Approach to skin nodules
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
what is a nodule?
a circumscribed solid elevation greater than 1cm in diameter that usually extends deeper layers of skin
what doe nodules usually result from?
infiltration of inflammatory cells, neoplastic cells or deposition of fibrin or crystals
what are the noninfectious differentials for nodules?
foreign body (plant / inorganic material —> calcinosis)
inflammatory (eosinophilic granuloma)
cutaneous drug eruption or injection reaction
sterile pyogranulomatous dermatitis and panniculitis
juvenile cellulitis
histiocytosis
what features of the clinical presentation of nodules should we consider?
location on the body
number (single vs multiple)
size
behaviour (acute vs gradual onset)
aspect / clinical features
warm or painful
hard, soft, elastic, moveable, fixed, etc.
alopecic, smooth or rough
ulcerated
hyper/hpopigmented
what cytology should we perform for nodules?
fine needle aspirate
apposition (if ulcerated or discharging)
what histology could we perform for nodules?
excision of whole nodule
punch / wedge biopsy
choice of histology depends on clinical presentation (number, size, location)
what diagnostic tests could we perform for nodules?
cytology
histology
immunohistochemistry, clonality
special stains (gram, PAS, ZN, GMS)
PCR
biochemistry, urinalysis (calcinosis cutis)
serology (e.g. Lesihmania, Toxoplasma, Neospora, cryptococcus)
what foreign body reaction may cause nodules?
plant material
grass awns
embedded insect mouth parts
suture material
procupine quills
endogenous material - hair, sebum, keratin, calcium salt, tyrosine crystals
what bacteria is usually seen in dogs with abscesses?
staphylococcus
what bacteria is usually seen in cats with abscesses?
polymicrobial anaerobic infections from bite wounds (Bacterioides, Fusobacterium)
what are possible filamentous bacteria causing infectious nodules?
Actinomyces - oral / GI tract commensal
Nocardia - cosmopolitan, soil saprophyte
Actinobacillus - commensal organism in oral cavity
what are the clinical signs of filamentous bacteria?
nodules and abscesses with ulcers, draining tracts and cellulitis
anywhere the bacteria are inoculated from bite wounds or penetrating foreign bodies
serosanguineous exudate
systemic signs - pyrexia, depression
with Nocardia - occasional systemic dissemination and pneumonia
how do we diagnose filamentous bacteria?
cytology (may need to use special stains - Gram, ZN)
histology (may need special stains) - see nodular to diffuse pyogranulomatous dermatitis and panniculitis, possibly with tissue grains ‘sulfur granules’
culture
molecular techniques - PCR, gene sequencing, MALDI-TOF
what is the treatment for filamentous bacteria?
surgical drainage and antimicrobial therapy
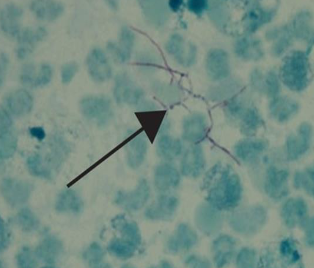
what does this Ziehl Neelsen stain FNA of a nodule show?