Lecture 8: Poxviruses
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
True or false: a lot of pox viruses don’t cross the species barrier
false- they do!
What type of shape are poxvirus virions?
brick-shaped, with complex symmetry.
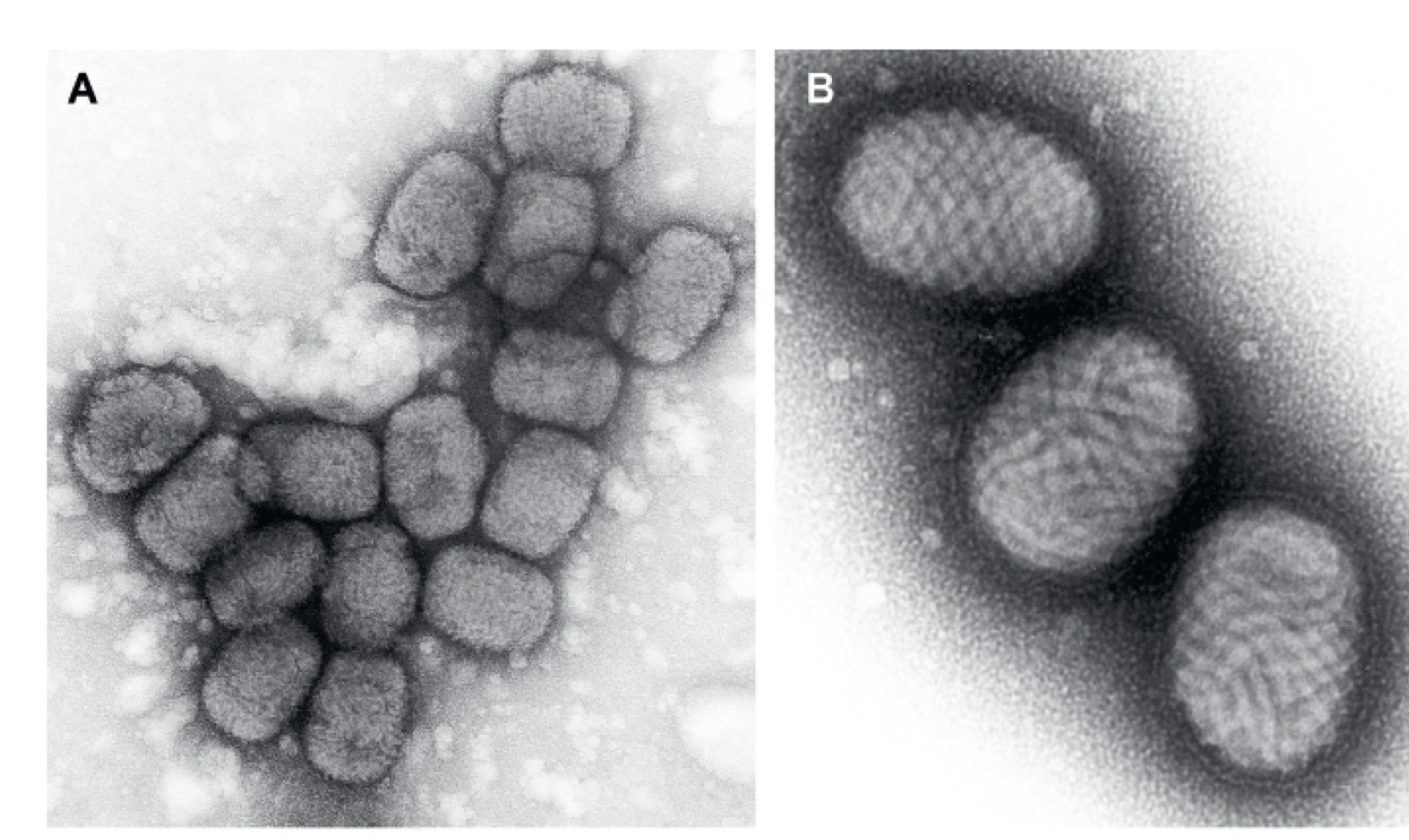
What function do the surface tubules and filaments serve on the envelope membrane?
They don’t actually have any attributing function. They may be a cause of dehydration.
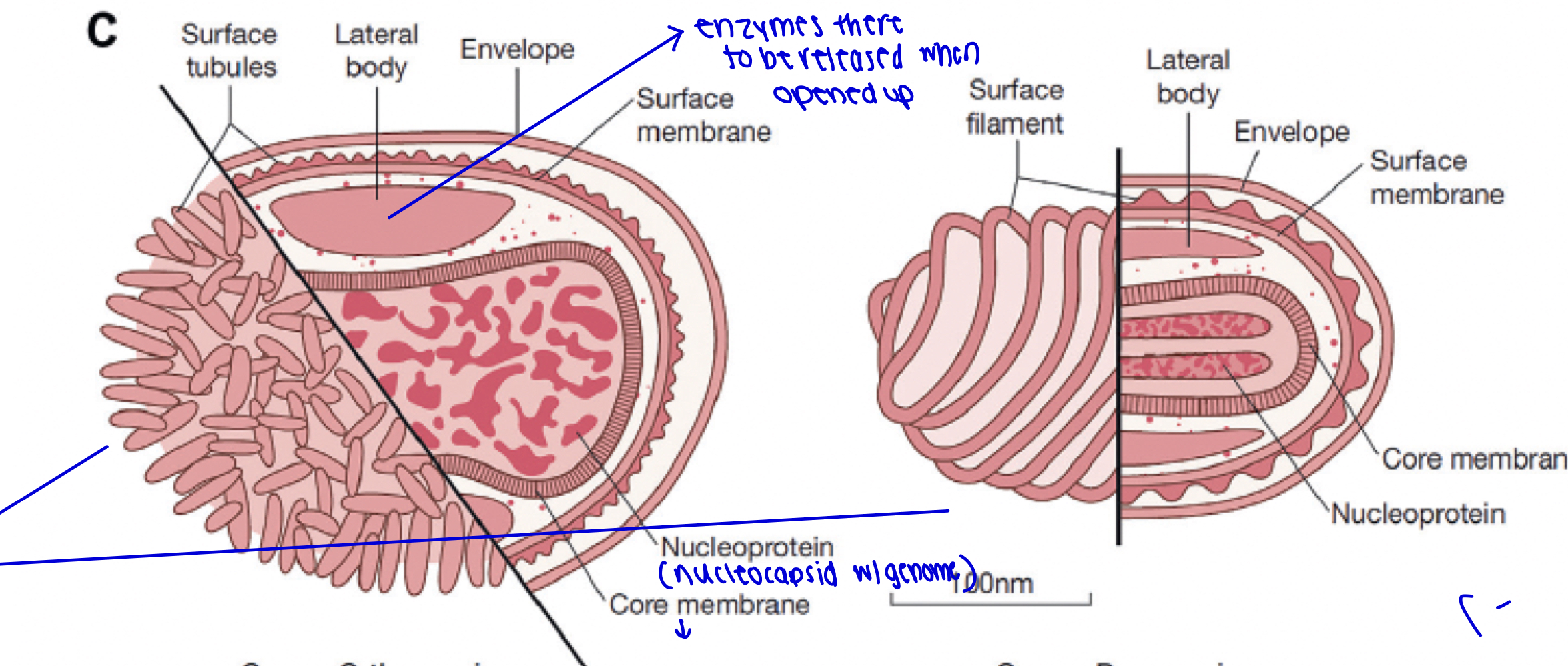
what is the function of the core membrane?
protects the whole nucleocapsid.
what is the purpose of the two lateral bodies inside the virion?
enzyme-packed, there to be released when opened up
what type of genome do poxviruses have?
dsDNA genome
true or false- both strands can code for genes in both directions
true
what is located at the ends of the genome?
covalent linkages, made of tandem repeats.
why does the hairpin structure at the ends of the genome help with replication?
it serves as a primer.
What are the covalent ends of the genome called?
ITRs, or inverted terminal repeats.
Which nucleotides are found in the ITRs?
A,T
Which region of the genome determines the host range?
Flanking region (half the genome in vaccina)
which genes are toward the center of the genome?
core genes- (things all poxviruses need to replicate in the cytoplasm) such as DNA dependent RNA polymerase
What are the modes of entry for poxviruses?
fusion and endocytosis
Where does replication take place for poxviruses?
in the cytoplasm of the host- which is unusual for DNA viruses.
Since replication takes place in the cytoplasm, what does that mean in terms of enzymes needed?
-needs a primer (ITRs)
-DNA polymerase needs to be ready
How fast from the time of infection is viral mRNA made?
within minutes. The consequence of this- short latent and eclipse periods.
How are the expression of proteins modulated in poxvirused?
Via the concentration of transcription factors. Early TF binds to promoters of Intermediate transcription factors, and Intermediate TF binds to the promoters of late TF.
How is assembly regulated?
By late proteins
What do the late proteins make?
The viroplasm (viral factory)
What are virions released by lysis?
mature virions
what are virions released by exocytosis?
enveloped virions
Why do enveloped virions have an extra envelope?
They wrap themselves in the golgi, making an additional membrane.
Which poxviruses can humans contract?
Orthopoxyviruses
-variola (smallpox)
-vaccina
-monkeypox
-human cowpox and buffalopox
Molluscipoxvirus
-molluscum contagiosum
Parapoxvirus
-milker’s nodule (milking cows)
-Orf (handling sheep and goats)
Which virus is responsible for smallpox?
variola- eradicated in 1980
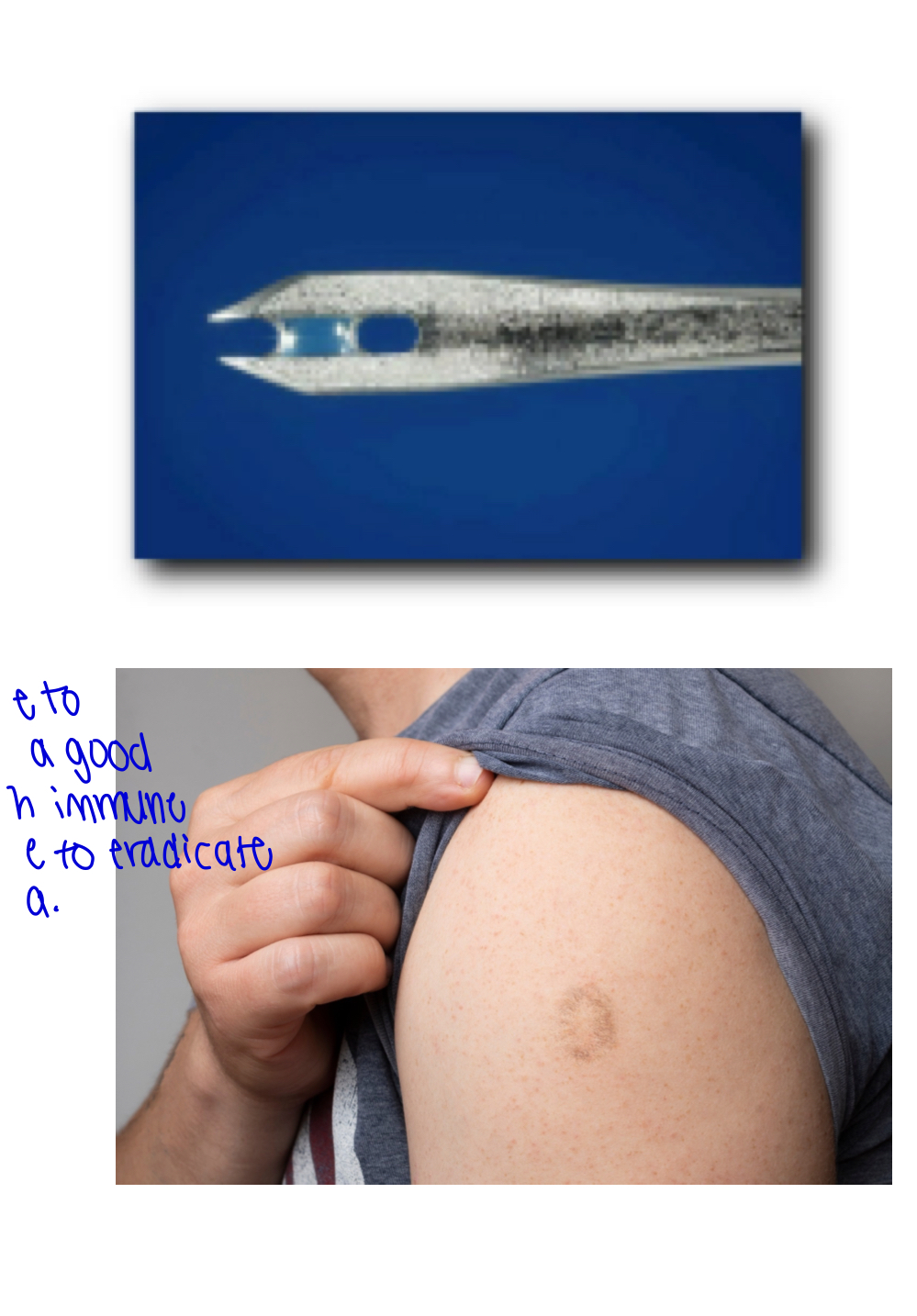
how did the vaccine for smallpox work?
the virus used was actually vaccina- NOT variola. It’s a less intense version of variola, but enough of this species was loaded into the vaccine to provide an adequate immune response to variola.
vaccine was administered by a multiple puncture technique on the upper arm
How was smallpox characterized?
By fluid-filled blisters all over the skin- they would scab over and fall off. 30% risk of death bruh
How is vaccina virus diagnosed, and what are its symptoms?
-through electron microscopy, followed by PCR. Best results when the cell is loaded with the virus.
-usually produces rash and fever- mild.
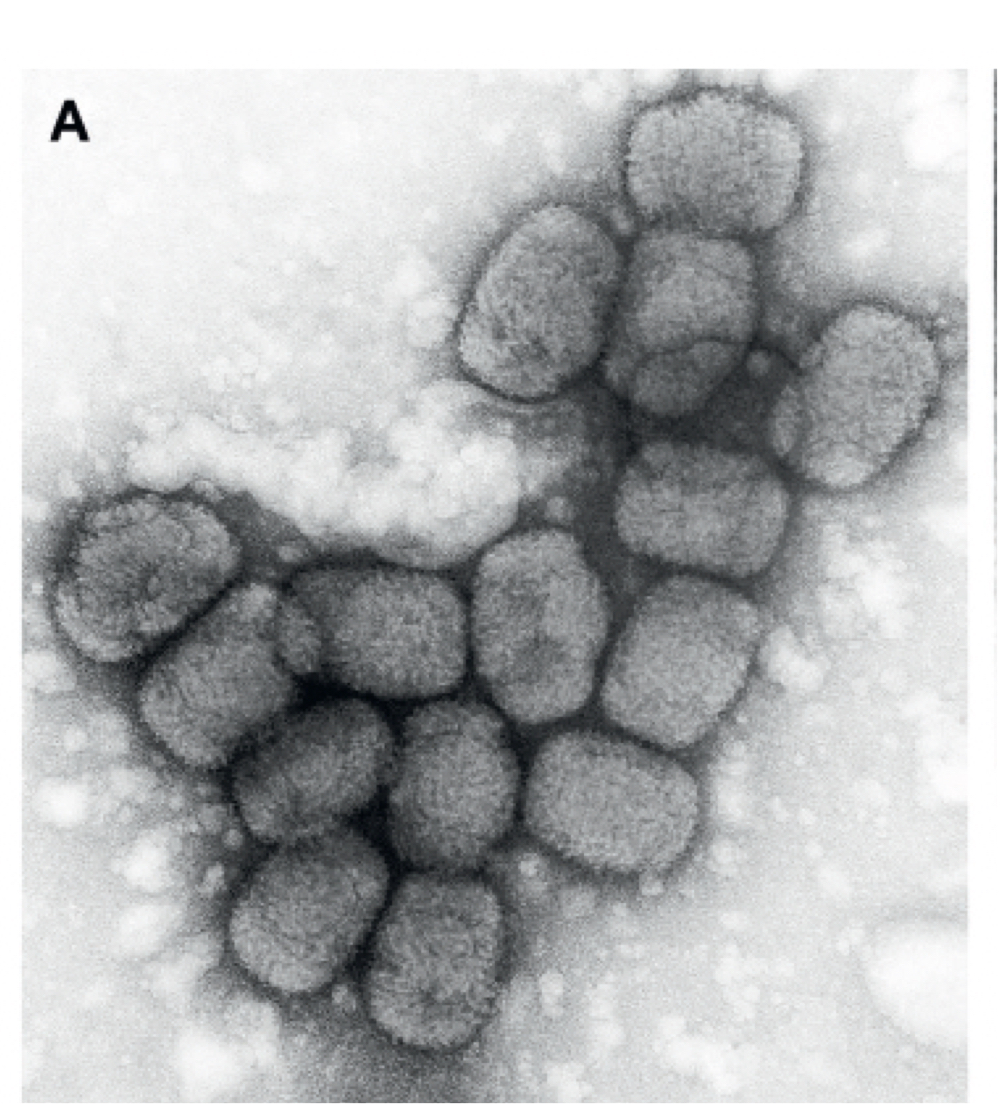
What are the symptoms of monkeypox, who gets it, and how?
-general rash, fever, and toxemia
-usually acquired by zoonosis
-wide range of species affected
-spreads through lots of direct contact
What are the symptoms of molluscum contagiosum, and who gets it?
-only humans get it
-pearly white/pink nodules on the skin with a central dent
-may last for several months