chemistry of life
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
DSFHISYAUIDYG
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Covalent Bond
Strongest Bond, electrons shared between two atoms
Non Polar Covalent Bond
Equal sharing
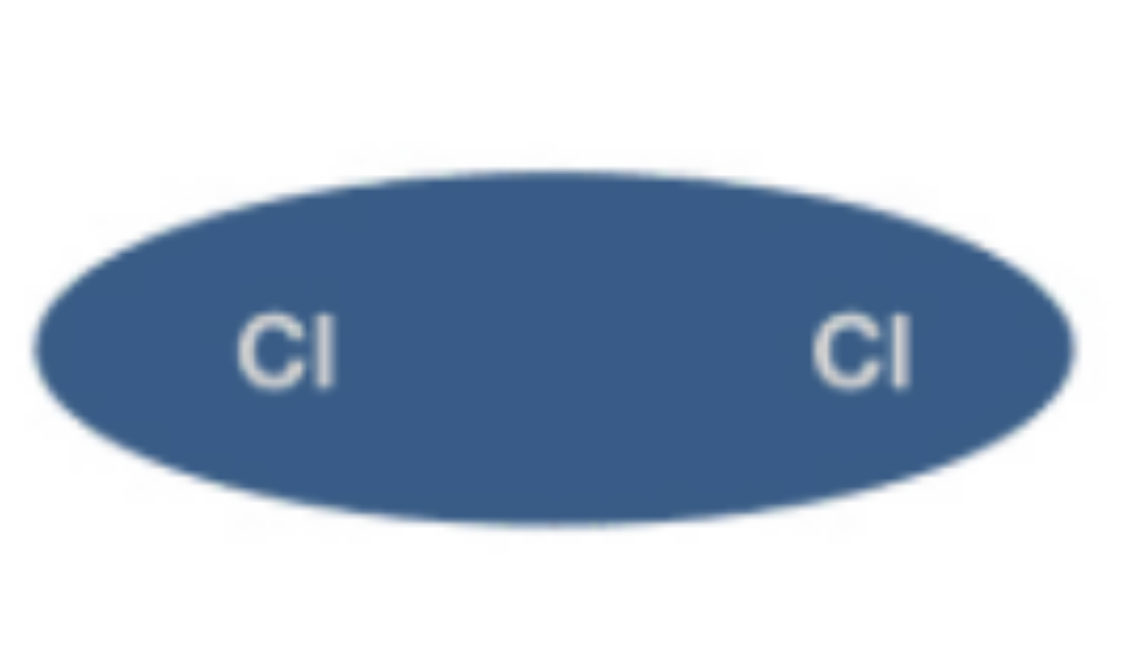
Polar Covalent Bond
Unequal sharing
Ionic Bond
Electrons transferred from one atom to another
Middle Strength Bond

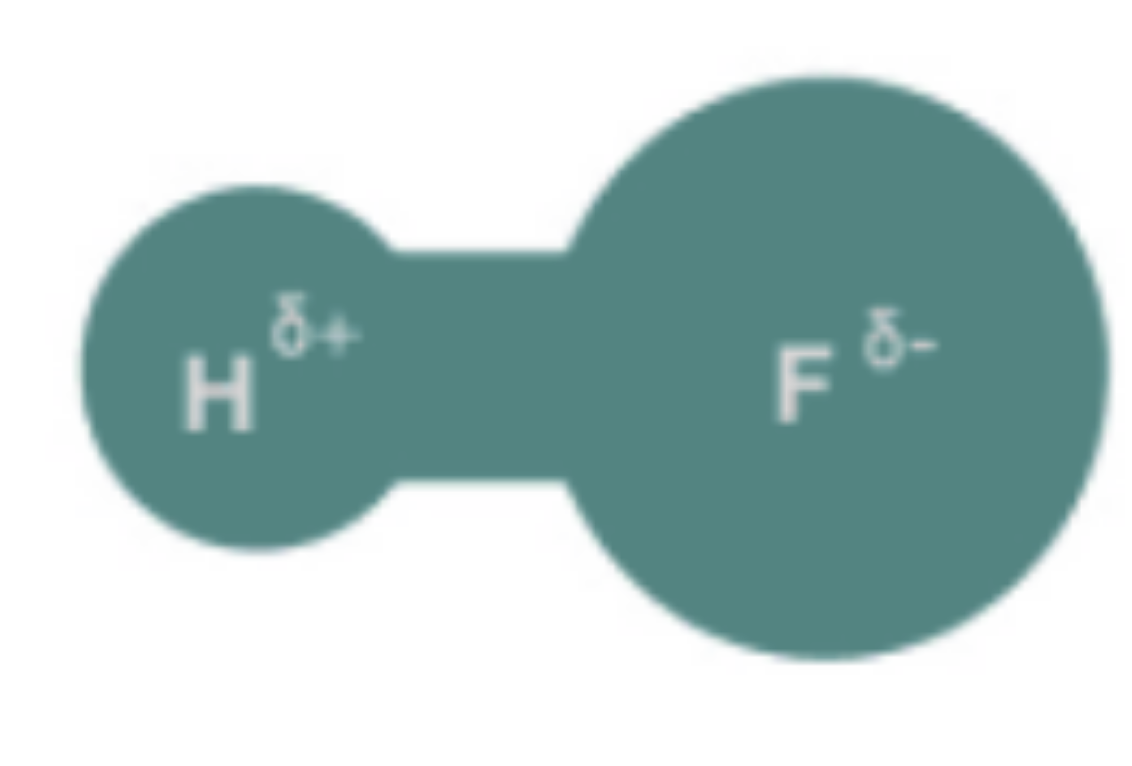
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak bond, electronegative atoms and hydrogen atoms.
Hydrophilic
Water loving, hydrogen bonds, polar, soluble
Hydrophobic
Water fearing, nonpolar, insoluable
High Specific Heat
Lots of energy needed to break hydrogen bonds, resists temperature changes
Water has high heat of vaporization
Lots of energy needed to go from liquid to gas, evaporative cooling
High surface tension
difficult to break the surface of the water due to hydrogen bonds, adhesion and cohesion
ice floats
crystal lattice, less dense than water
sulfur
used in proteins
nitrogen
proteins/nucleic acids
phosphorus
phospholipids and nucleic acids
hydrocarbon
backbone of organic molecules, carbon chains surrounded by hydrogen bonds
functional groups
groups of atoms that bind to the carbon skeleton of an organic molecule to give ins specific properties
hydroxyl
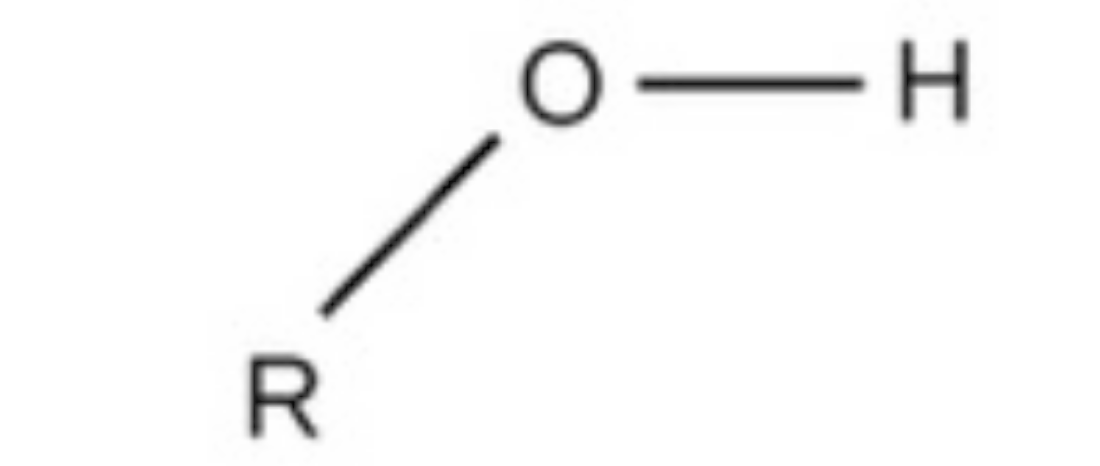
hydroxyl, polar, found in sugars and alcohols
methyl
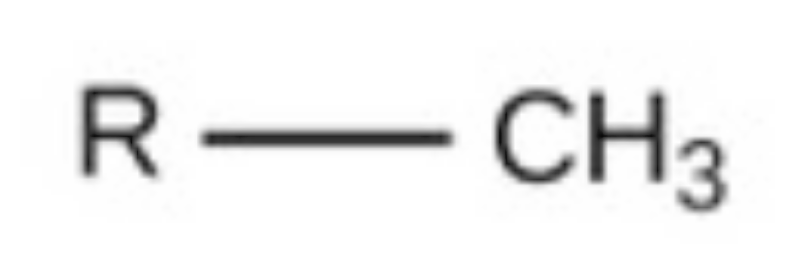
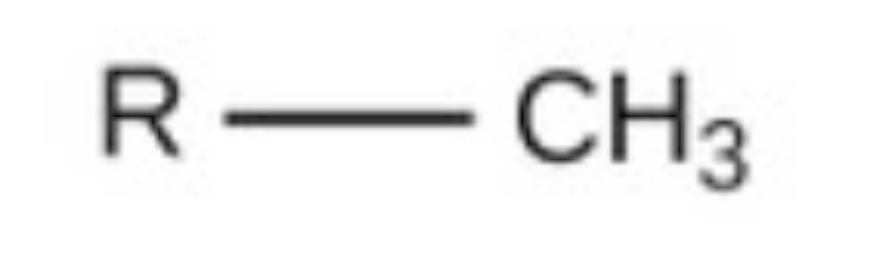
methyl, nonpolar, found in carbs
carbonyl
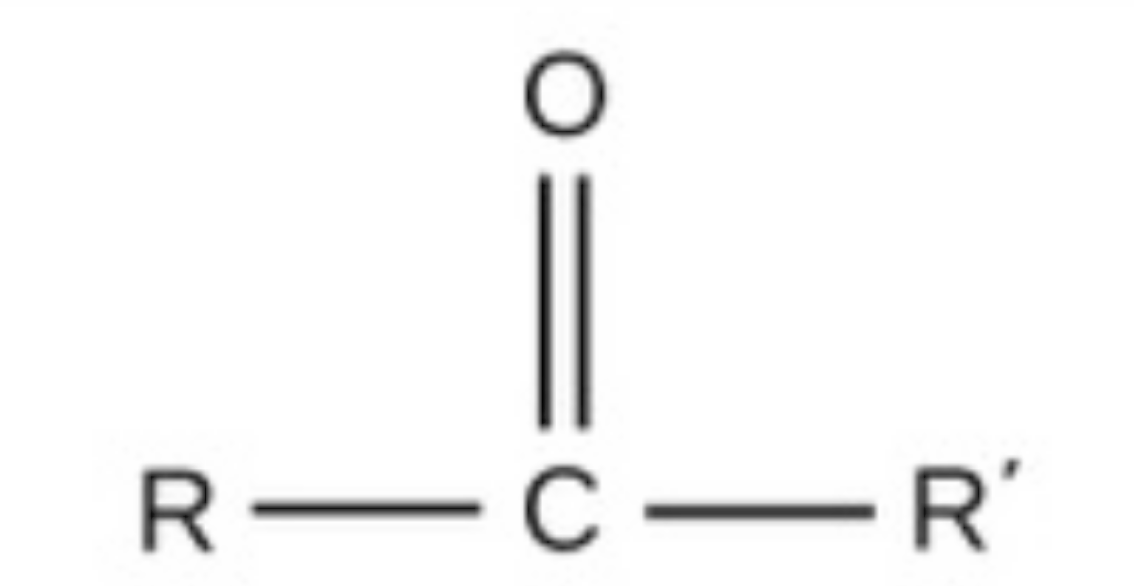
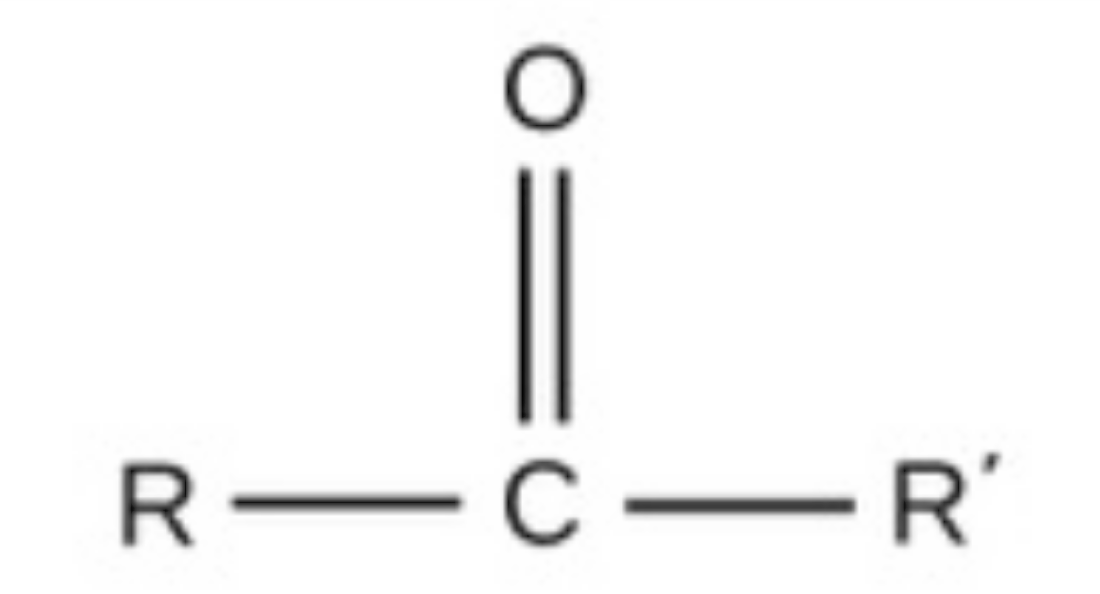
carbonyl, polar, found in carbs
amino
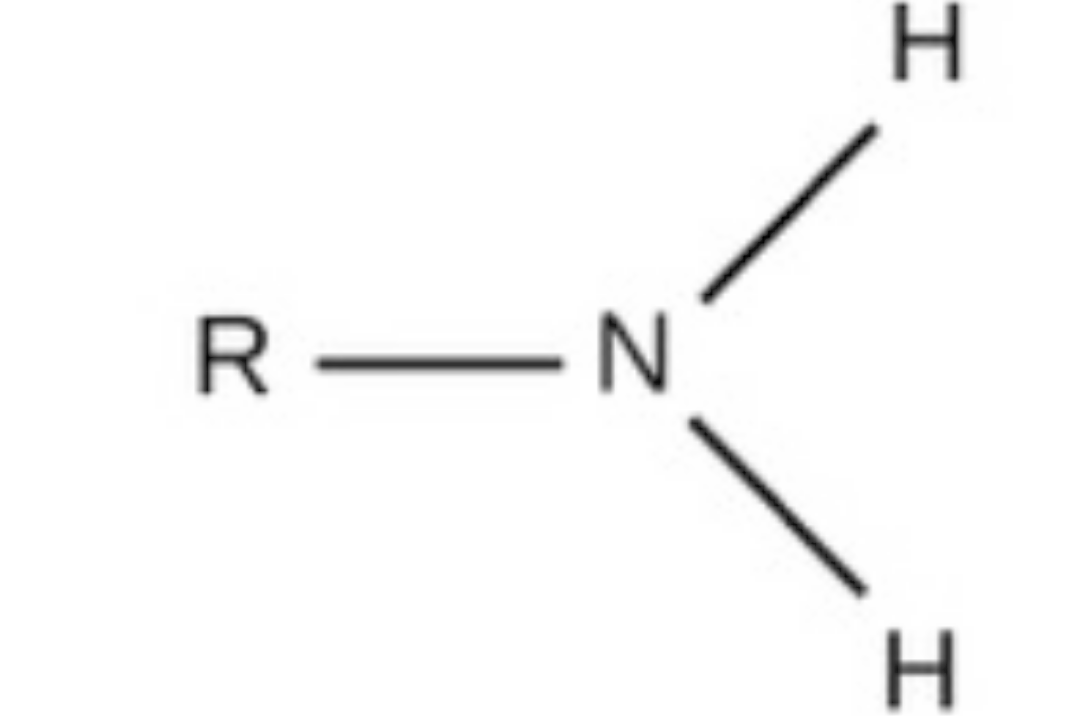
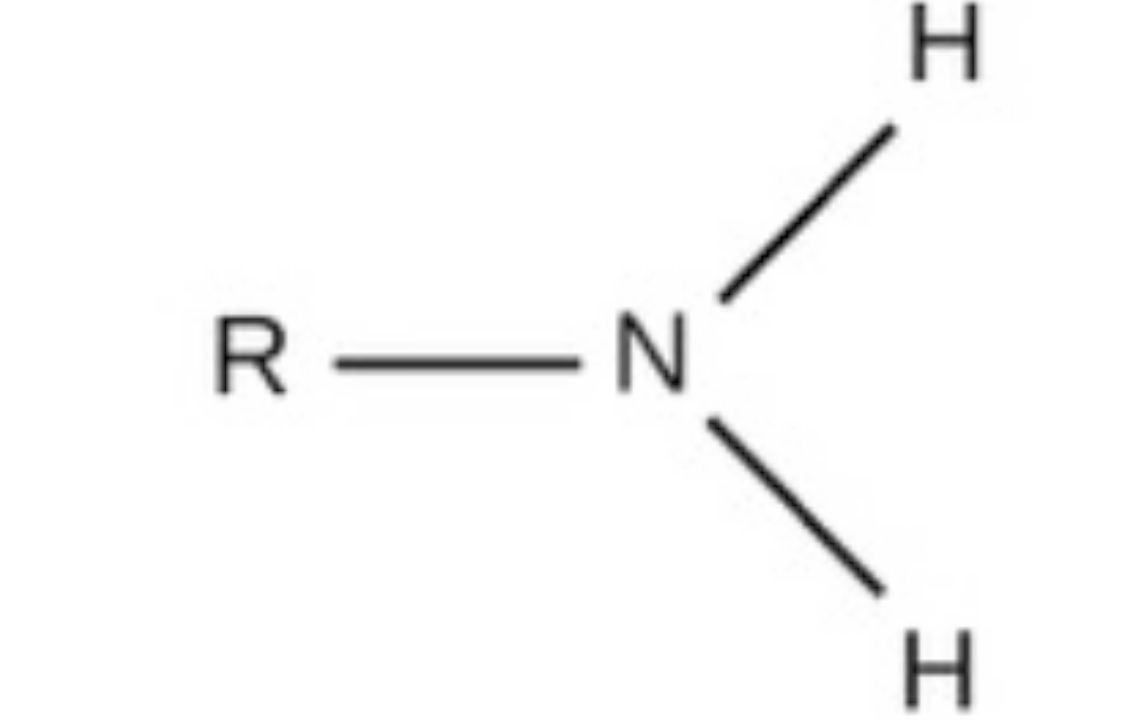
amino, charged, acidic, found in amino acids, fatty acids and other acids
phosphate
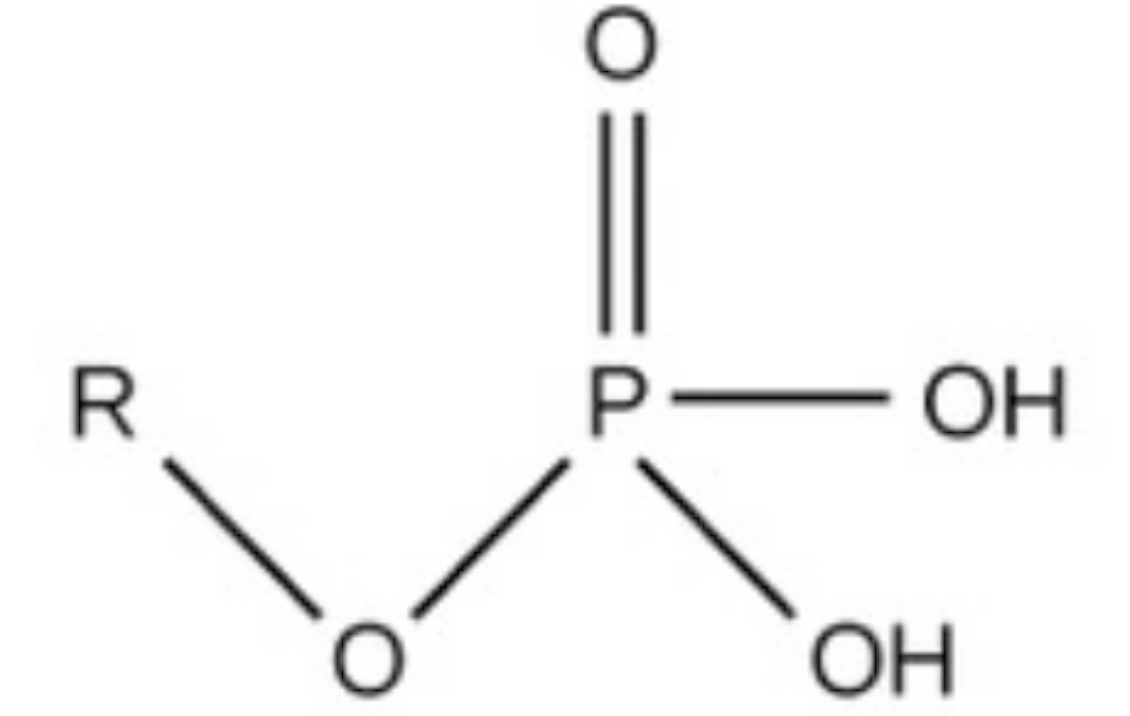
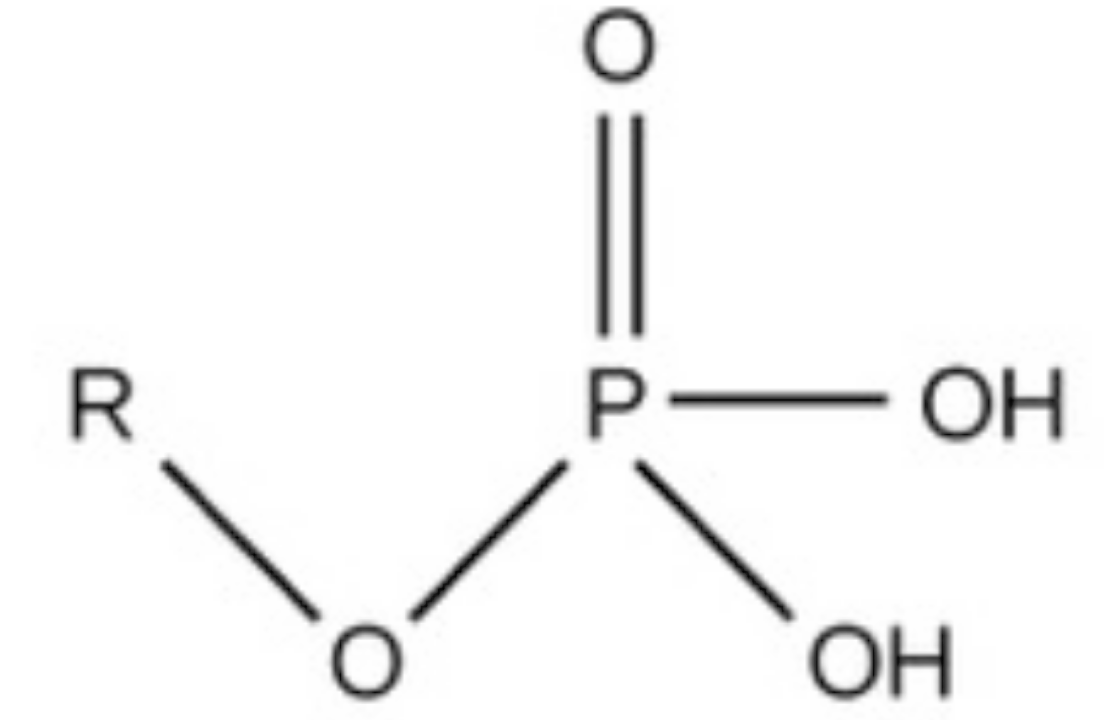
phosphate, charged, considered acidic, found in phospholipids, dna backbone (hydrocarbon), and proteins
sulfhydryl
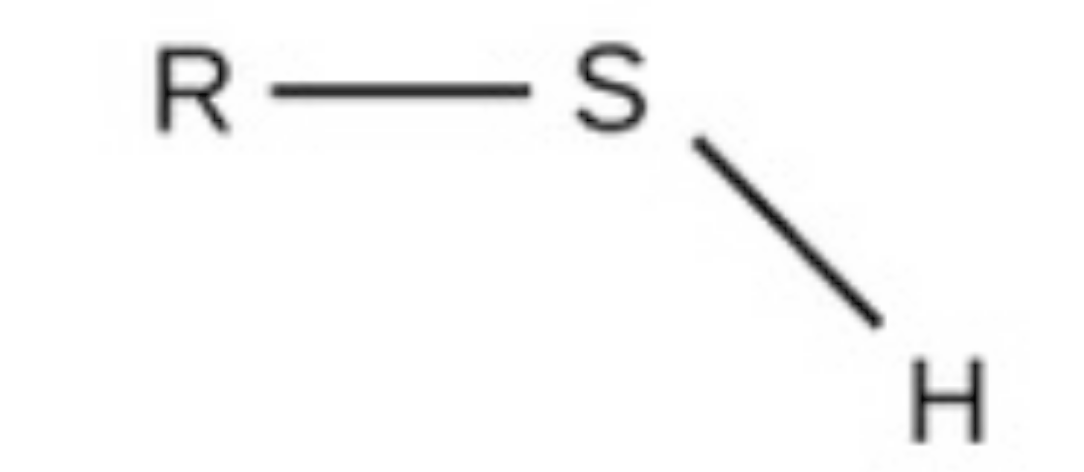
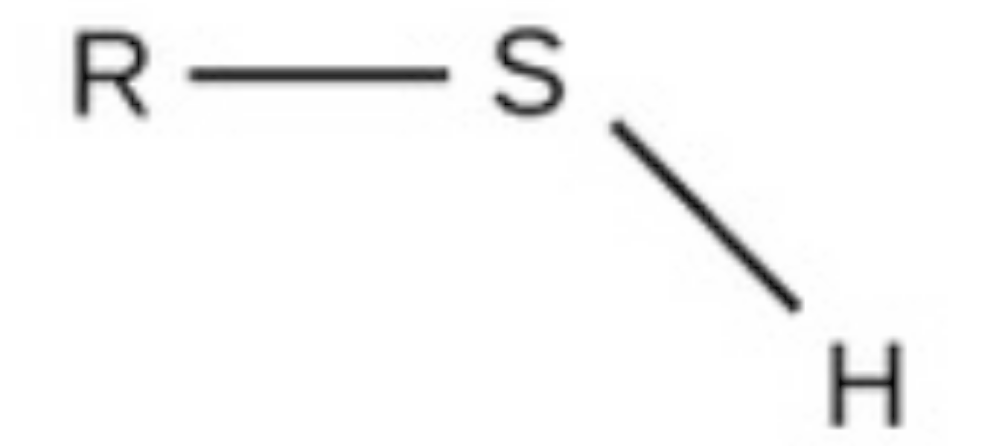
sulfhydryl, polar, found in amino acids and acetyl-coa
dehydration synthesis
monomers join together while losing water. building bonds
hydrolysis
monomer is split by adding water. breaking bonds
carbohydrates
CHO (1:2:1)
carbohydrate monomer
monosaccharide forms polysaccharides via glycosidic bonds
carb function
short term energy, structure/support, cell-cell communication
carb examples
sugars (end in ose), starches, cellulose in cell walls
short monosaccharide chains
quick energy, if not used its stored in the liver as a glycogen (animals) or as starch (plants)
long monosaccharide chains
branched, support in cell walls (cellulose, chitin, peptidoglycan)
lipids
cho
lipid monomer
no true monomer, glycerol and fatty acid tails can combine to form polymers through an ester bond
lipid polymer
phospholipid (glycerol, 2 fatty acids), triglyceride (glycerol, 3 fatty acids), steroids
lipid function
long term energy storage, cell membrane
lipid examples
fats, oils, waxes
saturated fatty acids
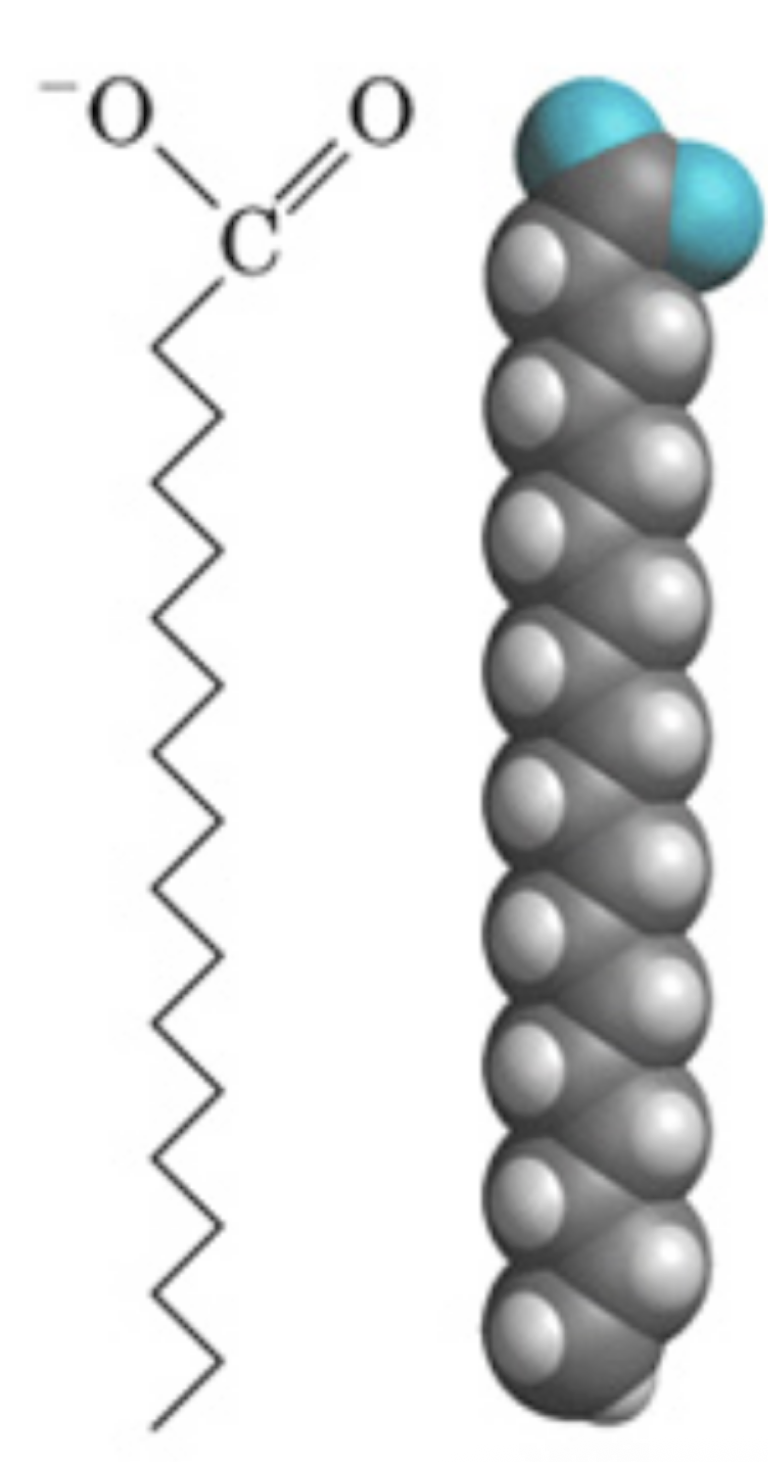
saturated fatty acid bonds
single bonds between carbons
unsaturated fatty acids
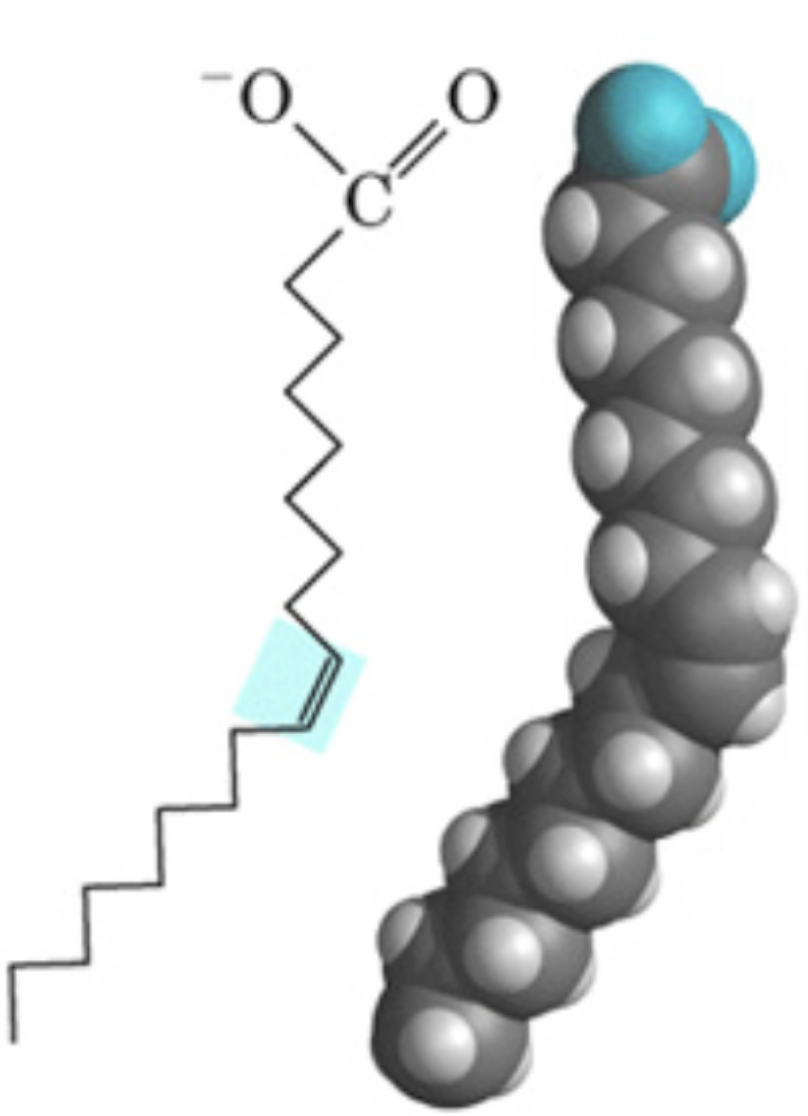
unsaturated fatty acid bonds
at least one double bond, causes a kink
more double bonds
more unsaturatedmo
more unsaturated
more liquid at room temperature
nucleic acid
chonp
3 parts of a nucleotide
phosphate, sugar, base (such as actgu)
nucleic acid monomer
nucleotide to make a polynucleotide via a phosphodiester bond
nucleic acid function
store genetic information or cell energy
nucleic acid examples
dna, rna, atp, adp, amp
antiparallel
run in opposite directions
3’
-oh group (goes down)
5’
phosphate group (goes up)
covalent bond in dna
nucleotide
hydrogen bond in dna
nitrogenous bases
dna nucleotides
adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine
rna nucleotides
adenine, cytosine, guanine, uracil
proteins
chon
protein monomer
amino acids make a polypeptide chain via a peptide bond
protein function
structure, support, cell communication, enzymes
protein examples
hemoglobin, amylase, growth hormones
how are proteins synthesized (1)
linear chains of animo acids, connected by the formation of peptide bonds between the carboxyl groups in amino acids and amine group
how are proteins synthesized (2)
r groups can be hydrophobic (nonpolar), hydrophilic (polar) or ionic. the interactions determine the structure and function of the group
primary protein structure
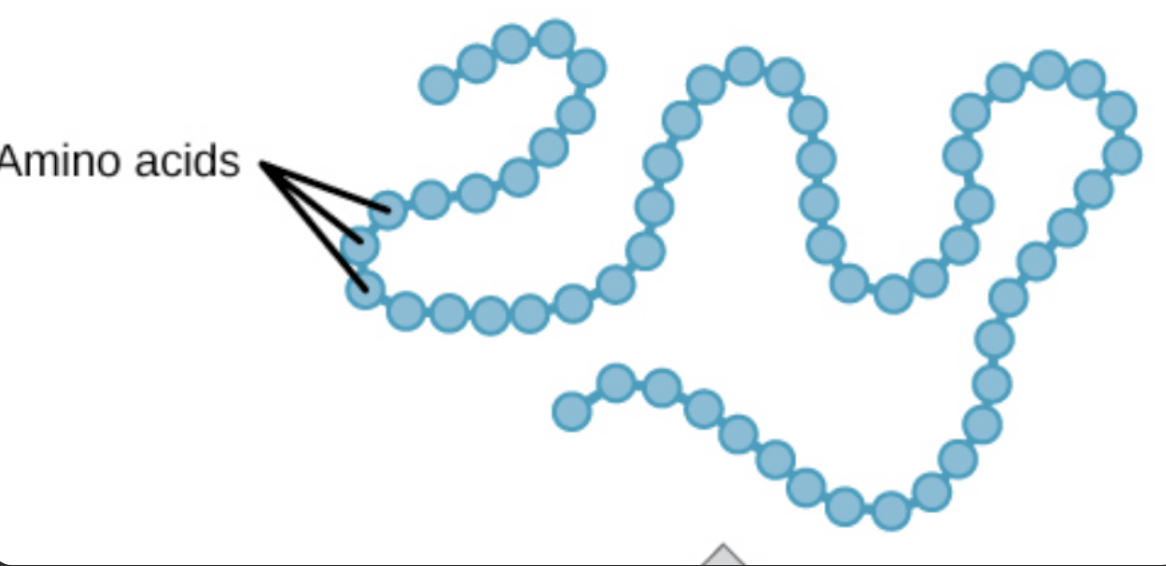
primary protein structure definition
sequence of a chain of amino acids
secondary protein structure
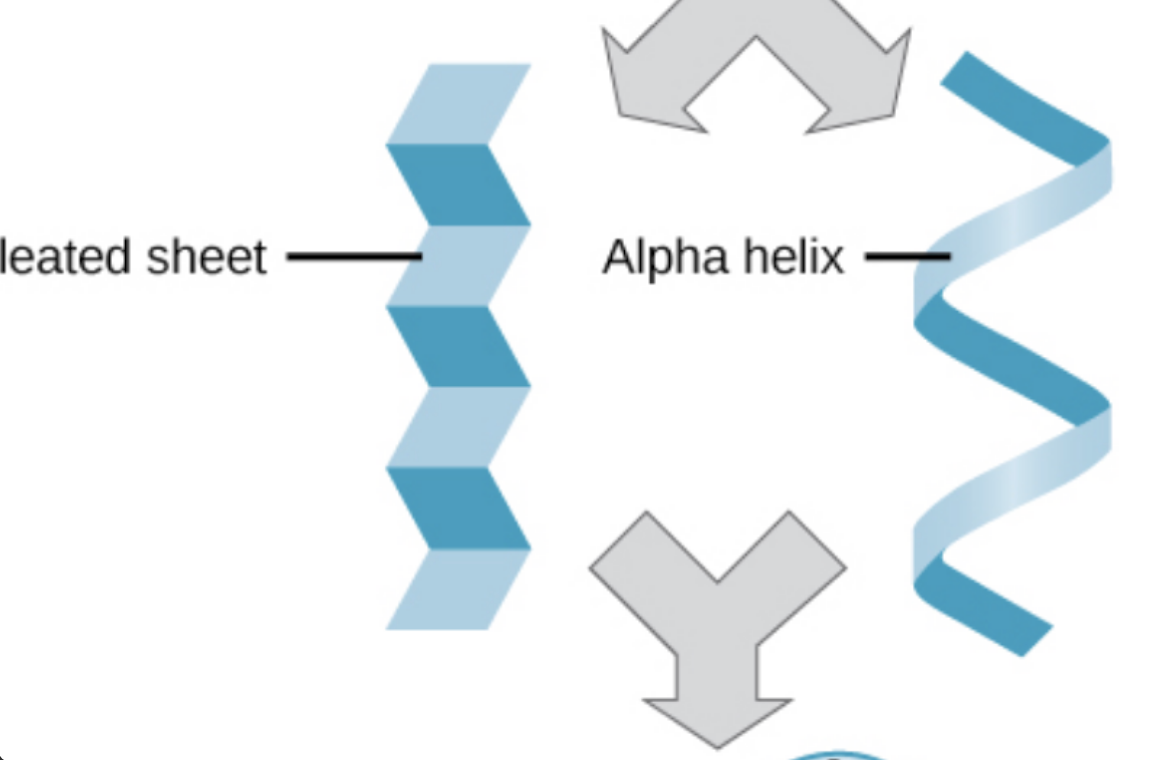
secondary protein structure definition
hydrogen bonding of the peptide backbone causes amino acids to fold into a repeating pattern
tertiary protein structure
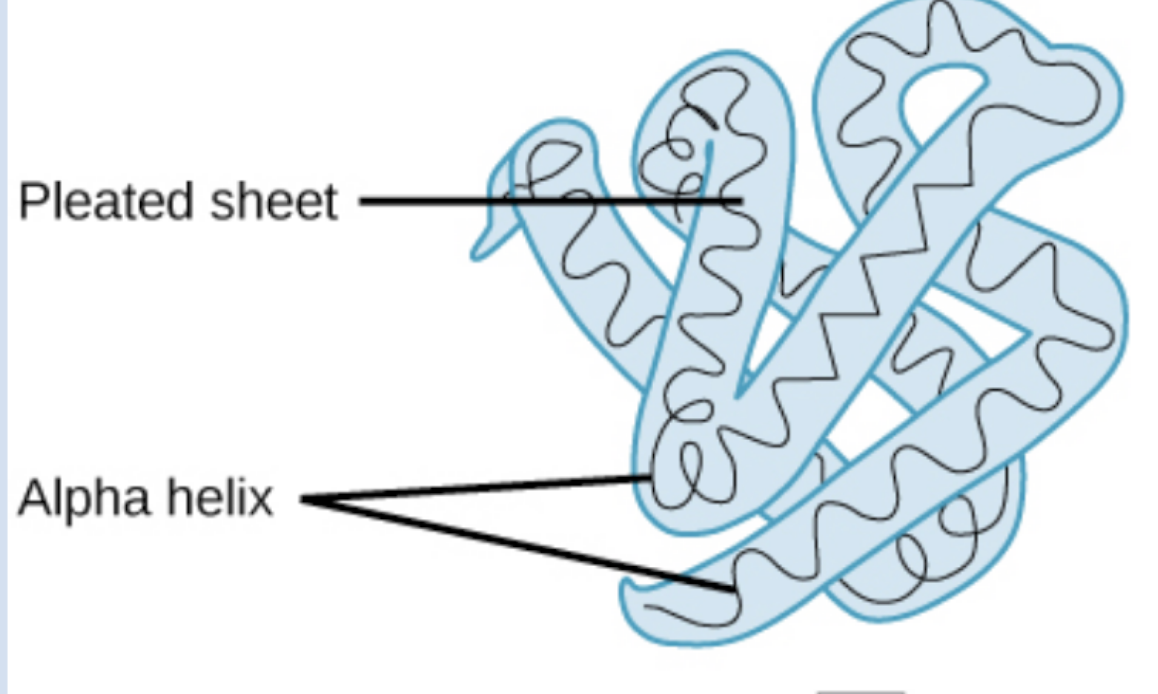
tertiary protein structure definiton
3d folding pattern of a protein due to side chain interactions
quaternary protein structure
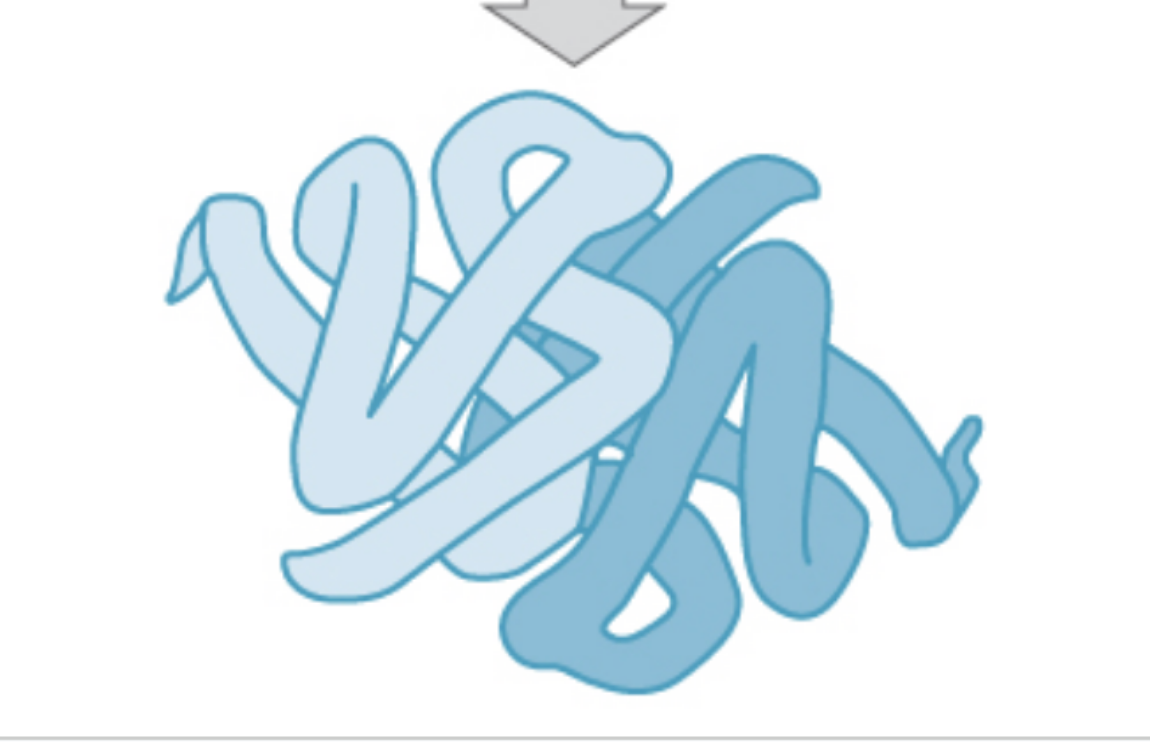
quaternary protein structure definition
protein consisting of more than one amino acid chain (optional)
pyrimidines
cytosine, thymine, uracil
purines
guanine and adenine