
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
euclidian geometry (father of geometry)
parallel lines remain parallel as they are extended in space
binocular vision advantages
Probability summation and Binocular summation
probability summation
The increased probability of detecting a stimulus from having two or more samples (more likely to see things with two inputs/eyes)
binocular summation
The combination (or “summation”) of signals from each eye in ways that make performance on many tasks better with both eyes than with either eye alone.
binocular disparity
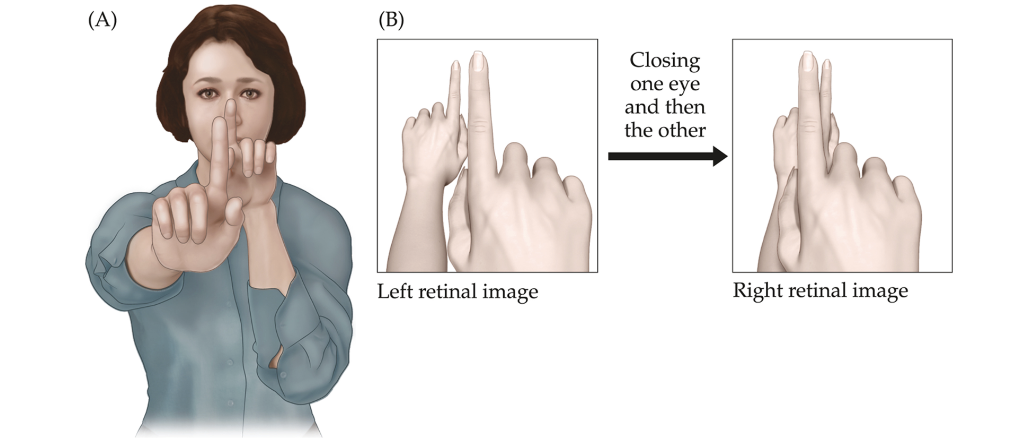
The differences between the two retinal images of
the same scene.
stereopsis
a vivid perception of the 3D of the world that is not available with monocular vision (most precise)
depth cue
info abt the 3D depth of visual space. can be for monocular, oculomotor, and binocular
metrical depth cue (M)
provides quantitative info abt distance in the third dimension
nonmetrical depth cue (M)
provides info exclusively abt depth order (relative depth) but not depth magnitude
occlusion (M) (relative depth order/nonmetrical depth cue*)
*important to know this
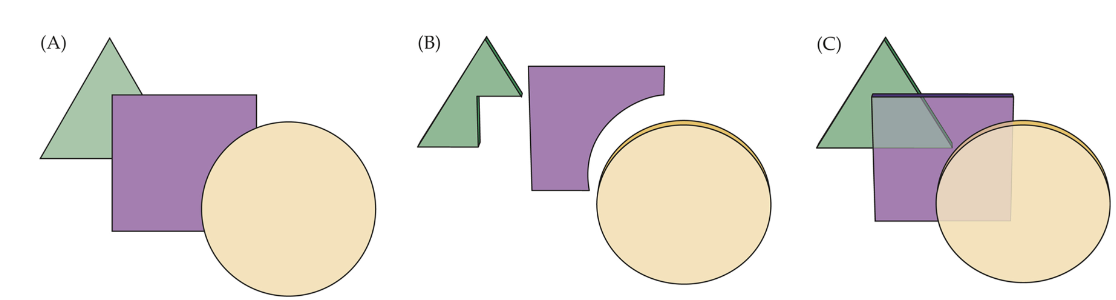
a cue to relative depth order in which, for example, one object partially obstructs the view of another object
relative size (M) (relative depth cue)
A comparison of size between items without knowing the absolute size of either one. smaller objects look further
relative height (M) (relative metrical depth cue)
For objects
touching the ground, those
higher in the visual field
appear to be farther away.
In the sky above the
horizon, objects lower in the
visual field appear to be
farther away.
texture gradient (M)
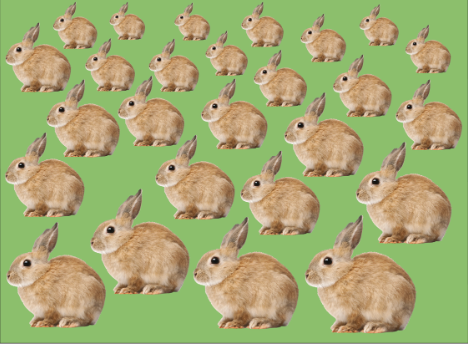
based on the geometric fact that items of the same
size form smaller, closer spaced images the farther away they get.
Apparent size is change by apparent depth.
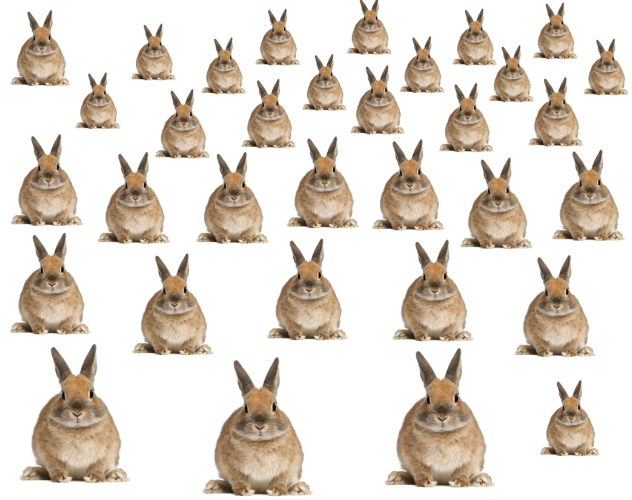

familiar size (M) (absolute metrical depth cue)
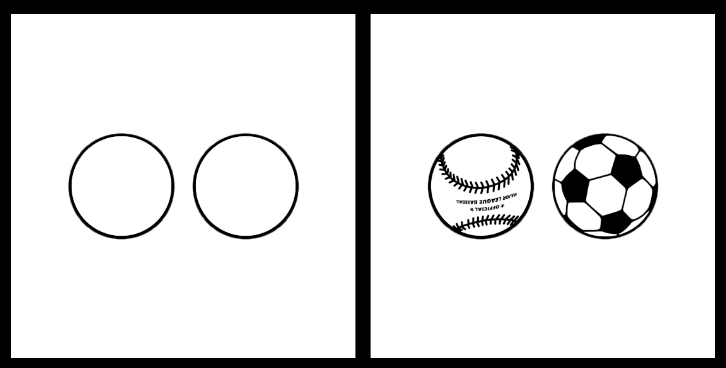
a cue based on knowledge of the typical size of objects. we perceive the baseball as closer because we know that baseballs are smaller than soccer balls.
aerial/atmospheric perspective (M)
a depth cue based on the implicit understanding that light is scattered by the atmosphere

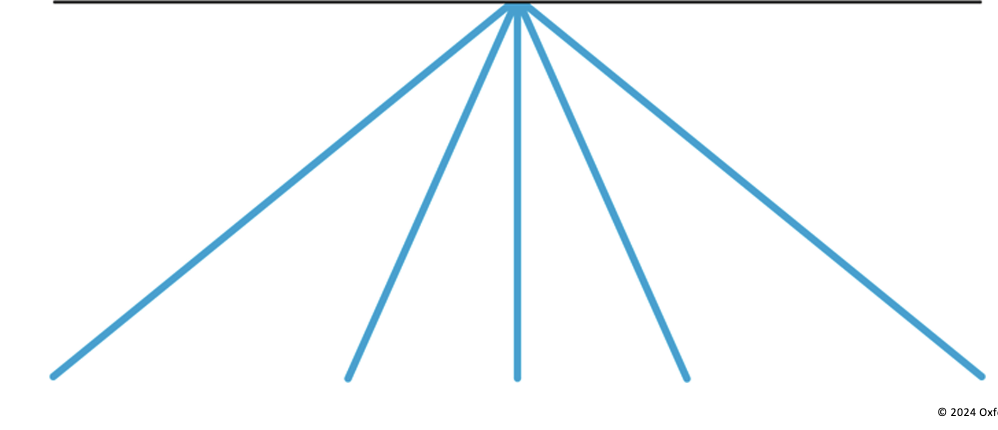
linear perspective and vanishing point
parallel lines appear to converge and makes you perceive that the road is continuing
_ and _ are monocular depth cues
shading and shadowing
_ and _ are monocular depth cues as a result of motion
deletion (gradual occlusion and disappearance of an object as it goes behind another) and accretion (gradual reappearance of object from behind another object)
ex: if i am next to a desk you would be able to tell I am behind it because when i walk behind it my legs get deleted behind the desk and reappear after i walk past the object

motion parallax (M)- motion
images closer to the observer move faster across the visual field than images farther away
ex: airplanes looks like they are moving very slowly when in reality they are moving 500 mph because they do not take up a lot of your retinal imaging
motion parallax caused by optic flow (M)- motion
a global pattern of visual motion that is both caused by and signals self-motion.
accommodation- oculomotor (O) depth cue
process by which the eye changes its focus
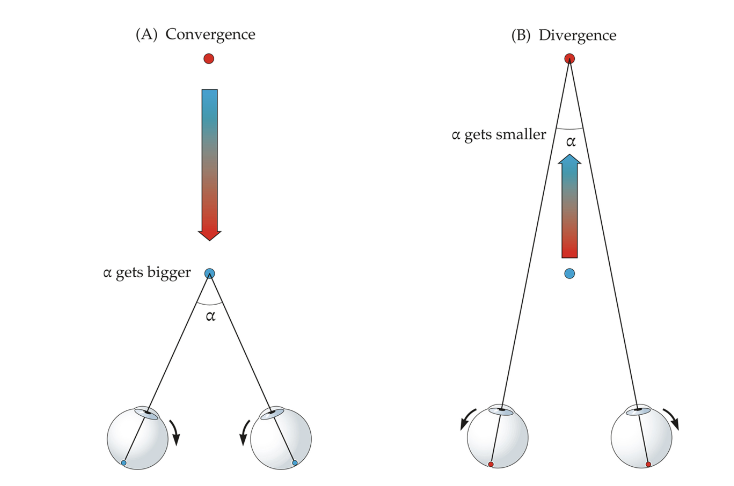
vergence (O)
convergence and divergence
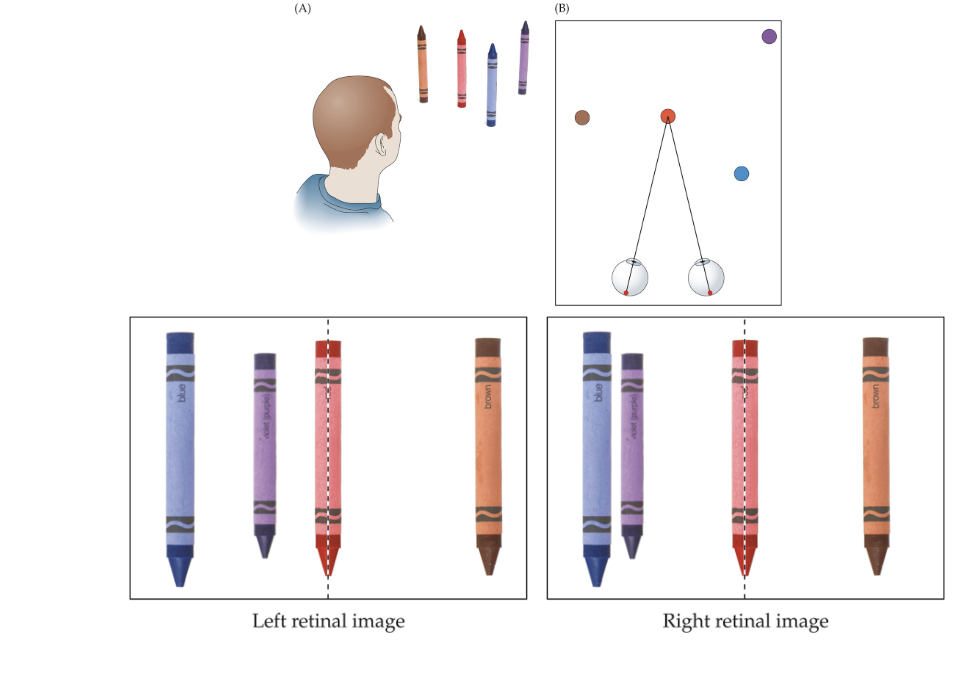
binocular disparity
The differences between the two retinal images of the same scene.
corresponding retinal points
A geometric concept stating that points on the retina of each eye where the monocular retina images of a single object are formed are at the same distance from the fovea in each eye.
horopter (same thing as vieth-muller circle)
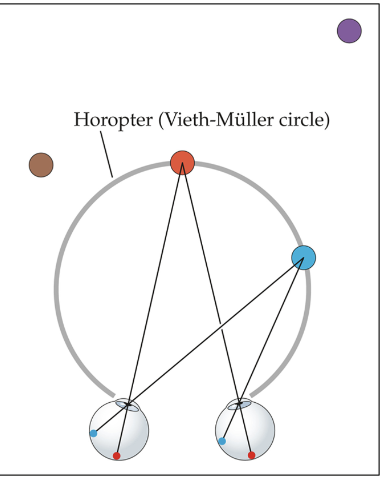
The location of objects whose images lie on the corresponding points. The surface of zero disparity. Objects on the horopter are seen as single images when viewed with both eyes.
vieth-muller circle
The location of objects whose images fall on geometrically corresponding points in the two retinas.
panums fusional area
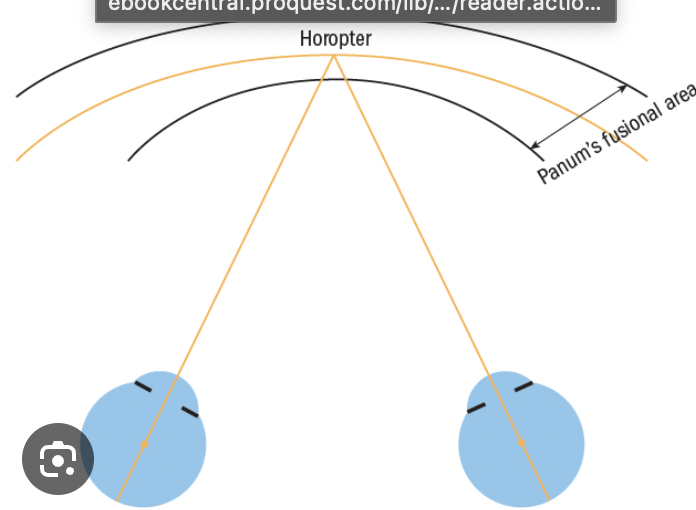
The region of space, in front of and behind the horopter, within which binocular single vision is possible.
diplopia
Double vision. If visible in both eyes, stimuli falling outside of Panum’s fusional area will appear diplopic.
stereoscope
a device for presenting one image to one eye and another image to the other eye
free fusion
the technique of converging (crossing) or diverging (uncrossing) the eyes in order to view a stereogram without a stereoscope
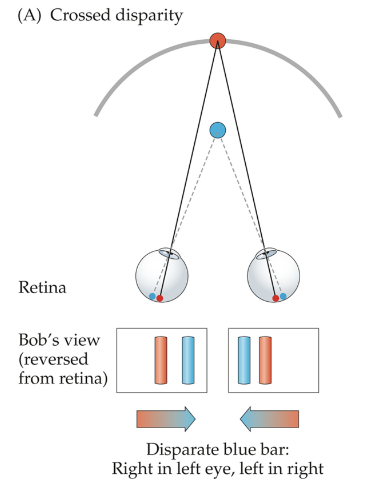
crossed disparity
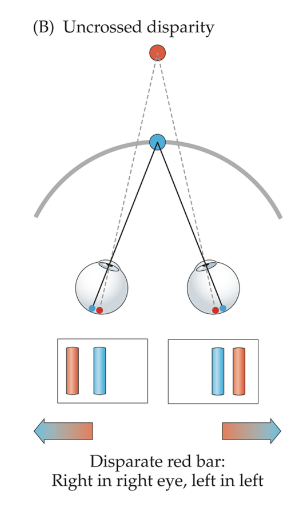
uncrossed disparity
stereoblindness
an inability to make use of binocular disparity as a depth cue
random dot stereogram
a stereogram made of a large number of randomly placed dots

correspondence problem
In binocular vision, the problem of figuring out which bit of the image in the left eye should be matched with which bit in the right eye. (brain trying to figure out what to do with binocular disparity)
– The problem is particularly vexing in images like random dot
stereograms.
solving correspondence problem
blurring the image, uniqueness constraint, continuity constraint, brain sensing dissimilar feature, motion disparity
blurring image
leaving only the low spatial frequency info helps
uniqueness constraint
the observation that a feature in the world is represented exactly once in each retinal image
continuity constraint
the observation that, except at the edges of objects, neighboring points in the world lie at similar distances from the viewer
stereopsis
can be used as both metrical and nonmetrical depth cue
– Some cells just code whether a feature lies in front of or behind the
plane of fixation (nonmetrical depth cue).
– Other cells code the precise distance of a feature from the plane of
fixation (metrical depth cue).
bayesian approach
A way of formalizing the idea that our perception is a combination of the current stimulus and our knowledge about the conditions of the world—what is and is not likely to occur.
– Thus, prior knowledge can influence our estimates of the probability
of an event.
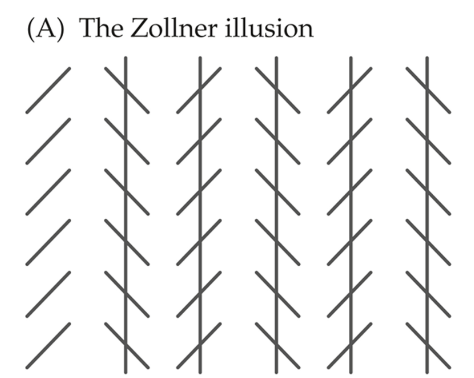
zollner illusion
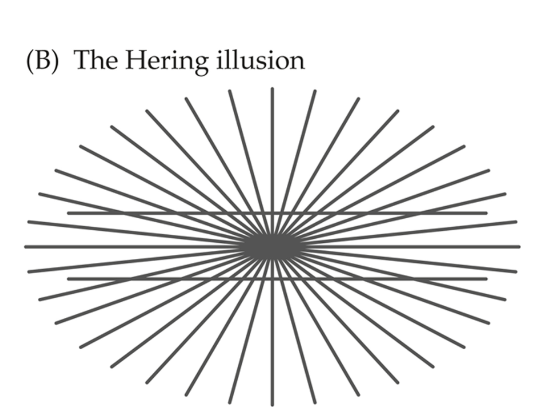
hering illusion
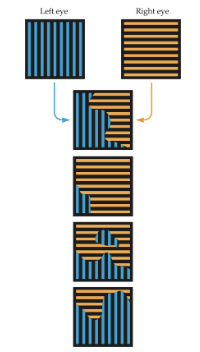
binocular rivalryq
The competition between the two eyes for
control of visual perception, which is evident when completely
different stimuli are presented to the two eyes. brain tries to stitch images together
stereoacuity
a measure of the smallest binocular disparity that can generate a sensation of depth
dichoptic
Referring to the presentation of two stimuli, one to
each eye. Different from binocular presentation, which could
involve both eyes looking at a single stimulus.
strabismus
A misalignment of the two eyes such that a single
object in space is imaged on the fovea of one eye, and on a
nonfoveal area of the other (turned) eye.
– Esotropia
– Exotropia
– loss of stereopsis
suppression
In vision, the inhibition of an unwanted image
yoking
tying two diff things together. eyes move in conjunction with one-another. eyes are yoked together