Chapter 4: Mechanical Ventilation Part 2
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What are the Positive Pressure Basic Ventilation Modes?
Control Modes
Mixed Modes
Spontaneous Modes
Other
What are the Control Modes?
Controlled Mode/Mandatory Ventilation (CMV)
Assist-Controlled Mode Ventilation (A/C)
Assist Mode (A)
What are Mixed Modes?
Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (IMV)
Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (SIMV)
What are Spontaneous Modes?
Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV)
What are the other types?
Positive End Expiratory Pressure (PEEP)
What are the types of Positive Pressure Ventilation Cycling Mechanisms?
Volume Cycled
Pressure Cycled
Flow Cycled
Time Cycled
Volume Cycled:
Inspiration terminated after delivery of a pre-set tidal volume
Pressure Cycled:
Inspiration terminated when a pre-set maximum pressure is reached
Volume delivered varies from breath to breath
Flow Cycled:
Inspiration terminated when a particular flow rate is reached
Time Cycled:
Inspiration terminated following a pre-set inspiratory time
(Mode Characteristics) What are the Parameters?
What initiates the breath? (Machine, Patient, Both)
What terminates the breath? (volume, pressure, flow, time)
What are the flow characteristics?
What are the pressure characteristics?
What is the tidal volume, VT?
Assist Control (A/C):
(Variation of CMV – now used predominantly)
Full ventilatory support
Patient controls respiratory rate (RR); but, can’t inspire sufficiently to reach or maintain Vmin
Uses either Pre-Set Volume OR Pre-Set Pressure parameters
AND–has a pre-set minimum RR
Triggers:
when patient initates a breath, the machine continues until the pre-set volume/pressure is achieved
if patient does not spontaneously inhale when the machine expects an inhalation based on RR
Does not allow for independent patient breathing at whatever effort (volume/pressure) the patient produces
Can be used indefinitely
What are the advantages of Assist Control?
Reduced work of breathing
Allows patient to increase Vmin
What are the disadvantages of Assist Control?
Potential for inappropriate hyperventilation (too much volume too often can result in this)
Leads to possibility of respiratory alkalosis (higher ph)
Airway pressures vary w/ changes in lung compliance (lung elasticity) → varying of pressures may be too much for patient to handle
What is Synchronized IMV (SIMV)?
Modified/Improved IMV
Partial ventilatory support
3 breath types are used:
Mandatory breath: a minimum number of fully assisted breaths per minute. Machine breaths can be patient- or time triggered, are flow limited, & volume-cycled
Synchronized breaths: Patient’s spontaneous inspiration + the machine breath (at or near the time of the mandatory breath)
If the patient’s breath is a bit quicker than anticipated, the machine senses the patient’s breath, synchronizes w/ it, & waits until exhalation has completed to deliver it’s next breath
Patient’s spontaneous breath w/o machine assist (in-between mandatory breaths)
What are the advantages of SIMV?
Decreases “air-stacking” issue of IMV
Helps preserve respiratory muscle strength
Decreases risk of barotrauma (too much pressure can cause lungs to burst
Facilitates weaning
What are the disadvantages of SIMV?
May be longer weaning times when compared to trach patients w/ t-pieces
NOTE: SIMV = A/C for the patient w/ weak respiratory drive
What is Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV, PS)?
Flow-cycled
Supplements/Aids spontaneous breathing by supplying preset positive pressure during the full INSPIRATION to overcome airway resistance / dead space
Higher pressure → large tidal volume delivered
Can be used w/ OR w/o other ventilator modes
Often see AC + PS, & SIMV + PS
If used, might be set higher than PEEP setting
What are the advantages of PSV, PS?
Reduced WOB
When used w/ intubated patients can help compensate for small lumen of ET tube
What are the advantages of PSV, PS?
Barotrauma (too much pressure)
Can deeter weaning bc patient cannot work as hard
(Internal Ventilator Monitoring) Machine Alarms:
Low pressure in the system (disconnection)
High pressure → increased airway resistance
May happen w/ use of Passy Muir Valve
Power failure
Exhaled tidal volume issue
Apnea
External Ventilator Monitoring:
Clinical Judgement!
Chest Movement
Auscultaion
Diminished or absent breath sounds?
Unusual breath sounds like wheezing, or crackles?
Pulse Oximetry = Oxygen saturation of Hemoglobin
Capnography (PetCO2) = level of CO2 exhaled (that passes across the sensor in the vent tubing!)
should, but doesn’t always correlate w/ PaCO2 in the blood
Transcutaneous Oxygen/CO2 monitoring
Arterial Blood Gases:
Blood drawn & send to lab for analysis
PaO2 & PaCO2
Measures only that point in time when blood was drawn
Ventilator Weaning:
Some facilities have protocols; some don’t
Some facilities have “Weaning Teams”
Typically includes an SLP
Generally:
Intubated patient? Spontaneous Breathing Trial; if ok, then, off the vent
Trached patient?
Progression from AC → SIMV → CPAP or Weaning Trials
Weaning trials = time off the ventilator (some facilities call “sprinting”)
If initially tolerated, then, time off is slowly increased over the course of days/weeks
Alternate the amount of time off/time on
May progress to off all day, on at night only, then, off completely
Trach Weaning:
“Decannulation” - removing trach
some facilities have protocols; others don’t
Progressive reduction in trach size (ex: 8 to 6 to 4)
Cuffed or cuffless
Or, cuffed to fenestrated trach (if that’s what ur facility uses) (TRY TO DISCOURAGE FENESTRATED)
Speaking Valve Trials
Capping Trials
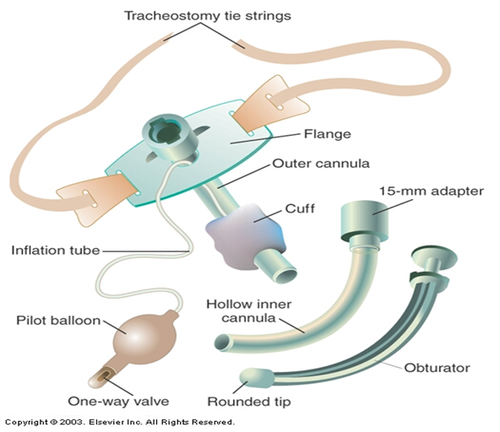
What are Capping Trials?
Progressively increase the time patient can tolerate being capped
Some facilities have a 3-day protocol:
Speaking valve x 48 hours
Cap x 24 hours
Decannulate
Weaning Issues:
Nutrition
Aspiration PNA
Anxiety
Nutrition:
High caloric demands
Must be able to maintain adequate nutrition orally or need DHT or PEG
swallowing is affected by Trach & Vent
how much swallowing is affected depends on the person
Aspiration PNA:
Colonization of bacteria on the ET tube or trach
Reflux
Oral diet
Anxiety:
Sense of dependency on the machine; fear of going off it
Fear of decannulation –not having access for “pulmonary toilet,” i.e., pulmonary hygiene via suctioning
Psychosocial Considerations:
Loss of control of the most basic function
Fear of not being able to breathe
Inability to communicate
Body Image from Trach
Isolation
Patient & Caregiver