YEAR 11 PSYCH UNIT 1 AOS2 KK3 - KK6
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
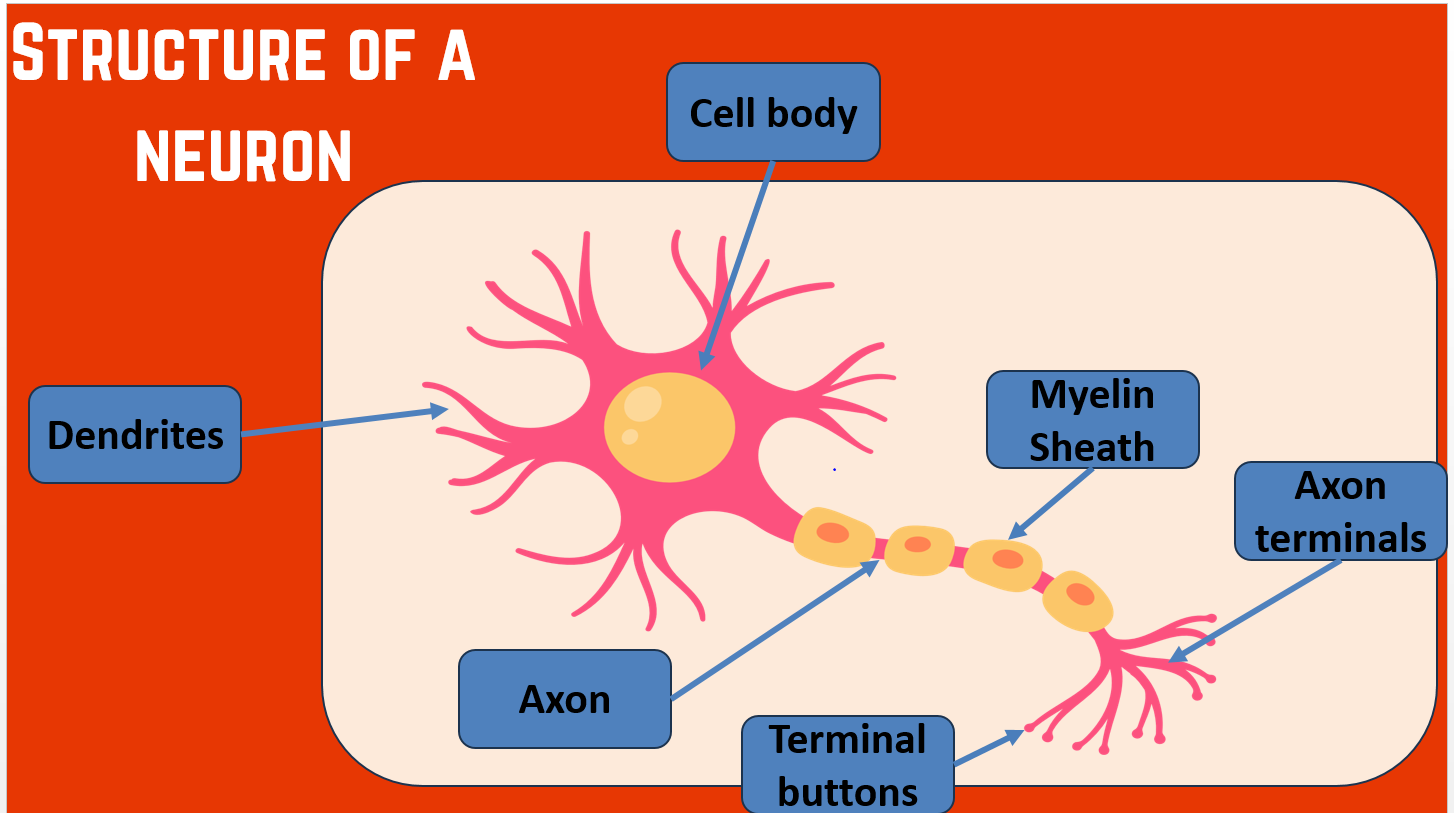
NEURON
The neuron is an individual nerve cell that receives and transmits neural information
THREE TYPES OF NEURONS
Sensory (Afferent) – carries messages from sensory receptors from PNS to CNS
Motor (Efferent) – carries messages from CNS to muscles & glands to allow movement
Inter (connecting) – only in CNS, provides connection between sensory & motor neurons
Central nervous system is brain and spinal cord and peripheral are nerves that extend throughout the body, outside the brain and the spinal cord
LABELLED NEURON
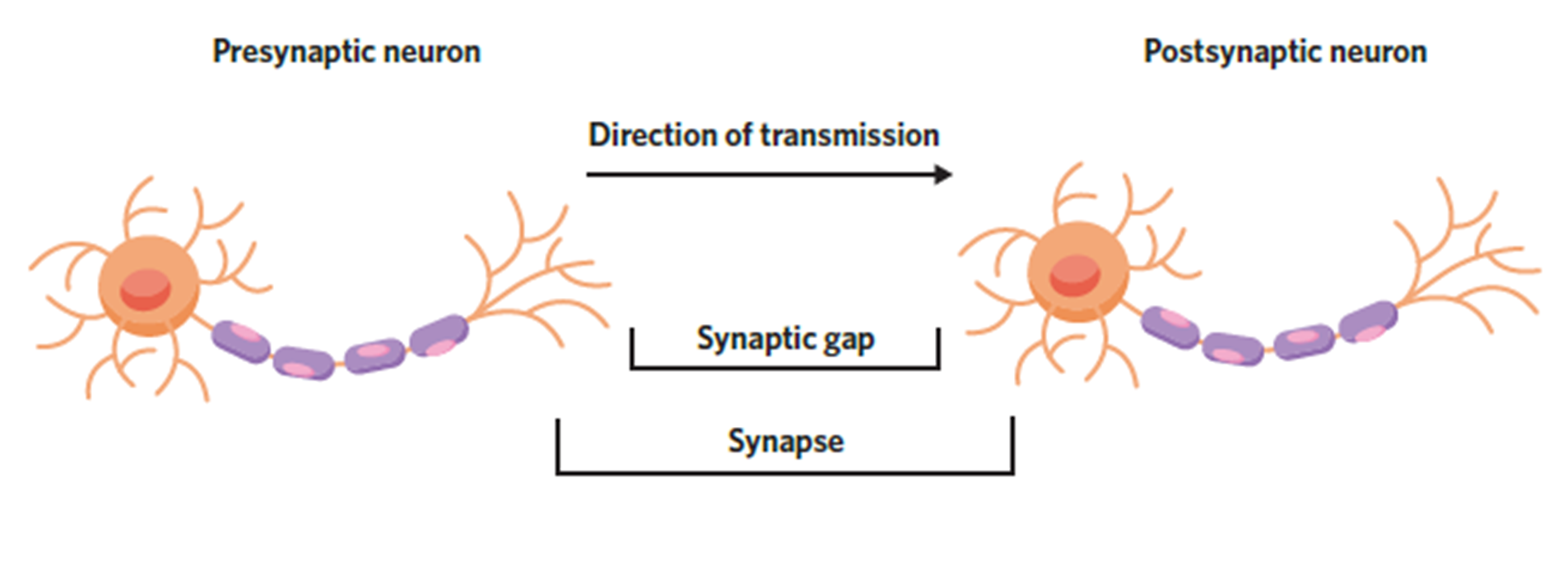
NEURAL TRANSMISSION
Neural information travels down the axon, through the axon terminals and released via the terminal buttons of the presynaptic neuron. The pre & post neuron do not touch, the neural message travels through the synapse and is received by the dendrites of the post synaptic neuron.
NEURAL PLASTICITY
ability of the brain to change in response to experience or environmental stimulation
two experiences are developmental and adaptive
DEVELOPMENTAL PLACTICITY
as we age we mature, learning through different environmental experiences
key influencers are synaptogenesis, synaptic pruning and myelination
SYNAPTOGENESIS
process where neurons form new connections which represents the learning and retention of the new information most prominent in infancy.
SYNAPTIC PRUNING
process where unused neurons are eliminated, this is done to free up space in the brain and allow for the strengthening of frequently used synapse/ neurons
MYELINATION
formation and development of myelin around the axon of the neuron, speeds up transmissions of electrical signals through nervous system
ADAPTIVE PLASTICITY
changes to the brain due to brain trauma or injury
key influencers are sprouting and rerouting
SPROUTING
neurons ability to develop new branches in the dendrites of axons
This expands the reach of the neuron enabling new neural connections to be formed in areas of the brain where the neural activity has been prevented or depleted.
REROUTING
neurons ability to form a new connection with another undamaged neuron
The neuron that is rerouting abandons its connection with a damaged neuron, enabling new neuronal connections to be formed after trauma. This allows re-development of cognitive functioning.
HOW TO HELP MAINTAIN BRAIN FUNCTIONING
mental stimulation - strengthens and prevents synaptic pruning of needed neural connections
diet - there are different types of food that contain vitamins that aid brain functioning
physical activity - physical activity increases blood supply to the brain and promotes the growth of new neurons in the hippocampus and other brain regions.
social support - having someone to listen to is associated with greater resistance to brain injury
ABI (AQUIRED BRAIN INJURY)
an damage to the brain that has occurred after birth, can be classified as traumatic or non traumatic
TRAUMAIC ABI
when the damage to the brain is cause by an external force like sports injuries or car accidents
NON TRAUMATIC ABI
occurs when the damage to the brain is caused by an internal factor like a stroke
BIOPSYCHOSOCIAL
BIO - organ or cellular functioning impairment like difficulty moving
PSYCHO - impairments in psychological functioning like personality changes, memory/ concentration
SOCIAL - impairment in social functioning, includes an increase in anti social behaviour
NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
diseases or events that affect the brain, spinal cord and the nerves that connect them
all result from damage to nervous system due to genetics or after birth due to environmental causes
ABIs
NEURODEGENRATION
Neurodegeneration means the gradual loss or damage of neurons in the brain or nervous system, which can lead to problems with thinking, movement, or memory, as seen in diseases like Alzheimer's or Parkinson's.
PARKINSONS DISEASE
progressive neurodegenerative disease of the nervous system and the loss of neurons in the brain. Some symptoms are tremors, reduced motor control, muscle stiffness and fatigue
EPILEPSY
neurological disorder that is associated with abnormal electrical activity in the brain characterised by recurrent seizures
SEIZURES - brief episodes of uncontrolled electrical discharging of neurons in the brain
some symptoms are involuntary shaking, loss of consciousness, loss of awareness
CTE (CHRONIC TRAUMATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY)
progressive and degenerative and fatal brain disease associated with repeated concussions to the head over a long period of time
EFFECTS OF CTE
tau protein tangles - when nerve cells are damaged the tau separates from the cytoskeleton and starts to clump up or form tangles in the brain cells, eventually they cause cells to become defective and lose their ability to function
SYMPTOMS OF CTE
headaches, loss of attention
anxiety, depression, suicidal thoughts, impulse control
impairments in planning or organising, severe memory loss
form of dementia, memory and cognitive impairments disrupting daily life
CTE DIAGNOSIS
only way to really diagnosis CTE is an autopsy of the brain after the individual has died.
when suspected thorough medical history testing of mental status and neurological examination and brain imaging can help rule out other causes
CTE TREATMENT
difficult to treat since only diagnosed after death, can only be assumed. treatments like behavioural therapy, pain management and regular exercise/ healthy food help manage any symptoms.
MACHINE LEARNING
an element of artificial intelligence that allows software to become more accurate at predictions by mimicking the way humans learn and utilise statistics to create algorithms
SUPERVISED LEARNING
use of labelled data to train algorithms on how to classify data or predict outcomes
can be used to diagnose neurological disorders and stages
UNSUPERVISED LEARNING
uses unlabelled data to find trends and patterns in data that have not been identified yet
often used to analyse demographics that may have been overlooked
GUT - BRAIN AXIS
refers to the bidirectional connection between the gut and the brain through the central nervous system and enteric nervous system
gut can influence brain due to the gut microbiota which are the organisms that live in the gut
imbalance can lead to potential disease in the central nervous system