Applied Biochemistry - RNA Structure, Synthesis, and Processing - Eukaryotic Gene Transcription
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Info from Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry by Emine E Abali; Susan D Cline; David S Franklin; Susan M Viselli (ONLY INCLUDES EUKARYOTIC RNA SYNTHESIS/TRANSCRIPTION)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What is the function of transcription factors?
Assembly of a transcription initiation complex at the promoter region and the determination of which genes are to be transcribed
Where are the most actively transcribed genes found?
Euchromatin
Where are the most inactive segments of DNA found?
Heterochromatin
What is chromatin remodeling?
The interconversion of euchromatin and heterochromatin
What is an important component of chromatin remodeling?
Covalent modification of histones
What is an example of the covalent modification of histones?
The acetylation of lysine residues at the amino acid terminus of histone proteins
What happens during acetylation of lysine residues?
The positive charge on lysine is eliminated by histone acetyltransferases (HATs)
What happens during deacetylation of lysine residues?
The positive charge on lysine is restored by histone deacetylases (HDACs)
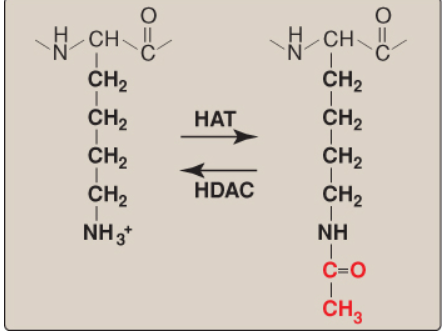
What is this a diagram of?
Acetylation of lysine residues
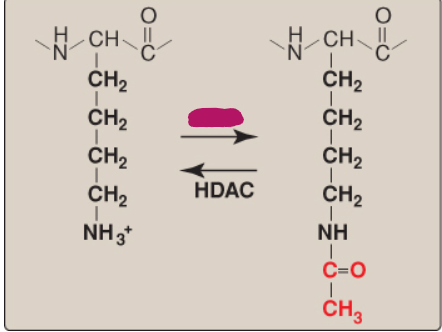
Name this component of lysine acetylation/deacetylation.
histone acetyltransferase
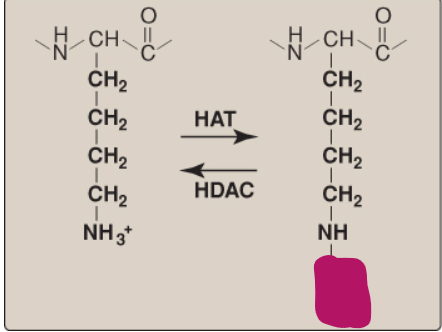
Name this component of lysine acetylation/deacetylation.
COCH3

Name this component of lysine acetylation/deacetylation.
Histone deacetylase (HDAC)
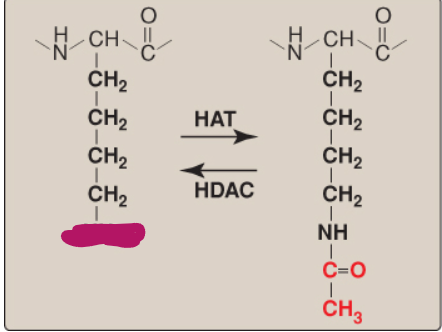
Name this component of lysine acetylation/deacetylation.
NH3+
What is the function of RNA pol I?
Synthesizing the precursor of the 28S, 18S, and 5.8S rRNA in the Nucleolus
What is the function of RNA pol II?
Synthesizing the nuclear precursors of mRNA, and synthesizing snoRNA, snRNA, and miRNA (small ncRNA)
What is the TATA/Hogness box?
A core promoter consensus sequence that activates RNA pol II
T/f: Majority of genes have a Hogness box.
False
What happens in transcription when there is no Hogness box?
Different core promoter elements are present that serve as binding sites for general transcription factors
What are general transcription factors?
The minimal requirements for recognition of the promoter, formation of the preinitiation complex, and initiation of transcription at a basal level.
Where are GTFs synthesized?
The cytosol
Are promoter elements or GTFs cis-acting?
Promoter elements
Are promoter elements or GTFs trans-acting?
GTFs
How does RNA pol II bind to the promoter?
TFIID binds to the TATA box/core promoter element and TFIIF brings the polymerase to the promoter
What is the function of transcription factor IID (TFIID)?
Binding to the TATA box/core promoter element using TATA-binding protein or TATA-associated factors
What is the function of transcription factor IIF (TFIIF)?
Bringing RNA pol II to the promoter
What is the function of transcription factor IIH (TFIIIH)?
Clears the promoter by melting DNA using helicase activity and phosphorylating polymerase by using kinase activity
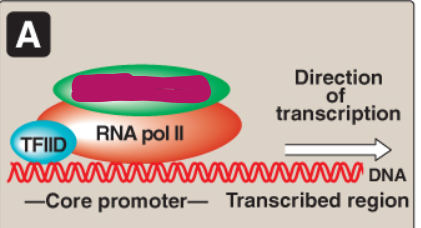
Label this section of the core promoter site.
TFIIA, B, E, F, H
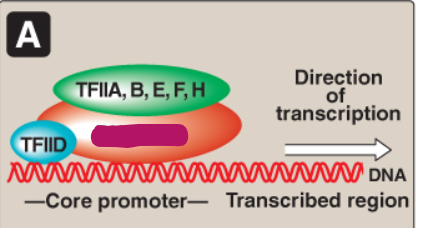
Label this section of the core promoter site.
RNA pol II
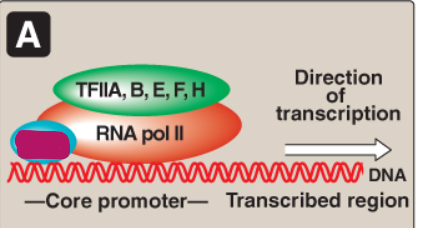
Label this section of the core promoter site.
TFIID
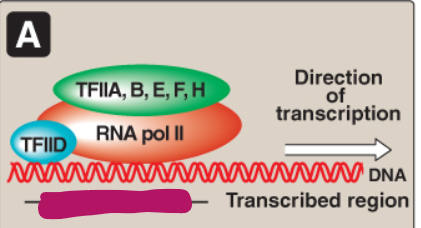
Label this section of the core promoter site.
Core promoter
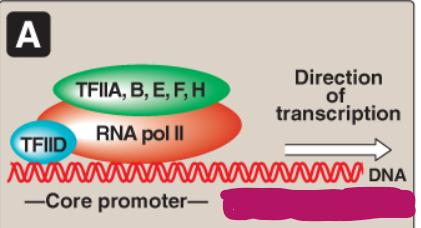
Label this section of the core promoter site.
Transcribed region
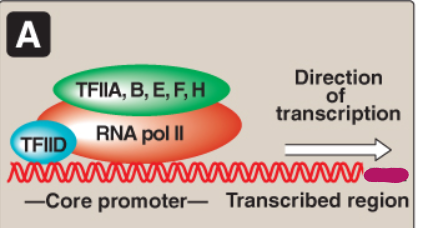
Label this section of the core promoter site.
DNA
Label this section of the core promoter site.
Direction of transcription
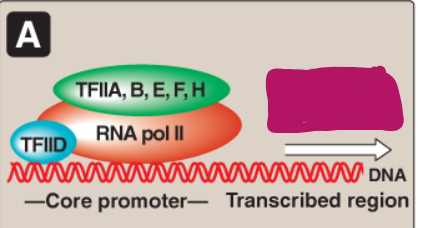
Label this section of the core promoter site.
Promoter
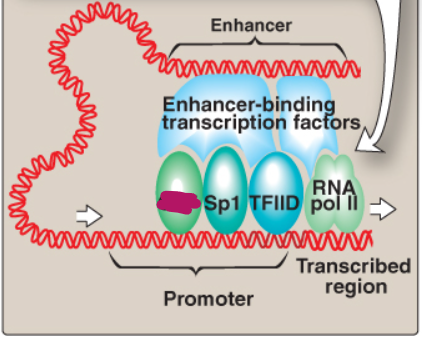
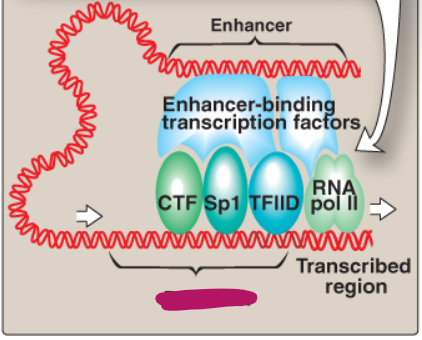
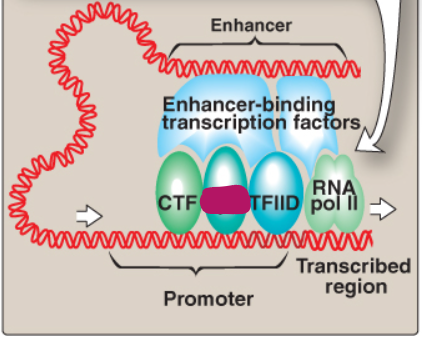
Label this section of the core promoter site.
CTF
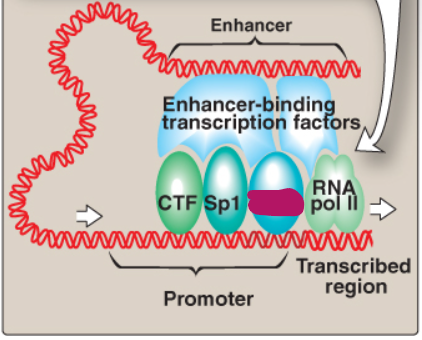
Label this section of the core promoter site.
Sp1
Label this section of the core promoter site.
TFIID
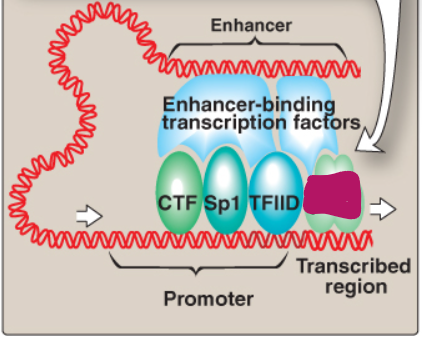
Label this section of the core promoter site.
RNA pol II
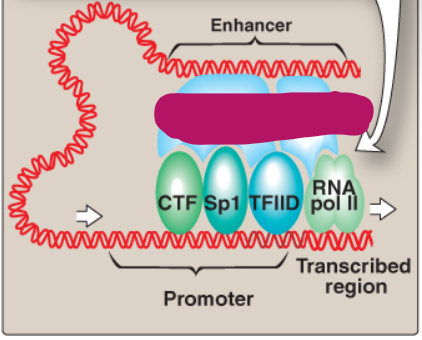
Label this section of the core promoter site.
Enhancer-binding transcription factors
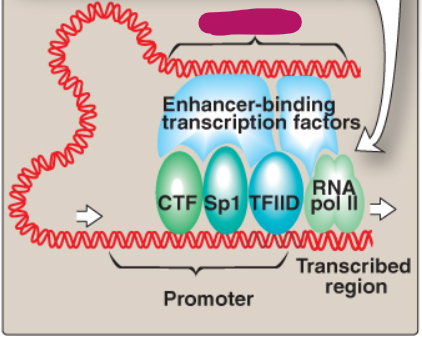
Label this section of the core promoter site.
Enhancer
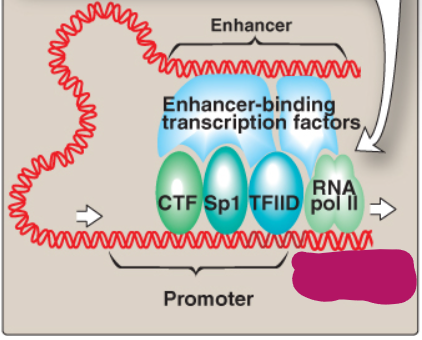
Label this section of the core promoter site.
Transcribed region
What are proximal regulatory elements?
Consensus sequences within 200 nucleotides of the core promoter
What are distal regulatory elements?
Consensus sequences more than 200 nucleotides away from the promoter region
What is the function of specific transcription factors (STFs)?
Regulating the frequency of transcription initiation via the DNA-binding domain and the transcription activation domain
What is the function of the transcription activation domain on STFs?
To recruit the GTF to the core promoter and coactivator proteins (such as HAT)
What is the function of the Mediator?
To activate RNA pol II-catalyzed transcription and regulating transcription initiation by binding the polymerase, the GTF, and the STF.
An 8-month-old male with severe anemia is found to have beta-thalassemia. Genetic analysis shows that one of his beta-globin genes has a mutation that creates a new splice acceptor site 19 nucleotides upstream of the normal splice acceptor site of the first intron. What will be wrong with the new messenger RNA molecule that can be produced from this mutant gene?
Exon 2 will be too long
A 4-year-old child who easily tires and has trouble walking is diagnosed with Duchenne muscular dystrophy, an X-linked recessive disorder. Genetic analysis shows that the patient’s gene for the muscle protein dystrophin contains a mutation in its promoter region. Which part of dystrophin synthesis and processing is most likely to be defective?
Initiation of dystrophin transcription
A mutation to which of the following sequences in eukaryotic mRNA would most likely affect the process by which the 3’-end poly-A tail is added to the mRNA? AAUAAA, CAAT, CCA, GU…A…AG, TATAAA
AAUAAA
Which protein factor identifies the promoter of protein-coding genes in eukaryotes?
TFIID
What is the sequence of the RNA product of the DNA template sequence GATCTAC?
5’-GUAGAUC-3’
What are some motifs through which transcriptional activators bind DNA?
Helix-loop-helix, zinc finger, leucine zipper
What are enhancers?
Special DNA sequences that increase the rate of initiation of transcription by RNA pol II
Where are enhancers usually found?
On the same chromosome as the gene whose transcription they stimulate (but can be farther away or even on the opposite strand of DNA)
What are response elements?
DNA sequences on enhancers that bind STFs, which then interact with other TFs bound to a promoter and with RNA poll II, which stimulates transcription
What is alpha-amanitin?
A toxin that binds RNA pol II and slows its movement, inhibiting mRNA synthesis
Where is alpha-amanitin found?
In a poisonous mushroom known as the death cap
What is the function of RNA pol III?
Synthesizing tRNA, 5S rRNA, and some snRNA and snoRNA