Comprehensive Neurobiology and Brain Function: Nervous System, Brain Structures, and Influence of Genes and Environment
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
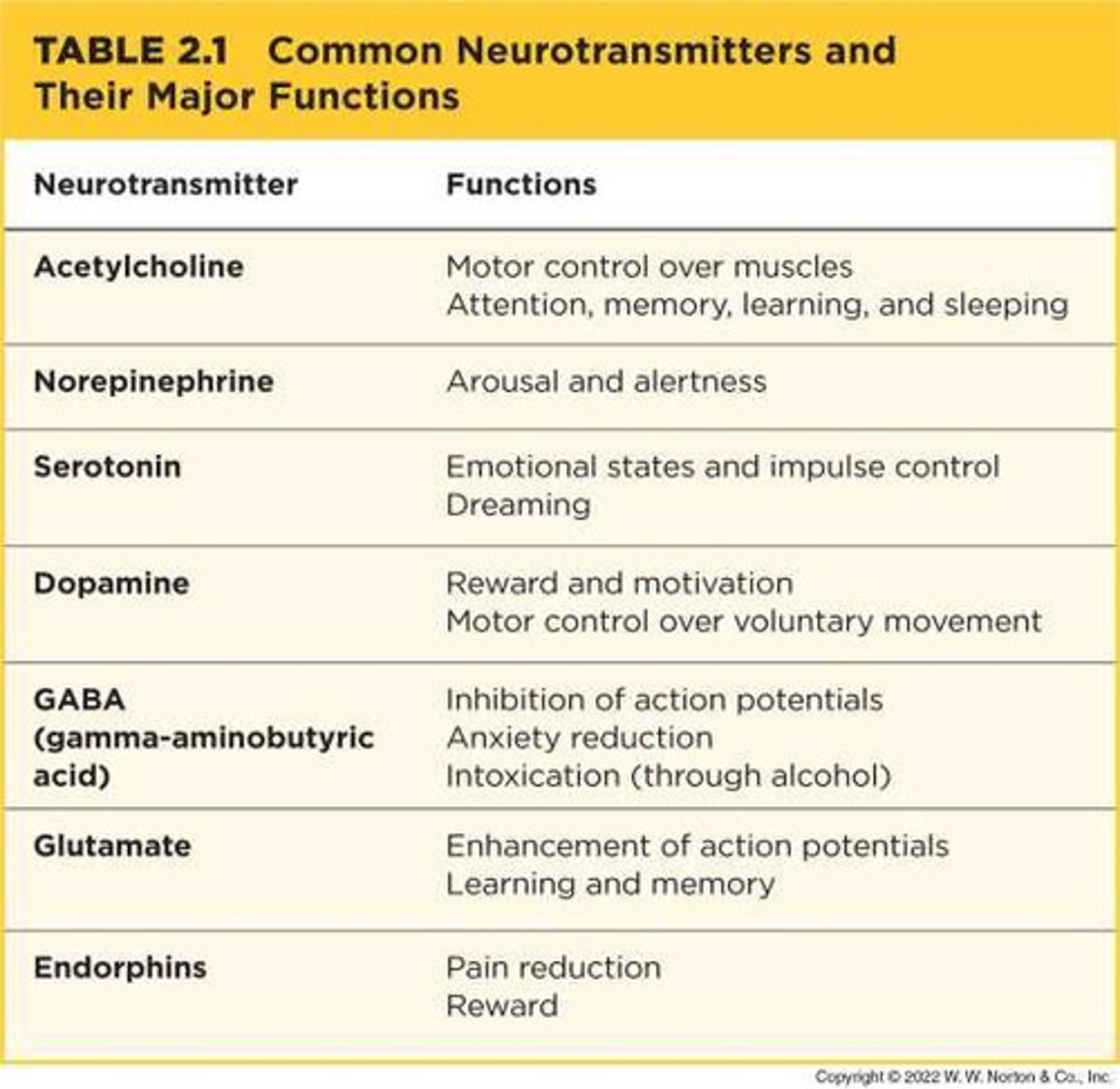
Nervous system
A network of billions of cells in the brain and the body, responsible for all aspects of what we feel, think, and do.
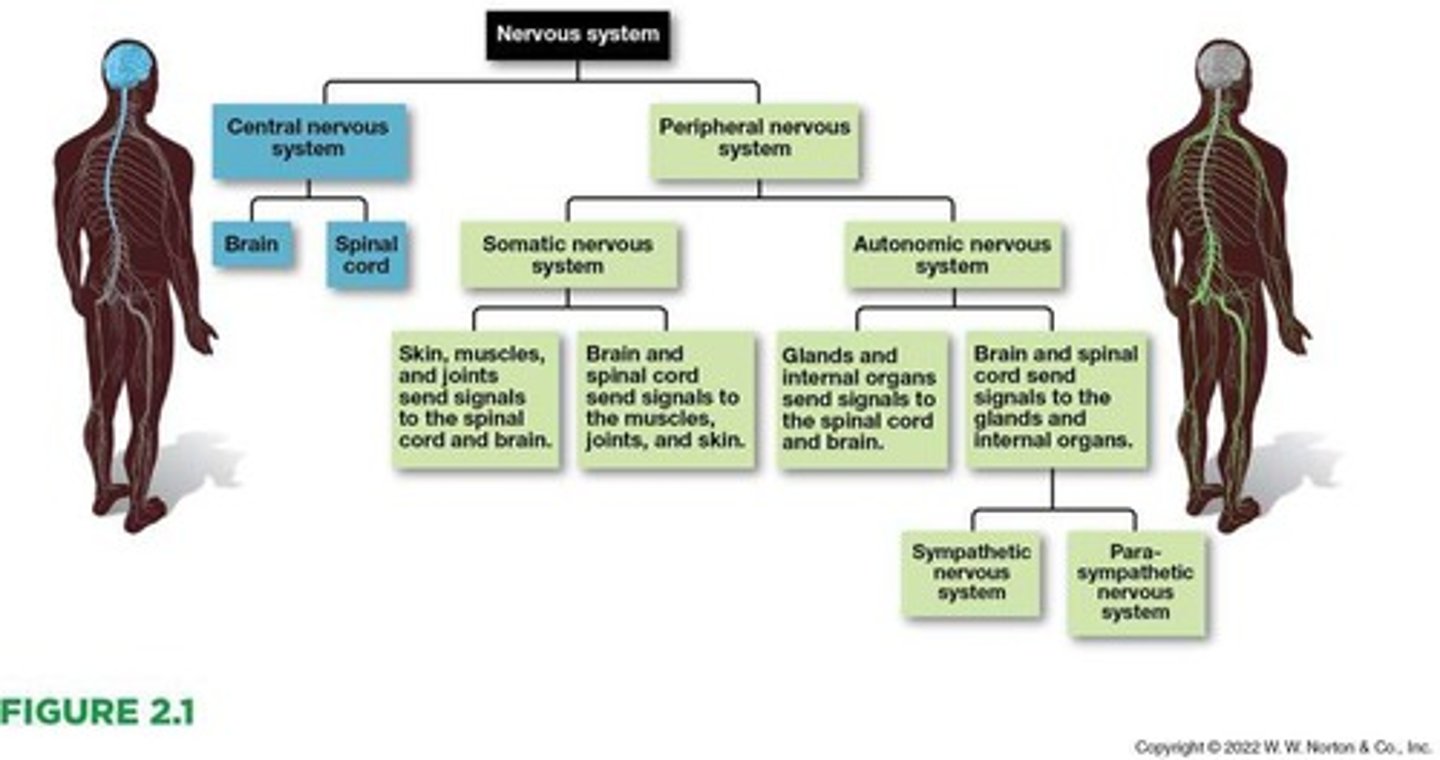
Central nervous system
The part of the nervous system that consists of the brain and the spinal cord.
Peripheral nervous system
The part of the nervous system that enables nerves to connect the central nervous system to the skin, muscles, organs, and glands.
Neurons
Cells that receive, integrate, and transmit information in the nervous system.
Dendrites
Branchlike extensions of the neuron with receptors that detect information from other neurons.
Cell body
The part of the neuron where information from thousands of other neurons is collected and integrated.
Axon
The long, narrow outgrowth of a neuron that enables it to transmit information to other neurons.
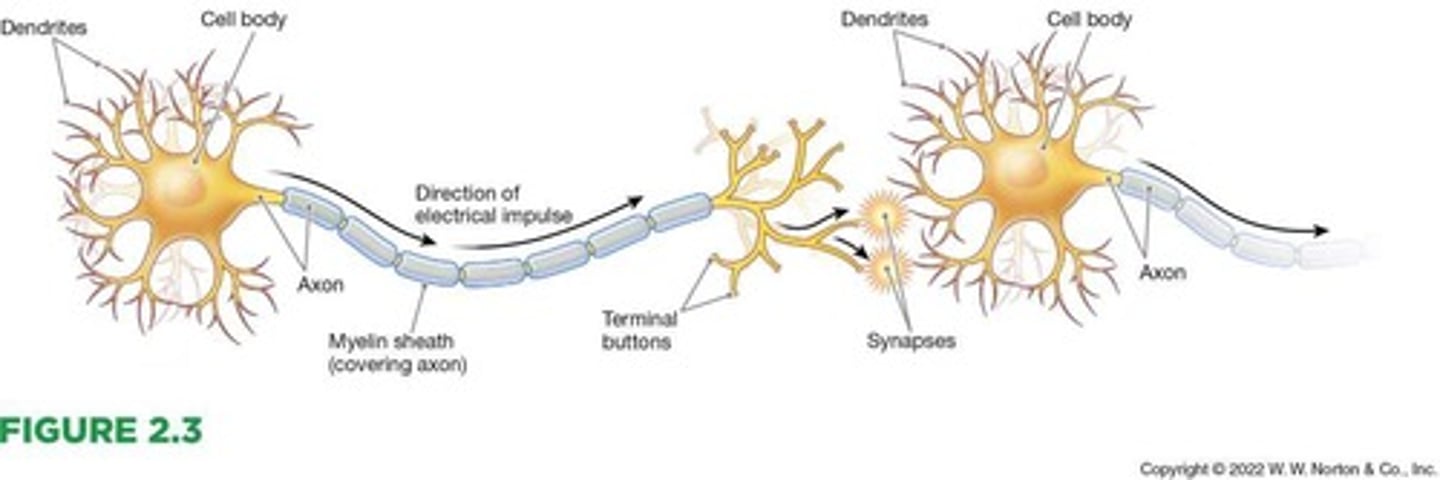
Terminal buttons
Parts of the neuron at the end of the axon(s) that release chemical signals from the neuron into the synapse.
Synapse
The site of communication between neurons through neurotransmitters.
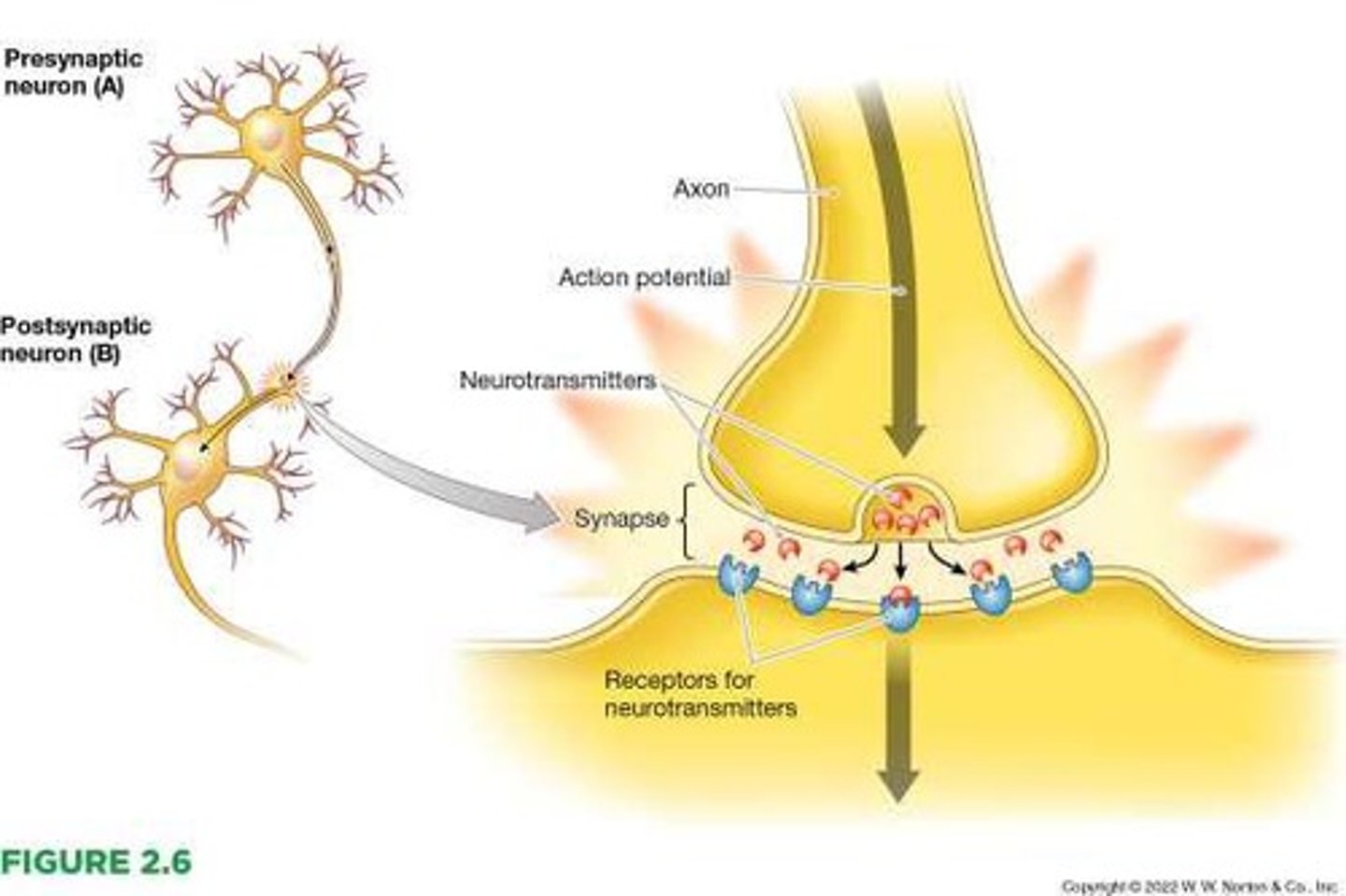
Neurotransmitters
Chemical substances that carry signals from one neuron to another.
Three basic functions of the nervous system
1. Receive sensory input from the world through vision, hearing, touch, taste, and smell. 2. Process the information in the brain by paying attention to it, perceiving it, and remembering it. 3. Respond to the information by acting on it.
Electrical properties of neurons
Parts of the neuron are covered with a membrane, which is semipermeable.
Neural networks
Connections formed by neurons that communicate selectively with each other.
Neurons operate
Through electrical impulses and connect with other neurons through chemical signals.
Neurons communicate
By selectively connecting with other neurons and forming networks.
Neurotransmitter function
To carry signals from one neuron to another across the synapse.
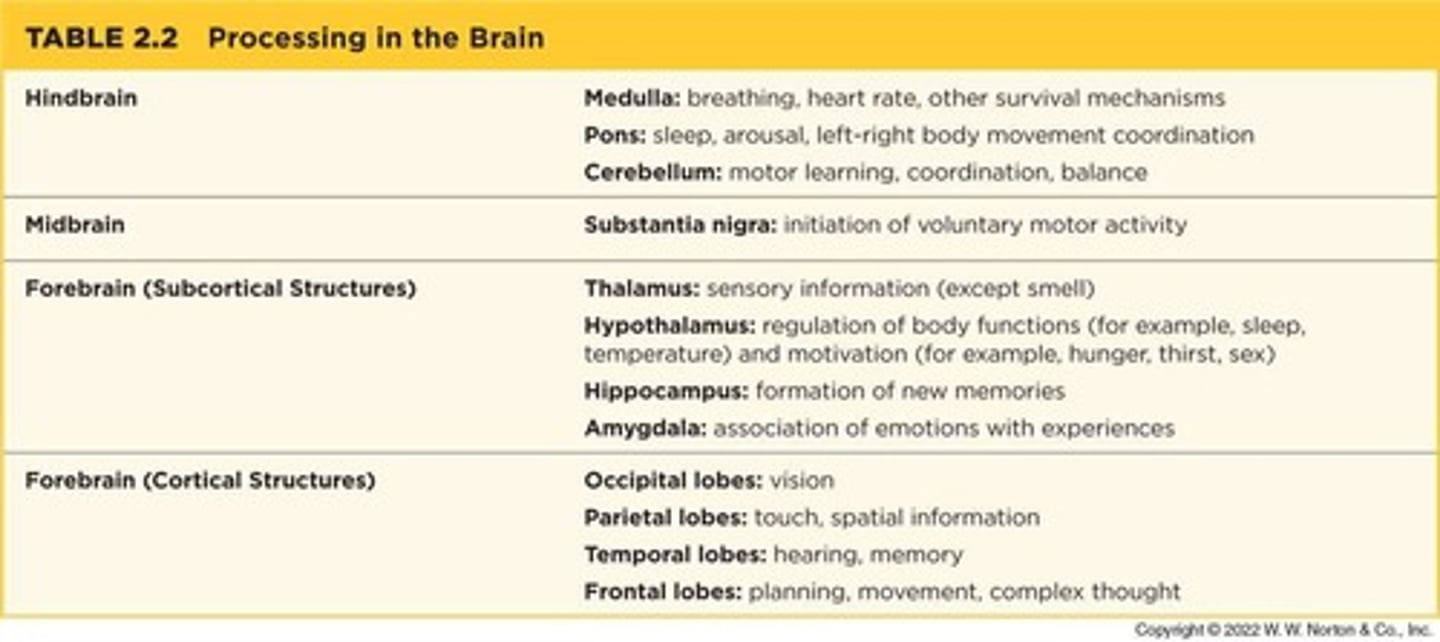
Survival programs in the brain
Basic programs housed in the hindbrain and midbrain that are essential for survival.
Forebrain subcortical structures
Control your motivations and emotions.
Cerebral cortex
Processes your complex mental activity.
Hemispheres of the brain
Work together with some specialization.
Learning disability
How psychology can be used in life to succeed despite challenges.
Endocrine system
Affects your behavior through hormones.
Genes and behavior
Your genes affect your mental activity and behavior.
Gene-environment interaction
Your genes interact with your environment to influence you.
Environmental impact on the brain
Your environment changes your brain.
Action potential
The neural impulse that travels along the axon and then causes the release of neurotransmitters into the synapse.
Myelin sheath
Fatty layer that insulates the axon.
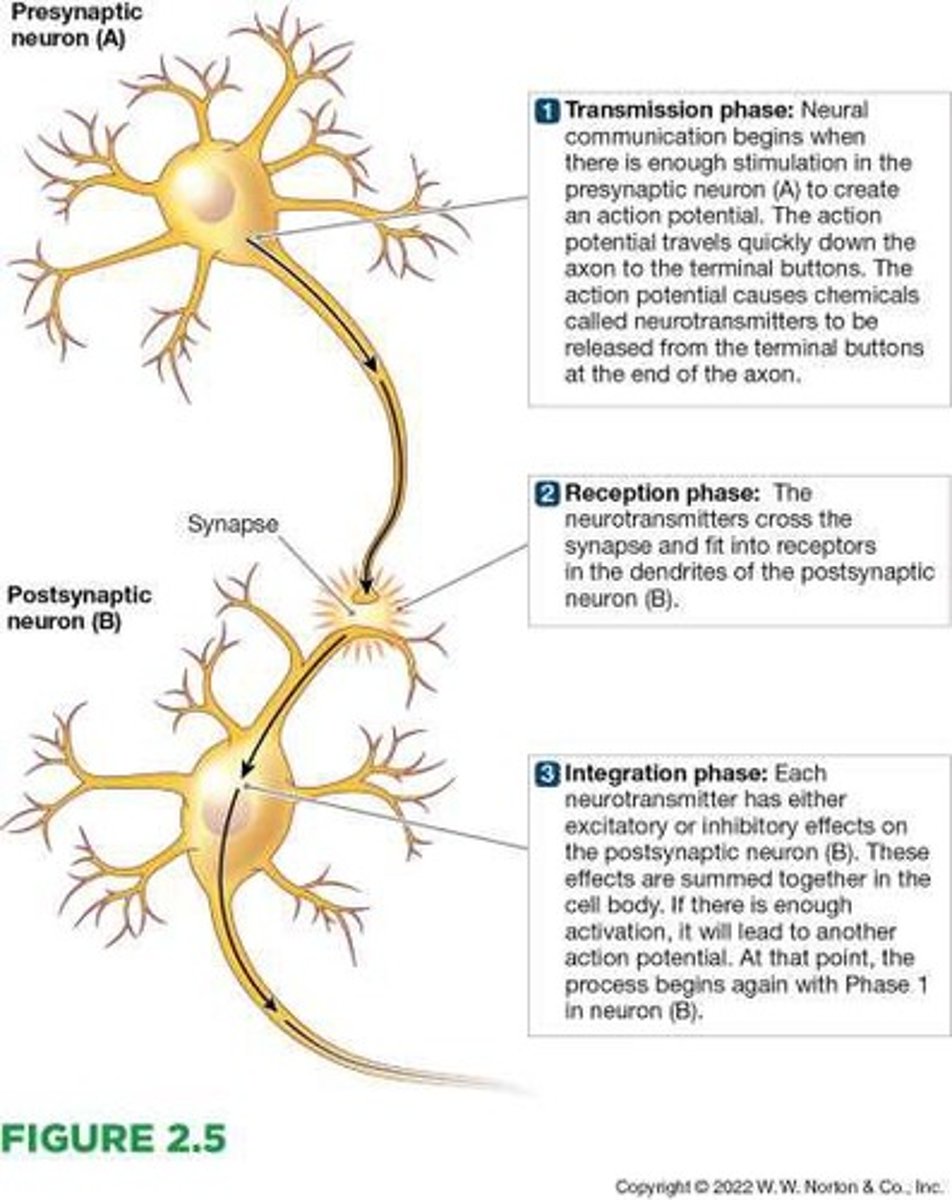
Transmission phase
Neurons pass signals to receiving neurons.
Reception phase
Neurons receive signals from neighboring neurons.
Integration phase
Neurons assess the incoming signals.
Reuptake
Involves reabsorbing neurotransmitters into the presynaptic neuron.
Enzyme degradation
Involves the breaking down of neurotransmitters.
Excitatory signals
Increase the likelihood that the neuron will fire an action potential.
Inhibitory signals
Inhibit the neuron and decrease the likelihood that the neuron will fire an action potential.
Agonists
Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
Antagonists
Drugs that inhibit the actions of neurotransmitters.
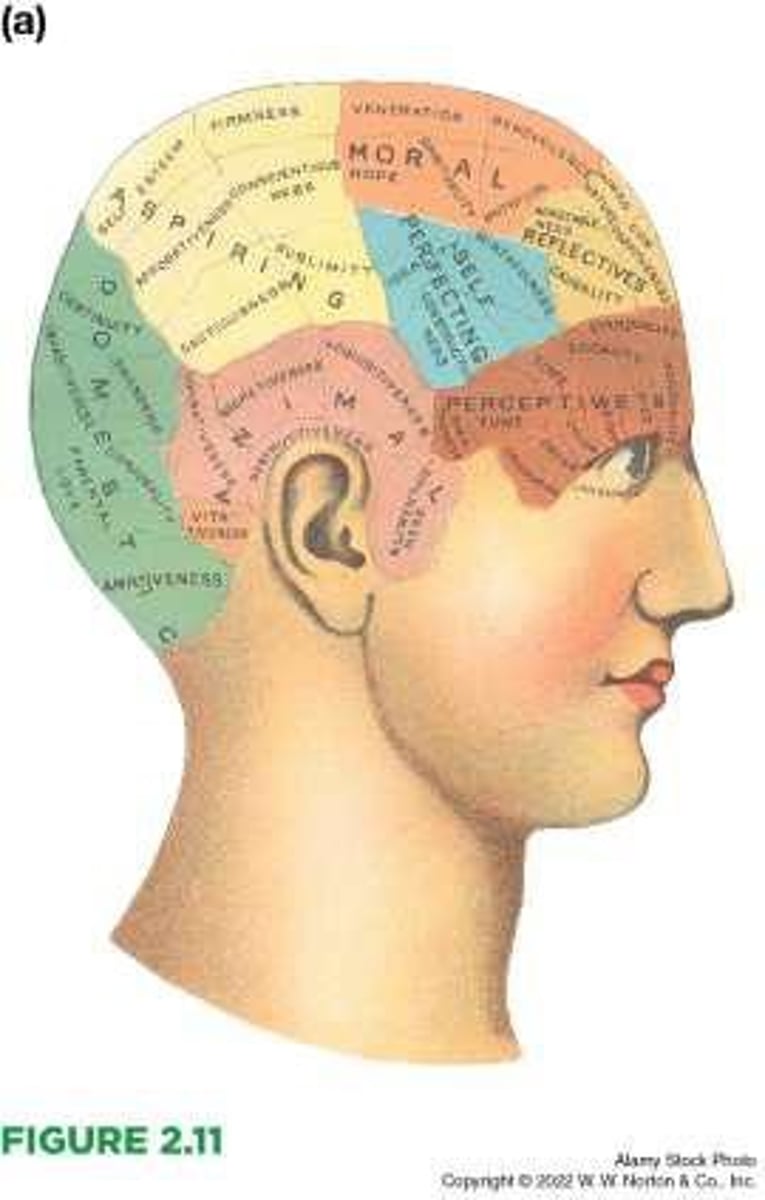
Phrenology
Analysis of personality based on the location and size of skull bumps.
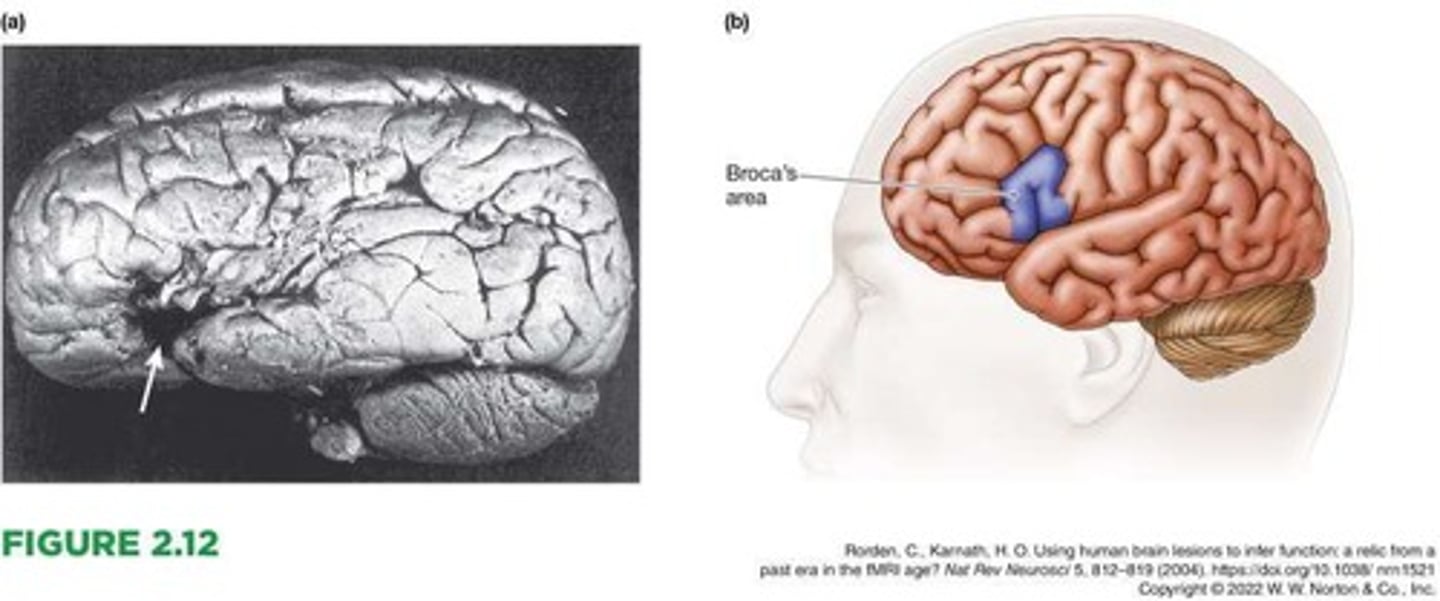
Broca's area
A small portion of the left frontal region of the brain, which is crucial for producing speech.
Presynaptic neuron
The neuron that releases neurotransmitters into the synapse.
Postsynaptic neuron
The neuron that receives signals through receptors.
Receptors
Specialized sites that specifically respond to certain types of neurotransmitters.
Fatty layer
The myelin sheath that insulates the axon.
Chemical communication
The process by which neurons communicate through neurotransmitters.
Electroencephalograph (EEG)
This measurement is useful because different behavioral states produce different and predictable EEG patterns.
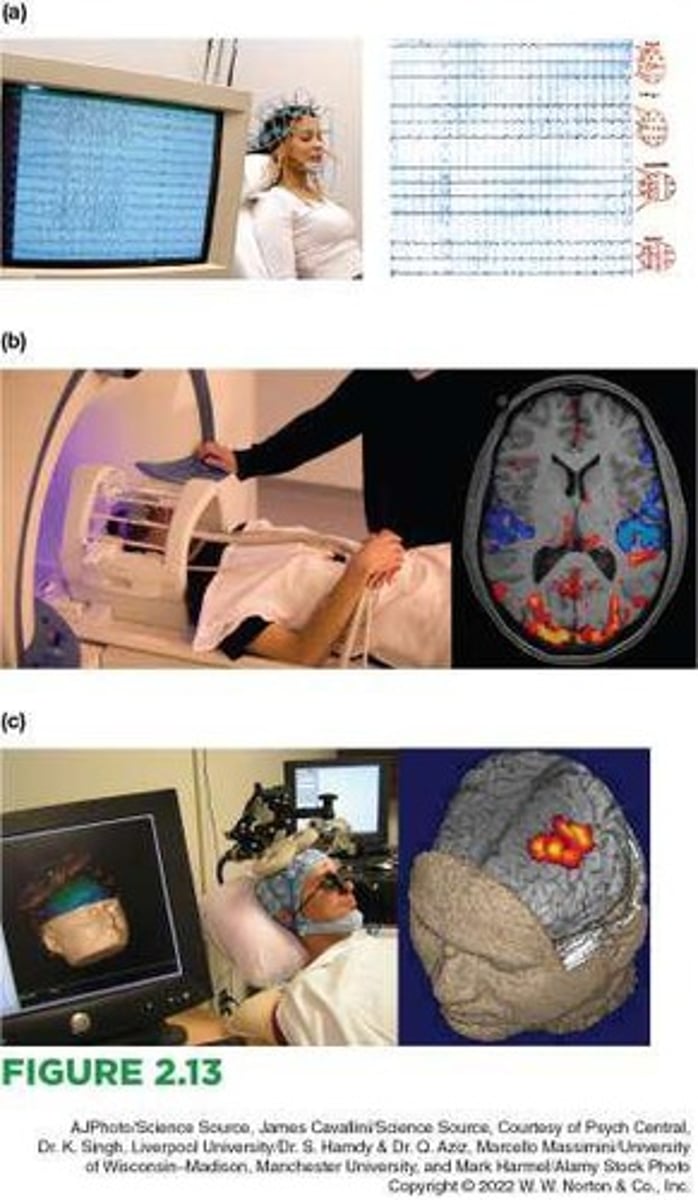
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
This technique measures changes in the blood's oxygen level.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
This technique uses a very fast and powerful magnetic field to momentarily disrupt activity in a specific brain region.
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is the gateway for information between the brain and body.
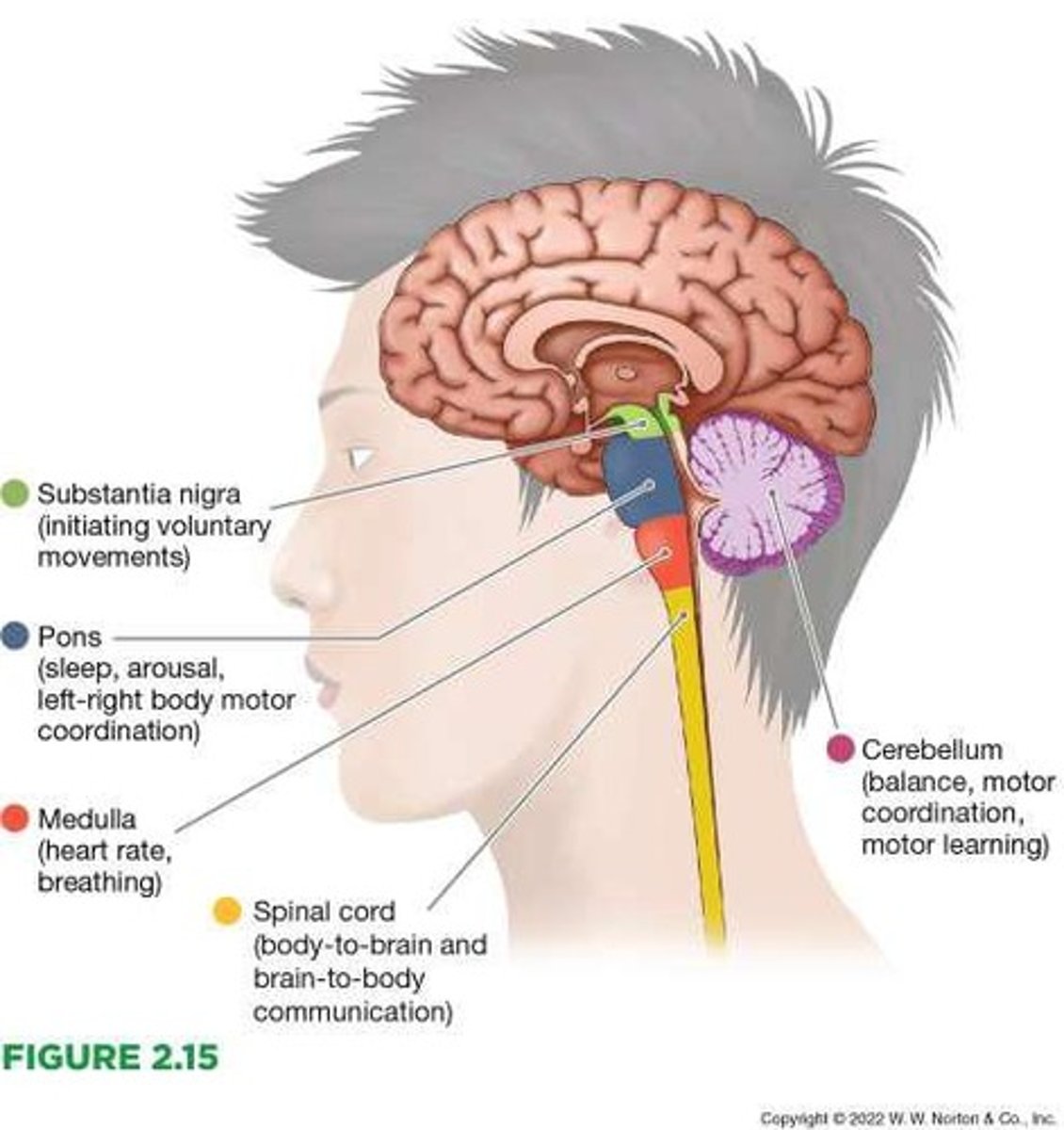
Medulla
Located at the top of the spinal cord, it controls survival functions such as heart rate and breathing.
Pons
Located above the medulla, it regulates sleep and arousal and coordinates movements of the left and right sides of the body.
Cerebellum
Located at the back of the brain stem, it is essential for coordinated movement and balance.
Midbrain
The midbrain is involved in reflexive movement of the eyes and body.
Substantia nigra
Initiation of voluntary motor activity; this region is critical for the production of dopamine.
Parkinson's disease
Caused by the death of substantia nigra cells and the resulting loss of dopamine produced by those cells.
Thalamus
Gateway to the brain for almost all incoming sensory information before that information reaches the cortex.
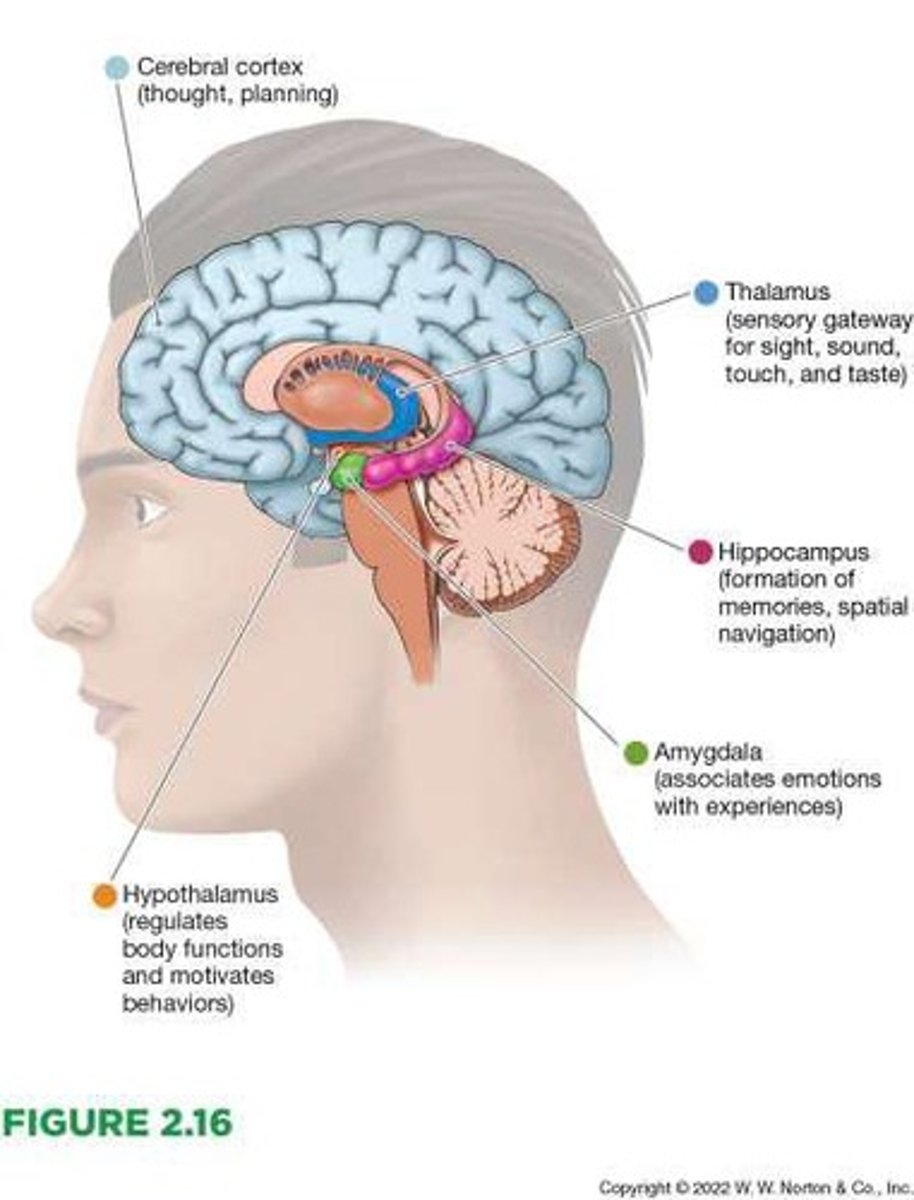
Hypothalamus
Involved in regulating bodily functions and influences our basic motivated behaviors.
Hippocampus
Associated with the formation of memories.
Amygdala
Vital for processing the emotional significance of stimuli, especially fear, and involved in memory processing during times of emotional arousal.
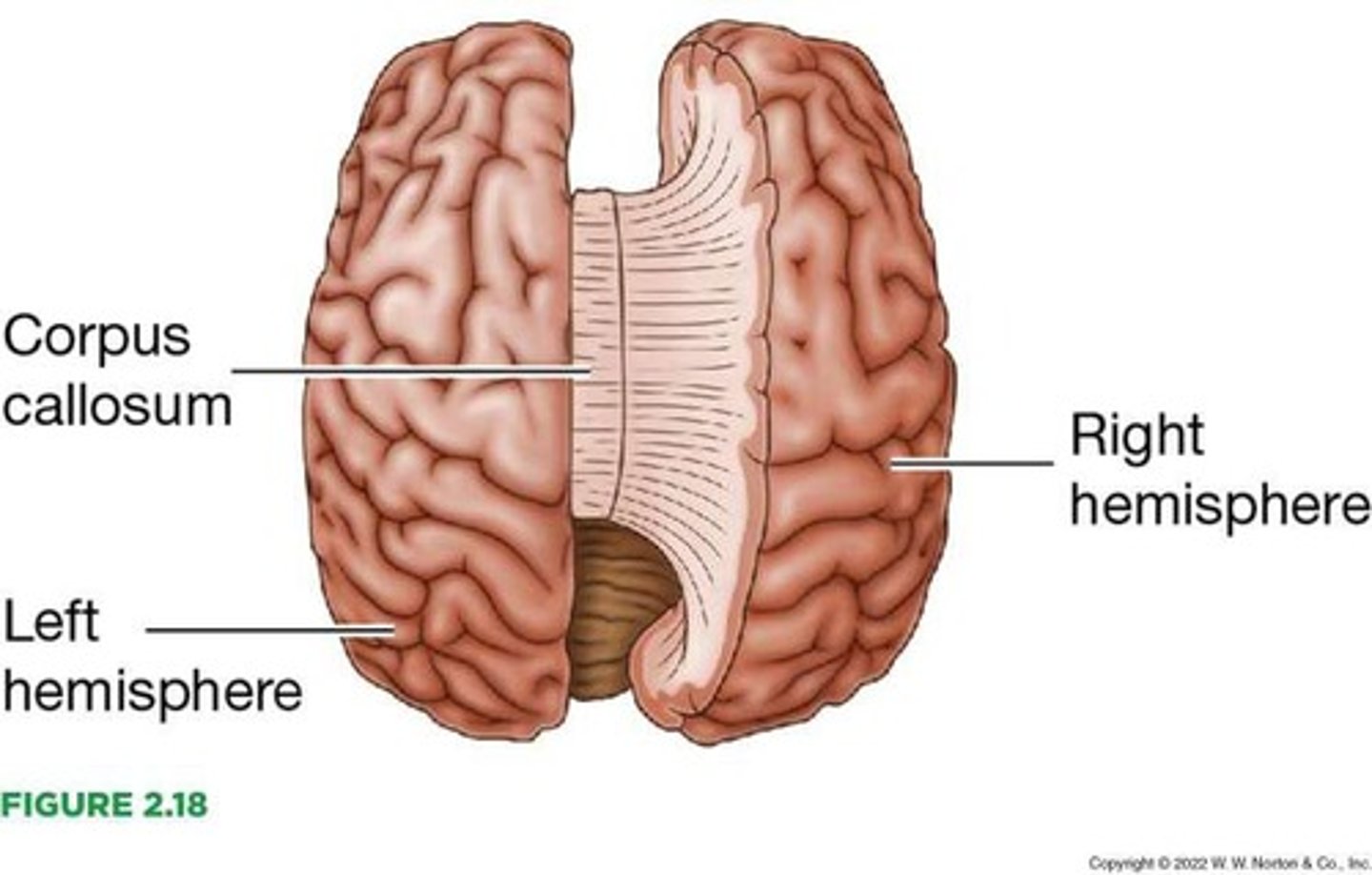
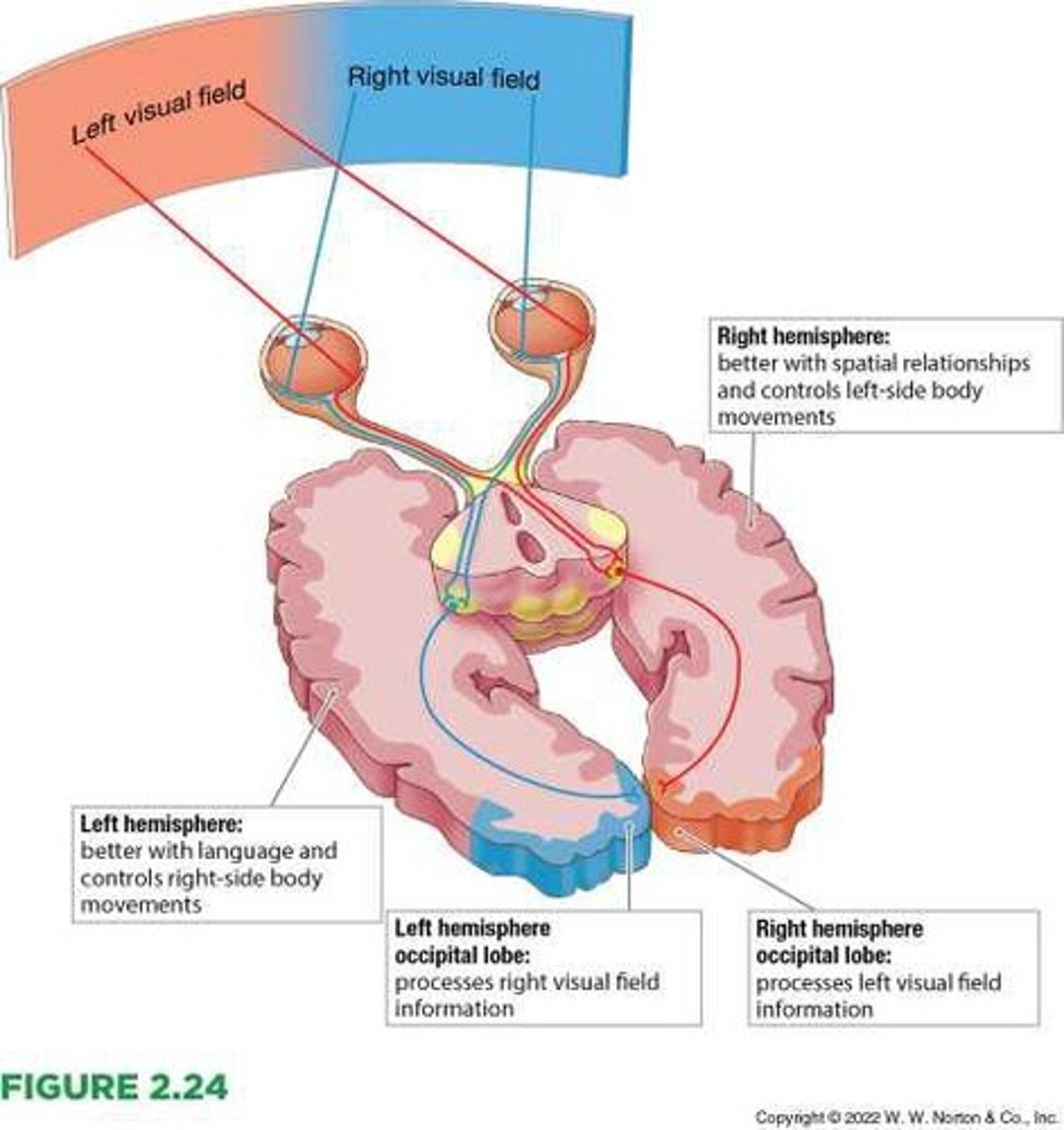
Left hemisphere
One of the two halves of the cerebral cortex.
Right hemisphere
The other half of the cerebral cortex.
Corpus callosum
A massive bridge consisting of millions of axons that connects the two hemispheres.
Occipital lobes
Regions of the cerebral cortex at the back of the brain; these regions are important for vision.
Parietal lobes
Regions of the cerebral cortex in front of the occipital lobes and behind the frontal lobes; these regions are important for the sense of touch and for picturing the layout of spaces in an environment.
Temporal lobes
Regions of the cerebral cortex involved in processing auditory information and memory.
Frontal lobes
Regions of the cerebral cortex associated with reasoning, planning, and problem-solving.
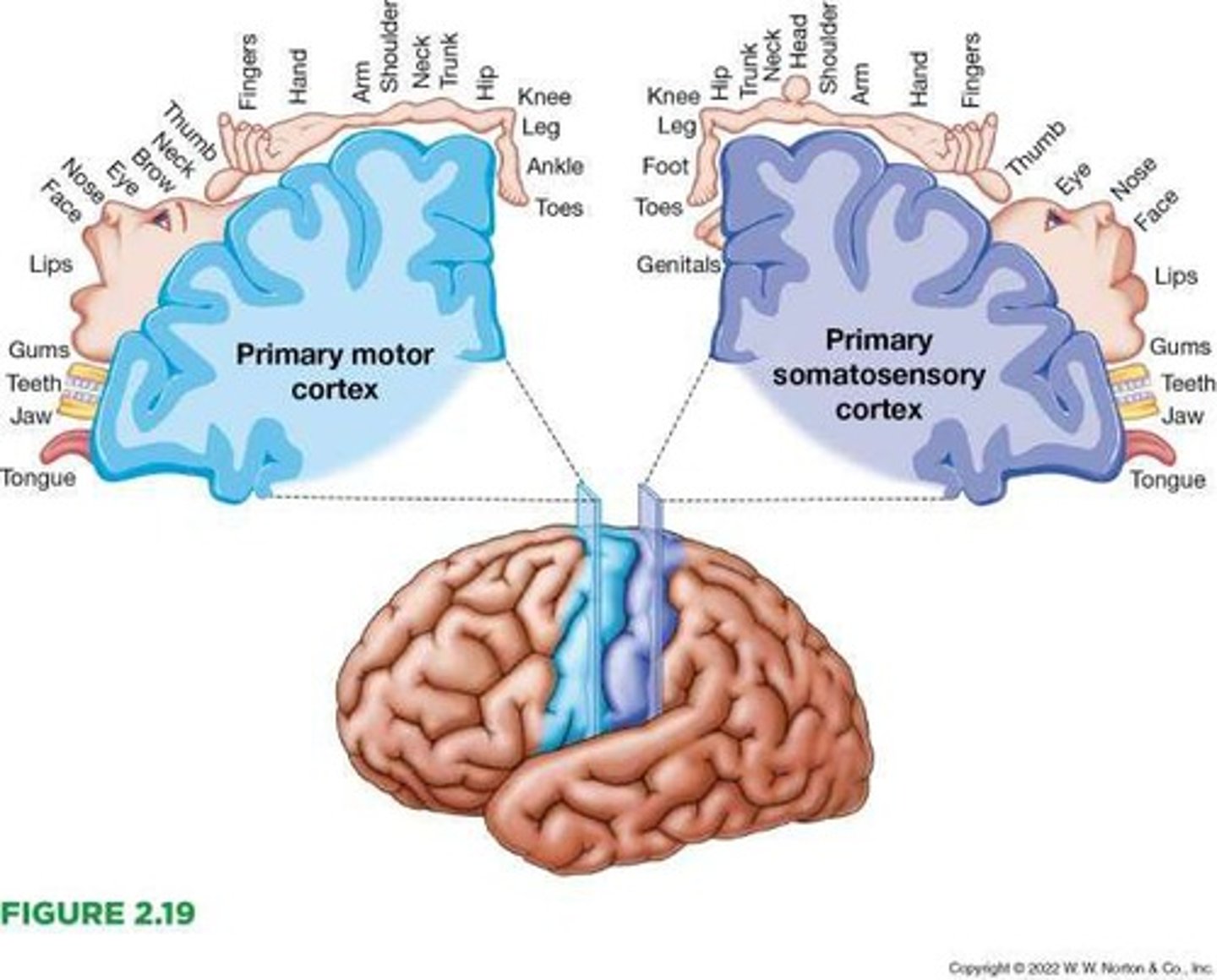
Homunculus
The primary somatosensory and motor representation in the brain.
Prefrontal cortex
Occupies 30 percent of the brain; its complexity and organization differ from those of other animals.
Lobotomy
A deliberate damaging of the prefrontal cortex to control behavior.
Split brain
A condition in which the corpus callosum is surgically severed, preventing direct information transfer between the two hemispheres.
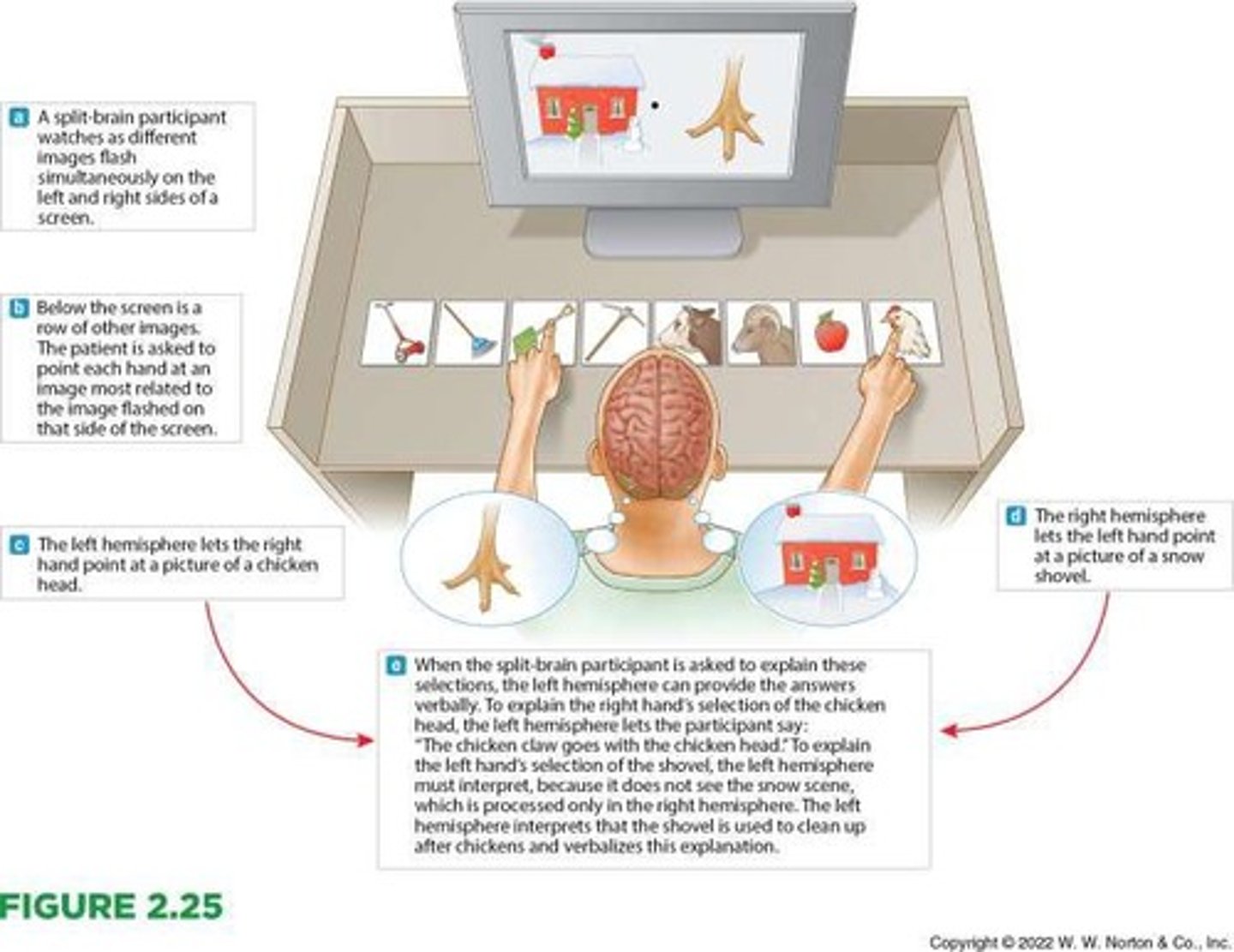
Split-brain patient
A patient whose hemispheres are separated, preventing information transfer between them.
Gazzaniga's experiment
Found that a split-brain patient could be aware of an object touched by the left hand but could not verbalize it due to lack of communication between hemispheres.
Left brain/right brain myth
The misconception that left-brain thinkers are more rational and analytical while right-brain thinkers are more creative and holistic.
Examples of learning disabilities
Whoopi Goldberg with dyslexia and Michael Phelps with ADHD.
Professional assistance for learning disabilities
Recommended if one suspects they may have a learning disability.
Equal opportunity in education
Schools must provide equal opportunity to the benefits of education for people with learning disabilities.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Includes the nerves throughout the body, in addition to the central nervous system (CNS).
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Somatic nervous system
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system that transmits sensory and motor signals between the central nervous system and the skin, muscles, and joints.
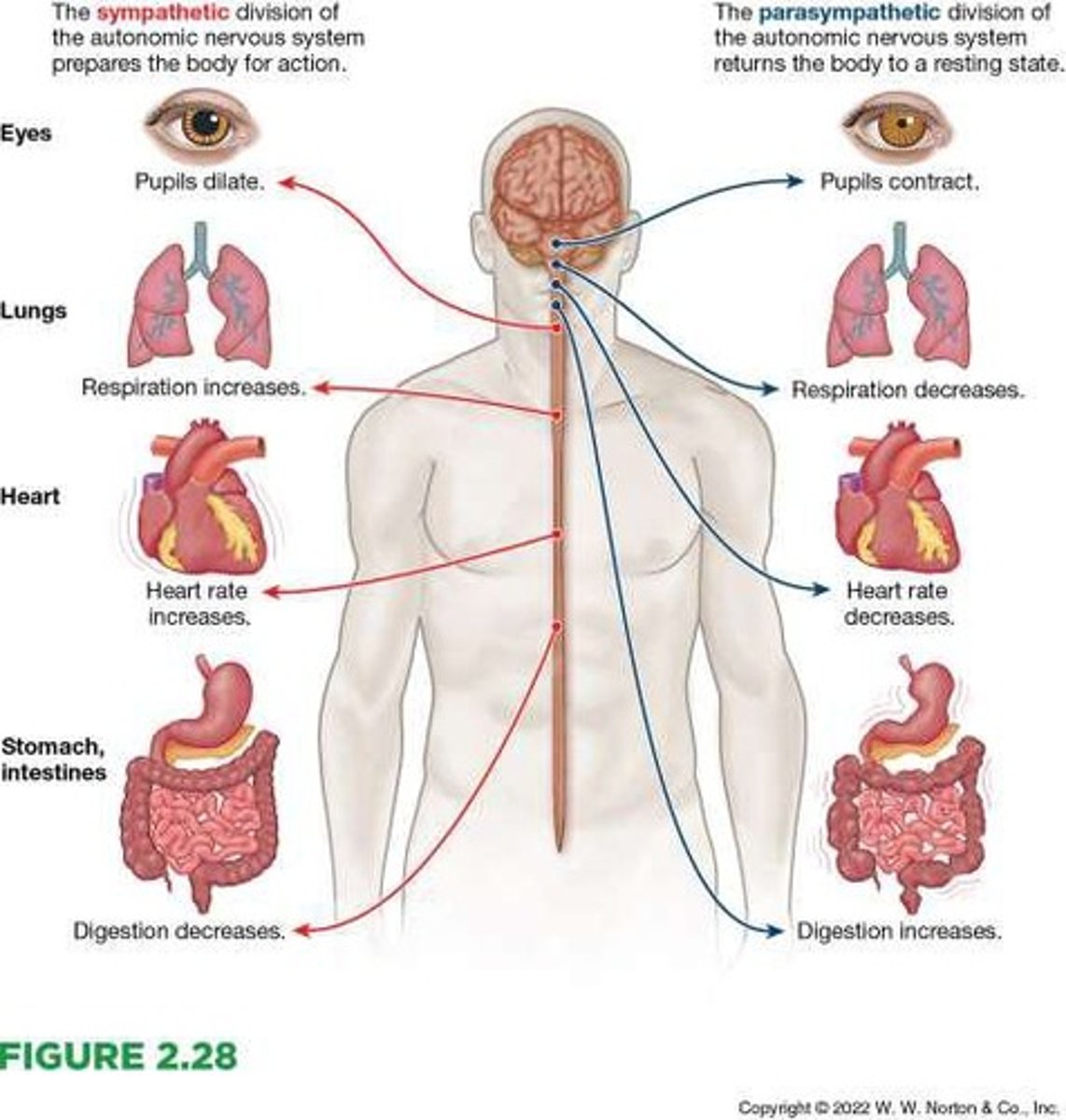
Autonomic nervous system
The second subdivision of the peripheral nervous system that transmits sensory and motor signals between the central nervous system and the body's glands and internal organs.
Sympathetic nervous system
One of the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system that controls the activity of organs and glands.
Parasympathetic nervous system
The second division of the autonomic nervous system that controls the activity of organs and glands.
Hormones
Chemical substances released from endocrine glands that travel through the bloodstream to targeted tissues, influencing them.
Gonads
The testes in males and the ovaries in females.
Androgens
Hormones, such as testosterone, that are more prevalent in males.
Estrogens
Hormones, such as estradiol, that are more prevalent in females.
Growth hormone (GH)
A hormone that prompts bone, cartilage, and muscle tissue to grow and helps them regenerate after injury.
Natural selection
The idea that those who inherit characteristics that help them adapt to their environments have an advantage over those who do not.
Genes
Units of heredity that partially determine an organism's characteristics.
Genotype
The genetic code that never changes.
Phenotype
The observable result of genetic code that can also be affected by the environment.
Behavioral genetics
The study of how genes and environment interact to influence mental activity and behavior.
Twin studies
Research methods that compare and contrast monozygotic (identical) twins and dizygotic (fraternal) twins.
Adoption studies
Research methods that compare the similarities between biological relatives and adoptive relatives.
Epigenetics
A field that studies how closely the environment affects gene expression.
Plasticity
A property of the brain that causes it to change through experience, drugs, or injury.
Neurogenesis
The production of new neurons, which can occur in some areas of the brain.
Neural pruning
The process where connections that are not strong and not needed are 'pruned' so that other connections can be strengthened.
Brain reorganization
The development of entirely new connections between neurons, which is a major factor in recovery from brain injury.