chem 107 final
1/200
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
201 Terms
halogens of periodic table
fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts), group 17 elements
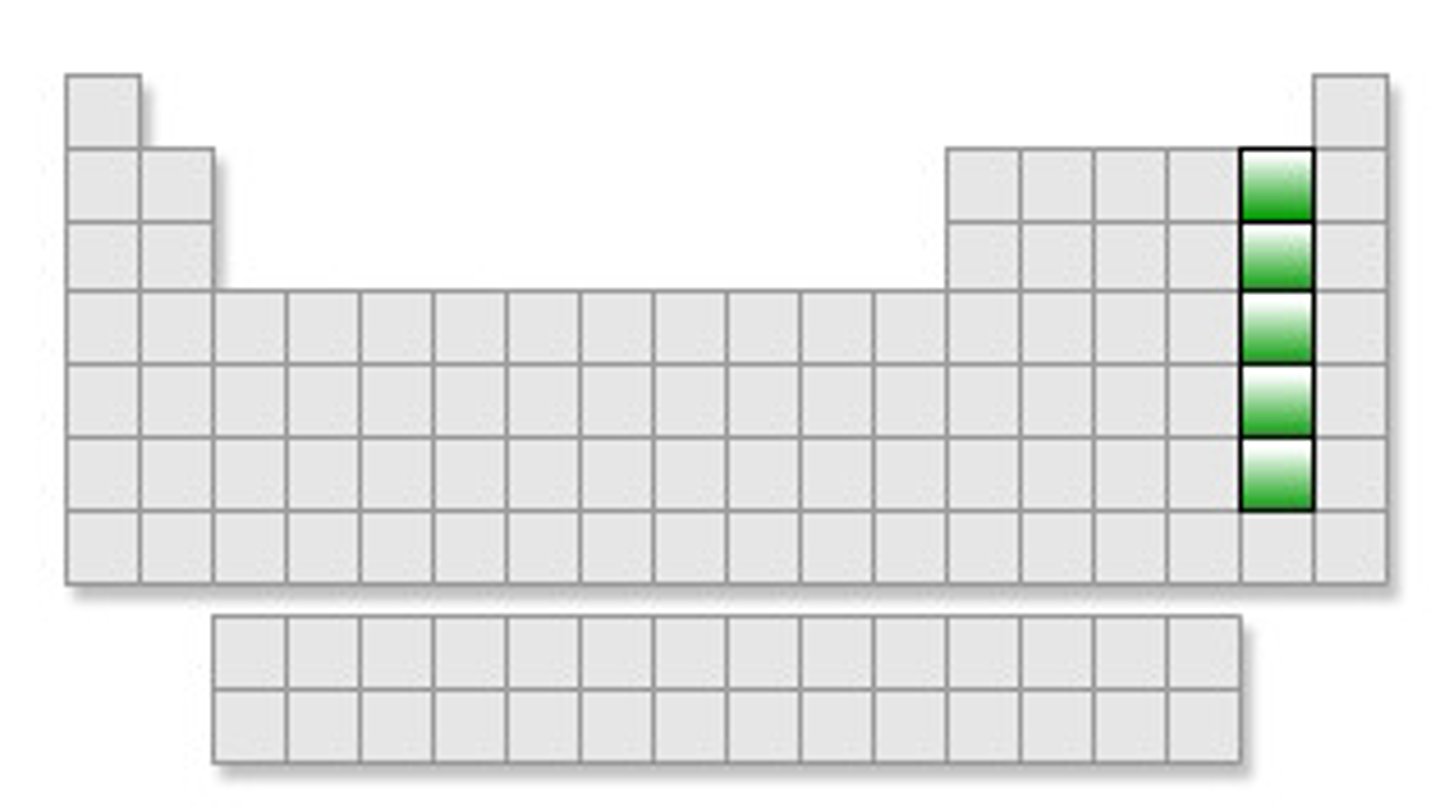
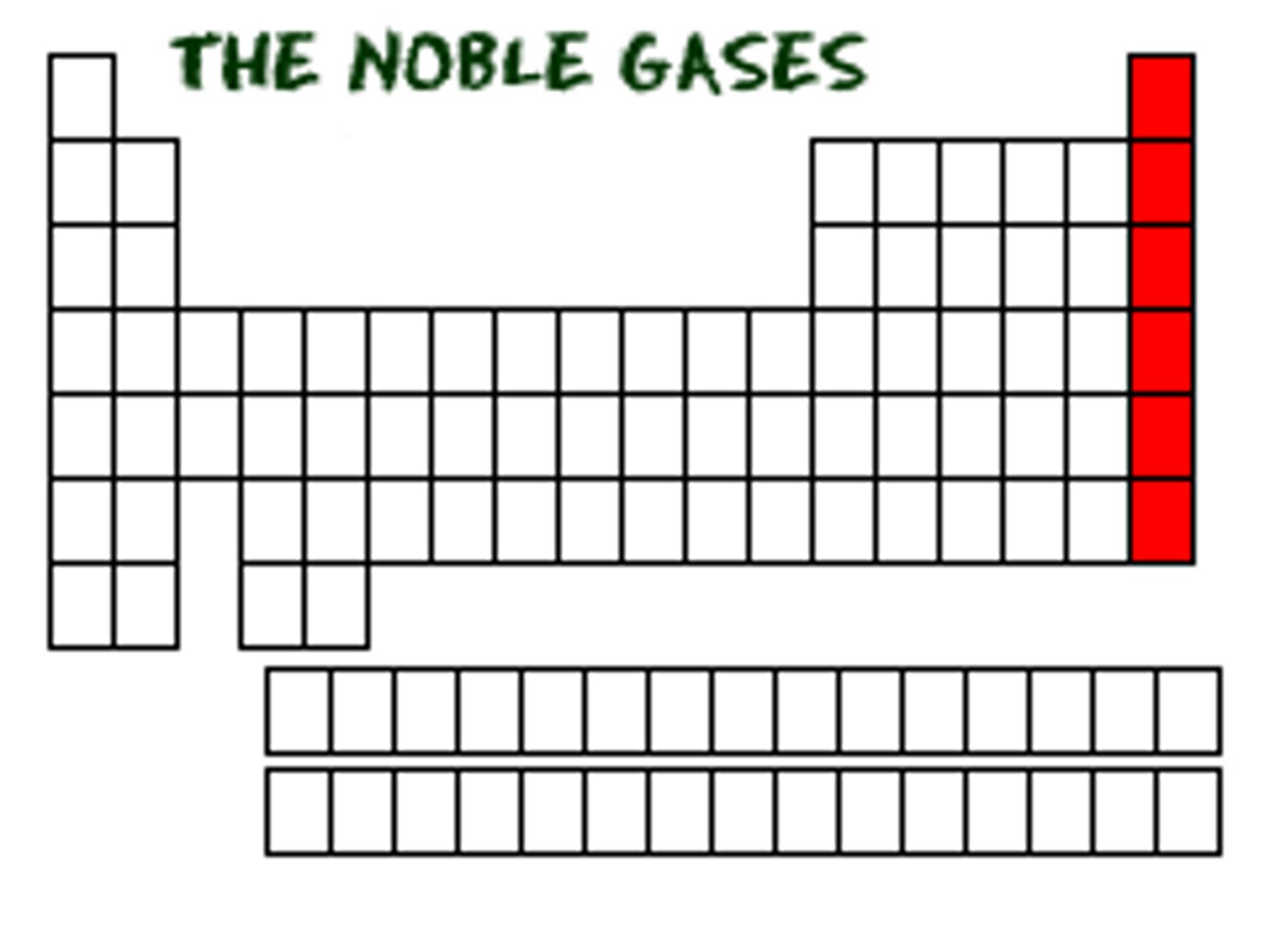
noble gases of periodic table
last column on the right of the periodic table, group 18
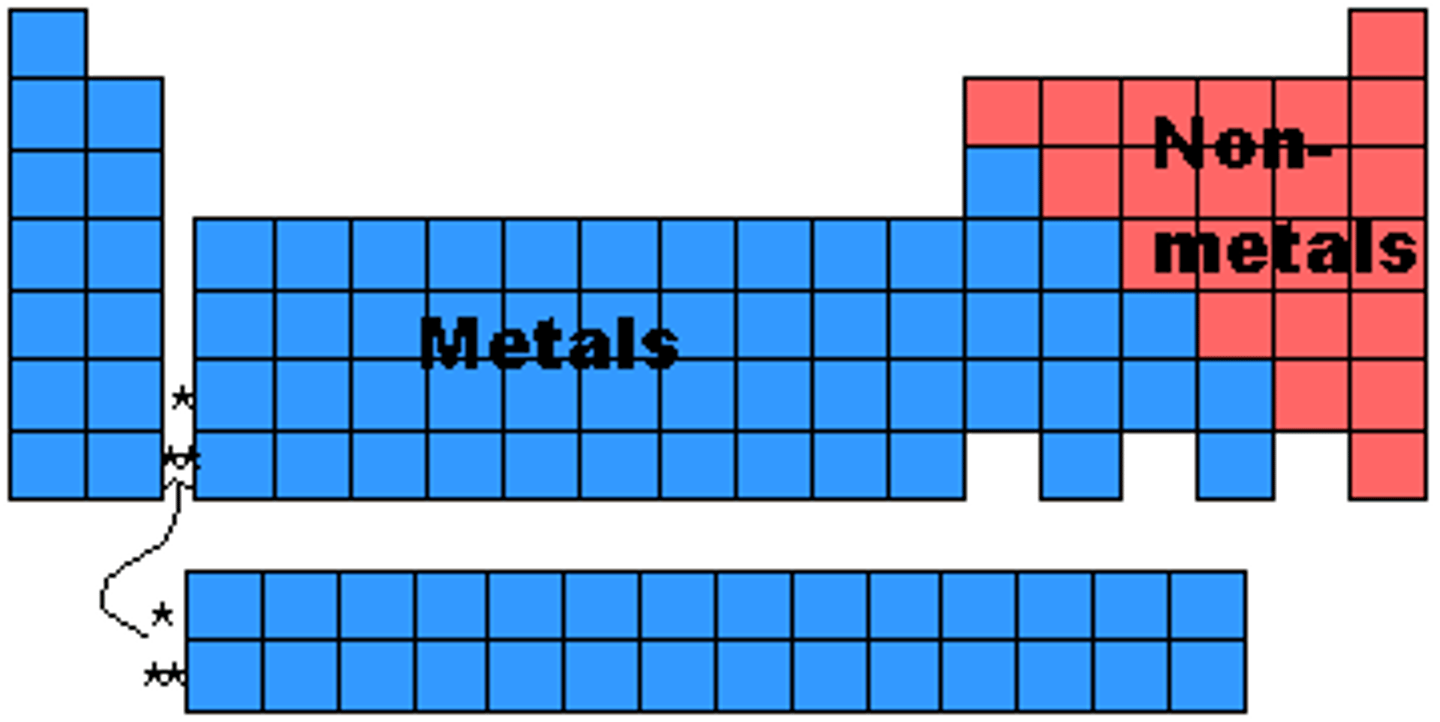
metals of periodic table
left of staircase (except hydrogen)
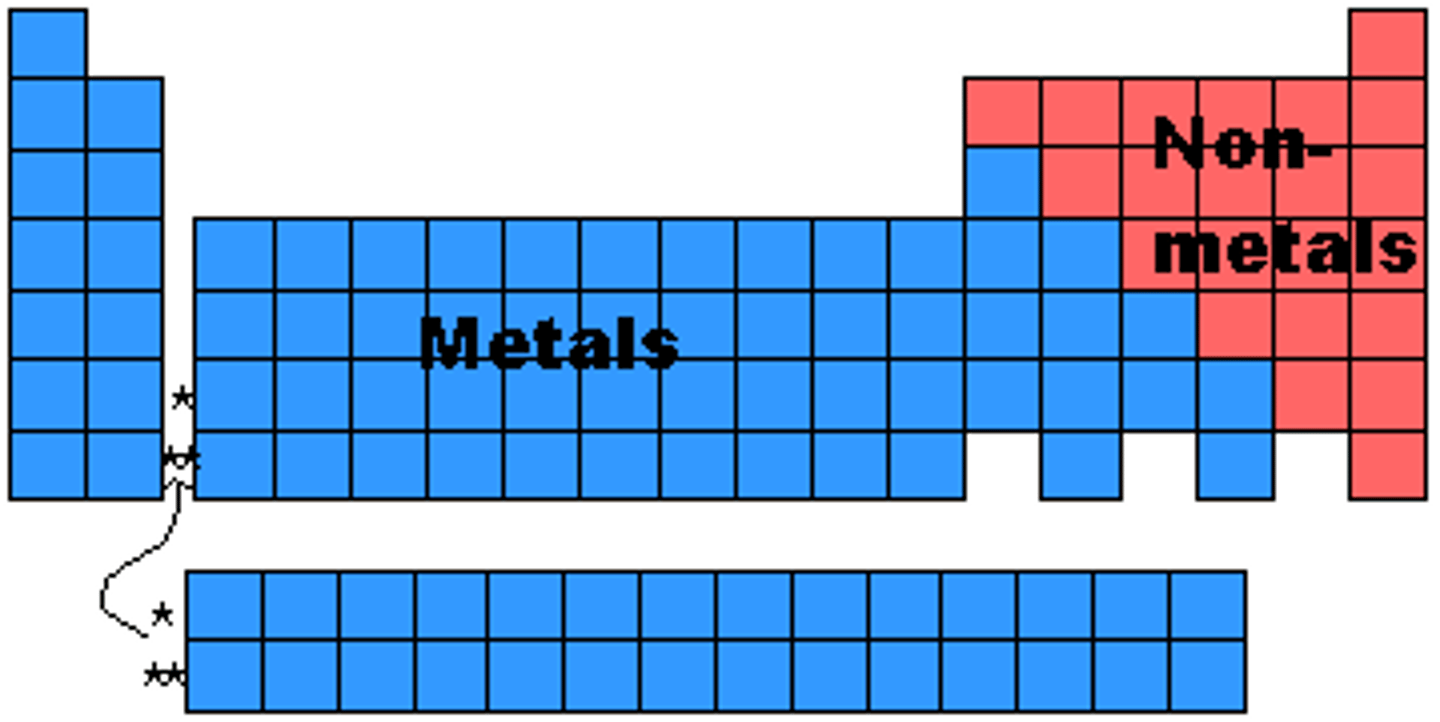
nonmetals of periodic table
right of the staircase and hydrogen
compound
a substance that can be broken down into two or more simpler substances by chemical methods is called a(n)
groups
on a periodic table, the columns of elements with similar properties are
metals
the most numerous of the elements are the
sodium chloride
which is not a mixture?
- a jar filled with rocks and sand
- a glass of Kool-Aid
- seawater
- sodium chloride
air
which is not a pure substance?
- sucrose
- air
- copper wire
- helium
a compound does not exhibit the individual properties of the elements of which it is composed
which differentiates a compound from a mixture of two or more elements?
- a compound is made up of only one element.
- the elements in a compound may be present in varying proportions.
- a compound does not exhibit the individual properties of the elements of which it is composed.
- a compound cannot be made up of more than two elements.
molecule
a(n) __________ is a fixed number of atoms held together by chemical bonds in a certain spatial arrangement
what is the chemical symbol for silver?
Ag
the nucleus of an atom contains
protons and neutrons only
what distinguishes the atoms of one element from another?
the number of protons
the atomic number is the
number of protons in a nucleus
green chemistry
the design of chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances
radon
Which air pollutant is the second-leading cause of lung cancer worldwide, behind tobacco smoke?
ppm
parts per million
troposphere; stratosphere
ozone is considered an air pollutant in the ________ but is a valuable protective layer in the ________
carbon monoxide
which pollutant are you more likely to encounter in dangerous concentrations indoors rather than outdoors?
maroon
which color, as used in the Air Quality Index, warns that the level of a pollutant is hazardous, the most dangerous level?
O2
which component of the air is an element?
toxicity and exposure
what two factors are considered when determining the risk assessment for air pollutants?
coal burning power plants
currently, the primary source of sulfur dioxide emissions into the atmosphere is
O2 and N2
which two gases make up more than ninety-five percent of an inhaled breath?
parts per million (ppm)
a method of expressing low concentrations; 1 ppm is equivalent to 1 milligram
air pollutant
any airborne gas or particle that occurs at a concentration capable of harming living things or disrupting the functioning of the environment
products
the substances that are formed by the chemical change
chemical reaction
the process by which one or more substances change to produce one or more different substances
reactants
elements or compounds that enter into a chemical reaction
balanced chemical reaction
chemical equation with the same number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation
air quality
a measure of the pollutants in the air that is used to express how clean or polluted the air is
atmosphere
the envelope of gases surrounding the earth or another planet
air quality directly affects
health and the environment, making its study crucial for understanding and addressing pollution
what contributes to the ozone hole
chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
ozone in our atmosphere is important because it
absorbs some UV radiation
wavelength
distance between successive peaks in a wave
electromagnetic spectrum
the range of wavelengths or frequencies over which electromagnetic radiation extend
subatomic particles
protons, neutrons, electrons
valance electrons
electrons in the outermost shell
electronic waves
waves that transfer electric and magnetic energy through the vacuum of space
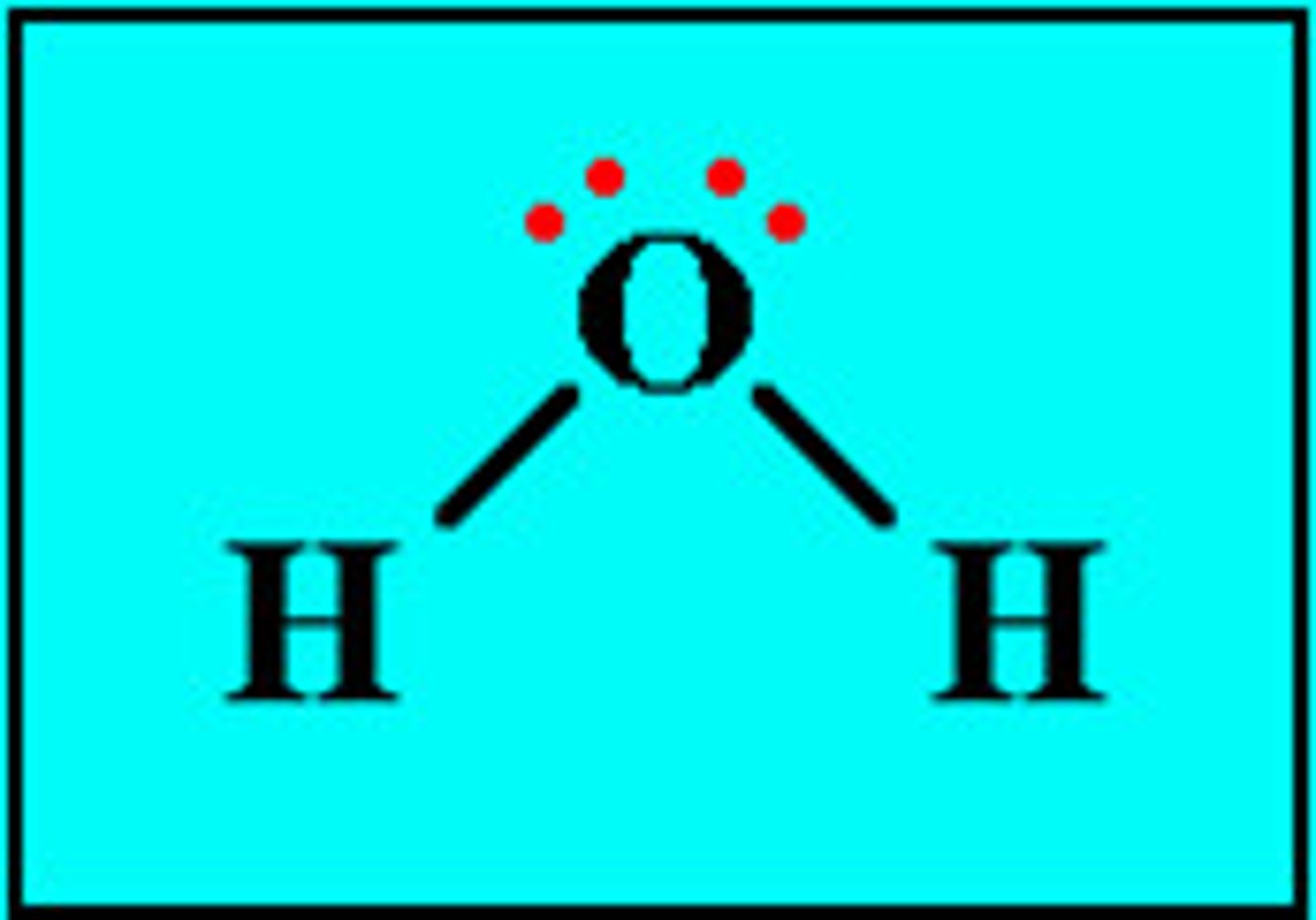
lewis structures
formulas in which atomic symbols represent nuclei and inner-shell electrons, dot-pairs or dashes between two atomic symbols represent electron pairs in covalent bonds, and dots adjacent to only one atomic symbol represent unshared electrons

uv radiation
damaging rays from the sun
frequency
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
ozone layer
a layer in the stratosphere (at approximately twenty miles) that contains a concentration of ozone sufficient to block most ultraviolet radiation from the sun
which process plays the most important role in the greenhouse effect?
energy radiated by the earth is absorbed by the atmosphere
carbon cycle
movement of carbon through living organisms, the atmosphere, the sea, and the earth
what is the effect of the absorption of infrared energy on matter?
it increases the vibration of chemical bonds
climate change
a change in global or regional climate patterns
thermal radiation (IR)
a form of heat transfer where energy is emitted as electromagnetic waves due to the thermal motion of particles within a material
greenhouse gases
gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapor, and ozone in the atmosphere which are involved in the greenhouse effect.
lewis dot structures
diagrams that show valence electrons as dots
molecule vibrations
a periodic motion of the atoms of a molecule relative to each other, such that the center of mass of the molecule remains unchanged
the energy that flows from a warmer body to a colder body is called
heat
in a refinery, the components of petroleum are separated by
fractional distillation
the process by which a solution is heated to its boiling point and the vapors are condensed and collected is known as
distillation
during petroleum refining, catalysts play an extremely important role during the
cracking and reforming processes
in an exothermic chemical reaction
heat is released as the reaction proceeds
a chemical reaction accompanied by a release of energy is called a/an
exothermic reaction
the first law of thermodynamics states that
energy is neither created nor destroyed
the energy of motion is called
kinetic energy
combustion is a chemical process in which a fuel combines with __________ to release energy and form products
oxygen
petroleum (crude oil) is a complex mixture of thousands of substances, the majority of which are
hydrocarbons
the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element
composed of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons
atoms
a positively charged subatomic particle located in the nucleus of an atom
the number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number and defines the element
proton
a neutrally charged subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom
neutrons contribute to the atom's mass and help stabilize the nucleus by reducing repulsion between protons
neutron
a negatively charged subatomic particle that orbits the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels
involved in chemical bonding and determine many of an atom's chemical properties
electron
the dense, central part of an atom that contains protons and neutrons. It holds most of the atom's mass
nucleus
the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
= protons + neutrons
example: a carbon atom with 6 protons and 6 neutrons has a mass number of 12
mass number
atoms of the same element (same number of protons) that have different numbers of neutrons, and therefore different mass numbers
example: Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon
both have 6 protons, but Carbon-12 has 6 neutrons and Carbon-14 has 8
isotopes
the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron of an atom
atomic radius
the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond
electronegativity
the amount of energy required to remove the outermost electron from a neutral atom
ionization energy
a chemical bond formed when two atoms share one pair of electrons
represented by one line: H-H
single bond
a chemical bond formed when two atoms share two pairs of electrons
represented by two lines: O=O
double bond
a chemical bond formed when two atoms share three pairs of electrons
represented by three lines: N≡N
triple bond
formed between metals and nonmetals
electrons are transferred from one atom to another
properties: high melting/boiling points, solid at room temperature, conducts electricity when melted or dissolved in water
ionic compounds
formed between two nonmetals
electrons are shared between atoms
properties: lower melting/boiling points, can be solid, liquid, or gas, poor conductors of electricity
covalent compounds
diagrams that show the valence electrons of atoms and how they are shared or transferred in a molecule
used to represent bonding and lone pairs
lewis structures
occurs when more than one valid Lewis structure can be drawn for a molecule
the actual structure is a blend (resonance hybrid) of all possible structures.
example: ozone (O₃)O=O-O ↔ O-O=O
(the double bond shifts positions; the actual structure is a hybrid of both)
resonance
a chemical reaction in which a substance (usually containing carbon and hydrogen) reacts rapidly with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy (usually as heat and light)
general form: Hydrocarbon + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O + energy
example: CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O + energy
a major source of energy in engines and power plants
combustion reaction
a reaction that releases energy to the surroundings, usually in the form of heat
surroundings feel warmer
example: combustion
exothermic reaction
a reaction that absorbs energy from the surroundings
surroundings feel cooler
example: photosynthesis
endothermic reaction
nonrenewable energy sources (such as coal, oil, and natural gas) formed from the remains of ancient organisms
contain stored chemical energy that is released when burned
drawbacks: Release carbon dioxide (a greenhouse gas), contribute to air pollution and climate change
fossil fuels
renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biomass that do not rely on fossil fuels
benefits: lower environmental impact, sustainable, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions
alternative energy
earth's water is unevenly distributed between saltwater and freshwater:
97%: saltwater (oceans)
3%: freshwater
of that 3%:
~69% is frozen in glaciers and ice caps
~30% is underground
<1% is accessible surface water (lakes, rivers)
water distribution
gases in the atmosphere that trap heat and contribute to the greenhouse effect
major GHGs: carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), nitrous oxide (N₂O), water vapor, and ozone (O₃)
greenhouse gases
increased GHGs from human activities (like burning fossil fuels) enhance the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming and climate change
effects include: rising sea levels, melting glaciers, more extreme weather, and disruptions to ecosystems
environmental impact of greenhouse gases
a scale that measures how acidic or basic (alkaline) a substance is
ranges from 0 to 14
pH < 7: acidic
pH = 7: neutral (e.g., pure water)
pH > 7: basic (alkaline)
significance: pH affects chemical reactions, biological processes, and environmental health
organisms often survive only within a narrow pH range
pH scale
the pH scale is logarithmic, meaning each whole number change represents a tenfold change in hydrogen ion concentration
formula:
pH = –log[H⁺]
(where [H⁺] is the concentration of hydrogen ions in moles per liter)
examples
a solution with a pH of 3 has 10 times more hydrogen ions than a solution with a pH of 4
a pH of 1 is 100 times more acidic than a pH of 3
relationship between pH and [H⁺] (hydrogen ion concentration
a large molecule made of repeating smaller units called monomers linked together by chemical bonds
can be natural (e.g., DNA, proteins, cellulose) or synthetic (e.g., plastics, nylon)
polymers
polymers that soften when heated and harden when cooled, allowing them to be remolded
properties: flexible, recyclable, lightweight
uses: packaging, bottles, plastic bags, 3D printing
thermoplastics
polymers that harden permanently when heated and cannot be remelted
uses: electrical insulation, adhesives, cookware handles
thermosetting plastics
A specific group of atoms in a molecule that determines the molecule’s reactivity and properties.
Functional Group | Structure | Common in | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
Hydroxyl | –OH | Alcohols | Polar, can form hydrogen bonds |
Carboxyl | –COOH | Carboxylic acids | Acidic, can donate a hydrogen ion (H⁺) |
Amino | –NH₂ | Amines, amino acids | Basic, involved in peptide bonds |
Ester | –COO– | Esters (fragrances, fats) | Sweet-smelling, used in flavors/scents |
Carbonyl | C=O (in ketones/aldehydes) | Sugars, solvents | Involved in reactivity and solubility |
functional group
the process of collecting and processing materials to make new products
plastics ______ involves sorting, melting, and reforming thermoplastics.
some polymers are difficult to recycle due to contamination or chemical structure.
recycling
problems: Many synthetic polymers are non-biodegradable, contributing to plastic pollution
solutions:
biodegradable plastics (break down naturally)
bio-based polymers (made from renewable sources)
improved recycling systems
reducing single-use plastics
sustainability in polymer use
a simple sugar (monosaccharide) and a primary energy source for the body
used in cellular respiration to produce ATP (energy)
found in carbohydrates such as fruits, bread, and pasta
glucose
a type of fat made from one glycerol molecule and three fatty acids
long-term energy storage
provide more energy per gram than carbohydrates or proteins
found in oils, butter, and fatty foods
triglycerides
essential organic compounds needed in small amounts to support metabolism, immune function, and overall health
vitamins
dissolve in water; not stored in the body
excess amounts are excreted in urine
must be consumed regularly
examples: vitamin C, b-complex vitamins
water-soluble vitamins