Atoms, Atomic Theory, Atomic Theory Diagram | Quizlet
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
TERM
neutrons
DEFINITION
subatomic particles that have a neutral or no charge
TERM
protons
DEFINITION
positively charged subatomic particles
atom
the smallest particle of an element that has all the properties of the element
TERM
orbital
DEFINITION
a space around the nucleus of an atom where an electron is likely to be found
TERM
electrons
DEFINITION
negatively charged subatomic particles
TERM
nucleus
DEFINITION
the central core of an atom; contains protons and neutrons
Modern Atomic Theory
the most recent version for the explanation and definition of an atom
Picture of Dalton's Model

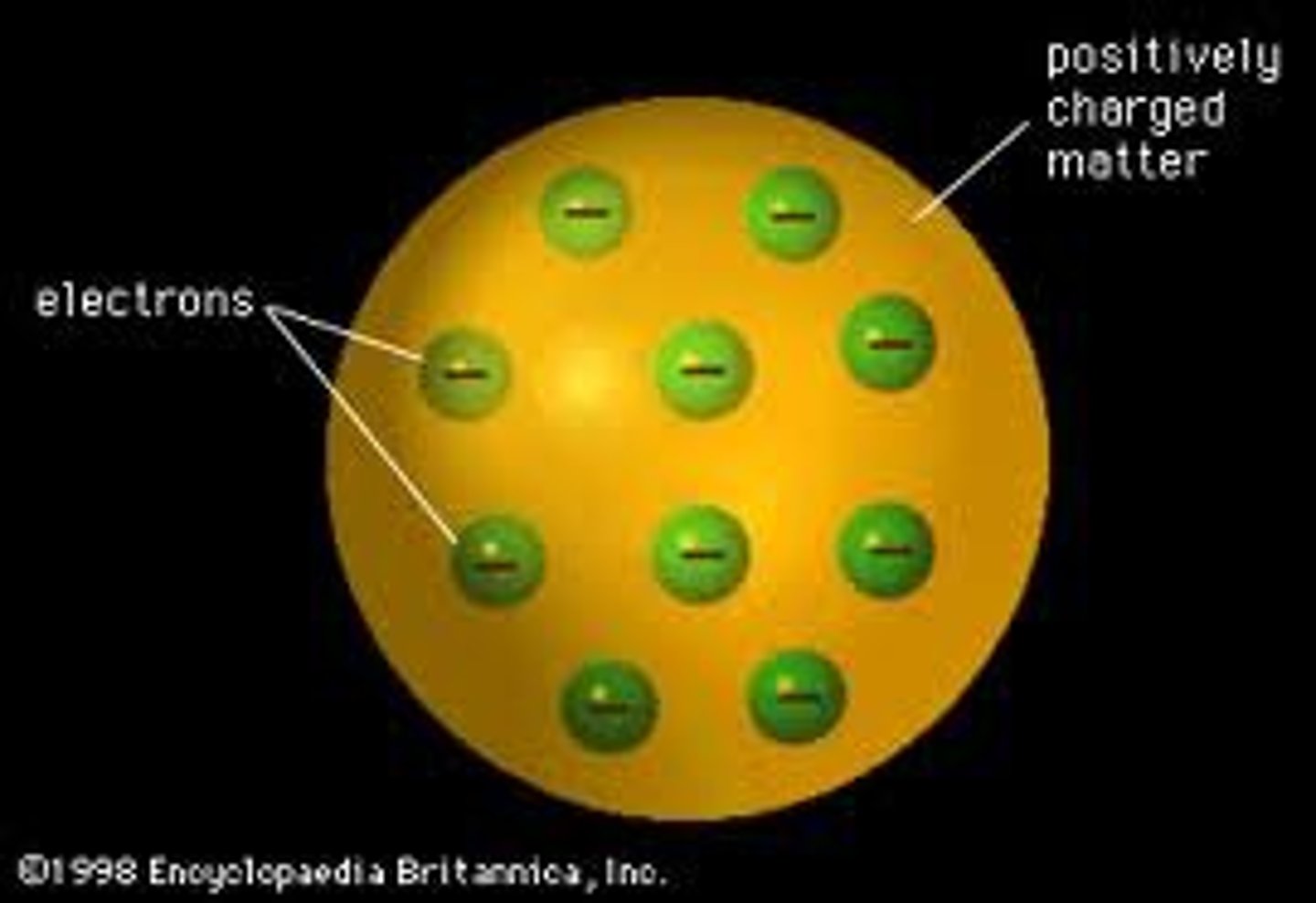
Picture of Thomson's Model
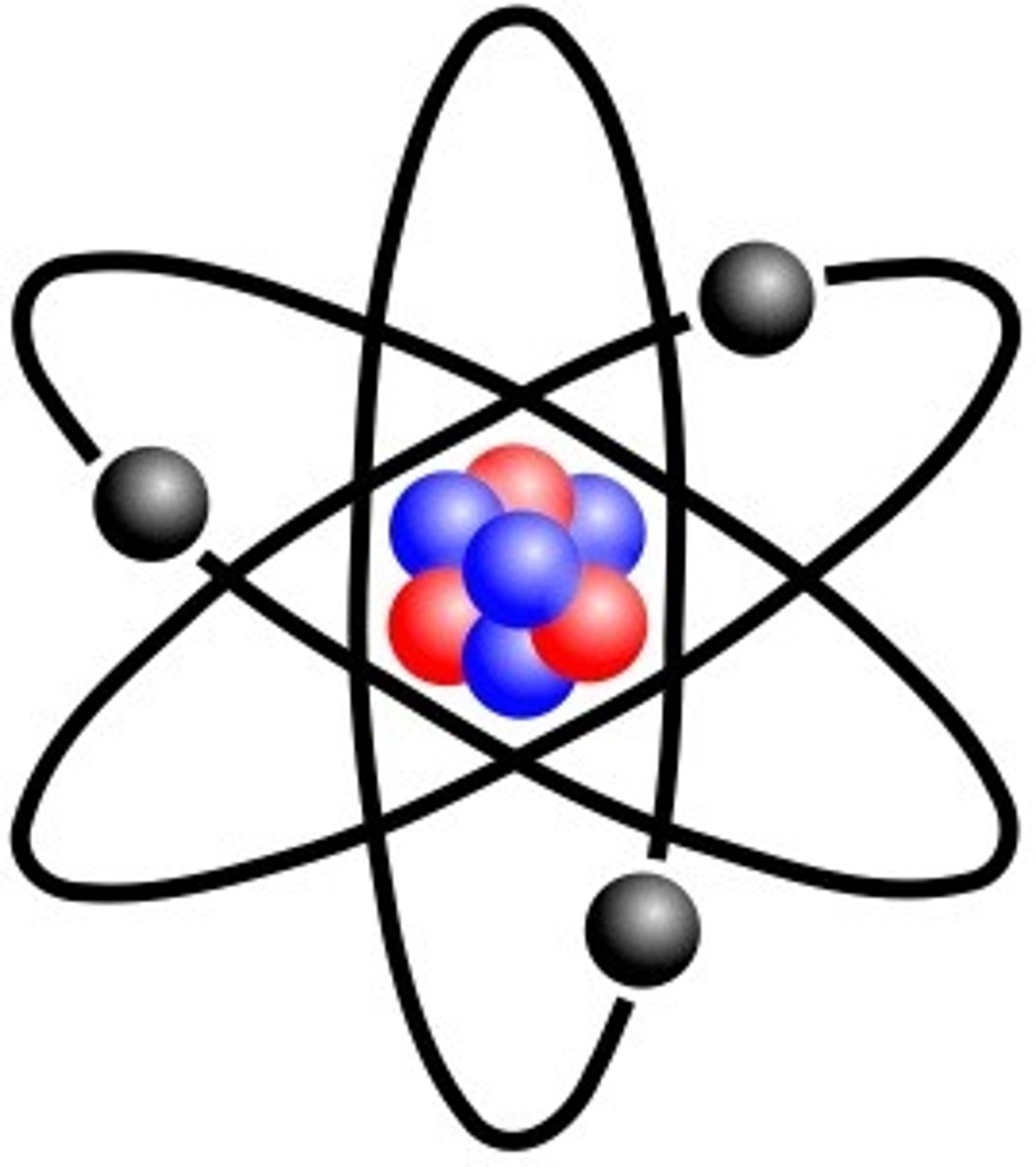
Picture of Rutherford's Model
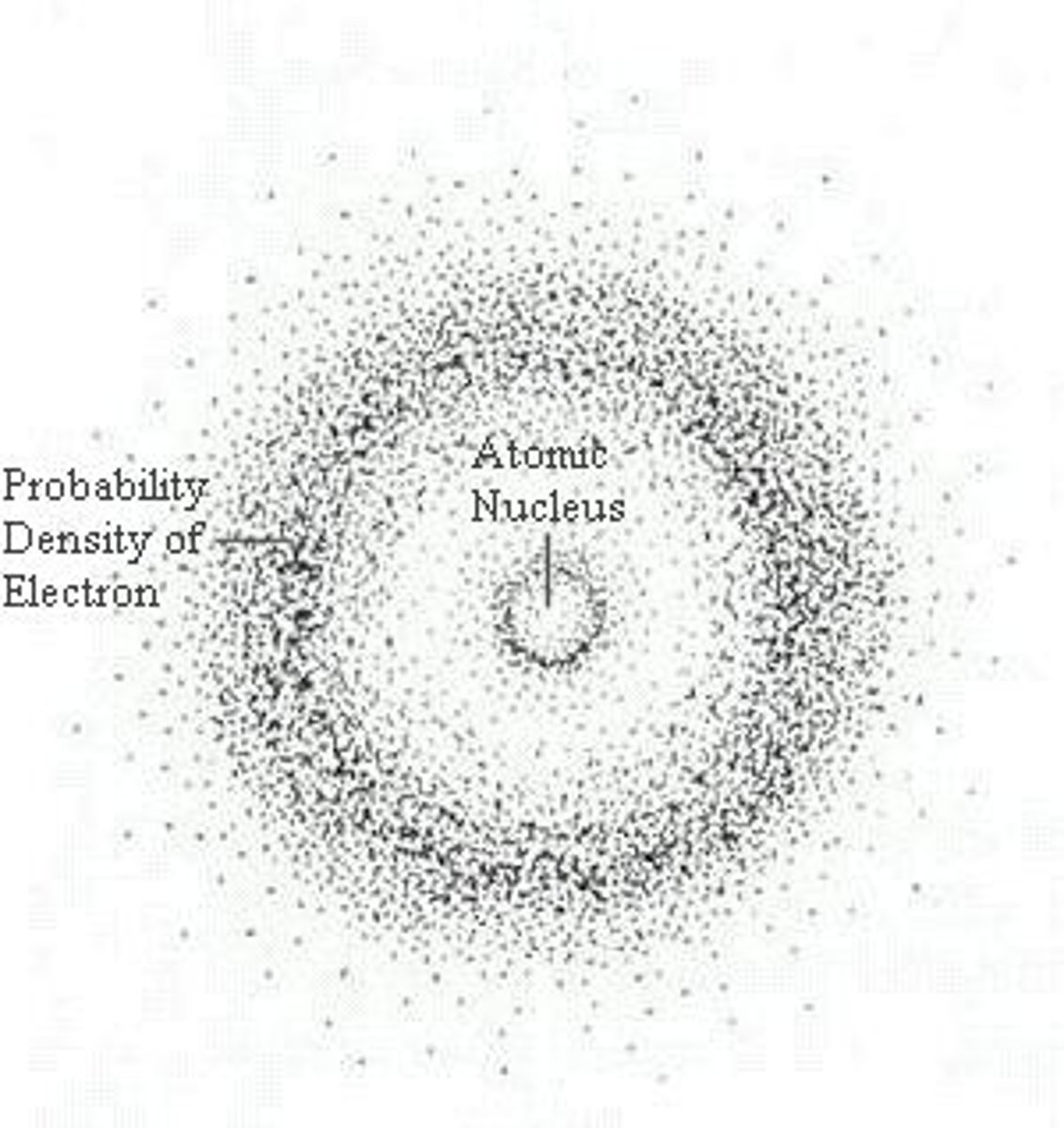
Picture of the Modern electron cloud model
Description of Dalton's Model
a small sphere that is the most basic thing; cannot be broken down
Description of Thomson's Model
A sphere that is positive with small negative particles mixed within it. Like pudding
Description of Rutherford's model
A small positive core with small negative particles circling it. Like our solar system.
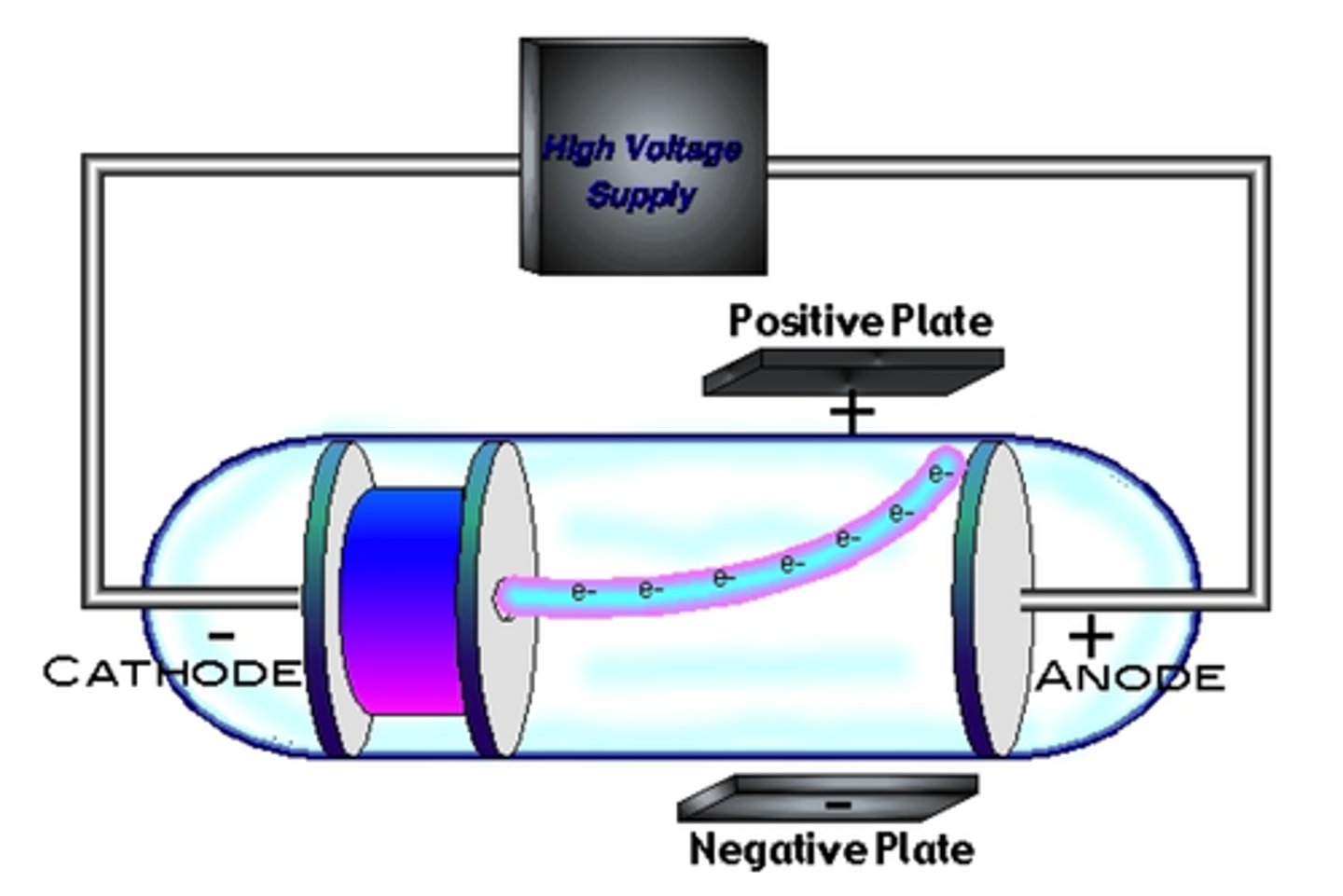
Cathode Ray
Experiment that showed atoms contained particles that were negatively charged.
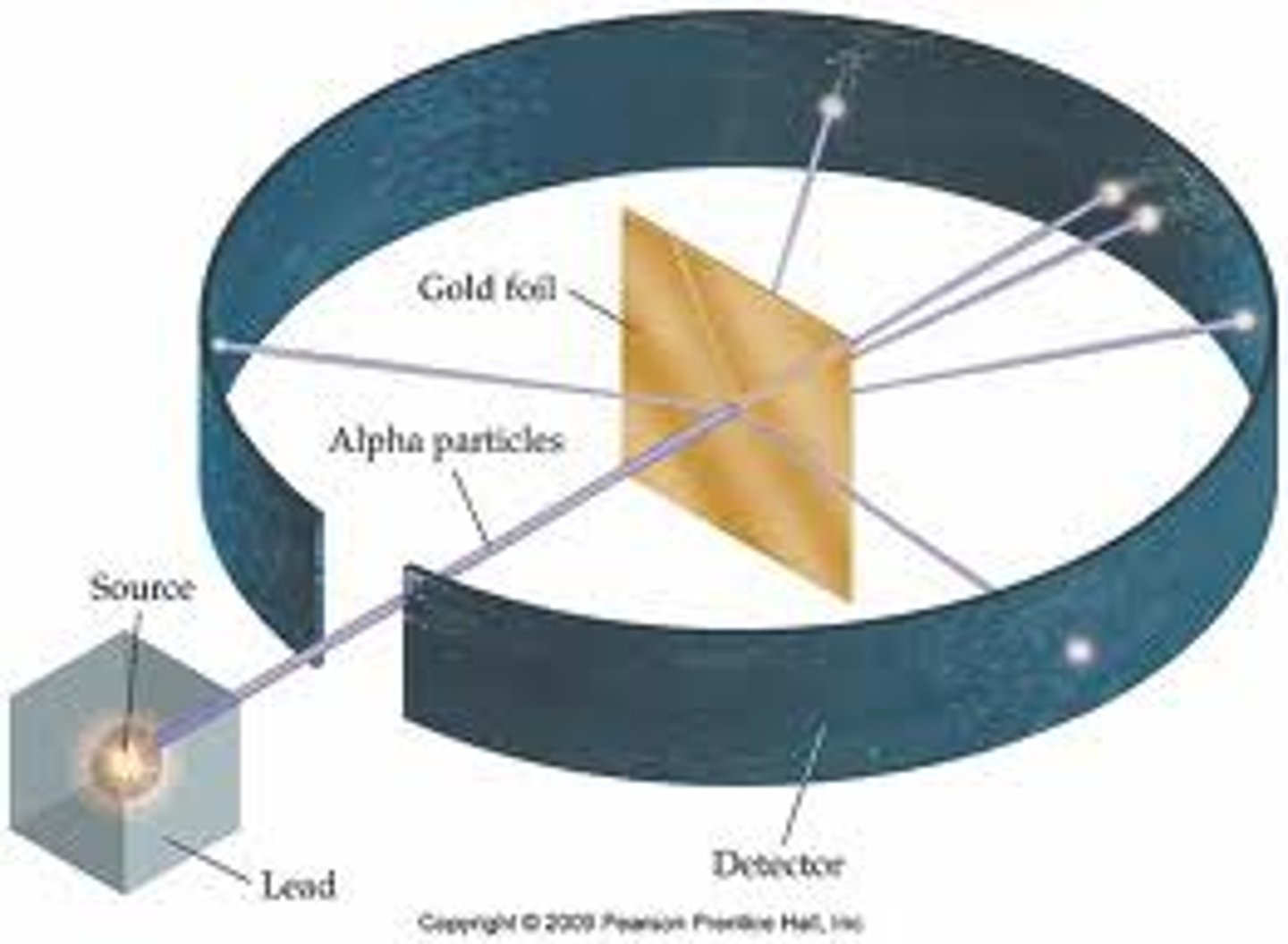
Gold Foil
Rutherford did this experiment using alpha particles. Deflected electrons proved there was a small positively charged nucleus.
Democritus
Greek philosopher that first proposed the idea of a "atomos". That was the word for a mass that cannot be divided further. This is where the term "atom" originates.
Scientist that discovered the nucleus
Rutherford

Scientist that discovered electrons.
Thompson

atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Mass number
the sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus
isotope
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
atomic mass unit
a unit of mass that describes the mass of an atom or molecule
valence electron
Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom