GEN CHEM DAT
What are the 7 diatomic molecules?
Hydrogen, Flourine, Bromine, Iodine, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Chlorine
What is the formula for E cell potential?
Ecell = Ered + Eox
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
What are the 7 diatomic molecules?
Hydrogen, Flourine, Bromine, Iodine, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Chlorine
What is the formula for E cell potential?
Ecell = Ered + Eox
True or false: Any # to the power of 0 is 1
True
True or false: Neutralization, Precipitation, and Hydrolysis reactions are redox reactions
False
What is the rate law equation?
rate=k[A]m[B]n
What are pure substances?
Pure substances are 1 formula and are either Elements (Au, Cu, H2) and Compounds (C6H12O6, H2O, NH4+)
What are mixtures?
Mixtures are 2+ formulas and are either homogenous (spread evenly like NaCl+H2O) or heterogenous (not spread evenly like dirt or concrete)
Why does effective nuclear charge increase across a row?
Because atomic size decreases across a row
Why does atomic size increase down a column?
Because of the increase in electron shielding as the molar mass increases
What is a combustion reaction?
Reacting a hydrocarbon with O2 to form CO2 and H2O
How many sig figs is in 0.000454?
3 (bc leading zeroes don't count)
How many sig figs are in 11.0?
3 (bc trailing zeroes are significant)
Define a Lewis Acid
a molecule that accepts electrons
Define a Lewis Base
a molecule that donates electrons
True or false: Only temperature can affect Ksp
True
What do all the 4 quantum numbers represent?
n= outer valence shell
l= 0,1,2,3 (for s,p,d,f)
ml= -l…….0…….+l
ms= +1/2 or -1/2 (ALWAYS)
What is the half-life equation?
mass remaining = (original mass) (1/2)t
3 Properties of ionic solids
high melting points, brittle, hard
3 Properties of network solids
High melting point, hard, nonconducting
What is paramagnetism?
When at least one electron is unpaired
What is diamagnetism?
When all electrons are paired
True or false: Bond dissociation energy is always positive
True because it's energy needed to break a bond
True or false: London forces increase down a column bc of increase molar masses which leads to increased boiling points
True
What is density of gas formula?
p=PM/RT
p=density
P=pressure
M=molar mass
R=ideal gas constant (0.0821)
T=temperature
Define colligative properties?
physical properties of solutions that depend on # of solute & solvent particles in solution REGARDLESS OF SOLUTE IDENTITY
What are 4 examples of colligative properties?
vapor pressure, osmotic pressure, freezing point, boiling point
True or false: Chemical changes do not result in a change in the chemical formula
False
True or false: Phase changes are chemical changes
False. They are physical changes
What is the osmotic pressure formula?
π=iMRT
π= osmotic pressure
i= van't Hoff (# of things compound will break into)
M= molarity
R= ideal gas constant (0.0821)
T= temperature (K)
What are the 7 strong acids?
HCl - hydrochloric acid
HBr - hydrobromic acid
HI - hydroiodic acid
HNO3 - nitric acid
HClO3 - chloric acid
HClO4 - perchloric acid
H2SO4 - sulfuric acid
What are the 7 strong bases?
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
Potassium Hydroxide (KOH)
Lithium Hydroxide (LiOH)
Cesium Hydroxide (CsOH)
Calcium Hydroxide (Ca(OH)2)
Strontium Hydroxide (Sr(OH)2)
Barium Hydroxide (Ba(OH)2)
What is the combined gas law equation?
P1V1/n1T1 = P2V2/n2T2
What is the unit for first-order reaction?
s-1
What is the unit for second-order reaction?
M-1 s-1
What is the unit for third-order reaction?
M-2 s-1
What is the Gibbs free energy equation?
∆G = ∆H - T∆S
2 Properties of Molecular solids
Low melting point, nonconducting
3 Properties of Metallic solids
Variable melting point, hardness, conducting
what do pH and pOH equal?
pH + pOH = 14
True or false: 10-pH=[H+]
True
define spectator ions
present unchanged in reactant & product side of equation
5 Solubles
Most Group 1 metal cations
Nitrate (NO3-)
Perchlorate (ClO4-)
Acetate (C2H3O2-)
Ammonium (NH4+)
7 Insolubles
Silver (Ag+)
Lead (Pb2+)
Sulfide (S2-)
Hydroxide (OH-)
Dimercury (Hg2+)
Carbonate (CO32-)
Phosphate (PO43-)
What is the rate constant equal to in a first and second-order equation?
-slope
What are the units and y-axis for a zero-order reaction?
M1s-1 and [A]
What are the units and y-axis for a first-order reaction?
s-1 and ln[A]
What are the units and y-axis for a second-order reaction?
M-1s-1 and 1/[A]
Where is the titrant placed in a titration?
buret
Where is the titrand placed in a titration?
Erlenmeyer flask
What equation has heat and work?
deltaE = q + w
Define electrolysis
decomposes compound into its constituents
What do the corners of a cubic cell equal
1/8
whats the relationship between Ka, pKa, and acidity
High Ka=low pKa=increased acidity
What level do the bottom (extra) rows of the periodic table represent?
4f level
term for same # of protons, diff # of electrons
ions
term for same # of protons, diff # of neutrons
isotopes
what is the equation for mass percent?
mass percent=mass of solute/total mass of solution x 100
what lab technique is used to separate a homogenous mixture?
distillation
what 3 pieces of lab equipment is used in a distillation experiment?
condenser, distillation flask, flask
Why does a nucleus weigh less than the sum of its neutrons and protons?
Some of the nucleus’s mass is converted into nuclear binding energy
what are the 4 steps to balance a reaction in an acidic medium?
Balance elements other than H & O
Balance oxygen by adding H2O
Balance hydrogen by adding H+
Add electrons to balance charges, if necessary
Under what conditions will a real gas exhibit ideal gas behavior?
High temperature and low pressure
What are the 5 assumptions of ideal gasses?
Particle sizes are insignificant
Zero intermolecular forces
Random motion
Perfectly elastic collisions
Kinetic energy only depends on temperature
How does Ksp relate to molar solubility for salts that have the same number of ions
low Ksp=least soluble
high Ksp=most soluble
What does pH plus pOH equal?
14
How do you find H+ or OH- concentration using pH and pOH?
H+ = 10-pH
OH- = 10-pOH
What is the equation for work?
w=-P*deltaV
w=work
P=pressure
deltaV=change in volume
If the system does work on the surrounding, is work positive or negative?
negative
If the surroundings do work on the system, is work negative or positive?
positive
How do you determine if a bond is polar?
If there is a significant difference in electronegativities
A spontaneous Ecell is positive or negative
Positive
Electrons always flow from anode to cathode
True or false
True
Where does oxidation and reduction occur in a Galvanic (voltaic) cell?
Oxidation at the anode and reduction at the cathode
Oxidation and reduction occur at the same sites in both Galvanic (voltaic) cells and electrolytic cells
True or false
True
What is the charge at the anode and cathode in a Galvanic (voltaic) cell?
Anode is negative and cathode is positive
What is the charge at the anode and cathode in a Electrolytic cell?
Anode is positive and cathode is negative
Between a galvanic and electrolytic cell, which one contains a salt bridge?
Galvanic cell
Describe the relationship between frequency, wavelength, and energy
shorter wavelength=higher frequency=higher energy
What is the relationship between vapor pressure and boiling point?
Inversely related
What are the 4 state functions?
Gibbs Free Energy, mass, volume, enthalpy
What are the 3 path (nonstate) functions?
work, heat, heat capacity
What is the ideal gas law?
PV=nRT
P= pressure
V= volume
n= moles
R= 0.082
T= temperature (in Kelvin)
What is an allotrope?
different structural forms of the same element
What are the ΔH, ΔS, -TΔS, ΔG conditions that will be spontaneous at all temperatures?
ΔH= -
ΔS= +
-TΔS= -
ΔG= -
What are the ΔH, ΔS, -TΔS, ΔG conditions that will be nonspontaneous at all temperatures?
ΔH= +
ΔS= -
-TΔS= +
ΔG= +
What are the ΔH, ΔS, -TΔS, ΔG conditions that will be spontaneous at low temperatures?
ΔH= -
ΔS= -
-TΔS= +
ΔG= depends
What are the ΔH, ΔS, -TΔS, ΔG conditions that will be spontaneous at high temperatures?
ΔH= +
ΔS= +
-TΔS= -
ΔG= depends
lower reduction potential (more negative)
stronger reducing agent (oxidized)
higher reduction potential (more positive)
stronger oxidizing agent (reduced)
3 steps to figure out the limiting reactant
B,C,D
Balance equation
Convert reactants to mols
Divide mols by the reactants coefficients. The smallest one is the LIMITING REACTANT
The higher the vapor pressure, the lower the boiling point
True or false
True
The weaker the IMFs, the more volatile a liquid is
True or false
True
percent composition formula
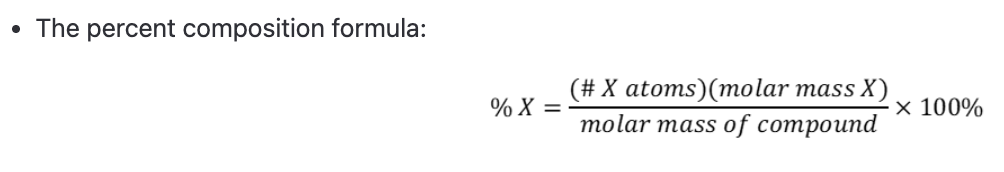
What will the pH at equivalence be between a strong acid and strong base?
7
What will the pH at equivalence be between a weak acid and strong base?
above 7
What will the pH at equivalence be between a weak base and strong acid?
below 7
In a zero-order reaction, the half-life decreases as the concentration of a substance decreases.
True or false
True
The half-life is constant as the concentration decreases. Which order reaction does the belong to?
First order
The half life increases as concentration decreases. Which order reaction does this belong to?
Second order
What is a neutralization reaction?
A reaction between an acid and a base that results in water and a salt