CSCI 4402: Database Systems - ALL Quizzes 1-6
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
A row of a table in relational model terminology is classified as _________
a. domain
b. relation
c. tuple
d. range
tuple
If two or more constraints are violated by using insert operation then by default the ________
a. insert is rejected
b. insert is accepted
c. insertion permanently blocked
d. insertion done for a default value
insert is rejected
In a relation schema, each key of schema having more than one key is classified as _________
a. foreign key
b. parallel key
c. simple key
d. candidate key
candidate key
In formal relational model, a set of indivisible values that could be a value for certain attribute is called ______________
a. tuple
b. relation
c. range
d. domain
domain
In relational model terminology, the table is considered as ____________
a. domain
b. relation
c. tuple
d. range
relation
In the data model schemas, the constraints that are expressed directly are classified as _________
a. parallel constraints
b. explicit constraints
c. flat constraints
d. implicit constraints
explicit constraints
In the data model, the inherent constraints are classified as ______________
a. implicit constraints
b. flat constraints
c. parallel constraints
d. explicit constraints
implicit constraints
The basic operations that can be performed on relations are _________
a. deletion
b. modification
c. all of the above
d. insertion
all of the above
The key which specifies that two different tuples cannot have the same value is classified as __________
a. simple key
b. conceptual key
c. parallel key
d. super key
super key
The number of the attributes of the relation is considered as the ___________ of the relation
a. domain
b. degree
c. cardinality
d. state
degree
The number of tuples in a relation is considered as the ____________ of a relation
a. cardinality
b. degree
c. domain
d. arity
cardinality
The operation which violates only one constraint called referential integrity when it is performed is called ______________
a. update operation
b. modify operation
c. insert operation
d. delete operation
delete operation
The state in which the database does not follow integrity constraints is classified as ___________
a. invalid state
b. candidate state
c. valid state
d. parallel state
invalid state
The state in which the database follows all the integrity constraints is classified as _______
a. parallel state
b. valid state
c. candidate state
d. invalid state
valid state
The type of constraint in which the value of each attribute (X) must be an indivisible value from domain(X) is classified as _________
a. atomic constraint
b. implicit constraint
c. domain constraint
d. explicit constraint
domain constraint
When the foreign key refers to a tuple which does not exists in subjected relation then the constraint violated is __________
a. insert integrity
b. modify integrity
c. inferential integrity
d. referential integrity
referential integrity
When the primary key is null of the new tuple then the constraint violated is __________
a. secondary integrity constraint
b. null integrity constraint
c. entity integrity constraint
d. primary integrity constraint
entity integrity constraint
Which of the following statement is not true about the attributes in a relation?
a. The relation attribute is unordered
b. The names of the attributes are unique inside a database
c. The names of the attributes are unique inside a relation
d. Attributes names are used to help interpreting the meaning of their values
The names of the attributes are unique inside a database
Suppose we want to list all students ids and names, but do not care about their addresses. Which of the following operations allows us to produce this relation?
a. Union
b. Set difference
c. Cross Product
d. Project
Project
Which of the following operations that is equivalent to combine certain selections and a cross product?
a. Intersection operation
b. Union operation
c. Join operation
d. Division operation
Join operation
Which of the following are the binary operations?
a. Rename, union, and set difference
b. Set difference, union, and project
c. Cartesian product, union, and set difference
d. Cartesian product, set difference, and project
Cartesian product, union, and set difference
If we have two relation R and S that are union compatible, the number of tuples in the output of their union equal __________
a. Number of the common tuples between R and S
b. Number of tuples in R +Number of tuples in S - Number of the common tuples between R and S
c. Number of tuples in R +Number of tuples in S
d. Could not be determined
Number of tuples in R + Number of tuples in S - Number of the common tuples between R and S
Which of the following relational algebra expression do?
σsalary>1200Employeeσsalary>1200Employee
a. Finds all the salaries in Employee where the number of values is greater than 1200
b. Finds the tuples in Employee where the salary is greater than 12000
c. Finds all the tuples in Employee
d. Finds all the tuples in Employee where the salary is greater than 1200
Finds all the tuples in Employee where the salary is greater than 1200
In relational algebra, the term relation is equivalent to ________
a. Column
b. Attribute
c. Row
d. Table
Table
The select, project, and rename operations are called________
a. Unary operations
b. Binary operations
c. Ternary operations
d. None of them
Unary operations
What does the following relational operation perform?
ρA1,A2,A3,...RρA1,A2,A3,...R
a. It rename the table R
b. It returns the results of table R renaming the attributes A1,A2,A3,...A1,A2,A3,...
c. It returns the results of table R with the previous attribute names
d. None of the mentioned
It returns the results of table R renaming the attributes A1, A2, A3, ...
In relational algebra, the term tuple is equivalent to ______
a. Row
b. Table
c. Attribute
d. Column
Row
The binary operation union, denoted as in the set theory by ___________
a. σ
b. ∩
c. π
d. ∪
∪
The output table schema always match the input table schema when we use the __________ operation
a. Select
b. Cross product
c. Project
d. Join
Select
The select operation selects tuples that satisfy a given predicate. We use the lower case __________ to denote selection
a. Greek letter pi (π)
b. Greek letter sigma (σ)
c. Greek letter rho (ρ)
d. Greek letter sigma (ρ)
Greek letter sigma (σ)
The project operation selects tuples with some attributes that we wish to include but some attributes we do not want to include in the final relation. We use the lowercase ______ to denote project operation.
a. Greek letter sigma (σ)
b. Greek letter pi (π)
c. Greek letter rho (ρ)
d. Greek letter sigma (ρ)
Greek letter pi (π)
Which of the following operations allows us to find the tuples that are in one relation but are not in another relation?
a. Set difference
b. Set intersection
c. Union
d. Cross product
Set difference
The expression R∩SR∩S is equivalent the expression ______________
a. (R∪S)−R
b. (R∪S)−S
c. R−(R−S)
d. R−(R∪S)
R−(R−S)
Which of the following is not a relational algebra operation?
a. Union
b. Project
c. Select
d. Manipulate
Manipulate
With SQL, how can you insert a new record into the "Student" table?Note: Student table has only two attributes, which are Fname and Lname.
a. INSERT VALUES (Fname, Lname) INTO Student
b. INSERT INTO Student VALUES ('Peter', 'Jackson')
c. INSERT VALUES ('Peter', 'Jackson') INTO Student
d. INSERT ('Peter', 'Jackson') INTO Student
INSERT INTO Student VALUES ('Peter', 'Jackson')
Which SQL keyword is used to sort the result-set?
a. ORDER BY
b. ORDER
c. SORT BY
d. SORT
ORDER BY
What is the difference between the CHAR(n) and VARCHAR(n) data types?
a. Both of them are string data types but CHAR has fixed length while VARCHAR is variable.
b. They are the same because both of them are string data types.
c. CHAR is for characters and VARCHAR is for strings data types
d. There is no data type called CHAR it is just VARCHAR for strings
Both of them are string data types, but CHAR has a fixed length while VARCHAR is variable.
With SQL, how do you select all the records from a table named "Student" where the value of the column "FirstName" ends with an "a"?
a. SELECT * FROM Student WHERE FirstName LIKE '%a%'
b. SELECT * FROM Student WHERE FirstName LIKE '_ a'
c. SELECT * FROM Student WHERE FirstName LIKE '%a'
d. SELECT * FROM Student WHERE FirstName LIKE 'a%'
SELECT * FROM Student WHERE FirstName LIKE '%a'
Which of the following is the full form of DDL?
a. Detailed Data Language
b. Data Definition Language
c. Data Derivation Language
d. Dynamic Data Language
Data Definition Language
With SQL, how can you insert "Salah" as the "LastName" in the "Student" table?
The Student table has two attributes FirstName and LastName.
a. INSERT ('Salah') INTO Student (LastName)
b. INSERT INTO Student VALUES ('Salah')
c. INSERT INTO Student (Salah) INTO LastName
d. INSERT INTO Student (LastName) VALUES ('Salah')
INSERT INTO Student (LastName) VALUES ('Salah')
With SQL, how do you select all the records from a table named "Student" where the value of the column "FirstName" is "Adam"?
a. SELECT * FROM Student WHERE FirstName='Adam'
b. SELECT * FROM Student WHERE FirstName<>'Adam'
c. SELECT All FROM Student WHERE FirstName LIKE 'Adam'
d. SELECT ALL FROM Student WHERE FirstName='Adam'
SELECT * FROM Student WHERE FirstName='Adam'
Which SQL constraint do we use to set some value to a field whose value has not been added explicitly?
a. DEFAULT
b. UNIQUE
c. CHECK
d. NOT NULL
DEFAULT
What command is used to create a new table in SQL?
a. BUILD Table
b. CREATE Table
c. CREATE Shema
d. GENERATE Table
CREATE Table
What does the following statement in SQL do?
DELETE FROM student;
a. Will do nothing because there is no where clause.
b. Delete all tuples in table student
c. Delete the table student and all its tuples
d. Delete the table student from the schema
Delete all tuples in table student
With SQL, how do you select all the columns from a table named "Products"?
a. SELECT all FROM Products
b. SELECT Products
c. SELECT *.Products
d. SELECT * FROM Products
SELECT * FROM Products
Which SQL statement is used to update data in a database?
a. MODIFY
b. SAVE AS
c. UPDATE
d. SAVE
UPDATE
With SQL, how do you select all the records from a table named "Student" where the "FirstName" is "Robin" and the "LastName" is "Williams"?
a. SELECT * FROM Student WHERE FirstName<>'Robin' AND LastName<>'Williams'
b. SELECT FirstName='Robin' , LastName='Williams' FROM Student
c. SELECT * FROM Student WHERE FirstName='Robin' OR LastName='Williams'
d. SELECT * FROM Student WHERE FirstName='Robin' AND LastName='Williams'
SELECT * FROM Student WHERE FirstName='Robin' AND LastName='Williams'
Which SQL statement is used to return only different values?
a. SELECT UNIQUE
b. SELECT DISTINCT
c. SELECT ALL
d. SELECT DIFFERENT
SELECT DISTINCT
What are rows of a relation known as?
a. Relation
b. Tuple
c. Entity
d. Degree
Tuple
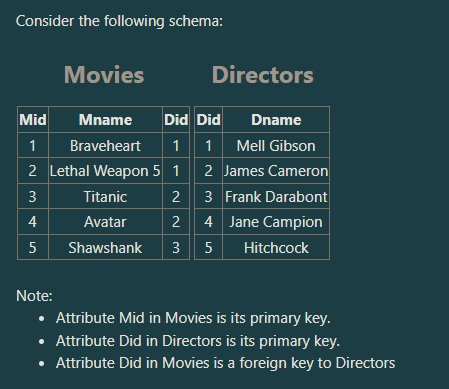
How many tuples does the following SQL statement retrieve?
SELECT Did FROM Movies;
a. Five tuples
b. Three tuples
c. Four tuples
d. empty (zero tuples)
Five tuples
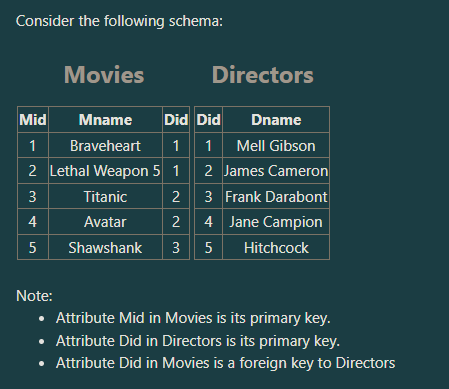
How many tuples does the following SQL statement retrieve?
SELECT Dname FROM Directors;
a. Three tuples
b. Four tuples
c. Five tuples
d. empty (zero tuples)
Five tuples
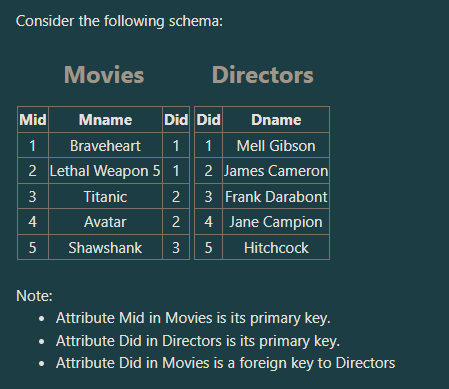
How many tuples does the following SQL statement retrieve?
SELECT Mname, Dname FROM Movies, Directors
a. Five tuples
b. Three tuples
c. Four tuples
d. 25 Tuples
25 Tuples
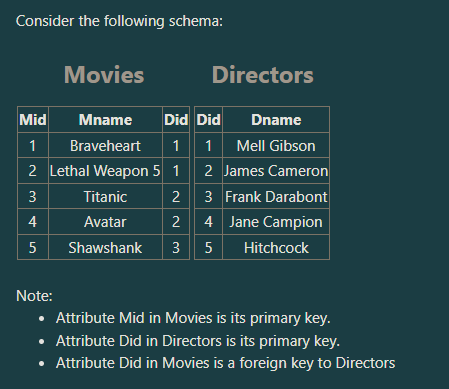
How many tuples does the following SQL statement retrieve?
SELECT DISTINCT Did FROM Movies;
a. Five tuples
b. empty (zero tuples)
c. Three tuples
d. Four tuples
Three tuples
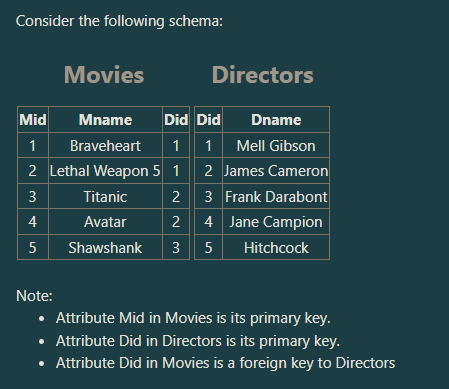
How many tuples does the following SQL statement retrieve?
SELECT Mname, Dname FROM Movies, Directors WHERE Movies.Did=Director.Did;
a. Three tuples
b. 25 Tuples
c. Four tuples
d. Five tuples
Five tuples
Suppose that we have the following table schema: Movies (id, name, director)
Which of the following queries could retrieve the movies names that doesn't have director in the database (the director attribute equal to NULL)?
a. SELECT * FROM Movies WHERE director=NULL
b. SELECT name FROM Movies WHERE director IS NULL
c. SELECT name FROM Movies WHERE director = NULL
d. SELECT * FROM Movies WHERE director IS NULL
SELECT name FROM Movies WHERE director IS NULL
With MySQL, how can you return the number of records in the "Student" table?
a. SELECT LEN(*) FROM Student;
b. SELECT NO(*) FROM Student;
c. SELECT COLUMNS(*) FROM Student;
d. SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Student;
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Student;
The system execute the rest of the trigger body that is satisfying the condition only for the ___________
a. Tuples
b. Relation
c. Instances
d. Attributes
Tuples
What is the clause that is responsible for adding a condition to an aggregate function?
a. HAVING Clause
b. GROUP Clause
c. ORDER Clause
d. WHERE Clause
HAVING Clause
What is the name of the function that is used to check whether the query result is empty or not?
a. EXIST
b. UNIQUE
c. AS
d. DISTINCT
EXIST
Which of the following is not from the typical trigger components?
a. Condition
b. Events
c. Action
d. Manipulation
Manipulation
Which of the operation are not specifies in triggers?
a. INSERT
b. ALTER
c. DELETE
d. UPDATE
ALTER
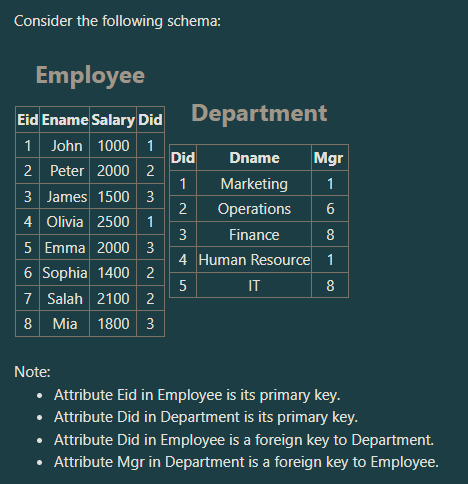
How many tuples does the following SQL statement retrieve?
SELECT Dname, sum(salary)
FROM Department,Employee
WHERE Department.Did=Employee.Did
GROUP BY Dname;
a. Four Tuples
b. One Tuple
c. Five Tuples
d. Three Tuples
Three Tuples
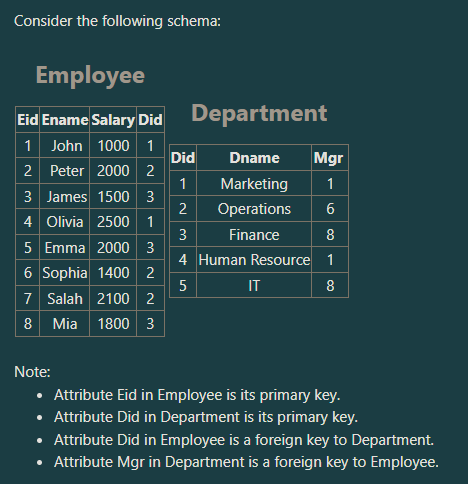
How many tuples does the following SQL statement retrieve?
SELECT sum(salary)
FROM Department, Employee
WHERE Mgr=Eid;
a. Three Tuples
b. Five Tuples
c. Four Tuples
d. One Tuple
One Tuple
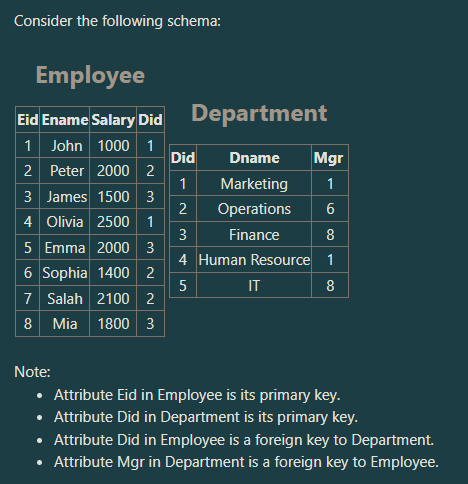
Suppose that the following SQL statement will retrieve one values. What is this value?
SELECT sum(salary)
FROM Department, Employee
WHERE Mgr=Eid;
a. 9700
b. 7000
c. 4200
d. 13400
7000
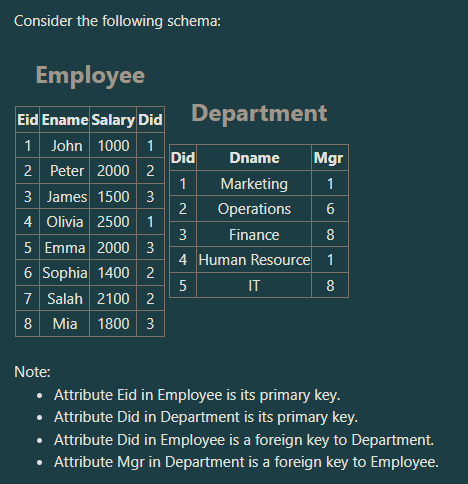
Suppose that the following SQL statement will retrieve one values. What is this value?
SELECT sum(salary)
FROM Employee
WHERE Eid in (SELECT DISTINCT Mgr FROM Department);
a. 7000
b. 9700
c. 4200
d. 13400
4200
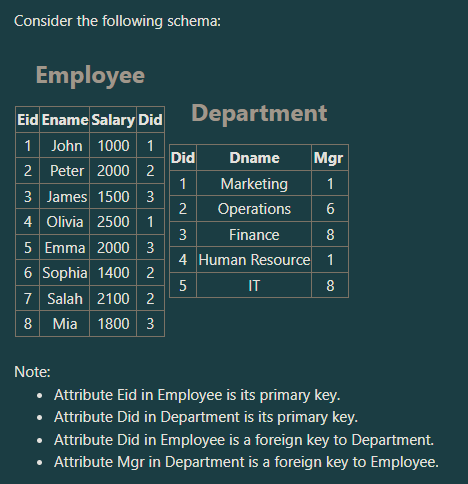
Which of the following SQL statements will retrieve the total salaries of all department
managers?
a. SELECT sum(salary)
FROM Department, Employee
WHERE Department.Mgr=Employee.Eid;
b. SELECT sum(salary) FROM Employee
WHERE Eid in (SELECT DISTINCT Mgr FROM Department);
c. SELECT sum(salary)
FROM Department, Employee
WHERE Mgr=Eid;
d. SELECT sum(salary)
FROM Department, Employee
WHERE Mgr=Eid
GROUP BY Department.Did;
SELECT sum(salary) FROM Employee
WHERE Eid in (SELECT DISTINCT Mgr FROM Department);
An entity set that does not have sufficient attributes to form a primary key is termed a __________
a. Variable set
b. Variant set
c. Strong entity set
d. Weak entity set
Weak entity set
For a weak entity set to be meaningful, it must be associated with another entity set, called the______________
a. Strong entity
b. Identifying entity
c. Owner entity
d. Neighbor entity
Identifying entity
If two entities have many to many relationships mostly results in how many tables.
a. Two
b. Four
c. One
d. Three
Three
If you were collecting and storing information about your music collection, an album would be considered a/an ___________
a. Relation
b. Instance
c. Entity
d. Attribute
Entity
Select from the following the multi-valued attribute.
a. Phone_number
b. All of the mentioned
c. Name
d. Date_of_birth
Phone_number
Select the attributes which made up of more than one single attribute.
a. Single value attribute
b. Composite attribute
c. Derived attribute
d. Multi-value attribute
Composite attribute
The attribute AGE is?
a. Single valued
b. Composite
c. Derived
d. Multi-valued
Derived
The number of entities to which another entity can be related through a relationship set is called?
a. Entity
b. Attributes
c. Cardinality
d. Schema
Cardinality
The primary key in a many to one relationship, acts as a foreign key on which side?
a. On both the sides
b. On the side where many relationships are defined
c. On the side where a single (one) relationship is defined
d. Neither of them
On the side where many relationships are defined
The Rectangles in ERD represents __________
a. Primary key
b. Attributes of a relationship
c. Entity
d. Relationship
Entity
The relationship is represented in E-R diagram as________________
a. Dashed lines
b. Diamond
c. Double diamonds
d. Undivided rectangles
Diamond
Weak entity set is represented as____________
a. Double diamond
b. Double rectangle
c. Underline
d. Double line
Double rectangle
Which of the following gives a conceptual structure of the database graphically?
a. Entity-relationship diagram
b. Architectural representation
c. Entity diagram
d. Database diagram
Entity-relationship diagram
Consider the relation R={A,B,C,D,E,F} and the set of functional dependencies {A→DE, B→C, DE→F, F→AB}.
How many different keys for the relation R?
a. one
b. Four
c. Three
d. Two
Three
Which forms simplifies and ensures that there are minimal data aggregates and repetitive groups?
a. 1NF
b. 2NF
c. 3NF
d. Normal forms do not reduce the redundancy
3NF
If the attribute of relation schema R is not a member of some candidate key then this type of attributes is classified as ______________
a. atomic attribute
b. candidate attribute
c. nonprime attribute
d. prime attribute
nonprime attribute
Considering the relational database, the functional dependency between two attributes A and B is denoted by ______
a. B←AB←A
b. R←ABR←AB
c. AB→RAB→R
d. A→B
A→B
The joining property which guarantees that spurious tuple generation problem is not created after decomposition is called _______________
a. lossless join property
b. outer join property
c. inner join property
d. additive join property
lossless join property
In the functional dependency between two sets of attributes A and B then the set of attributes A of database is classified as _________________
a. down left side
b. left hand side
c. right hand side
d. top right side
left hand side
In the __________ normal form, a composite attribute is converted to individual attributes.
a. BCNF
b. First
c. Third
d. Second
First
In the tuples, the interpretation of the values of the attribute is considered as __________
a. semantics of relation
b. clauses of relation
c. schema of relation
d. commands of relation
semantics of relation
The normalization form which is based on the transitive dependency is classified as _______________
a. third normal form
b. second normal form
c. first normal form
d. no relation between normalization and transitive dependency
third normal form
The normal form which only includes indivisible values or single atomic values is classified as __________
a. BCNF
b. third normal form
c. first normal form
d. second normal form
first normal form
Considering the functional dependency, the one in which removal from some attributes must affect dependency is called __________________
a. partial dependency
b. prime functional dependency
c. transitive dependency
d. full functional dependency
full functional dependency
Consider the relation R={A,B,C,D,E,F} and the set of functional dependencies {A→DE, B→C, DE→F, F→AB}.
Which one of the following is not considered a key for the relation R?
a. FF
b. AA
c. DEDE
d. AC
AC