Zoology Exam 1 - VOCABULARY
1/262
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
263 Terms
taxonomy
the science of naming, describing and classifying organisms
embryology
the branch of biology and medicine concerned with the study of embryos and their development
homology
similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms based upon their descent from a common evolutionary ancestor
convergent evolution
the process whereby distantly related organisms independently evolve similar traits to adapt to similar necessities
homoplasy
similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms based upon independent evolution
monophyletic
a group of organisms that share a common ancestor
paraphyletic
a group of organisms that originated from a common ancestor, but does not include all descendents
polyphyletic
a group of organisms that have descended from more than one ancestor
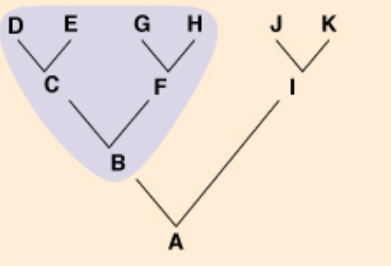
monophyletic
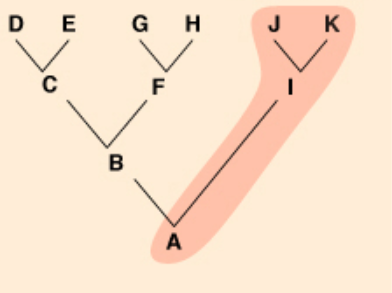
paraphyletic
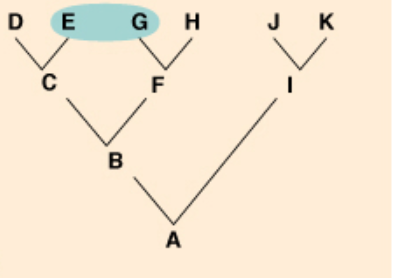
polyphyletic
Pre-Cambrian organisms
these organisms consisted of single celled organisms - cyanobacteria
Cambrian organisms
these organisms were the first invertebrates and “exploded” into the world
Ordovician organisms
these organisms are characterized by plants allowing the survival of land animals, and marine life
Carboniferous
period of coal formation
End of Permian
period of mass animal extinction
Mesozoic
period of dinosaurs!
Triassic
period of mammal origination (in the beginning/middle)
Tertiary
period of birds! which are dinosaurs
Cenozoic
period of human development, age of mammals
Wegener
proposed Continental Drift Theory
Wallace’s Line
separates two distinct modern terrestrial faunas, corresponds to a deepwater separation of two former land masses
Bering land bridge
Asia and North America were broadly connected when glaciation lowered sea level
biome
a large naturally occurring community of flora and fauna occupying a major habitat
boreal forest
Very wet, cool, lots of spruces, lots of recent fires as it becomes hotter and drier
temperate forest
forest found between the tropical and boreal regions, located in the temperate zone. regions with high levels of precipitation, humidity, and a variety of deciduous trees. 4 seasons
desert
a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation
denudiation
the geological processes in which moving water, ice, wind, and waves erode the Earth's surface, leading to a reduction in elevation and in relief of landforms and landscapes.
tropical rainforest
found closer to the equator where it is warm. very high annual rainfall, high average temperatures, nutrient-poor soil, and high levels of biodiversity (species richness). these are the some of the world's wettest ecosystems.
subtropical rainforest
rainforests that share characteristics of both tropical rainforests and temperate forests. these forests are wet, receiving precipitation in the form of heavy rain and coastal fog, and have lush plant growth. They differ from tropical rainforests in that they experience mild temperatures in both summer and winter
rainforest giants
trees that are much larger than average (ex: redwoods)
layered forest
forests which contain distinct layers of vegetation, each supporting different kinds of animals. have a canopy, understory, floor
convergent canopy
canopy which has no gaps for sunlight
leaf cutter ants
serve as keystone species that affect and advance diversity, productivity, and nutrient flow in tropical habitats
cloud forests
characterized by rising air which cools and forms clouds. a generally tropical or subtropical, evergreen, montane, moist forest characterized by a persistent, frequent or seasonal low-level cloud cover, usually at the canopy level. often exhibit an abundance of mosses covering the ground and vegetation, in which case they are also referred to as mossy forests.
tropical cloud forest
vegetation grows very richly, most precipitation comes as fog which condenses, which means lots of aerial plants
tropical dry forest
rare and highly endangered. Because of human activity, less than 5% of the original ecosystem remains. These forests occur in regions with heavy rainfall for part of the year followed by a long dry season. trees lose their leaves in the dry season since they can’t photosynthesize.
home of the turquoise-browed motmot
tropical dry forest (HOME of animal answer)
savannah
very dry. Prominent in Africa but exist in South America, some in Asia. Sparse vegetation. Enormous concentrations of grazing animals, which means lots of speciation.
home of termites and large biomass of ants
Savannah (HOME of animal answer)
stony desert
deserts primarily with stones and pebbles on the surface, shrubs, intense heat and cold
home of the beisa oryx
stony desert (HOME of animal answer)
Beisa Oryx
a species of medium-sized antelope from East Africa. don’t need to drink water - get all water from shrubs and vegetation
home of fogstand beetle
Namib Desert (HOME of animal answer)
fogstand beetle
cool winds blow off of ocean and create fog onshore, the beetles stand and sit and collect condensation on their bodies and drink the water, sit on top of sand dunes to do so
rich desert
found in American Southwest. a subtropical desert considered by some to be the biologically richest desert in the world. characterized by cacti
temperate rainforest
rainforests with coniferous or broadleaf forests that occur in the temperate zone and receive heavy rain. home to Northern Spotted Owl
temperature deciduous forest
a variety of temperate forest 'dominated' by deciduous trees that lose their leaves each winter. home of white-tailed deer
deciduous
trees that lose their leaves at the end of each growing season. leaves. spread seeds using flowers
coniferous
trees that do not change color or lose leaves in the fall/winter. needles. use cones to spread seeds
boreal forest/muskeg
the Earth's northernmost forests. a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces, and larches. has been called the world's largest land biome. known for spruces and firs
Arctic tundra
a vast, dry, rocky place, with few trees. characterized by permafrost. extremely wet surface with lots of lakes and ponds of permafrost melt.
home of polar bear
arctic tundra (HOME of animal answer)
permafrost
perpetual frost in soil. a permanently frozen layer on or under Earth's surface. It consists of soil, gravel, and sand, usually bound together by ice. usually remains at or below 0°C (32ºF) for at least two years.
temperate zone salt marsh
coastal wetlands that are flooded and drained by salt water brought in by the tides. where oceanic fish and crabs come in to breed. extremely threatened by sea level rise and global warming
taller mangroves
found on Costa Rican pacific shores. rich animal biodiversity, but low plant diversity.
temperate zone rocky shores
biologically rich environment that can include several distinct habitat types like steep rocky cliffs, platforms, rock pools and boulder fields. Because of the permanent action of tides and waves, it is characterized by erosional features. organisms must be hardy, as they must tolerate salinity, temperature, moisture, and wave action changes to survive
gyres
ocean currents generated by the rotation of the Earth. low diversity of life
coral reef
an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. formed of colonies of polyps held together by calcium carbonate.
home of orange-fin anemonefish
coral reef (HOME of animal answer)
protozoans
microscopic unicellular eukaryotes that have a relatively complex internal structure and carry out complex metabolic activities
plastid
membrane-bound organelle considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria
cytoskeleton
a structure that helps cells maintain their shape and internal organization, and it also provides mechanical support that enables cells to carry out essential functions like division and movement.
microtubules
tubulin dimers arranged in a coil. give internal structure to cilia and flagella. associate with motor protein and function in transport within cell, moving chromosomes during cell division, moving messenger RNA, transporting vesicles between plasma membrane, stiffening plasma membrane
Endosymbiotic Theory
Eukaryotes evolved through a symbiotic relationship between different prokaryotic cells
microfilaments
also called actin filaments, are protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that form part of the cytoskeleton. They are primarily composed of polymers of actin. may form a lattice beneath the cell membrane to give it shape. make long chains of actin subunits. important in cell movement and shape, particularly in amoeboid cells
locomotion of protozoa
cilia, flagella, pseudopodia
pseudopodia (general)
projections of cytoplasm commonly observed in amoebas and other unicells
lobopodia
projections of cytoplasm in large, bunt extensions
filopodia
projections of cytoplasm in pointed extensions
phagocytosis
mannerism of consuming. cell creates a an internal membrane bound vacuole, then the outer edges fuse together, food particles outside are now internal. the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle, giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome
cilia and flagella structure
made of microtubules, 9+2 arrangement, each of 9 pairs is attached to radial spoke that holds them in the center. attached to the base is a kinetosome
9+2 arrangement
9 pairs of tubules on the outside, 2 independent microtubules in the center
kinetosome
a structure in some flagellate protozoans which forms the base of the flagellum, consisting of a circular arrangement of microtubules
sliding microtubule hypothesis
the basic motive force for ciliary motion is produced as the doublet microtubules of the ciliary axoneme, with- out changing length, move with respect to one another by means of their two rows of dynein arms, powered by hydrolysis of ATP. dynein binds ATP, breaks it, gets energy, energy is used to grab neighboring pair of tubules, power stroke! bends cilia/flagellum
axopodia
arrays of microtubules to extend plasma membrane outwards. present in protozoa with test. supported by core of microtubules arranges in spiral or geometric shape
axoneme
core of microtubules in axopodia
reticulopodia
branch-like mesh develops to capture prey, form cytoskeleton, carry out cell attachment, cell movement. cytoplasm moves bi-directionally throughout the reticulum
axostyle
a rigid structure found in some protozoa, particularly certain flagellates. It serves a supportive function, providing structure and stability to the cell.
pellicle
a protective envelope or membrane that surrounds the cell membrane of certain protozoa. It helps maintain the cell's shape and provides a barrier against external factors.
basal body
a cellular structure that plays a crucial role in the formation of cilia and flagella. It acts as a template for the assembly of these hair-like appendages and anchors them to the cell membrane.
glideosome
manner of cell movement used by some parasitic protozoans
cristae
inner membrane folds of mitochondria. used to identify and classify some protozoans
hydrogenosomes
a hydrogen-producing organelle, evolutionary related to mitochondria. double membraned with no internal features, convert energy along a different pathway that uses pyruvate for anaerobic conditions
lysosomes
organelle containing digestive enzymes
osmoregulation
the maintenance of constant osmotic pressure in the fluids of an organism by the control of water and salt concentrations.
vacuole
a space or vesicle within the cytoplasm of a cell, enclosed by a membrane and typically containing fluid.
cysts
stages with a protective membrane or thickened wall. those which must survive outside the host usually have more resistant walls than those that form in tissues. typically resting, dormant and/or resistant stages in the full life cycle of many protozoan species, sometimes playing a role in dispersal of the organism.
alveolus
like a soft, movable balloon - empty sacs which actin anchors to in glideosome
clades
a group of organisms believed to have evolved from a common ancestor, according to the principles of cladistics.
Diplomonada
includes Giardia. no mitochondria. typically parasites, not sure if they have any alternate energy producing structures. have mitochondrial genes/DNA, so likely had them at some point then lost them. absorb intestinal nutritional things. attach via suction cup to intestinal wall. part of metamonada. ex: giardia lamblia
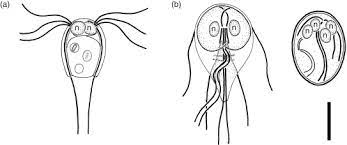
Diplomonada (image answer)
Euglenozoa
grouped together based on shared mitochondrial structure. Cristae in the mitochondria are used to identify eukaryotes. microtubule stiffener under the cell membrane creates a structure to their bodies and adds strength to it. creates pellicle. includes Euglena
pellicle
unique cell covering which characterized euglenids. a complex structure consisting of a proteinaceous layer or ‘membrane skeleton’ that is underlain by microtubules and covered by the plasma membrane of the cell. organized into individual strips that extend along the entire length of the cell, the number and position of which is often diagnostic for various species
Euglena
fairly common protozoan that has flagellum and chloroplasts. has red eye spot as a light detector. swims around if they want to. can photosynthesize in sunlight. when not photosynthesizing, can take in food across cell membrane.

Euglena (image answer)
Ciliophora
characterized by cilia. some are completely covered, others have bands or tufts. rich with cilia. most are free living. they are incredibly common, lots found in hay infusion. cilia can be localized around mouth structures or in these bands/tufts around the cell
free-living
describes an organism that is not parasitic
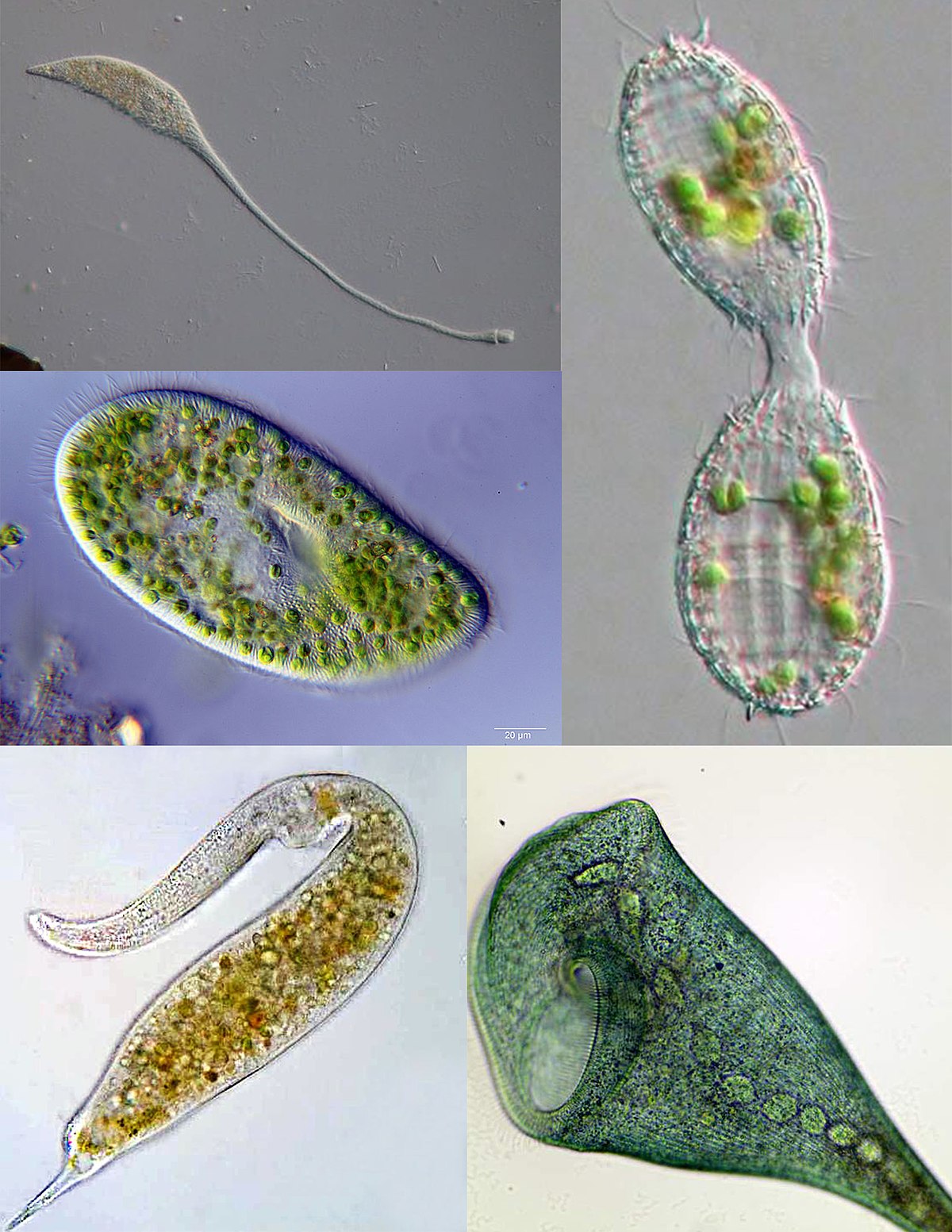
Ciliophora (image answer)
paramecium
ciliate which has cilia all over the body and beat in one direction, coordinated by electrical potential charges. the edge of the cell has positive and negative ends, which coordinate. very good at moving with cilia, reversing their beat if they bump into something, showing that it is due to an ion channel that opens and reverses their movement (using Ca++). have trichocytes, contractile vacuole, more than one kind of nucleus, and both go through mitosis. does complicated sexual reproduction. has oral groove (pseudomouth). can reproduce asexually.