Anatomy Lab 2 FINAL
1/359
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
360 Terms
60
in the reproductive system, what percentage of secretion is done by the seminal vesicle?
30
in the reproductive system, what percentage of secretion is done by the prostate gland?
5
in the reproductive system, what percentage of secretion is done by the bulbourethral glands?
cowpers
Whats the other name for bulbourethral gland?
produce fructose for sperm energy, clotting enzymes and prostaglandins, yellow pigment
What does the seminal vesicle do for male glands?
secrete nutrients and milky acidic substance to active sperm, fibrinolysin
What does the prostate gland do for male glands?
alkaline mucus to neutralize acidity
What does the bulbourethral gland do for male glands?
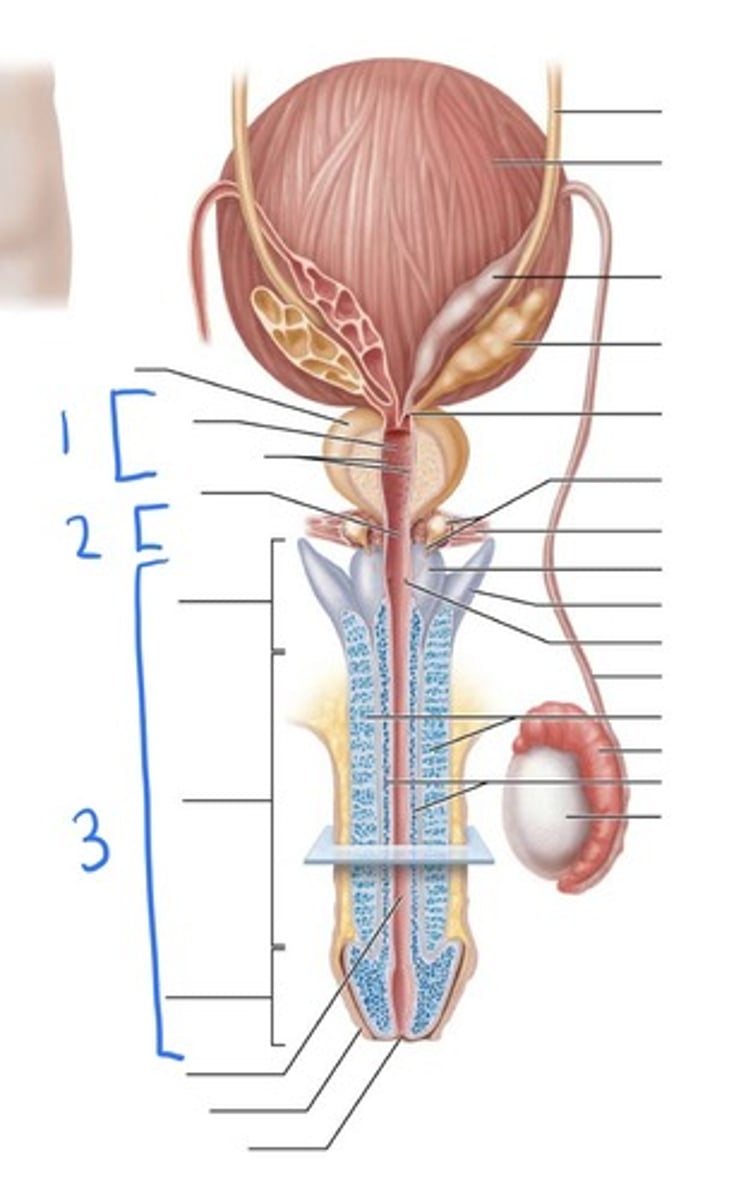
prostatic urethra
1
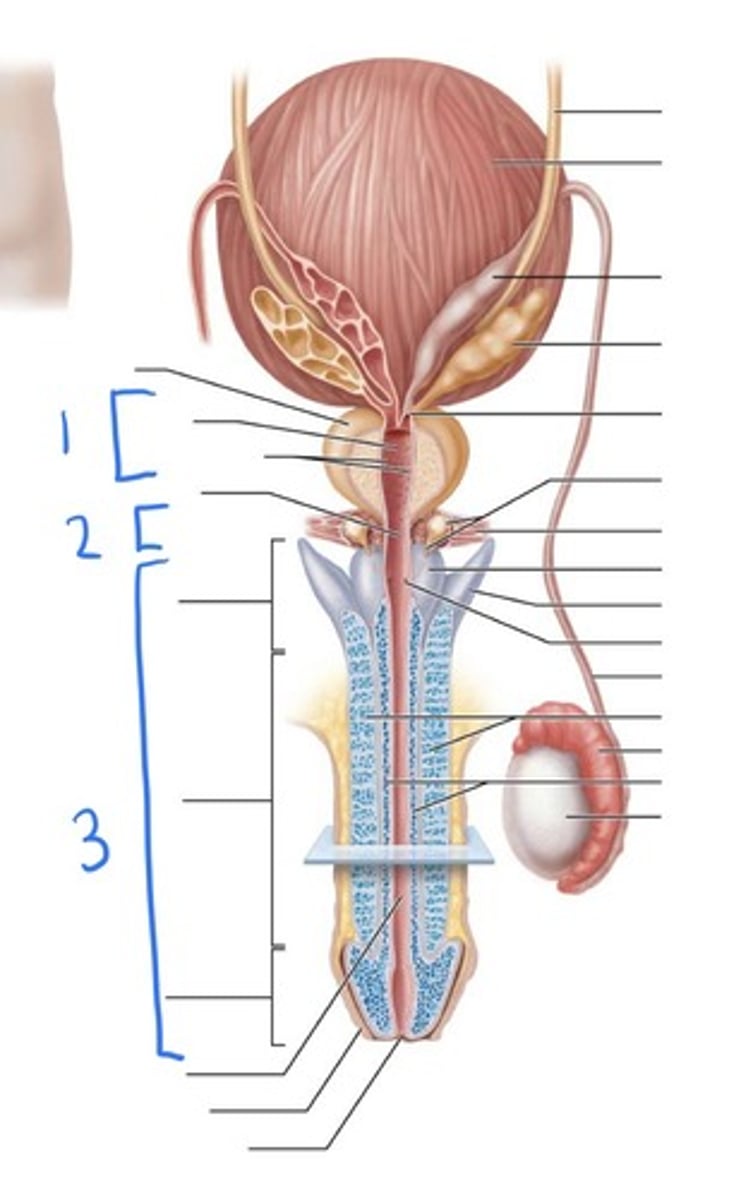
membranous urethra
2
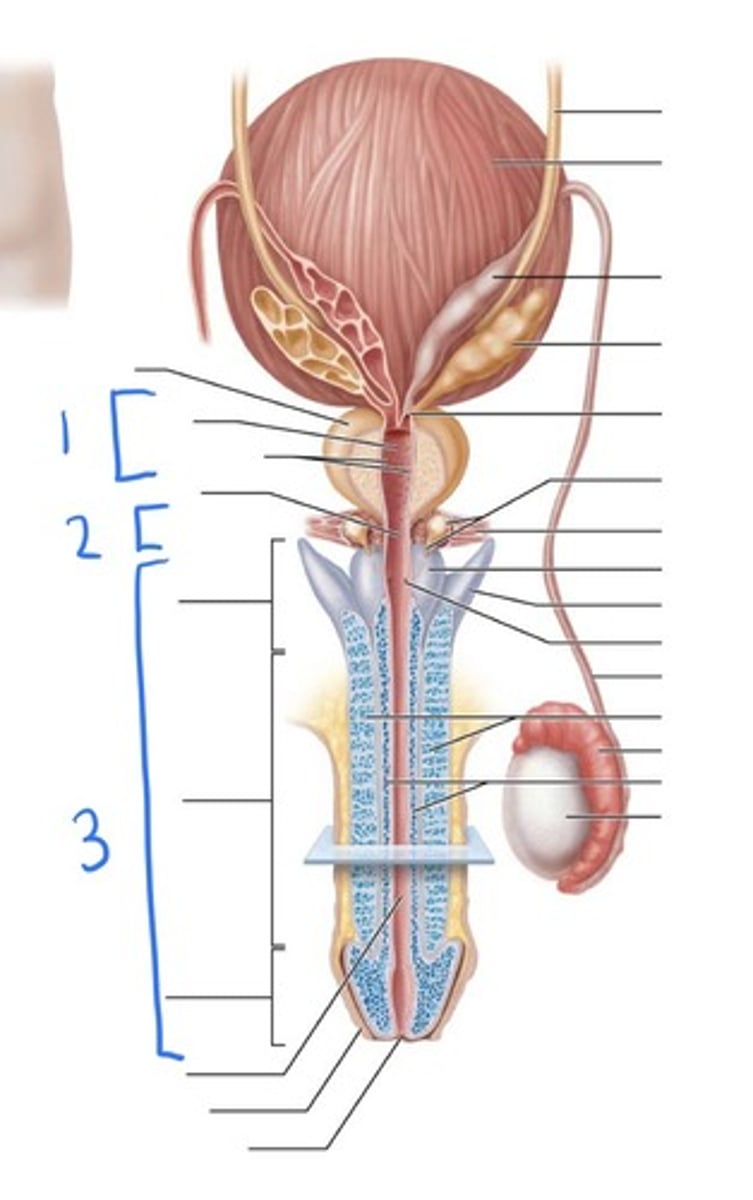
penile urethra
3
meiosis II
What is the next step to a follicle is fertilization occurs?
follicle forms corpus luteum and menstruation
What happens if fertilization does not occur?
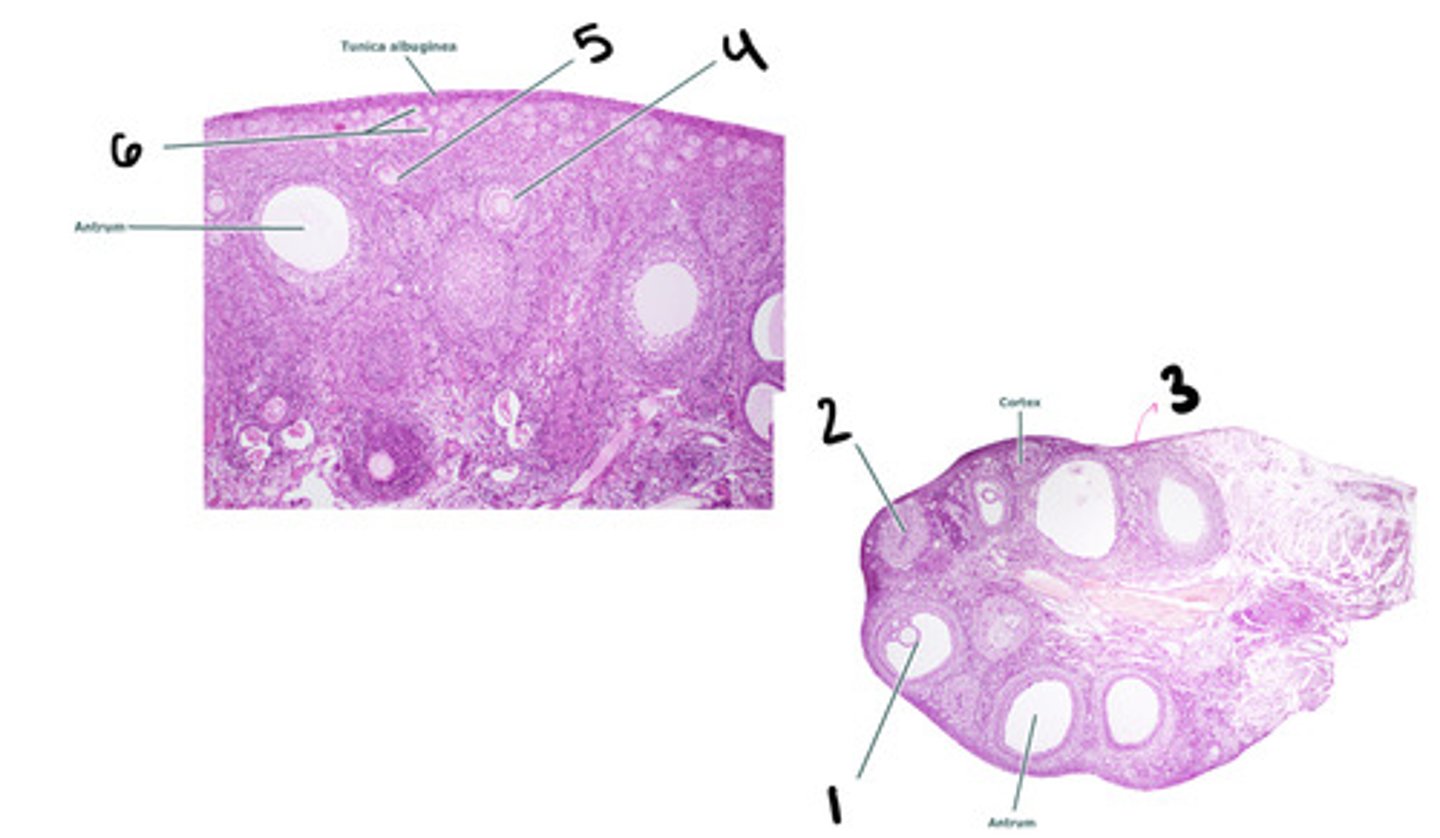
mature tertiary follicle
1
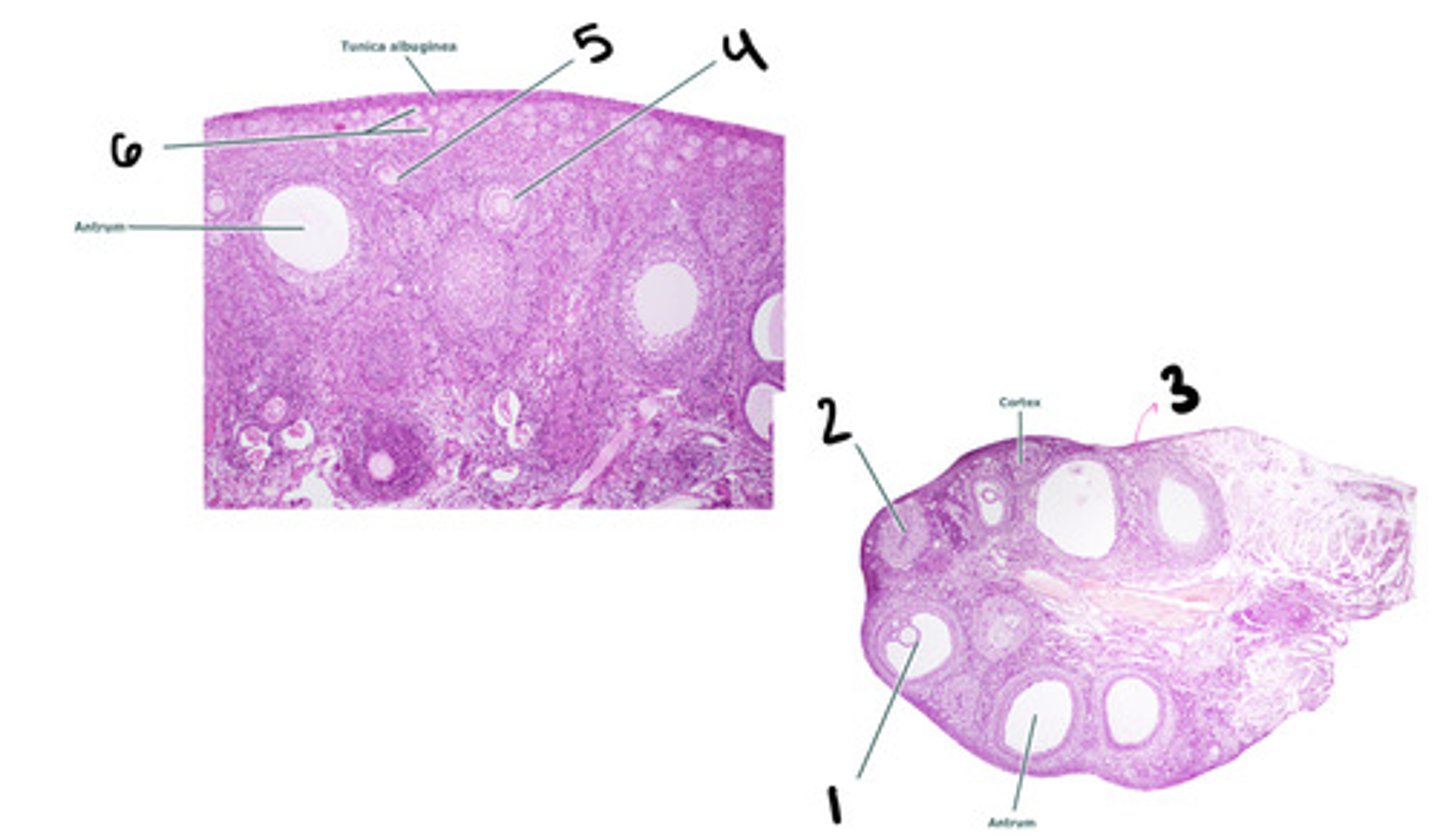
corpus luteum
2
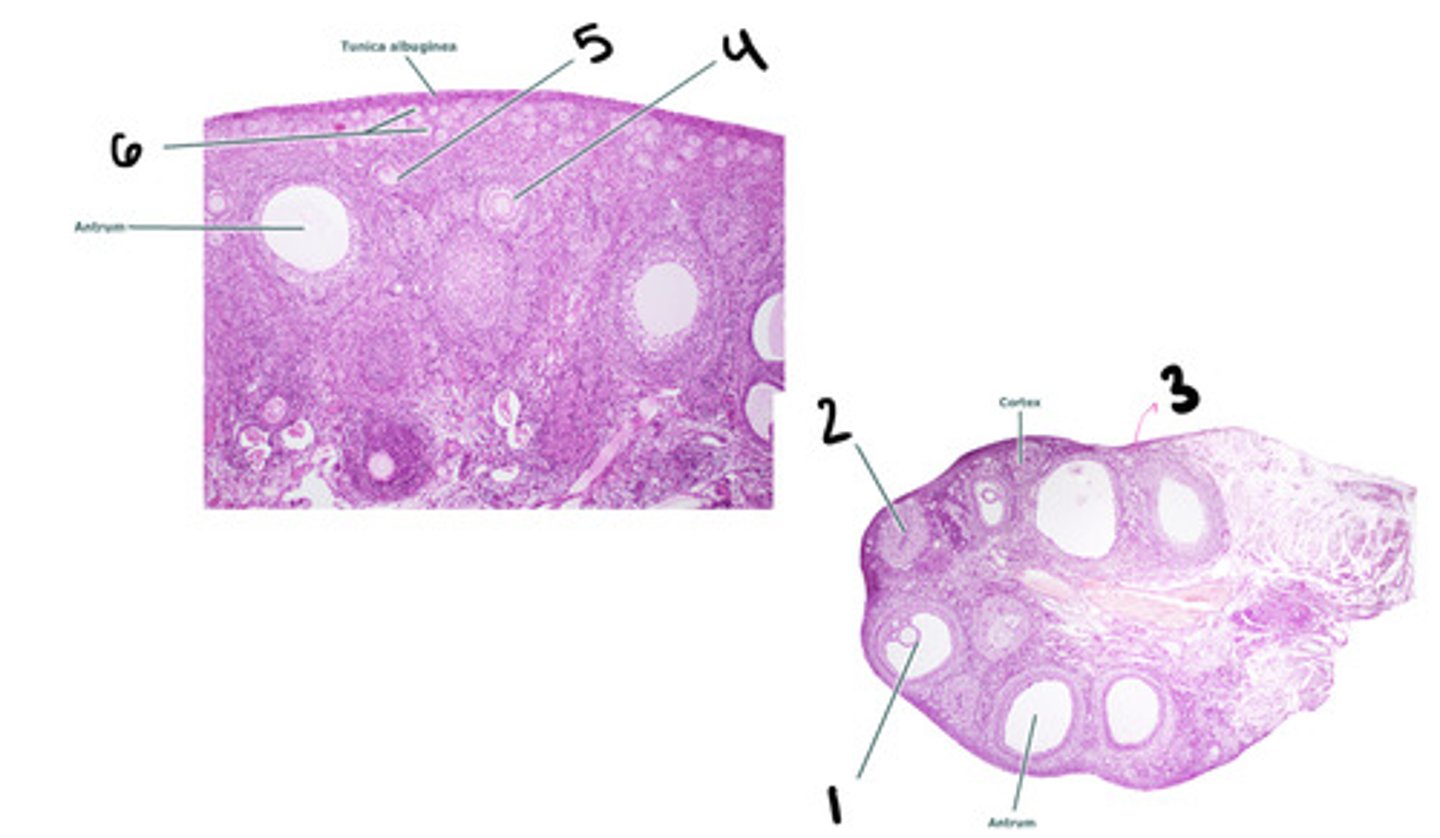
stroma
3
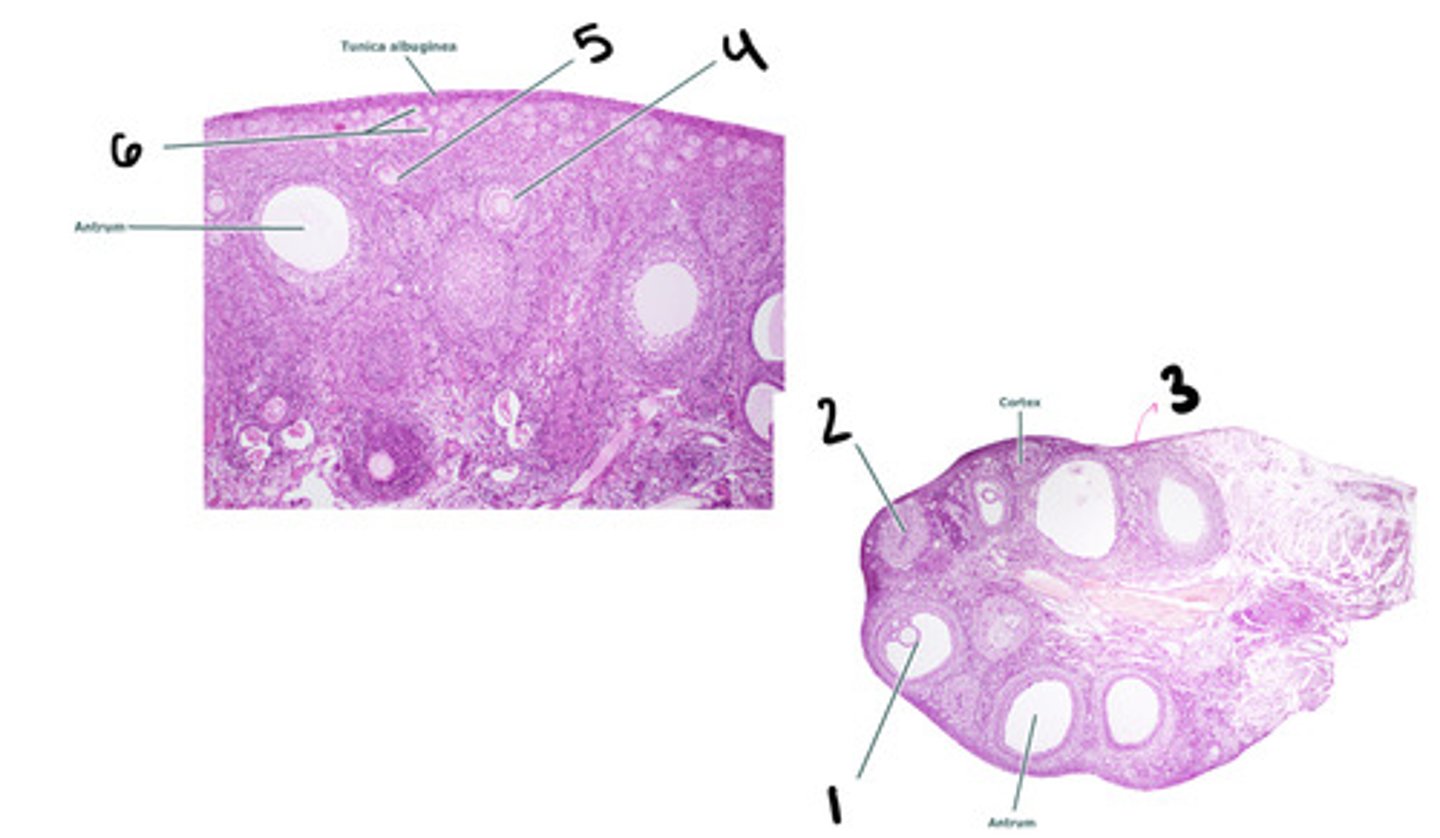
secondary follicle
4
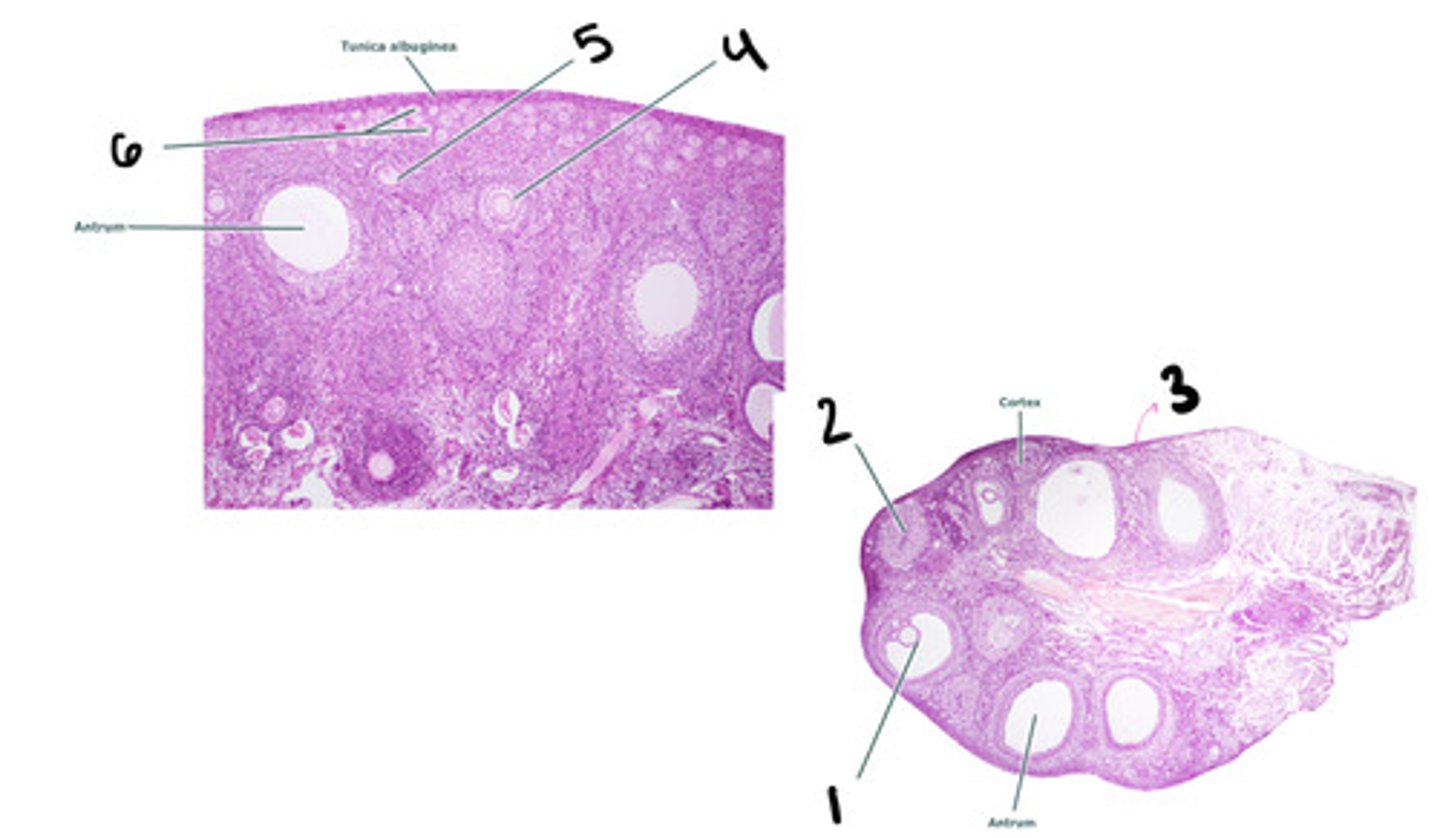
primary follicle
5
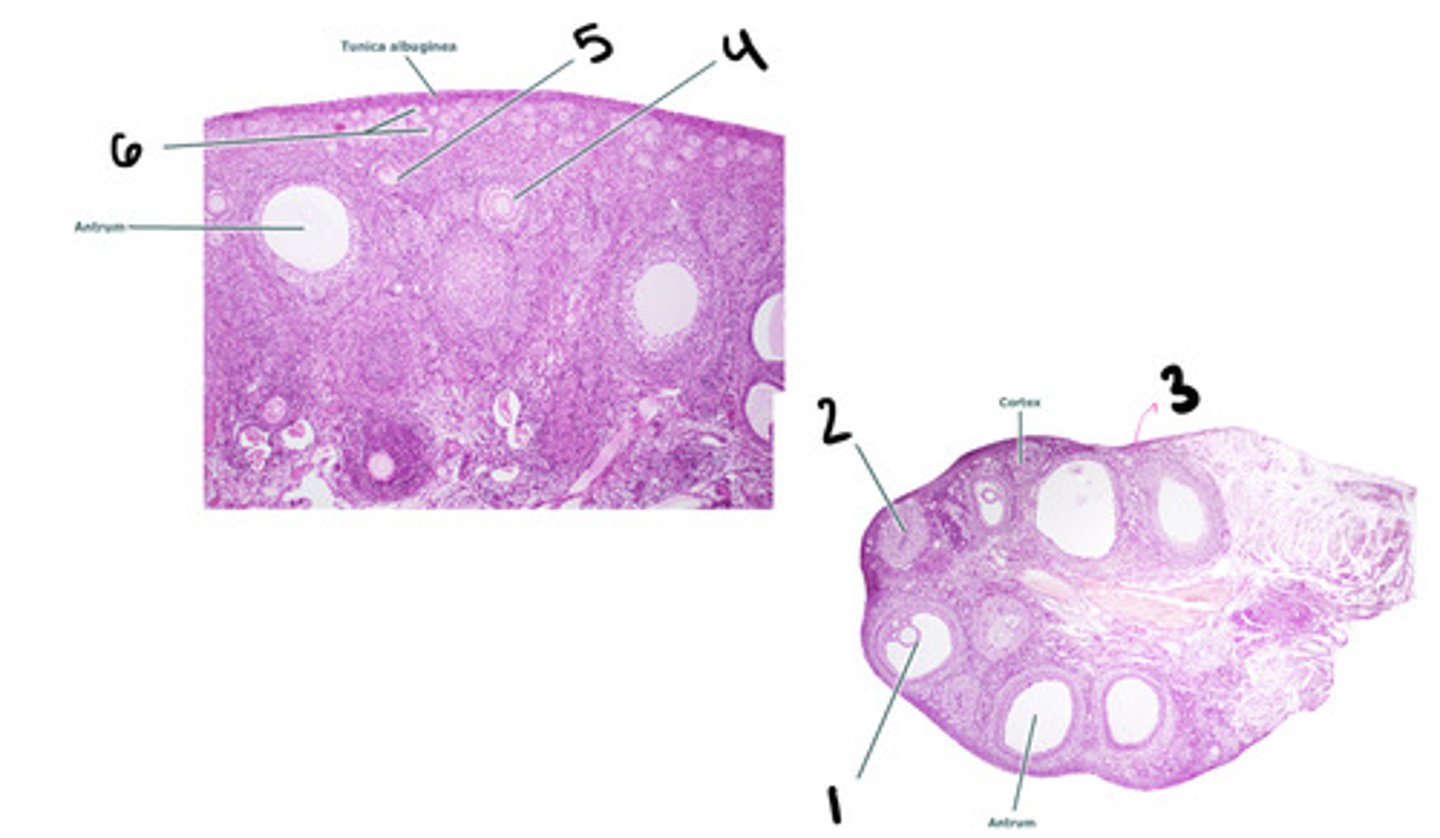
primordial follicle
6
Leydig cells (interstitial cells)
1
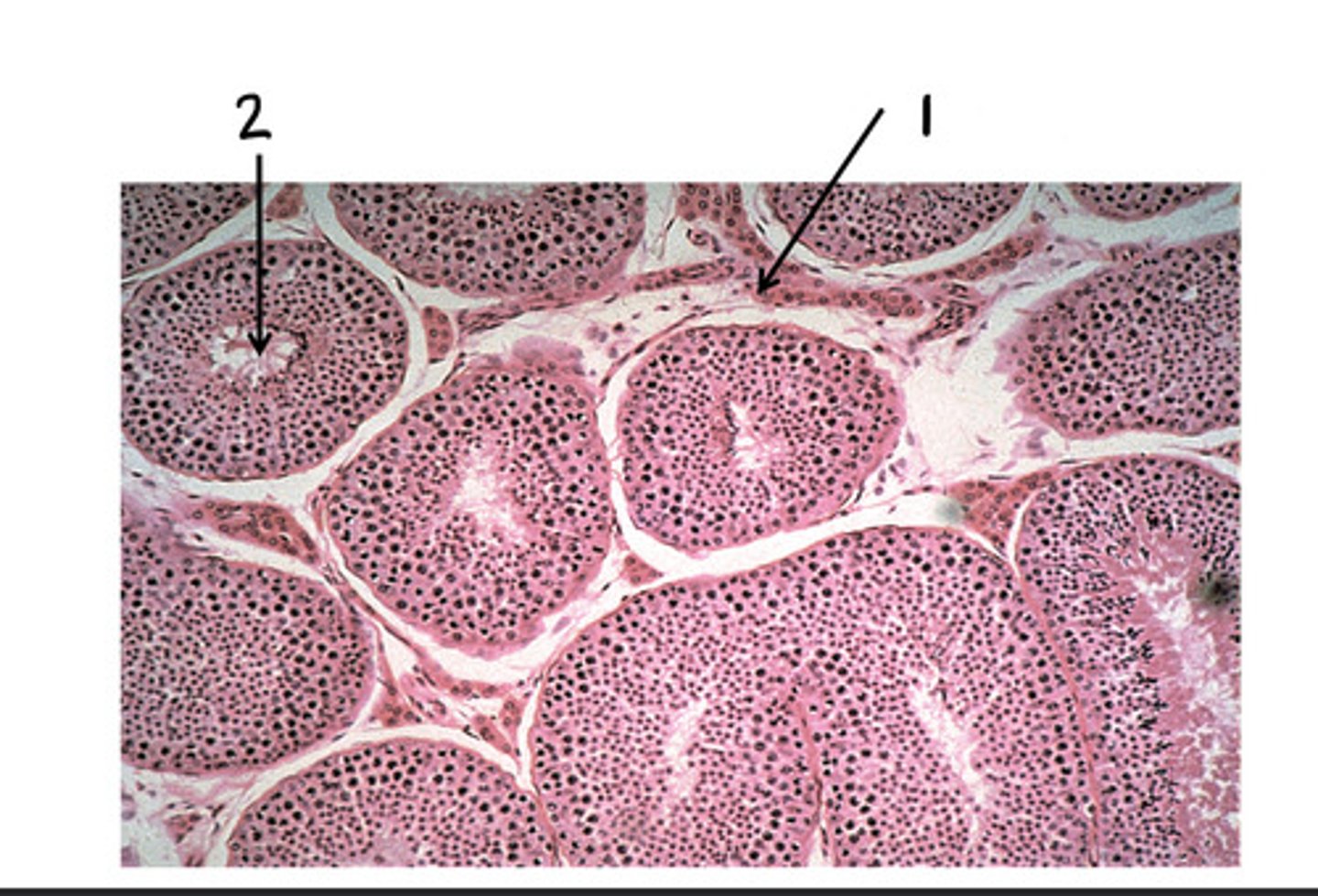
seminiferous tubules
2
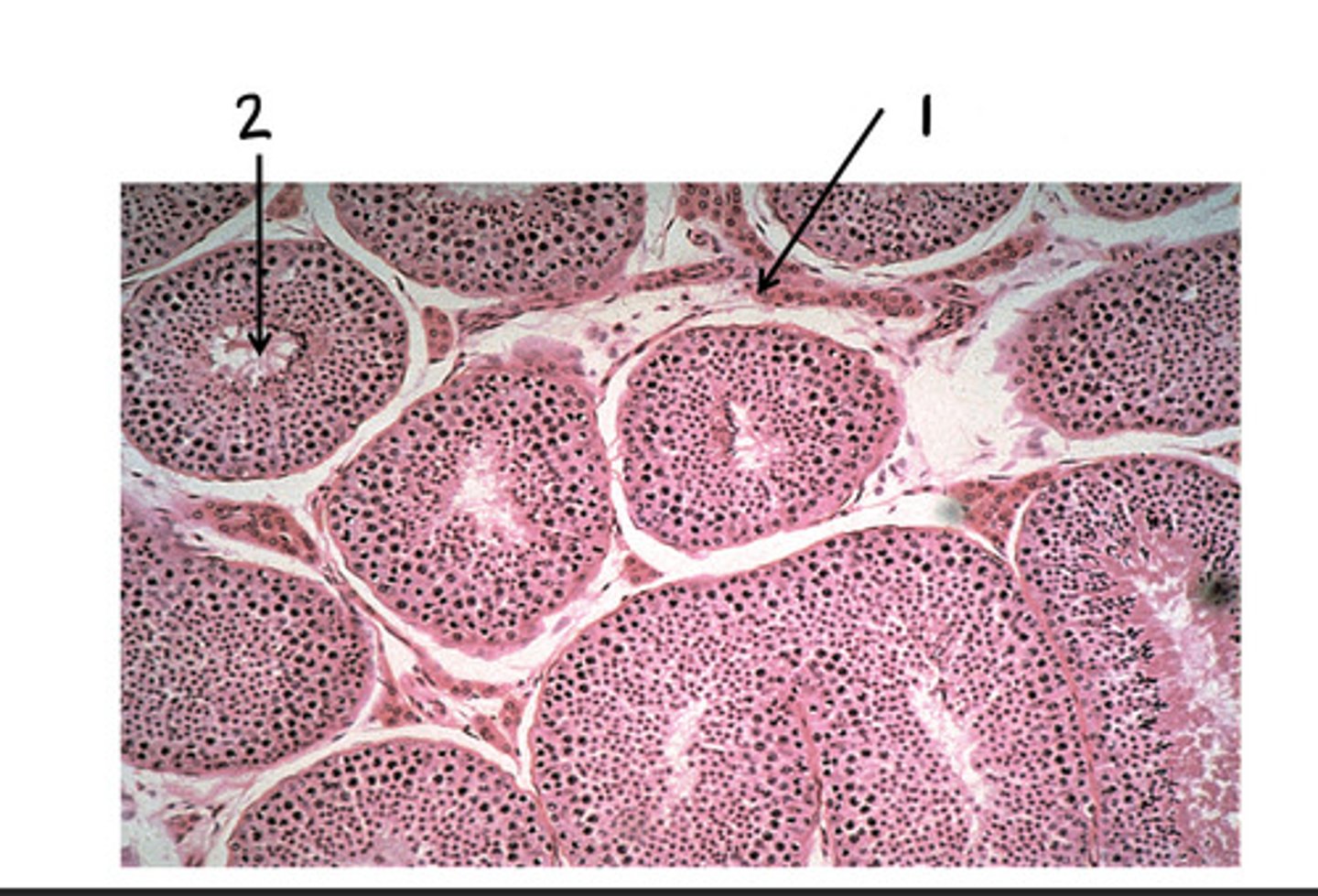
testosterone
What is produced in 1?
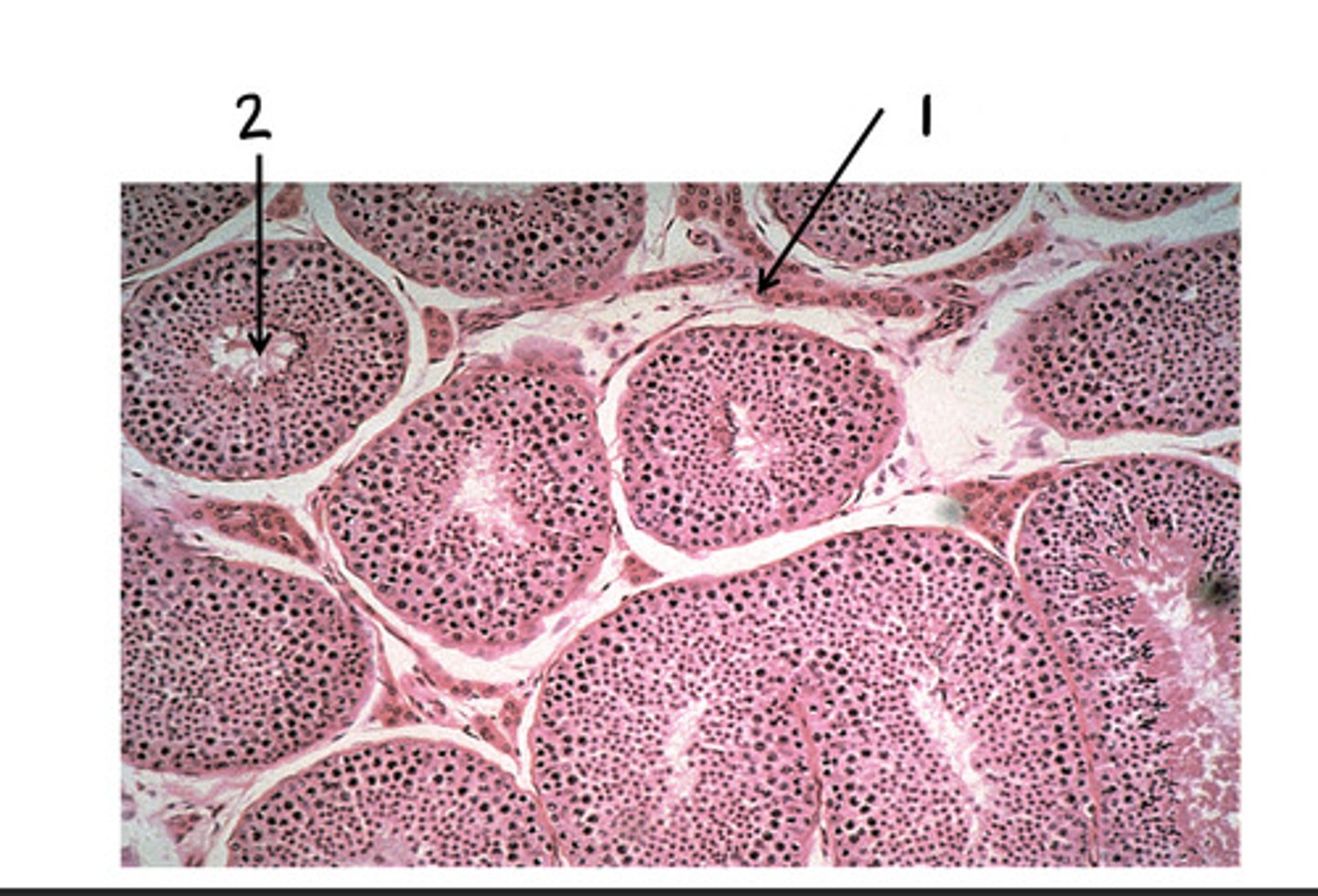
sperm
What is produced in 2?
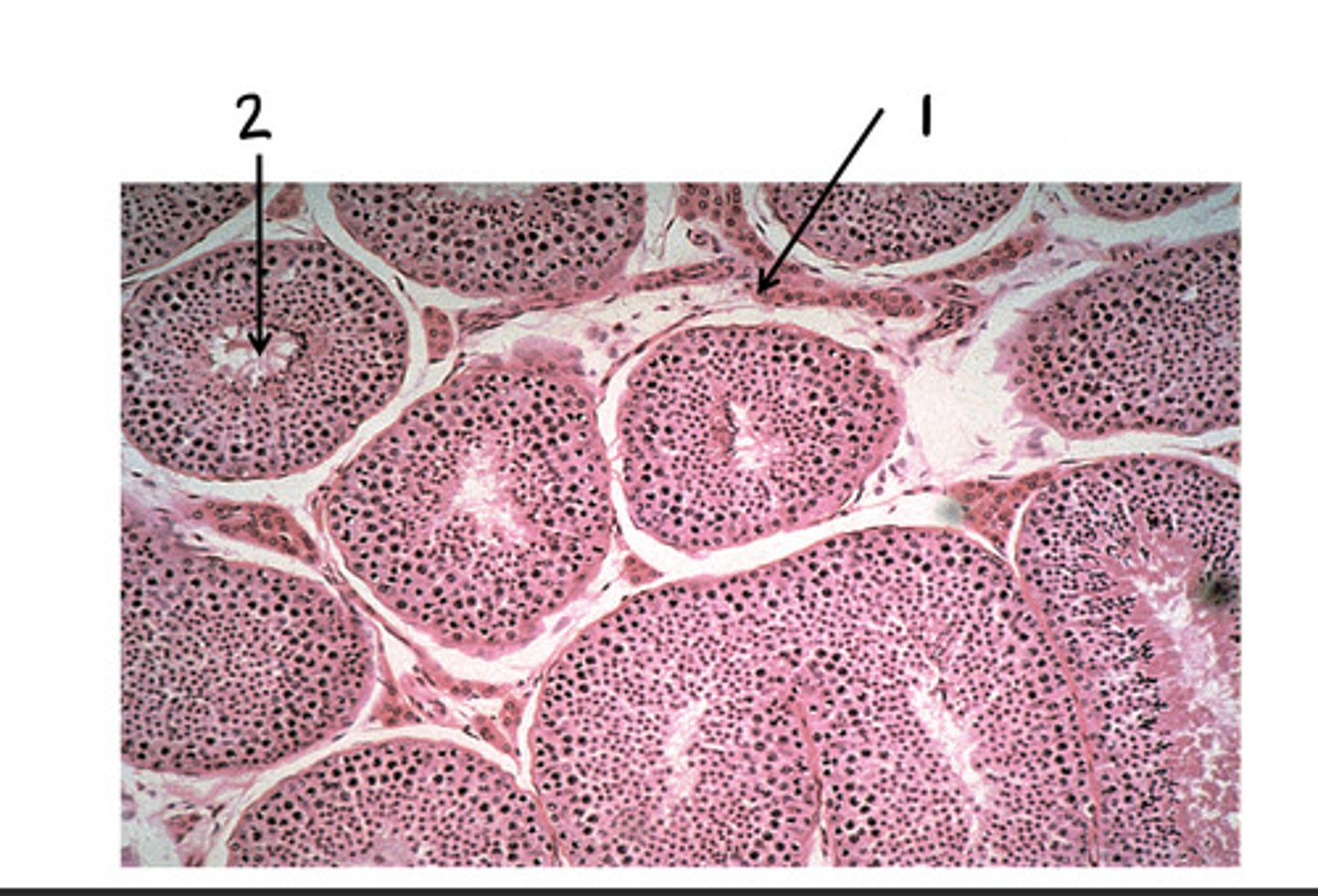
spermatogenesis
What is the term for the formation of sperm?
23
How many chromosomes are in spermatids?
2
How many daughter cells do you get from each primary speratocyte?
FSH and LH
What pituitary hormones are involved in spermatogenesis?
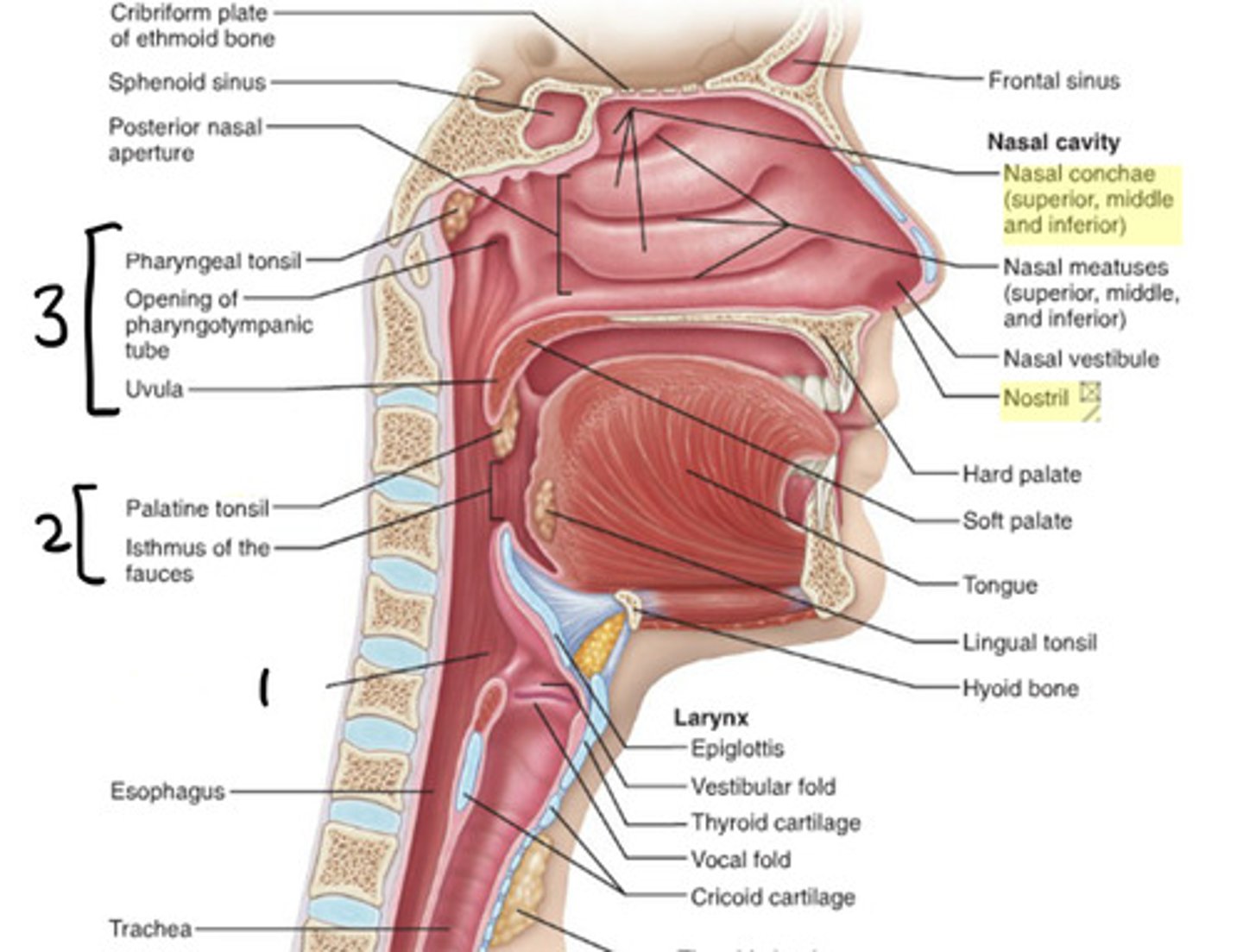
laryngopharynx
1
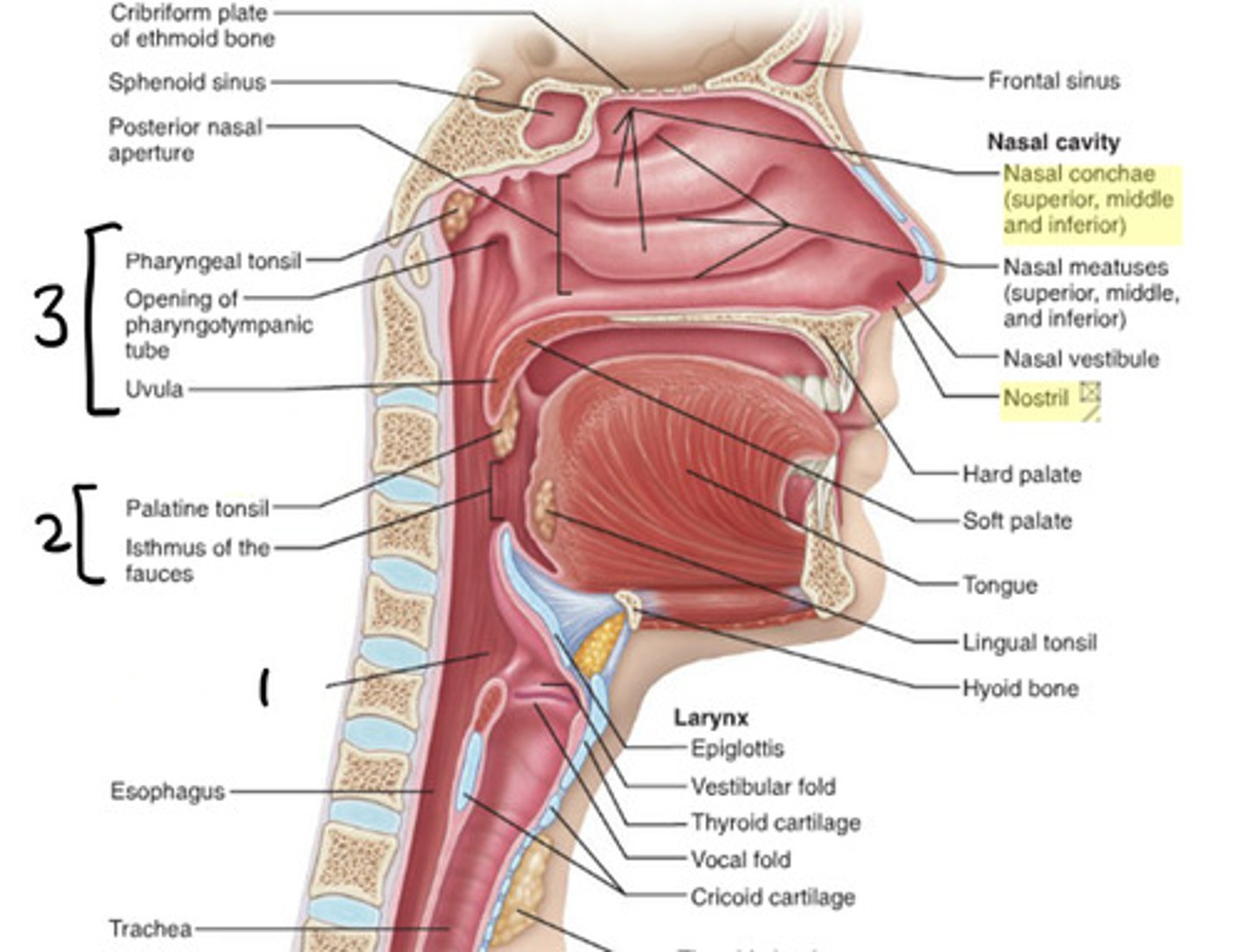
oropharynx
2
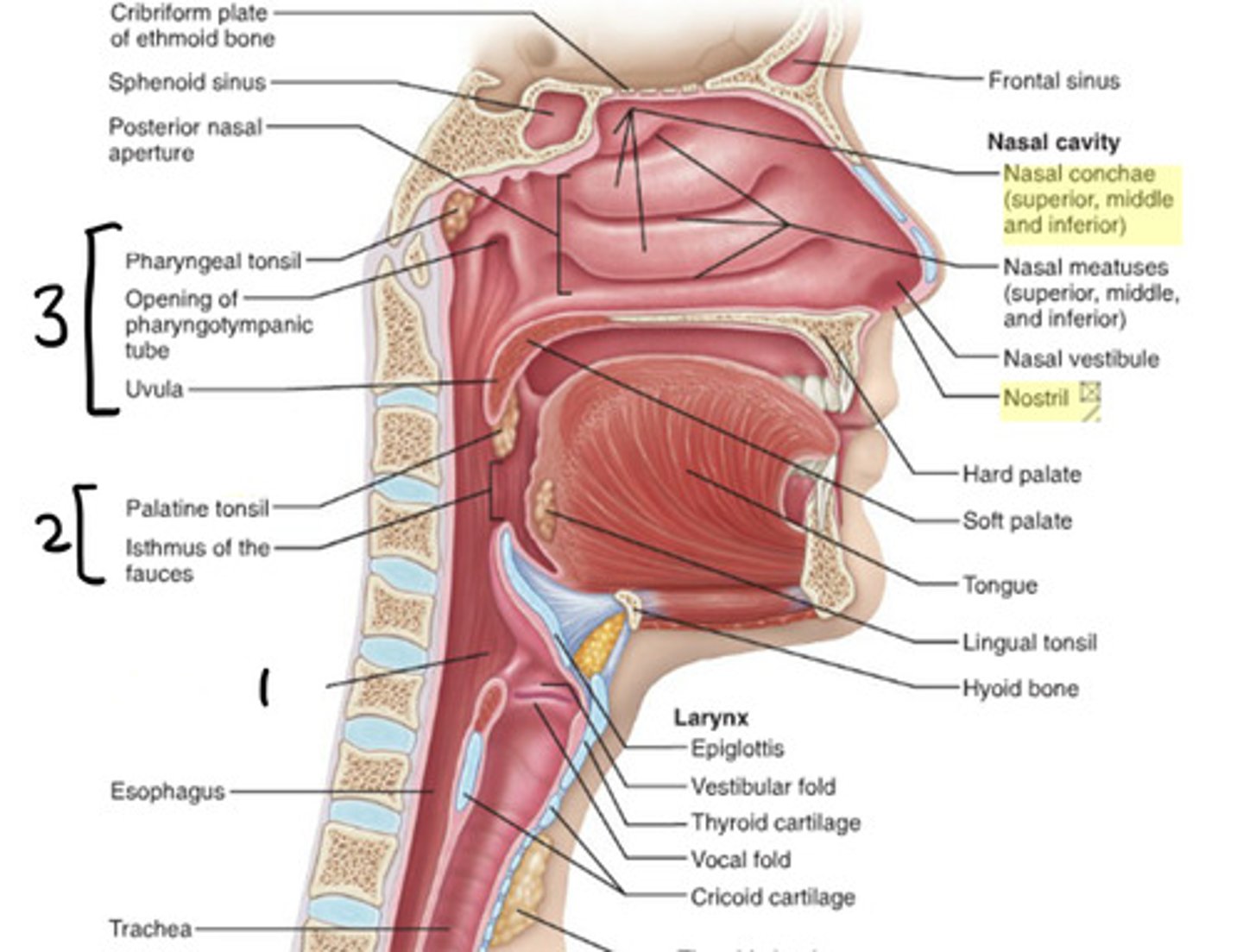
nasopharynx
3
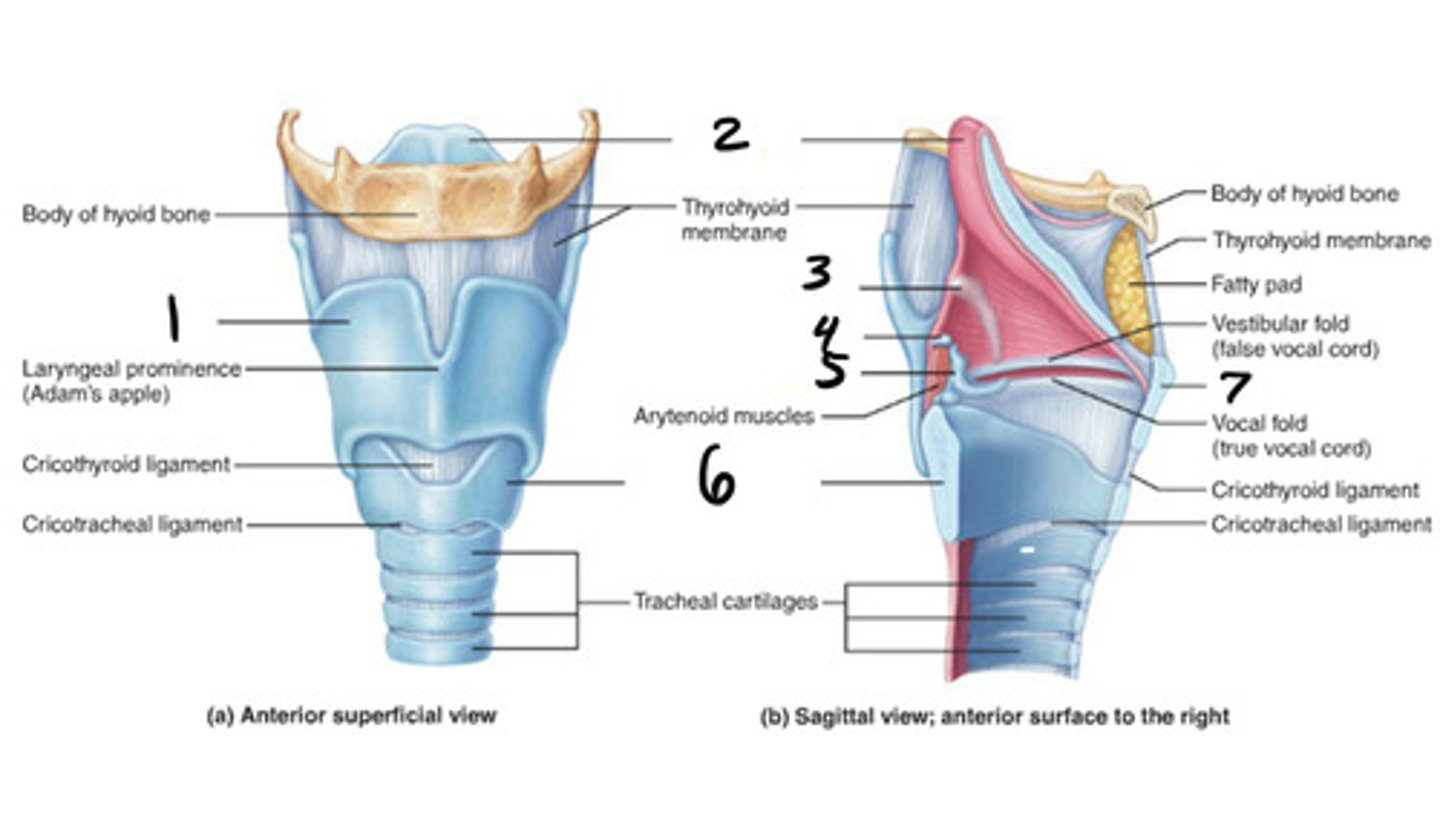
thyroid
1
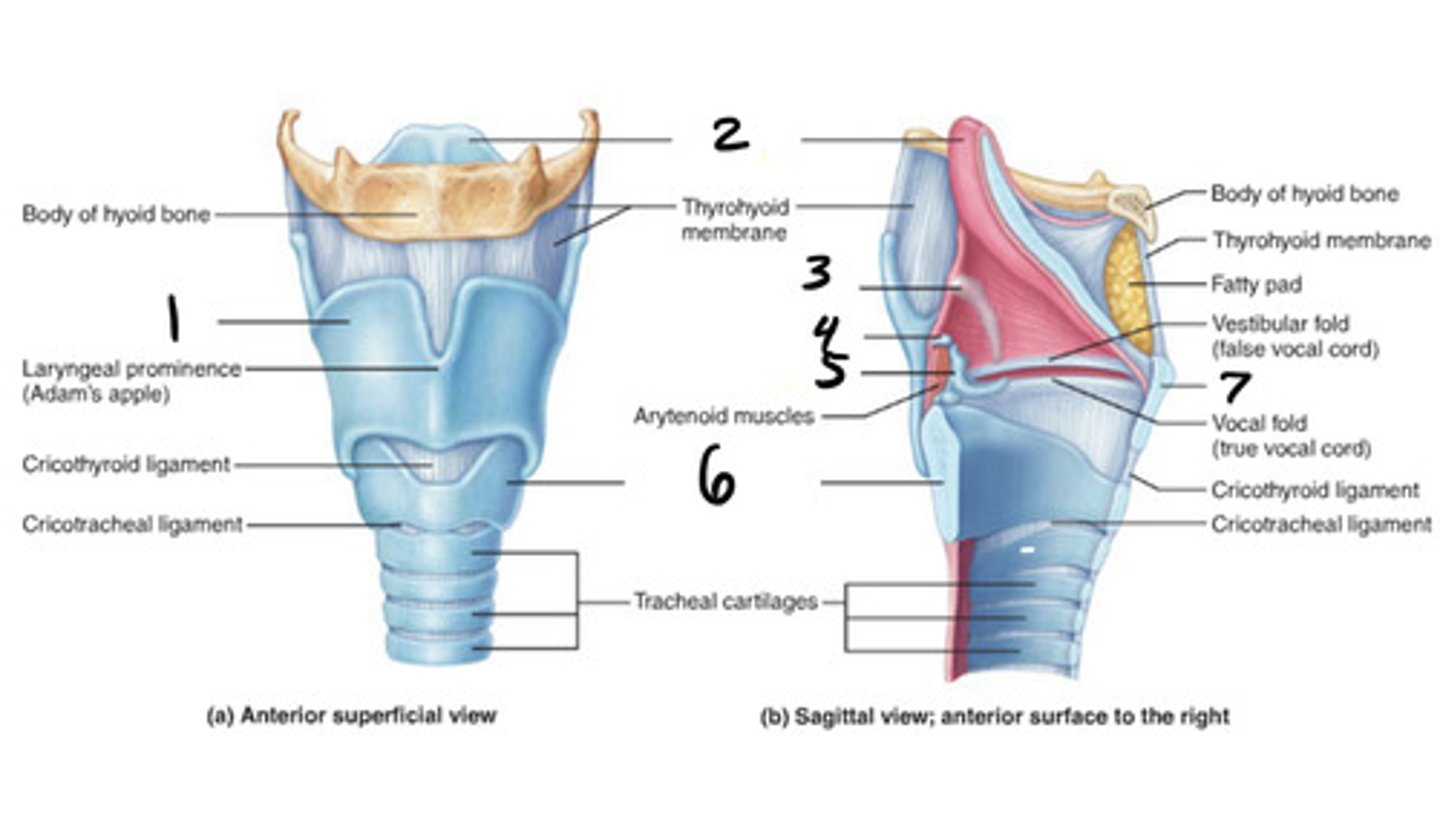
epigottis
2
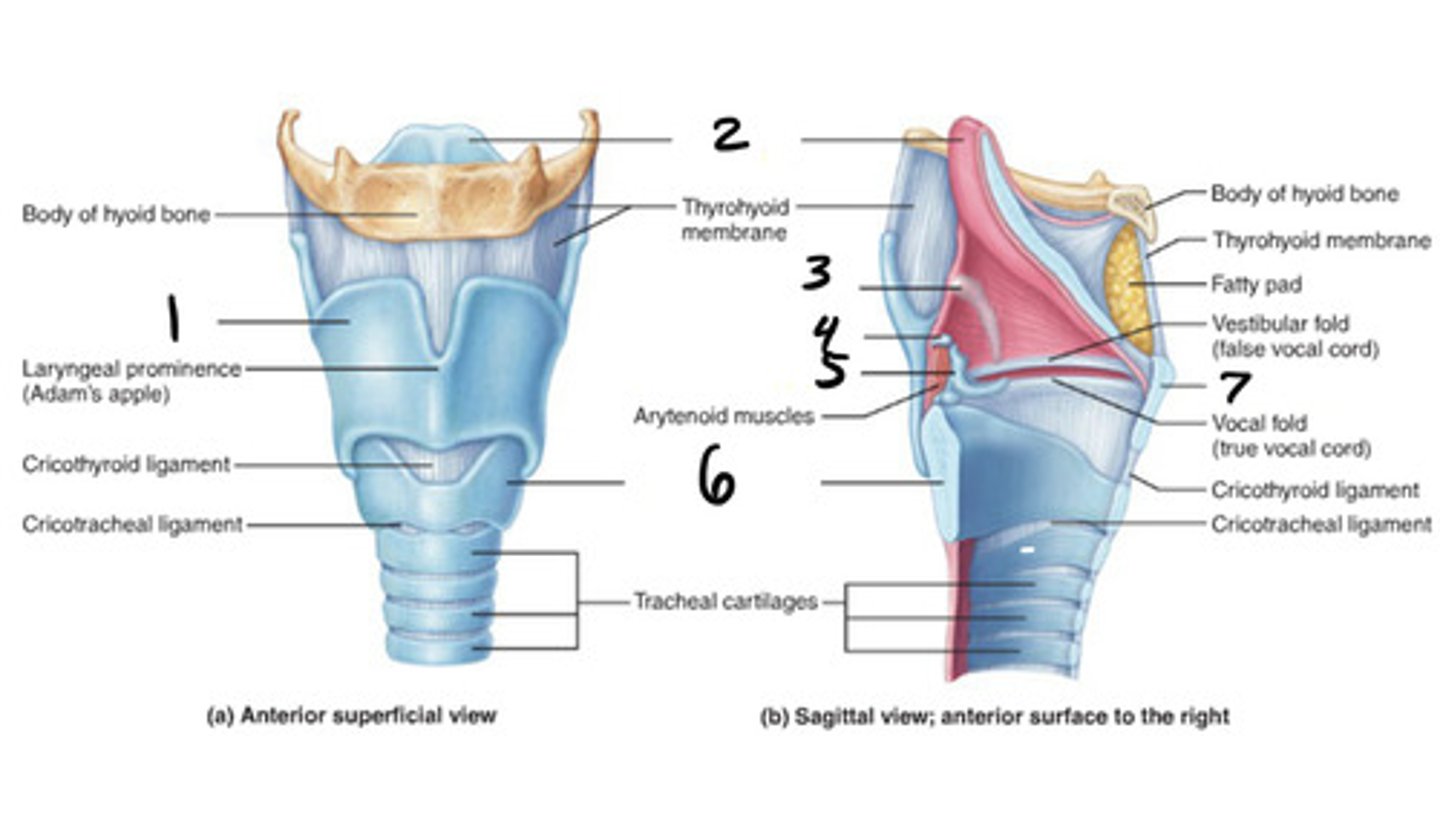
cricoid cartilage
6
turbinates
6
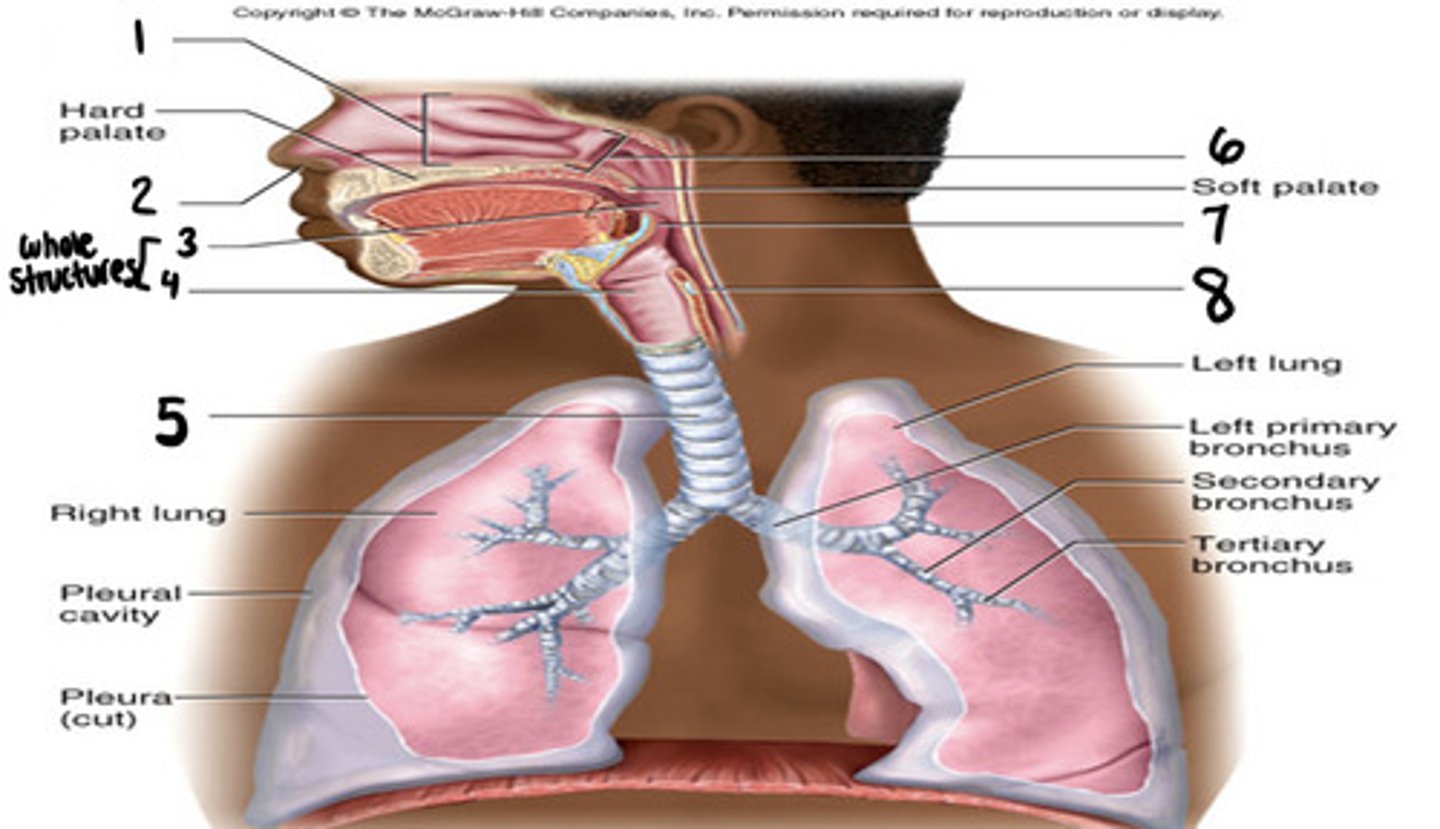
warm, humidify, filter air
Function of turbinates
nose
1
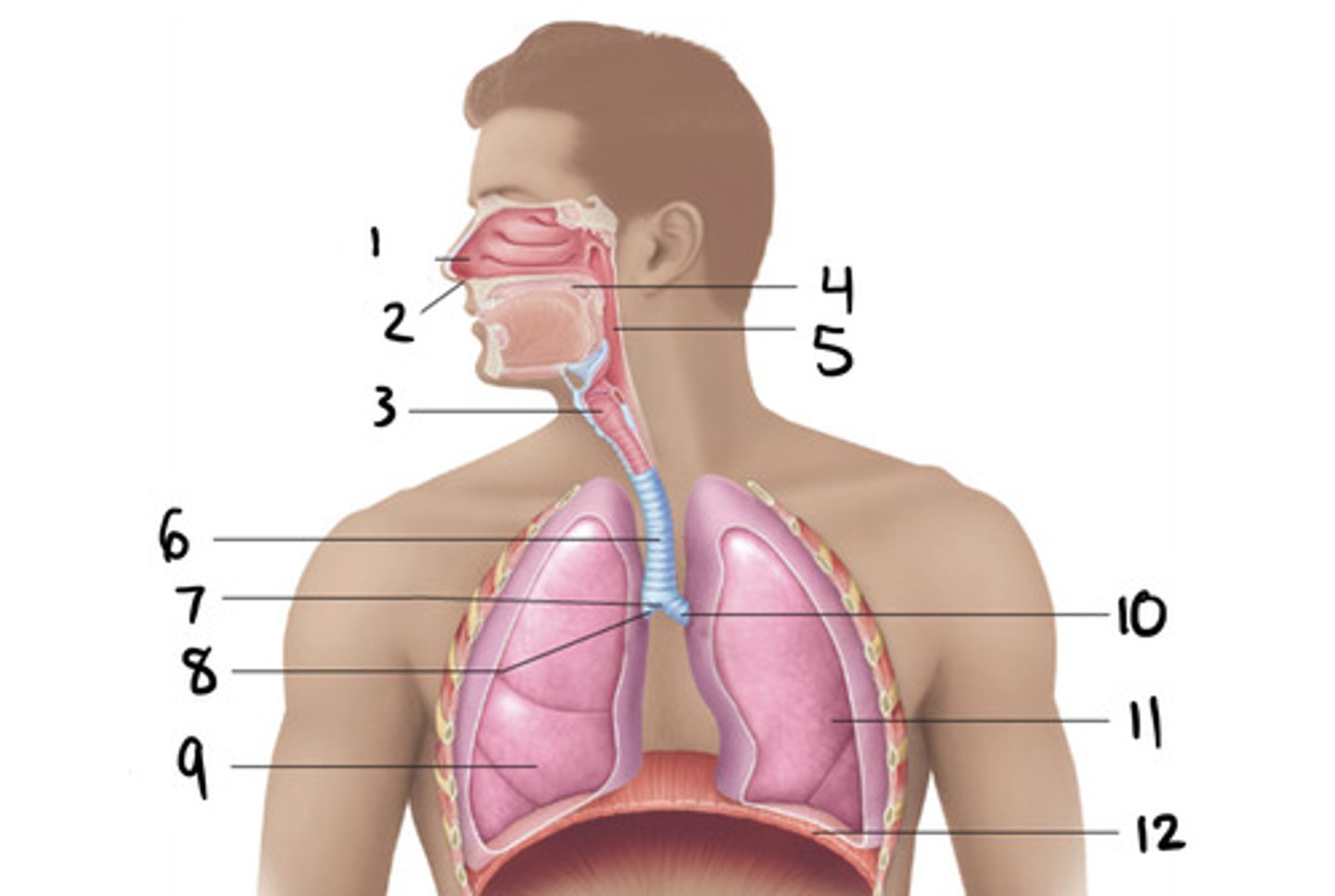
trachea
6
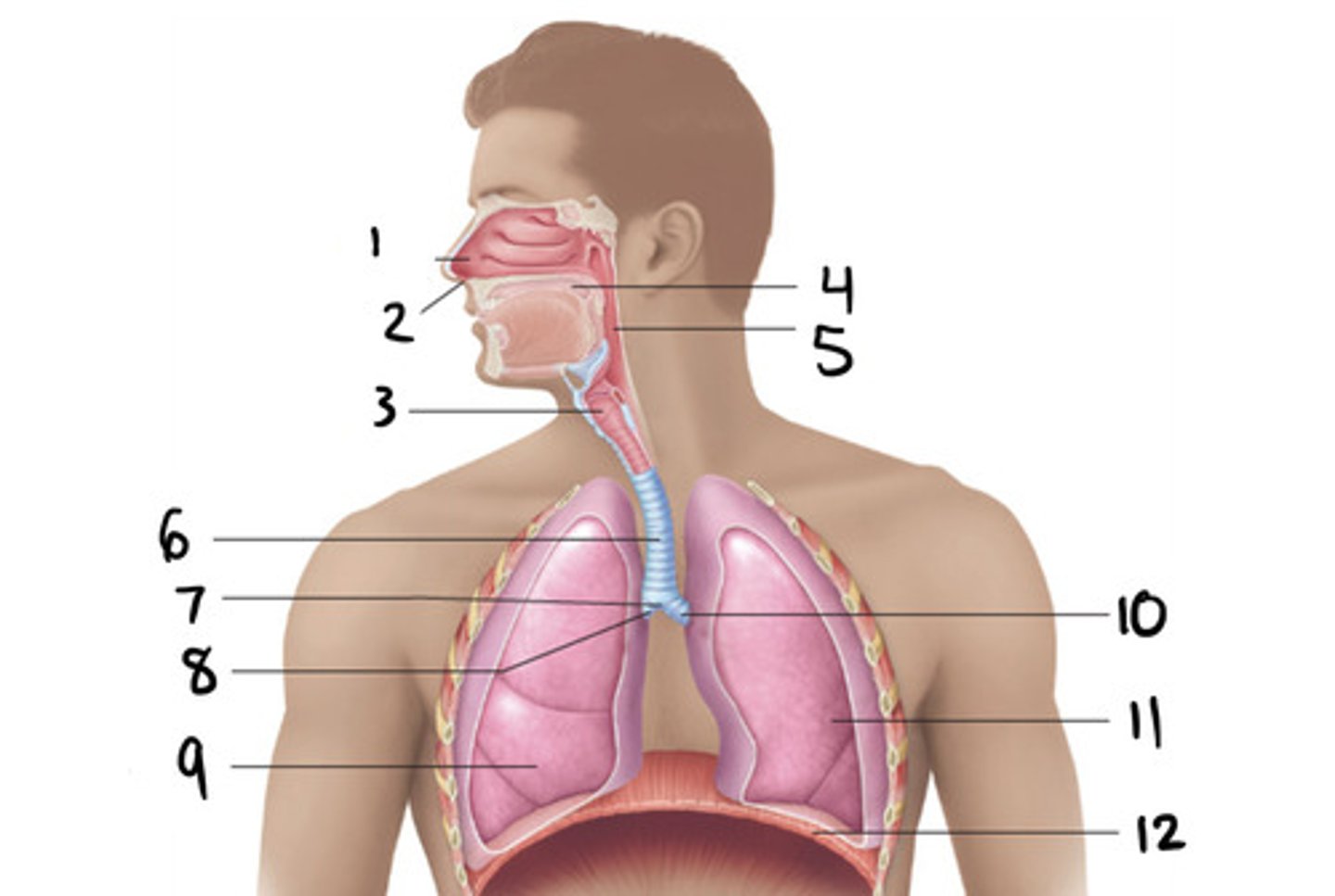
c
What shape is the trachea?
hyaline cartliage
What makes the c shape in the trachea?
carina
What is the last tracheal cartilage that causes a strong cough reflex?
carina
7
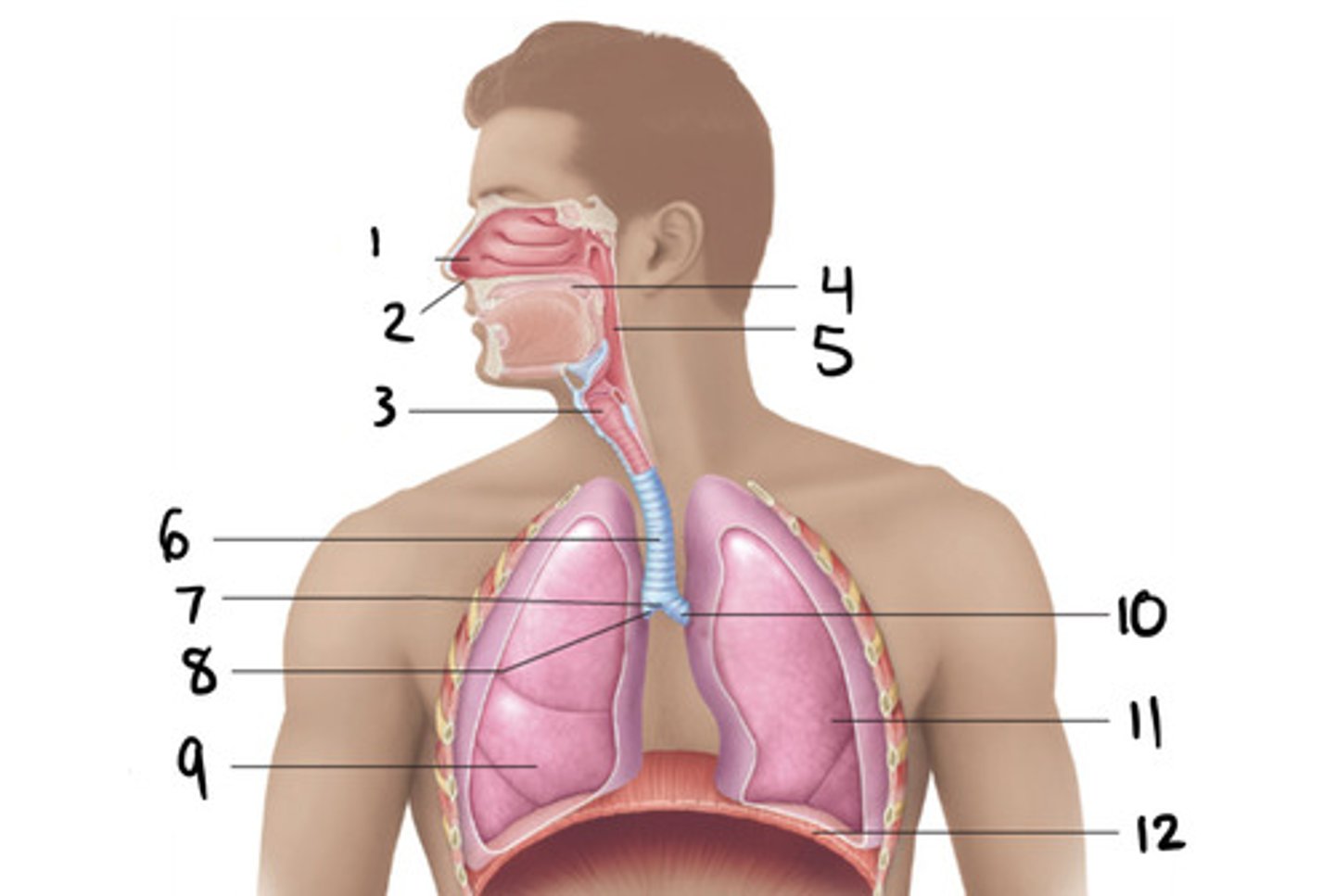
primary bronchi
10 and 8
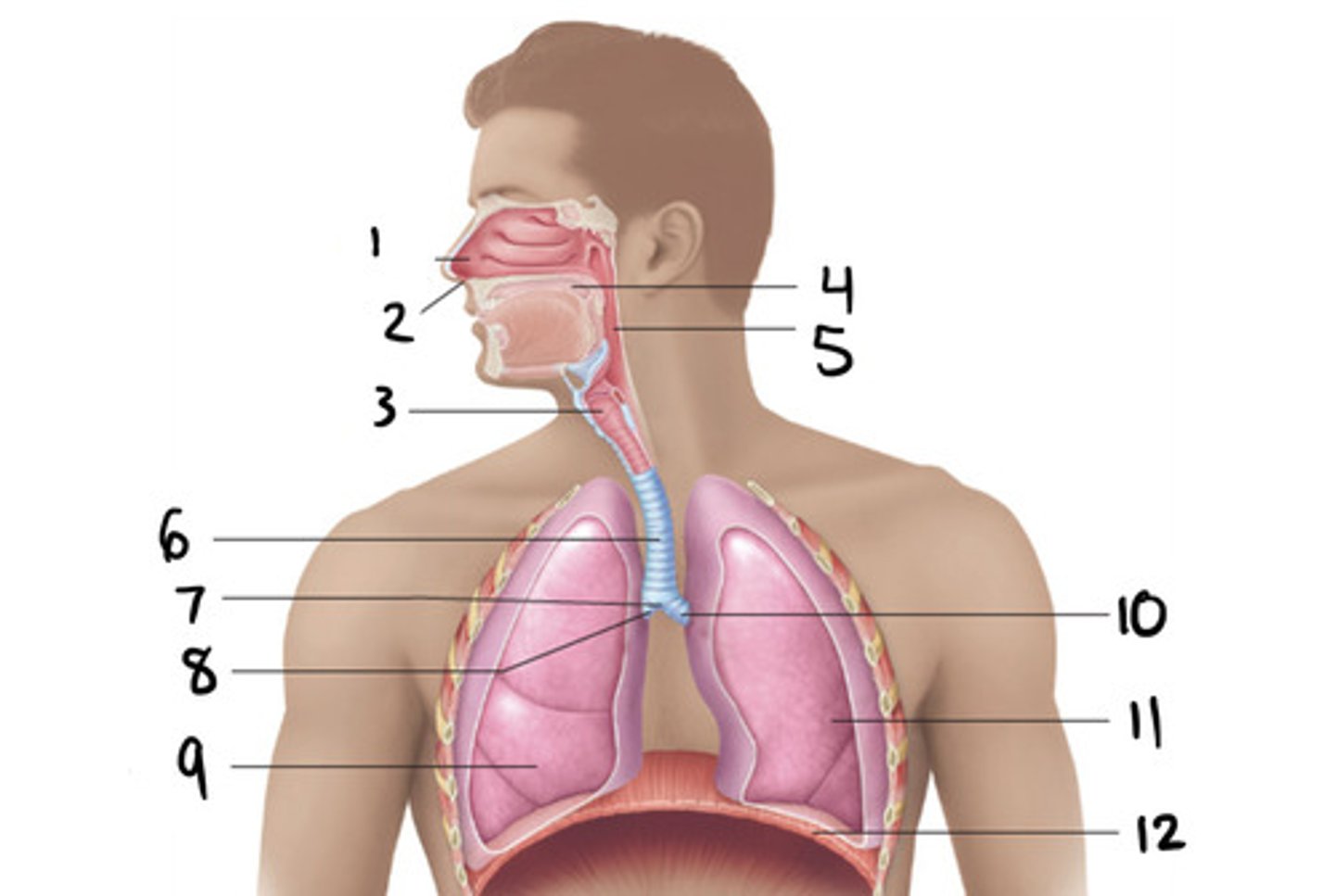
2
How many primary bronchi are there?
2
How many secondary bronchi are there are on the left?
3
How many secondary bronchi are there are on the right?
respiratory bronchioles and alveoli
What is the respiratory zone?
alveoli and pulmonary capillaries
What is the respiratory membrane composed of?
2
How many lungs does the left lung have?
3
How many lobes does the right lung have?
heart
The left lung have less lobes than the right to make room for what?
puncturing the pleura
What is a pneumothorax?
parietal
What is the outer layer of the pleura?
visceral
What is the inner layer of the pleura?
reduce friction
What does the pleural membranes do?
surfactant and negative interpleural pressure
What stops the lungs from collapsing?
surfactant
What changes the surface tension around alveoli to keep the lungs inflated?
-4
The negative interpleural pressure is around what?
nose to terminal bronchioles
From what to what is the conducting zone?
upper and lower respiratory tract
what is the structural way to separate the respiratory system?
conducting and respiratory zone
what is the functional way to separate the respiratory system?
larynx
What separates the upper and lower respiratory tract?
diaphragm, external intercostals
What are the muscles of inspiration?
none, but under stress internal intercostals and rectus abdominus
What are the muscles of expiration?
p=1/v
What is boyle's law?
inflates
In the bell jar, what happens the the balloon as the diaphragm contracts?
decreases
As the diaphragm contracts, what happens the to the pressure inside the lungs?
500ml
Normal TV
TV
What is the amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal quiet breathing?
700-1200ml
Normal ERV
ERV
What is the amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled after a normal TV?
IRV
What is the amount of air that can be forcibly inhaled after a normal TV?
1900-3100ml
normal IRV
3100-4800ml
normal VC
IRV+ERV+TV
VC equation
VC
What is the total lung capacity available for air movement?
RV
What is the immoveable amount of air remaining within the lungs?
1200ml
normal RV
VC+RV
TLC equation
RRx(TV-DAS)
equation for AVR
RRxTV
equation for MRV
VC-ERV-TV
equation for IRV
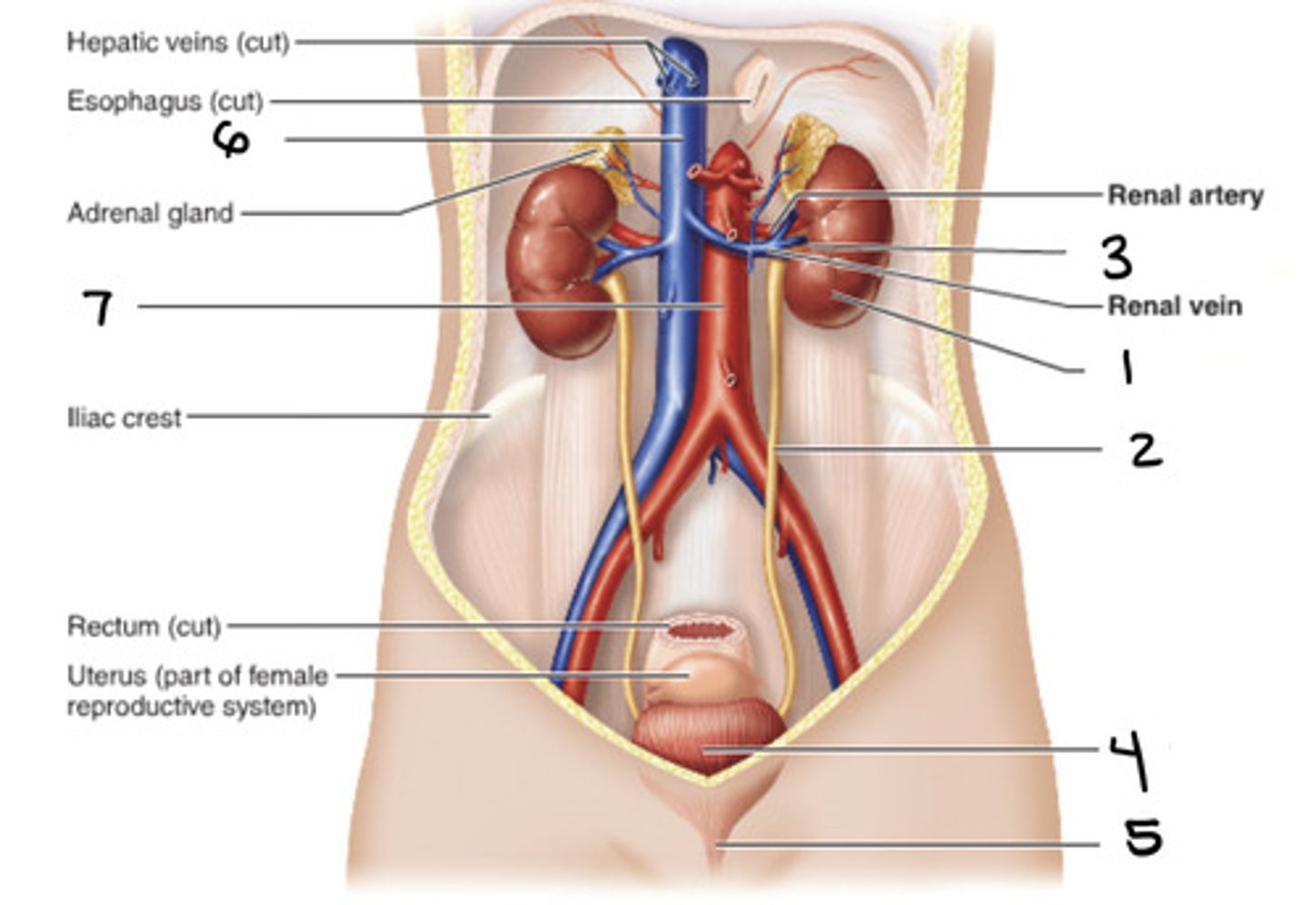
kidney
1
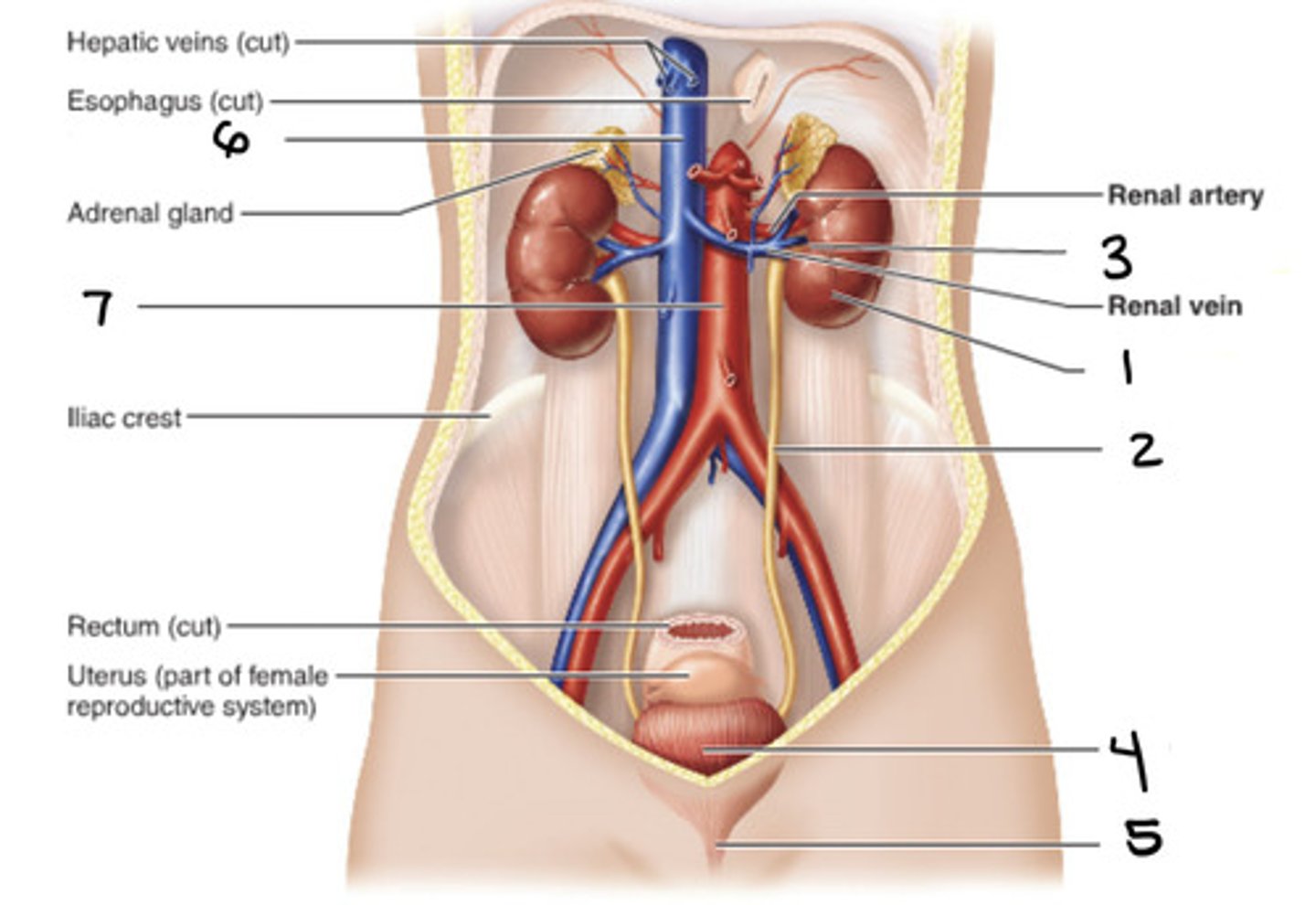
ureter
2
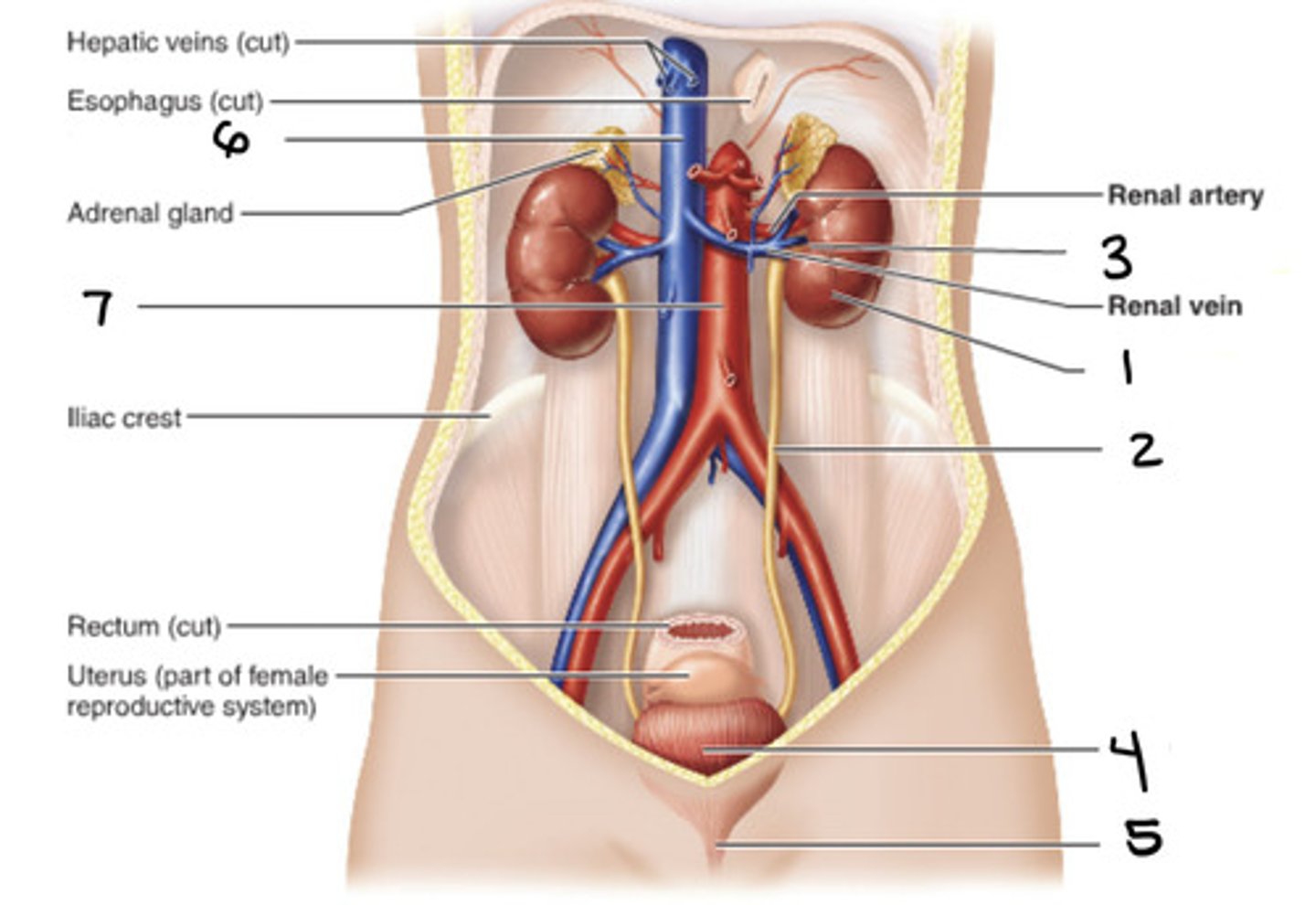
hilum
3
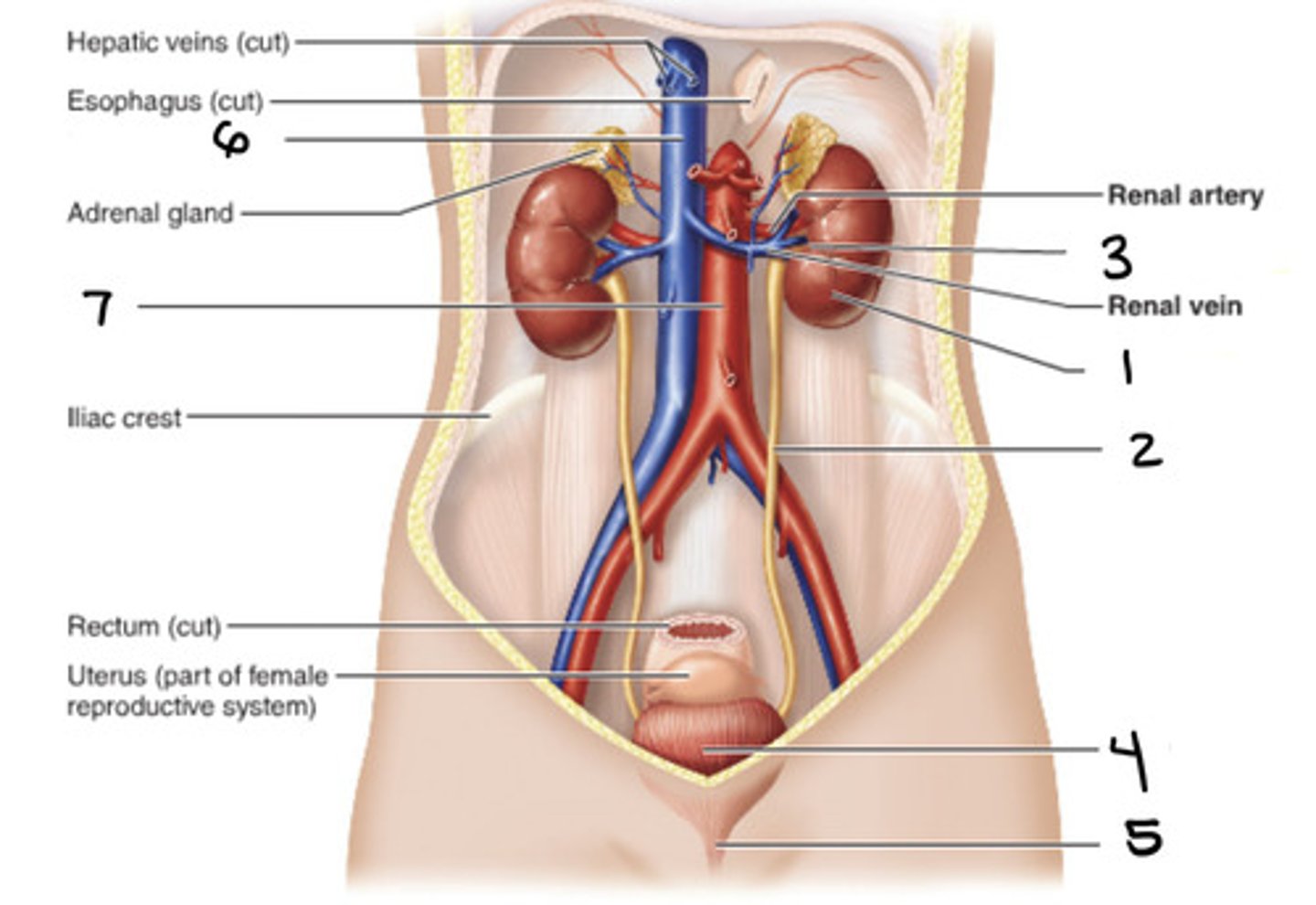
bladder
4
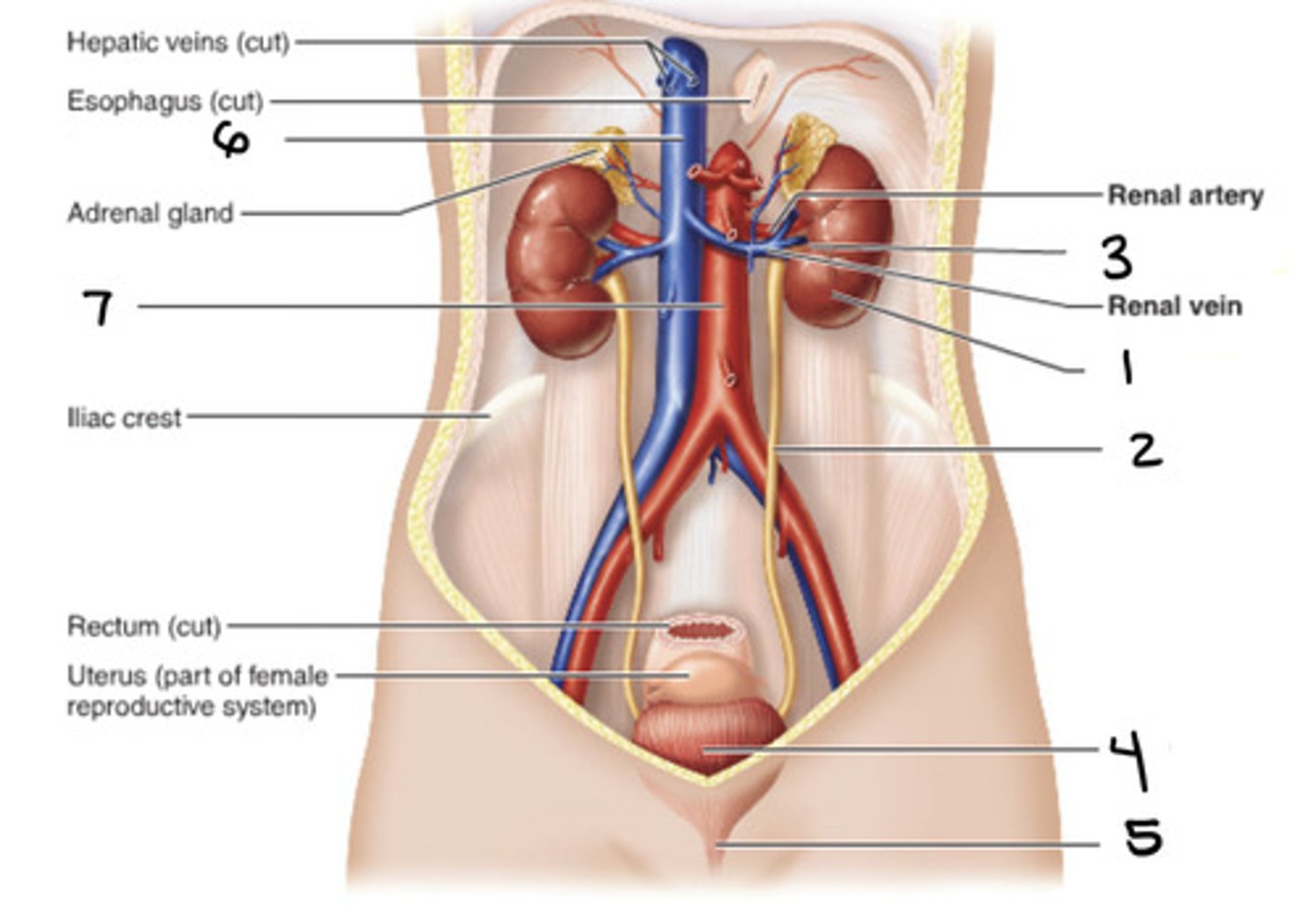
urethra
5
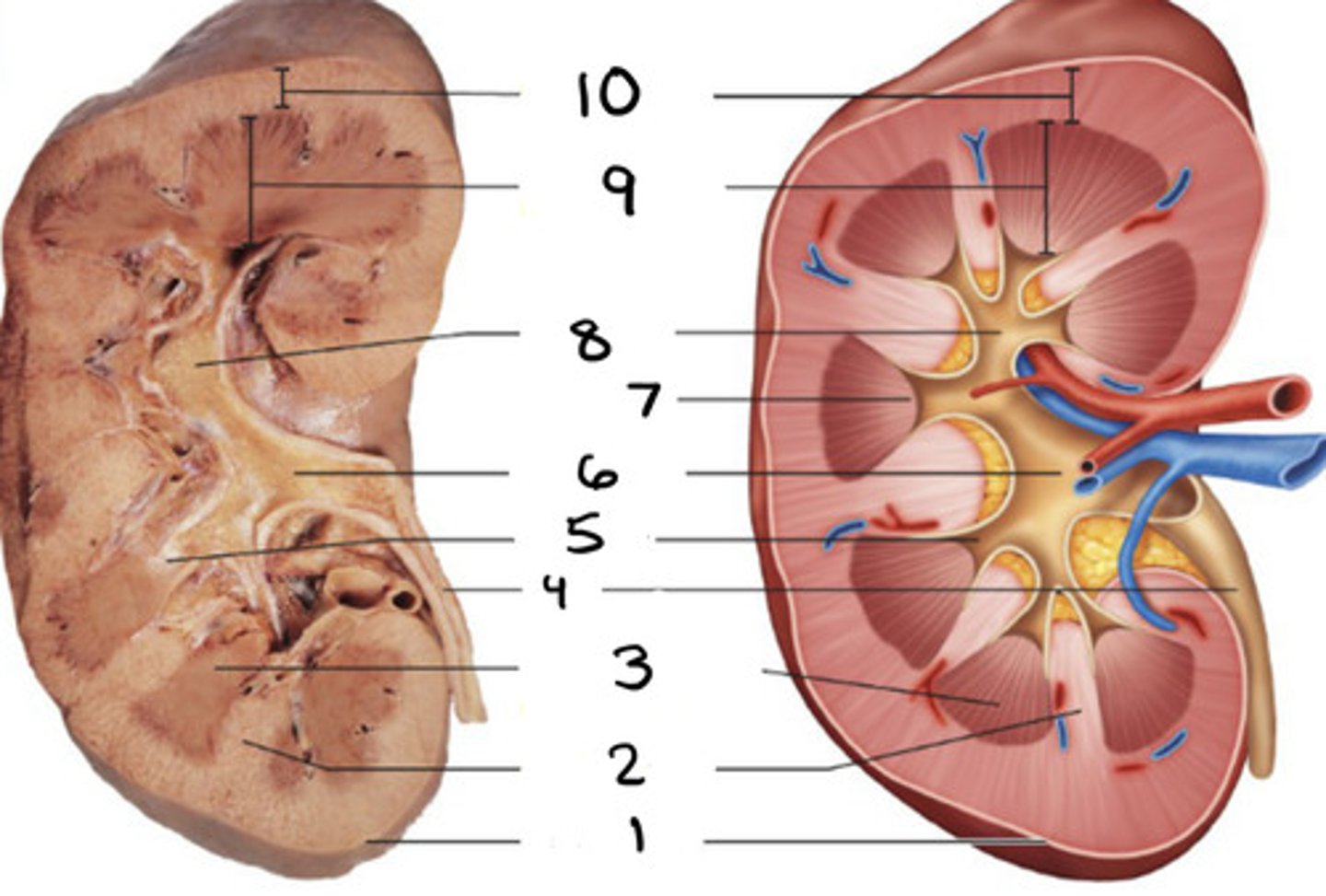
renal column
2
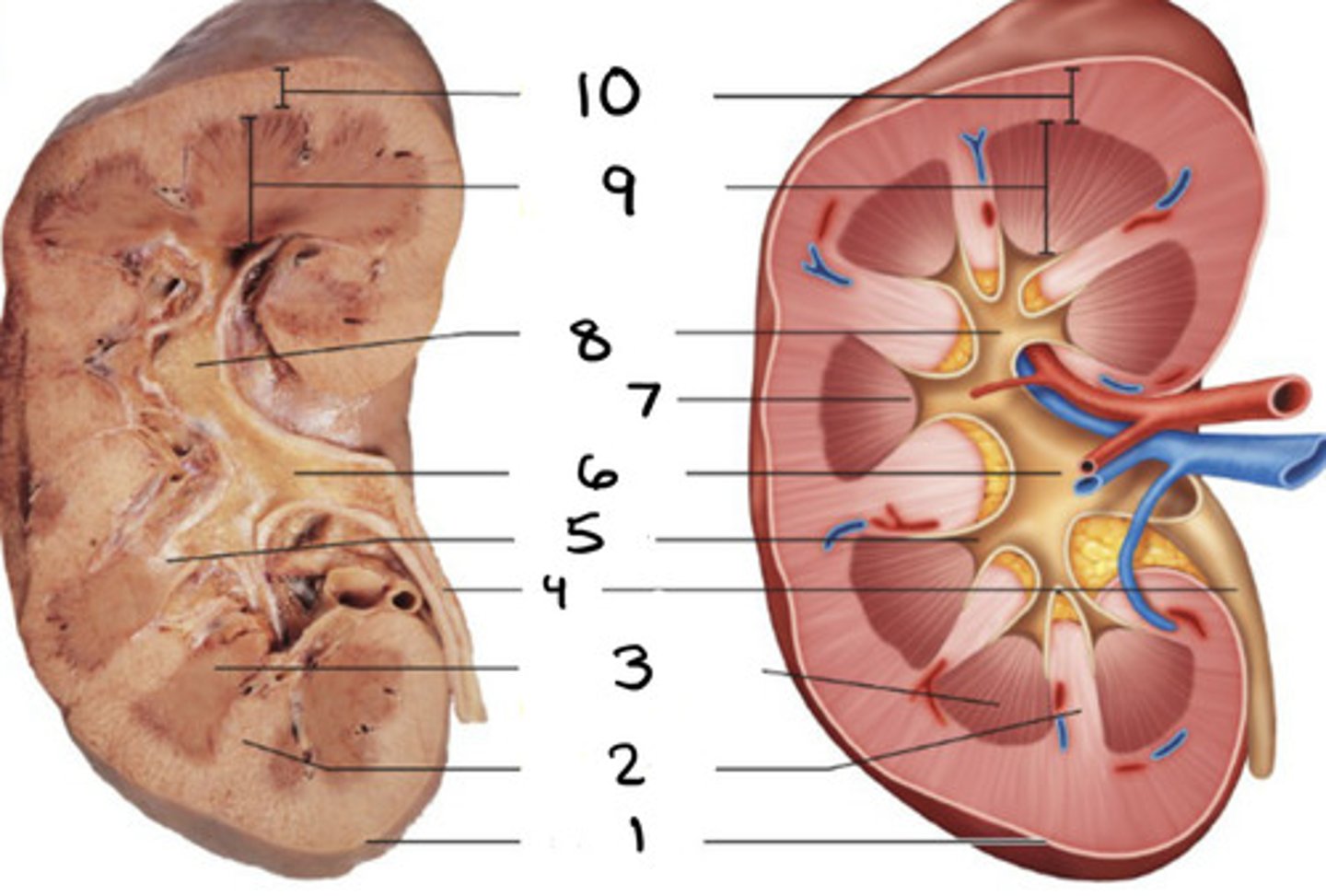
renal pyramid
3
minor caylx
5
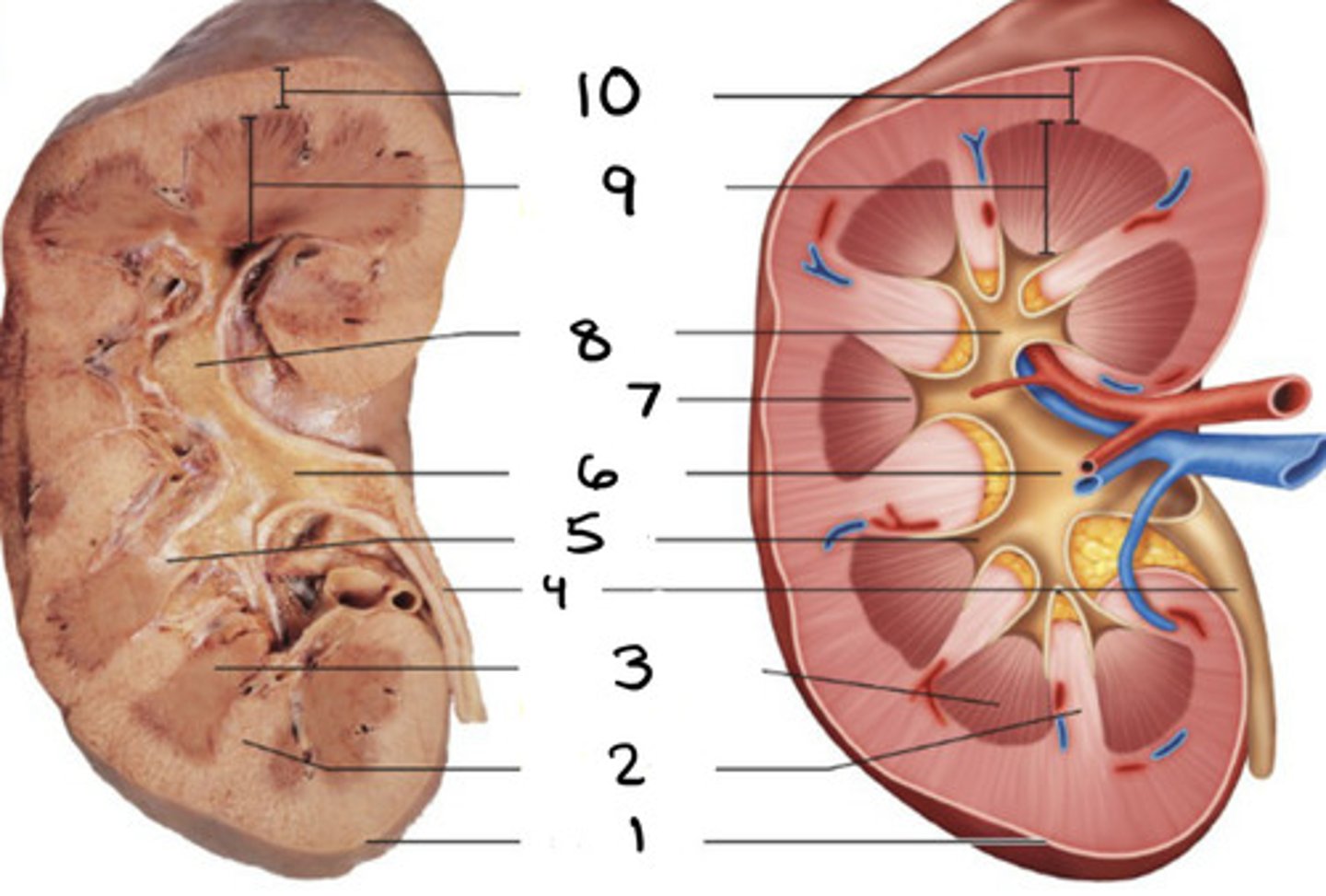
renal pelvis
6
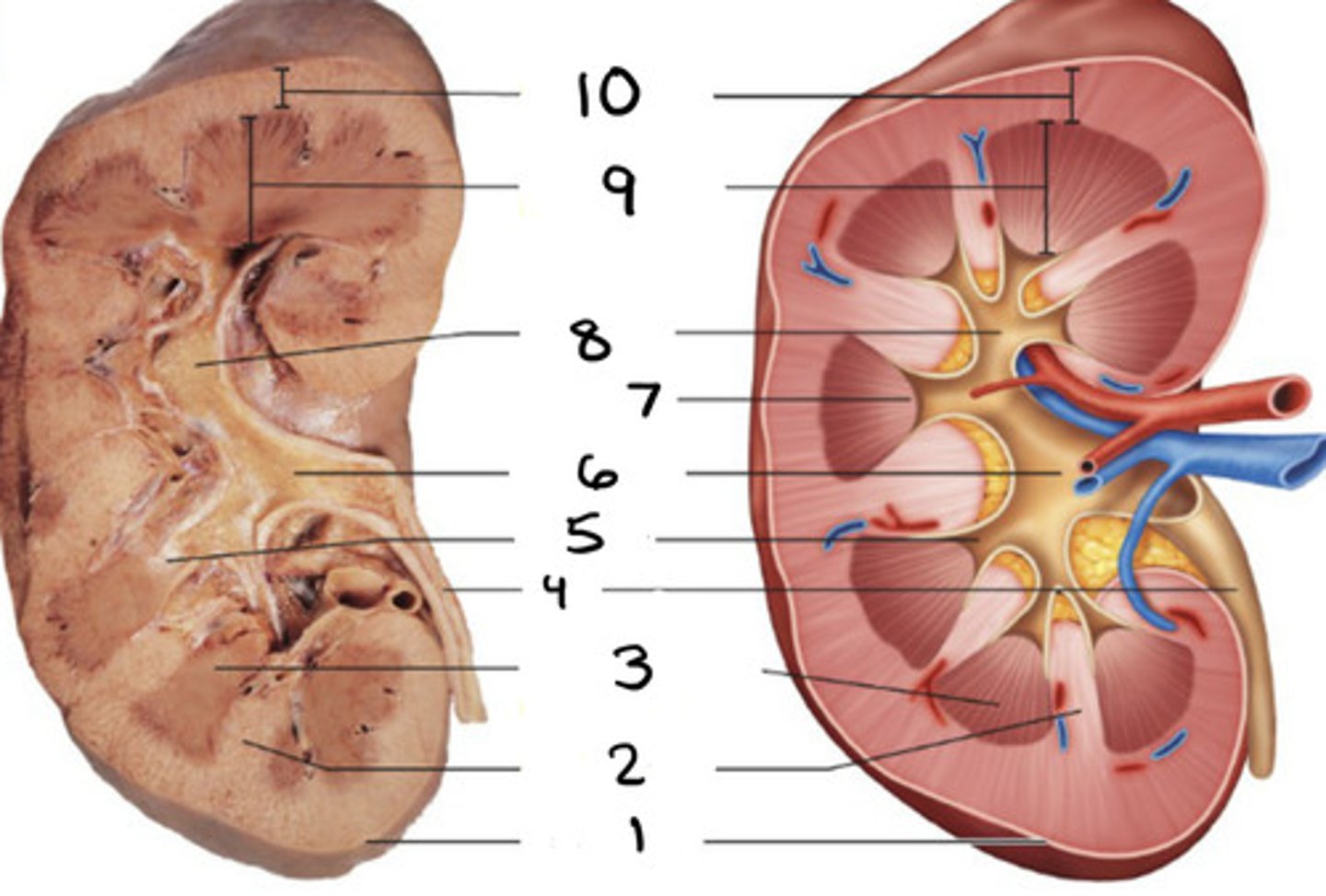
papilla
7
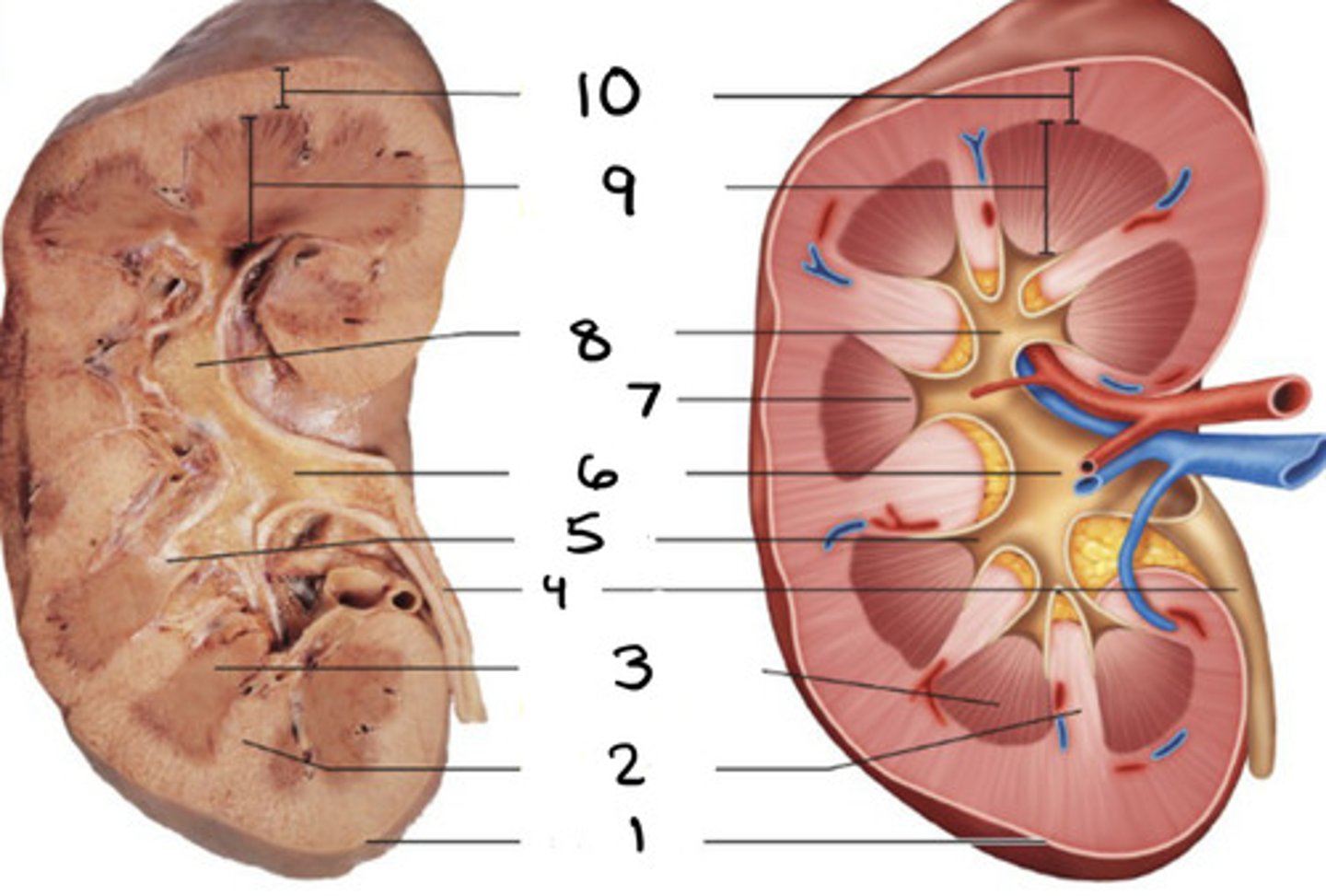
major caylx
8
medulla
9
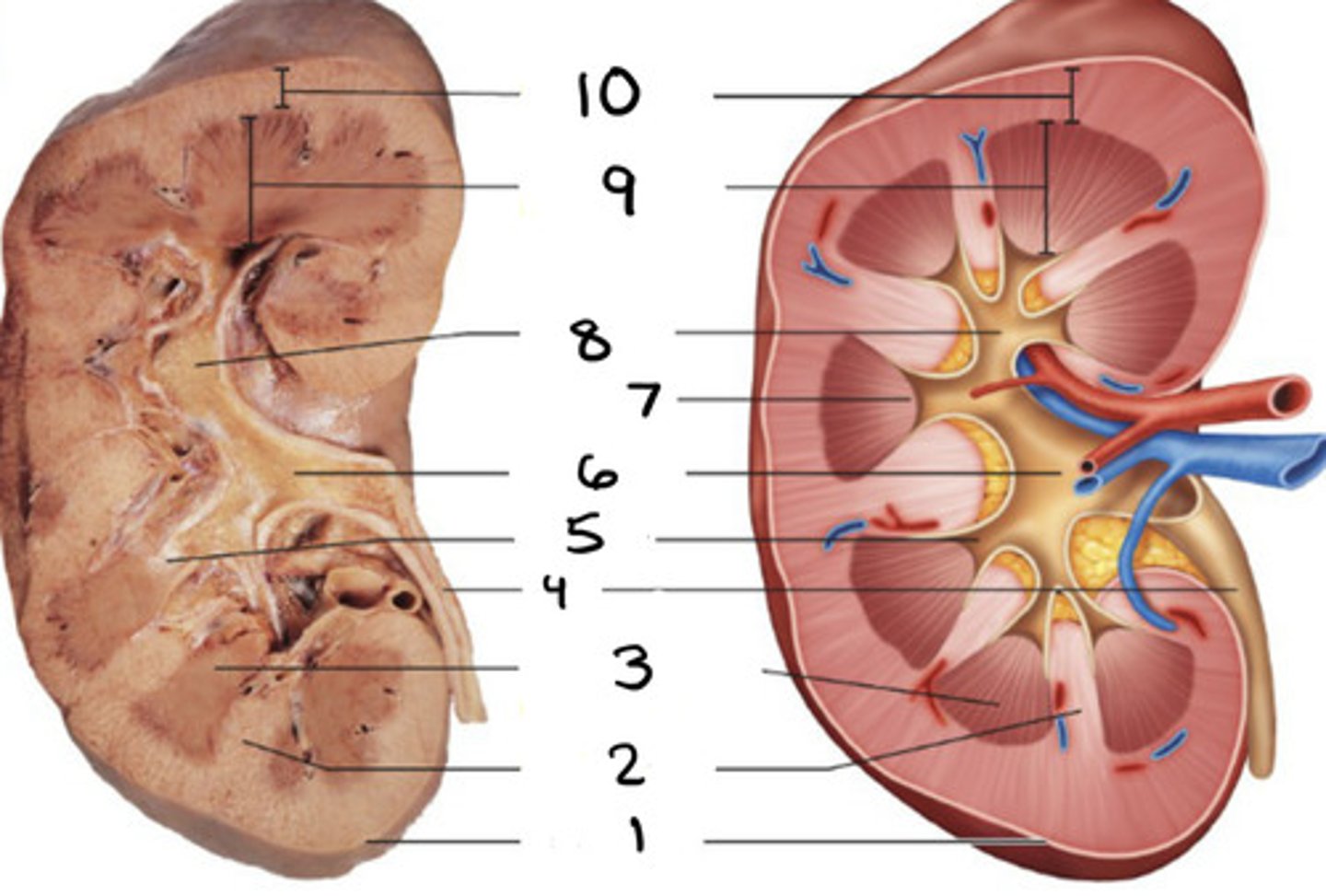
cortex
10
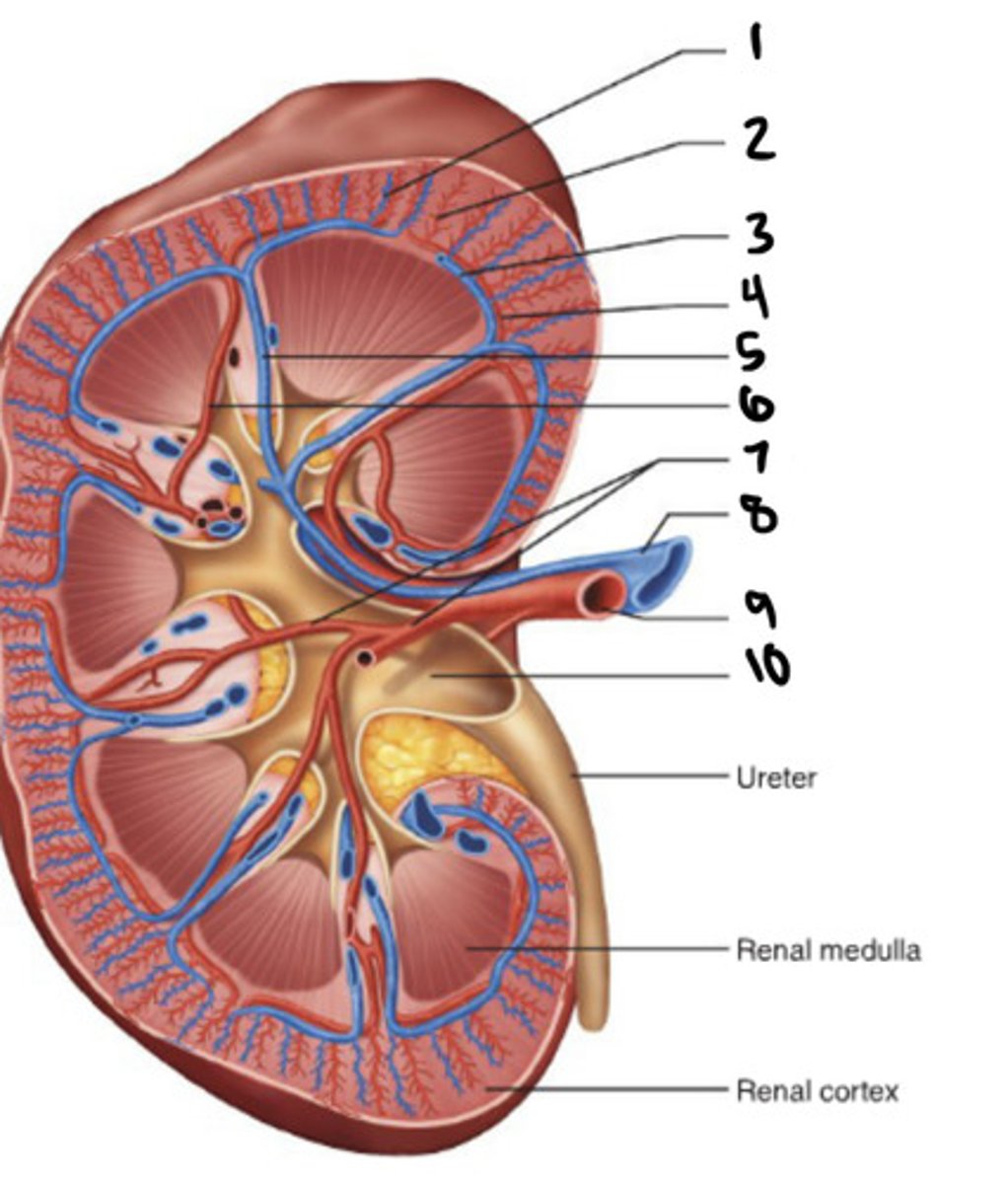
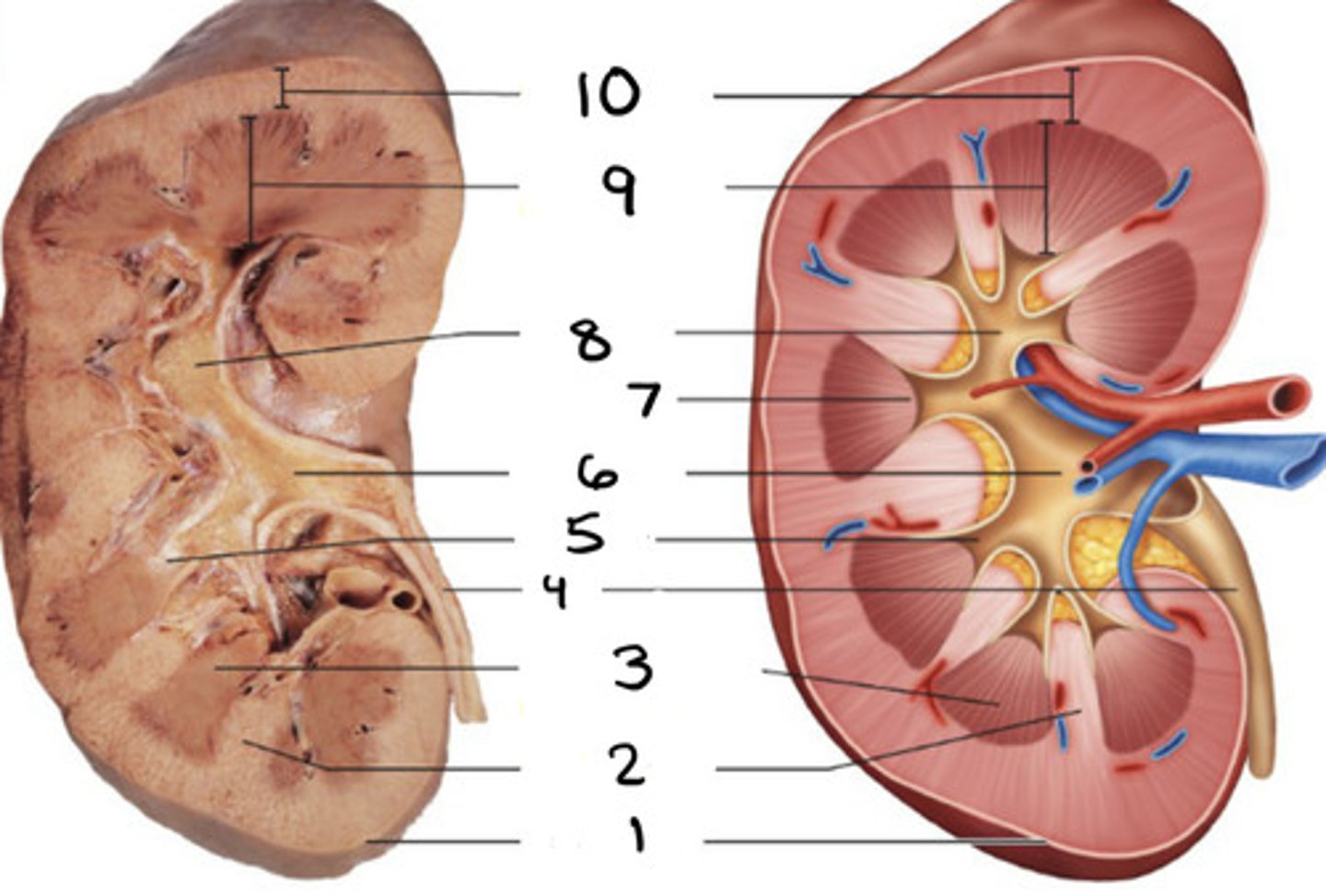
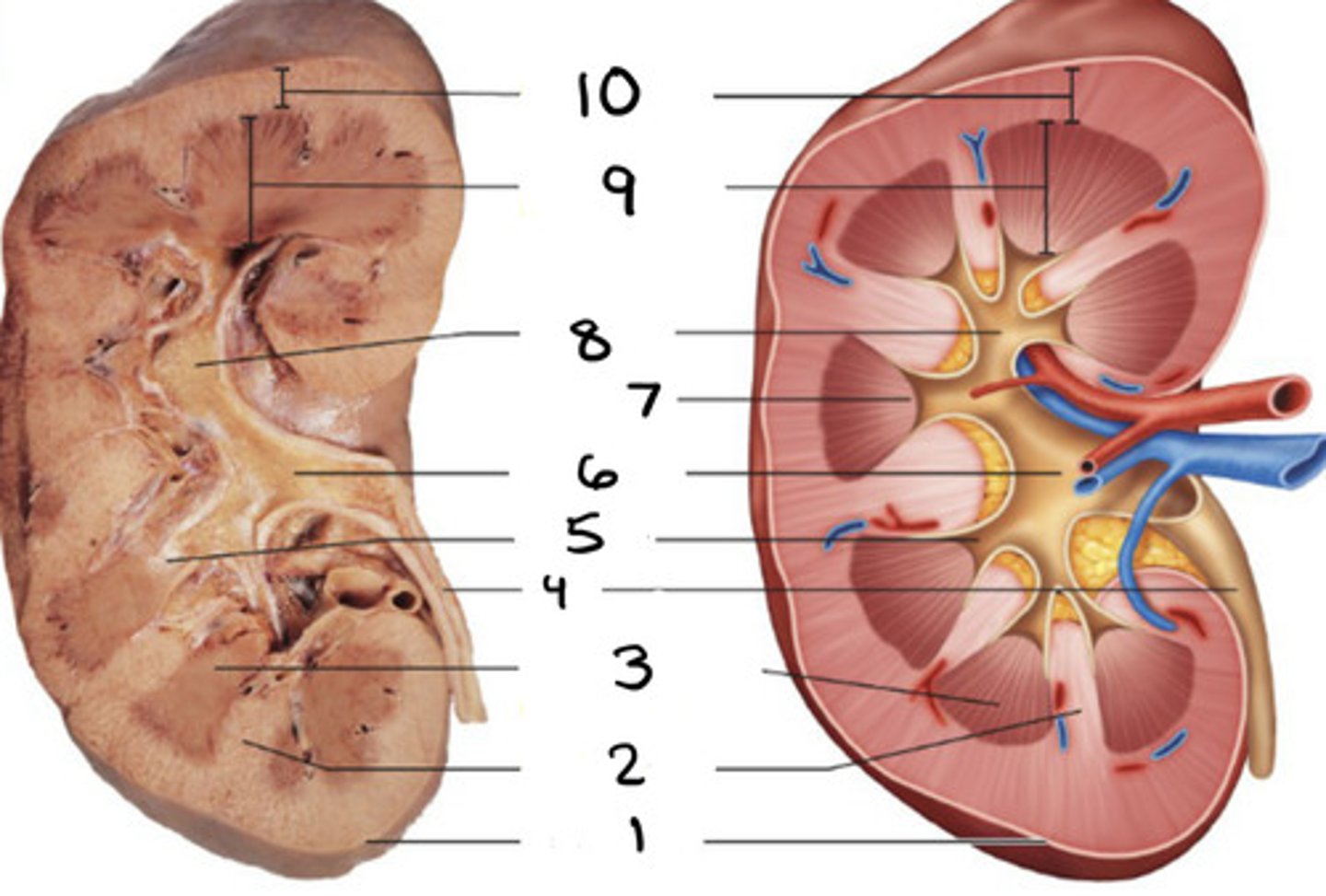
cortical radiate vein
1
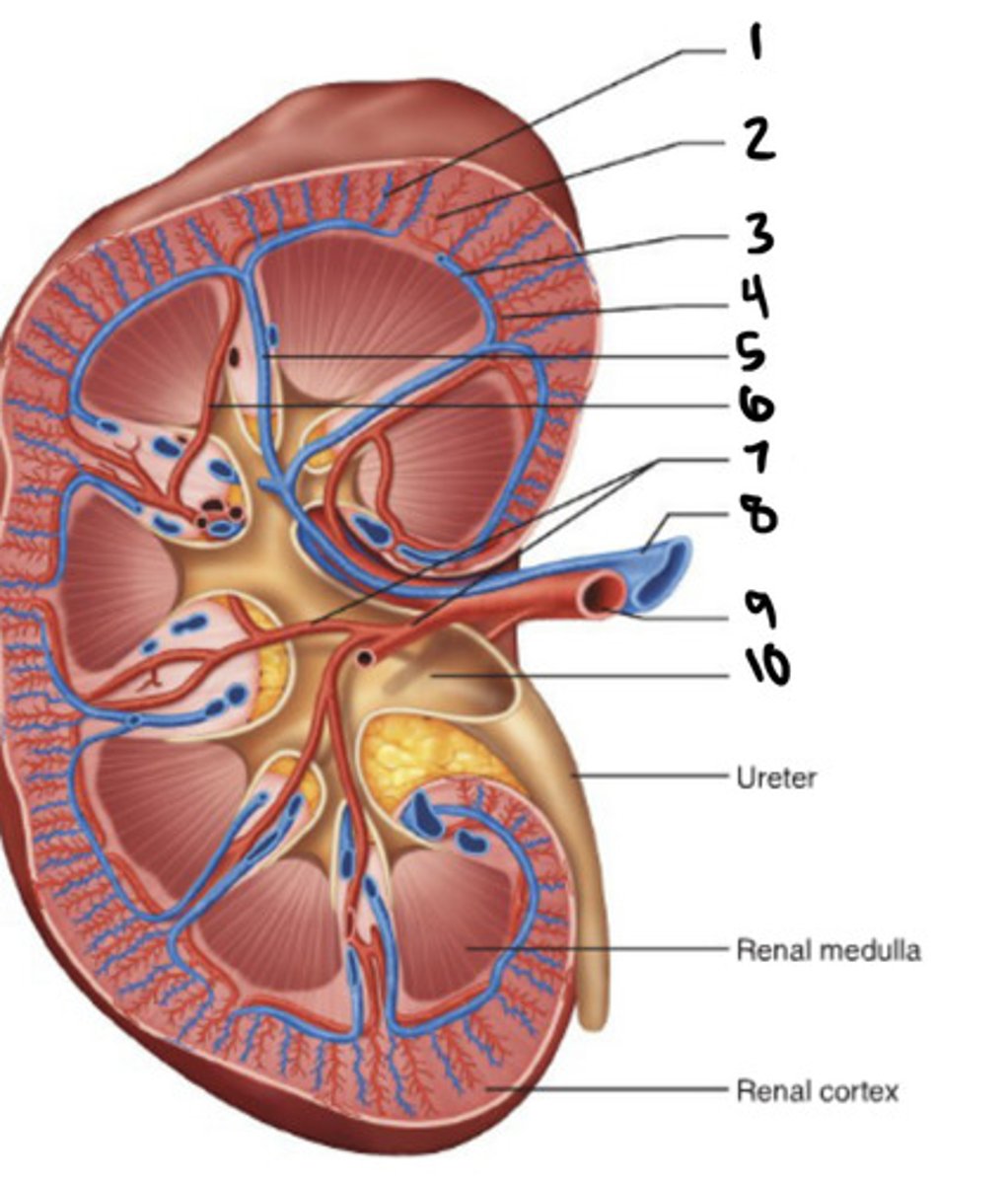
cortical radiate artery
2
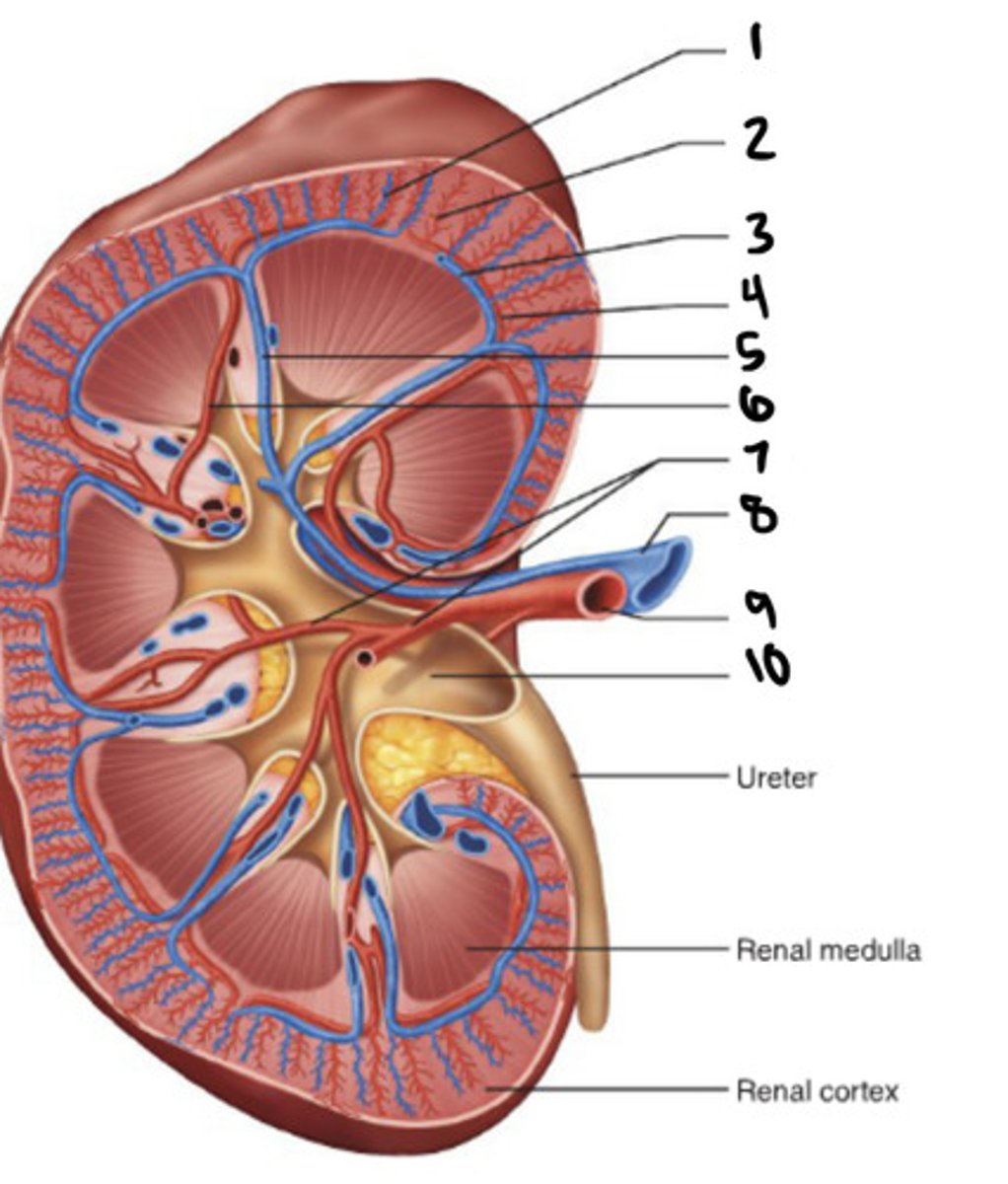
arcuate vein
3
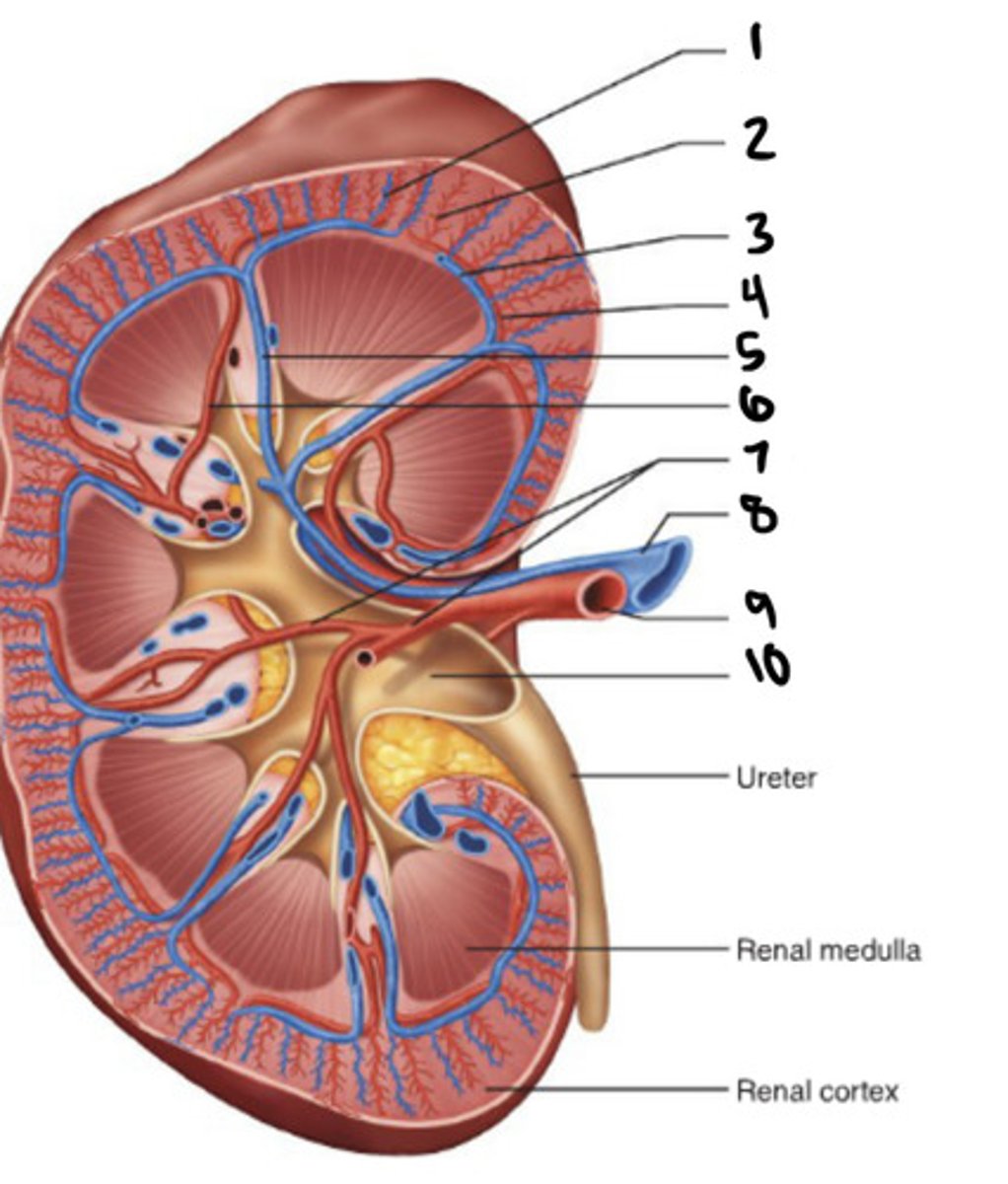
Arucate artery
4
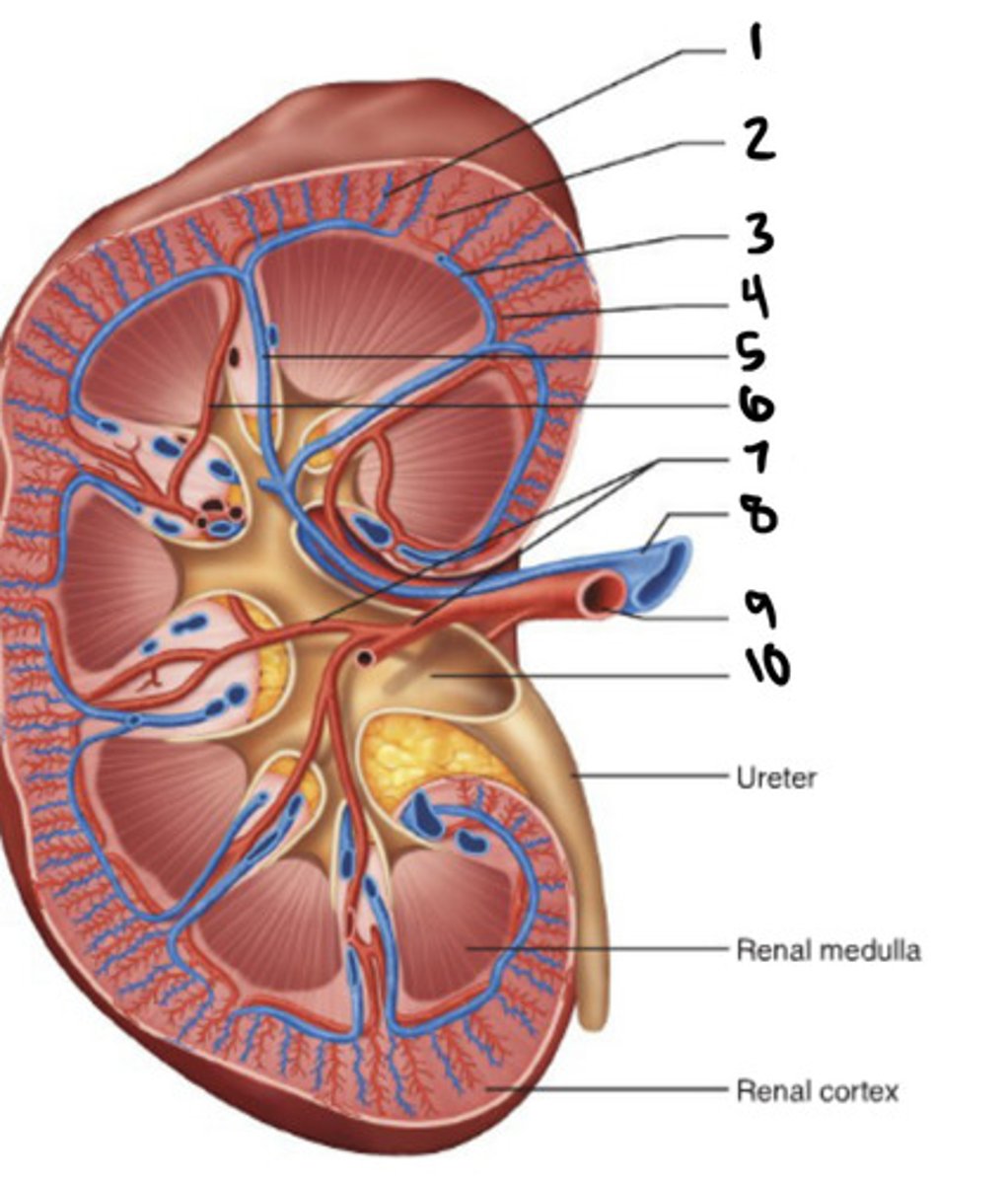
interlobar vein
5
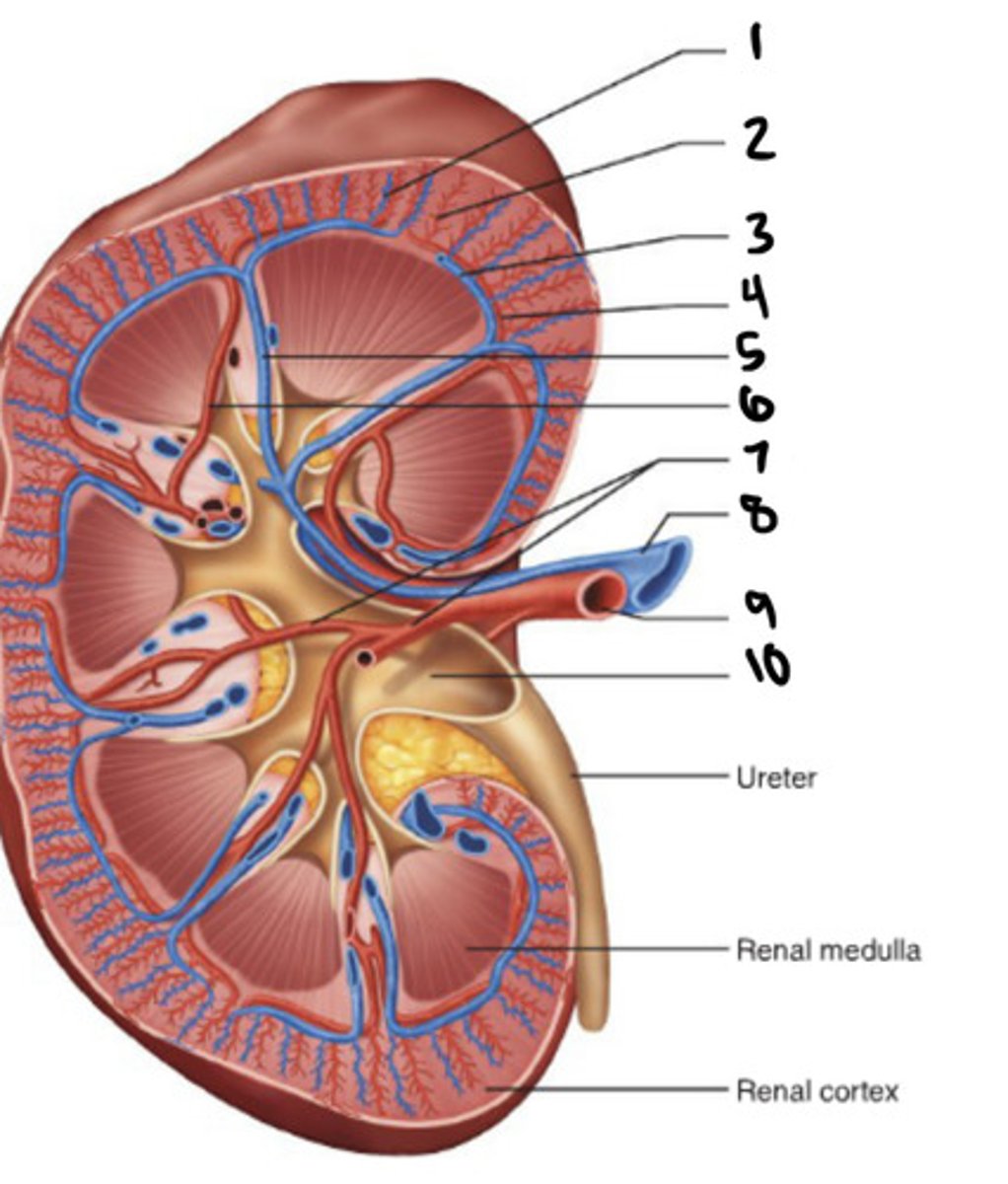
interlobar artery
6
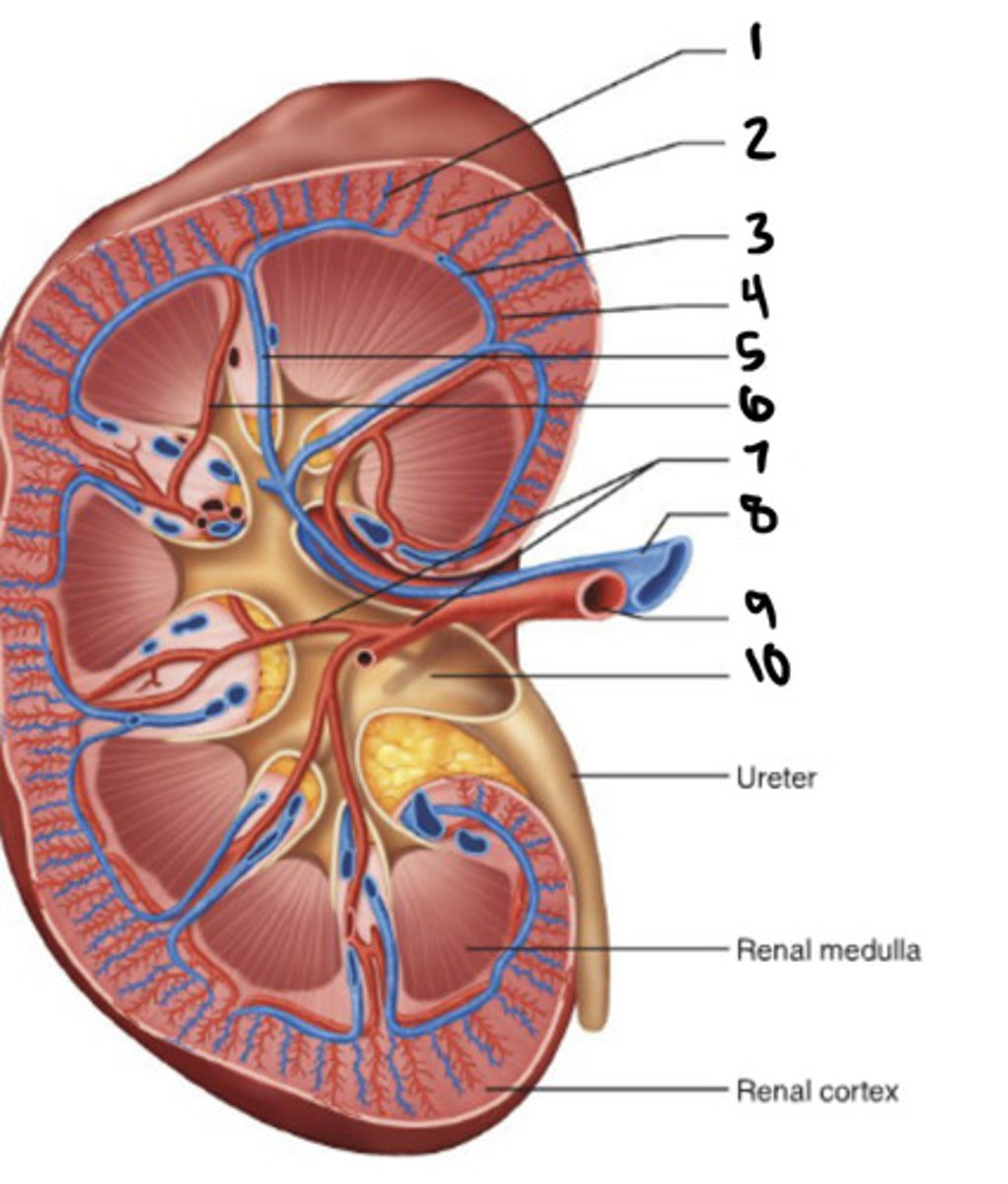
segmental artery
7