UK PPL Operational Procedures
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
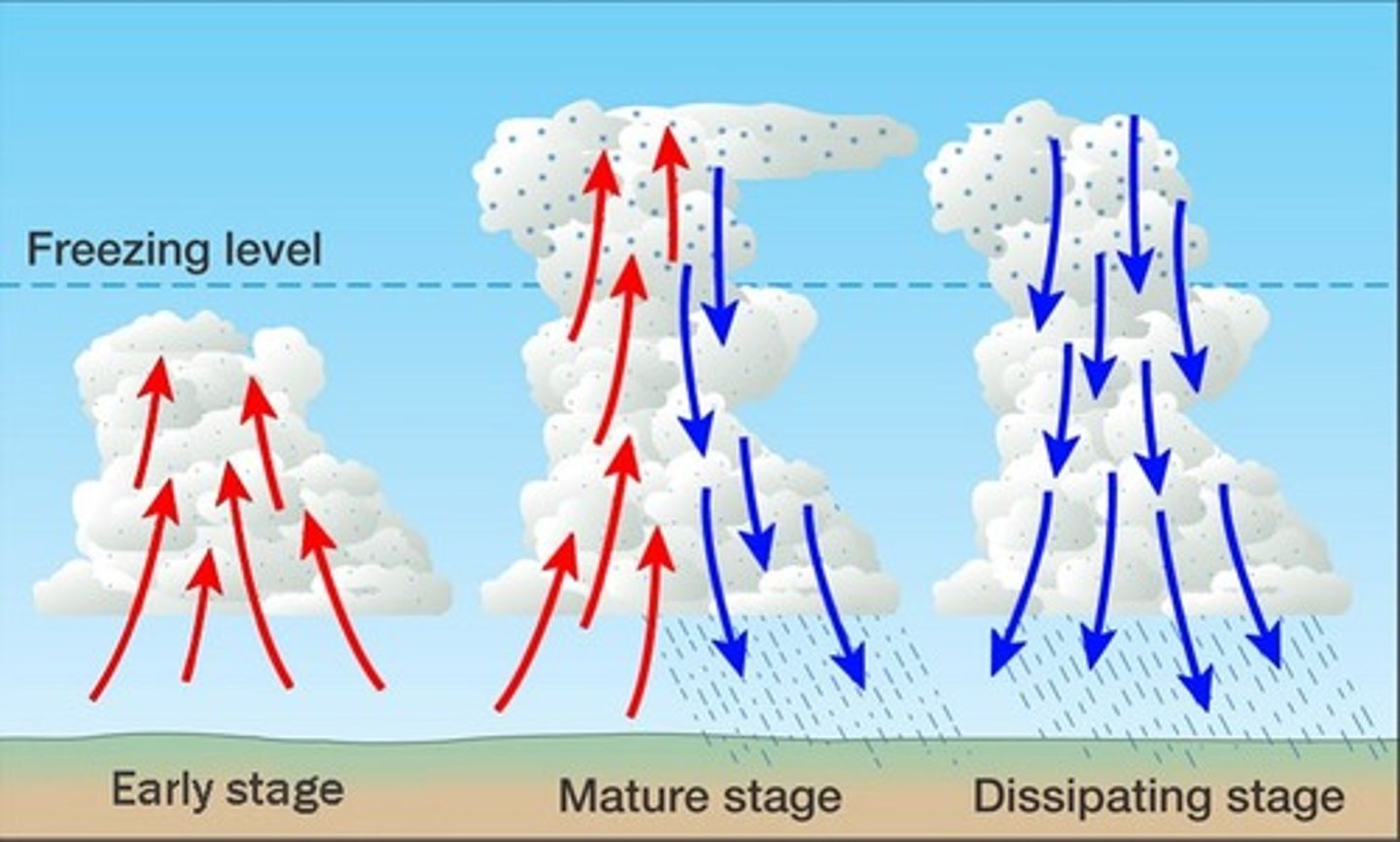
What are updrafts and downdrafts?
Vertical components of wind.
What are the six acts of unlawful interference?
-Unlawful seizure of aircraft in flight
-Unlawful seizure of aircraft on the ground
-Hostage-taking on board an aircraft or on aerodromes
-Forcible intrusion on board an aircraft, at an airport or on the premises of aeronautical facility
-Introduction on board an aircraft of a weapon or hazardous device or material intended for criminal purposes
-Communication of false information as to jeopardise the safety of an aircraft in flight etc.
What is aerial work?
Aircraft operation in which an aircraft is used for specialised services such as agriculture or surveying

What are Aerodrome Operating Minima (AOM)?
The limits of usability of an aerodrome for take-off, landing in precision approach, landing in approach which vertical guidance, landing in non-precision approach
What is an Aircraft Operating Manual?
A manual containing the normal, abnormal and emergency procedures relating to the operation of the aircraft
What is a Take-Off Alternate Aerodrome?
An alternate aerodrome at which an aircraft would be able to land shortly after take-off and it is not possible to use the aerodrome of departure
What in an En-Route Alternate Aerodrome?
An alternate aerodrome at which an aircraft can land at if a diversion becomes necessary while en route
What is a Destination Alternate Aerodrome?
An alternate aerodrome at which an aircraft can land should be inadvisable to land at the aerodrome of intended landing
What is Area Navigation (RNAV)?
navigation that allows aircraft to fly any desired path within coverage of ground or space navigation aids
What is Continuing Airworthiness?
The set of processes by which an aircraft remains in a condition safe for operation throughout its operating life
What is an Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT)?
Equipment which broadcasts distinctive signals on designated frequencies
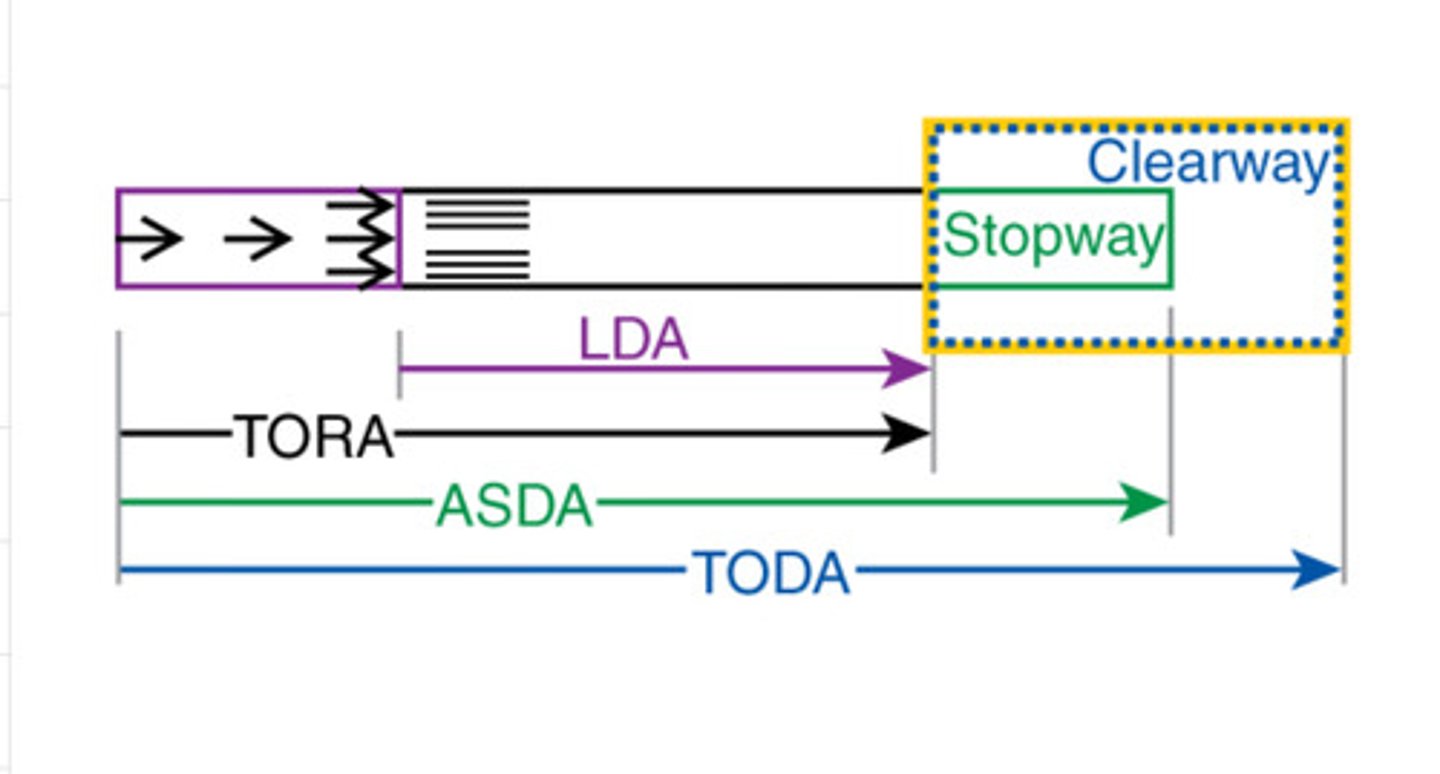
What is take-off run available (TORA)?
The length of runway declared available and suitable for the ground run of an aeroplane taking off
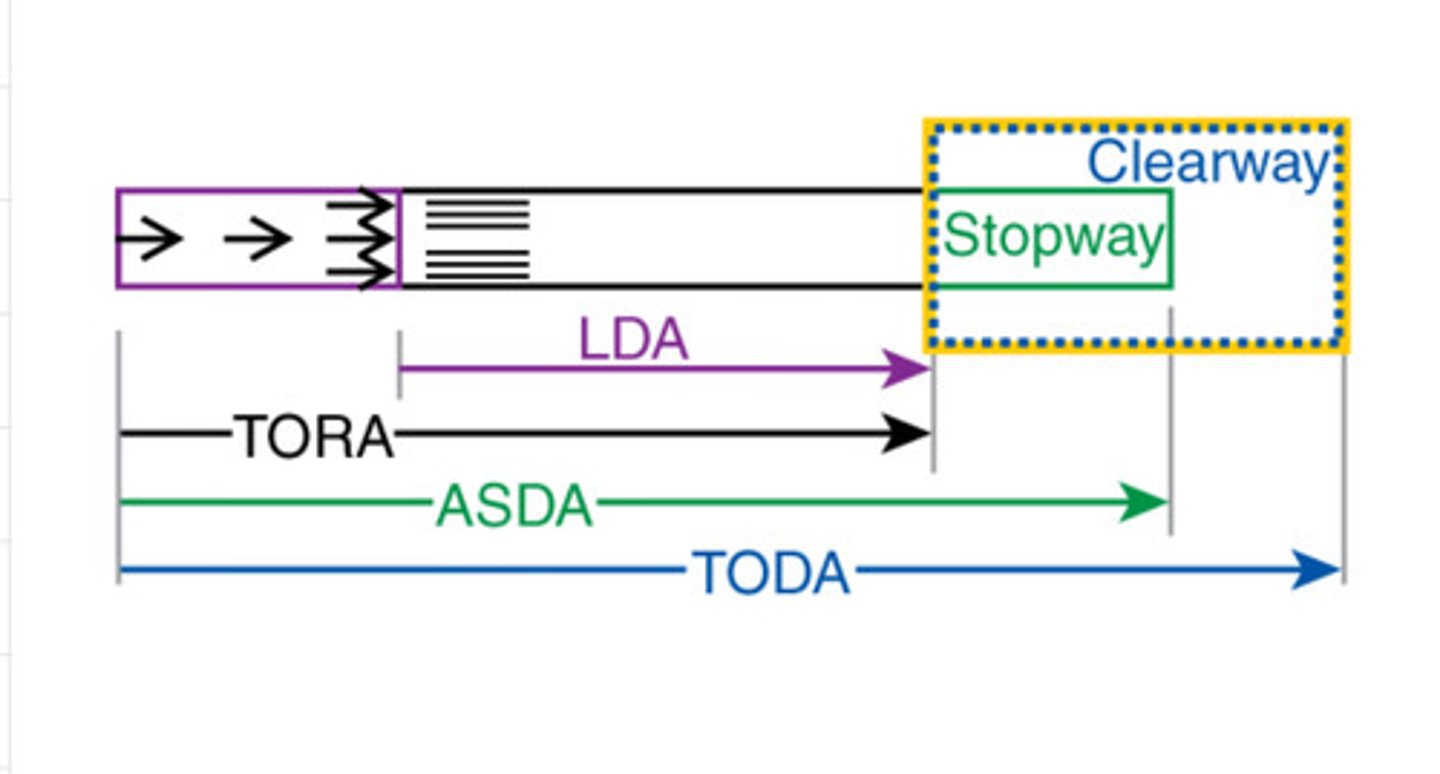
What is take-off distance available (TODA)?
The length of the take-off run available plus the length of the clearway, if provided
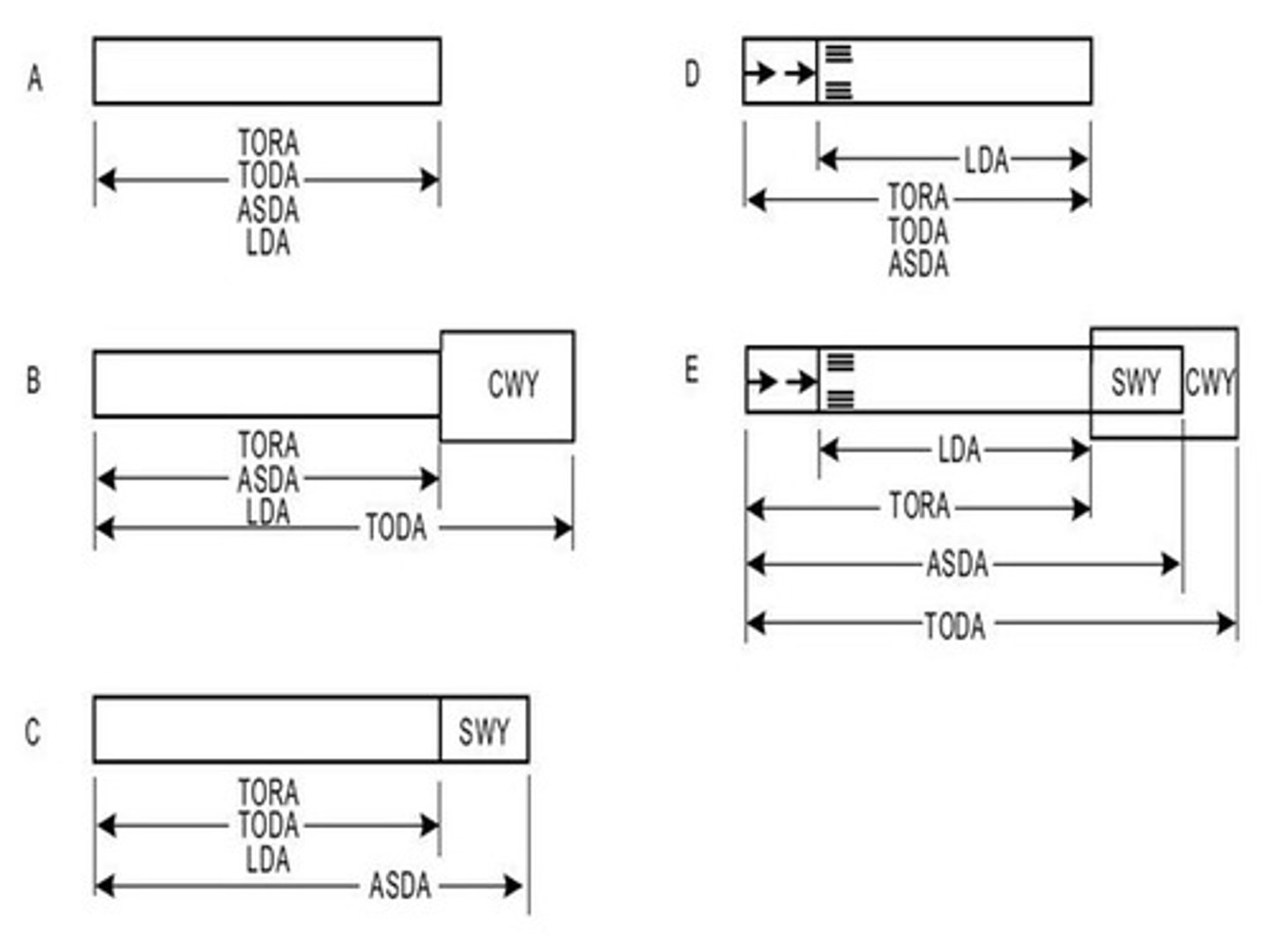
What is accelerate-stop distance available (ASDA)?
The length of the take-off run available plus the length of the stopway, if provided
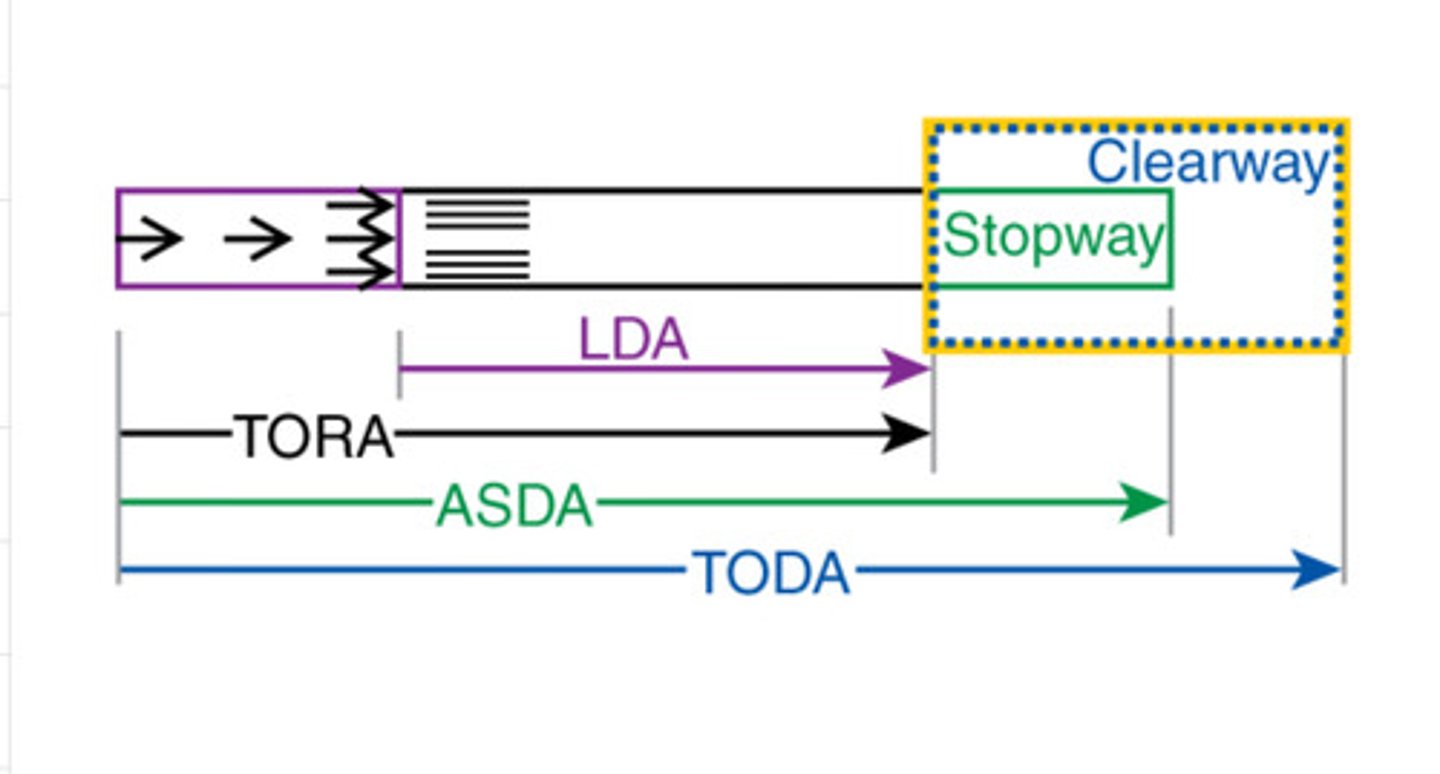
What is landing distance available?
The length of the runway declared available and suitable for the ground run of an aeroplane landing
What should a pilot do if they are in an emergency situation which endangers the safety of the aeroplane or people and requires the pilot to take action which violates local regulations or procedures?
They should notify the appropriate authority as soon as possible
What should the pilot in command make sure of before commencing a flight?
That the aerodrome facilities, communication facilities and navigation aids required are adequate for the safe operation of the aeroplane
What must the pilot in command make sure the crew members and passengers are briefed on?
Seat belts, emergency exits, life jackets, oxygen equipment, any other emergency equipment
What must the pilot in command be satisfied with before beginning a flight?
The plane is airworthy, the instruments are appropriate to expected conditions, necessary maintenance has been completed, weight and balance are within safe limits for flight, cargo is correctly stowed, operating limitations will not be exceeded
What conditions during flight should be reported?
Weather conditions likely to affect the safety of other flights, or hazardous flight conditions such as volcanic ash and dust storms
What must an aeroplane be equipped with?
First aid kit, fire extinguisher, a seat for each person on board, seat belts for each seat, Flight Manual, suitable aeronautical charts, procedures for interception, spare fuses
What must aeroplanes operating on VFR flights be equipped with?
Magnetic compass, accurate timepiece, altimeter, airspeed indicator, additional instruments
What must an aircraft on an extended flight over water more than 50 nm from land be equipped with?
One life jacket for each person on board
What must an aircraft on an extended flight over water more than 100 nm from land be equipped with?
One life jacket for each person on board, life saving rafts, equipment for making pyrotechnic distress signals
What must the amount of fuel to be carried permit when the flight is under VFR by day?
For at least 30 minutes at cruising altitude
Where should flight crew members be during take-off and landing?
Flight deck duty at their stations
Where should flight crew members be en route?
Remain at their stations except when their absence is necessary for performance duties in connection with operations of the aeroplane or for psychological needs
What is an Enhanced Vision System?
A system to display electronic real-time images of the external scene achieved through the use of image sensors
What is the definition of dangerous goods?
Articles or substances which are capable of posing a risk to health, safety, property, or the environment and which are shown in the list of dangerous goods in the Technical Instructions or which are classified according to those Instructions
What is the definition of an extended flight over water?
A flight operated over water at a distance of more than 93 km (or 50nm), or 30 minutes at normal cruising speed away from land for making suitable emergency landing
What is the definition of an error?
An action or inaction by an operational person that leads to deviations from organisational or the operational person's intentions
What is a flight crew member?
A licensed crew member charged with duties essential to the operation of an aircraft during a flight duty period
What is a flight manual?
A manual, associated with the certificate of airworthiness, containing limitations within which the aircraft is to be considered airworthy, and instructions and information necessary to the flight crew members for safe operation of the aircraft
What is a flight plan?
Specified information provided to air traffic service units relative to an intended flight or portion of a flight of an aircraft.
What is a flight recorder?
Any type of recorder installed in the aircraft for the purpose of complementing accident/incident investigation
What is flight time in aeroplanes?
The total time from the moment an aeroplane first moves for the purpose of taking off until the moment it finally comes to rest at the end of the flight
What are general aviation operations?
An aircraft operation other than a commercial air transport operation or an aerial work operation
What is the definition of a large aeroplane?
An aeroplane of a maximum certified take-off mass of over 5700 kg
What is the maintenance programme?
A document which describes the specific scheduled maintenance tasks and their frequency of completion and related procedures
What is the maintenance release?
A document which contains a certification confirming that the maintenance work to which it relates has been completed in a satisfactory manner
What is the definition of night?
The hours between the end of evening civil twilight and the beginning of morning civil twilight
What is an operation flight plan?
The operator's plan for the safe conduct of flight based on considerations of aeroplane performance, other operating limitations and relevant expected conditions on the route
What is the operations manual?
A manual containing procedures, instructions and guidance for use by operational personnel in the execution of their duties
What is an operator?
A person, organisation or enterprise engaged in or offering to engage in aircraft operation
What is performance based navigation?
Area navigation based on performance requirements for aircraft operating along an ATS route, on an instrument approach procedure or in a designated airspace
What is repair?
The restoration of an aeronautical product to an airworthy condition to ensure the aircraft continues to comply with the design aspects of the appropriate airworthiness requirements
What is required navigation performance?
The level of navigation performance which must be achieved by a suitable equipped aircraft
What is runway visual range?
Horizontal distance seen by looking down runway at APPROACH end
What is a safety management system?
A systematic approach to managing safety, including the necessary organisational structure
What is the State of Registry?
The State on whose register the aircraft is entered
When can the CAA prosecute the environmental noise impact before approving an airspace expansion?
If an aircraft has broken one of the low flying rules- there must be sufficient evidence before doing so
What kind of penalties can operators impose on pilots who break Noise Abatement procedures?
Verbal briefing from tower, re-training, restrictions on operating times, monetary fine, temporary or permanent ban
Summarise the Noise Certificate
-Legal action cannot be taken against an aircraft for noise emissions
-The flying community take their responsibilities towards being good neighbours very seriously
-All aircraft have a noise certificate which remains valid unless engine or airframe modifications take place
-Airfield operators can impose their own penalties for NAP offenders
What is common in NAPs for large tubroprop or turbojet aircraft?
A reduction in thrust with a departure route
What are NADP1 and NADP2?
The two types of Noise Abatement Procedures defined by the ICAO
True or false: NAPs still apply in the event of an emergency
False
What is the definition of a runway incursion?
Any occurrence at an airport involving the unauthorised or unplanned presence of an aircraft, vehicle or person on the runway
What does a white T on the signals area indicate?
The aircraft taking off or landing shall do so parallel with the shaft of the T and towards the cross arm
What does a white disk at the head of a T on the signals area indicate? How is this shown on a mast?
The direction of landing and take=off do not necessarily coincide. May also be indicated by a black ball suspended from a mast
What colour flag indicates a right-hand circuit is in force?
Green
What does a white dumb-bell in the signals area indicate?
Movement of aircraft on the ground shall be confined to hard surfaces only. Black strips indicate that take-off and landing must be done on a runway, but movement on the ground is not confined to hard surfaces
What does a red square with a single yellow diagonal stripe in the signals area indicate?
State of maneuvering area is poor
What does a red square with a yellow cross in the signals area indicate?
Aerodrome is unsafe for the movement of aircraft and landing is prohibited
What does a white letter H in the signals area indicate?
Helicopters must take-off and land only within a designated area
What does a double white cross or two red balls suspended from a mast indicate?
Glider flying is taking place at the aerodrome
What does a yellow cross indicate?
The tow-rope dropping area
What does two seperated white crosses on a section of runway or taxiway indicate?
The area is unfit for movement of aircraft
What do orange and white markers spaced not more than 15m apart indicate?
The boundary of that part of taxiway, apron or runway is unfit for movement of aircraft
On what side are the broken yellow lines at a taxi holding point?
The runway side
What do orange and white wedge-shaped markers indicate?
The boundary of an aerodrome and the boundary of an unpaved area which is unserviceable for aircraft movement
What do white, flat rectangular markers indicate?
The boundary of an unpaved runway or of a stopway
What does a white letter L on the maneuvering area indicate?
That part is to be used only for the taking off and landing of light aircraft
What does a dumb-bell with a letter L superimposed indicate?
Light aircraft can take off and land either on a runway or on the area designated with a white L
What does a white cross displayed at each end of a runway indicate?
Landing is dangerous and the aerodrome is used for storage purposes only
What does a white cross with a single white bar displayed at each end of a runway indicate?
Runway fit for emergency use only
What does a permanently displaced threshold look like?
White arrows that indicate the pre-threshold area is available for taxi and take-off, but not for landing, or white crosses that indicate it is unsuitable for movement of aircraft and unsuitable as a stopway
What does a temporarily displaced threshold look like?
No piano keys
What does a yellow and red chequered flag indicate?
Aircraft may move on the manoeuvring area and apron only with permission of ATC
What is a runway hotspot?
An area which has potential of having a higher number of runway incursions because of complexity
What does a holding point that looks like a yellow ladder indicate?
A closer visual taxi-holding position is provided after
What does a single yellow dashed line holding point represent?
It is an intermediate taxi-holding position
What does a single yellow line followed by a double yellow line with many perpendicular yellow dashes as a holding point represent?
A paved a shoulder of bearing strength less than taxiway or area beyond mark is not intended for aircraft use
What do Stop Bars do?
They act like traffic lights- you must not cross a lit red stop bar
What are CAT 1, 11, and 111?
Categories of Instrument Landing System which aircraft use in bad weather
What is the 'sterile cockpit' policy?
Where only tasks relating to the handling and safety of the aircraft for the related phase of flight are carried out
What is a conditional clearance?
Where an ATC issues an instruction that becomes valid after another event has occurred
What are the three components that make up a fire?
Oxygen, fuel, ignition
What are the four causes of a fire in an aircraft?
Engine start, inflight, electrical, post-crash
What are 'memory items'?
Checks performed by commercial operators that should be memorised
What is a result of overpriming the engine?
Excess fuel enters the air intake- this may ignite if the engine backfires during start. It may be hard to detect as the fire may be contained within the carburettor
What should you first do if you detect there has been a carburettor fire?
Continue turning the engine over and draw excess fuel back into the induction system. If the fire persists or it was present before the engine started running, the engine must be shut down and the aircraft evacuated
In what ways can you detect an engine fire mid-flight?
Fuel check, pressure drop (may indicate a leak), or rough running (may indicated damaged cylinder)
What does a black flame indicate?
It is an oil based fire
What is the most common cause of a fire in the cabin?
Electrical fire caused through arcing within the wire circuitry or a faulty avionic component
What are the different classes of fire?
Class A- solids
Class B- flammable liquids
Class C- electrical
Class D- metals
What fire extinguisher type should be used for each class of fire?
Class A- cooling agent (water or gycol)
Class B- foam or halon
Class C- non-conducting (halon)
Class D- special powder
What does the mnemonic PASS stand for?
Pull the pin
Aim the fire extinguisher
Squeeze the top handle or lever
Sweep the fire extinguisher from side to side
What are the two main toxic gasses in smoke?
Carbon Monoxide and Hydrogen Cyanide
How can you provide protection against smoke in an aircraft which is not fitted with oxygen masks?
Cover the nose and mouth with a damp cloth
What is windshear?
A change in wind direction or speed within a short amount of time