CH 3: Cell Structures/Functions (PT 1)
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(3.1-3.3)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
(3.1)
What is the cytoplasmic membrane, and what is its primary role in the cell?
It’s a thin, delicate structure that surrounds the cytoplasm and defines the boundary of the cell
basically it’s a BARRIER BETWEEN THE CELL AND EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
Describe the arrangement of phospholipids in the cytoplasmic membrane. Which part is hydrophobic, and which part is hydrophilic?
There’s HYDROPHOBIC TAILS TOWARDS LAYER
HYDROPHILIC HEADS that are OUTWARDS
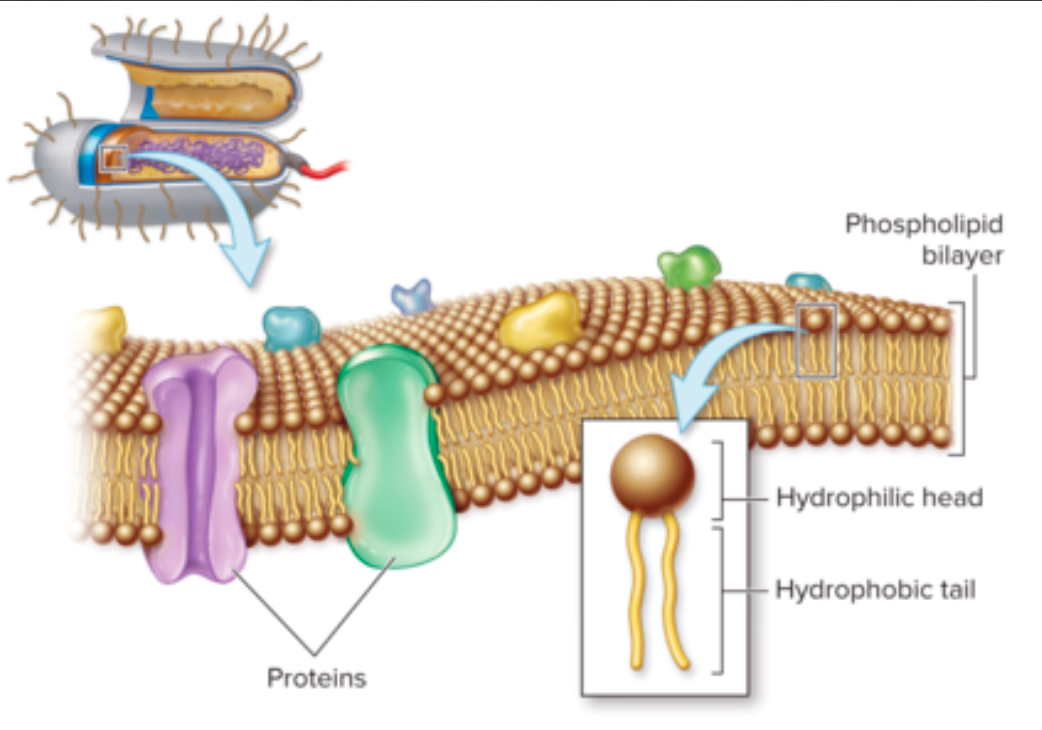
What is the fluid mosaic model, and why is it important for membrane function?
It describes the STRUCTURE OF CELL MEMBRANE and showing how FLEXIBLE and made of different molecules
This model tells us how the cell membrane is structured and how different parts come together to form it
What is selective permeability? What types of molecules can freely pass through the cytoplasmic membrane?
Selective permeability means that CERTAIN SUBSTANCES CAN CROSS THE MEMBRANE
O2, CO2, N2, and SMALL HYDROPHOBIC COMPOUNDS can pass through
What is simple diffusion, and how do molecules move during this process?
PASSIVE TRANSPORT PROCESS (doesn’t need energy for moving) where molecules go from HIGH TO LOW CONCENTRATION until equilibrium is reached
Downhill movement
Since it’s just going down (a concentration), not a lot of energy is really needed
What is osmosis, and how does water move in relation to solute concentration?
MOVEMENT OF WATER CROSS MEMBRANE FROM DILUTE (has A LOT OF WATER) TO CONCENTRATED SOLUTION (not a lot of water)
LOW TO HIGH SOLUTE CONCETRATION
Low solute concentration means that THERE’S GOING TO BE A LOT OF WATER
High solute concentration means that you POURED A LOT OF SALT INTO THE WATER, so it’s very diluted and not have a lot of water
Explain the terms hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic in relation to osmosis.
Hypotonic: HIGH TO LOW SOLUTE CONCENTRATION
When looking at the cell, there ISN’T A LOT OF WATER INSIDE, so H2O WILL ENTER THE CELL AND CAUSE BURST
Hypertonic: LOW TO HIGH SOLUTE CONCENTRATION
When looking at the cell, there’s A LOT OF WATER INSIDE and less water out, so WATER FLOWS OUT OF CELL and SHRINK
Isotonic: SOLUTE CONCENTRATION IS THE SAME
Explanations are in the notion (CH 3)
What happens to a cell if its wall is damaged under osmotic pressure?
The cell could BURST OR SHRIVEL (depending if it’s hypotonic or hypertonic)
What is the key difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in energy transformation?
The CONVERSION OF ENERGY IN EUKARYOTE AND PROKARYOTES ARE DIFFERENT.
In a prokaryote, the CYTOPLASMIC MEMBRANE CONVERTS ENERGY INTO ATP
In eukaryotes, different MEMBRANE-BOUND ORGANELLES CONVERT ENERGY INTO ATP
What is the electron transport chain (ETC), and how does it contribute to energy generation?
It’s a BUNCH OF PROTEINS EMBEDDED IN THE CELL MEMBRANE (for prokaryotes) or iNNER MITOCHONDRIA MEMBRANE (for Euk) THAT MOVES PROTONS ACROSS THE MEMBRANE
PLAY CRUCIAL ROLE IN ENERGY GENERATION
⭐️ The ETC creates a GRADIENT THAT DRIVES THE CREATION OF ATP
What is proton motive force, and why is it compared to energy stored in a battery?
It’s the ENERGY CREATED BY PROTONS MOVING ACROSS A CELL MEMBRANE
When ETC creates a proton gradient, within that gradient is a FORM OF ENERGY that could help facilitate ATP production
Compared to energy stored in battery because BOTH INVOLVE BUILD-UP OF ENERGY THAT CAN BE USED LATER
(Better explanation on notion)
What is the role of membrane transport proteins in moving molecules across the cytoplasmic membrane?
Transport proteins HELP MOVE NUTRIENTS/SMALL MOLEC ACROSS CYTOPLASMIC MEMBRANE
What is facilitated diffusion, and why is it rarely used by prokaryotes for nutrient intake?
Process that MOVES COMPOUNDS ACROSS MEMBRANE (down a concentration gradient) WITHOUT USING ENERGY
Since prokaryotes live in environment where the environment concentration is HIGH (there’s an abundance of nutrients), the nutrients can easily enter the prokaryotes without problem
How does active transport differ from facilitated diffusion, and what energy sources does it use?
Active transfer is when CELLS MOVE MOLECULES/NUTRIENTS ACROSS MEMBRANE and AGAINST CONCENTRATION GRADIENCE (the high to low concentration)
This NEEDS ENERGY while facilitated didn’t
The energy is either ATP or form of proton motive force
What is group translocation, and how does it differ from other forms of active transport?
This is a TYPE OF PRCESS that CHEMICALLY CHANGES A MOLECULE WHEN IT PASSES THROUGH
Unlike the other transport methods, this is the oNLY ONE THAT CHANGES A MOLECULE chemically
How does the cell move the exoenzyme to the outside of the cell?
Through SECRETION
Secretion is a RELEASE A SUBSTANCE FROM A CELL OR TISSUE
(3.2)
What are TWO main groups of bacteria’s?
Gram positive and Gram negative
What is a gram positive bacteria?
Bacteria’s that HAVE THICCC LAYER OF PEPTIDOGLYCAN, NO OUTER MEMBRANE, and when stained, it turns PURPLE and there's NOT A LOT OF ENDOSPORES PRESENT
What is a gram negative bacteria?
Bacteria that has TWO CELL MEMBRANES (the inner and outer membrane), HAS A THIN PEPTIDOGLYCAN IN THE MIDDLE, and STAINS PINK
Think of it like a sandwich (3 layers in total — maybe more but still)
What is peptidoglycan, and why is it essential for bacterial cell walls?
A MACROMOLECULE that GIVES STRENGTH TO CELL WALL of bacteria
ONLY IN BACTERIA
What are the two subunits of peptidoglycan, and how do they form a glycan chain?
NAM (N-acetylmuramic acid) and NAG (N-acetylglucosamine)
They are COVALENTLY JOINED TO ONE ANOTHER
Forms a GLYCAN CHAIN which BECOMES A BACKBONE of the peptidoglycan
What is periplasm, and why is its presence significant in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria?
It’s a GEL-LIKE MATERIAL that
FILLS the region between the main cell membrane and outer membrane of a gram negative bacteria OR
fills region between the peptidoglycan and cell membrane of SOME gram positive bacteria
This is important because It helps with NUTRIENT TRANSPORT, SECRETION, AND MAINTAIN CELL WALL
What is the role of the outer membrane in Gram-negative bacteria, and how does it provide additional strength?
The role of the outer membrane ACTS AS A LAYER THAT SURROUNDS PEPTIDOGLYCAN LAYER and PROTECTS THE INSIDES FROM EXTERNAL PROBLEMS.
It could help MAINTAIN CELL SHAPE and WITHSTAND TURGOR PRESSURES
What is lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and why is it medically important?
LPS’s are the MOLECULES THAT MAKES THE OUTER MEMBRANE of gram-negative bacteria
It’s medically important because Researchers study LPS effects to understand bacterial infections and immune responses.
Why is LPS called endotoxin, and what effects can it have on the body?
Endotoxins are TOXIC SUBSTANCES FOUND IN THE OUTER MEMBRANE that’s RELEASED when bacteria dies.
When the endotoxins are released after cell death, it could CAUSE INFECTION SYMPTOMS
LPS’s are called endotoxins because of the LETHAL EFFECTS THAT IT CAN HAVE WHEN INJECTED INTO AN ANIMAL
These effects include FEVERS AND OTHER SYMPTOMS OF INFECTIONS BY LIVE BACTERIA
What are the two notable parts of the LPS molecule?
Lipid A
O Antigen
What is Lipid A, and how does it contribute to the body's immune response?
Lipid A is a PART OF THE LPS that ANCHORS IT DOWN TO THE OUTER MEMBRANE
It helps RECOGNIZE INVADING BACTERIA and RESPONSIBLE FOR THE TOXIC EFFECTS OF LPS
Connection: LPS is an ENDOTOXIN because of the LIPID A that are embedded onto the LPS
The lipid A is responsible for the toxic effects so that’s why there could be infectious symptoms when the cell dies and releases LPS
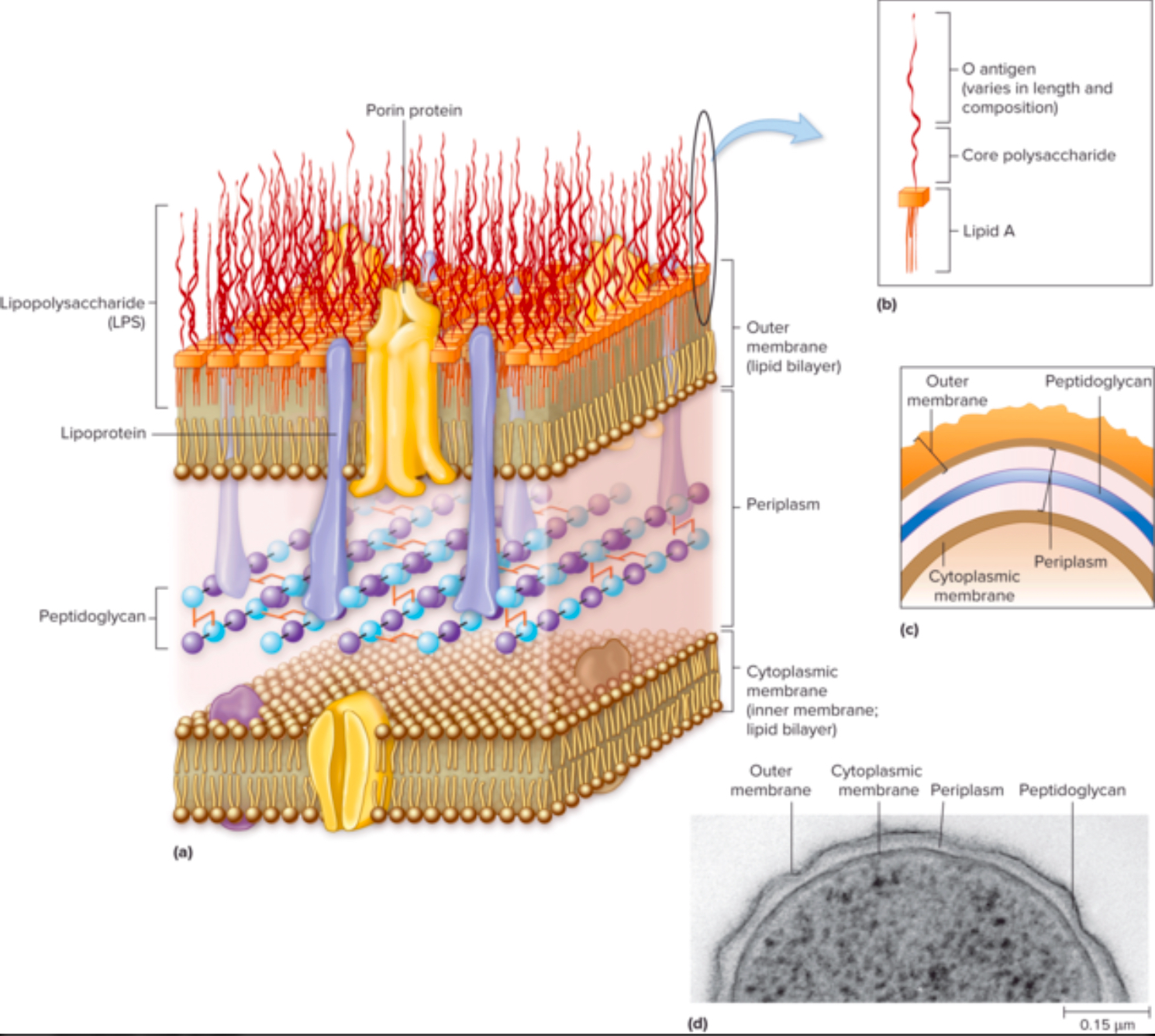
What is the O antigen, and how is it used to identify bacterial species or strains?
A part of the LPS that’s ALSO FOUND IN THE OUTER MEMBRANE
It HELPS BACTERIA AVOID THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
COULD IDENTIFY DIFFERENT BACTERIAL STRAINS
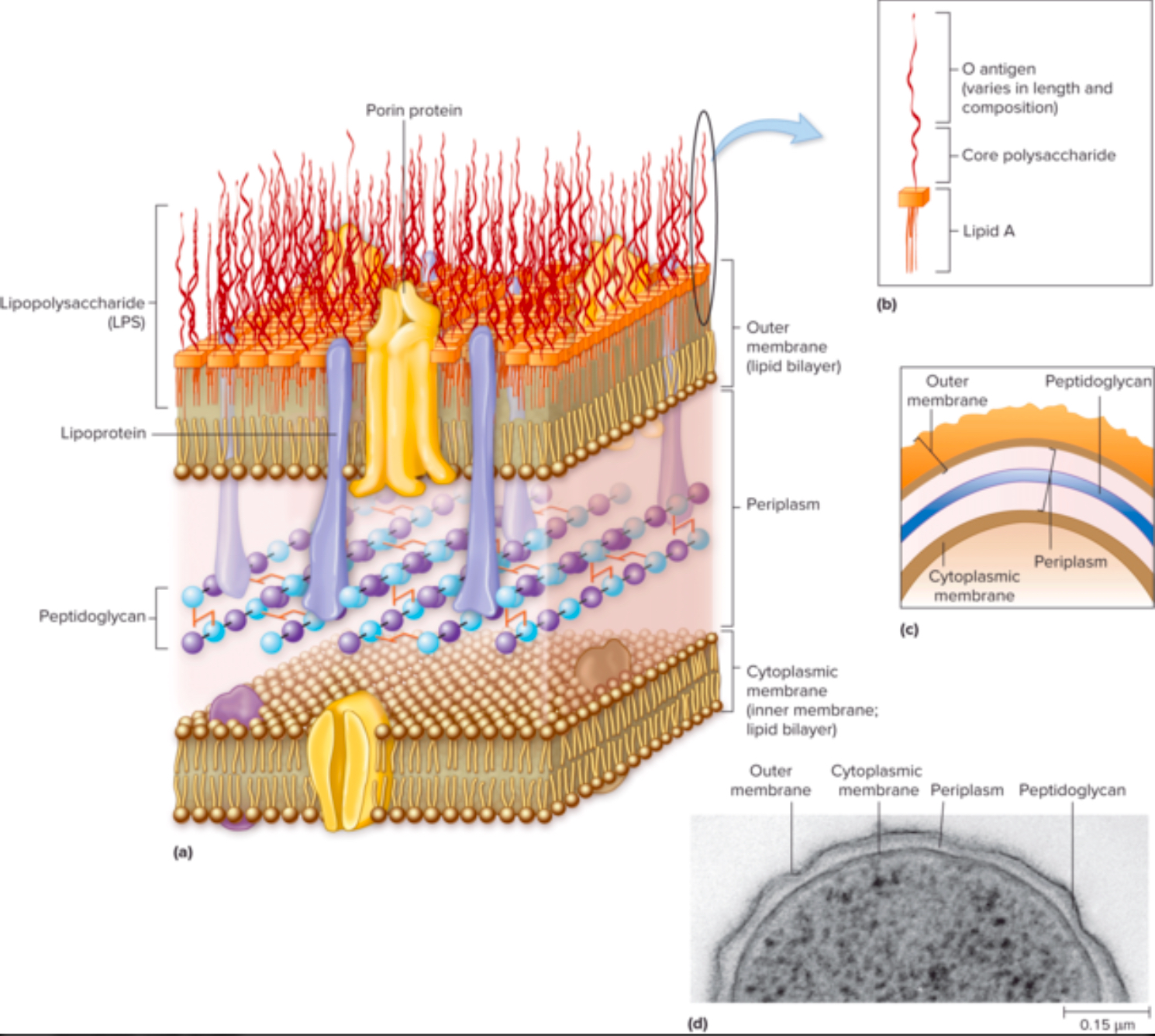
What are porins, and what is their function in the Gram-negative outer membrane?
PROTEINS (channels) IN THE OUTER MEMBRANE THAT ALLOW SMALL MOLECULES TO PASS
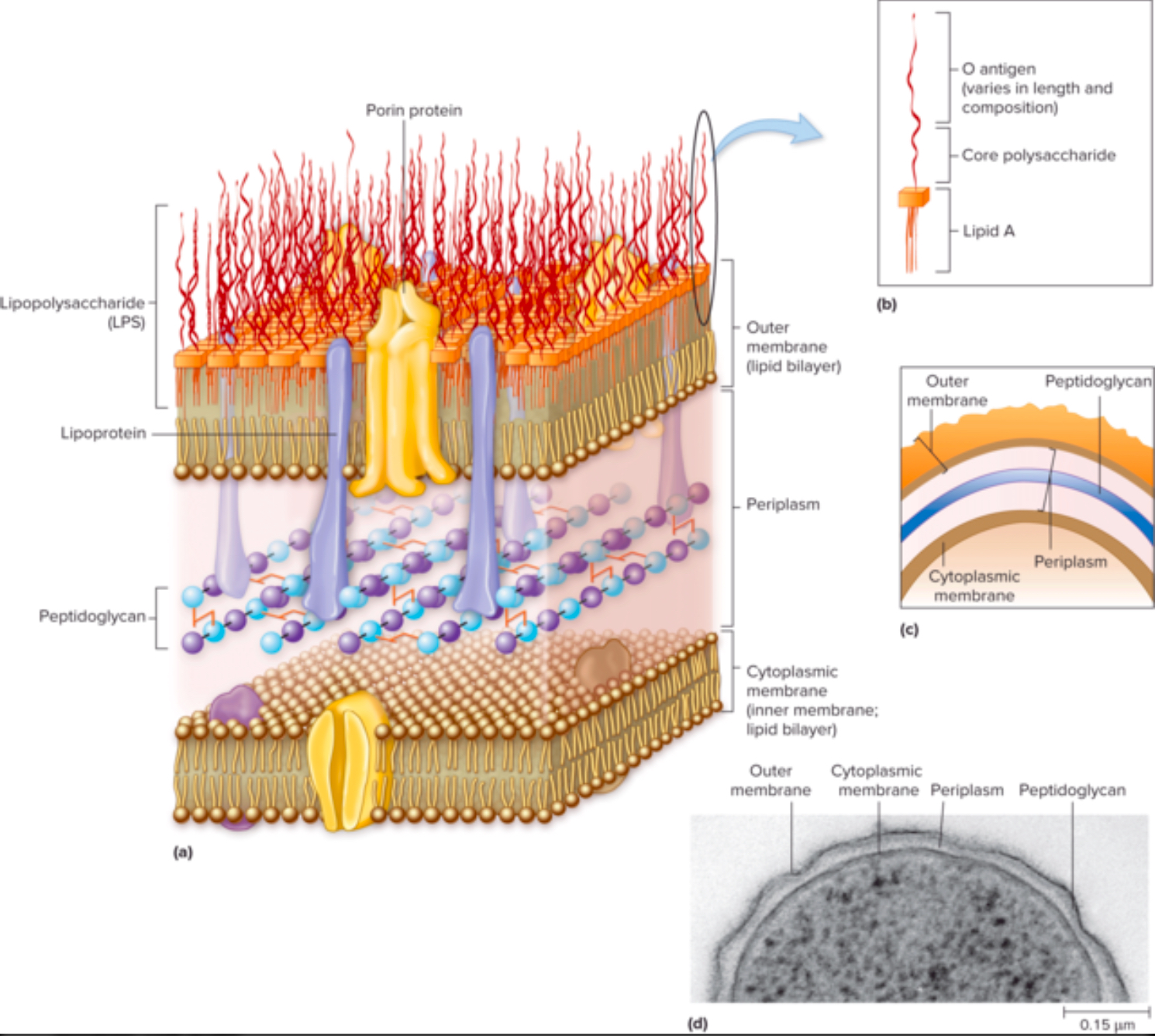
What is the periplasmic space, and what does it contain in Gram-negative bacteria?
Region BETWEEN CELL MEMBRANE AND OUTER MEMBRANE
Contains the periplasma (the gel-like substance that's within the periplasmic space)
How does penicillin work to interfere with bacterial cell walls, and why is it more effective against Gram-positive bacteria?
It STOPS ENZYMES THAT CATALYZE THE CORSS-LINKING STEP
It means that the enzymes that strengthens the cell walls by cross-linking those peptidoglycans won’t function anymore which WEAKENS THE CELL WALL, ultimately leading to BURSTING
This affects the gram positive bacteria more because the gram positive bacteria doesn’t have an outer membrane (unlike the gram negative), and it’s easier to kill it
What is the function of lysozyme, and why is it more effective against Gram-positive bacteria?
Lysozymes are ENZYMES that BREAKS DOWN PEPTIDOGLYCAN LAYER which weakens the cell walls.
Just like penicillin, it could target gram positive bacteria’s easier because it doesn’t have an outer membrane to protect the peptidoglycan layer
(3.3)
What is the difference between a capsule and a slime layer in bacteria? What is the main functions of the capsule and slime layer?
A CAPSULE is a THICK GELATINOUS material that SURROUNDS SOME MICROORGANISMS (it’s TIGHTLY BOUND)
A SLIME LAYER is an IRREGULAR MATERIAL that surrounds some microorganisms (this is LOOSER)
The function of both is that it’s meant to PROTECT THE BACTERIA FROM ANTIBIOTICS AND HELPS STICKS TO SURFACES
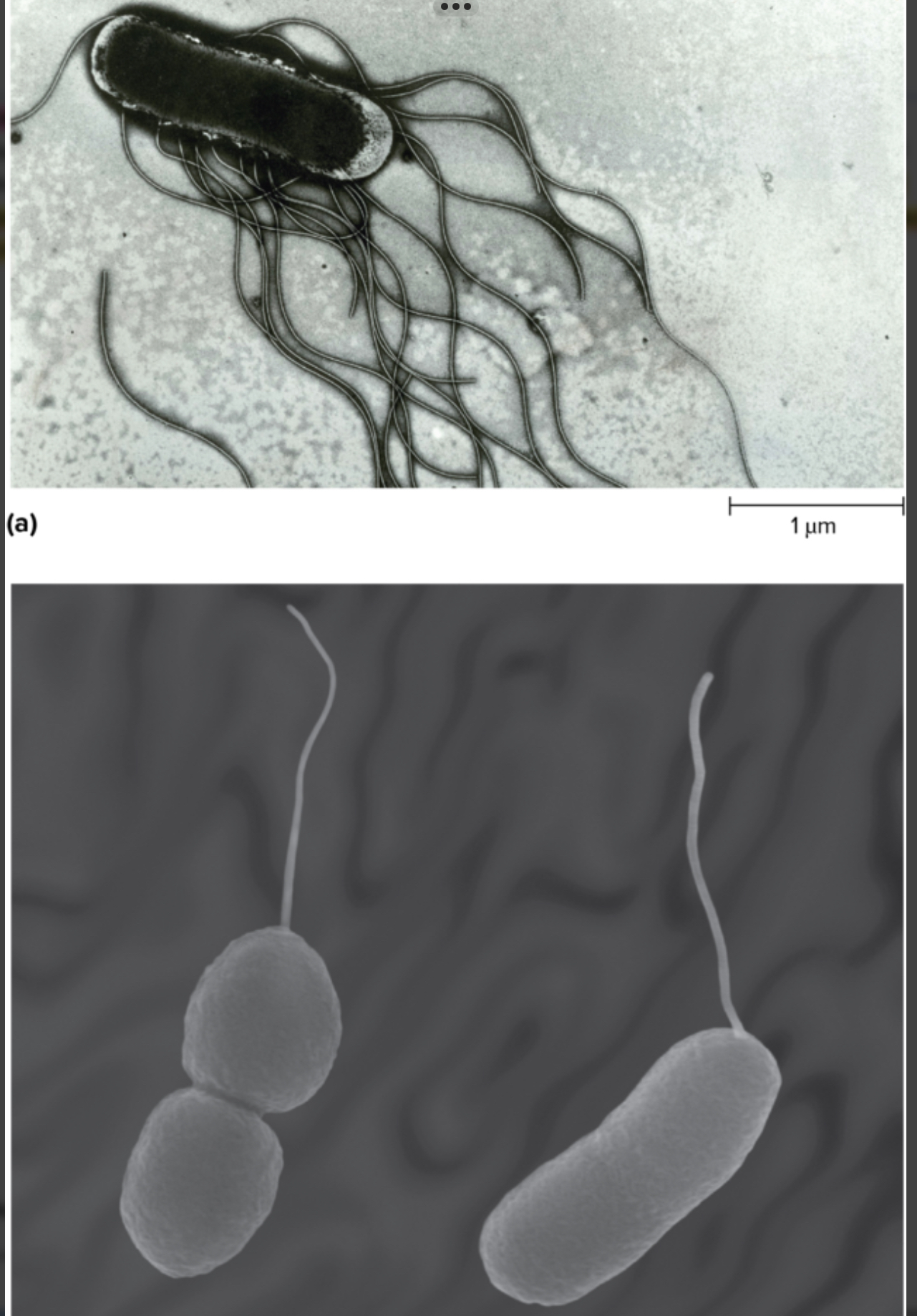
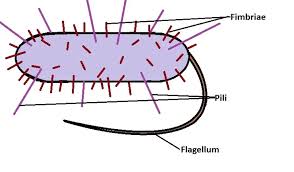
What are flagella? What is the function of flagella in bacteria, and how do they help with motility?
Flagella are LONG PROTEINS RESPONSIBLE FOR MOST BACTERIAL MOTILITY
Basically the flagella helps most bacteria’s to move
It FUNCTIONS by SPINNING LIKE PROPELLERS, pushing the cell through liquid (like how a ship pushes through water)
The liquid isn’t super easy to push through though (think of humans trying to push through honey or molasses)
What are the different flagella arrangements, and how do they help in identifying bacterial species?
The different flagella arrangements would be:
Peritrichous is when the FLAGELLA IS AROUND THE SURFACE OF THE CELL
Polar is when there’s a SINGLE FLAGELLA AT ONE END (it would end up looking like a sperm)
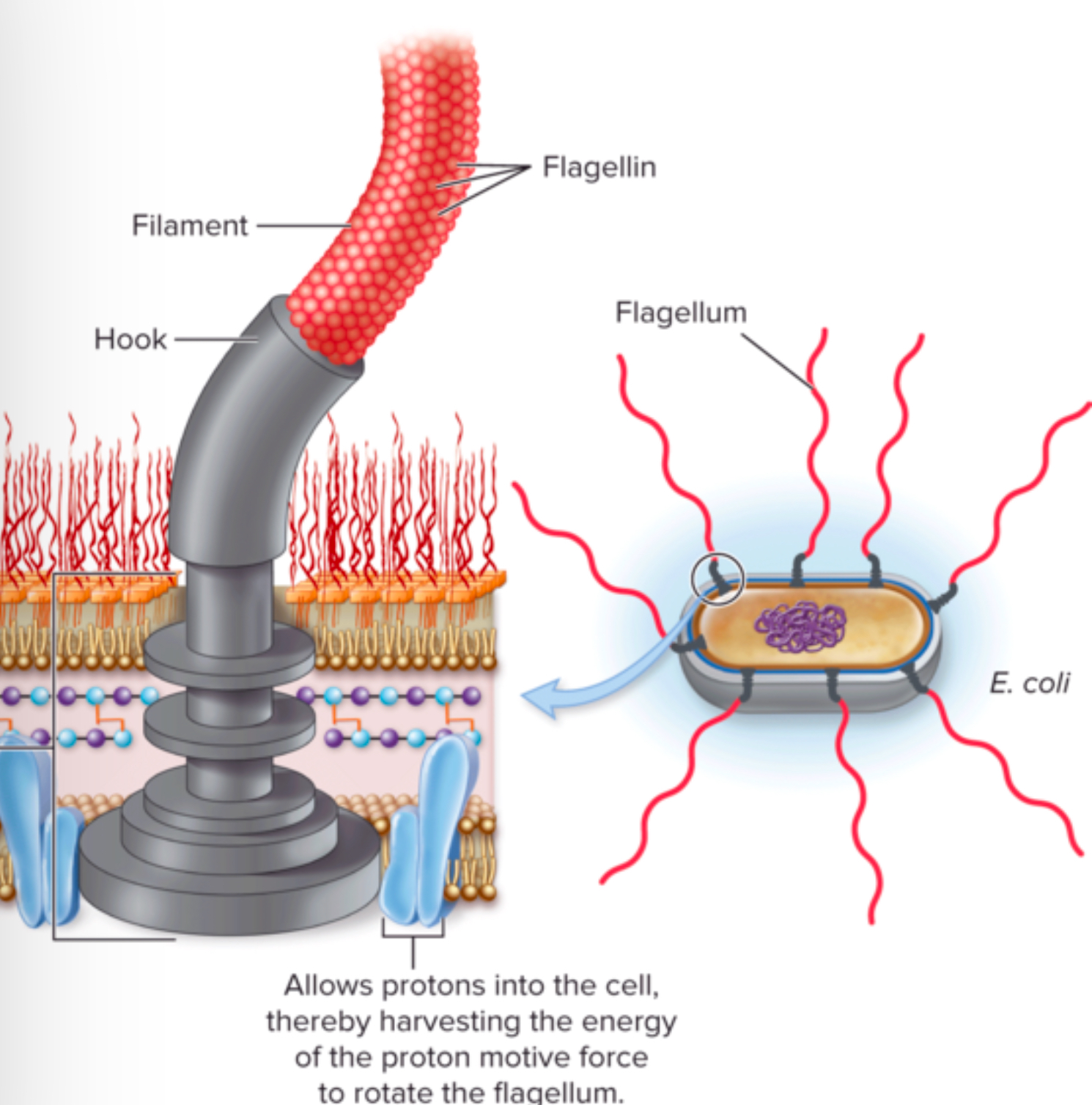
What are the three basic parts of a flagellum, and what role does each play in its function? (BHF)
Basal body: ATTACHES THE FLAGELLA TO CELL MEMBRANE which ALLOWS IT TO ROTATE AND MOVE THE BACTERIA
Hook: CONNECTS BASAL BODY AND FILAMENT
Filament: ACTS LIKE THE PROPELLER and PUSHES BACTERIA FORWARD (OR CHANGE DIRECTION)
It’s like a WHIP that rotates like a propeller
What is chemotaxis, and how do bacteria respond to different chemicals?
It’s the MOVEMENT OF A CELL TOWARDS/AWAY FROM CERTAIN CHEMICALS
If it’s a chemical that they sense is good for them, the bacteria will move towards it
If it’s BAD CHEMICALS, they’ll try to GET AWAY
What are aerotaxis, magnetotaxis, thermotaxis, and phototaxis, and how do bacteria respond to these stimuli?
Aerotaxis: ORGANISM RESPONSE TO O2
Need oxygen → go towards
Doesn’t need it → go away
Think of “Aero” as in AIR as in OXYGEN
Magnetotaxis: BACTERIAL RESPONSE TO MAGNETIC FIELD
Thermotaxis: BACTERIAL RESPONSE TO TEMPERATURE
Phototaxis: BACTERIAL RESPONSE TO LIGHT
How do pili differ from flagella in structure and function?
Pili are SHORTER AND THINNER (compared to flagella) cell structures that ALLOW THEM TO STICK TO CERTAIN SURFACES and ALSO BE INVOLVED IN DNA TRANSFER
While the flagella is LONG and helps with MOTILITY
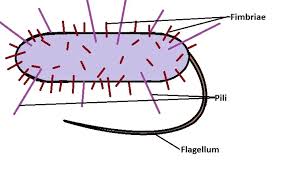
What is a fimbriae?
SHORT AND THIN hair-like structures that is MAINLY FOR ATTACHING ONTO SPECIFIC SURFACES
NOT INVOLVED IN DNA TRANSFER
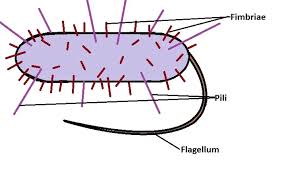
⭐️ What’s the difference between Pili and Fimbriae?
Pili are LONGER AND LESS AMOUNT compared to Fimbriae
Fimbriae focuses SOLELY ON ATTACHMENT IN SURFACES
Pili is ATTACHMENT AND DNA TRANSFER
What is a sex pilus?
Sex pilus is a HAIR-LIKE STRUCTURE that HELPS TRANSFER GENETIC MATERIAL TO ANOTHER BACTERIA