Lecture 10 - Overview of the Brain: Hindbrain, Midbrain and Forebrain
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
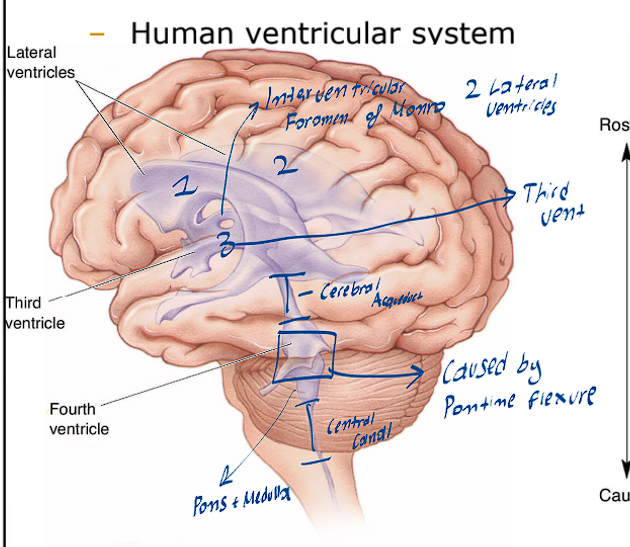
What are the various ventricles of the Brain
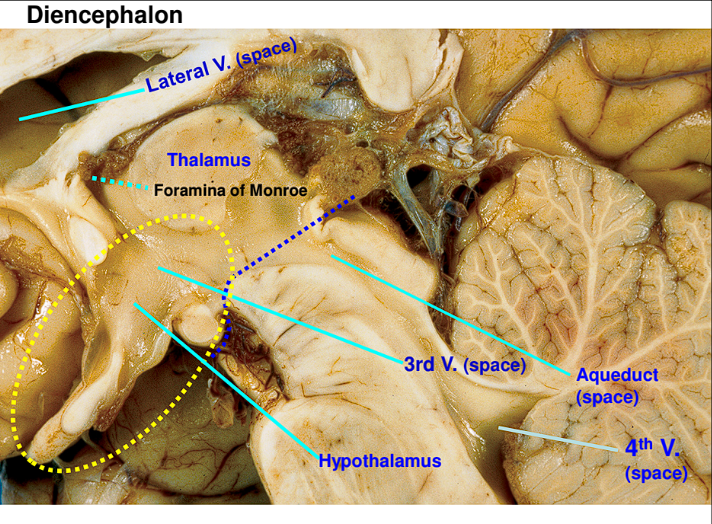
There are two Lateral ventricles (One on the left side and the other on the right side)
There is the 3rd ventricle (this is found in the middle and is very slim)
There are the 4th ventricle
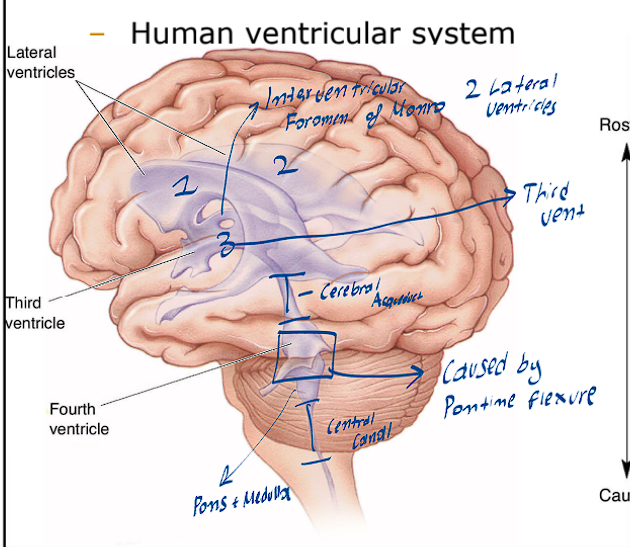
What structure divides the lateral ventricles and the 3rd ventricle
This structure is known as the interventricular foramen of Monro
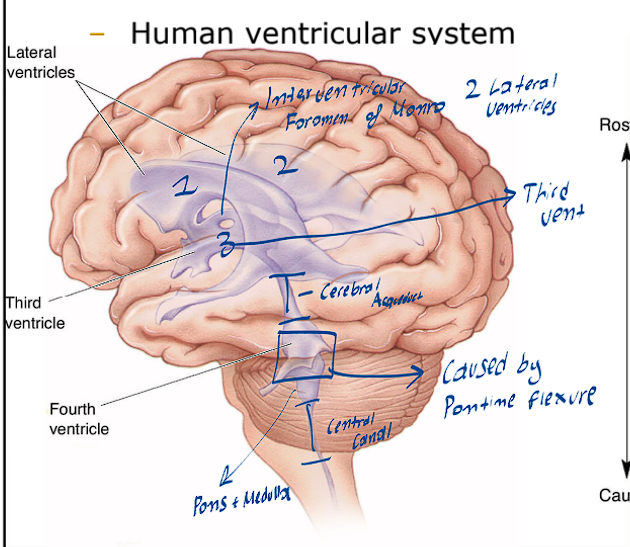
What structure divides the 3rd and 4th ventricle
This structure is known as the cerebral aqueduct
The Choroid Plexus is important because it produces what substance?
This structure produces the CSF (Cerebral spinal fluid)
What is the subarachnoid Space, what is its significance?
This space allows for the CSF to circulate around the brain, and thus also acts as a cushion for the brain.
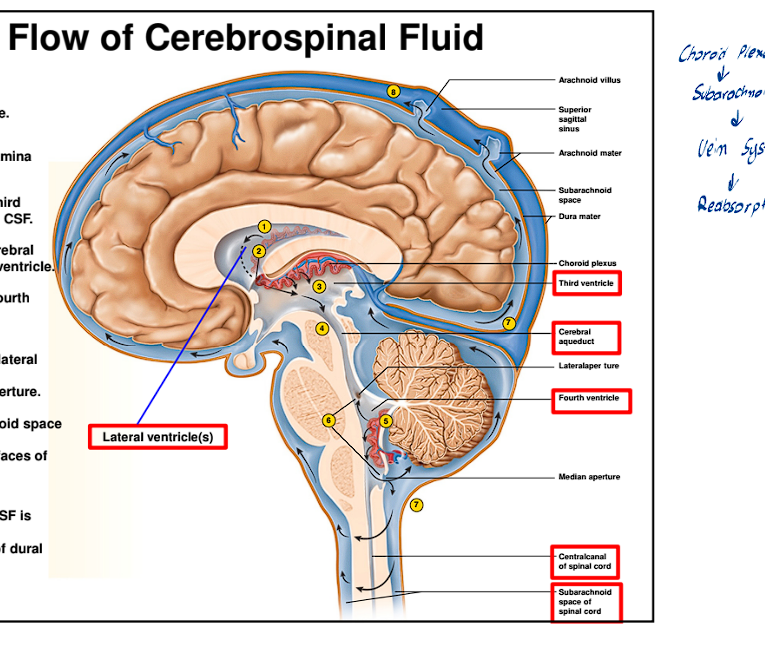
What is the simple flow of the CSF
It is formed through the Choroid Plexus
Will flow through all the ventricles
Then move back into the subarachnoid space
Lastly moving into the Vein System, where it gets reabsorbed into the blood
What is the formal name for the Forebrain, what secondary vesicles does it divide into
The Formal name for the Forebrain is the Prosencephalon
It is further divided into two secondary vesicles:
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
The Telencephalon (2ndary vesicle) of the Prosencephalon divides into what further structures
Also what cavity is found here
The Telencephalon will further divide into the:
Cerebral Cortex
Basal Ganglia
Corpus Striatum
The Cavity found in this locations is the Lateral Ventricles (An easy way to remember is the cerebral cortex is split into two halves which each have a ventricle)
The Diencephalon (2ndary vesicle) of the Prosencephalon divides into what further structures
Also what cavity is found here
The Diencephalon will further divide into the:
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Retina
The Cavity found in this location is the 3rd ventricle
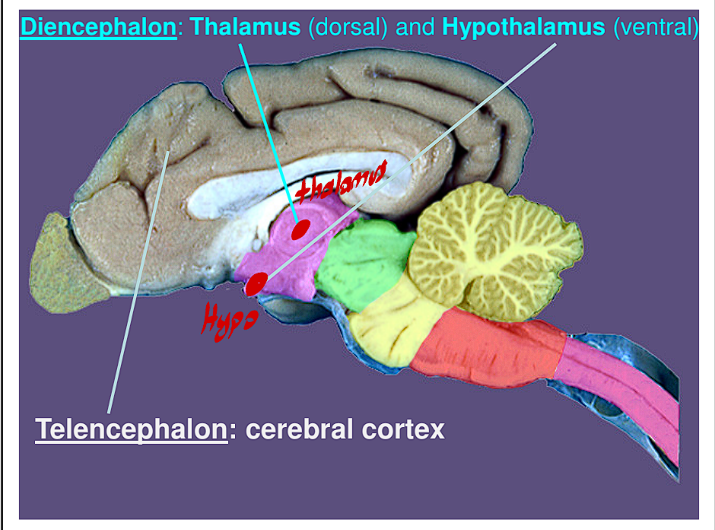
In the Diencephalon the Thalamus is always in what location?
This structure is always always Dorsal
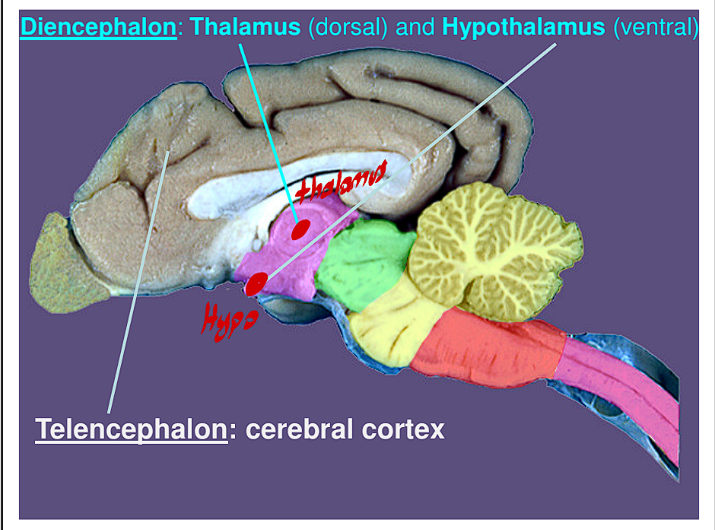
In the Diencephalon the Hypothalamus is always in what location?
This structure is always always Ventral
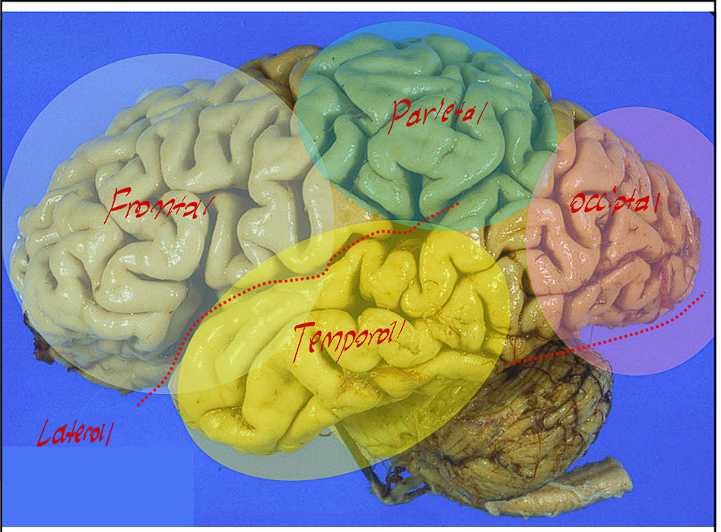
The Cerebral Cortex of the Telencephalon contains what lobes?
The Cerebral Cortex is home to the main lobes of the brain
Frontal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Temporal Lobe
*These are in order in their development pattern sequence)
What are the numerous folds and gaps of the Cerebral Cortex called?
The Numerous folds are referred to as Cortical Gyri
The Numerous gaps of the folds are referred to as sulci
What are Fissures? What are the fissures of the cerebral cortex where are they found?
Fissures are similar to sulcus but are far more deeper in the sense, that these are are much larger gaps and or separations.
The Cerebral Cortex has these main fissures:
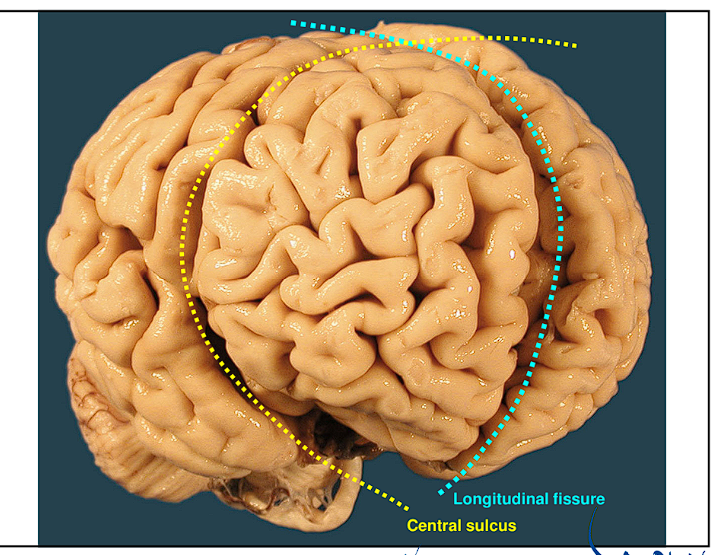
Central Fissure (Sulcus)
Sylvian Fissure (Lateral Sulcus/Fissure)
The Longitudinal Fissure
Transverse Cerebral Fissure
Parieto Occipital fissure
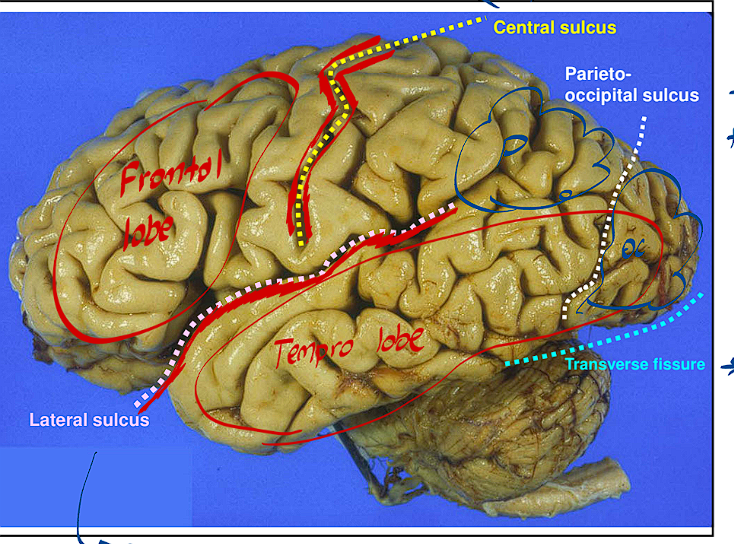
The Central Sulcus/Fissure divides the brain how?
This fissure divides the frontal brain from the rest of the brain
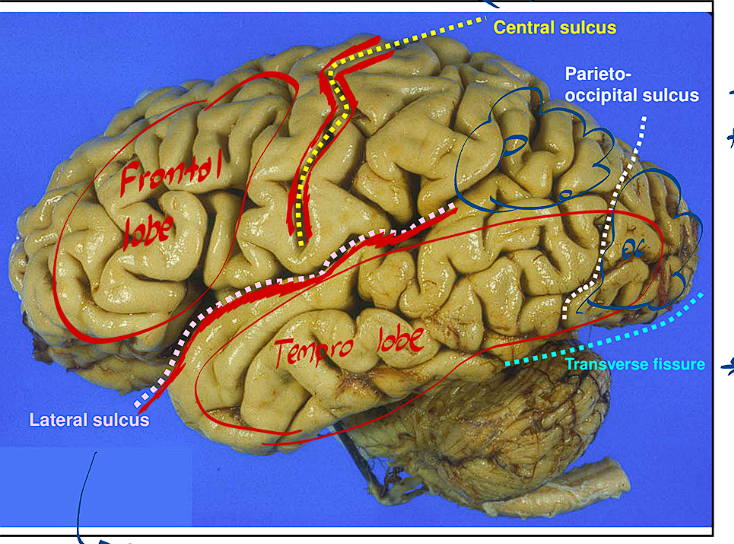
The Longitudinal Fissure divides the brain how?
This Fissure divides the brain into Right and Left Halves
The Parieto Occipital Sulcus divides the brain how?
It separates the Parietal lobe from the occipital lobe
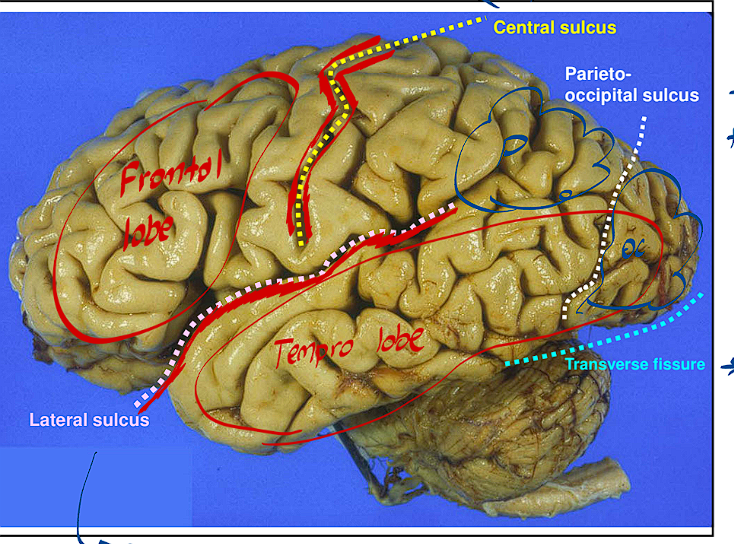
The Transverse Fissure divides the brain how?
It separates the Cerebellum from the rest of the brain
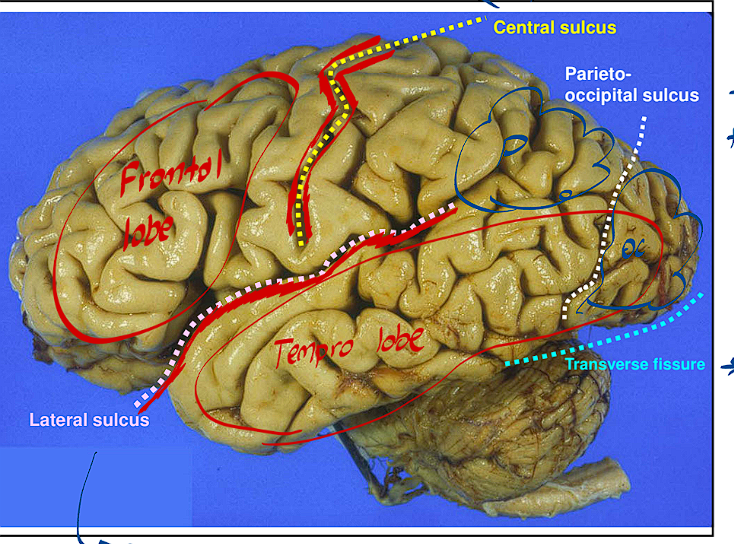
The Lateral sulcus is found where, what does it divide?
It is above the temporal lobe and below the frontal lobe
It divides the Frontal and Temporal Lobes from each other
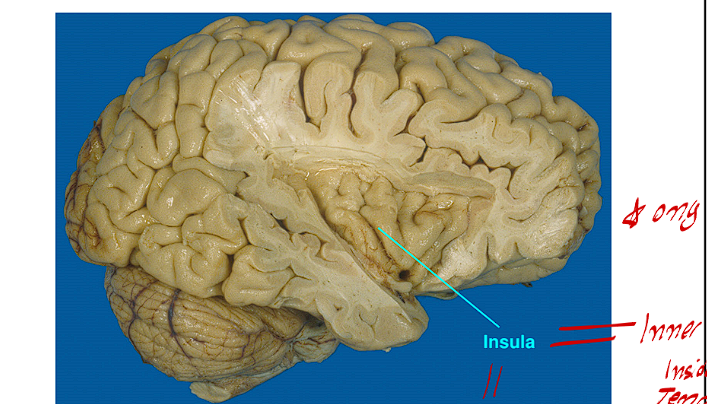
What is the Insula of the Forebrain, where is it found?
The insula is the inner foldings of the inner cerebral cortex of the temporal areas
It includes the Gustatory Cortex
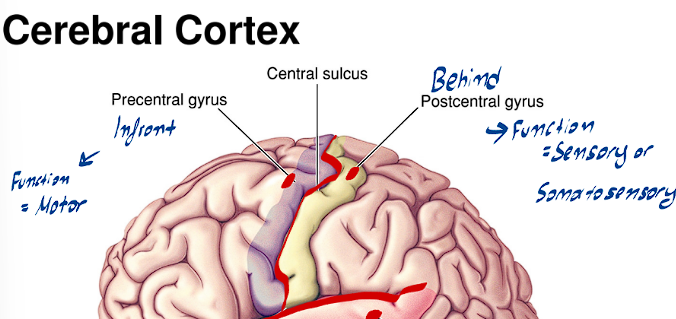
What is the function of the Precentral Gyrus of the Cerebral Cortex, where is it found
It is anterior to the central sulcus
The function of this Gyrus is strictly motor (it houses the Primary Motor Cortex)
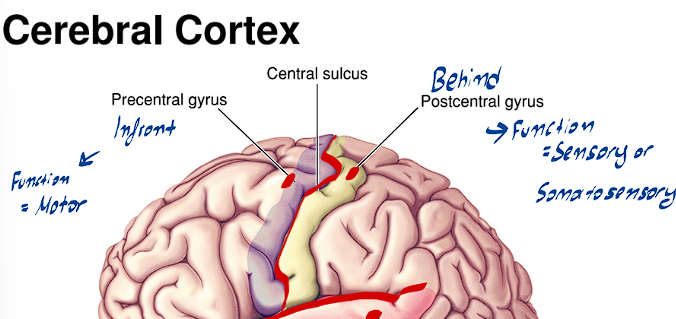
What is the function of the Postcentral Gyrus of the Cerebral Cortex, where is it found
It is posterior to the central sulcus
The function of this Gyrus is strictly somatosensory/sensory (it houses the somatosensory cortex)
What is the function of the Superior Temporal Gyrus
This is located in the temporal lobe
It is very important for speech and it houses the auditory system/cortex
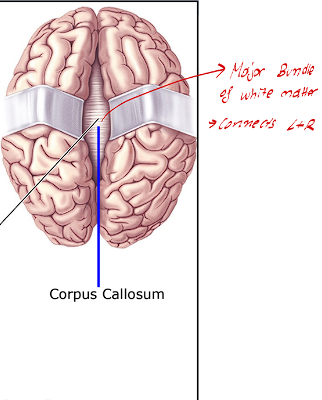
What is the corpus callosum of the cerebral cortex
This is a major bundle of white matter, that connects the right and left halves of the brain
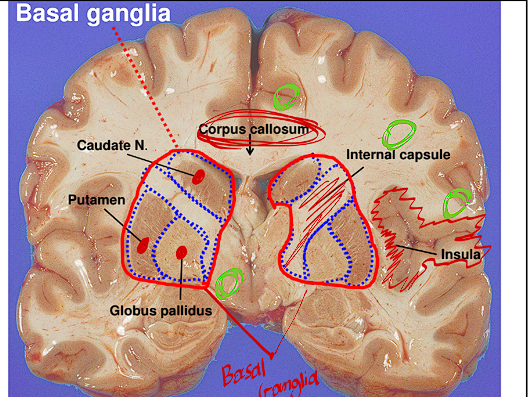
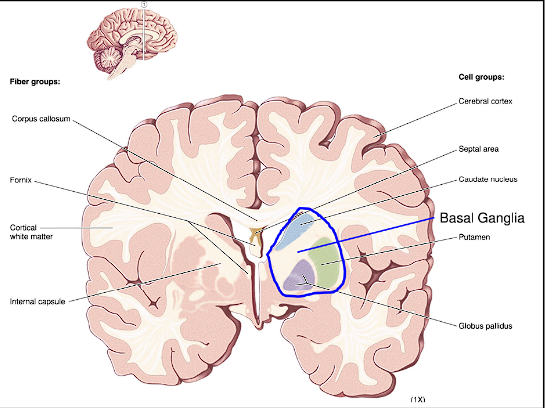
The Basal Ganglia of the Cerebral Cortex is called what? where is it located
This structure is also referred to as the Corpus striatum
This area is very dense in axons and white matter (inside the internal capsule)
it is located deep in the cerebral cortex
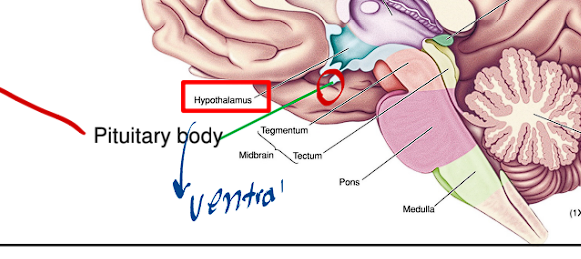
The Hypothalamus of the Diencephalon holds what important structure, where is it found?
This structure holds the pituitary body/gland, it is commonly referred to as the master gland.
It hangs ventrally from the hypothalamus via the pituitary stalk
Diencephalon Structures on a real brain
Click this for diencephalon structures
What is the roof and ground of the 4th ventricle
The Roof of the 4th ventricle is the cerebellum and the ground of the 4th ventricle is the pons
What is the formal name for the midbrain, what secondary vesicle does it further divide into
The Formal name for the midbrain is the mesencephalon
The second part is a trick question, the mesencephalon contains no secondary vesicle
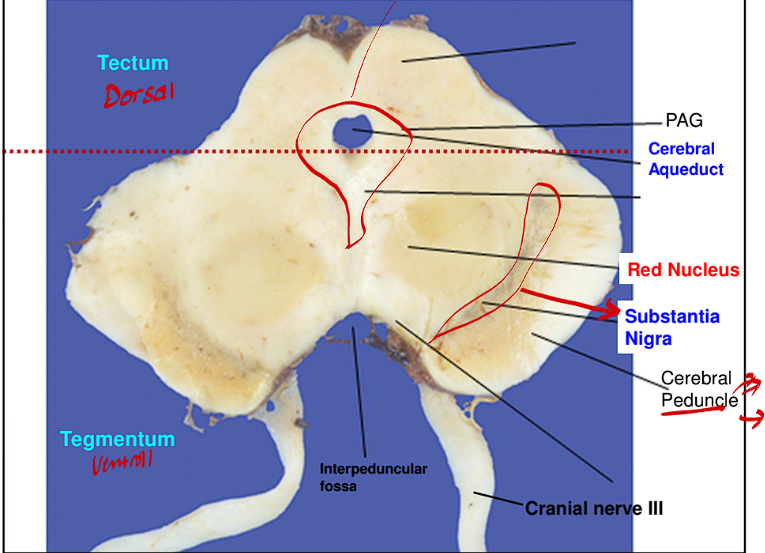
What are the neural derivatives of the Mesencephalon?
What cavity is found in the Mesencephalon
The Neural Derivatives
Tectum
Tegmentum
Cerebral peduncles
The Cavity found in this location is:
The Cerebral Aqueduct
The Tectum of the midbrain is always in what location
This structure of the midbrain is always in the Dorsal location of the midbrain
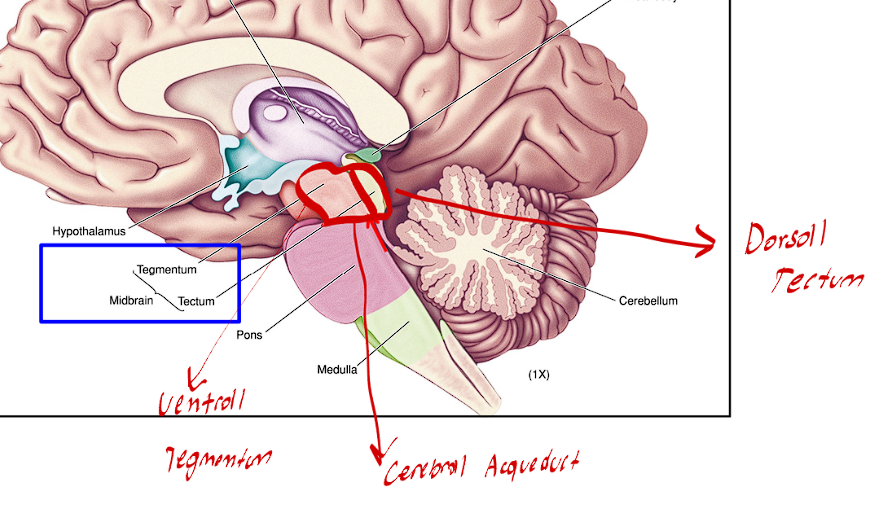
The Tegmentum of the midbrain is always in what location
This structure of the midbrain is always found in the Ventral Location of the midbrain
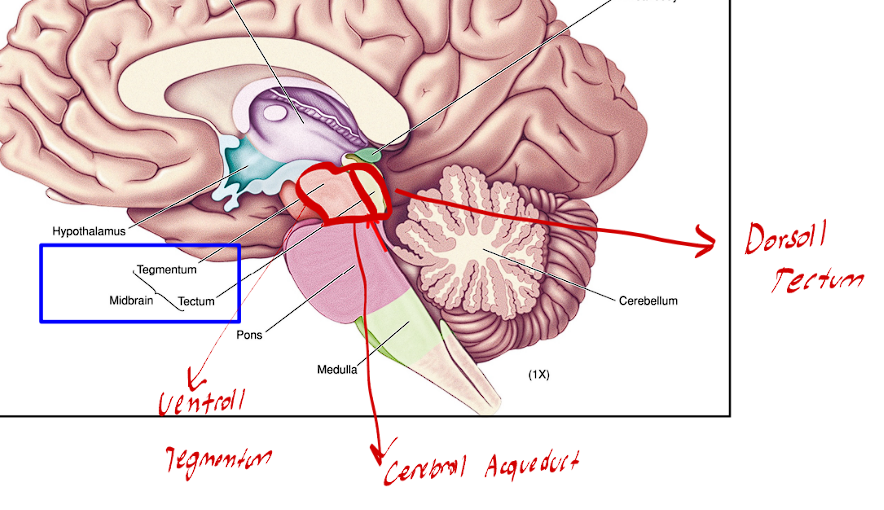
The Cerebral Aqueduct separates what two structures of the midbrain
This cavity divides the Tectum from the Tegmentum
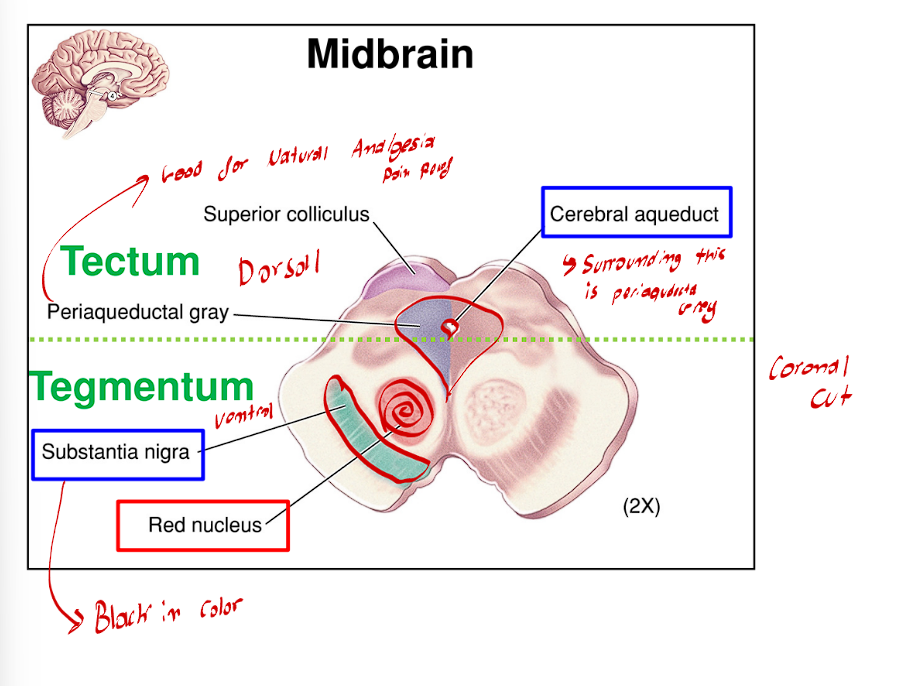
Within the Tegmentum, there is a reticular formation. Liying right on top of the cerebral peduncles is what structure?
Degeneration of this structure can cause what?
Lying right on top of the cerebral peduncles are the Substantia Nigra (this is a heavily pigmented black nuclei
Degeneration of this area is the main cause for Parkinson’s disease
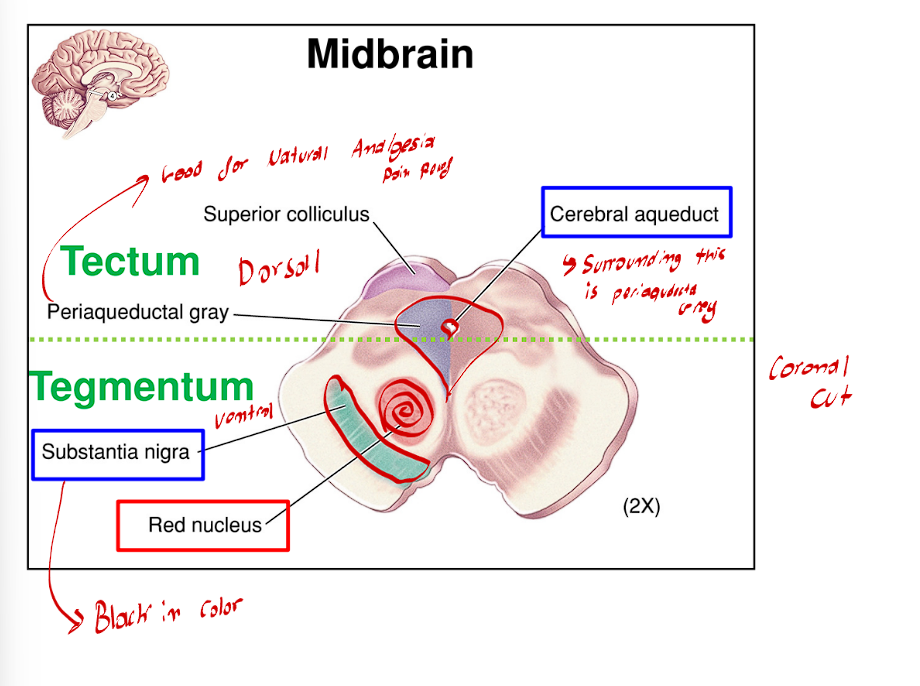
The Midbrain also contains these two large round nuclei that are directly adjacent to the midline
These two large nuclei are referred to as the red nuclei
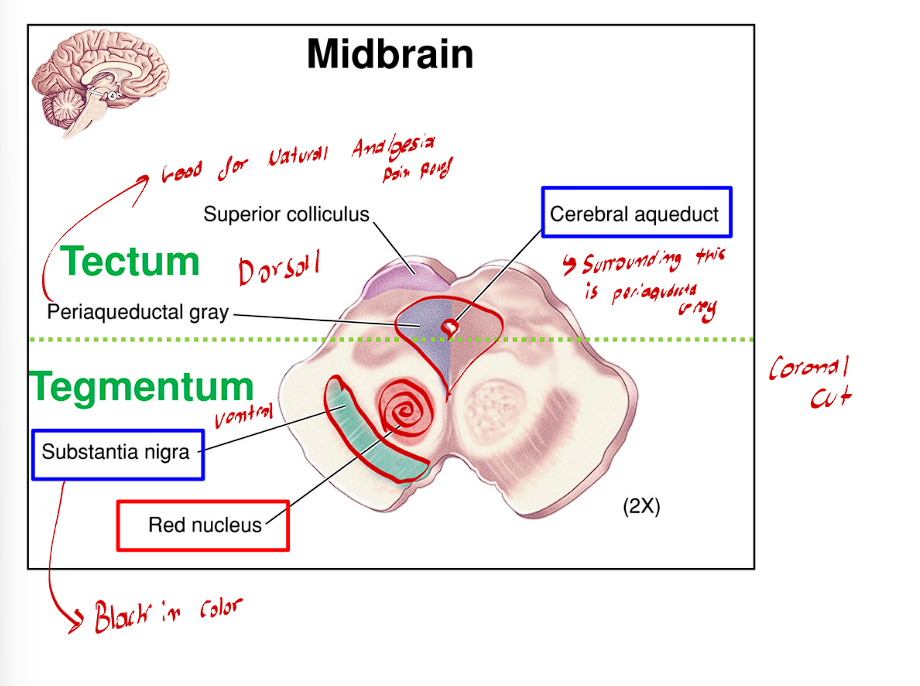
The Periaqueductal Grey directly surrounds the cerebral aqueduct, what is this area’s importance?
This area is very important to natural analgesia (pain relief)
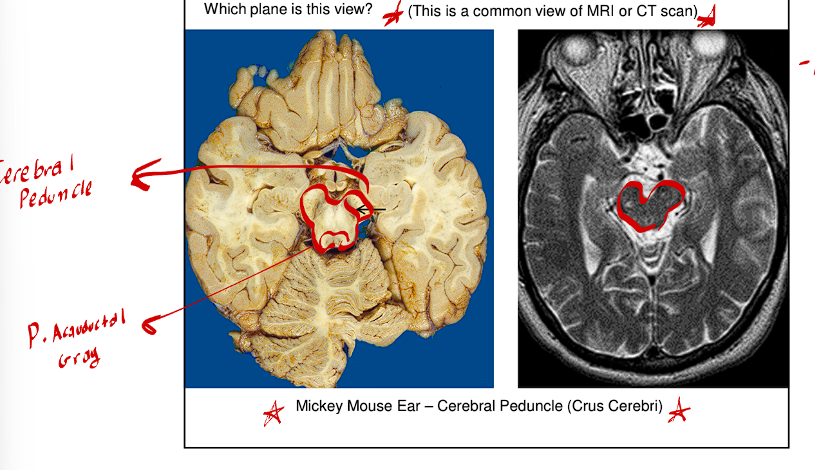
The Cerebral Peduncle is the most ventral structure of the midbrain appears like Mickey Mouse ears or two feet
Click this for cerebral peduncle
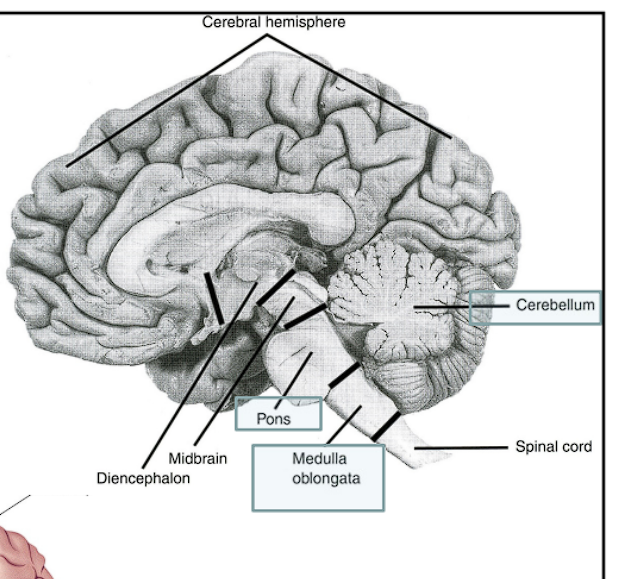
The Hindbrain is formally referred as what?
What are the secondary vesicles that the Hindbrain divides into?
This structure is formally referred to as the Rhombencephalon
It divides into two secondary vesicles
The Metencephalon
The Myelencephalon
The Metencephalon of the Hindbrain divides into what two neural derivatives?
What cavity is found here
This structure divides into these neural derivatives:
The Pons
The Cerebellum
The Cavity found in the location is the 4th ventricle
The Myelencephalon of the Hindbrain divides into what neural derivative?
What cavity is found here?
This structure divides into this neural derivatives
The Medulla Oblongata
The cavity found here is the central canal (Connects the Brain to the spinal cord)
The Pons and Medulla make up what structure
these two together form the Brainstem
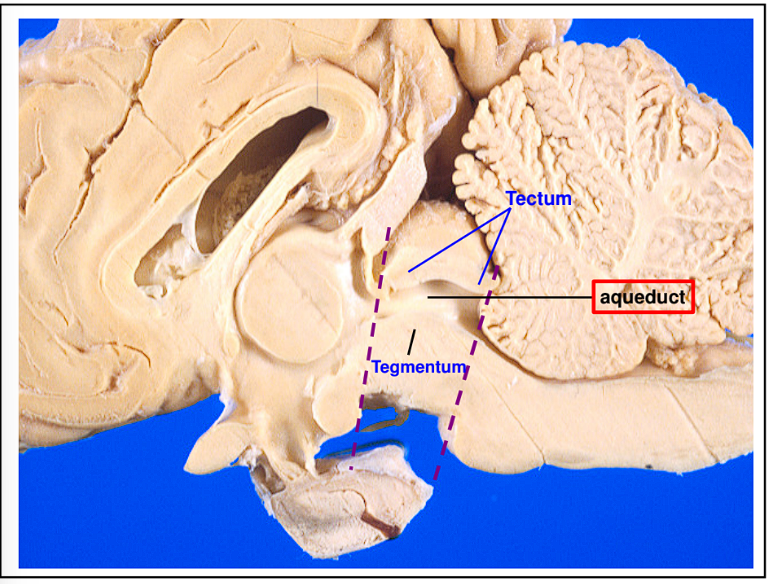
This is a good structure for the structures of the Midbrain
Click this for good midbrain
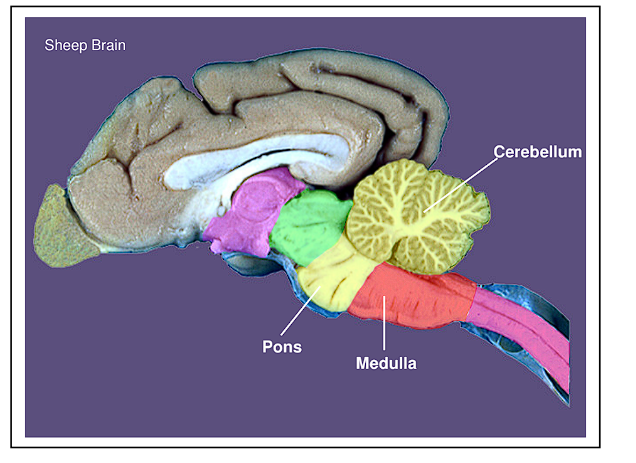
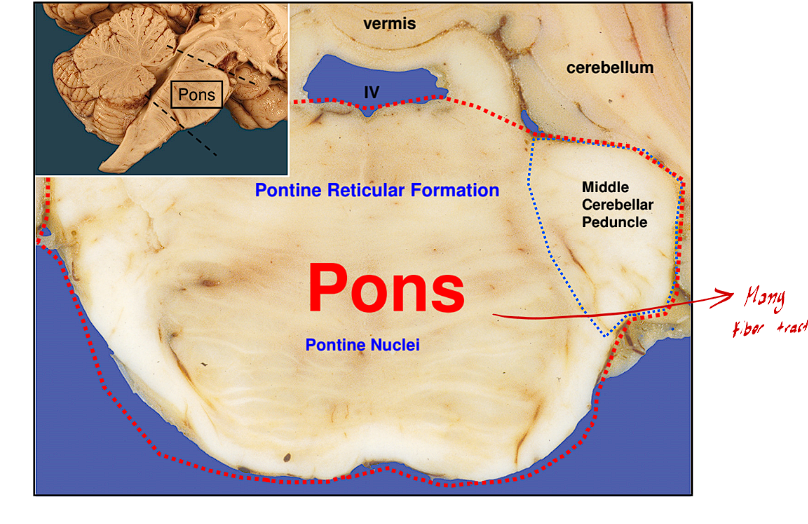
What are some traits of the Pons
The Pons is the ventral part of the metencephalon
It contains many pontine nuclei and pontine reticular formation
This is the net-like fiber tract formation
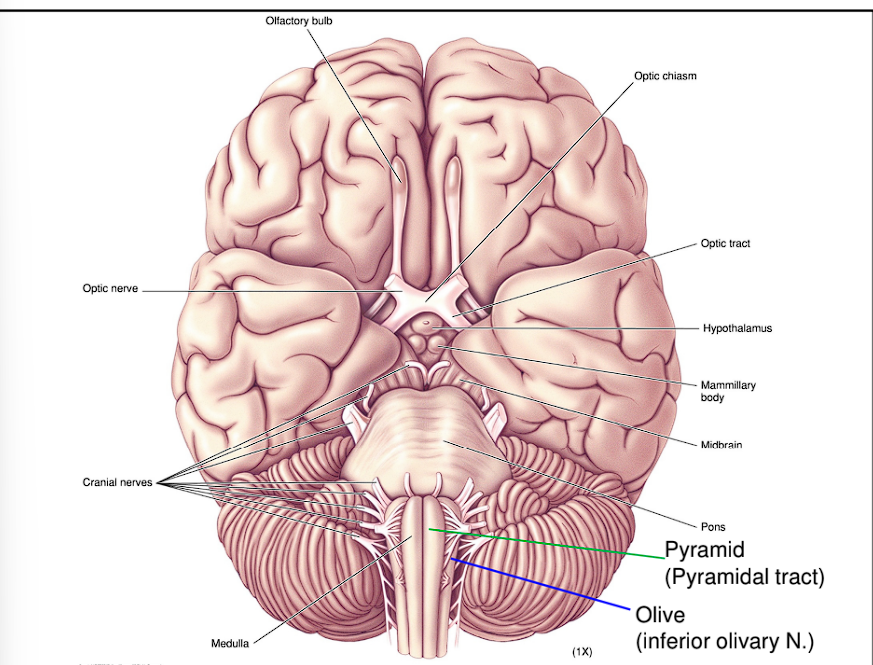
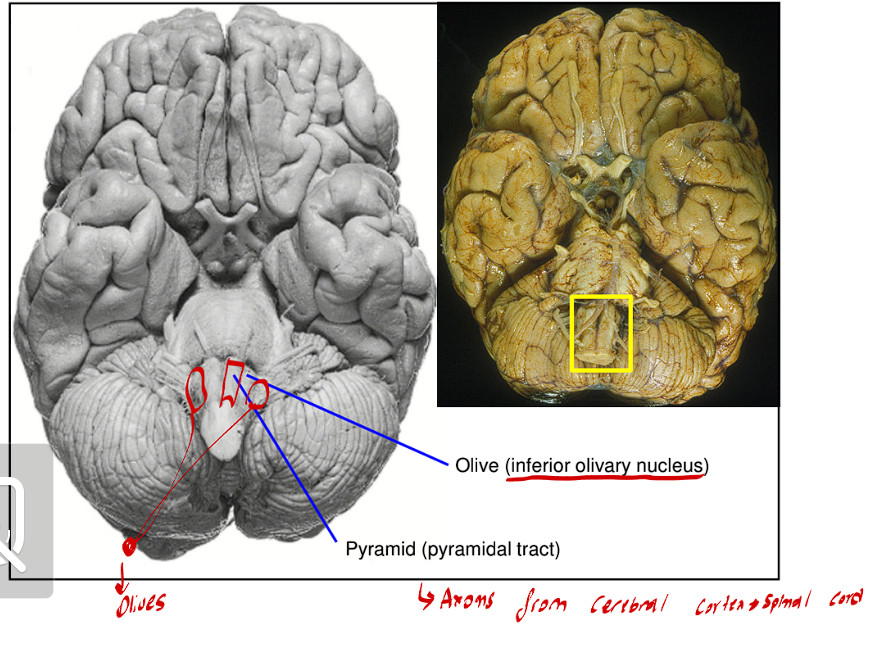
The Medulla Oblongata contains Ventral and Ventrolateral surfaces, what are these?
The Pyramidal tracts
These are two large fiber bundles
They are the major motor pathways that take origin in the cerebral cortex and terminate in the ventral horn of the spinal cord
It is the most medial and central
Olives
These are two olive-like bulges that result from the large inferior olivary nuclei
These are found right next to the pyramidal tracts
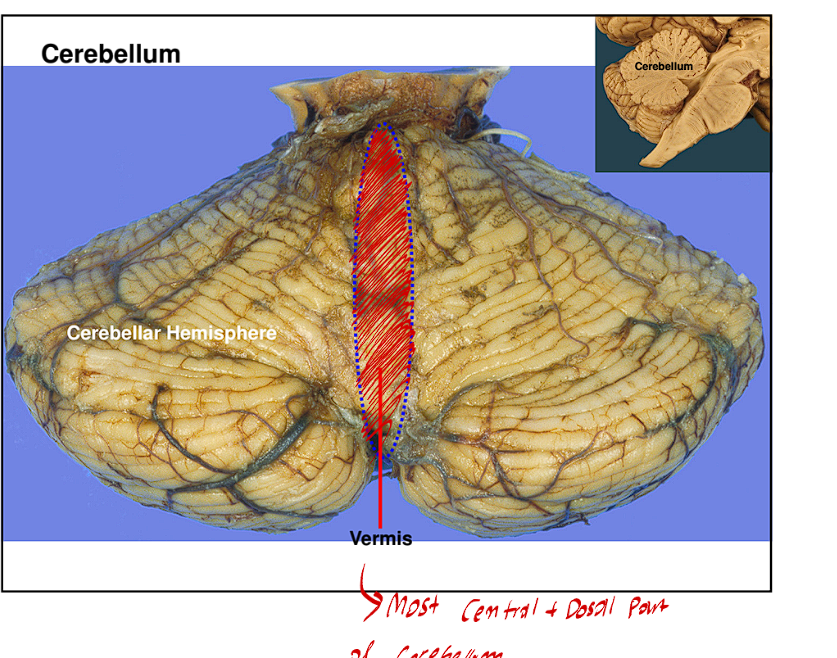
The Cerebellum Traits
This is the most dorsal part of the metencephalon.
It means Little Brain
It is directly above the 4th ventricle
It contains two structures
A midline called the Vermis
2 large hemispheres