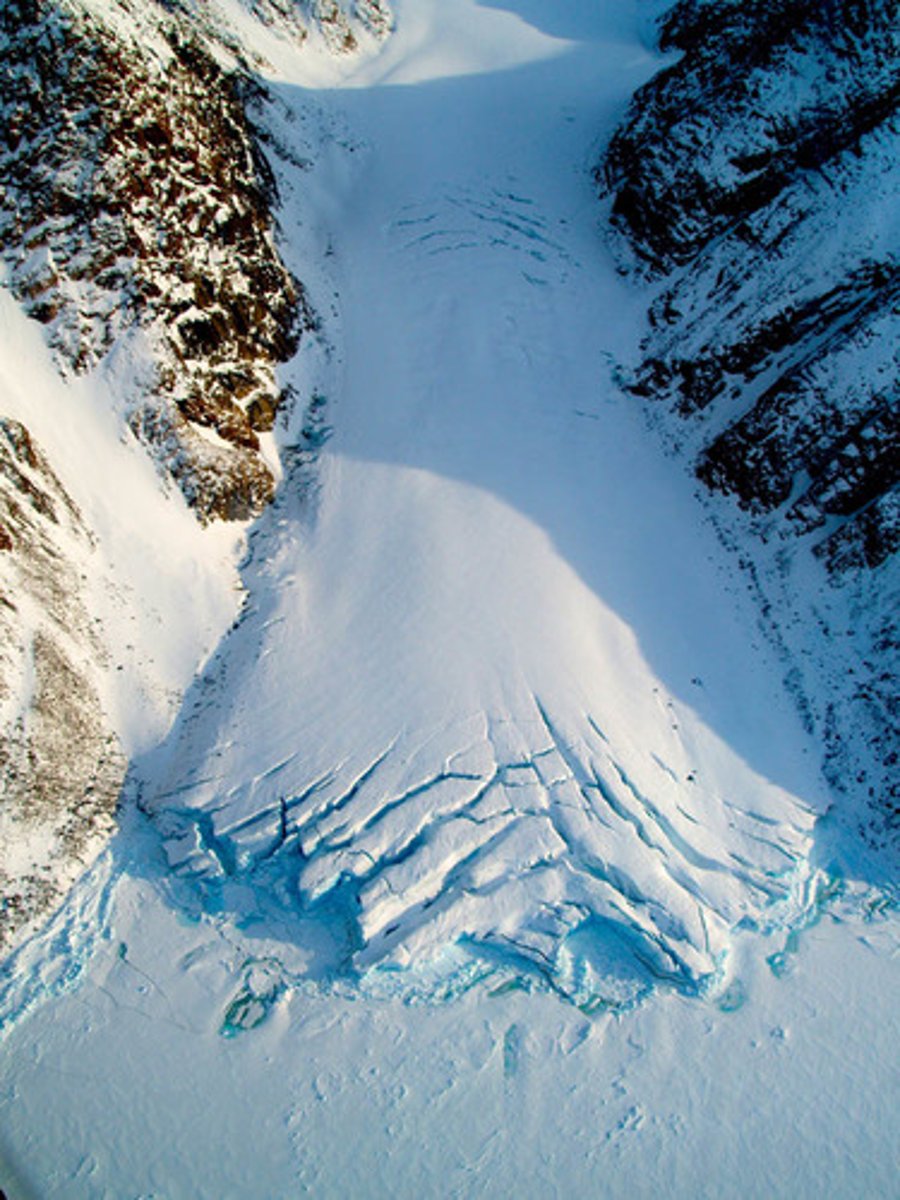

Piedmont glaciers
a valley glacier that flows out into an open field, they usually spread out into a fan, or a bulb shape. When multiple of these come together, they form ice fields and ice sheets.
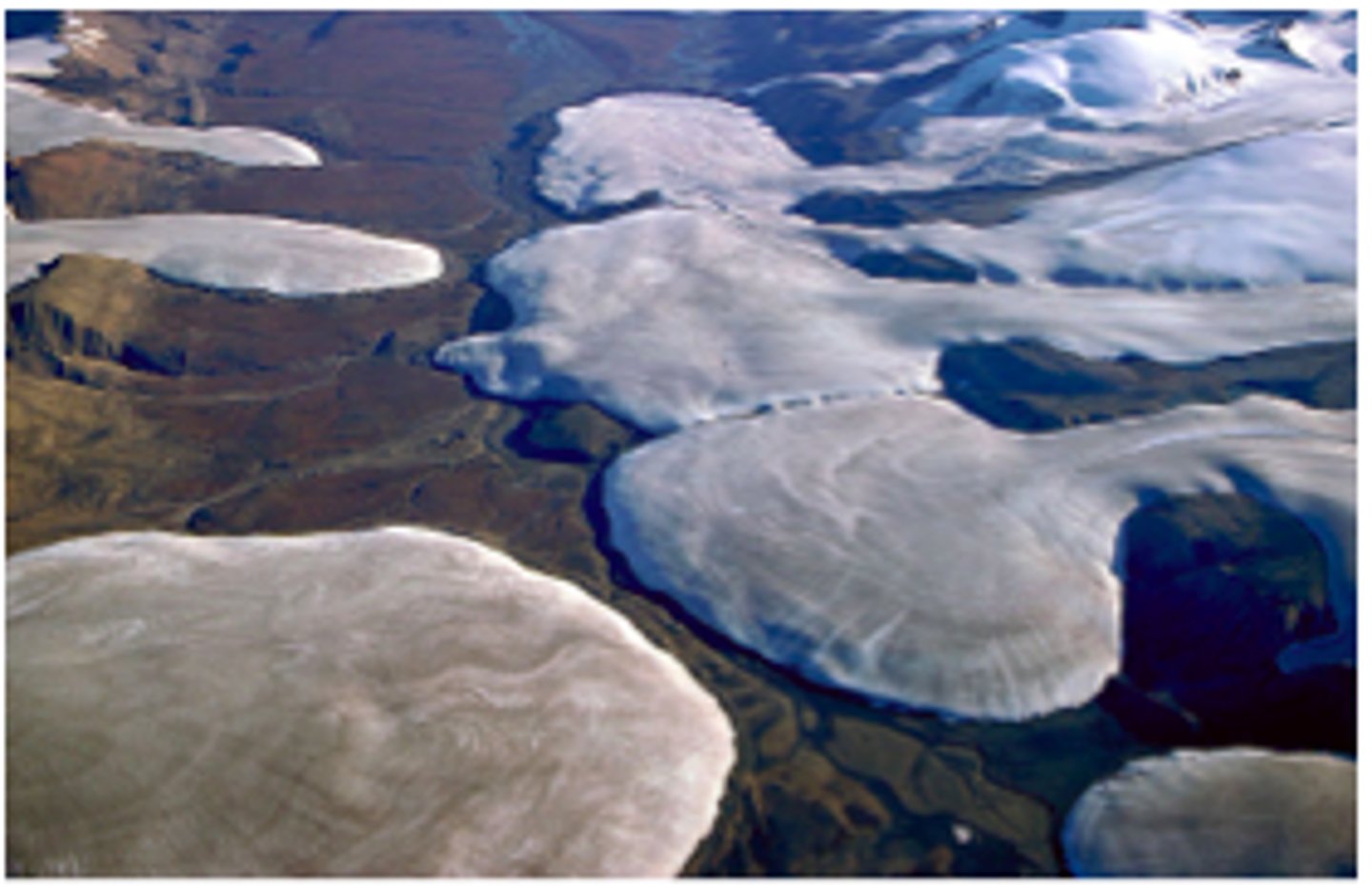

ice fields
large areas of interconnected glaciers, they usually cover everything but the mountain peaks, which are called nunatuks when they stick out of the ice.
outlet glaciers
when ice fields feed out ice to a valley beyond the coverage of the ice field.
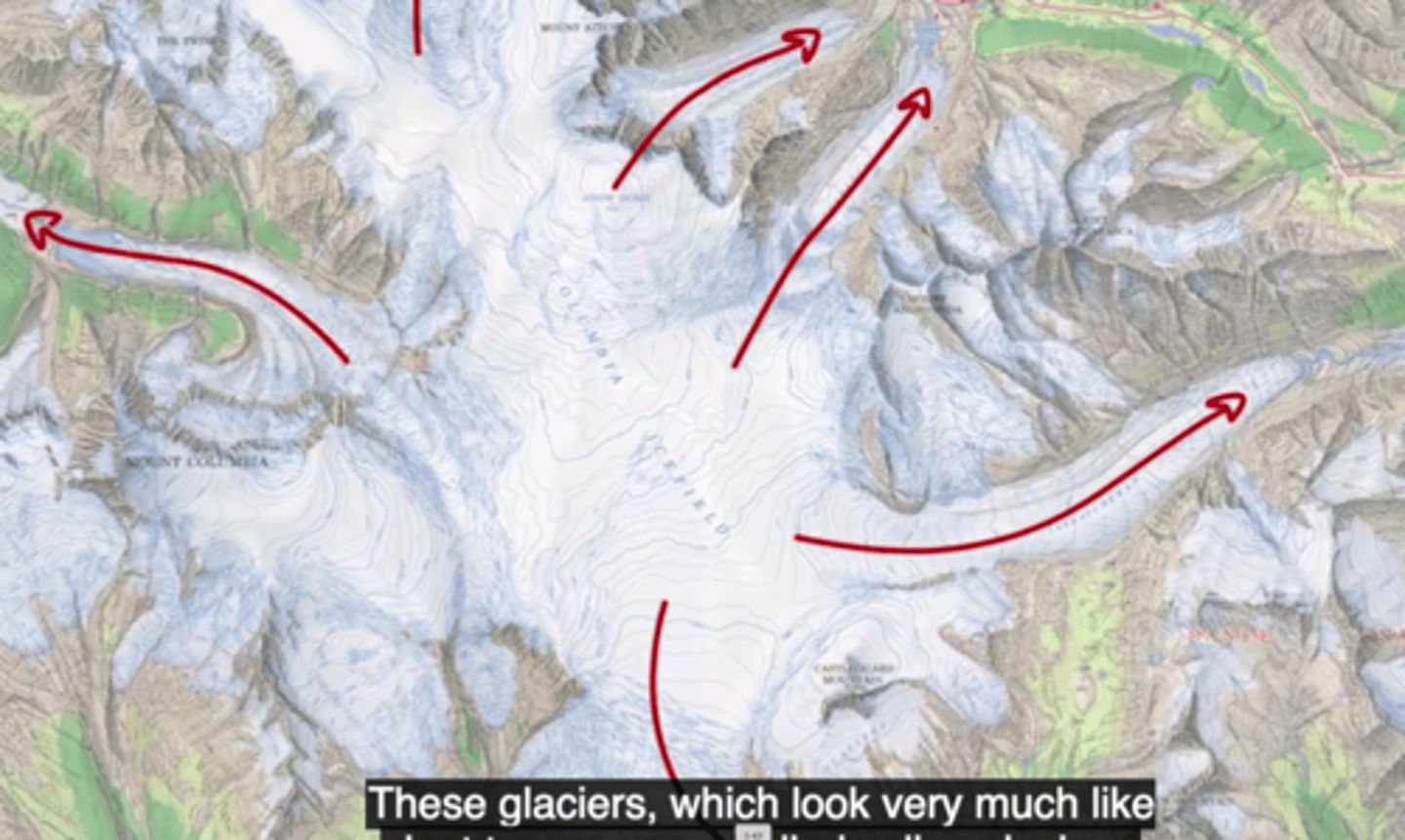
tidewater glaciers
when a glacier reaches a water body, and it terminates at the shore line, and starts calving pieces into the ocean.
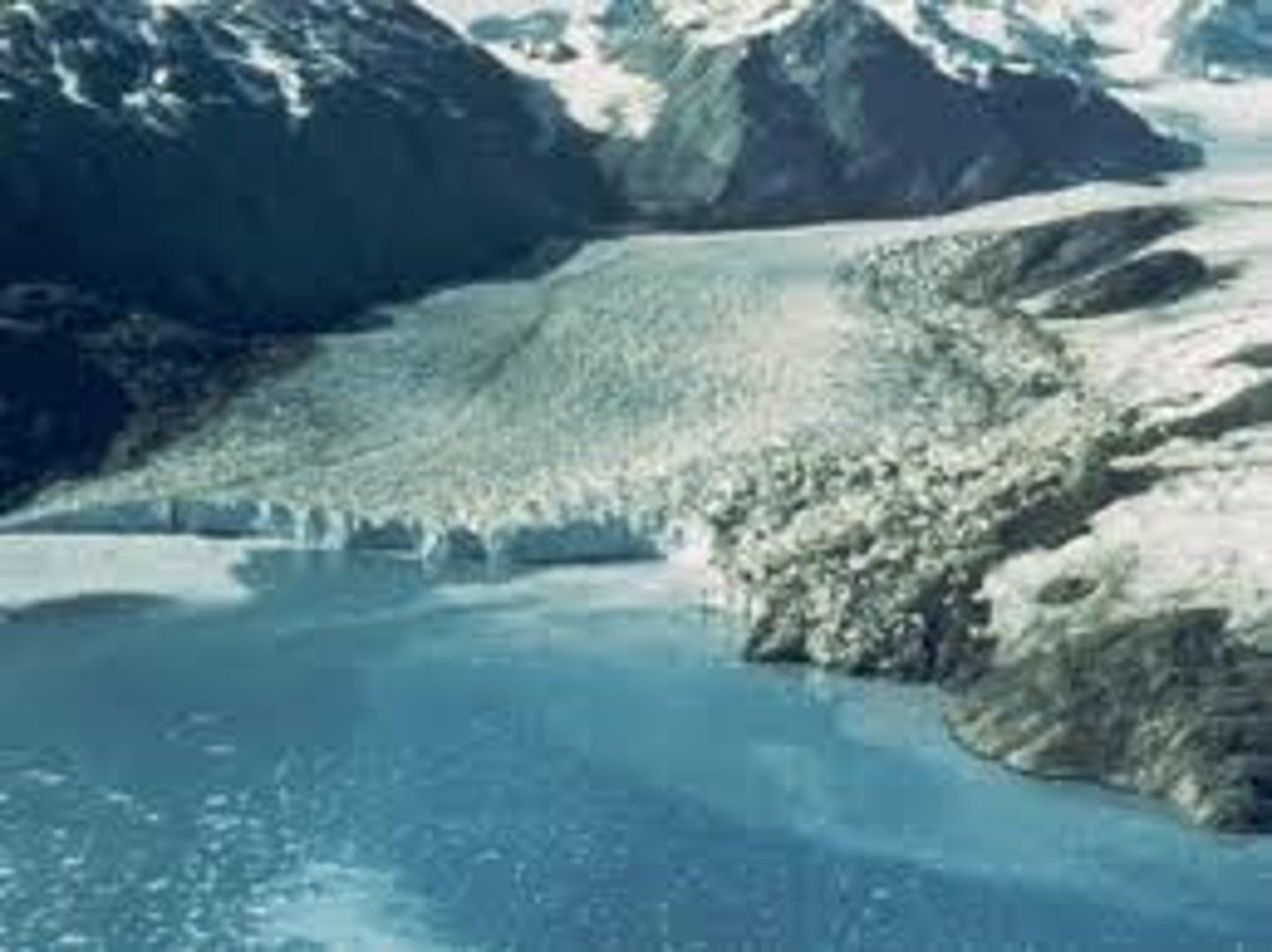

hanging glacier
when a valley glacier retreats to a high plain, but a part is still resting on the slope of the previously carved valley.
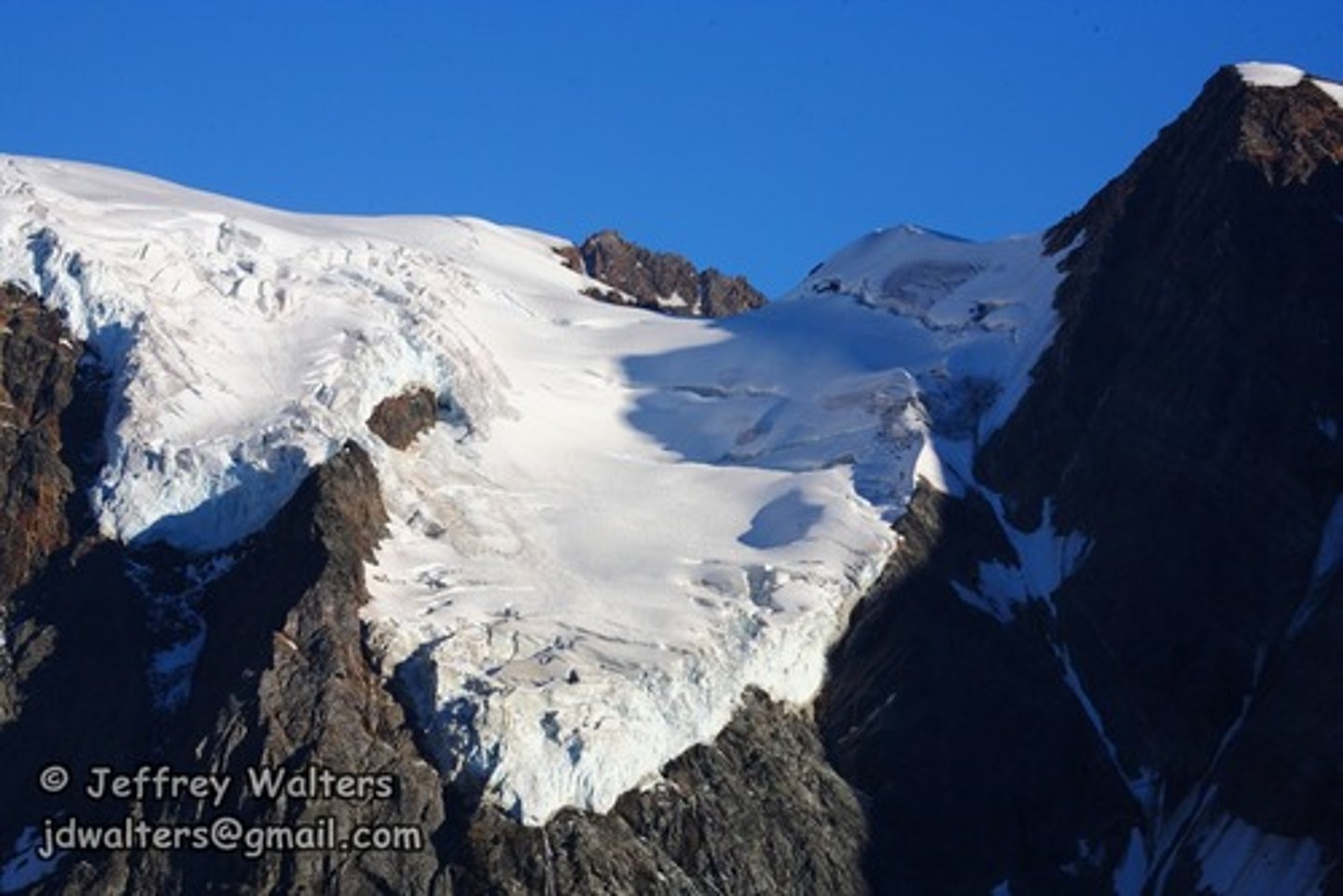

ice streams
narrow and flat parts of a glacial system that flows much faster then the glacier, they are heavily crevassed and are known to have abrupt shear margins.
ice sheet
a mass of glacial land ice greater than 50,000 km^2
subglacial lakes
lakes contained deep within the layers of an ice sheet
ice shelves
glacial ice that is connected to a landmass, and floats, or extends out towards the sea.
ice rise
when ice gets on top of rock in the seabed, these happen to ice shelves, they are usually dome shaped.
ice cap
a mass of glacial ice that covers less than 50,000 km^2
ice tongue
a long and narrow sheet of ice projecting out from the coastline to the ocean.
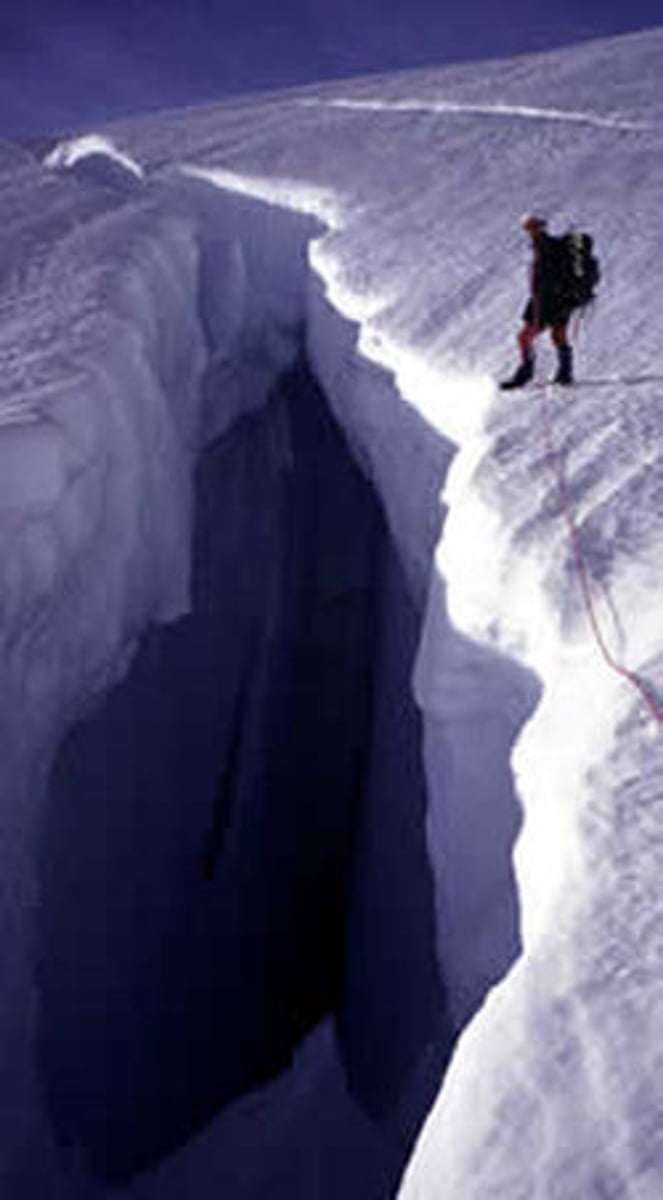
crevasses
cracks in a glaciers surface usually caused by moving over a rocky terrain {indicates the glacier is flowing over rocky terrain}

icefalls
when a glaciers flow through a really steep surface or has to squeeze through a tight space, and moves really fast and stretches and thins and becomes heavily crevassed. {indicates flow is down a steep surface or into a tight space}
ogives
Alternating bands of light and dark ice that forms ridges. Dark= summer, Light=winter. They kind of bend towards the middle. {indicates the middle of the glacier flows faster than the sides}
cirque
A bowl shaped basin carved by a glacier (erosional)
tor
a high rock, a high rocky hill, or pile of rocks
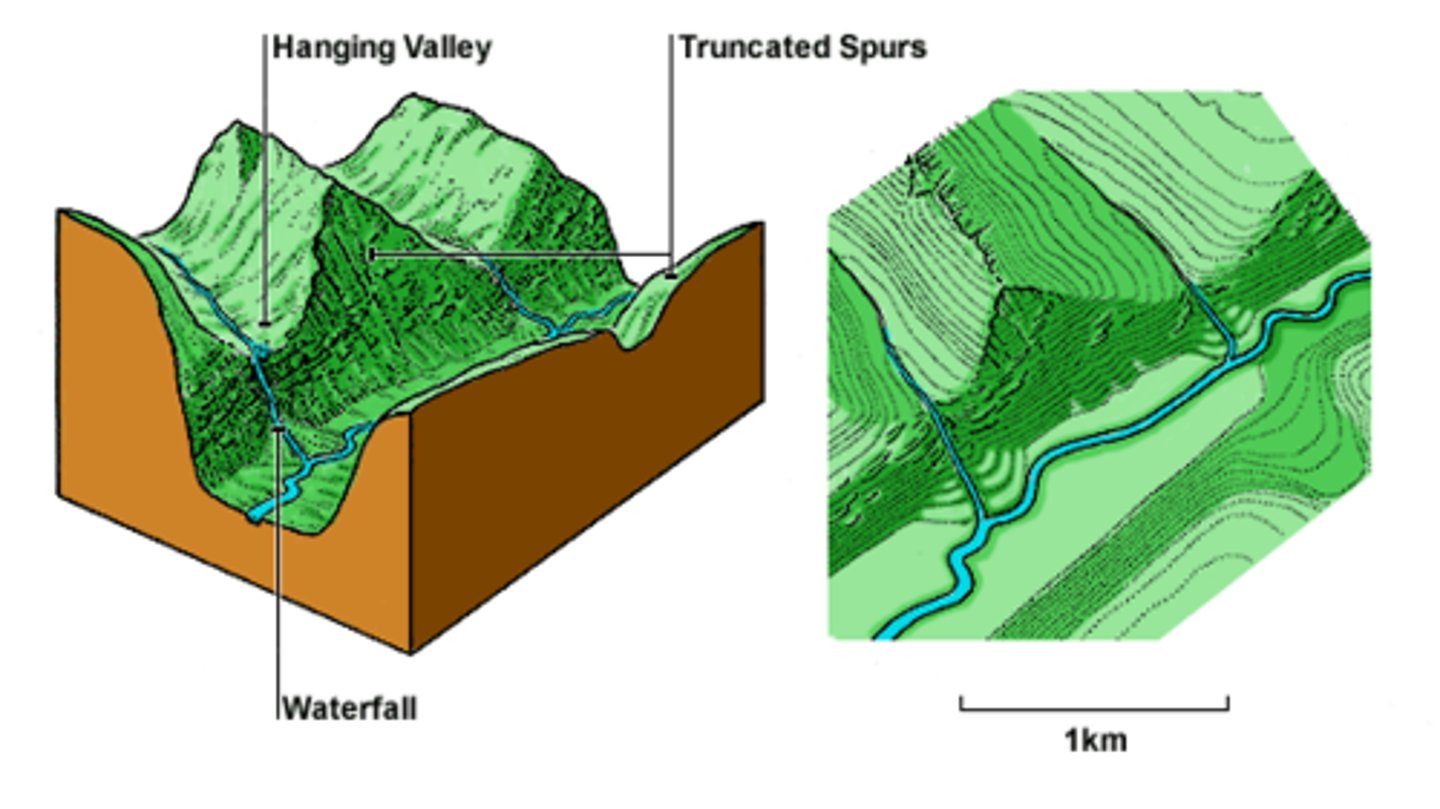
u-shaped valley
The shape of a valley formed by the erosion of a glacier
hanging valley
A valley left by a melted tributary glacier that enters a larger glacial valley above its base, high up on the valley wall.
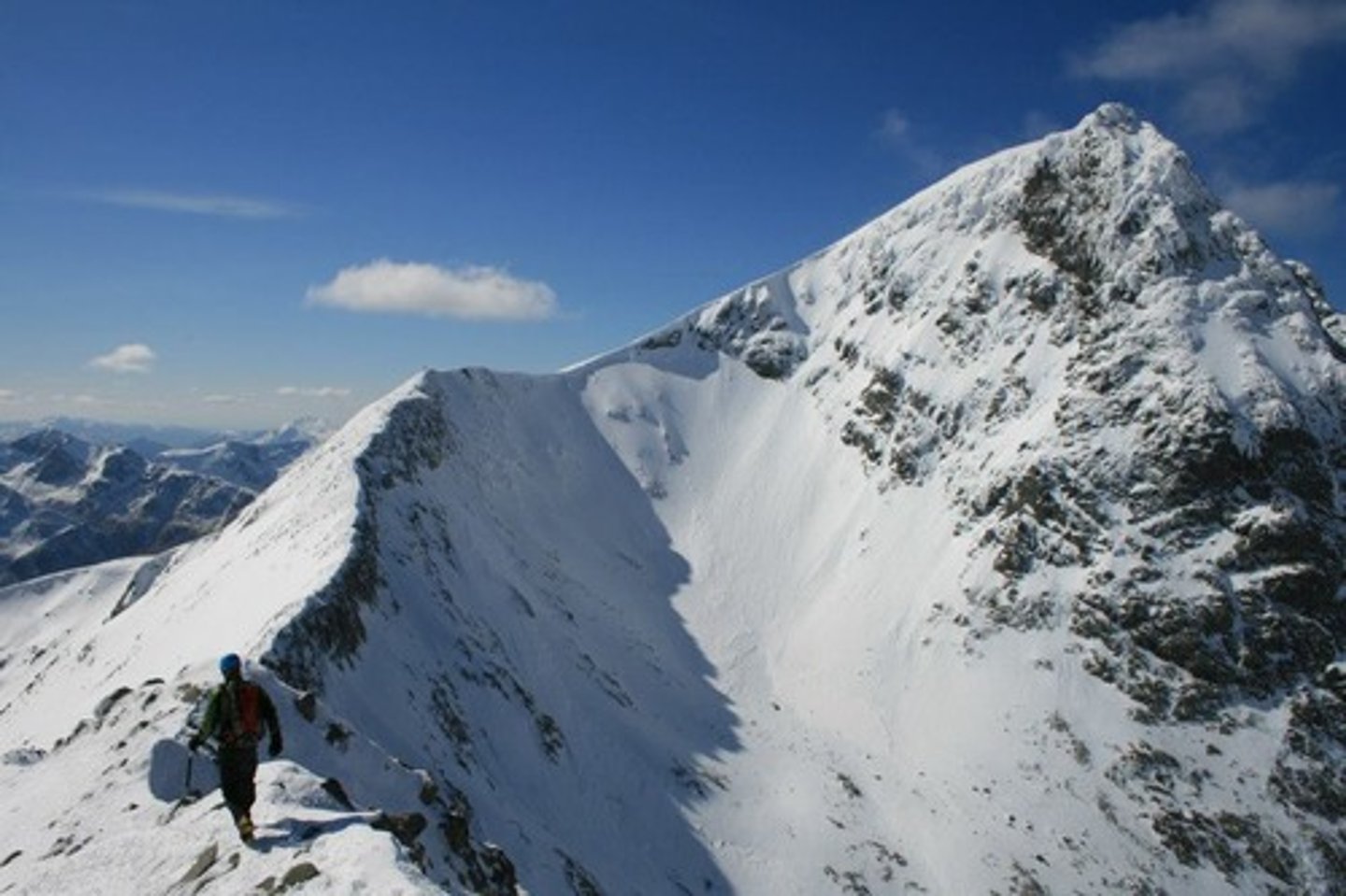
arete
a sharp parallel ridge of rock formed when two cirque glaciers come together but don't join.

horns
a pyramidal peak that forms when three or more cirque glaciers that come together.
Grooves & striations
they are gouged and scratched into the bedrock as the glaciers move downstream.
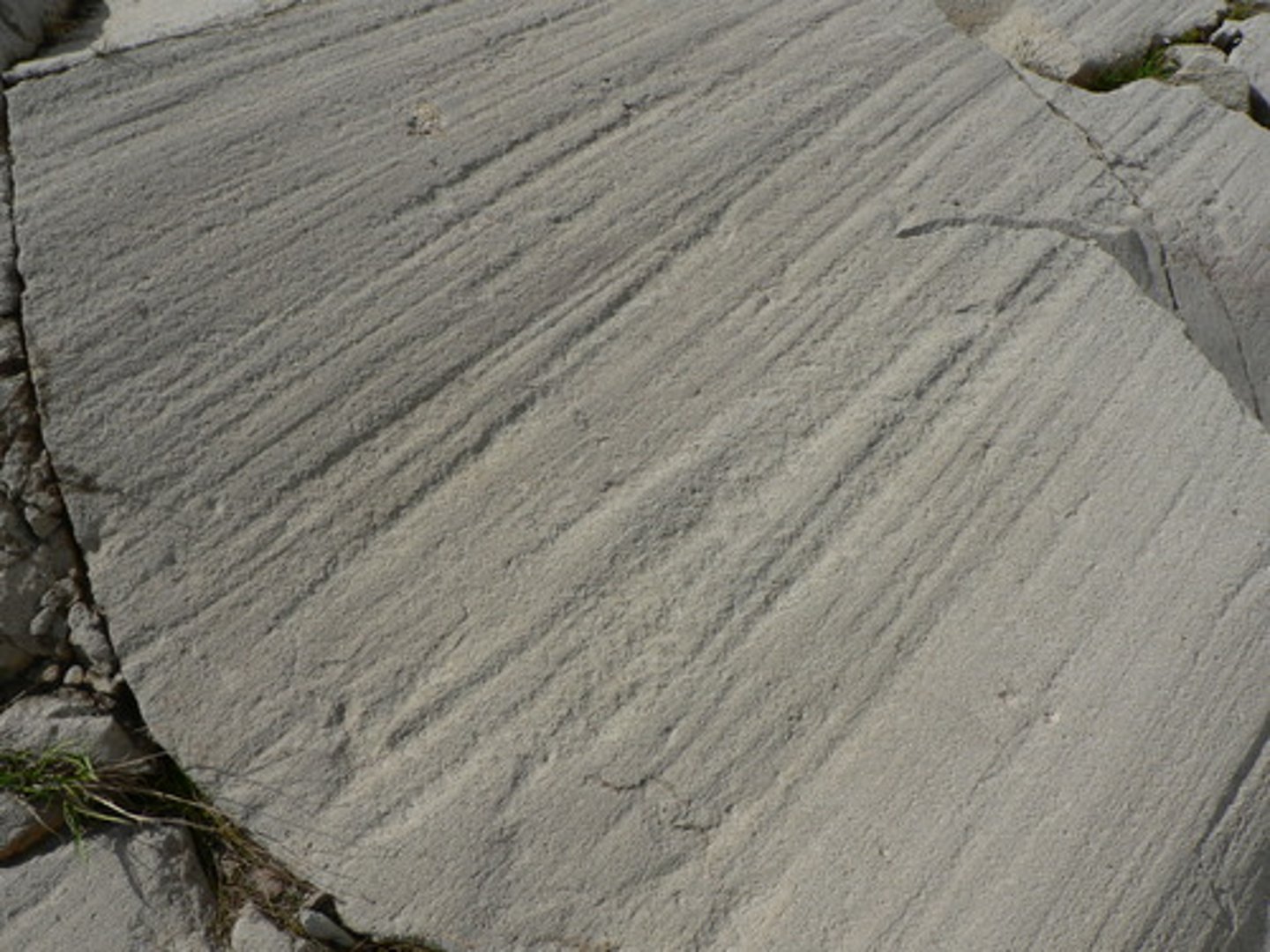

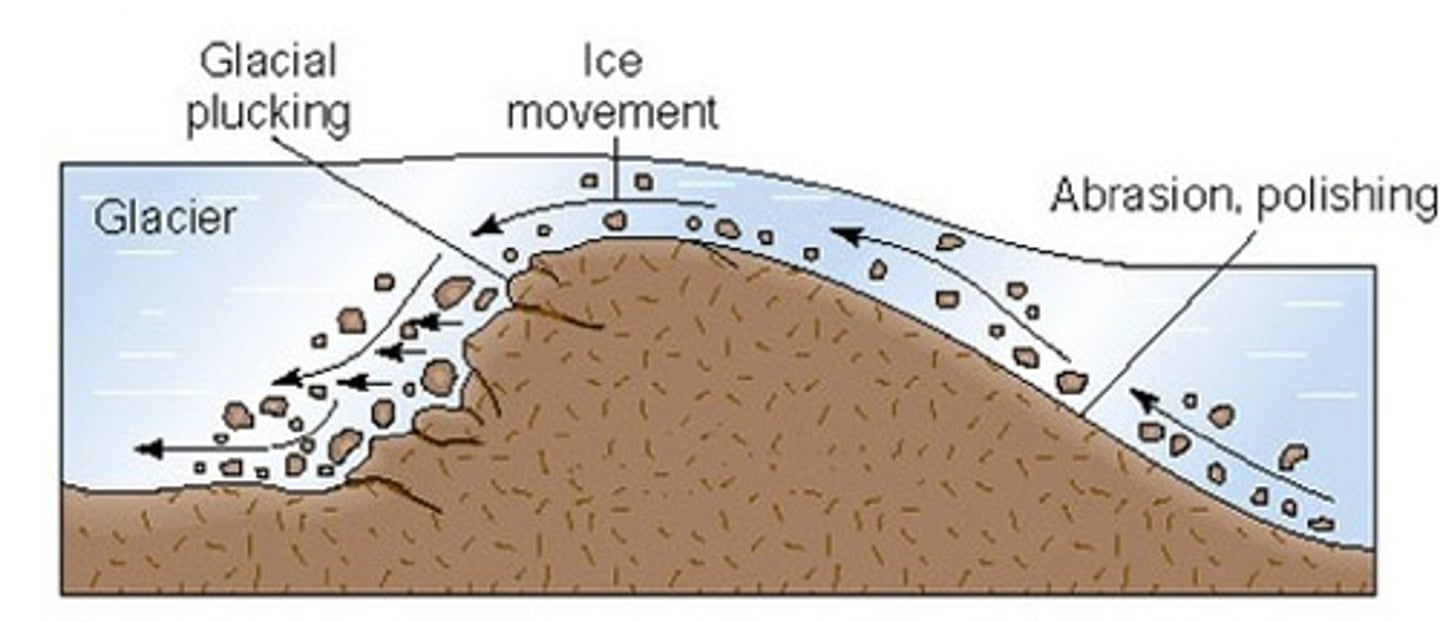
roche moutonnee
a knob of bedrock that is carved into an asymmetrical hill, and in the "stoss" end, the glacier smooths it out by abrasion, and the "lee" end, the glacier does plucking.
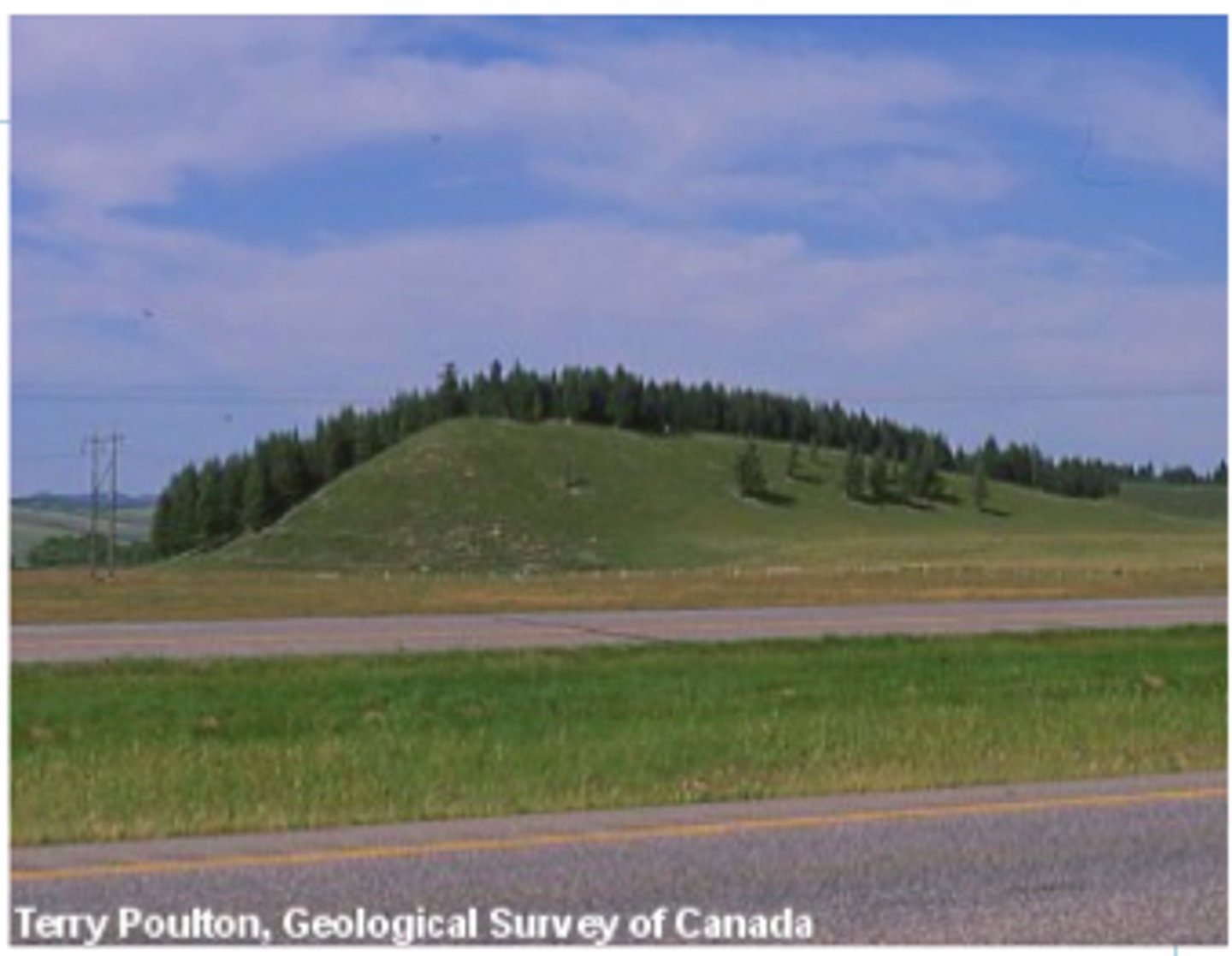
drumlins
small hill or mound in a streamlined shape that is made out of deposited till. Stoss end is the steep side with a possible resistant rock, and the lee end is the smoothed out end. The ice flow is from stoss end to lee end

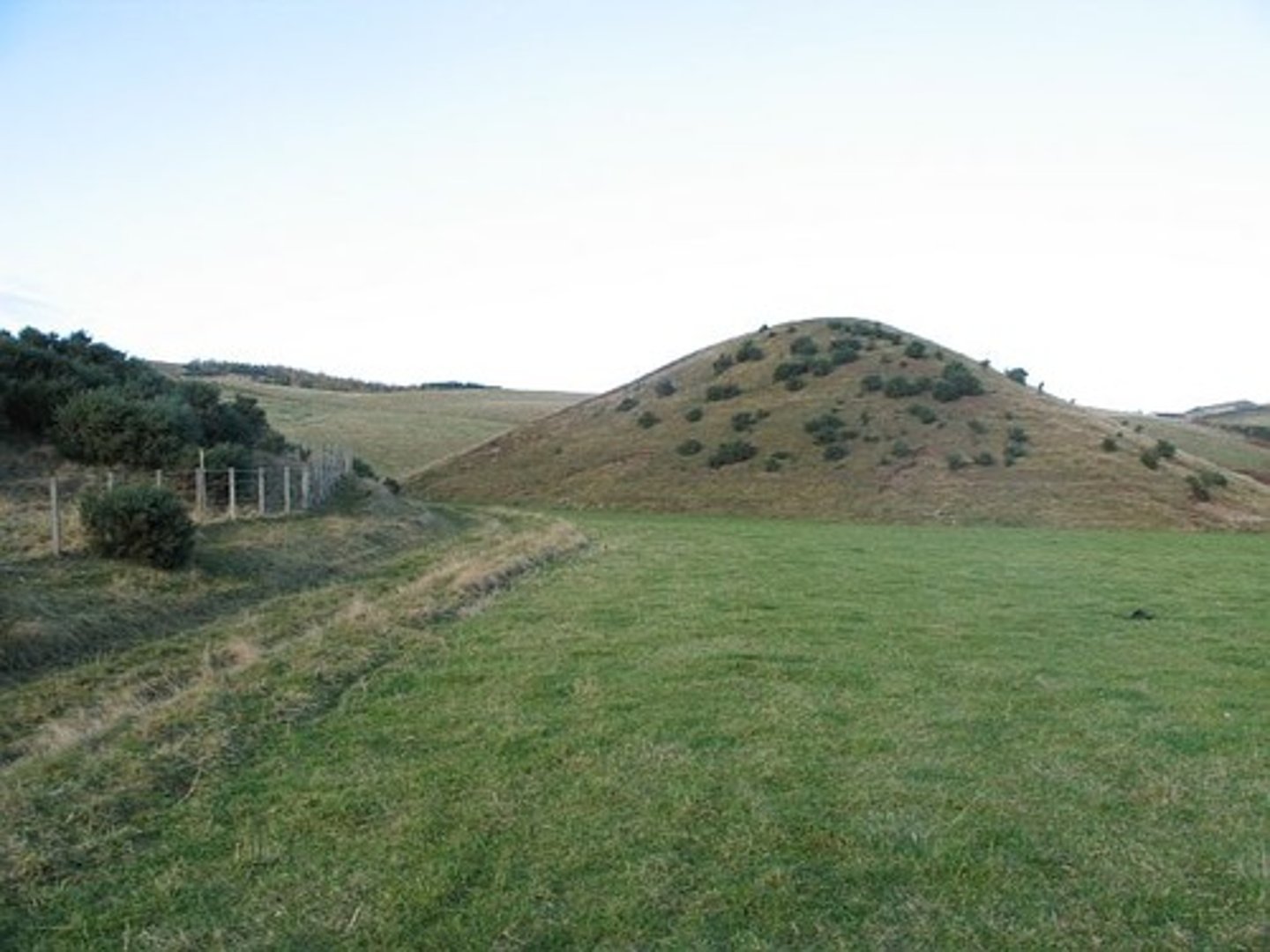
kames
smaller than drumlins, irregular shaped mounds of deposit that accumulate as a glacier retreats.

esker
long ridge of material deposited by a melt water stream flowing beneath a glacier

kettles
bits of glacial ice that breaks and forms a depression in the ground, then melting, forming these.
erratics
rocks and boulders that are picked up and transported by a glacier and left when the glacier melts, these rocks usually are "native" to the area they are left in.
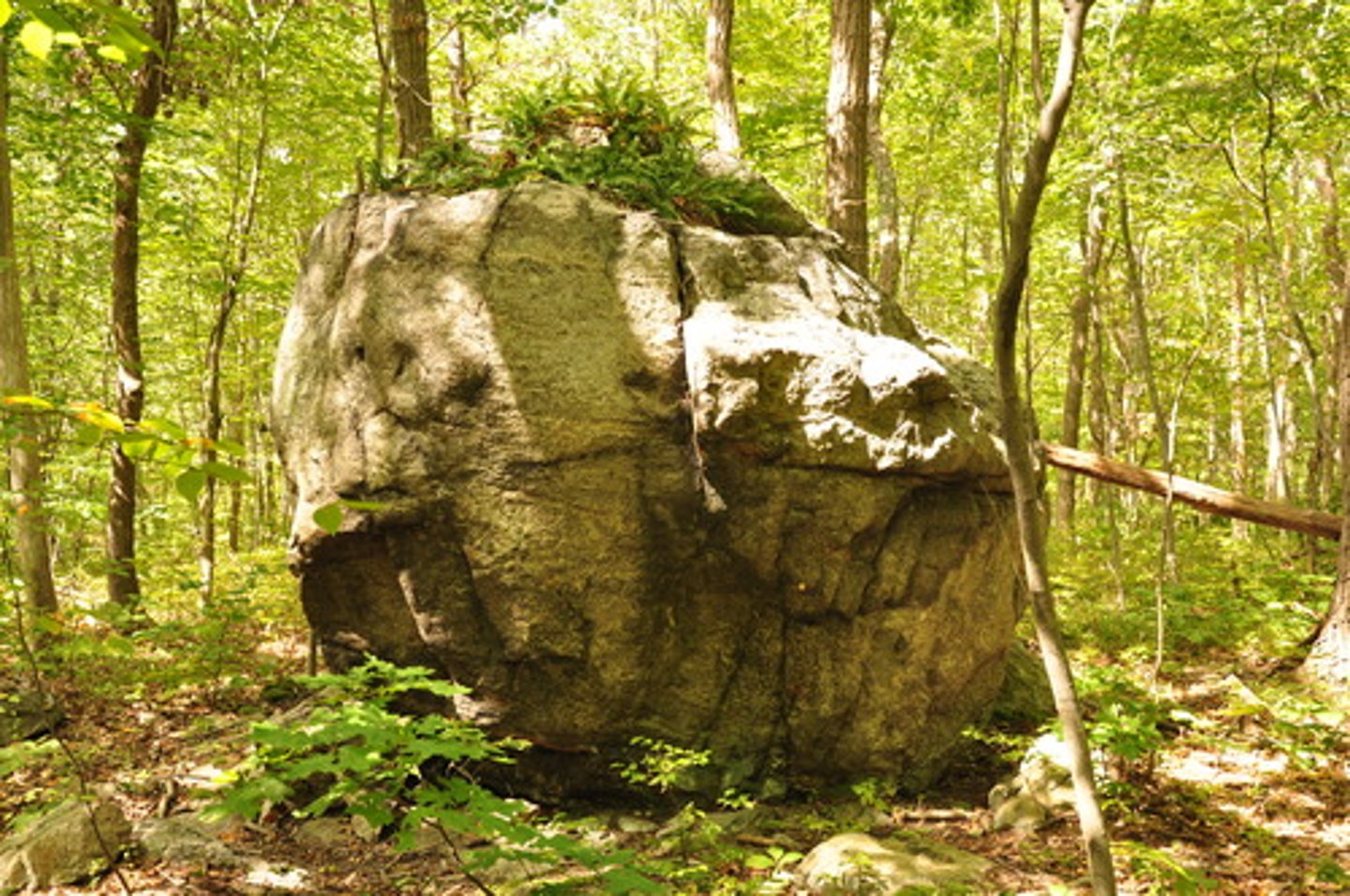

till
The sediments deposited directly by a glacier
moraine
glacial debris that is classified based on how it is deposited
entrainment
a glacier picking up loose material around it, this can happen by regelation or the glacier just picking it up.
reccessional moraine
when the glacier is in a general retreat, and it stagnates or advances, sediment is deposited, and this is what it's called. These are behind the terminal moraine.
terminal moraine
the deposit that marks the furthest advance of the glacier
englacial debris
sediment carried within the body of a glacier
plucking
the glacier freezing onto masses of rock, and glacier flow causing this mass being pulled and broken off, and carried by the glacier.
supraglacial debris
Material transported on the surface of the glacier, medial moraines and lateral moraines are supraglacial debris
lateral moraine
material that has been pushed off to the sides by the glacier.
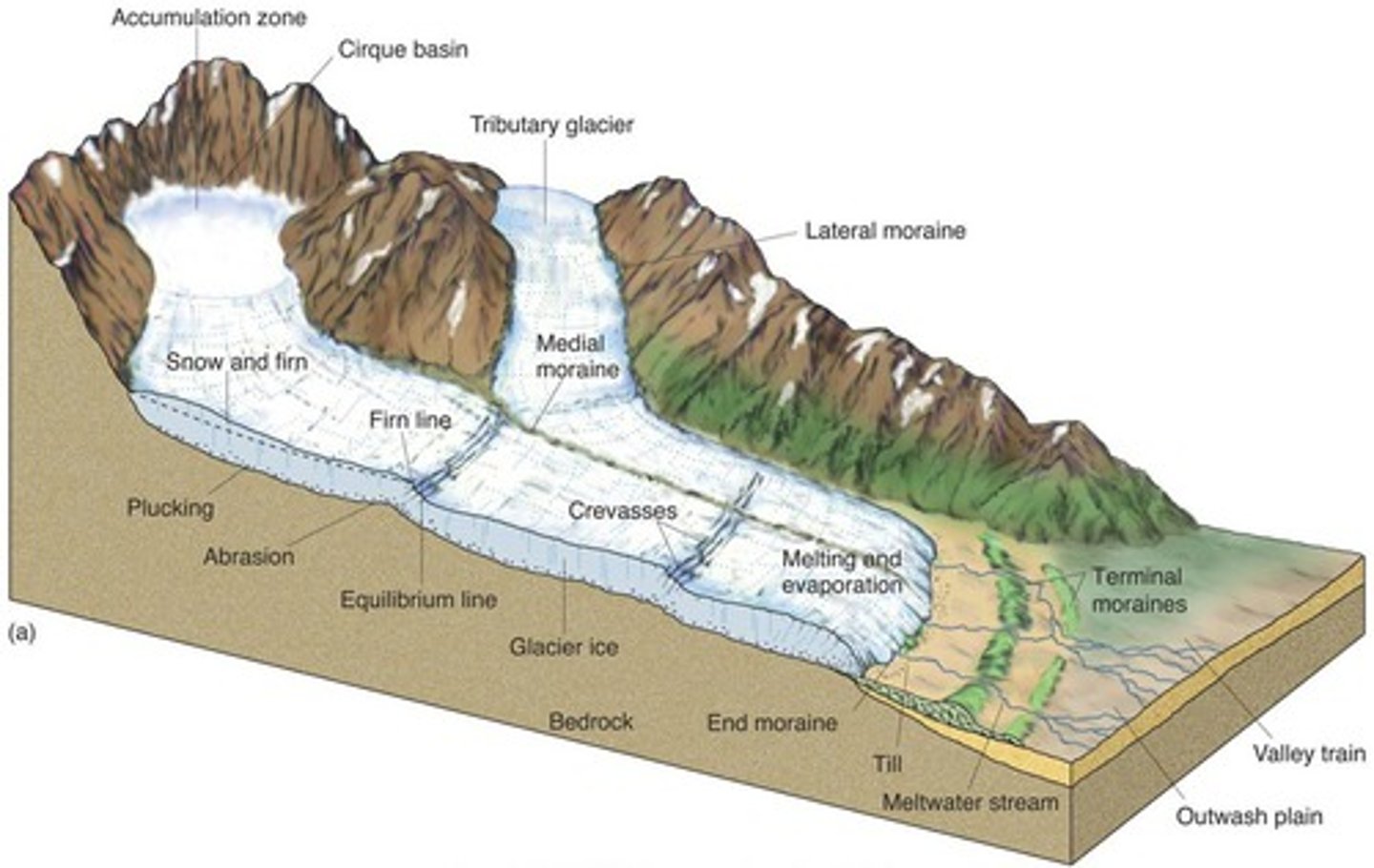
medial moraine
when two valley glaciers converge, their lateral moraines come together and this is the outcome.
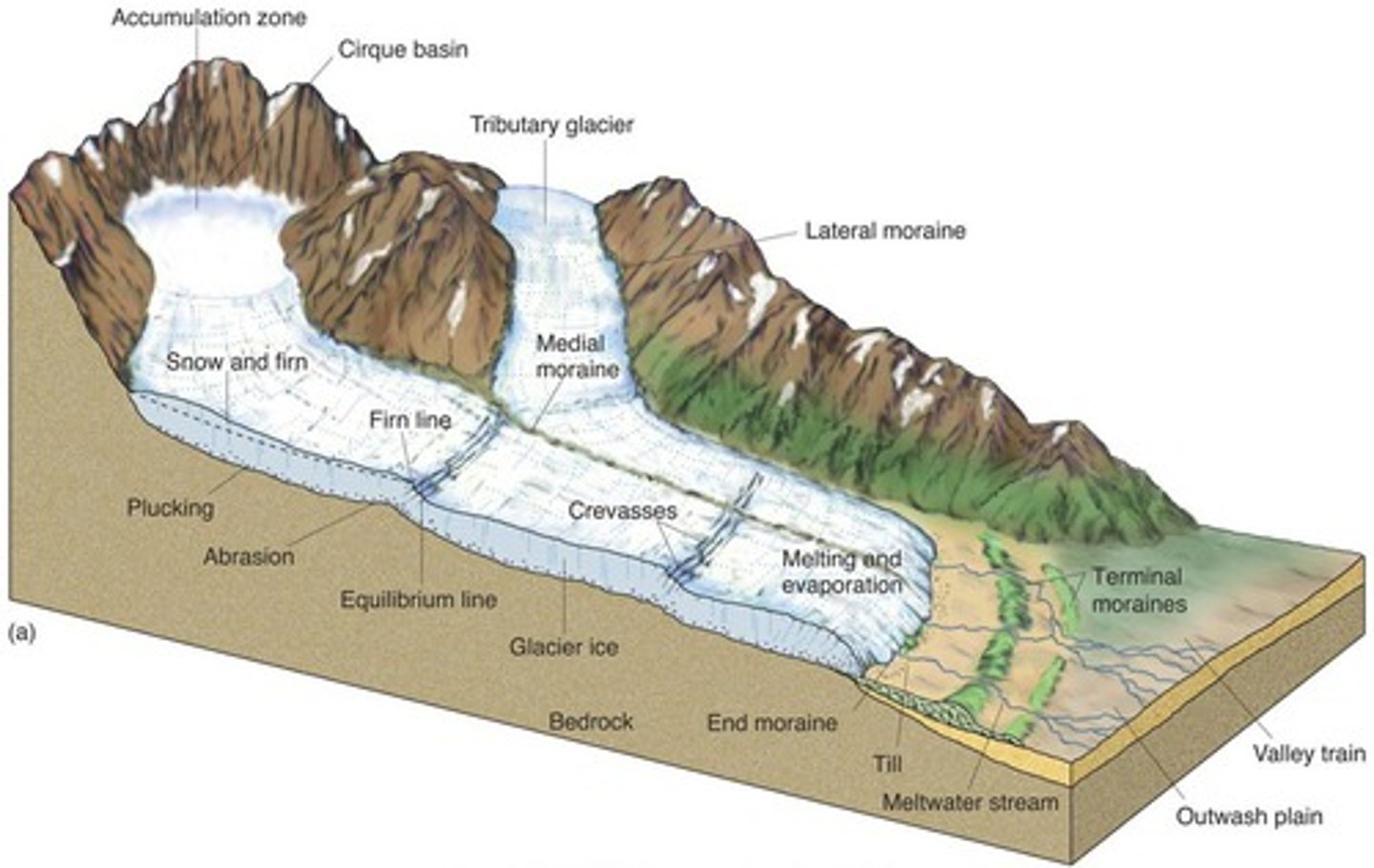
ground moraine
a layer of till under the glacier (subglacial
debris) deposited as the glacier retreats
supraglacial lakes
lakes formed by surface melt
swamp zone
firn in the accumulation zone that is saturated with water caused by surface melt.
surface melt
ablation on the surface
moulins
A cylindrical, vertical shaft that extends through a glacier and transports water from the surface to the base. They are carved by melt water from the glacier's surface. they can lubricate the base, and speed up flow.
drainage
melt water moving from moulins, crevasses, and other holes to englacial or subglacial systems
subglacial lake
a lake under a glacier, typically in ice sheets and ice caps
proglacial lake
a moraine acting as a dam to a melting glacier, forming a lake.
Jökulhlaup
any large/abrupt release of water from subglacial/proglacial lakes/reservoirs
connections to the atmosphere
|| Greenhouse gasses: heat-trapping gasses that are the major cause of glacier retreats in the past 50 years, they trap the heat that came form the sun inside the atmosphere. || Insolation: exposion to sun's rays, also causing glacier retreat || Aerosols: particles in the air that reflect the suns rays back, meaning less heat trapped by green house gasses, but it's believed that aerosols decrease the amount of precipitation, resulting in less accumulation in glaciers, and causing glacier retreat. ||
connection to the hydrosphere
sea level change: as glaciers melt, the sea levels rise.
connections to the lithosphere
Glacial isostatic adjustment: the rebound of the Earth's crust after the heavy weight of the glacial ice in the last glacial period.