Gram negative Bacteria
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Pathogenic features of Gram negatives:
Infections: Intraabdominal, UTI, pneumonia, cellulitis, osteomyelitis, meningitis
Endotoxin- lipopolysaccharide
Enterotoxins- E Coli, Shigella, infectious diarrhea
Enteric gram-negative bacilli
Enterobacterales
Escherichia coli
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Klebsiella oxytoca
Klebsiella aerogenes (formerly Enterobacter aerogenes)
Proteus mirabilis and vulgaris
Serratia marcescens
Citrobacter spp.
Morganella morganii
Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter
Enterobacterales
→Enteric gram-negative bacilli
considered part of the normal flora of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
→Primary cause of clinically significant gram negative infections
Currently considered a Threat by the CDC
Enterobacterales- Food borne illness
Salmonella, Campylobacter, E Coli, Vibrio
What is the Most common shiga toxin producing E. Coli
Escherichia coli O157:H7
Resistant Enterbacterales Currently considered a Threat by the CDC
Drug resistant salmonella serotype typhi
Carbapenem resistant enterobacteriaceae
Drug resistant resistant campylobacter
Extended Spectrum Beta lactamase (ESBL) producing enterobacteriaceae
Drug resistant shigella
Drug resistant non typhoidal salmonella
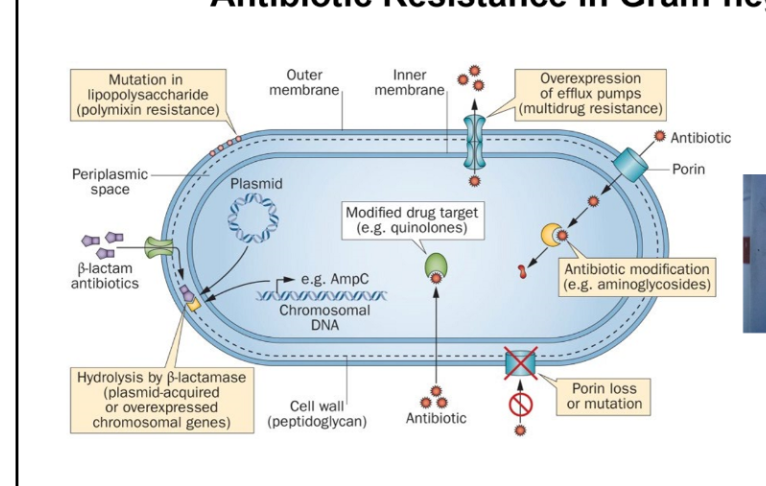
Antibiotic resistance in Gram negatives
Mutation in lipopolysaccharide (e.g., polymyxin resistance)
Hydrolysis by β-lactamase (plasmid-acquired or overexpressed chromosomal genes)
Overexpression of efflux pumps (multidrug resistance)
Modified drug target (e.g., quinolones)
Antibiotic modification (e.g., aminoglycosides)
Porin loss or mutation (reduces antibiotic entry
Non enterobacterales
Non-fermentative, Gram negative bacilli
Organisms
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Acinetobacter baumannii
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
Burkholderia cepacia
Not normal flora
Nosocomial infections
Multi-drug resistant organisms
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pathogenesis
Acute→Invasive, hospital associated
Chronic→Decreased cytotoxicity, resistance, biofilm and adhesion
Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections
CNS infections, Ear and eye infections, bacteremia, skin burn wounds, localized infections, UTIs, Resp tract infections, musculoskeletal tissue, surgical wounds
Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistance
1)Intrinsic
2)Acquired
3)Adaptive
Acinetobacter baumannii
Very similar to Pseudomonas
Mostly found in hospitals- can last days to week on equipment, infection control is key
Infects immunocompromised host
High crude mortality
Infections: pneumonia, open wounds, lines
SUPER RESISTNAT! URGENT THREAT
Acinetobacter baumannii approved agent
Sulbactam-durlobactam (Xacduro)
When should you cover for pseudomonas
Suspected hospital infection until pathogen identified
Important clincial pear for non enterobacterales
INFECTION CONTROL AND PREVENTION
Gram negative Cocci
Haemophilus Influenzae |
Nisseria meningitidis |
Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
Moraxella |
Haemophilus Influenzae
Encapsulates facultative anaerobe 7 serotypes- type b more clinically important Infections → Mostly children: CAP, meningitis, sinusitis, otitis media , conjunctivitis |
Nisseria meningitidis
Treatment required noth higher bacteridicdal antibiotics & high CSF penetration- CEFTRIAXONE |
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Transmission through sex or birth Complications: Pelvic inflammatory disease, epididymitis, disseminated gonococcal disease Very limited options to treat- Zoliflodacin & Gepotidacin (not yet approved) |
Chlamydia trachomatis
Number 1 bacteria STD in the USA 75% women no sx, 50% men no sx |
Gram negative anaerobes
Metronidazole susceptible Bacteroides fragilis- Most common and pathogenic, Lower GI, abdominal ascesses |