Rabbits 1
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
taxonomy
order = lagomorpha
family =lepordiae
all domestic are descendants of european wild rabbit
they’re not rodents
important data
head
large erect pinnae
large proturbent eyes
cleft lip
twitchy nose
vibrissae
specialised dentition
ears
useful for bunny = thermoregulation, funnelling sound - can rotate 270^o
useful for us = administrating meds and fluids, blood sampling - use marginal ear vein for blood sampling
can be sensitive - blood vessesl fragile and easily damaged, use local aneasthetic and be gentle
eyes
positioned laterally - wide field of view
have 3rd eyelid - nictitating membrane
harderian gland - produces very stable tear film
single ventral lacrimal punctum draining into nasolacrimal duct - runs so close to apices of cheek teeth so may cause problems
proturbent eyes = higher risk of trauma
underlying dental disease leads to eye issues
ophthalmic exam = merangiotic retina - blood vessels coem out the cente and run out horizontally in arrow band , no tapetum - have to look upwards in exam to see the blood vessels, no light reflection
large retrobulbar venous plexus(orbital venous sinus)
can cause eyes to become more proturbent looking - frightened rabbit with increased blood pressure or diseased venous plexus
blindspots = very tip of nose and directly behind them
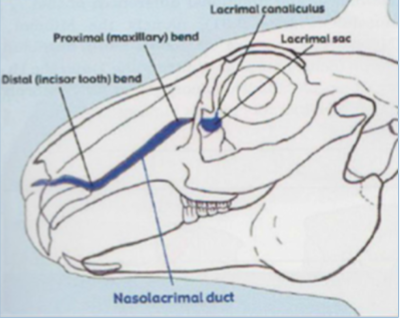
ocular muscles and drainage
additional extraocular muscle - depressor palpebrae
rectus dorsalis m. = used to stabilise globe during surgery
large retrobulbae venous sinus outside extraocular muscles
drain via external jugular
dentition
hypsodont teeth - reserve crown, enamel extends below gumline, aradicular/elodont (open rooted/ no true root)
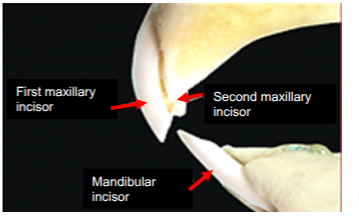
peg teeth
rate of eruption = incisors = 3mm/ week, cheek teeth = 3mm/month
dental formulae = I 2/1 C 0/0 PM 3/2 M 3/3
dental disease common - chronic alters skull morphology, can evelop dentalspur in not enough fibre in diet
high CHO low fibre diet results in reduced tooth wear and elongation of crown of teet, leads to occlusion of cheek teeth at rest which puts pressure on crowns
continues the mouth is forced open resulting in retrograde pressure forcing apices of teeth back into bone( bony swelllings develop on mandible)
chewing becomes difficult and anatomy of chewing altered - up and down instead of side to side
results in formaation of enamel spurs
jaw forced apart and incisor teeth wear incorrectly and then see incisor malocclusion and elongation
full dental examination and corrective dentisty requires anaesthetia
very strong tongue(torus), fleshy teeth and small gape makes it difficult to fully examine mouth of conscious rabbit
nose
twitching is normal even at rest
rate increases if interested in something
v sensitive to touch
blind spot here
sensitive pads on nares
presence of vibrissae
respiratory system
obligate nasal breathers
30-60 bpm
small thoracic cavity - tidal volume = 4-6ml/kg
high chest wall compliance
low functional residual capacity
diaphragmatic contraction drives breathing
very sensitive to respiratory irritants
R lung = cranial, middle, caudal and accessory
left lung = cranial, middle, caudal
thymus persisits in adult rabbit, found in cranial mediastinum
intubuation hard- long tongue, small glottis, narrow oropharynx, laryngospasm
CV system
HR = 150-300 bpm
systolic blood pressure = 90-135mmHg
total blood volume = 50-75ml/kg
little collateral circulation
electrical conduction system simple - SAN consists of small group of cells
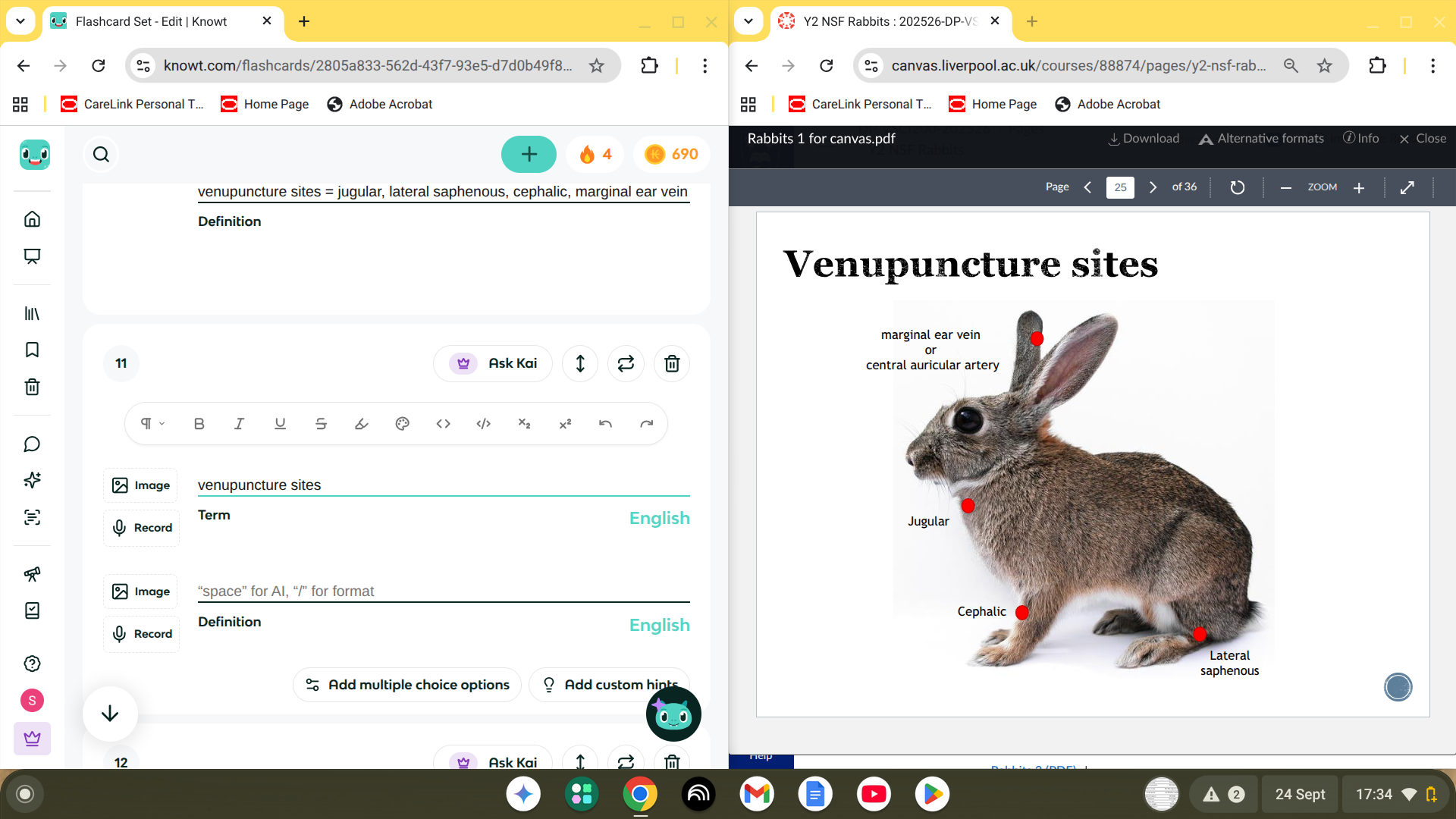
venupuncture sites = jugular, lateral saphenous, cephalic, marginal ear vein
most useful site depends onw ahtyou want to do
venupuncture sites
cephalic good for catheterising
digestive systen
hindgut fermenter - large stomach, huge caecum
highly efficient food converters
select concentrates over fibre
dental disease tends to occur secondary to - poor diet
fibre essential for gut health
have a gall bladder
starts at mouth
grinding action of cheek teeth
strong tongue ensures all food is masticated prior to swallowing
4 pairs of salivary glands - parotid, sublingual, zygomatic, mandibular
amylase rich saliva released in response to presence of food in mouth
oesophagus = 3 layers of striated muscle extending all way to cardia of stomach
stomach = lies left to midline. thin walled and j-shaped. well developed cardiac sphincter meaning no vomitting - ruptured stomach is common postmortem finding - not necissarily cause of death
pH 1-2 means stomach and SI are practically sterile - neonates have 5-6.5 = more suceptible to bacteria, milk oil produced from 0-6 weeks
SI = accounts for 12% digestive tract volume, secretes enzyme called MOTILIN - stimulates motility in SI,colon and rectum(no effect on caecum), released in response to fat, inhibited by carbohydrate
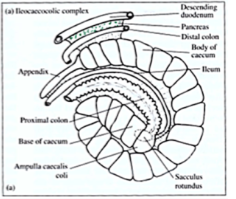
terminal ilieum ends in sacculus rotundus at junction with colon and caecum - sometimes called caecal tonsil
sacculus rotundus is composed of lymphoid tissue - defence against bacteria
caecum = 40% of GI volume, ends in veriform appendix
proximal colon - 50cm, 3 subsections - 3 haustra/ sacculations, single haustra, fusus coli(regulates passage of ingesta into distal colon, separates hard from soft pallate
distal colon = 90 cm , no sacculation, long
veriform appendix composed of lymphoid tissue
hindgut fermentation
in caecum microorganisms perform fermentation producing VFAs which absorb across caecal wall
bacteria replicate in caecum, forming vital source of protein
caecal contents are expelled as caecotrophs which are eaten from anus
caecal pellet protected from stomach pH by mucus covering - bacterial replication continues
digestion of caecal pellet delivers protein to animal
main VFA produced by caecal fermentation is acetete( then butyrate then proprionate)
gut motility
derangement of GIT motility in rabit is common and often fatal
ANS controls GI tract motility, particularly fusus coli
hormonal control - motilin/ prostaglandin
presence of indigestible fibre in gut (cellulose and lignin) - encourages motility, reduces caecal retention time
hard faeces
contractions in proximal colon separate indigestible particles from liquid component
indigestible contents move to centre of lumen further water absorbed
hard pellets produced
soft faeces
smaller particles and liquid content move into peripheral lumen
antiperistalysis returns them to caecum for further fermentation
caecum contracts to exspel contents into proximal colon which then move rapidly through distal colon with no further absorption
caecotrophs
produced about 8 hrs post feeding - eaten directly from anus
provide source of protein, vit B and vit K
high protein, low fibre diet discourages consumption
high fibre, low protein diet encourages consumption
diarrhoea uncommon
repro system
when do rabbits reach sexual maturity - small breeds = 4-5 months, large breeds = 5-8 months
reproductive capacity of around 60 kits per yr - can rebreed immediately after giving birth
induced ovulator - no well defined oestrus cycle but periods of sexual receptivity, ovulation occurs around 10-13hrs after coitus
gestation length = 30-33 days
parturition = called kindling, lasts around 30mins, rarely problems with dystocia, young born altricial and require maternal care
kit care
feed only once or twice daily for 3-5mins at a time - rabbit milk has higher fat, protein and calorie content than other mammalian milk, high nutritive value(13% protein, 9%fat, 1%lactose, 2.3%minerals)
maternal immunty is placental - hand reared kits prone to mortality due to lack of milk of oil - milk oil is a antimicrobial substances produced by a reation between mothers milk and neonates substance
kits start to take solid food around day 18-21
lactating does have increased water requirement - up to 10 fold
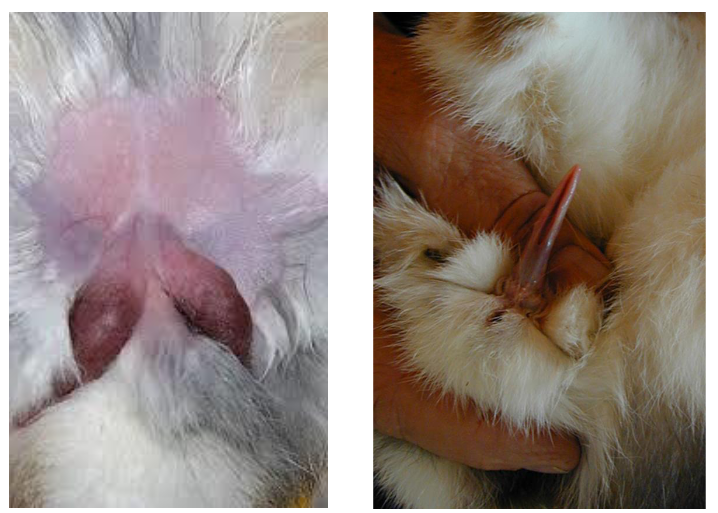
sexing rabbits
best sexed at weaning = 5-8weeks
check and double check
male rabbit - no nipples
female = doe
male = buck
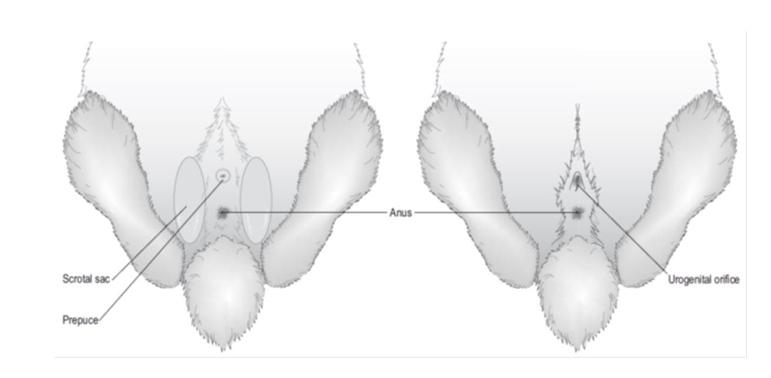
male repro system
penis sits within rounded penile sheath - can be extruded using gentle digital pressure from 2 mo old, no os penis
2 hairless pockets can be seen either side of urogenital area = scent glands, often have hard/crusty material within
scrotal sacs cranial to penis - large epidydimal fat pads, open inguinal canal meaning testes can easily be retracted into abdomen
accessory sex glands - seminal vesicle, prostrate, paired bulbourethral glands
castration can be carried out from 3 months age - make sure testes present in scrotum - castrate to - stop ability to breed, easier to litter train, reduce aggression and allow safe pair bonding with other rabbits of either sex
testes descend into scrotal sacs at around 10-14 weeks
female repro system
has duplex uterus - large saccular vagina, 2 cervices - left and right
long convulated oviducts
mesometrium stores fat = increases with age - can be challenging to neuter later
uterus and ovarian pedicle - friable
pseudopregnancy is possible - caused by infertile mating or presence of a male
caused by secretion of progesterone from CL - see enlarged mammary glands and abdomen, may pluck belly and make nest
regresses naturally but can reoccur multiple times
can be neutered from 10-12 weeks but uterus may be hard to find, witing until 16-20 weeks means larger
why spay = negates risk of uterine pyometra or carcinoma, reduces risk of mammary tumours, reduces aggression and risk of fighting, reduces phantom pregnancies, population control
haematological features
RBCs - HCT 33-55%, RBCs smaller than canine but larger than feline, anisocytosis and polychromasia are normal on a smear, lifespan 57 days
WBCs - lymphocyte most common circulating leucocyte, neutrophils called heterophils as cytoplasm stains pink-red, eisonophils have a bilobed nucleus and bright pink staining granules
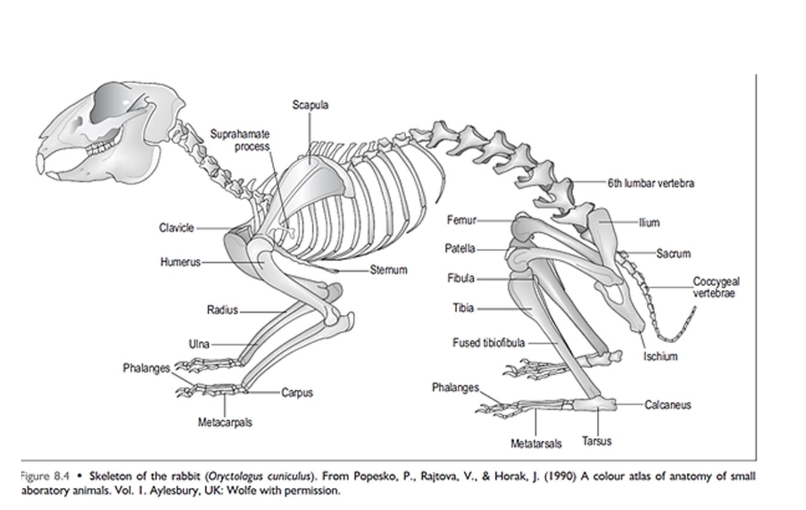
musculoskeletal system
skeleton very light and flexible - accounts for only 6-8% BW
vertebral formula - C7, T12, L7, S4,Cd16 - powerful epaxial and hindlimb muscles
tibia and fibula partially fused
5 digits on forelimb
4 on hindlimb - at rest entire plantar aspect of hindlimb from toes to hock rests on ground
no footpads - furry feet
why does lifestyle of domestic rabbit make them prone to fractures and osteoporosis - low calcium levels, reduced exposure to sunlight, lack of exercise
integument
rabbit skin is really thin and elastic
3 hair types - long guard hairs, short guard hairs, undercoat
fur types - satin, rex, wool, normal
fury all over except nose, scrotum and inguinal area
have twice yearly molt - spring/autumn - starts at head, travels down body
does develop large dewalps
normal to have some hair in stomach through self grooming
scent glands - present in anal glands, inguinal glands and chin glands, found in both sexes
feet
no footpads just fur
can predispose to ulcerative conditions - ulcerative pododermatitis, generally exacerbated by hard cage surfaces and unhygienic conditions, more common in overweight animals or those with thin coat
scent glands present in both sexes - 3 sets
urinary system and calcium excretion
kidneys unipapillate - single medullary pyramid
dangerously high serum levels avoided by action of PTH, calcitonin and active vit D3 - excess calcium excreted by kidney, forms calcium carbonate crystals in urine once reabsorptive capacity kidney is reached
urine = pale yellow to dark red - usually cloudy
excessive prolonged dietary calcium intake can result in urolithiasis
pH = 8-9
rabbits absorb all available dietary calcium through cut then deal with it by excretion via kidneys
serum calcium conc = 3.25-3.75 mmol/l
rabbit physiological data
lifespan = 5-10 yrs
adult weight = 2-5kg
sexual maturity = 4-8 months
litter size = 1-8
gestation length = 30-32 days
behaviour
social and gregarious species - live in small bonded family groups
prey species
use subtle means of communication = scent marking, body language
crepusular - most active at dawn and dusk
ensure of stability of - environment and population
handling
avoid touching nose
stroking rountod cheeks and chin can mimic natural mutual grooming behaviour
dont pick up unless have to
support hindlimbs to avoid damage to spine
tonic immobility
cortisol increase
respiraotry rate increases
HR increases
a fear response and should not be used as routine restraint or instead of sedation or anaesthesia
diet and feeding
hindgut fermenters - fibre is essential
browsing creatures
can use food as enrichment
increased dietary fibre = decreases stress - ad lib feeding of long fibre essential
very selective - choose grains and pulses over grass pellets in conc diet - problematic because - low fibre = increased dental disease and reduced gut health, high concentrates = lots of energy in small meal
feeding
cereal and concentrate mixes bad
high protein, high calorie
selective feeding
reduced caecotrophy
boredom
dental disease
obesity
starchy foods lead to GI disturbances
feed grass - 80% diet ad-lib
mixture of timothy, fescue, cocksfoot and meadowgrass ideal
alfalfa - only growing rabbits as high protein and clacium levels, lower fibre
clover is very high energy = weight gain
supplement with edible wild leafy plants and leafy greens(carrot tops, beet tops, spinach, rocket), fruit only as treat or training aid
fibre
indigestible fibre - vital for gut motility
ligin and cellulose - from secondary plant wall
no nutitional value
not easily fermented
digestible fibre - for energy
smaller particles from primary plant wall
fermeneted in caecum
results in VFA production
excess digestible fibre → caecal dysbiosis
calcium
amount absorbed depends on amount of calcium in gut
calcium regulation is done by kidneys not gut - adapted to absorb calciumm if body needs and excrete if levels are adequate
0.6-1% required for optimal health
intake depends on calcium content of food its offered and how much it chooses to eat
neonates
stomach pH 5-6.5
milk oil produced due to reaction of doe’s milk with digestive enzymes = antimicrobial
as kit starts to take plant matter in bacteria colonise caecum and pH in stomach drops - milk oil no longer necessary once stomach pH down to 1-2
housing
space to - sit up with ears erect, hop,lie down fully stretched, play, eat and drink, maintain hygiene
10-20 degrees
variety of levels and spaces
scent marking surfaces
access to outside
always be large enough to accomodate 2 rabbits
min enclosure of 6ft X 2ft X 2ft plus access to an outdorr run of 8ft
management regime depends on environment
keep it clean - preserve scent marking
clean toilet ares at least daily - urine/faeces
dirty environment predisposes to flystrike/ myiasis, pododermatitis, respiratory disease
routine health care
vaccinations - myxomatosis, RHD(viral heamorrhagic disease - caused by calcivirus)