The cell ANATOMY
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What a cells 4 main function?
1) building block plants and animals
2) produced by preexisting cells
3) form all structures in body
4) perform all vital functions in body
Two types of cells
S___& S_____
1) sex cells or gametes
sperm or oocytes
2) somatic cells
body cells
ex: liver, etc.
12 parts Cell anatomy, describe function or structure or mention their subdivision part
1) cytoplasm
cytosol: intracellular fluid of cell
2) organelles
intracellular structures w/in cell
3) plasma membrane→
cell membrane→ cholesterol, glycolipids, proteins, & phospholipid
4) Nucleus → DNA storage & control
5) Ribosomes → protein synthesis
6) Rough ER → protein modification
7) Smooth ER → lipid synthesis (steroids & even carbs), detox, ca 2+
😎 Golgi apparatus → modify& packaging & shipping
9) Mitochondria → ATP production
10) Lysosomes → digestion & waste removal
11) centriole→ spindle fibers
12) peroxisome→ catalases break down hydrogen peroxide→ h20 & oxidants
microvilli in cells? Like what? Does what with what movement? Location?
fingerlike projections
absorption via back and forth movement; especially the small intestine
apical surface
Upclose: Cell membrane 4 Major functions. What kind of barrier? Regulates what? Sensitive to what? What communication, ability, and support?
1) physical barrier
2) regulate exchange
3) sensitive to changes in fluid
4) cell to cell communication, ahesion, structural support
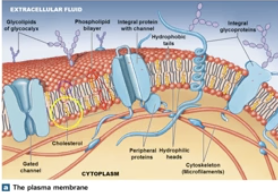
Composition of Plasma membrane
1) phospholipids
2) glycolipids (carbohydrate structures)
3) proteins
4) sterols (cholesterol→ help the membrane rigid or not rigid depending on temp)
What is the phospholipid bilayer of membrane? How many? Which is hydrophilic, v.s. hydrophobic? What does glycocalyx come from and help with?
2 layers; hence phospholipid bilayer
Hydrophilic heads on outside
hydrophobic heads on inside
glycolipids→glycocalyx→ layer helps w adhesion
What is another function of cholesterol besides maintaining fluidity?
1) preventing the membrane from being to “leaky” and acts like another “filter”
UPCLOSE: Proteins of Membrane
Integral→ WITHIN layer of membrane→ acts like channels, some are“gated” channels
Peripheral→ attached to inner or outer layer→ NOT within the plasma membrane like integral
UPCLOSE: Glycolipids (Location, Made of WHAT, & role)
1) outer layer
2) carb+glycerol
3) acts like receptor
UPCLOSE: sterols (does what to membrane & what is an example of one)?
1) Stabilize structure
2) cholesterol
What is membrane permeability?Which 2 types of processes? What 3 types are there?Which is concentration motivated? Briefly know what they are
SELECTIVE
Passive (no ATP)
a) diffusion (high to low)
b) osmosis (water& aqua porin→ high to low)
c) facilitated (integral protein; polar don’t cross easily v.s. nonpolar things; No ATP)
ALL concentration MOTIVATED (High to LOW)
active (need ATP)
a) active transport ( LOW to HIGH & proteins channel use ATP)
b) endocytosis (letting things in & out)
phagocytosis (vesicle→engulf→cell eating)
pinocytosis (vesicle→ take in fluid→cell drinking)
c) exocytosis (vesicle→ secreted unwanted→ cellular excretion)
Types of Permeability
1) impermeable
2) freely permeable
3) selectively permeable
1) nothing passes
2) everything freely passes
3) only SOME come in; others don’t
Does the mitochondria have it’s own separate membrane? How many?
Yes; doubled membrane
Another active type of endocytosis…
______-mediated endocytosis
Recopetor-mediated endocytosis→ receptor/ligand channels→ have targeted receptor→ form vesicle w/receptors inside
Which organelles are NON MEMBRANOUS (outside structures→ Cal, Cooked, Revolutionary, Fried, Chicken)
v.s. MEMBRANOUS (inside→ Micky Loathes Pink Goofy Nasty Elephants)
WON’t Test but js look and know
1) NONMEMBRANOUS
cytoskeleton
centrioles
cilia
flagella
ribosome
2) MEMBRANOUS
mitochondria
nucleus
endoplasmic reticulum
golgi apparatus
lysosome
peroxisome
UPCLOSE: CYTOSKELETON
4 types & briefly describe function
A__
Neurofilaments
Mysosin
tublin
1) Microfilaments→ actin→ change shape & interact w myosin for movement
2) intermediate→ strength, stabilize organelles & transport
Neurofilaments→ support axons
3) THICK→ myosin→muscle cells & contraction
4) Microtubules→ tubulin→ cytoskeleton, shape, movement, cell division, & cilia/flagella locomotion
CENTRIOLE up close
location
function
centrosome
produce microtubules needed in cell reproduction
CIlia UPCLOSE
Location
Anchored by what
Beat how to move
1) cell surface
2) basal body
3) beat RHYTHMICALLY to move fluid or secrtions
FLAGELLA UPCLOSE
Location
Function in sexual reproduction
Cell surface
Help sperm move to egg
Attached v.s. Free ribosome, difference v.s. similarity.
1) Attached to endoplasmic
2) free floating
BOTH still make protein
Structure of NUCLEUS upclose
1) p___space
2) n____pores
3) _____plasm
4) has what
1) perinuclear space
2) Nuclear pores
3) nucleoplasm→ filaments→ nuclear matrix
4) has chromatin
what is chromatin to chromosome
1) DNA+ histones→ chromatin→ tightly coiled→ chromosome
True or False endoplasmic reticulum sends out vesicles of protein to golgi to modify and package
true
What is membrane flow?
continous movement and recycling of membrane that involve vesicles from ER and GOLGI
How does intercellular attachment occur 2 ways:
via (CAMs) or cell adhesion molecules
cellular cement proteoglycan→ hyaluronan
2 types of cell junctions (GT). Which is cell to cell which is sealing?
1) Gap junctions→ cell to cell communication
2) Tight junctions→ seal tightly, no passage
ex: desmosomes
2 Main Cycles of Cell (Know major phases & function/occurs)
1) Interphase (most of time here)
G0→cell performs normal
G1→duplication
SPHASE→ DNA synthesis
G2phase→ protein synthesis
2) MITOSIS
Prophase→ 1st phase chromosome condense & nuclear chromosome breaks
Metaphase→ chromosome in middle
Anaphase (cytokinesis begins here)→ chromosome away to opp sides
Telophase (cytokinesis occurs)→2 nuclear membranes form
3) Cytokinesis (cytokinesis of phase ends here)
Interphase UPCLOSE 8 steps (DNA REPLICATION) until G& M phase
1) DNA replication→
2) helicase unwinds nitrogenous bases→
3) h-bond broken→
4) forms 3-5’ & 5-3’ strand→
5) DNA polymerase will form complementary strand via nitrogenous bases→
6) ligases glues→
7) duplicate DNA molecule
😎 G& M phase
Mitotic rate
frequency when cell reproduction occurs
Stem cells (____ cells that undergo reproduction & help____)
somatic cells that undergo reproduction→ help cells transform