Conflict Theory
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Who is Hegel and why is he important?
ideas of George Hegel impacted Carl Marx
Carl Marx is founder of conflict theory
Hegelian Dialect
Thesis
accepted by everyone
e.g: everyone loves chocolate
antithesis
opposite of thesis
e.g: everyone hates chocolate
synthesis
combined parts of thesis and antithesis; new ground/understanding
becomes thesis and becomes challenged again
e.g: people have mixed feelings about chocolate
daddy of conflict theory
Karl Marx
focus on economic well-being of ind (poorer ppl were focus)
applied dialect to economy
always ruling class in control (thesis)
overthrown by working class through conflict/turmoil (antithesis)
wanted antithesis: wanted equal access for poor and rich people.
so synthesis become new thesis.
who brought conflict theory into diadic (2 people like lovers) romantic relationships?
Georg Simmel
Interpersonal Dimensions
opposing dimensions in relationships
e.g: love, and hatred
security, and jealousy
harmony and repulsion
people go back and forth between dimensions in relationship
what remains: human beings need to be loved, and wanted
who brought conflict theory into familes?
jetse spray
according to jetse, conflict is
part of every relationship
families with conflict can be understood by
manage conflict
part of family structure
does not not mean it’s bad
different within families vs. other conflicts
Basic Assumption of Conflict Theory
nature of humans is self-oriented no matter how much you care for family
societies operate under continuous scarcity of resources
group dynamics are different within families than other groups
conflict is a confrontation over control of scare resources
conflict can be classified
conflict has positive aspects.
assumption 1
nature of humans is self-oriented no matter how much you care for family
human nature is to be selfish
ppl are symbol producing
so we prescribe meanings to things
e.g: one sibling is prettier so it makes other feel like shit
humans have limitless hope=limitless desire for prestige
causes competitive nature automatically even if you don’t desire it
assumption 2
societies= species survival
the state of flux=social change
social change helps us manage inequality.
conflict=challenging status quo=social change
assumption 3
group dynamics are different in families compared to other groups
groups have voluntary membership
family is involuntary
person with least interest (least desire to be there) has the most power
assumption 4
conflict is a confrontation over control of scarce resources
internal conflict
smaller groups/relationships
external conflict
something pressing on us
e.g: conflict at school, jobs, COVID
factors in confrontation
management
negotiation and bargaining
meeting in middle ground/compromise
resolution
consensus
agreement; neither satisfied but agree
assumption 5
conflict can be classified
macro social
issues and conflict between classes
e.g: money, race, gender
which groups have most privilege? how do ppl manage being not privileged?
shared meaning of what ppl “deserve”
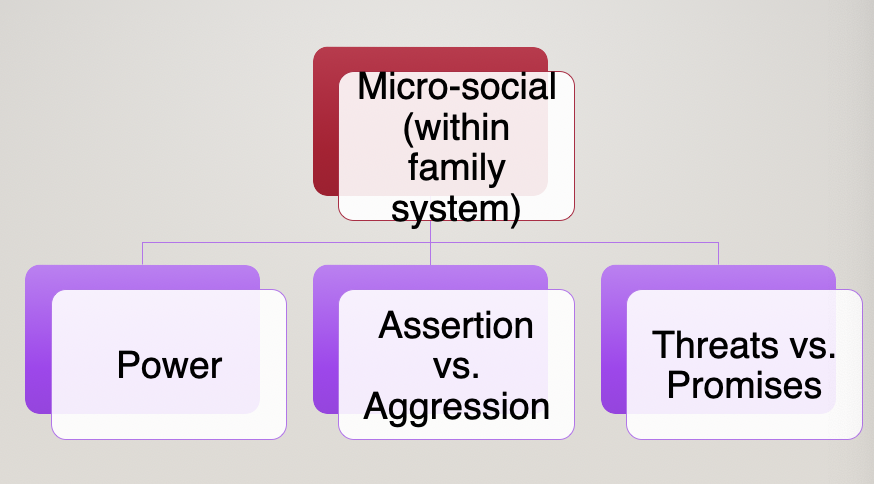
micro social (within family)
power
distributed by age and gender
assertion vs aggression
2 ways family have conflict
assertion: asserting your rights without hurting someone (not at expense of someone)
aggression: agressively giving opinion; might be at expense of someone
threats vs. promises
threat: delivery of punishment if demand is not met
promises: message, not behaviour
assumption 6
conflict has positive aspects
aftermath of conflict is beneficial
root of progress and change
after the storm is when the flower blooms
4 horse men of apocolypse
criticism
contempt
defensiveness
stonewalling
criticism
attacking character
e.g: you don’t do shit
contempt
insults, disrespctful
e.g: yeah cuz you’re so perfect.
defensiveness
trying to protect self from percevied attack
e.g: i do work you just don’t recognize it
stonewalling
overwhelmed
no contact or verbal response