05: WBC
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Types of WBCs
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
Monocytes
Lymphocytes
WBC that doesn’t proliferate in bone marrow
Lymphocytes (→ lymphoid tissue!)
Most prevalent WBC in most animal species
Neutrophils
Most prevalent WBC in ruminants
Lymphocytes
WBCs classified as granulocytes
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
How do neutrophils stain
Basophilic nucleus with neutral granules that stain really poorly and are faintly pink/purple
How do eosinophils stain
Basophilic nucleus with bright red/orange granules
How do basophils stain
Basophilic with bright blue/purple granules
Which granulocyte is also called a polymorphonuclear leukocyte
Neutrophil
WBCs classifies as mononuclear
Monocytes
Lymphocytes
Monocyte function
Becomes macrophages in tissues, indicator of chronic inflammation
Lymphocyte function
Immune responses (B and T cell proliferation)
Where do lymphocytes live
LNs
Spleen
Other lymphoid tissue
Neutrophil function
Acute inflammation
Eosinophil function
Worms, wheezes, and weird diseases
Hypersensitivity reactions
Basophil function
Shows up with eosinophils
What is an analyzer counting when it gives the WBC count
Total amount of nucleated cells
Why is the WBC not always accurate
In regenerative anemias, there are nRBCs that get counted as WBCs
We ignore the WBC. What do we look at instead
Cell differentials
The cell differential is reported in two ways, which do we use clinically
Absolute number (discard the %)
I repeat: WHICH PART OF THE CELLULAR DIFFERENTIAL DO YOU INTERPRET
Absolute count (don’t disappoint Meinkoth)
Test done to confirm the WBC numbers from the analyzer
Blood smear :))
Additional benefit of doing a blood smear for WBCs
Allows you to look at morphology
Common changes in WBC morphology
Left shift (younger)
Toxic change (manufacturing errors)
Larger
What part of the blood smear do you look at to estimate WBC number
Monolayer
Why do analyzers get differentials wrong in sick animals
The machine is really bad when it comes to abnormal morphologies, and things get categorized incorrectly
Main use of looking at a dot plot/histogram from a CBC report
If the segments all run together, there is an error in the analyzer differential count
Term for immature neutrophils
Bands
Characteristics of band morphology
No segments in their nuclei
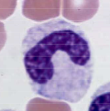
When are bands present
When there is lots of inflammation and the bone marrow is kicking out neutrophils before they mature all the way
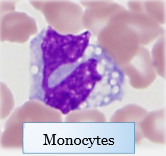
How to differentiate bands and monocytes on a blood smear (since they both look mononuclear)
Monocytes are larger and have darker blue cytoplasm, often with distinct vacuoles
Characteristics of neutrophils/bands with toxic change
Darker blue cytoplasm with foamy and indistinct vacuoles, ± ring nuclei
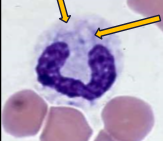
When do we see toxic changes
With bands; when the bone marrow is cranking out cells so fast that there are production errors, and leaking lysosomal enzymes cause damage in the cytoplasm
How are toxic changes rated
1-4
Where do neutrophils get produced
Bone marrow
How are neutrophils cleared
Tissue use
Where do neutrophils carry out their function
In tissues, not blood
T/F: low neutrophil count means low production
False, it could also mean really high demand in the tissues
How quickly can neutrophil counts change
VERY
What is meant by a “left shift” of neutrophils
The cell population is less mature because the marrow cannot meet the demand, and there are less segs and more bands, maybe even metamyelocytes
Three neutrophil populations in the bone marrow
Proliferating: actively dividing
Maturation: no division, just maturing
Storage pool
Neutrophil storage pool function
Provides 2-3 days of neutrophils, an “emergency fund”
Two neutrophil populations in the blood
Circulating pool
Marginated pool
Why are some blood neutrophils marginated
They are temporarily stuck to the vessel wall, sensing the ECF for inflammatory mediators that would signal for the neutrophil to extravasate
T/F: the proliferation pool and the maturation pool are roughly the same size
False; immature cells produce exponentially more mature cells
How long does it take for the bone marrow to produce and release a mature neutrophil
4-6 days
2-3 days to reach the maturation pool
2-3 days to mature for relase
In most animals, how does the size of the circulating pool compare to that of the marginated pool
Roughly equal
How does the size of the circulating pool compare to the marginated pool in cats
The marginated pool is 2x the size of the circulating pool
When we get a WBC differential of neutrophils, what is that number measuring
Neutrophil count in the circulating pool
Mechanisms of neutrophilia
Epinephrine/physiologic response
Glucocorticoid/stress response
Inflammatory response
Which type of leukogram is most important to discern from the prior list
Inflammatory leukogram
How does epinephrine cause neutrophilia
Instantaneously and temporarily causes the marginated neutrophils to move into circulation
How high can an epinephrine-induced neutrophilia get
2x reference interval, up to 3x in cats
What other WBC change will be seen with an epinephrine leukogram
Mature lymphocytosis up to 2x reference interval
How do glucocorticoids cause neutrophilia
Redistributes marginated pool to circulation
Some mobilization of the storage pool
Stops neutrophils from leaving the blood
How high can a glucocorticoid-induced neutrophilia get
2x reference interval, 3x in cats
What other WBC change will be seen with a glucocorticoid leukogram
Lymphopenia
Why do glucocorticoids cause lymphopenia
They cause redistribution of lymphocytes to lymphoid tissue and also kill lymphoblasts
How does inflammation cause neutrophilia
Mobilization of storage pool
Proliferation in bone marrow
Why does inflammation cause bone marrow proliferation
Inflammatory cytokines cause an increase in WBC production
What type of change may be seen with a neutrophilia that immediately tells you its inflammation
Left shift
How high can an inflammatory neutorophilia get
Any magnitude
What species has an almost non-existent bone marrow response
Cattle
Criteria for a left shift
Bands above reference interval, AND/OR
Bands >10% of neutrophil differential
Types of left shifts
Regenerative and degenerative
Regenerative left shift
Neutrophilia where there are more mature/segs than bands
Degenerative left shift
Neutrophilia with more bands than segs, OR
Neutropenia with a left shift
Pelger-Huet Anomaly
Inherited condition where the neutrophils never segment
What will you see on a blood smear from a patient with Pelger-Huet
Every neutrophil will have a band-like nucleus, but they will have a perfectly clear cytoplasm with no vacuoles
What is the rare 4th mechanism of neutrophilia
Neoplastic neutrophilia
Causes of neoplastic neutrophilia
Neutrophilic/granulocytic leukemia
Paraneoplastic neutrophilia
Categories of granulocytic leukemia
Acute: lots of blast cells
Chronic: lots of mature cells
When to consider a neoplastic neutrophilia instead the three common mechanisms
MARKED neutrophilia
No obvious explanation (doesn’t fit the three common mechs)
List the two mechanisms for neutropenia
Lack of production
Increased tissue consumption
Signs associated with neutropenia from increased consumption
Very sick patient (always look at the patient in front of you!)
Left shift
Toxic change
Signs associated with neutropenia from low marrow production
Pancytopenia → if the bone marrow can’t make neutrophils, it can’t make anything
No left shift: the cells aren’t coming out early, they just aren’t coming out at all
Which WBC differential will not drop if you have low marrow production
Lymphocytes
Where do lymphocytes proliferate
Lymphoid tissue
Causes of lymphopenia
Stress leukogram, so common that it is usually dismissed
If a very stressed/sick animal has no stress leukogram (normal lymphocyte count), what alarm bell should be going off in your head
Hypoadrenocorticism (Addison’s disease)
Steroids kill lymphoblasts, no steroids → normal lymphocyte count
Three lymphocytosis mechanisms
Epinephrine leukogram
Chronic disease
Neoplasia
How does epinephrine cause lymphocytosis
Demargination, causing a mild increase
How does chronic disease cause lymphocytosis
Immune stimulation, usually mild
Types of cancers that cause lymphocytosis
Lymphoid leukemia (bone marrow) and leukemic lymphoma (lymphoid tissue)
How high with a neoplastic lymphocytosis get
HIGH (>>>20k)
Reasons to do a blood smear for a patient with lymphocytosis
Can help you diagnose abnormalities in the lymphocyte population
Characteristics of abnormal lymphocytes
Larger than neutrophils
Immature: less condensed chromatin → lighter purple nucleus
LARGE nucleus
Causes of monocytosis
Stress leukogram or acute/chronic inflammation
Clinical significance of monocytopenia
It’s not
Causes of eosinophilia
Parasites
Hypersensitivity reaction
Neoplasia
If you have an eosinopenia in a patient that is very sick, what alarm bells should be going off
Hypoadrenocorticism (Addison’s, again)