Chemistry II Lesson 11: Aromatics and Carboxylic Acid
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
True or False? There is no difference between a compound that is resonance stabalized and one that is aromatic. Resonance and Aromaticity are essentially the same thing.
False. Aromatic compounds are more stable than resonance-stabalized compounds.
You can consider a compound to be aromatic if it meets what two criteria?
(1) It is a ring of continuously overlapping p orbitals and is thus planar.
(2) It follows Huckel's Rule.
What is Huckel's Rule?
Huckel's Rule is follwed when a compound has 4n + 2 π electrons.
A compound has 12 π electrons. Does it follow Huckel's Rule?
No. 4(2) + 2 = 10 and 4(3) + 2 = 14. A compound with 12 π electrons does not follow Huckel's Rule.
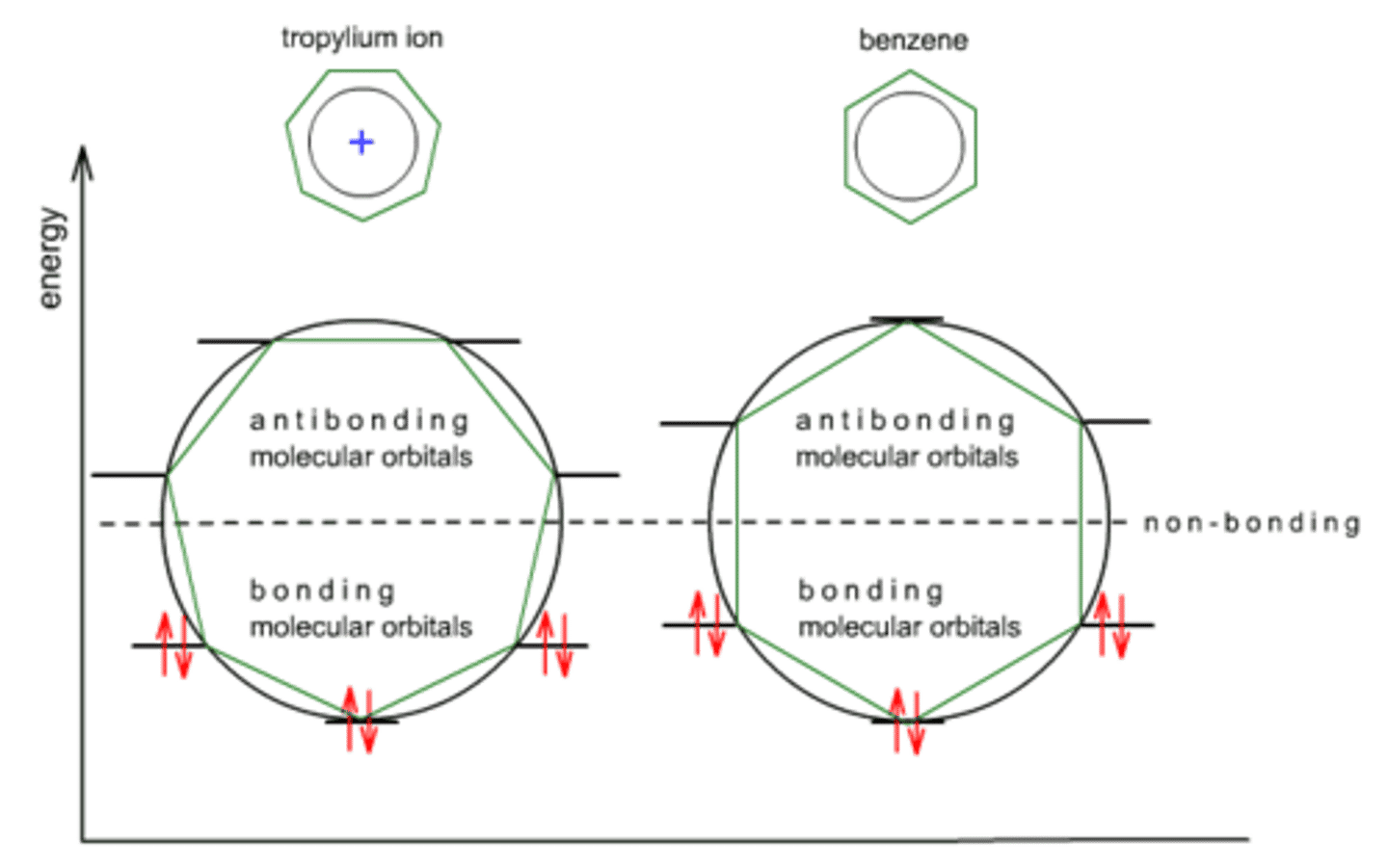
What does the Frost Circle reveal about the stability of a compound that is aromatic?
A Frost Circle allows you to depict the energy levels of the Bonding and Antibonding orbitals. For a compound that follows Huckel's Rule, the electrons only fill in the Bonding Orbitals, making it a very stable compound.
Which of the following are Heteroatoms?
I. Oxygen
II. Nitrogen
III. Sulfur
(A) I Only
(B) II Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
Heteroatoms are any atom that isn't carbon.
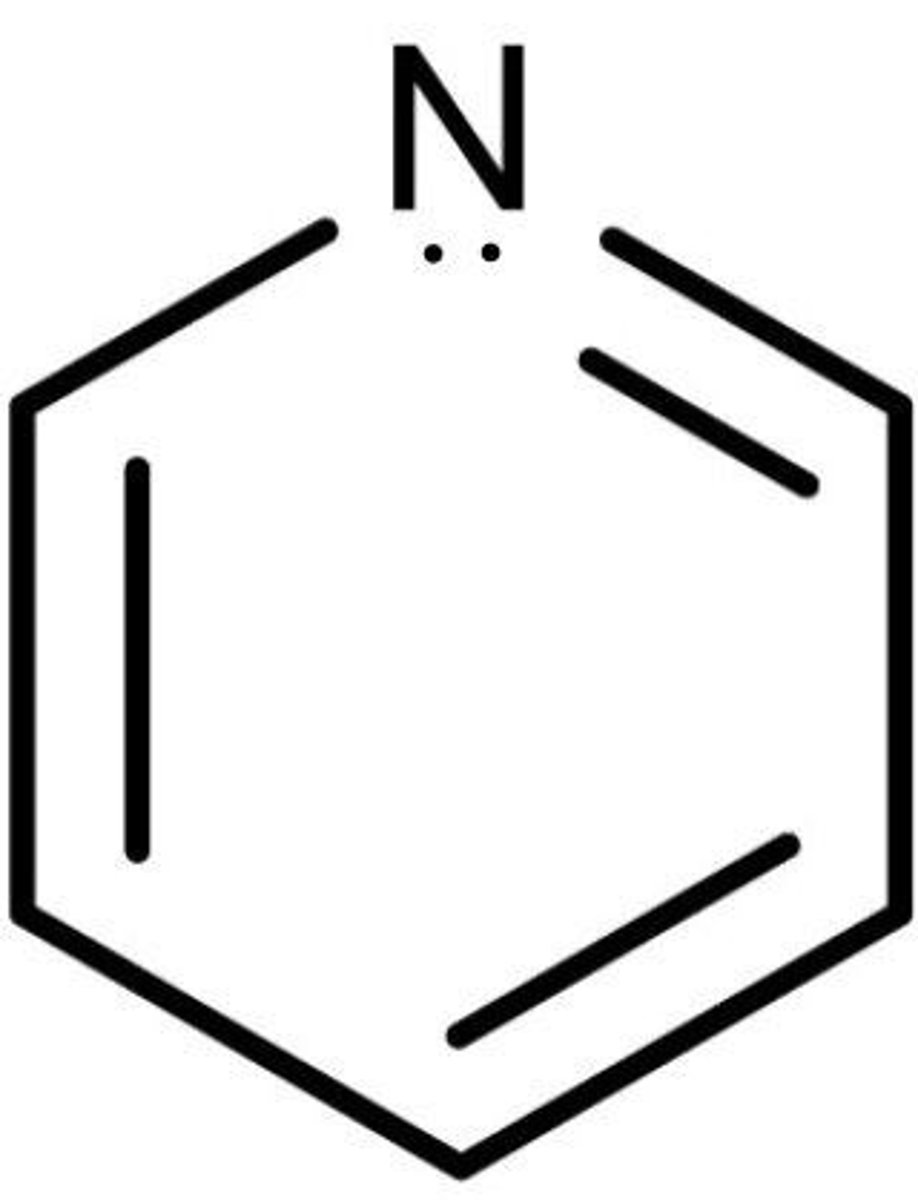
Why is Pyridine considered aromatic? Doesn't it have 8 π electrons? (Pyridine structure: http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/content/dam/sigma-aldrich/structure8/141/mfcd00011732.eps/_jcr_content/renditions/mfcd00011732-medium.png)
Pyridine has 6 π electrons. The lone pair of electrons on the Nitrogen are not π electrons. They are in an sp2 hybridized orbital.
Note: if a heteroatom is already contributing π electrons for aromaticity, its lone pair must be localized to the heteroatom.
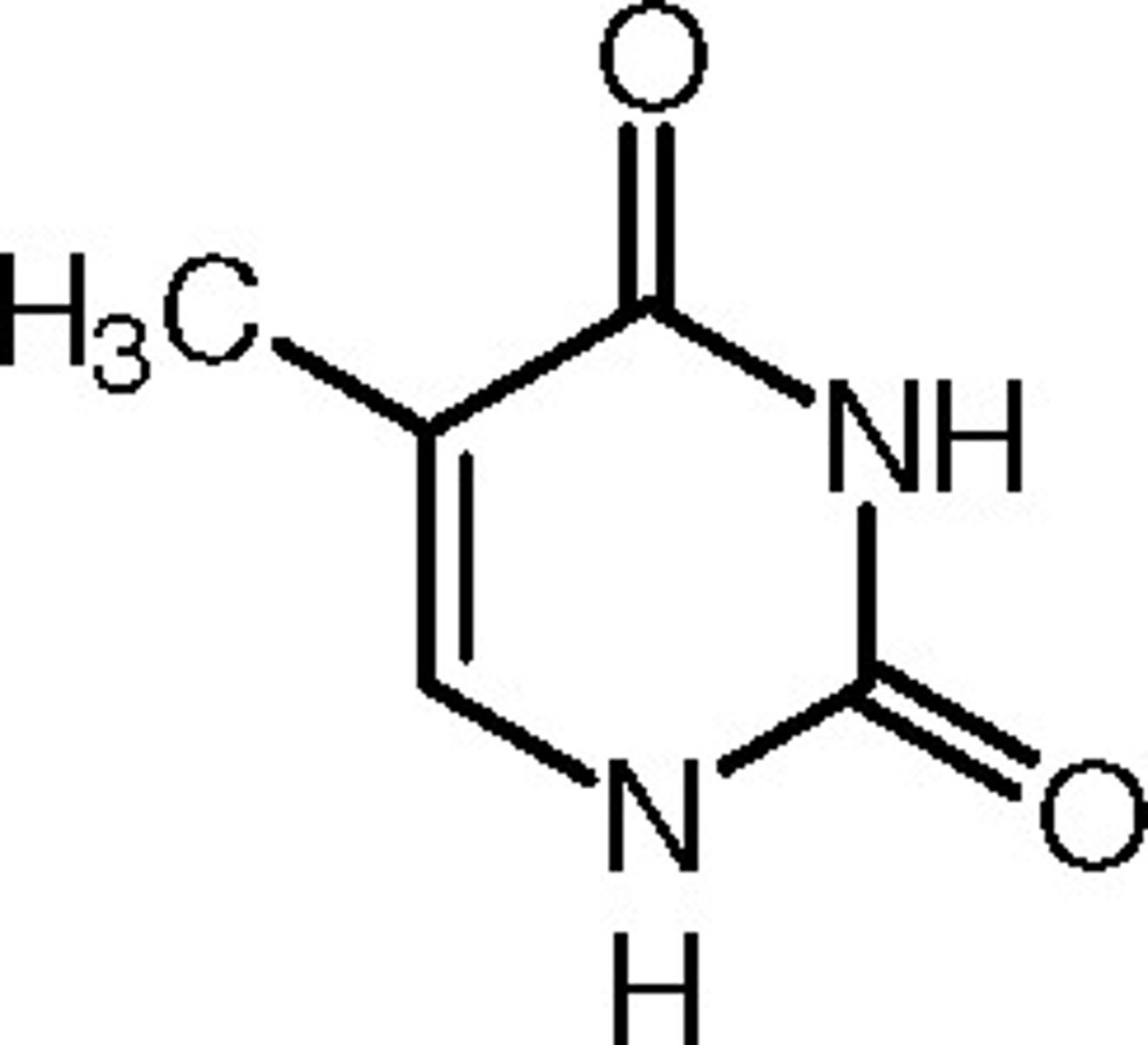
Thymine and other pyrimidine rings play a special role within biochemistry. Is Thymine considered aromatic or not? Why? (NOTE: You should have the structures of the 5 major nucleotides memorized)
Thymine is aromatic because the lone pairs on the Nitrogens are delocalized, bringing the total number of π electrons up to 6.
Test yourself on your ability to identify aromatic compounds using this short 20-question game: https://www.sporcle.com/games/sproutcm/am-i-aromatic
Answers can be found at the same site: https://www.sporcle.com/games/sproutcm/am-i-aromatic
CRB Carboxylic Acids are synthesized by strong oxidizing agents. Which of the following can oxidize primary alcohols to Carboxylic acids?
I. Dichromate Salt (Na2Cr2O7)
II. Potassium Permanganate (KMnO4)
III. Chromium Trioxide
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
Each of the following are strong oxidizing agents and can oxidize a primary alcohol to a carboxylic acid:
I. Dichromate Salt (Na2Cr2O7)
II. Potassium Permanganate (KMnO4)
III. Chromium Trioxide
CRB The common-name prefixes are the same for carbonyl-containing compounds and carboxylic acids. How many Carbons do each of the following prefixes have?
-Form
-Propion
-Acet
Form- 1C
Propion- 3C
Acet- 2C
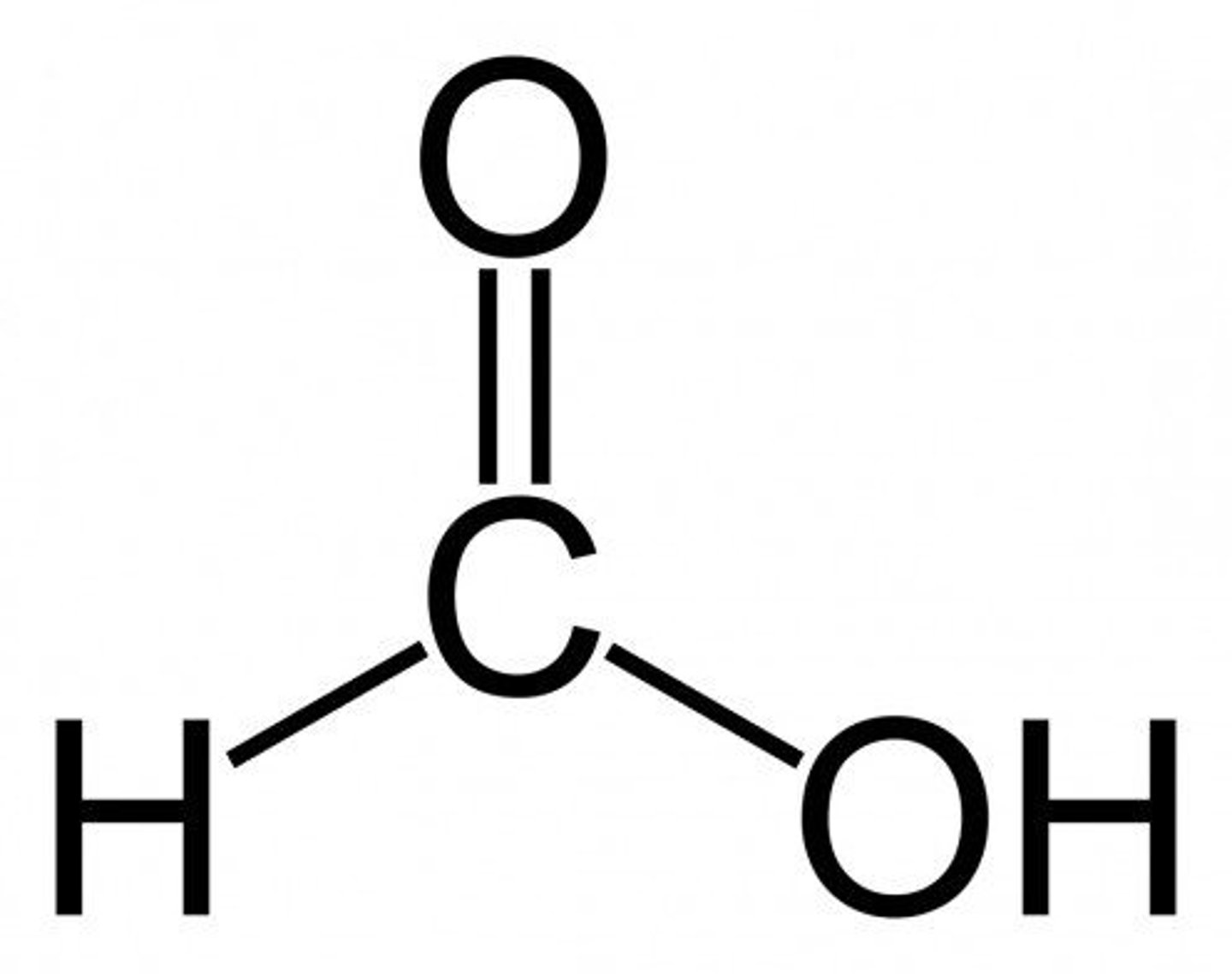
Draw Methanoic acid (Formic Acid)
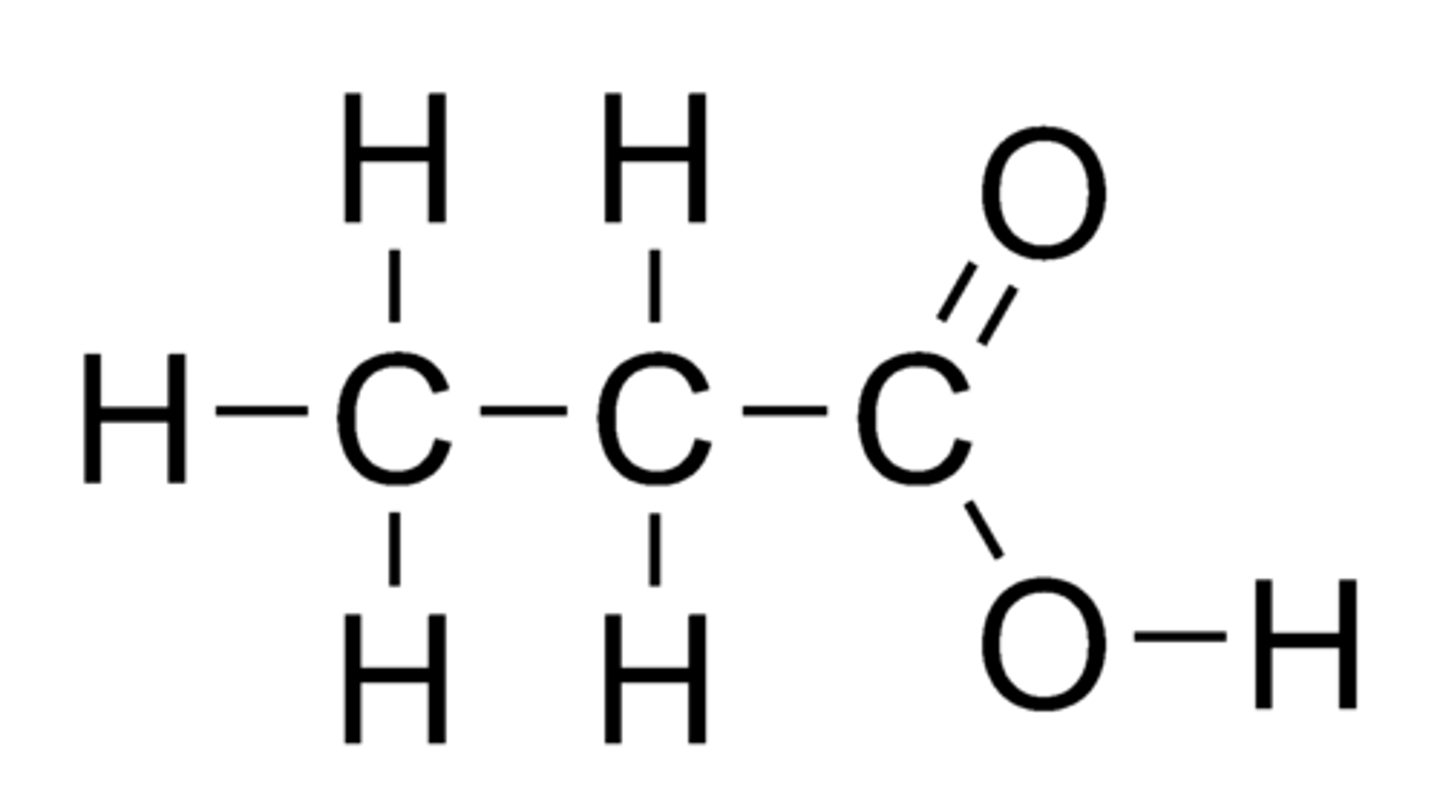
Draw Propanoic Acid.
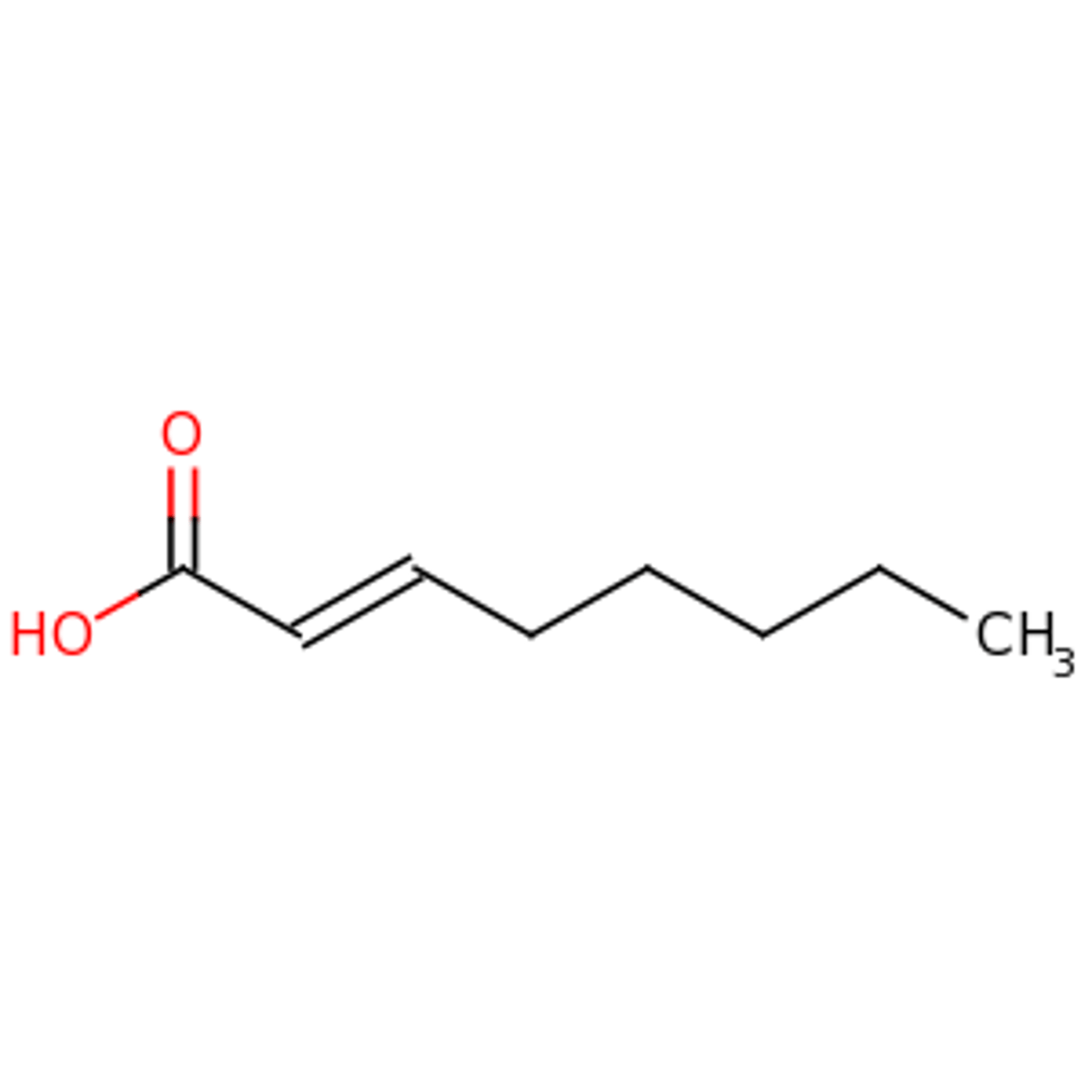
Draw 2-Octenoic Acid.
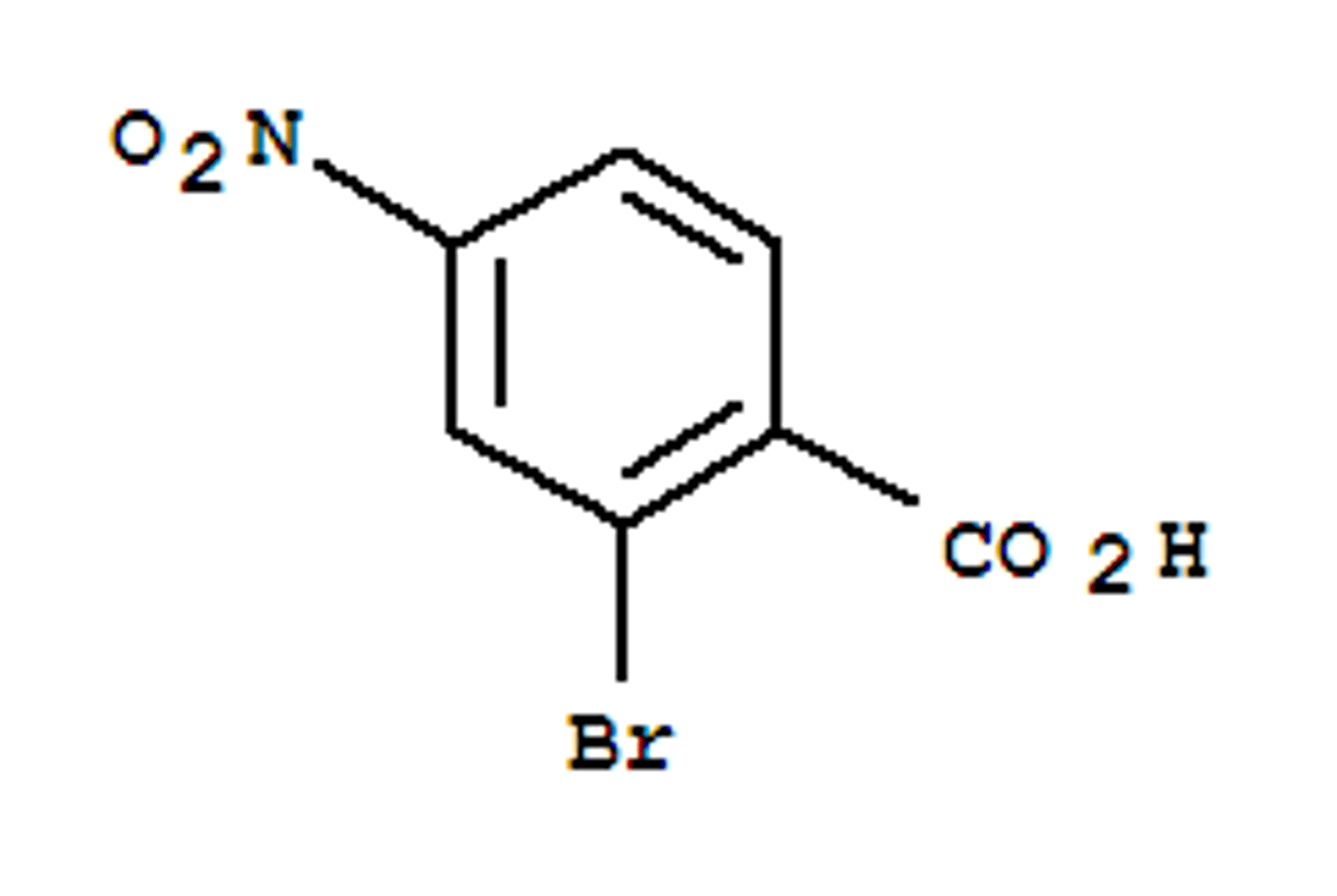
Draw 2-bromo-4-nitro-benzoic acid.
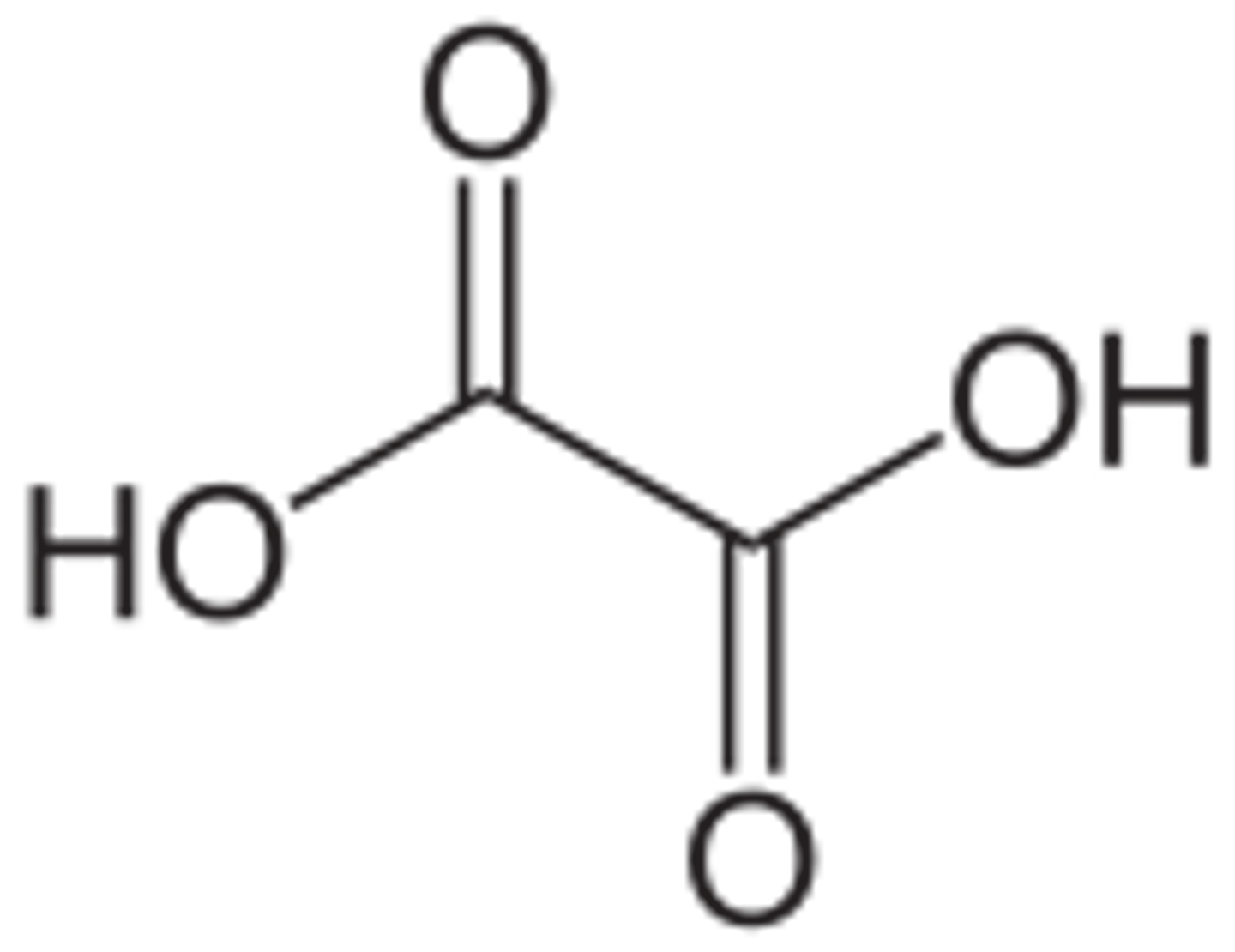
What is the common name for Ethanedioic Acid? Draw this structure.
Oxalic Acid
Which has a higher boiling point? Ethanol or Ethanoic Acid? Why?
Ethanoic Acid has a higher bp than Ethanol due to its stronger Hydrogen bonding.
CRB True or false? Due to their strong hydrogen bonding, Carboxylic Acids tend to form tetramers.
False. Due to their strong hydrogen bonding, Carboxylic Acids tend to form DIMERS.
Draw the Mechanism for the reduction of a Carboxylic Acid using Lithium Aluminum Hydride (LiAlH4).
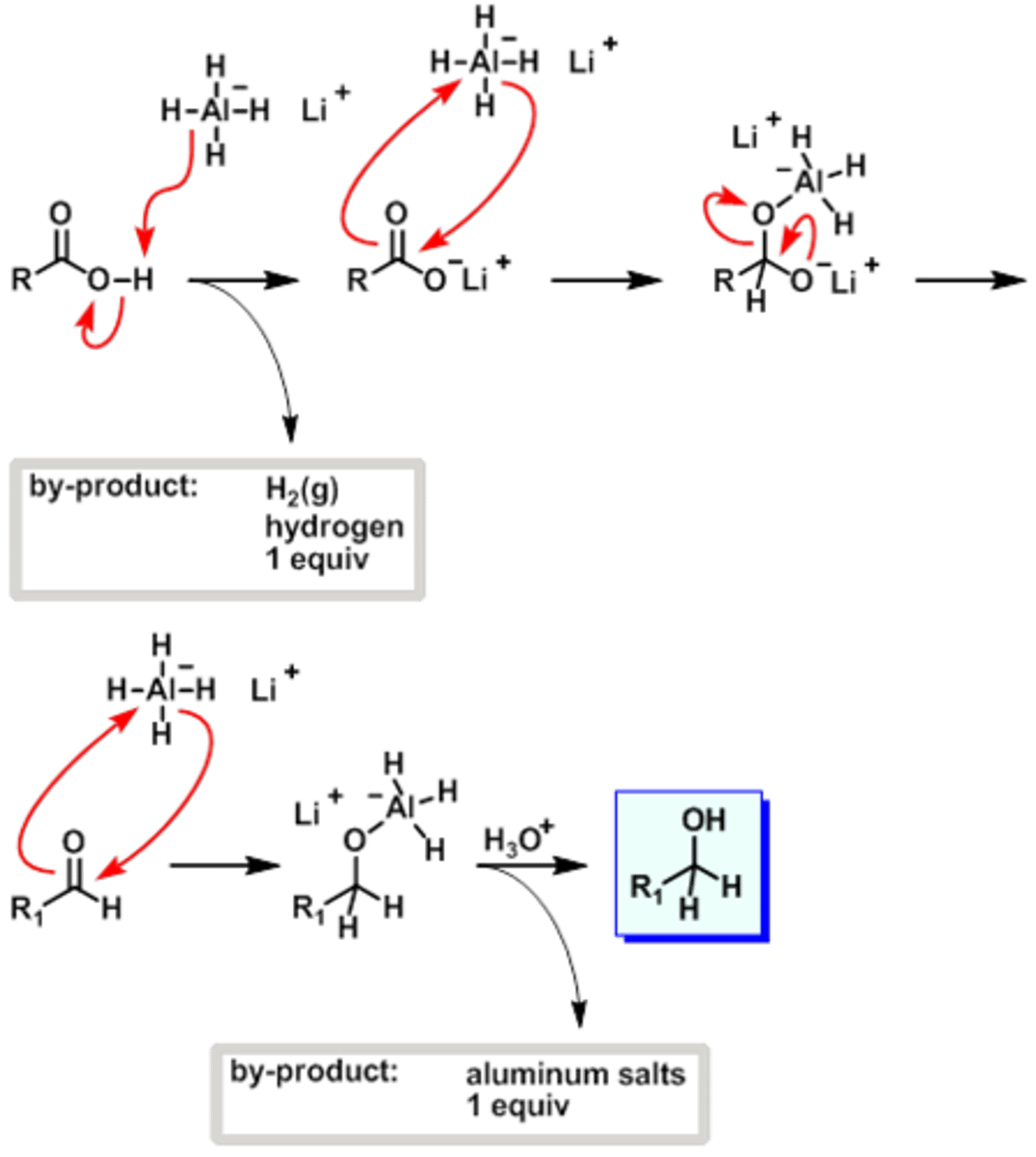
CRB Could NaBH4 be used instead of LiAlH4 to reduce that carboxylic acid? Why or why not?
No, NaBH4 cannot reduce carboxylic acids. This is because Boron is more electronegative than Aluminum, making the B-H bonds less polarized and less likely to act like a hydride (H-).
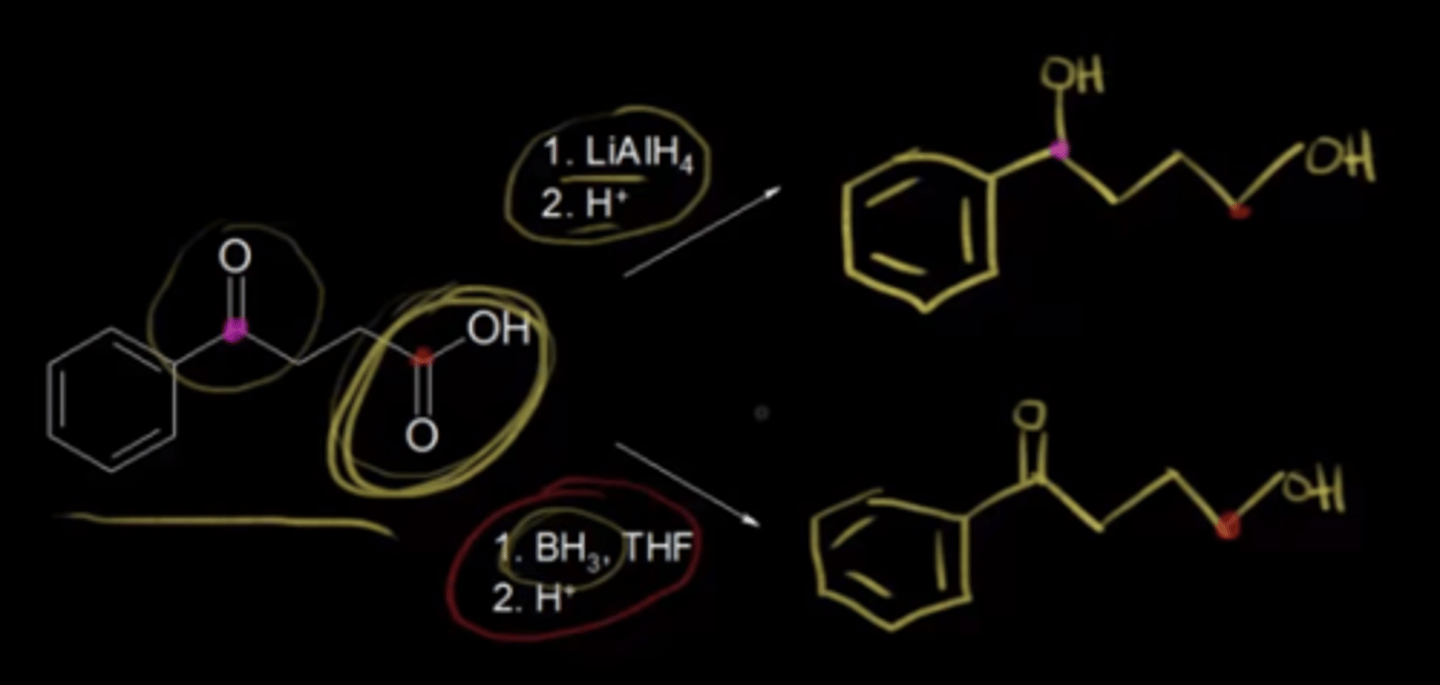
LiAlH4 is used to reduce a compound with a ketone and a carboxylic acid functional group. What functional groups result? What about if BH3 is used instead of LiAlH4?
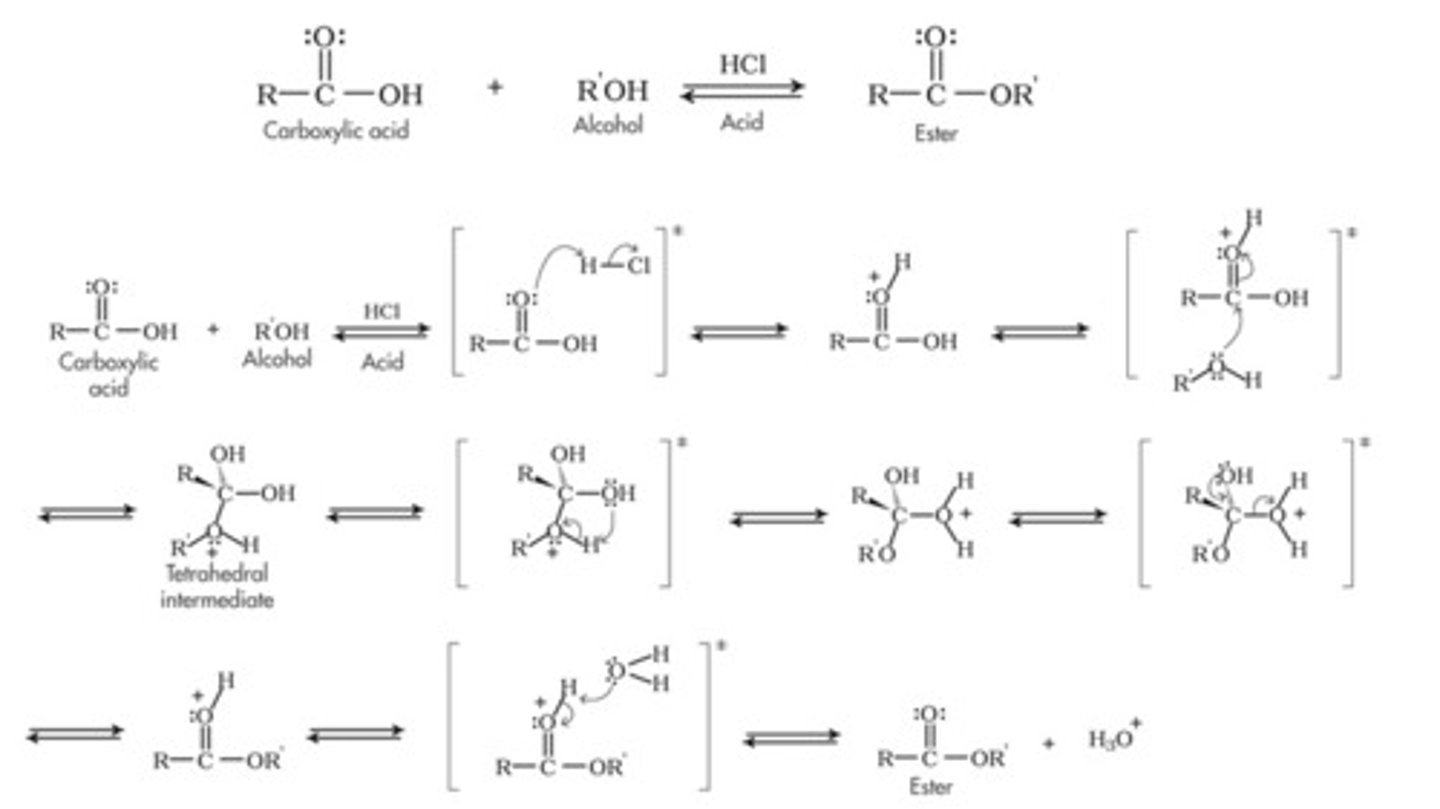
Draw the Fischer Esterification Reaction Mechanism in acid.
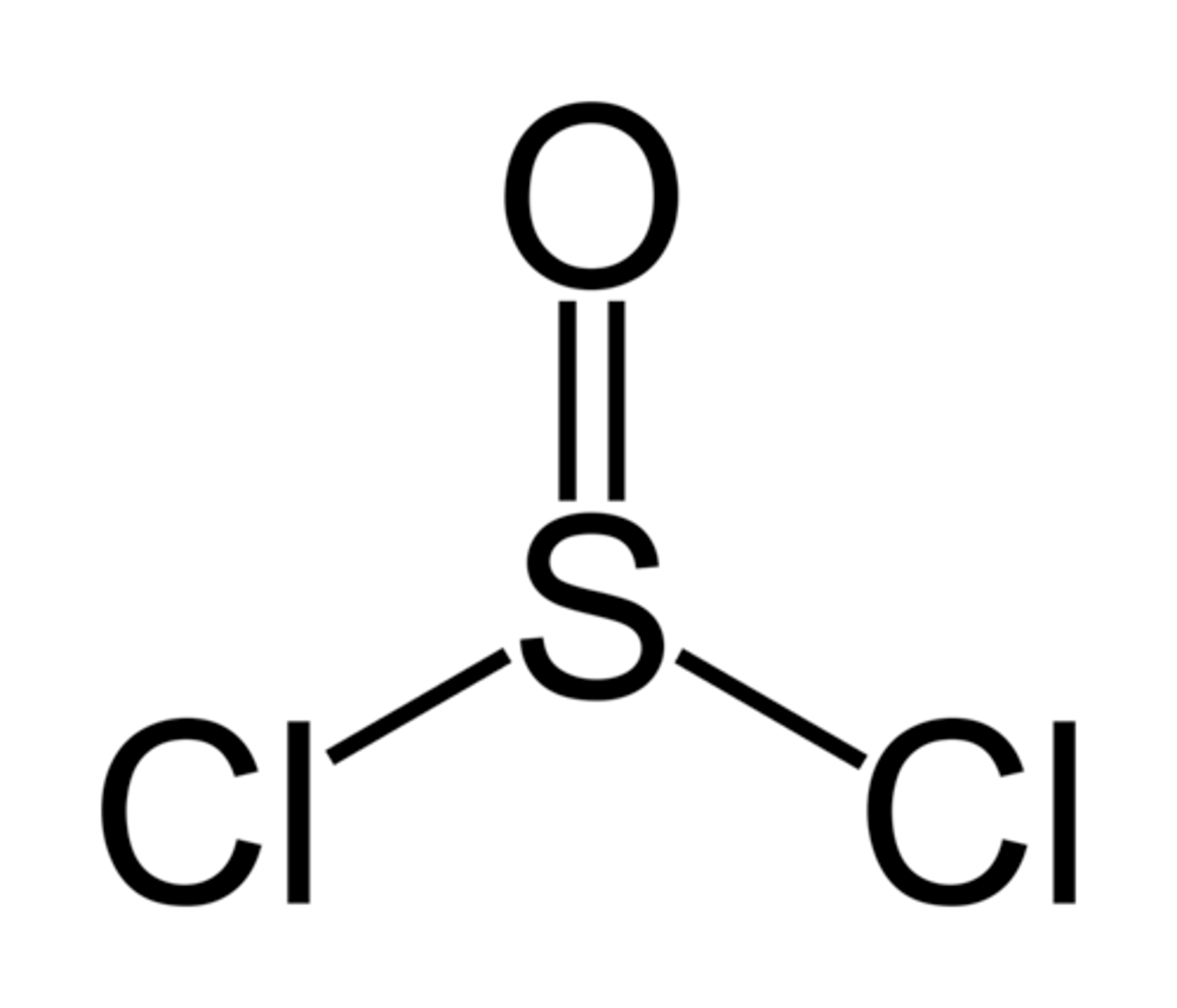
Draw the structure of Thionyl Chloride (SOCl2).
Draw the Acyl Chloride Formation Reaction Mechanism using Thionyl Chloride (SOCl2).
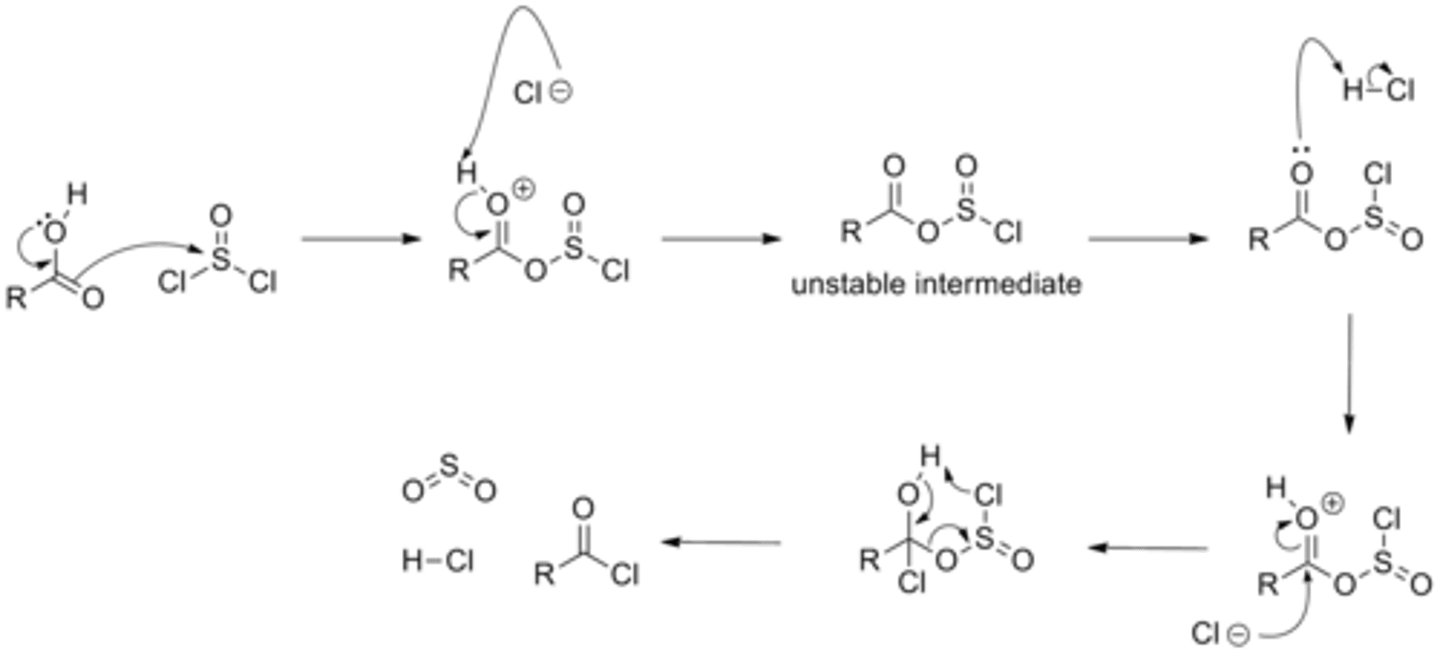
Draw the Acid Anhydride Preparation Mechanism.
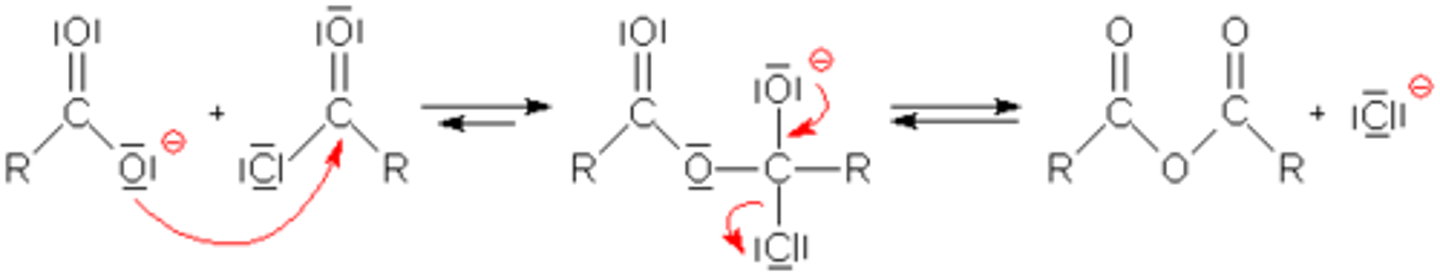
To form an Anhydride from acetic acid, which of the following will you need for your reaction conditions?
(A) Acid
(B) Base
(C) Polar Aprotic Solvent
(D) Heat
(D) Heat
The heat will assist in the condensation. Acetic acid can react with itself by adding just heat.
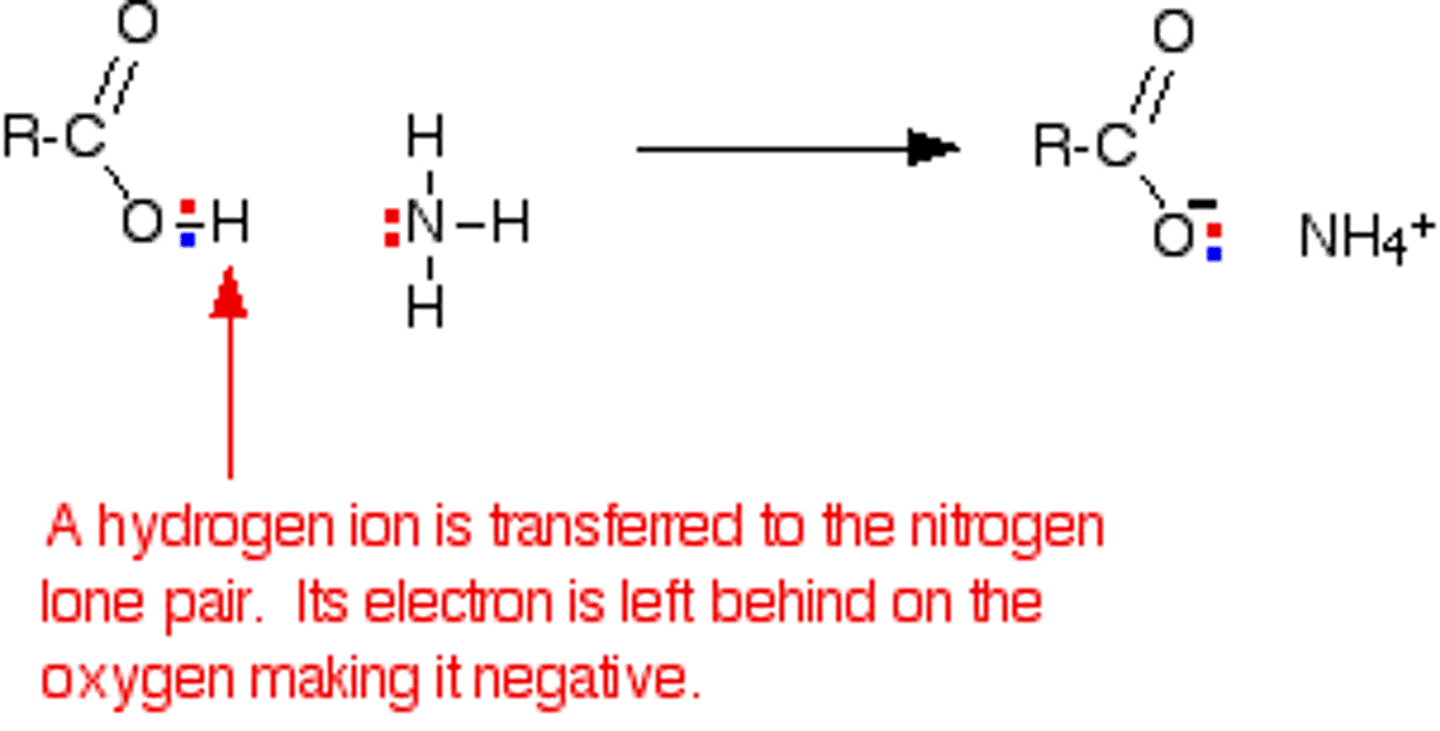
What functional group results when Ammonia is added to a solution containing a Carboxylic Acid?
(A) Carboxylic Acid
(B) Ester
(C) Amide
(D) Carboxylate
(D) Carboxylate
Ammonia will act as a base and steal the proton from the Carboxylic Acid. You might be able to force it into becoming an amide using heat, but this may not work.
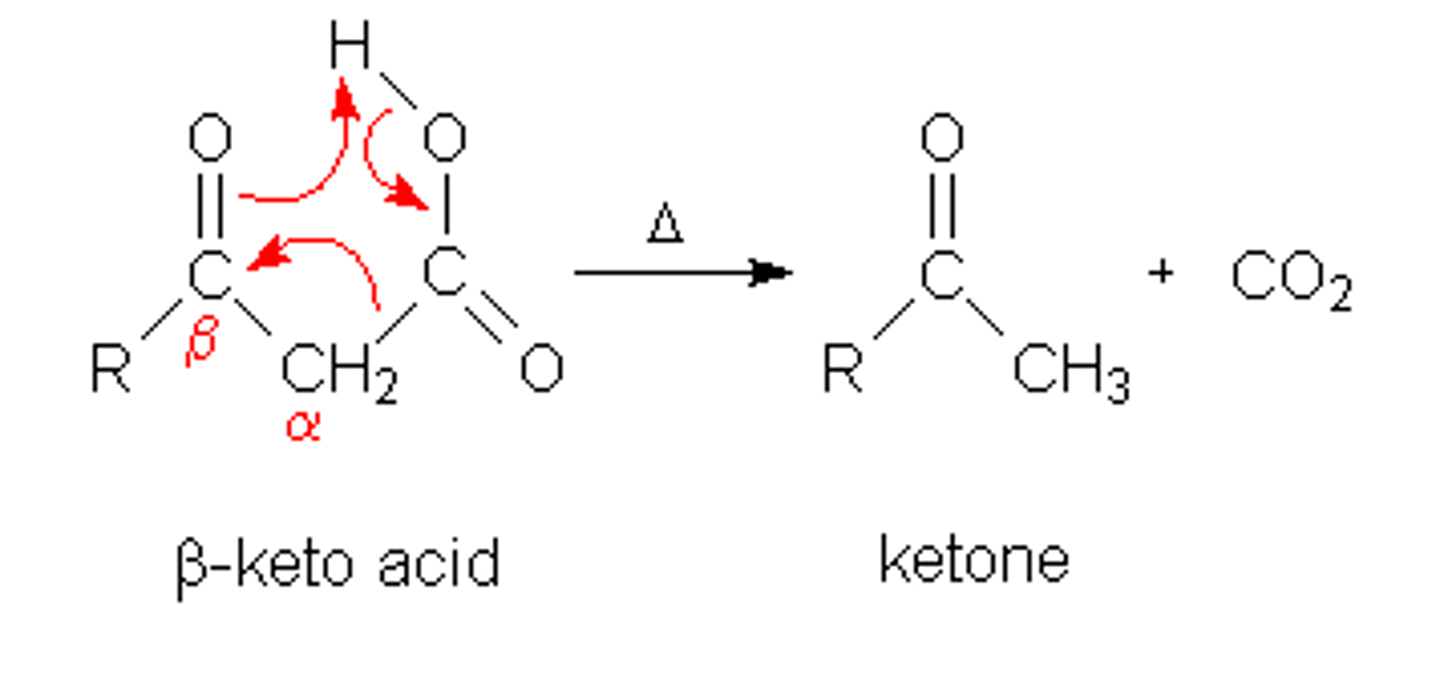
CRB β-keto Carboxylic acids, as the name suggests, have a carbonyl two carbons away from the carboxylic acid. This is a very unstable molecule. Which of the following reactions is a β-keto Acid likely to undergo?
(A) Carboxylation
(B) Condensation
(C) Reduction
(D) Decarboxylation
(D) Decarboxylation
The carboxylic acid will likely be lost, leaving a ketone after the decarboxylation reaction has occured.
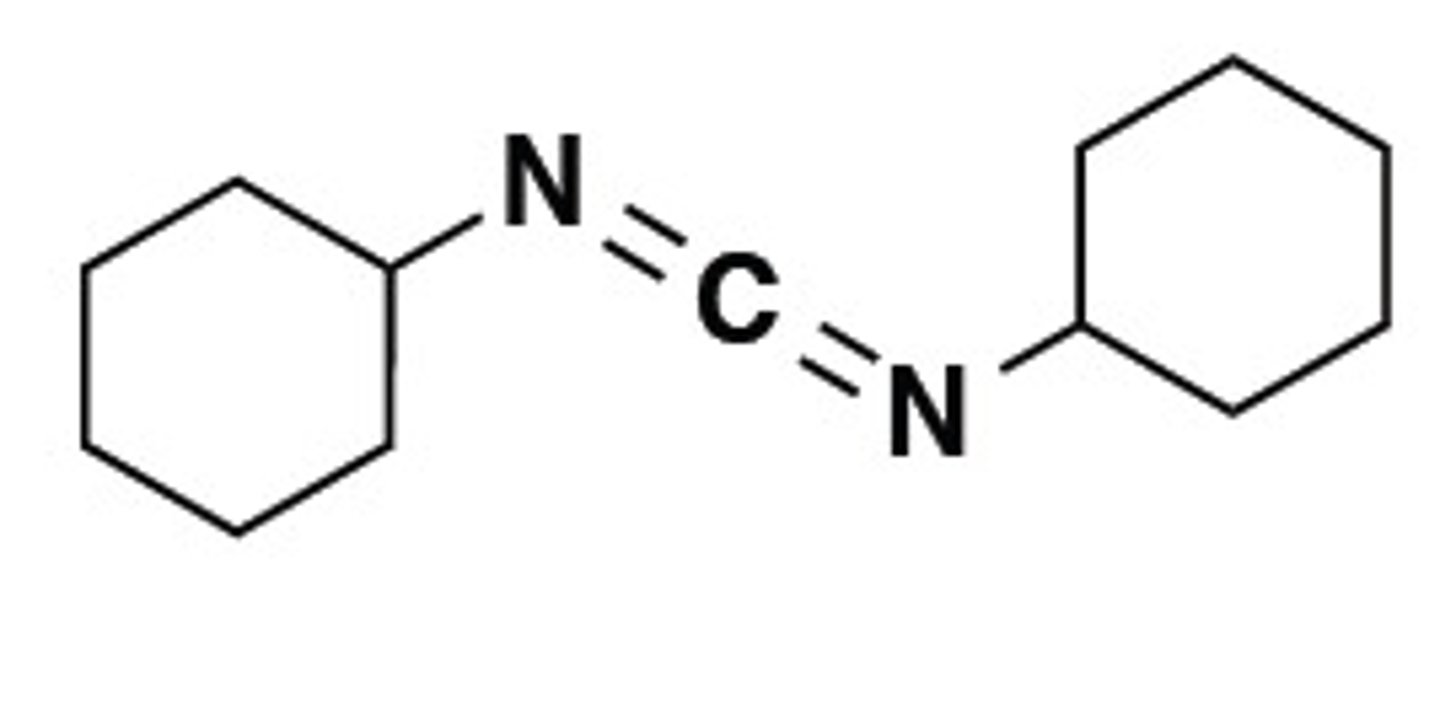
Draw Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC).
Draw Amide Formation Reaction Mechanism using DCC.
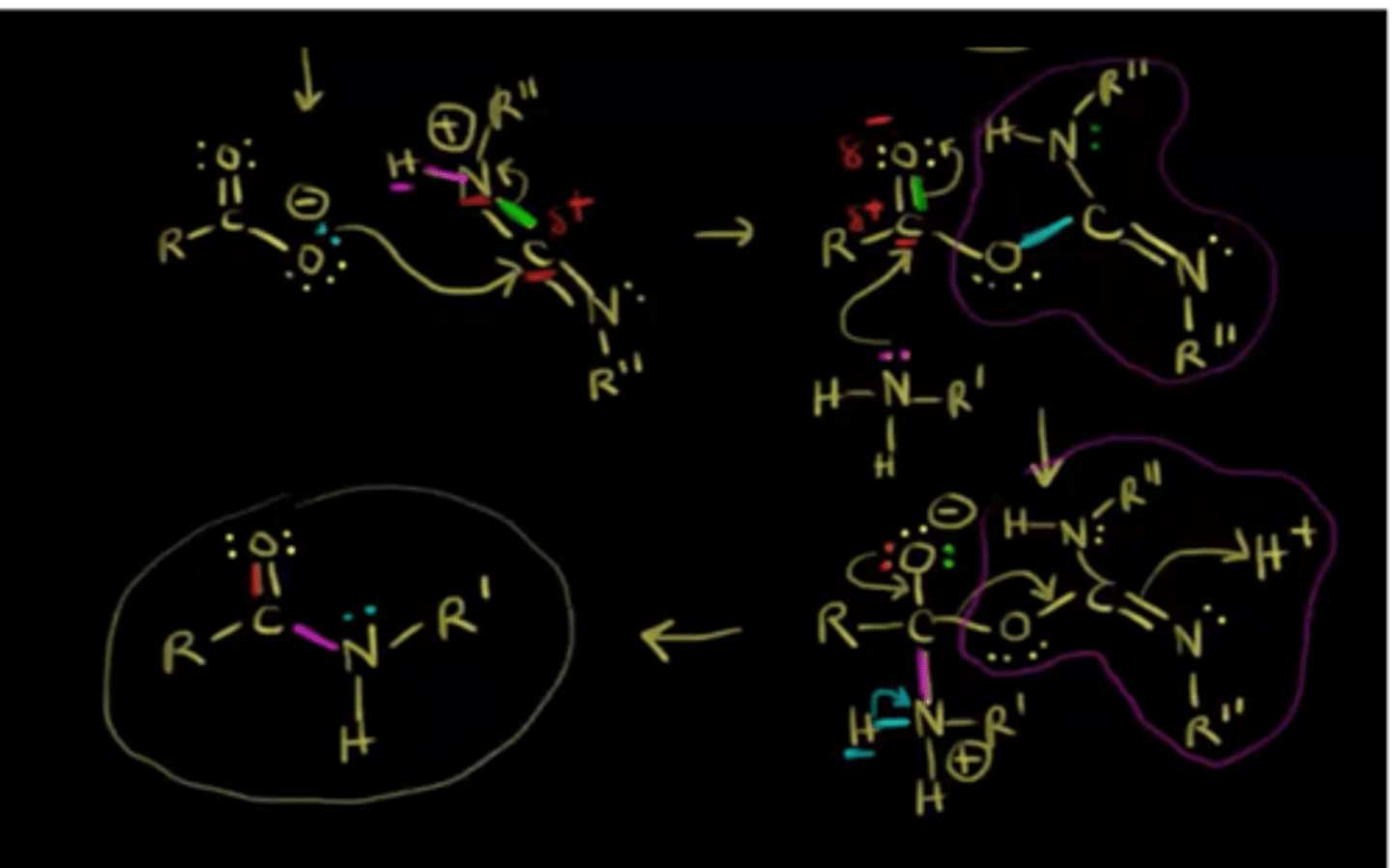
DCC can be used to synthetically produce what important biochemical bond?
(A) Phosphodiester bond
(B) Peptide Bond
(C) Ionic Bond
(D) Metallic Bond
(B) Peptide Bond
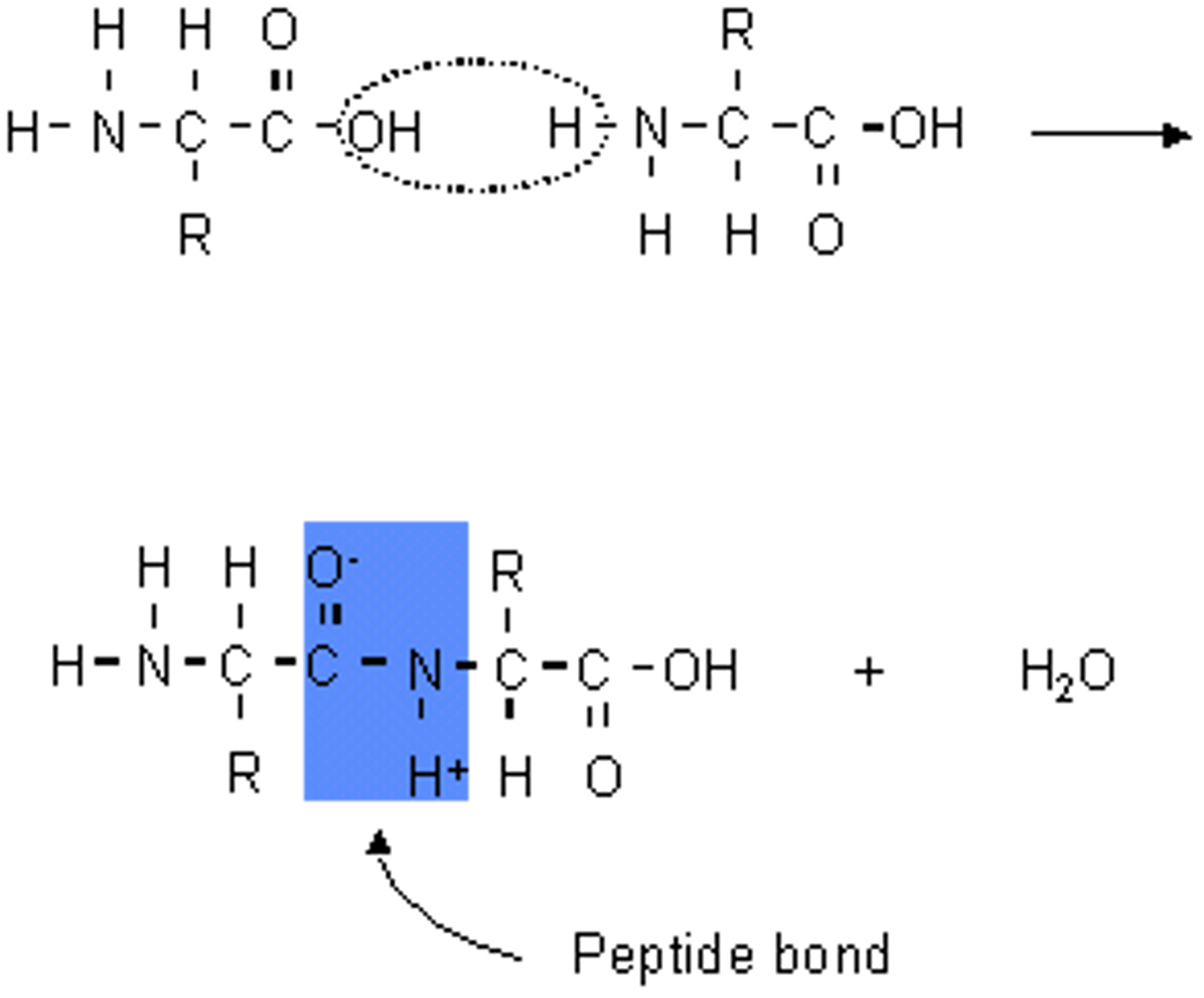
CRB Compare Lactones and Lactams.
Both Lactones and Lactams are cyclic carboxylic acid derivatives.
Lactams are cyclic amides, whereas Lactones are cyclic esters.
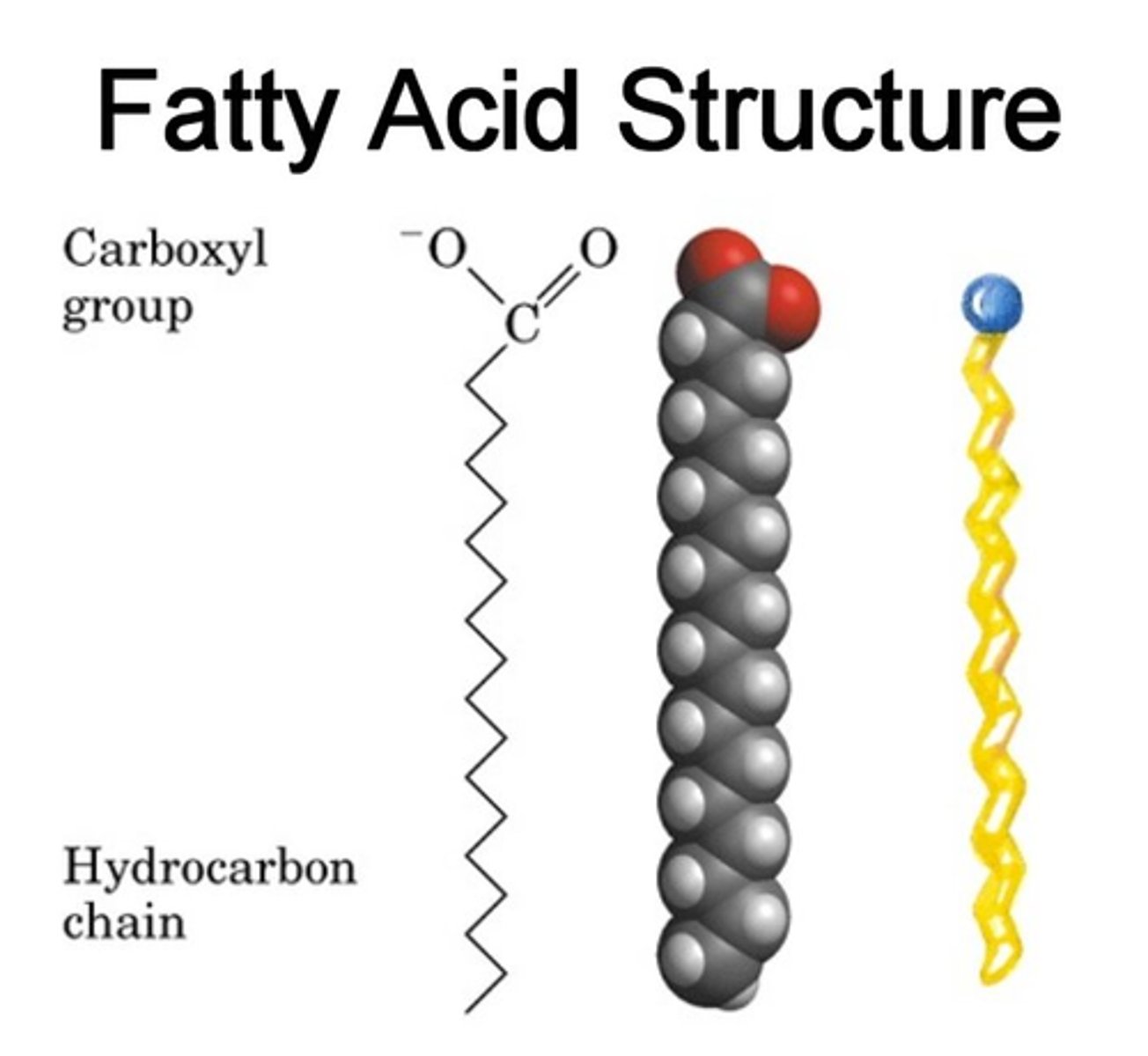
CRB True or false? A long chain carboxylic acid is functionally the same as a fatty acid.
True. A long chain carboxylic acid is functionally the same as a fatty acid.