BIOL 260 Exam 1
1/203
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
204 Terms
Anatomy
The branch of biology that studies the science of body forms (aka structures) and relationships between them
Gross (macroscopic) anatomy
The study of anatomical structures visible to the naked eye, including organs and organ systems.
Microscopic anatomy
The branch of anatomy that deals with structures that cannot be seen with the naked eye and require magnification, such as cells and tissues.
Cytology
Study of the structure and function of individual cells
Physiology
The branch of biology that studies the science of body functions
What are the levels of organization
Atom
Molecule
organelle
Cell Tissue
Organ
System
Organism
Molecules
Made up of two or more atoms sharing electrons
Atoms
The smallest unit of matter that can participate in chemical reactions
Made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Nonliving
Macromolecules
The largest molecules, such as proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids
What atoms are essential for maintaining life?
Ca, P, N, O, C, S, and H
Cells
Made up of molecules coming together
Smallest living element of an organism that carry out all the basic functions of life
Which of the following INCORRECTLY pairs the
structure with the organization level?
A. Lipid = macromolecule
B. Neuron = cell
C. Nitrogen = molecule
D. Nucleus = organelle
C. Nitrogen = molecule
Tissues
Groups of cells and the materials around them that work together to perform a particular function
Four basic tissue types are?
Epithelial tissue - covers body surfaces, lines body cavities, and forms glands.
Connective tissue - supports, binds, and protects other tissues and organs (e.g., bone, blood, fat, cartilage).
Muscle tissue - specialized for contraction and movement (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle).
Nervous tissue - specialized for communication and control by transmitting electrical impulses (neurons and supporting glial cells)
Organs
Made up of at least two different types of tissues joined together
They have specific functions and usually have recognizable shapes
Skin is biggest organ
A single tissue can belong to two organ systems
Organ system
A group of organs with a common function
Some are categorized into several different organ systems
What are the eleven human organ systems?
Integumentary
Skeletal
Muscular (aka musculoskeletal)
Nervous
Endocrine
Cardiovascular
Lymphoid
Respiratory
Digestive
Urinary
Genital
What is organismal organization?
Any living individual
All parts of the human body functioning together
A group of organs responsible for the filtration
of blood and excretion of liquid waste would
mostly likely be called the:
A. Digestive system
B. Endocrine system
C. Musculoskeletal system
D. Urinary system
D. Urinary system
Metabolism
Sum of all chemical process that occur in the body
two types:
Catabolism: Reactions that break complex molecules into smaller ones
Anabolism: Reactions that build complex molecules from smaller ones
Cellular composition
Living matter is always compartmentalized into one or more cells
Responsiveness
Ability to detect and respond to changes to maintain homeostasis
Movement
Motion of the whole body, individual organs, single cells, and tiny structures inside cells
Development
All of the changes the body goes through in life
Two major processes:
Differentiation: Transformation of cells with no specialized function into cells that are committed to a particular task
Growth: Increase in size or number of cells, contributing to overall body mass.
Reproduction
Formation of new cells for tissue growth, repair, or replacement, or the production of a new individual
Evolution
Living species exhibit genetic change from generation to generation (only seen in population, not individual)
Variation
Differences in traits among individuals within a population, often due to genetic differences.
Homeostasis
Tendency of a living body to maintain relatively stable internal conditions in spite of great changes in its external environment
Set point: The physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates
Dynamic equilibrium: Fluctuation around the set point as the body maintains homeostasis
Intracellular fluid
The fluid found inside cells, crucial for cellular processes and maintaining homeostasis.
Cytosol
Extracellular fluid
Fluid found outside cells, playing a key role in nutrient transport and waste removal.
Interstitial, blood plasma, lymph plasma
What can a disruption in homeostasis cause?
Disruptions in homeostasis can lead to diseases, dysfunctions, or a failure of normal physiological processes, ultimately affecting health and survival.
________ and ________ systems work together to restore internal environment balance
Nervous, Endocrine
Nervous systems use nerve impulses
Endocrine system uses hormones
Three parts of the feedback systems
Receptor (or sensor) = Detects change
Control center = sets range of controlled conditions; processes the information, relates it, and makes a decision about what the appropriate response should be
Effector = produces response
Negative feedback and example
Self-corrective mechanism; bodily change is detected and responses are activated that reverse the change and restore
Ex: Blood pressure
Baroreceptor detects pressure decrease
brain receives signal and triggers nerve impulses to heart
Heart rate increases to increase BP
Positive feedback and example
Self-amplifying; physiological change leads to an even greater change int he same direction
Ex: Childbirth
Pressure on cervix from contractions detected by nerve receptors
Brain receives signal and triggers secretion of oxytocin hormone
Oxytocin increases strength of uterine contractions
Hydrochloric acid and pepsin are enzymes secreted by
cells in your stomach to digest proteins. The presence
of partially digested protein in the stomach triggers
the secretion of more hydrochloric acid and pepsin.
Thus, once digestion begins, it becomes a self-
accelerating process.
A. Negative feedback
B. Positive feedback
B. Positive feedback
Human hiearchy
The organism is composed of organ system s
Organ systems are composed of organs
Organs are composed of tissues
Tissues are composed of cells
Cells are composed of partly organelles
Organelles are composed of molecules
molecules are composed of atoms
Types of inspections
Palpitation: Feeling a structure with the hands
Auscultation: Listening to the natural sounds made by the body
Percussion: Tapping on the body and feeling for abnormal resistance; pockets of air
Dissection: Cutting and separating tissues to reveal their relationshops
Lying down as two positions; they are?
Prone: Face-down orientation
Supine: Face-up orientation
Anterior (ventral)
Front; toward the front
Ex: Toes are anterior to the foot
Posterior (dorsal)
Back; toward the back
Ex: Buttocks is posterior to the patella
Superior (cranial)
Above; toward the head - rarely used for limbs
Ex: Oris is superior to abdomen
Inferior (caudal)
Below; toward the feet or around the tail
Ex: Pelvis is inferior to the abdomen
Lateral
The side; toward side of the body
Ex: The thumb is lateral to the digits
Medial
Middle; toward the middle of the body
Ex: The sternum is medial to the ribs
Proximal
Closer to the point of attachment or trunk of the body
Ex: The elbow is proximal to the wrist.
Distal
Farther from the point of attachment or trunk of the body
Ex: The fingers are distal to the wrist.
Superficial
Position closer to the surface (skin)
Ex: The skin is superficial to the bones
Deep
Position farther from the surface of the body
Ex: The brain is deep to the skull
Sagittal
Divides the body or an organ vertically into left and right
Midsagittal (median): equal right and left sides
Parasagittal (longitudinal: unequal right and left sides
Frontal (coronal)
Divide into anterior and posterior position
Transverse
Divides the body or organ horizontally into upper and lower portions
Oblique
Any type of angle other than horizontal or vertical
Body cavities: Dorsal (posterior)
Cranial cavity: Houses the brain - protected by the cranium
Vertebral canal: Encloses the spinal cord
protected by skull, vertebral column, and cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid
A clear fluid that surrounds and protects the brain and spinal cord, providing cushioning and nutritional support.
Body cavities: Anterior (ventral)
Thoracic: More superior subdivision. Enclosed by the rib cage and contains the lungs and heart
Diaphragm: forms floor of the thoracic cavity
Abdominal cavity
Largest cavity in the body
Protects the digestive organs, spleen, kidneys, urinary bladder, rectum, and reproductive organs
Lined by peritoneum membrane lining
Pleural cavity
The thin space between the visceral and parietal pleura surrounding each lung, which contains pleural fluid to reduce friction during breathing.
Pericardial cavity
Cavity surrounding the heart, provides a protective environment and contains fluid to reduce friction during heart movements.
Pelvic cavity
The space bounded by the pelvic bones, containing the reproductive organs, urinary bladder, and distal part of the gastrointestinal tract.
Label the abdominal regions and quadrants
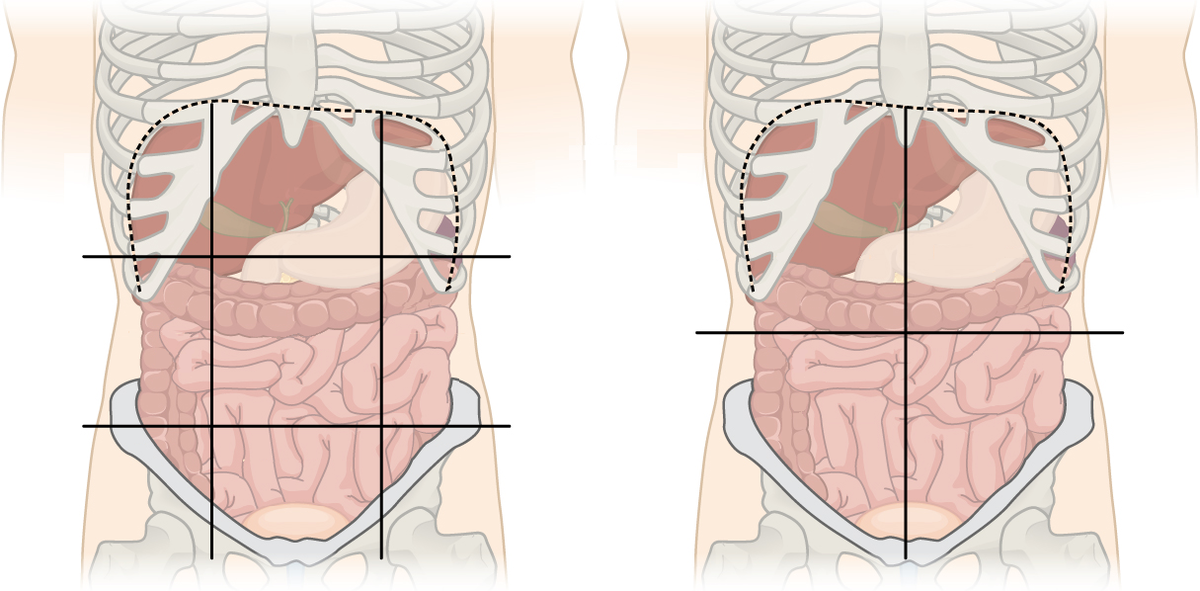
Membranes of the anterior (ventral) body cavity
Parietal layers: lines the walls of the body cavity - more superficial layer
Visceral layers: covers the organs
Serous membrane
a thin layer of tissue that covers the walls and organs in the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
What are the 3 serous cavities + associated membranes
Pleura: covers the lungs Pericardium: covers the heart Peritoneum: covers abdominal organs
Axial region
Consists of the head, neck, and trunk
Trunk region
2 regions
Thoracic: above the diaphragm
Abdominal: below the diaphragm
Systems of protection, support, and movement
Integumentary system
Skeletal system
Muscular system
Systems of internal communication and control
Nervous system
Endocrine system
Systems of fluid transport
Circulatory system
Lymphatic system
Systems of intake and output
Respiratory system
Urinary system
Digestive system
Systems of reproduction
Male reproductive system
Female reproductive system
Principal organs and functions: Integumentary system
Organs: Skin, hair, nails, cutaneous glands
Function: protection, water retention, thermoregulation, vitamin D synthesis, nonverbal communication
Principal organs and functions: Skeletal system
Organs: bones, cartilage, ligaments
Function: support, movement, protective enclosure of viscera, blood formation, mineral storage, electrolyte and acid-base balance
Principal organs and functions: Muscular system
Organs: skeletal muscles
Function: Movement, stability, communication, control of body openings, heat production
Principal organs and functions: Lymphoid system
Organs: lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, thymus, spleen, tonsils
Function: recovery of excess tissue fluid, detection of pathogens, production of immune cells, defense against disease
Principal organs and functions: Repiratory system
Organs: Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs
Function: absorption of oxygen, discharge of carbon dioxide, acid-base balance, speech
Principal organs and functions: Urinary system
Organs: kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
Function: elimination of wastes; regulation of blood volume and pressure; stimulation of red blood cell formation; control of fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balancer detoxification
Principal organs and functions: Nervous system
Organs: brain, spinal cord, nerves, ganglia
Function: rapid internal communication, coordination, motor control and sensation
Principal organs and functions: Endocrine system
Organs: pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, thymus, adrenal glands, pancreas, testes, ovaries
Function: hormone production, internal chemical communication
Principal organs and functions: Circulatory system
Organs: heart, blood vessels
Function: distribution of nutrients, oxygen, wastes, hormones, electrolytes, heat, immune cells, and antibodies; acid-base balance
Principal organs and functions: Digestive system
Organs: teeth, tongue, salivary glands, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
Function: nutrient breakdown and absorption. liver functions include metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins; disposal of drugs, toxins, and hormones; cleansing of blood
Principal organs and functions: Male reproductive system
Organs: testes, epididymides, spermatic ducts, seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral glands, penis
Function: production and delivery of sperm; secretion of sex hormones
Principal organs and functions: Female reproductive system
Organs: ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, mammary glands
Function: production of eggs, site of fertilization and fetal development; fetal nourishment; birth; lactation; secretion of sex hormones
In anatomical position they are:
Standing upright
Facing the observer, head level
Eyes facing forward
Feet flat on the floor
Arms at the sides
Palms turned forward
Gradient
A difference in a chemical concentration, electrical change, physical pressure, temperature, or other variables between one point and another
Down the gradient
Matter or energy moves from the point of higher value to the lower point
high to low
Up the gradient
Matter or energy moves form the point of lower value to the higher point
low to high
Pressure gradient
High pressure to low pressure
unkinking a water hose
Electrical, concentration, and thermal gradient
Electrical: The difference in electric potential
Concentration: The difference in solute concentration
Thermal: The difference in temperature across a distance
Chemical element
Simplest form of matter to have unique chemical properties
cannot be broken down or created by ordinary chemical means
Matter
Anything that occupies space and has mass
All living and nonliving things consist of matter
Mass
The amount of matter in any object
mass does not change
Weight
The force of gravity acting on matter
Major elements vs Lesser elements vs Trace elements
Make up 96% body weight
includes oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen
Make up about 3.6% body weight
includes calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, sodium, chlorine, magnesium, and iron
Present in tiny amounts; 0.7% body weight
Iodine, copper, and zinc
Isotopes
Atoms of an element that have different #’s of neutrons and therefore different mass numbers
Electron shell vs Valence electrons
Electron shell shows where an electron could be
Valence electrons are those in the outer shell that can participate in chemical reactions and determines the likelihood that an atom will form a chemical bond with another atom
Mass number
Sum of its protons and neutrons
Compound vs Ion
A substance that can be broken down into 2 or more different elements
An atom with an electrical charge
Cation vs Anion
Cation: Atom that has lost an electron (positive charge)
Anion: Atom that has gained an electron (negative charge)
Cohesion vs Adhesion vs Surface tension
Cohesion: Attraction between like molecules; results in surface tension.
Adhesion: Attraction between different molecules; helps liquid stick to surfaces.
Surface tension: Measure of the difficulty of stretching or breaking the surface of a liquid