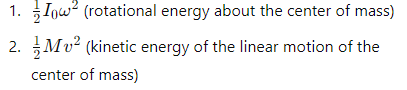8- Moment of inertia
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is the moment of inertia of a rotating body?
Its the coefficient of proportionality between the angular momentum Lz and the angular velocity ω along the axis of rotation
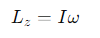
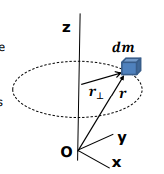
How is the moment of inertia defined for a system of rotating particles?
mj= the mass of each particle
r⊥,j =the distance of the particle from the axis of rotation.
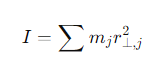
What is the unit of moment of inertia?
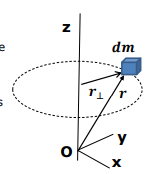
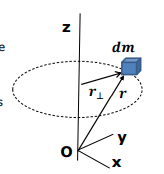
How is the moment of inertia expressed for continuously distributed matter?
r⊥= the distance from the axis of rotation
dm = the mass element.
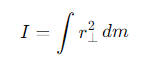
How is the mass element dm expressed in the integral for moment of inertia?
ρ(r)= the mass density at point r
dV = the volume element.
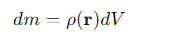
In Cartesian coordinates, how is the moment of inertia integral written?
(x2+y2)= the distance squared from the axis of rotation
ρ(x,y,z)= the mass density.
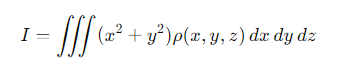
What does the Parallel Axis Theorem describe?
It describes how to calculate the moment of inertia of a body about any axis parallel to the axis through its centre of mass.
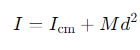
What is the formula for the moment of inertia about an axis displaced by a distance d from the centre of mass?
Icm= the moment of inertia about the centre of mass
M =the mass of the body
d =the distance between the two axes.
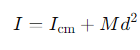
How is the Parallel Axis Theorem applied to a rod for calculating moments of inertia through the center of mass and at the end?
The moment of inertia through the centre of mass is Icm=1/12ML2
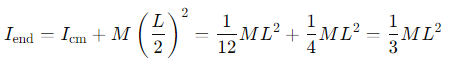
What is the Summation Rule for Moment of Inertia?
The combined moment of inertia of several bodies about the same axis is the sum of the moments of inertia for the component bodies about that axis.
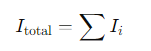
How is motion involving both translation and rotation described?
Motion involving both translation and rotation can be described as the superposition of two components:
Translational motion of the centre of mass.
Rotation around the centre of mass.
What are the three types of motion for a body rolling on a surface?
Slipping
Skidding
Rolling
When does slipping occur?
When Vc>0 (centre of mass moves faster than the rotational motion).
This happens when V>ωR
When does skidding occur?
When Vc<0 (centre of mass moves slower than the rotational motion).
This happens when V<ωR
When does rolling occur?
When Vc=0 (the motion of the centre of mass is synchronized with the rotation).
This happens when V=ωR
What happens during skidding?
The centre of mass moves slower than the point of contact, meaning V<ωRV
The point of contact slides backward relative to the centre of mass causing the object to spin too fast compared to its forward motion.
What happens during rolling?
The centre of mass and the point of contact move at the same velocity, meaning Vc=0 and V=ωR.
The object moves without slipping or skidding, and the rotational motion is synchronized with the translation.
How does friction affect slipping and skidding?
Friction causes the point of contact to slide along the surface, either in the direction of motion (slipping) or against the motion (skidding).
This frictional force produces a torque that either speeds up (slipping) or slows down (skidding) the rotation, eventually bringing the object to rolling motion.
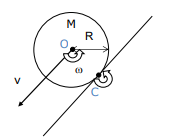
What is the key property of a symmetric body in rolling motion?
The combination of translational motion of the centre of mass and rotation around the centre of mass is equivalent to pure rotation around the point of contact C.
How are the angular velocities around the centre of mass O and point of contact C related in rolling motion?
The angular velocities are the same, denoted as ω
What is the equivalent motion of a body rolling on a surface in terms of rotation?
The motion is equivalent to pure rotation around the point of contact C, where the angular velocity is the same as the rotation around the centre of mass.
How is the moment of inertia about the point of contact related to the moment of inertia about the centre of mass?
I0 = the moment of inertia about the axis of symmetry (centre of mass)
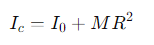
What is the formula for the kinetic energy of a rolling cylinder described as a single rotation around the point of contact?
ω=is the angular velocity
R= the radius of the rolling body.
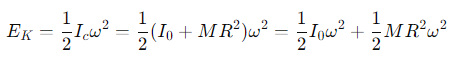
What two components make up the rotational kinetic energy of a rolling body?