Signal Transduction II: Neurotransmitter-Gated Ion Channel Receptors and GPCR Signaling
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms and concepts from the lecture notes on neurotransmitter-gated ion channels and GPCR signaling.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Neurotransmitter-Gated Ion Channel Receptors
Ion channels that open in response to neurotransmitter binding, allowing rapid ion flow across the membrane.
Desensitization involves covalent modification-phosphorylation of the the receptor by either?
receptor-specific kinases or second messenger systems.
Gating
Process by which a ligand- or voltage-activated ion channel opens or closes.
Inactivation
temporary channel closure
Deactivation
return to resting state after ligand dissociation
G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)
Seven-transmembrane receptors that activate heterotrimeric G proteins to relay signals inside the cell.
Heterotrimeric GTP-binding Proteins
G proteins composed of α, β, and γ subunits that cycle between GDP- and GTP-bound states to transmit signals.
Gα Subunit
The alpha subunit of G proteins; binds GDP/GTP and has intrinsic GTPase activity to regulate effectors.
Gβγ Dimer
The beta and gamma subunits that dissociate from Gα upon activation and regulate downstream targets.
cAMP (cyclic AMP)
Second messenger produced by adenylyl cyclase that activates PKA.
Adenylyl Cyclase
Membrane enzyme converting ATP to cAMP; regulated by Gs (activating) and Gi (inhibiting) G proteins.
Protein Kinase A (PKA)
cAMP-activated kinase with regulatory and catalytic subunits that phosphorylates various substrates.
CREB
cAMP response element-binding protein; transcription factor activated by PKA to regulate gene expression.
IP3 (inositol trisphosphate)
Second messenger produced by PLC that releases Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum.
DAG (diacylglycerol)
Second messenger produced by PLC that activates protein kinase C (PKC).
Phospholipase C (PLC)
Enzyme that hydrolyzes PIP2 into IP3 and DAG.
PI(4,5)P2 (PIP2)
Membrane phospholipid substrate for PLC in GPCR signaling.
Gs Protein
Stimulatory G protein that activates adenylyl cyclase to raise cAMP levels.
Gi Protein
Inhibitory G protein that suppresses adenylyl cyclase to lower cAMP levels.
Desensitization
Receptor becomes functionally uncoupled from G proteins despite ongoing agonist binding but remains on cell surface
GRK (G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase)
Kinase that phosphorylates activated GPCRs to promote arrestin binding and desensitization.
β-Arrestin
Protein that binds phosphorylated GPCRs, blocking G protein coupling and promoting receptor internalization and signaling.
Internalization
Endocytic uptake of a GPCR into endosomes, often followed by recycling or degradation.
Biased Agonist
Ligand that preferentially activates one signaling pathway over another (e.g., G protein vs arrestin).
Neutral Agonist
Ligand that activates a receptor without bias toward a particular downstream pathway.
Inverse Agonist
Ligand that reduces constitutive (basal) activity of a receptor.
Rhodopsin
GPCR in visual signaling; archetypal GPCR whose activation initiates the phototransduction cascade.
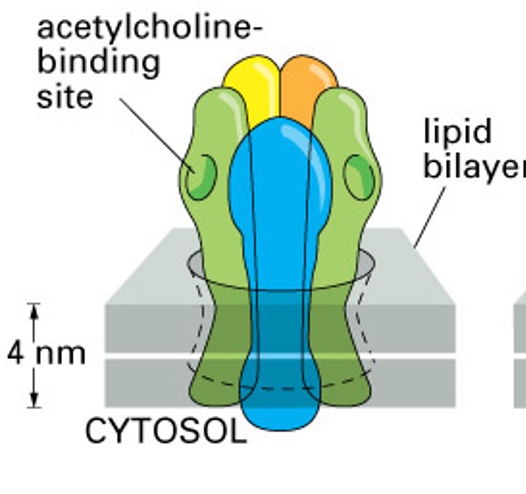
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor (nAChR)
Pentameric LGIC in the Cys-loop family activated by acetylcholine.
P2X Receptor
ATP-gated ligand-gated ion channel; part of the LGIC family.
GABA_A Receptor
Ligand-gated chloride channel that mediates fast inhibitory neurotransmission.
AMPA Receptor
Ionotropic glutamate receptor mediating fast excitatory synaptic transmission.
NMDA Receptor
Glutamate receptor permeable to Ca2+; voltage-and ligand-gated, critical for synaptic plasticity.
5-HT3 Receptor
Serotonin-gated ligand-gated ion channel in the Cys-loop receptor family.
GLP-1 Receptor
GPCR that binds glucagon-like peptide-1 and stimulates insulin secretion.
Trulicity (dulaglutide)
GLP-1 receptor agonist used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
SERT (Serotonin Transporter)
Presynaptic transporter that reuptakes serotonin; targeted by SSRIs.
SSRI (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor)
Drug class that blocks SERT to increase synaptic serotonin levels.
IP3 Receptor
ER calcium-release channel activated by IP3.
Ca2+ Homeostasis
Regulation of intracellular Ca2+ levels via ER/PM pumps, exchangers, and channels.
Ca2+-Release Pathways via IP3/DAG
GPCR signaling that mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ through IP3-mediated release and PKC activation by DAG.
PKC (Protein Kinase C)
A family of serine/threonine kinases activated by DAG and Ca2+; regulates many substrates.
PKC Subtypes (Conventional, Novel, Atypical)
Classification of PKCs by activation requirements: conventional (DAG and Ca2+), novel (DAG only), atypical (neither require DAG nor Ca2+).
Phosphodiesterases (PDEs)
Enzymes that break down cyclic nucleotides (cAMP, cGMP) to terminate signaling.
Four Major Families of G Proteins (Gs, Gi, Gq, G12/13)
Classification of heterotrimeric G proteins guiding distinct GPCR signaling cascades.
Signal termination
Involves internalization of the receptor into specialized endosomes which then recycle back to the plasma membrane
Overall structure : nicotinic AcH receptor