Theme 1
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
An economic model
A simplified version of reality that helps you observe, understand and make predictions about economic behaviour
Ceteris paribus
All of things remain equal
Positive statement
Statements about economics which can be proven true or false. supported or refuted by evidence. fact which can be proven or disproven. For example, “the service sector will grow by 30% in the next five years.”
Normative statement
Statements which cannot be supported or refuted conclusively. opinions about how economics and markets should work. Contains a value judgment i.e. subjective. for example, ‘the government should increase the state pension.’
Positive economics
A scientific or objective study
Normative economics
is value judgements and policy recommendations
Scarcity
A situation that arises when people have unlimited wants in the face of limited resources
Free goods
Goods such as the earths atmosphere that are not normally regarded as being scarce
Economic goods
Goods that are scarce
Opportunity cost
The value of the next best alternatives forgone
Marginal analysis
An approach to economic decision making based on considering the additional (marginal) benefits and cost of a change in behaviour
the three key groups of decision makers in economic analysis
Consumers
Government
Producers
Factors of production
resources used in the production process; inputs into production, particularly including:
Land
Enterprise
Labour
Capital
rewards for the 4 factor inputs
land - rental income to owners of land
Enterprise - profits
Labour - wages and salaries from employment
Capital - interest from savings + dividends from shares
Renewable resources
natural resources that can be replenished, such as forests that can be replanted, or solar energy that does not get used up
Non-renewable resources
natural resources that once used cannot be replenished, such as coal or oil
Production possibility frostier (PPF)
a curve showing the maximum combinations of goods or services that can be produced in a given period
Trade-off
a situation in which the choice of one alternative requires the sacrifice of another
Capital goods
goods used as part of the production process, such as machinery or factory buildings (like an investment)
Consumer goods
goods produced for present use (consumption)
Gross Domestic Product
The measure of the total output of an economy
Market demand is the sum of ________
All individual demands in the market
What are some things that influence supply
production cost
technology of production
Taxes and subsidies
Price of related goods
firms’ expectations about future prices
the number of firms operating in the market
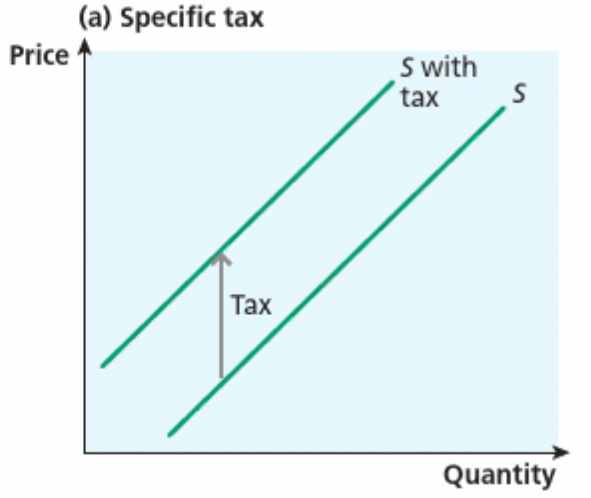
Which way will the supply curve shift when taxes are add
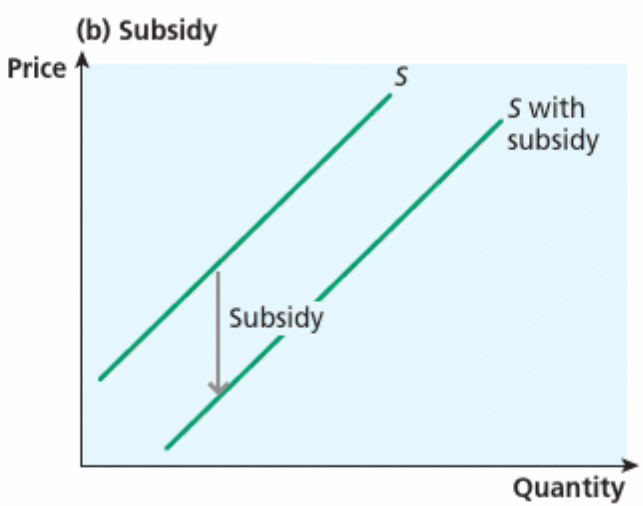
Which way will the supply curve shift when the government pays firms a subsidy
Right
What will companies do if they think prices will go up
Save some to sell later
What will happen to the supply curve if more firms join the market
Shift right
What’s cartel
an agreement between firms in a market on price and output with the intention of maximising their joint profits
What’s excess supply
a situation in which the quantity that firms are willing and able to supply exceeds the quantity that consumers wish to demand at the going price
Excess demand
a situation in which the quantity that consumers wish to demand at the going price exceeds the quantity that firms are willing and able to supply
Market equilibrium
a situation that occurs in a market when the price is such that the quantity demanded by consumers is exactly balanced by the quantity supplied by firms
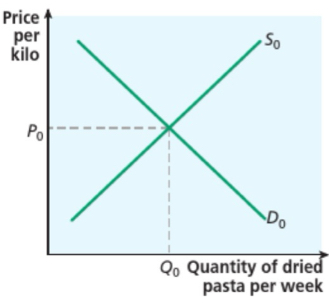
What can affect market equilibrium
A change in consumer preferences
A change in the price of a substitute
An improvement in the ‘good’s technology
An increase in labour costs
What’s the difference between a free market and a centrally planned economy
In a free market, market forces are allowed to allocate resources but in a centrally planned economy the state plans and directs resources. (In between these is the mixed economy)
Consumer surplus
the value that consumers gain from consuming a good or service over and above the price paid
Marginal social benefit (MSB)
the additional benefit that society gains from consuming an extra unit of a good
What’s indirect tax
a form of taxation where the tax is collected by an intermediary, such as a manufacturer or retailer, and then passed onto the consumer through the price of a good or service
Direct tax
A tax you pay directly to the government
Subsidy
A sum of money granted by the state or a public body to help a firm keep their prices low
Marginal utility
When you have more and more of a product the satisfaction you get from having one more unit diminishes.
Disposable income
Measures an individuals or households purchasing power after accounting for inflation and taxes, reflecting the actual amount of goods and services that can be bought
Normal good
An item that demand increases when consumer income rises and decreases when income falls Ceteris paribus
Inferior good
A good whose demand decreases as consumer income increases and vice versa
Joint demand
When demand for two or more goods is interdependent and they are consumed together
Competitive demand
When two goods are substitute for each other
Derived demand
Demand for a factor of production that is derived from the demand for the final product
Revenue
total income a business generates from selling its core products or service