PEU: Council of the European Union
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
The Council is considered a ____ institution
Intergovernmental
What are other names for the Council of the European Union
council of ministers
The council
Main functions of the Council
“The Council shall, jointly with the European Union, exercise legislative and budgetary functions. It shall carry out policy-making and coordinating functions as laid down in the Treaties”
What does the Council of the EU do?
negotiates and adopts EU law (with EP)
Coordinates member states policies (economic and fiscal policies; education, culture, youth and sport, employment policy)
Developed EU’s Common Foreign and Security Policy (executive)
Concludes international agreements (provides the mandate, decides on the signature and adopts the final decision to adopt the agreement)
Adopts the EU budget
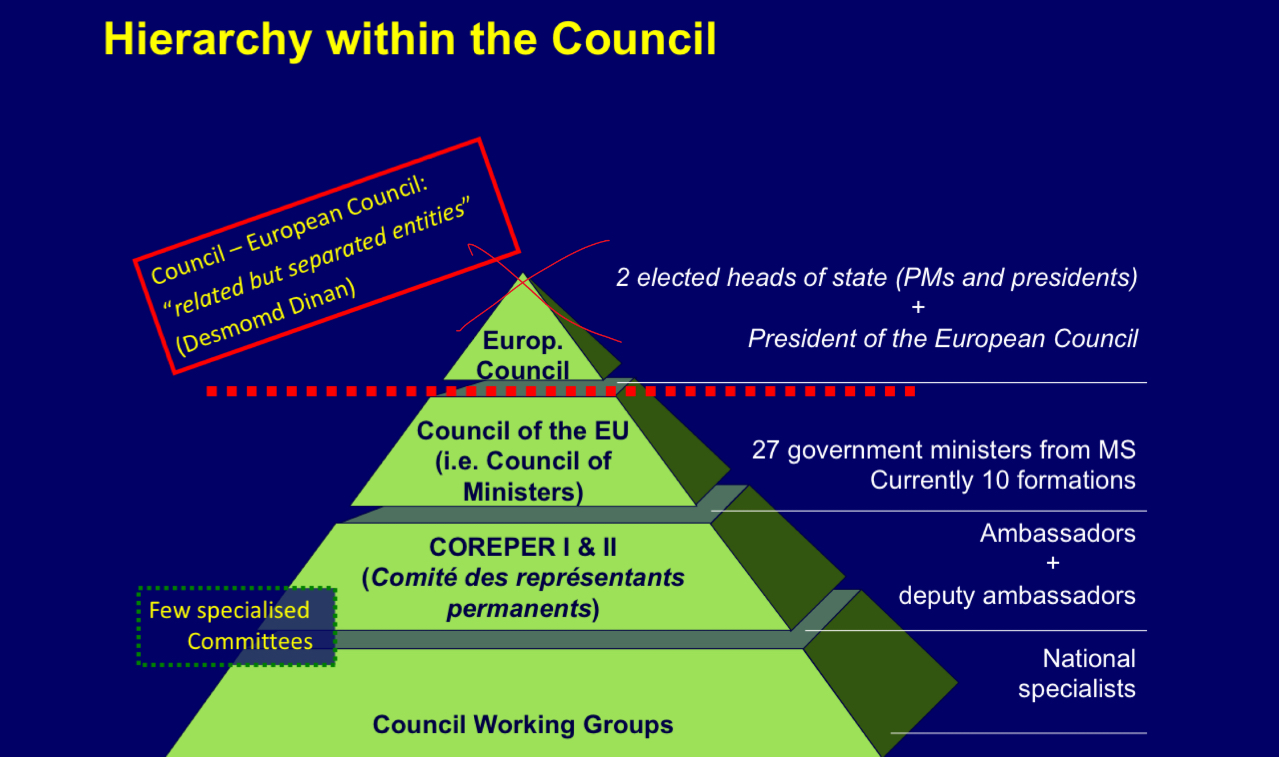
Hierarchy within the Council
Ambassadors - Coreper 2
Deputy ambassadors - coreper 1
Each department has someone from each member states that represents and attends meetings for that topic
10 Configurations of the Council
General affairs
Foreign affairs
Economic and Financial affairs
Justice and Home affairs
Employment, Social Policy, Health and Consumer affairs
Competitiveness (Internal Market, Industry, Research and Space)
Transport, Telecommunications and Energy
Agriculture and Fisheries
Environment
Education, Youth, Culture and Sport
Who attends council meetings?
Ministers —> usually the one that fits the configuration (aka the agricultural meeting is attended by agriculture minister)
Is there 10 councils?
Legally there is ONE council with 10 formations
It could happen that an agriculture minister signs off on something involving finance bc they are in the same council
General Affairs Council (GAC)
Prepares and follows-up the European Council meetings
GAC needs to find solutions to as many problems as possible before hand so that meetings go smoothly and can move at a quicker pace
General coordination of policies
Institutional and administrative questions
Horizontal dossiers affecting more than one Union policy (eg MFF)
Any dossier sent by the European Council
Ensures the consistency in the work of all Council configuration in cooperation with the European Commissions
Who attends GAC meetings?
Foreign affairs ministers or European affairs ministers (if they have them)
If the ministers are busy/unable to attend, the permanent representative can take their place
Representatives of the European Commission —> always present at every council meeting (do not have a vote)
Foreign Affairs Council (FAC)
Chaired by the high representative (HRVP) EXCEPT when discussion is on trade
Rotating presidency takes over then
Deals with the EU’s external relations (+ ensures consistency)
CFSP (Common Foreign and Security Policy)
CSDP (Common Security and Defense Policy)
CCP (Common Commercial Policy) (aka trade)
Development and Humanitarian Aid
Ministers should ensure that there is consistency in the EUs approach
What does ‘doorstep’ refer to
When they arrive and when they leave they speak to the press → can express opinions on what will be talked about, give information about who they are agreeing with, etc
Rotating Presidency
switches every 6 months
Meetings chaired by the President
President duty is to uphold the everyday function of the council
President is taken over by the whole government of the country in the chair
Each government will bring up things they find important
Line every 3 presidencies —> triple presidency (trio)
Priority list for a year and a half (how they work de facto)
Mix of representation from bigger and smaller countries in each of the trios
Exception to Presidency?
common foreign and security policy: HRVP and the External Action Service (EEAS)
Here there is a high representative elected (minister level)
Created chaos when was rotating bc the priorities would change with each new president —> better to keep priorities stable
Role of President in Council
Organizational role
Broker role
Leadership role
External representation
Role of President in Council: organizational role
supported by the Council Secretariat General
Convenes Council meetings
Announces the dates seven months in advance
Role of President in Council: broker role
facilitates consensus during the meetings
not push your own agenda
Presidency should be rather independent
Role of President in Council: leadership role
six-month working program
Trio-Presidency multi-annual program
Role of President in Council: external representation
represents the Council towards the EP, Commission and the “outside world” (in its competences)
Involved in external policies as well
Committees and the Working Groups
Political and Security Committee (PSC): key to security and defence
Trade Policy Committee (TPC)
Special Committee on Agriculture (SCA)
Economic and Financial Committee

Qualified majority
at least 55% of the members of the council, must comprise of at least 15 member states and must represent at least 65% of the population of the EU
Blocking minority
included at least 4 member states
How does the council vote?
By qualified majority except where the Treaties provide otherwise
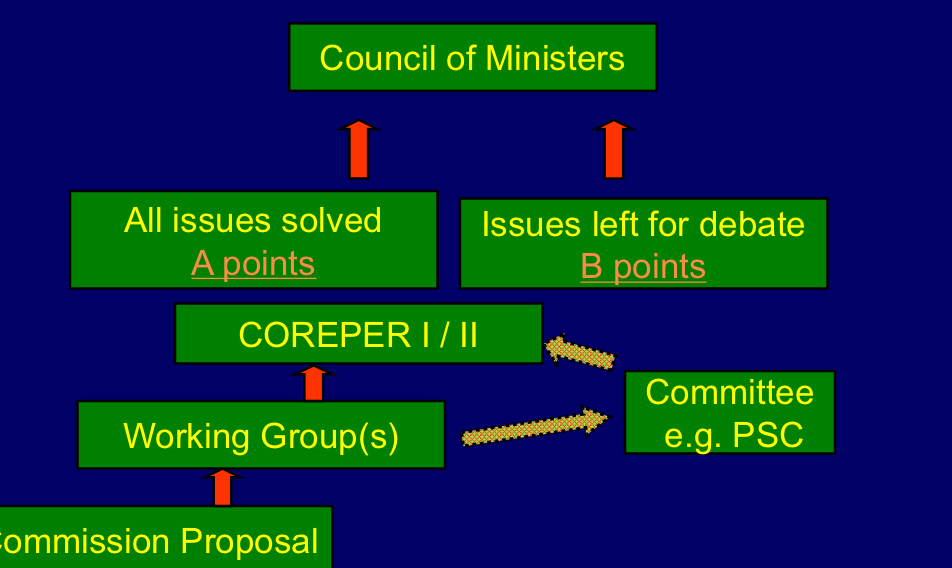
Moving of dossiers
The Council: summary
The Council is the representation of the member states
Thought of as an intergovernmental institution
Negotiates and adopts EU law (with EP), coordinates member states policies, developed CFSp, concludes international agreements and adopts EU budget
10 formations/configurations of the Council
Presidency is rotations (every 6 months)
Except for common foreign and security policy