Topic 3: Genetics
1/55
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What is a gene?
A heritable factor that consists of a sequence of DNA and influences a specific trait
What is the locus?
The position of a gene on a chromosome?
What are alleles?
The alternate forms of a gene that code for the different variations of a specific trait
How are new alleles formed?
Gene mutations
What is the correlation between genetic complexity, chromosome numbers, genome size, and number of genes?
None
What is a genome?
The totality of the genetic information in an organism, including all genes and non-coding sequences
What was the Human Genome Project?
A mapping of the entire base sequence of the human genes:
Human cells typically have 46 chromosomes
The human genome consists of ~3 billion base pairs
It contains roughly 21,000 genes (estimates vary)
When was the Human Genome Project completed?
2003
What is a gene mutation?
A change in the base sequence of a section of DNA coding for a particular characteristic that can be beneficial, detrimental, or neutral
How can gene mutations be described?
Somatic → occurs in a body cell and affects a tissue
Germline → occurs in a gamete and affects offspring
What could mutations include?
Substitutions → silent, missense, or nonsense
Frameshifts → insertions or deletions
How do mutations occur?
They can occur spontaneously as copying errors during DNA replication or can be induced by mutagenic agents
What is the cause of sickle cell anemia?
A base substitution of GAG → GUG at the 6th codon of ß-haemoglobin resulting in the amino acid change from glutamic acid to valine
What are the consequences of sickle cell anemia?
Alters haemoglobin structure → forms insoluble strands
Cannot transport oxygen effectively → causing fatigue
Red blood cells adopt a sickle shape → may form clots
Sickle cells are destroyed at a higher rate → anemia
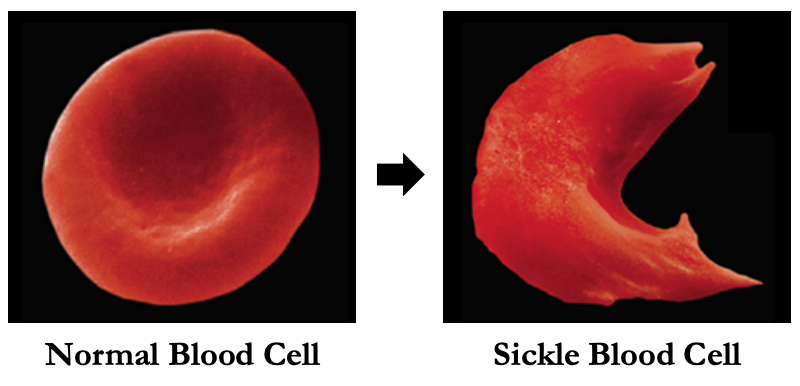
What is the ‘heterozygous advantage’ in sickle cell anemia?
Sickle cell anemia is a co-dominant trait and heterozygous individuals demonstrate an increased resistance to malaria
How do chromosomes present in prokaryotes?
Prokaryotes:
Have a single circular molecule made of naked DNA (DNA without proteins)
May have additional plasmids (autonomous DNA units)
How do chromosomes present in eukaryotes?
Eukaryotes:
Have multiple linear DNA molecules packaged with histones (proteins)
Do not have plasmids (unless genetically modified)
What is autoradiography?
A technique for measuring the length of DNA molecules when uncoiled
Who developed autoradiography?
John Cairn
How does autoradiography work?
Radioactive thymidine is incorporated into a cell’s DNA
Chromosomes were fixed to a photographic surface and treated with silver bromide (AgBr)
Radiation converts silver ions into insoluble grains that are visible via electron microscopy when a film is developed
What does diploid mean?
2 sets of chromosomes
What does haploid mean?
1 set of chromosomes
What cells in humans are haploid?
Sex cells/gametes
How many pairs of chromosomes do humans have?
23
What type of chromosomes are 22 pairs out of 23 for humans?
Homologous autosomes
Each pair has identical genes and loci
Alleles may differ (one from each parent)
What type of chromosomes are the 23rd pair in humans?
Sex chromosomes
Females have two X chromosomes (XX)
Males have X and Y chromosomes (XY)
What does the Y chromosome do?
Develop the male sex characteristics
Who determines the sex of the a baby, the mother or the father?
The father
What are homologous chromosomes?
Paired chromosomes inherited from both parents in sexually reproducing animals with the same genes at identical loci positions, however specific alleles may different
What is a characteristic genetic feature of species?
The chromosome number
What do karyotypes do?
They identify the number and types of chromosomes in a cell
How is karyotyping used during pregnancy?
Karyotyping is performed pre-natally to identify the sex of offspring or diagnose potential chromosome abnormalities
What occurs during amniocentesis?
Cells are collected from the amniotic fluid of the pregnant mother
Conducted at ~16 weeks with a slight risk of miscarriage (~0.5%)
What occurs during chorionic villi sampling?
Cells are collected directly from the placental tissue
Conducted at ~11 weeks with a higher risk of miscarriage (~1%)
What does a karyogram show?
The chromosomes of a cell in homologous pairs of decreasing length
What is meiosis?
The reduction division of a diploid cell to produce four haploid cells (gametes) that are genetically distinct; involves two divisions:
Meiosis I separates homologous chromosomes
Meiosis II separates sister chromatids
What are the differences between mitosis and meiosis?
DISCO PUG
Divisions → one in mitosis, two in meiosis
Independent assortment → no in mitosis, yes in metaphase I
Synapsis → no in mitosis, yes in meiosis (bivalents/tetrads)
Crossing over → no in mitosis, yes in prophase I
Outcome → two cells in mitosis, four in meiosis
Ploidy → dipoid-diploid in mitosis, diploid-haploid in meiosis
Use → body cells in mitosis, sex cells in meiosis
Genetics → identical in mitosis, variant in meiosis
What occurs during crossing over?
Crossing over occur via synapsis in prophase I
Homologous chromosomes form bivalents (or tetrads)
Chiasmata represent the points where genetic information has been exchanged between the homologous pair
The non-sister chromatids that have exchanged DNA are called recombinants
What occurs during random assortment?
The homologous pairs orient randomly in metaphase I
This means there is an equal chance of a resulting gamete containing either the maternal or paternal chromosome
As humans have a haploid number of 23, there are 223 potential gamete combinations (>8 million)
What is non-disjunction?
The failing of chromosomes to separate, resulting in gametes with extra or missing chromosomes involving either the homologous pairs in anaphase I or the sister chromatids in anaphase II
What happens if non-disjunction occrs?
If a gamete with an extra chromosome fuses with a normal gamete, the resulting zygote will have three copies (ex. trisomy 21)
What influences the chances of non-disjunction?
Parental age → older parents are at higher risk of non-disjunction events
Who established the principles of inheritance?
Gregor Mendel
What discoveries did Mendel make?
Organisms have heritable factors (genes)
Parents contribute equally to inheritance by supplying one version of the gene each (alleles)
Gametes contain only one allele of each gene (haploid)
Fusion of gametes results in zygotes with two alleles of each gene (diploid)
What is a genotype?
The allele combination for a specific trait
What are the three possible types of allele combinations?
Homozygous → both alleles are the same
Heterozygous → alleles are different
Hemizygous → only one allele
What is a phenotype?
The physical expression of a specific trait determined by genotype and environmental factors
What are the two modes of inheritance?
Complete dominance and codominance
What is complete dominance?
When one allele is expressed over another
Dominant allele is expressed in heterozygote
Recessive allele is masked in heterozygote
What is co-dominance?
When both alleles are equally expressed in the phenotype
Heterozygotes have a distinct phenotype
What is an example of an autosomal recessive disease?
Cystic fibrosis:
Cystic fibrosis is caused by a mutated CFTR gene
Produces thick mucus that clogs airways and causes respiratory issues
What is an example of an autosomal dominant disease?
Huntington’s disease:
Huntington’s disease is caused by a mutated HTT gene
An amplification of CAG repeats leads to neurodegeneration
What is an example of an autosomal codominant disease?
Sickle cell anemia:
Sickle cell anemia is caused by a mutated HBB gene
Sickling of blood cells leads to anemia and other complications
What is the result of radiation exposure?
Radiation and mutagenic chemicals increase mutation rates and can cause genetic diseases
What are two examples of radiation exposure?
Nuclear bombing of Hiroshima (1945)
Chernobyl (1986)
What are long term consequences of radiation exposure?
Increased incidents of cancer
Reduced immunity due to lowered t cell count
Congenital abnormalities (Chernobyl only)
Variety of organ-specific health effects