ARCH 210 Midterm 1 Monuments
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
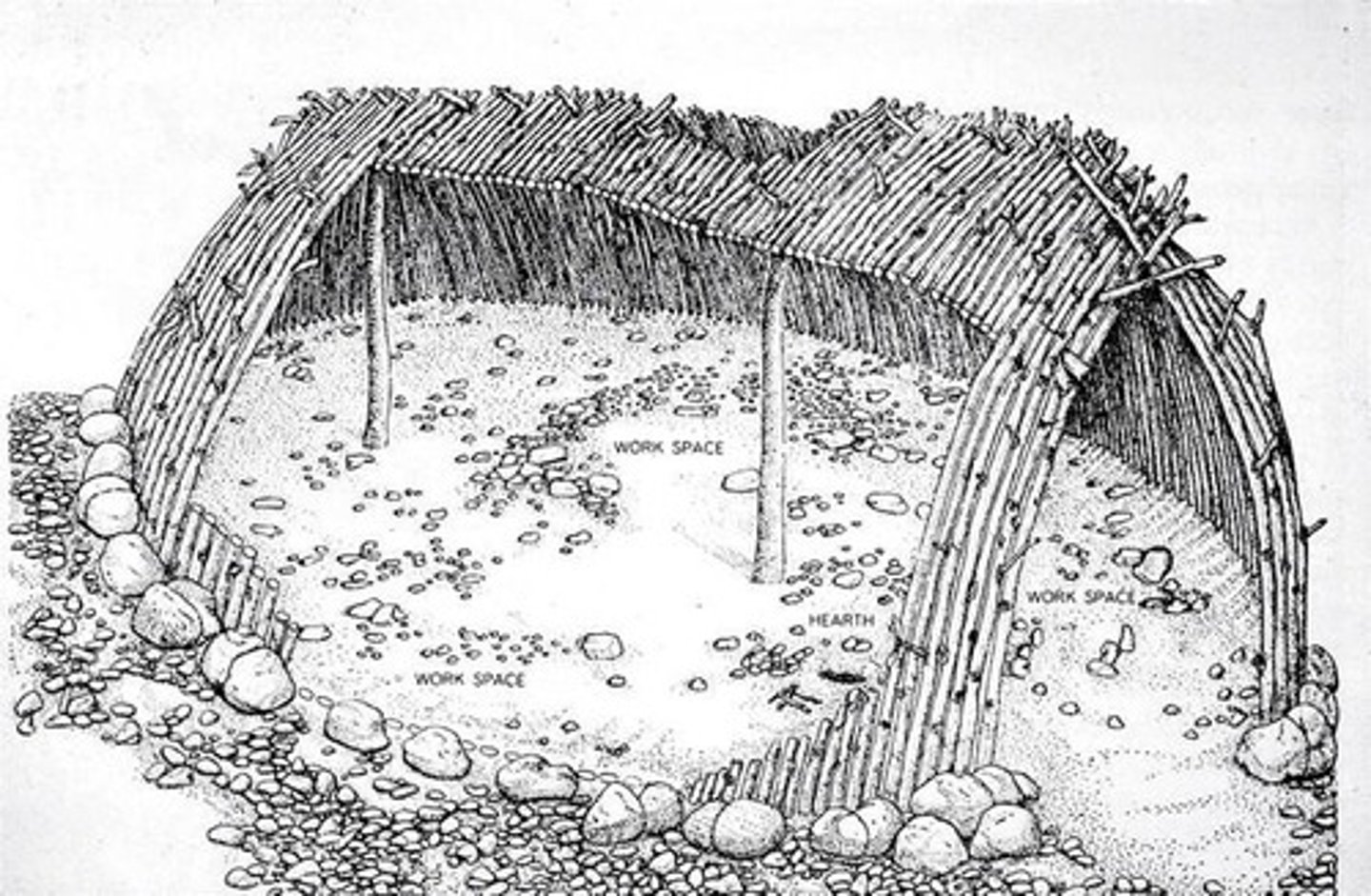
Prehistoric Hut, Terra Amata, (southern) France, dating to c400,000 BCE, Paleolithic
Hypothetical reconstruction of the earliest known huts
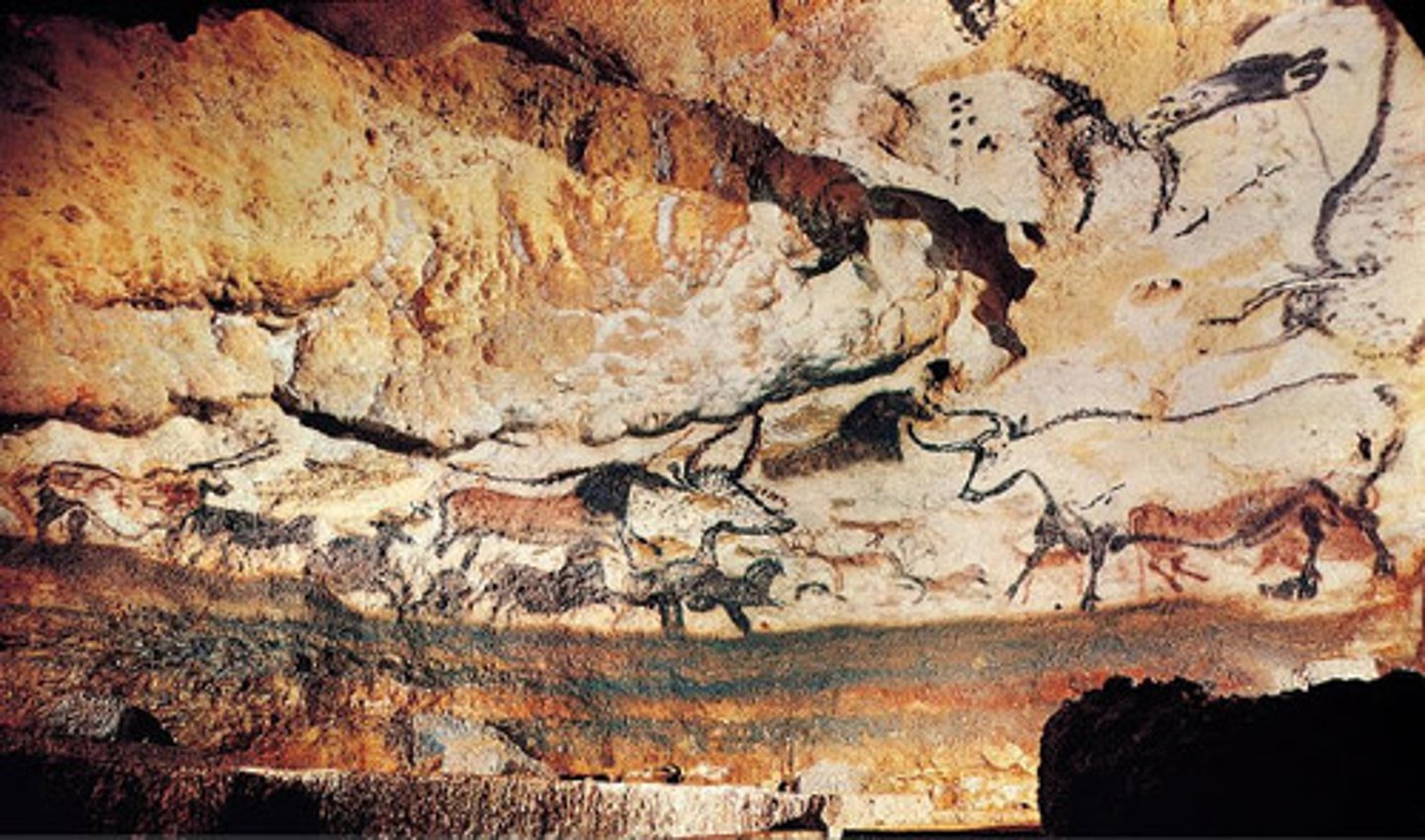
Cave at Lascaux, France, c.c17,000-10,000 BCE, Paleolithic
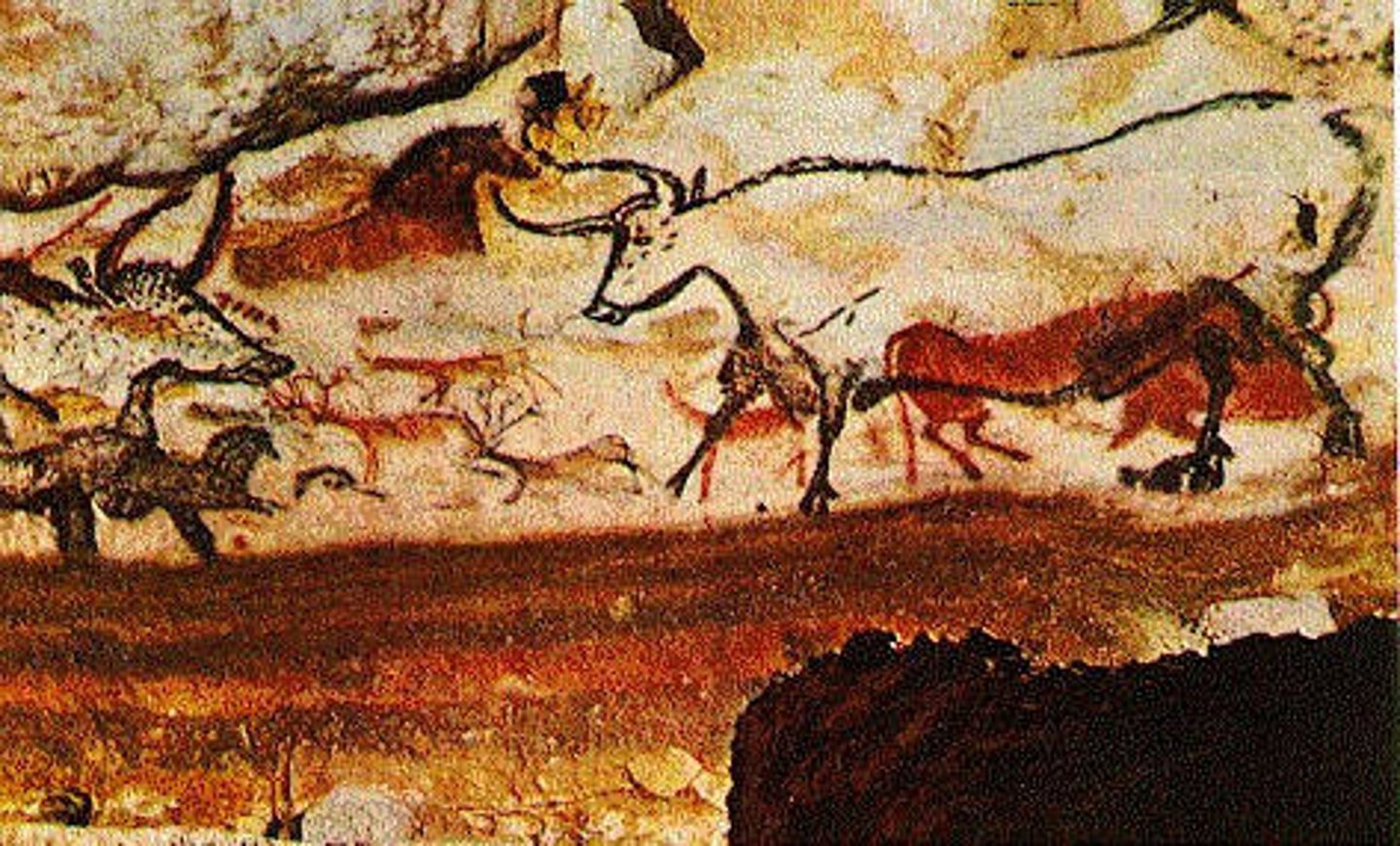

Hall of the Bulls (Aurochs), Lascaux, France, c17,000-10,000 BCE, Paleolithic.
Pigment on limestone; the largest bull painting is 18 feet long

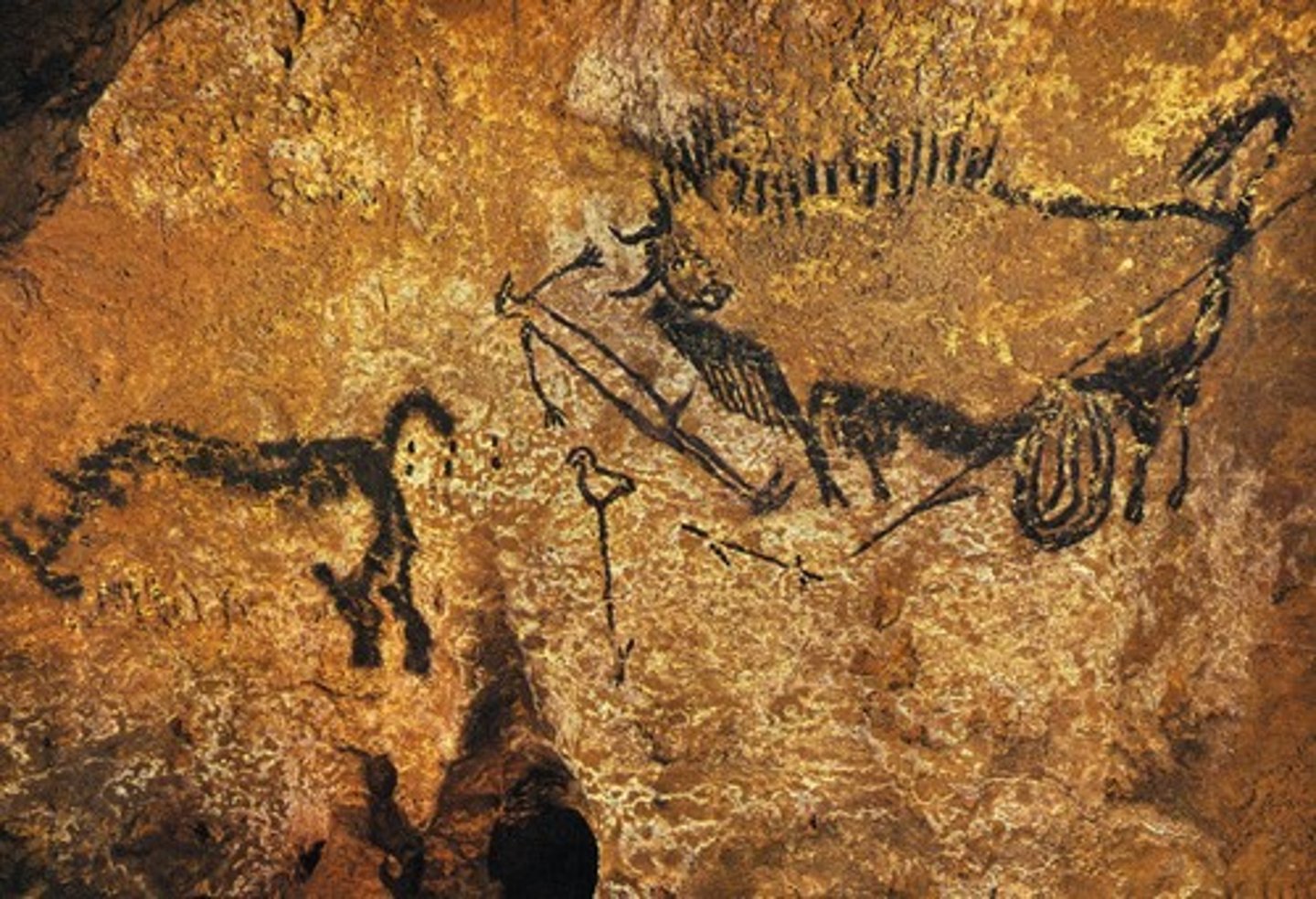
Shaft of the Dead Man, Lascaux, France, c17,000-10,000 BCE, Paleolithic
Pigment on limestone

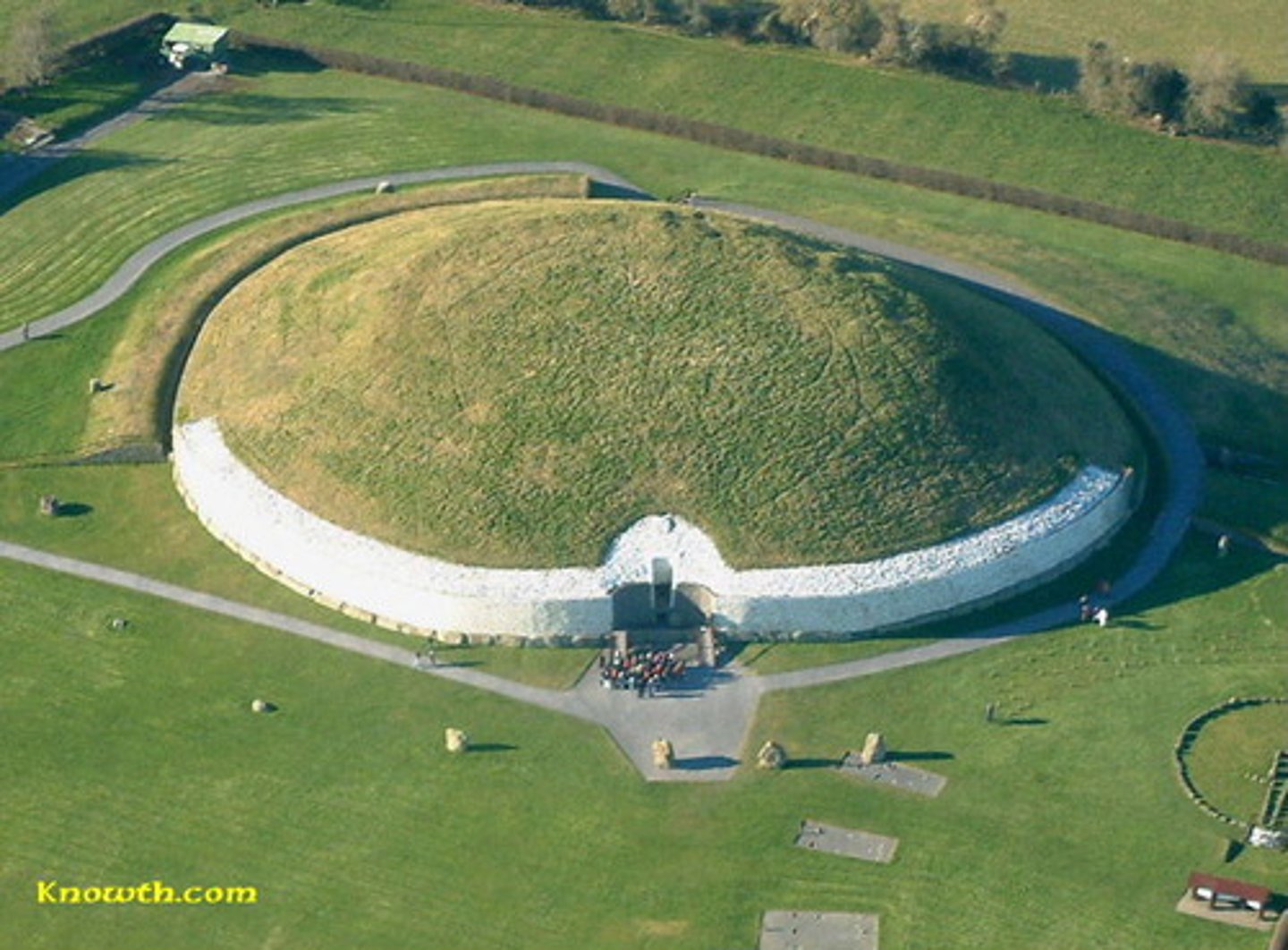
Newgrange Cairn with Passage Grave, Newgrange, Ireland. c. 3000-2500 BCE, Neolithic
burial chamber, note the circular forms inscribed in the megaliths

Stonehenge, Salisbury Plain, England, 2900-1500 BCE, Neolithic
Phases of Construction:
A: 3000-2750 BCE: 56 Aubrey holes inside a circular ditch and bank (the henge)
B: late 3000 BCE: circle of bluestones (from Wales 130 miles away) at center (possible link to ancestral home of Stonehenge's builders); later re-arranged; avenue begun from the opening
C: the sandstone/sarsen circle and horseshoe added; avenue to the woodhenge at Durrington made (living and dead realms)
D: 1500 BCE?: additional smaller enclosures and bluestones moved again; also added two series of pits/holes at outside of sarcen circle (Y and Z holes)

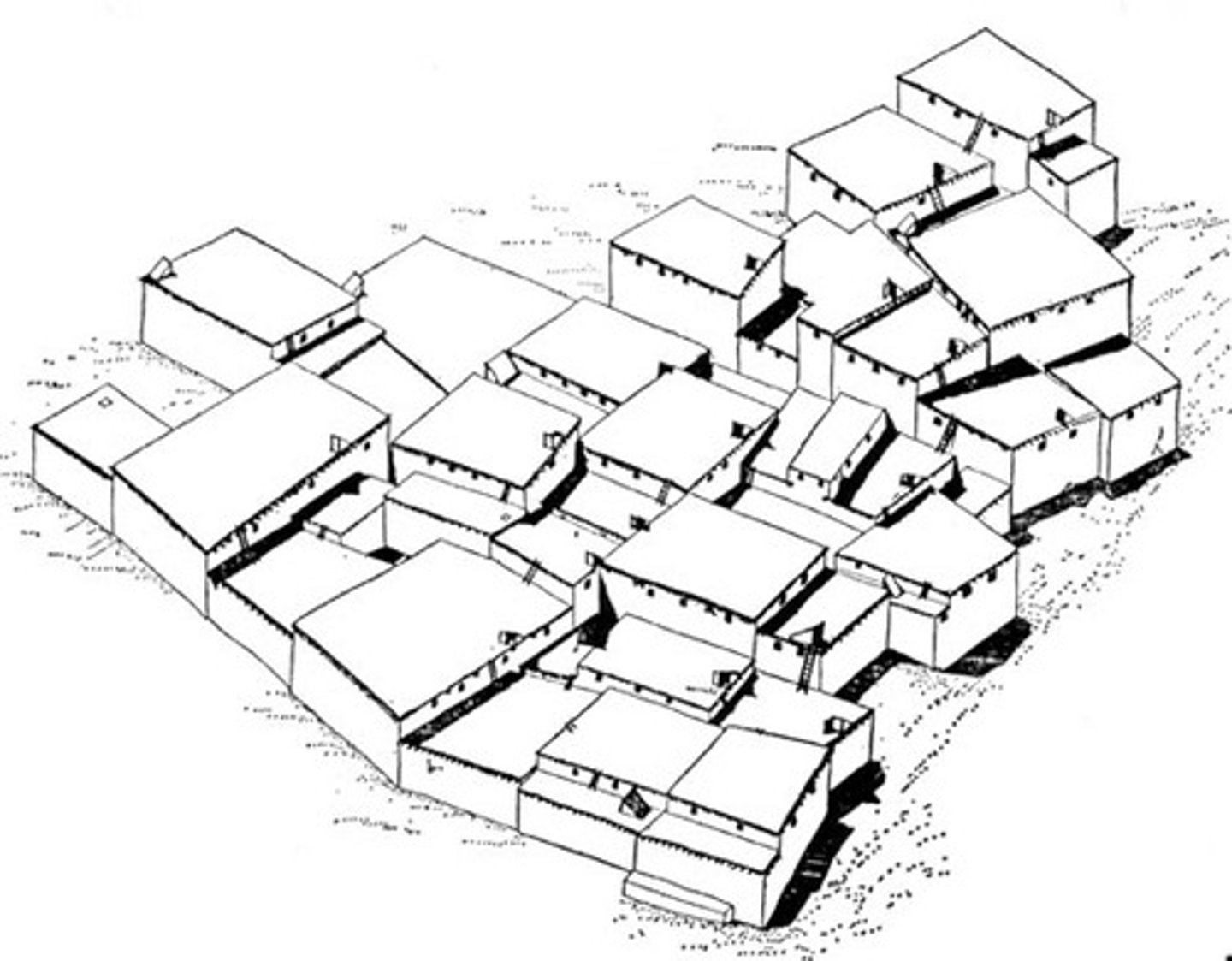
Çatalhöyük, near Konya, Turkey, c. 7,400 to 5,700 BCE, Neolithic
1. individual units, with platforms and internal divisions
2. party walls connecting the units (no doors, entry through roofs)
3. courtyards between units
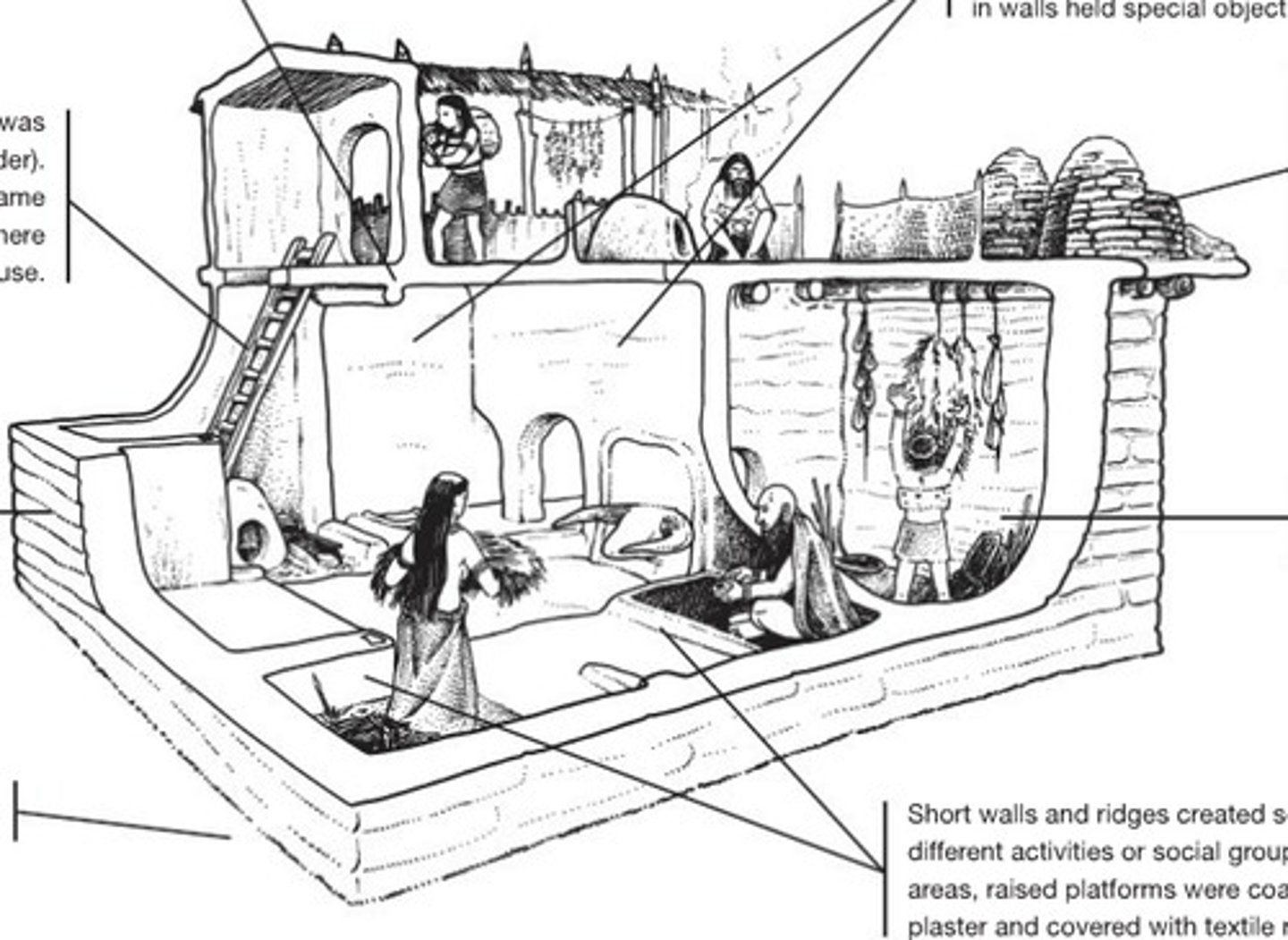
Çatalhöyük, near Konya, Turkey, c. 7,400 to 5,700 BCE, Neolithic Period: domestic structure
• Burial in the home
• Fresco wall decoration
• Shrine room with Bucrania
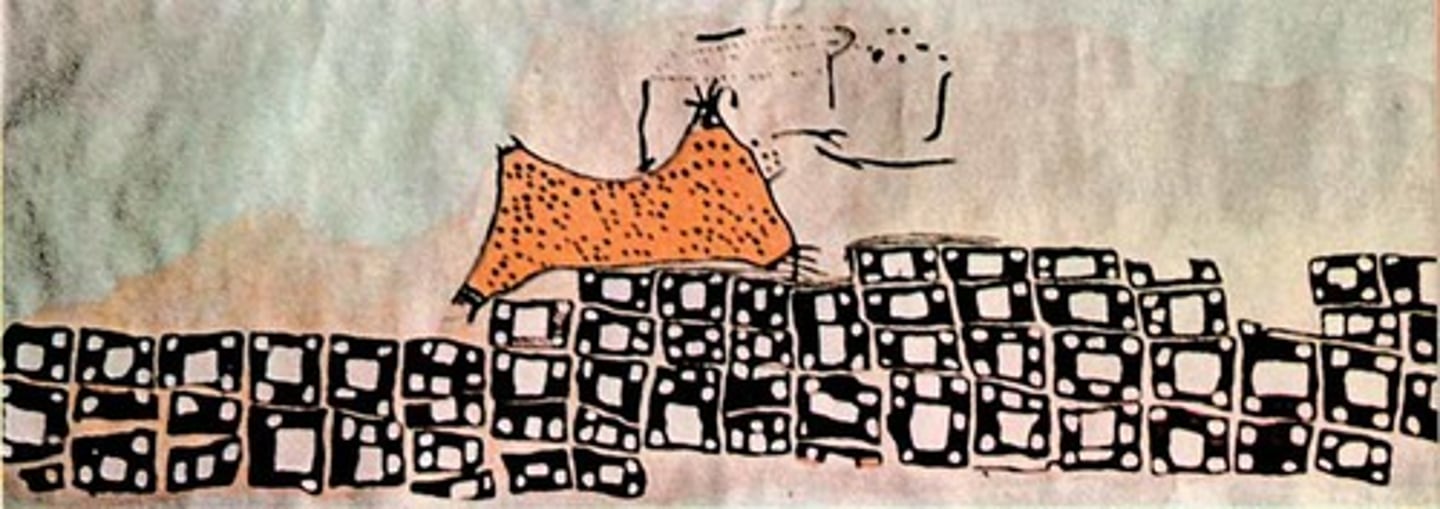
City map and volcano, Çatalhöyük, near Konya, Turkey, c. 5800 BCE. Neolithic.
Painted wall plaster

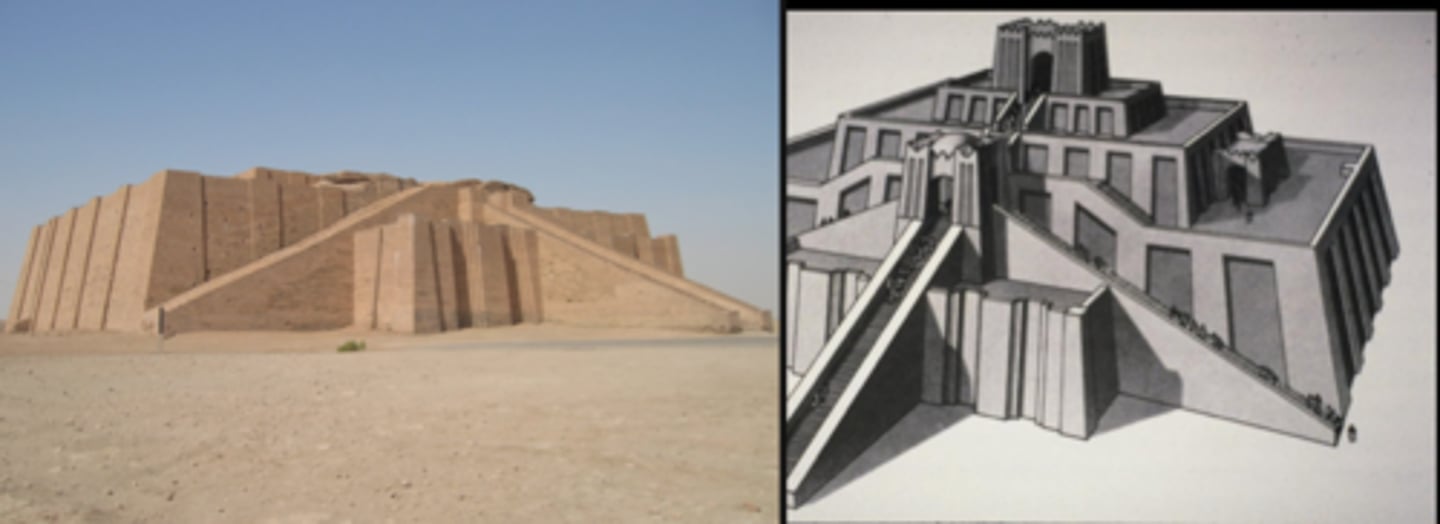
Ur, Iraq, c. 2200-2000 BCE, aerial view with the archaeological remains of the ziggurat and other elements of the city
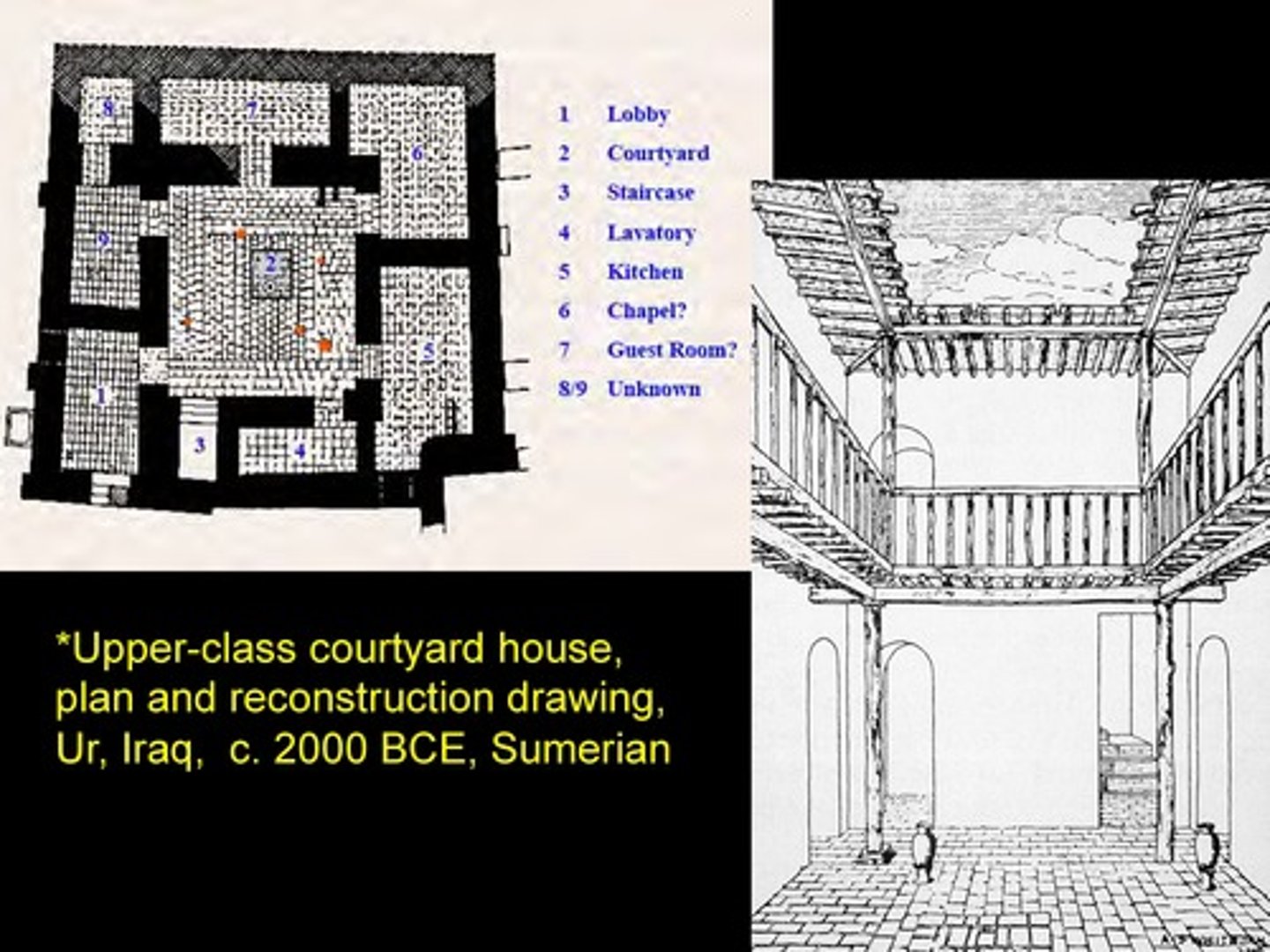
Upper-class courtyard house, plan and reconstruction drawing, Ur, Iraq, c. 2000 BCE, Sumerian
Ziggurat and Temple of Nanna, Ur, Iraq, 2100-2050 BCE, Paron: King Ur-Nammu (and his son, Shulgi); Sumerian

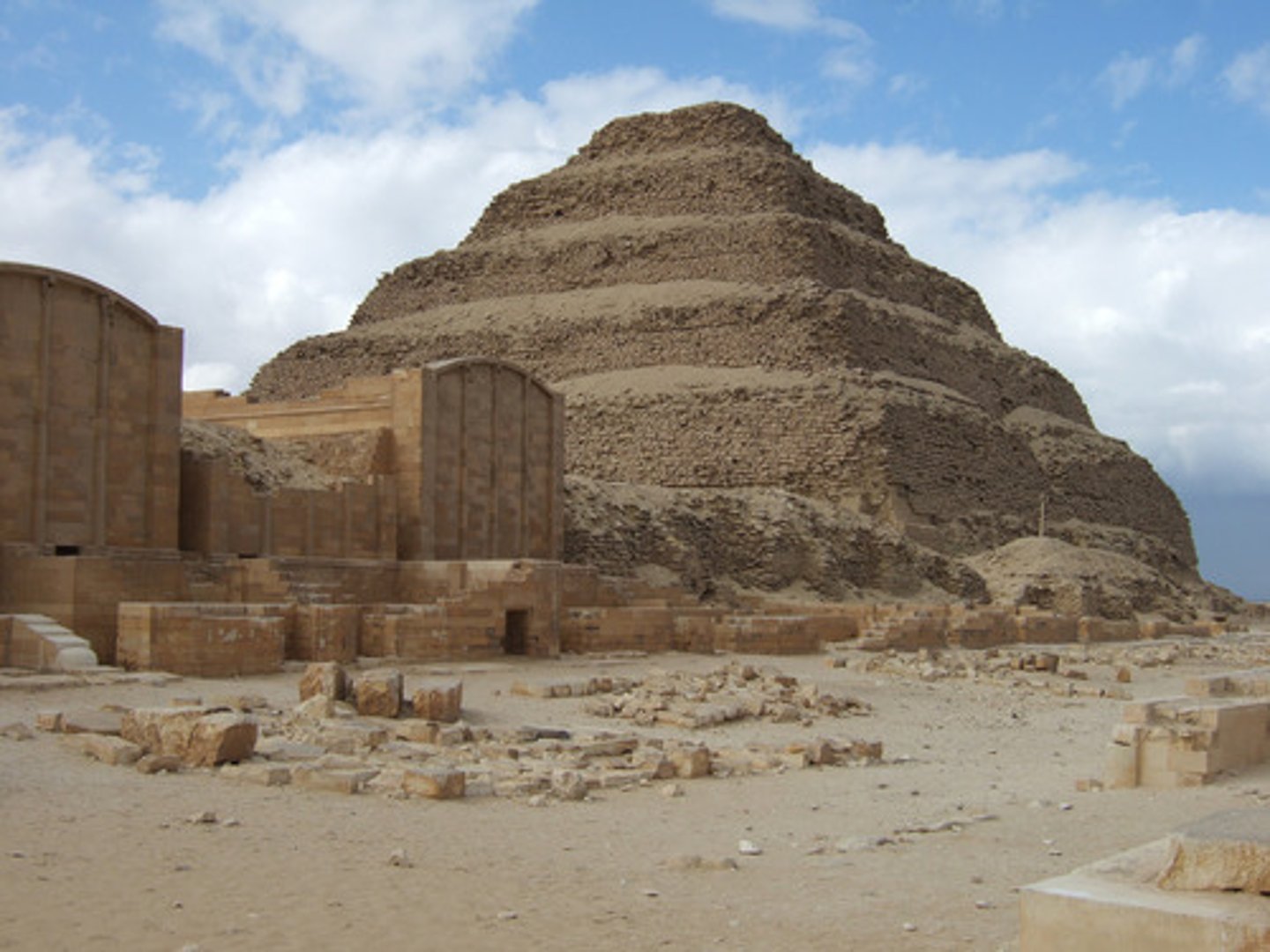
Pyramid and Palace Complex of Pharaoh Djoser, Saqqara,
Egypt, c2650 BCE, Old Kingdom Egypt
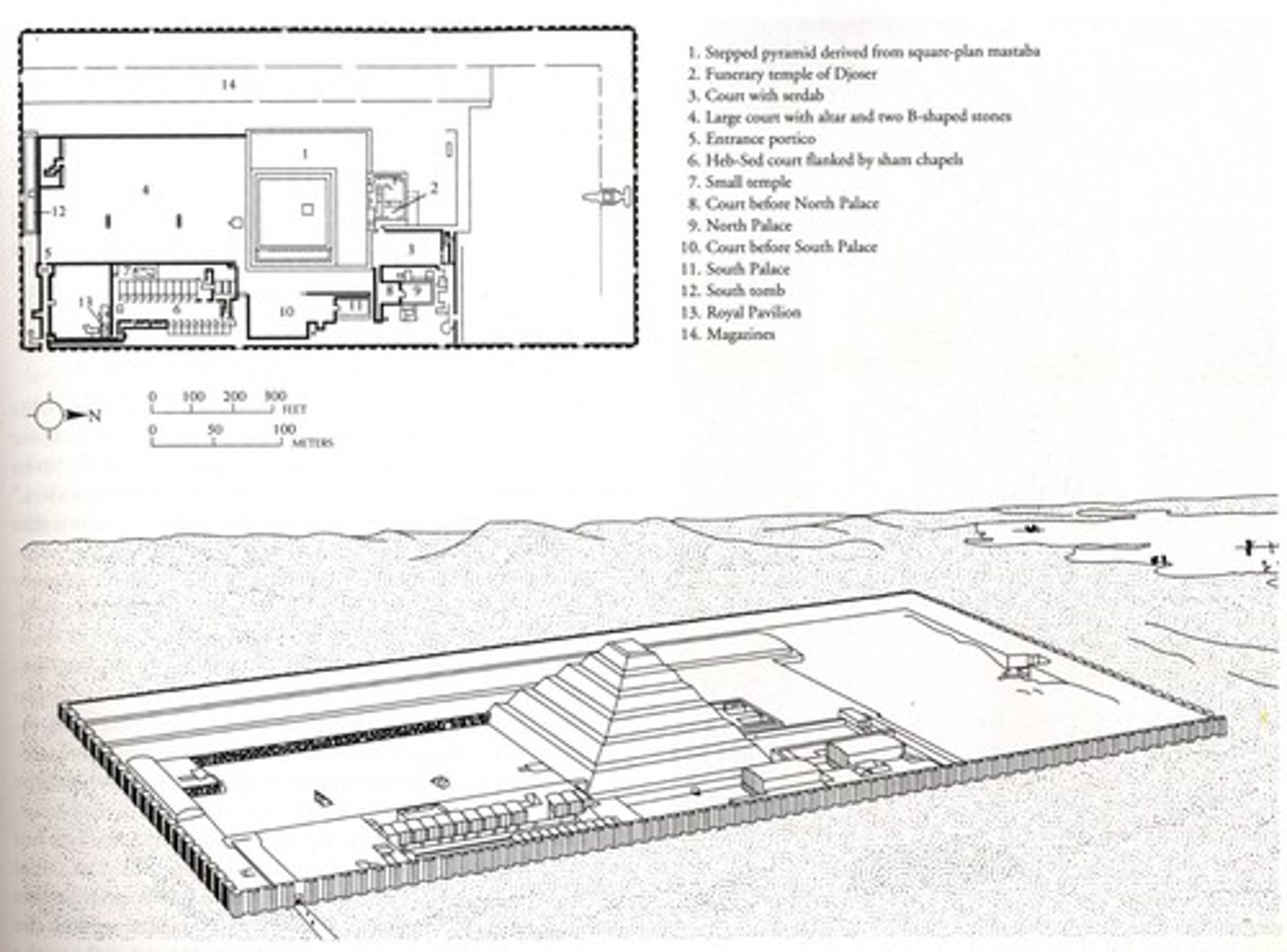
The Step Pyramid of Djoser, Pyramid Complex of Djoser, Saqqara, Egypt, c2650 BCE, Old Kingdom Egypt
Created with superimposed Mastabas

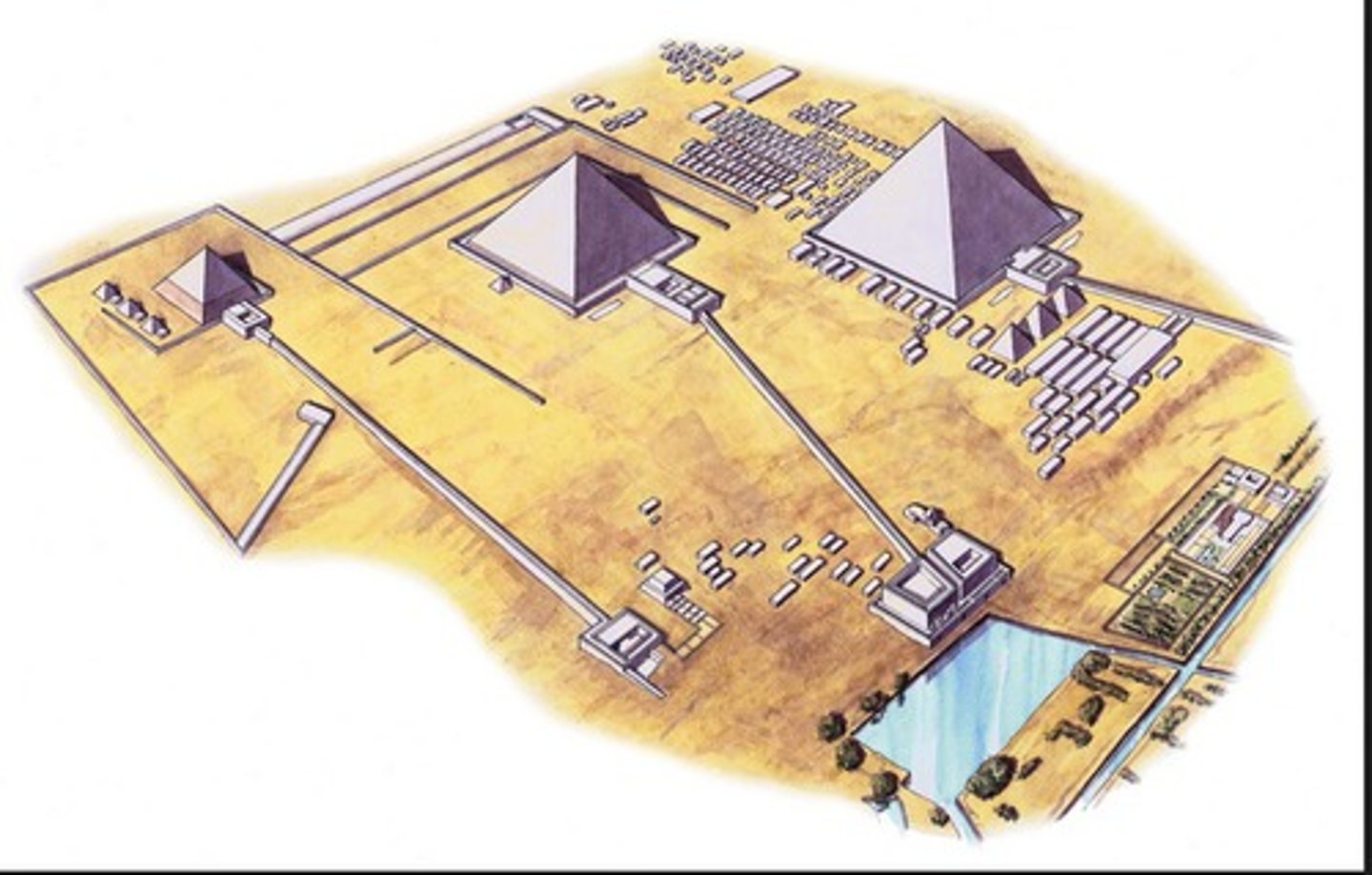
Great Pyramids, Giza, Egypt, 2600-‐2400 BCE, Old Kingdom

Pyramid of Khufu (Cheops), Giza, Egypt, c. 2570 BCE, Old Kingdom Egypt
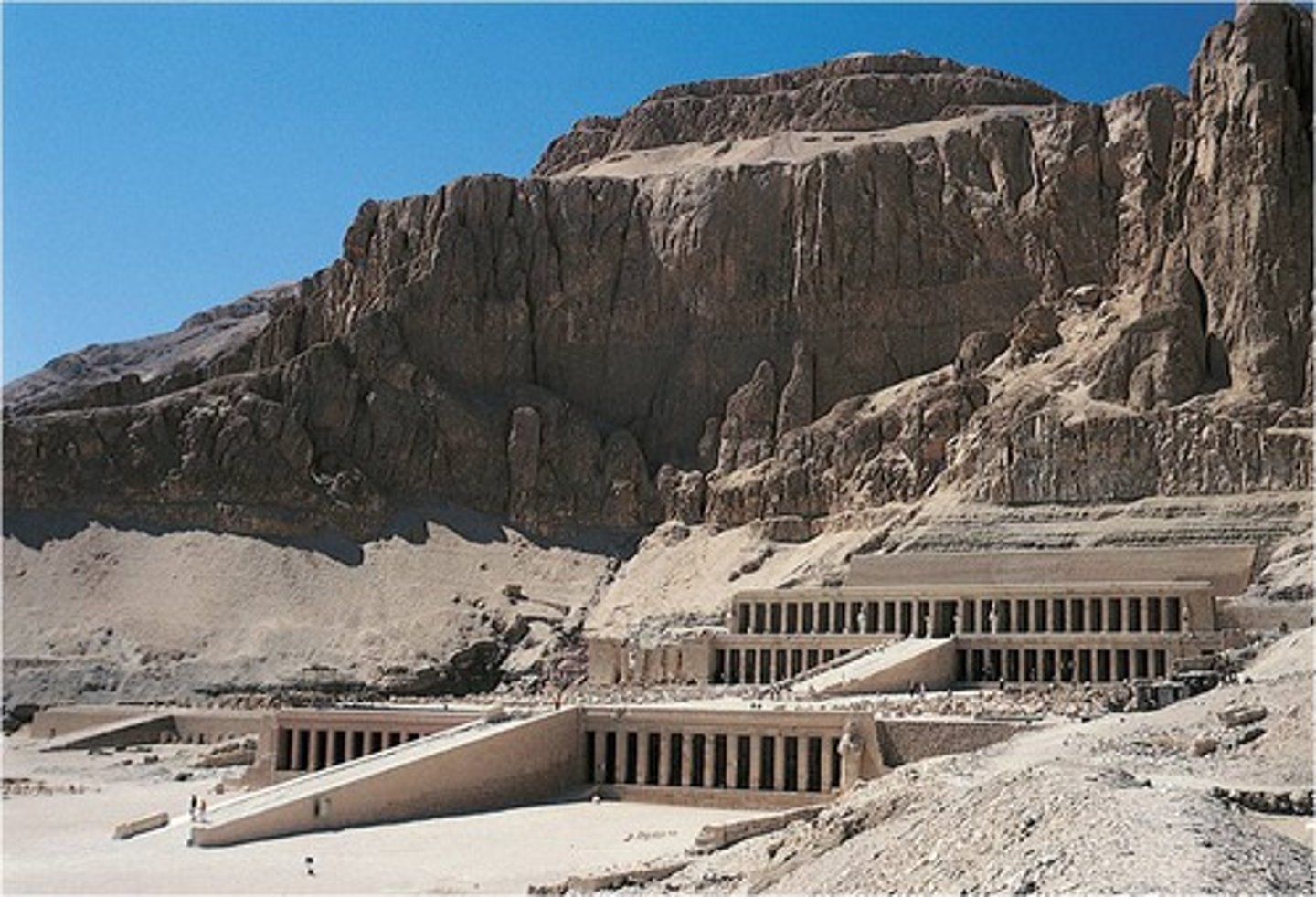
Funerary Temple of Queen Hatshepsut, Deir el-Bahri, Egypt, c.1480 BCE, New Kingdom
Changes: 1. now carved into hillside rather than rising from landscape. 2. One dominant axis rather than approachable from all sides. (Axiality; carved from the living rock/cliff-face)

Temple Complex of Amun-Re, Karnak, Egypt, 1417-1379 BCE, New Kingdom
Pylon & Hypostyle
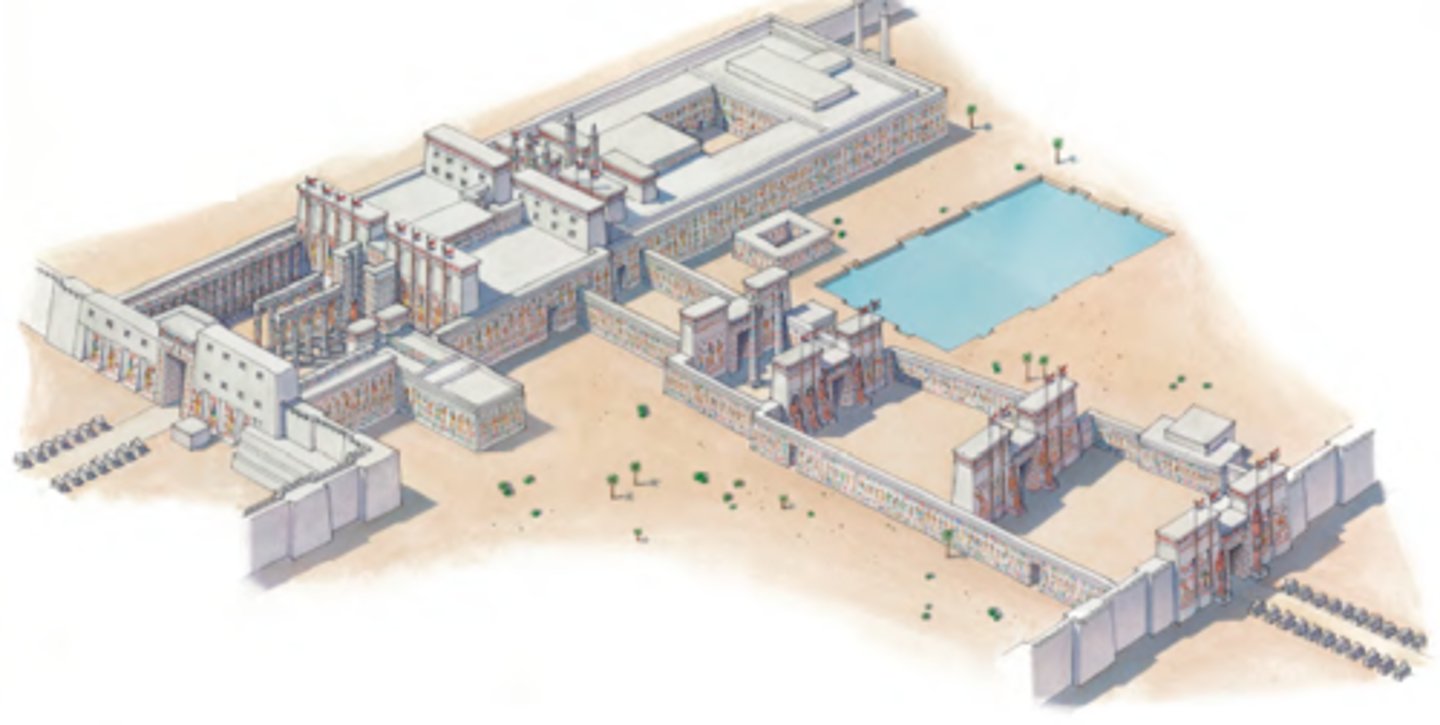
Palace of Knossos, Knossos (Crete), Greece, c. 1450 BCE, Minoan
• Non-fortified site, largely open to the surrounding countryside
• Large storerooms (west/left) for gathered commodities made in the area, more palatial/ceremonial rooms (east/right); central courtyard
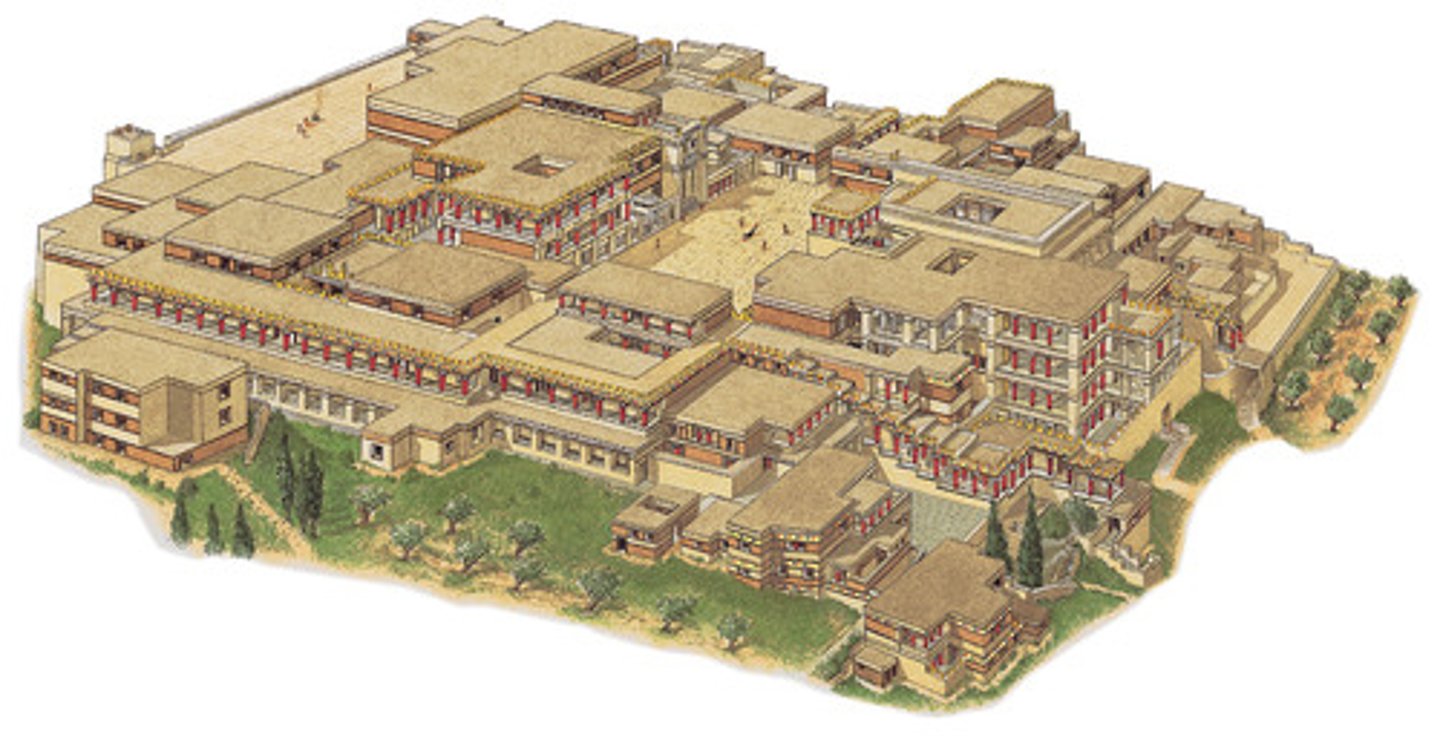
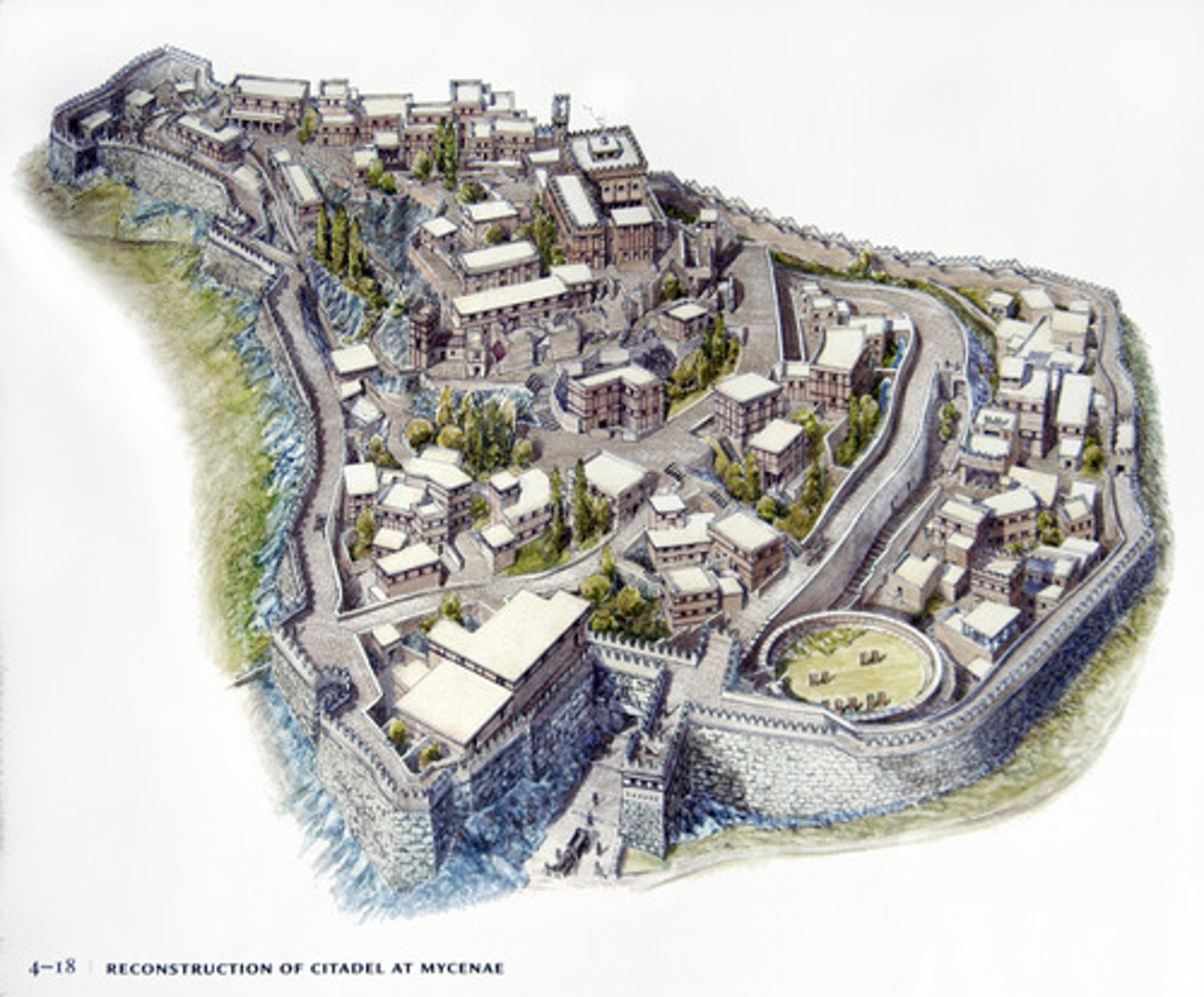
Citadel, Mycenae, Greece, 1600-1200 BCE, Mycenaean
Naturally fortified site, reinforced over time with a strong wall
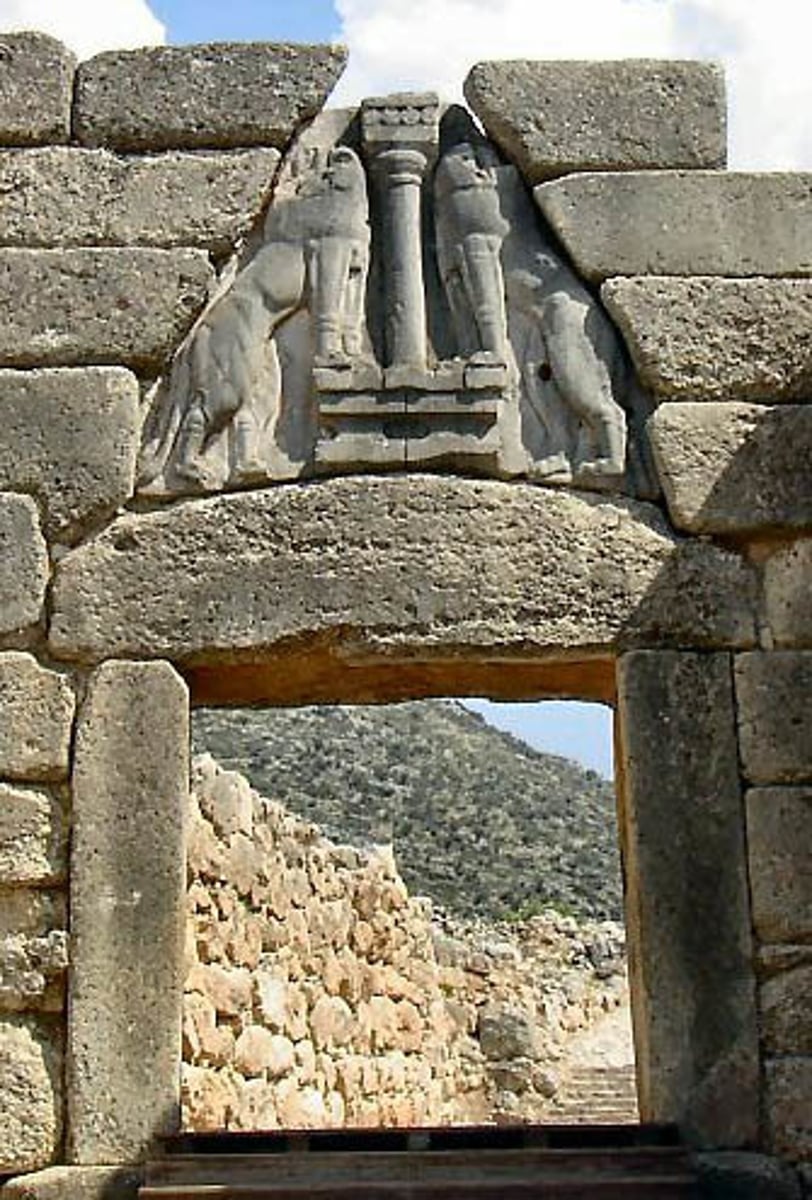
Lion Gate, Citadel, Mycenae, Greece, 1250 BCE, Mycenaean
limestone relief , 9 ½ feet high

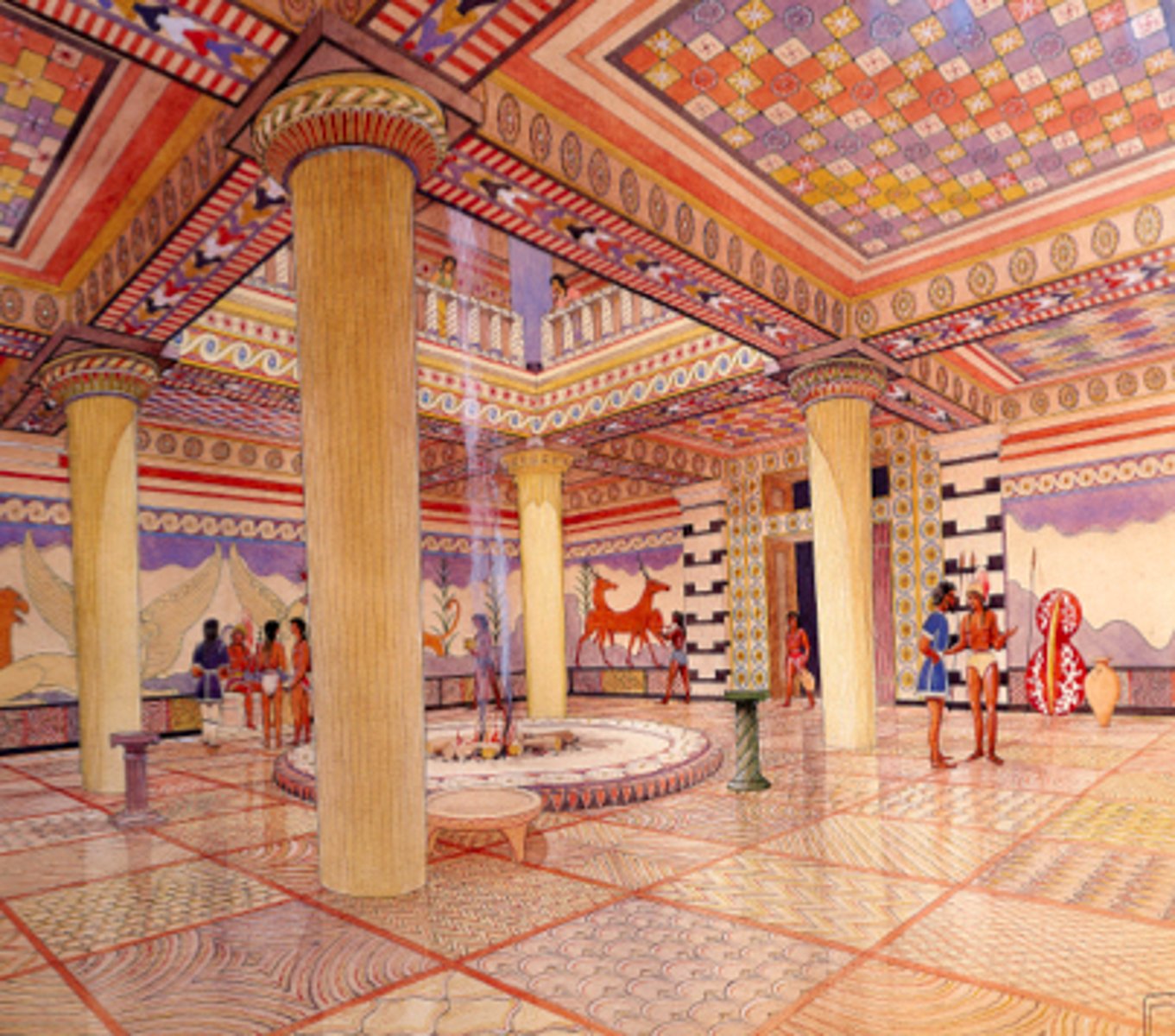
Megaron, Citadel, Mycenae, Greece, 1600-1200 BCE, Mycenaean

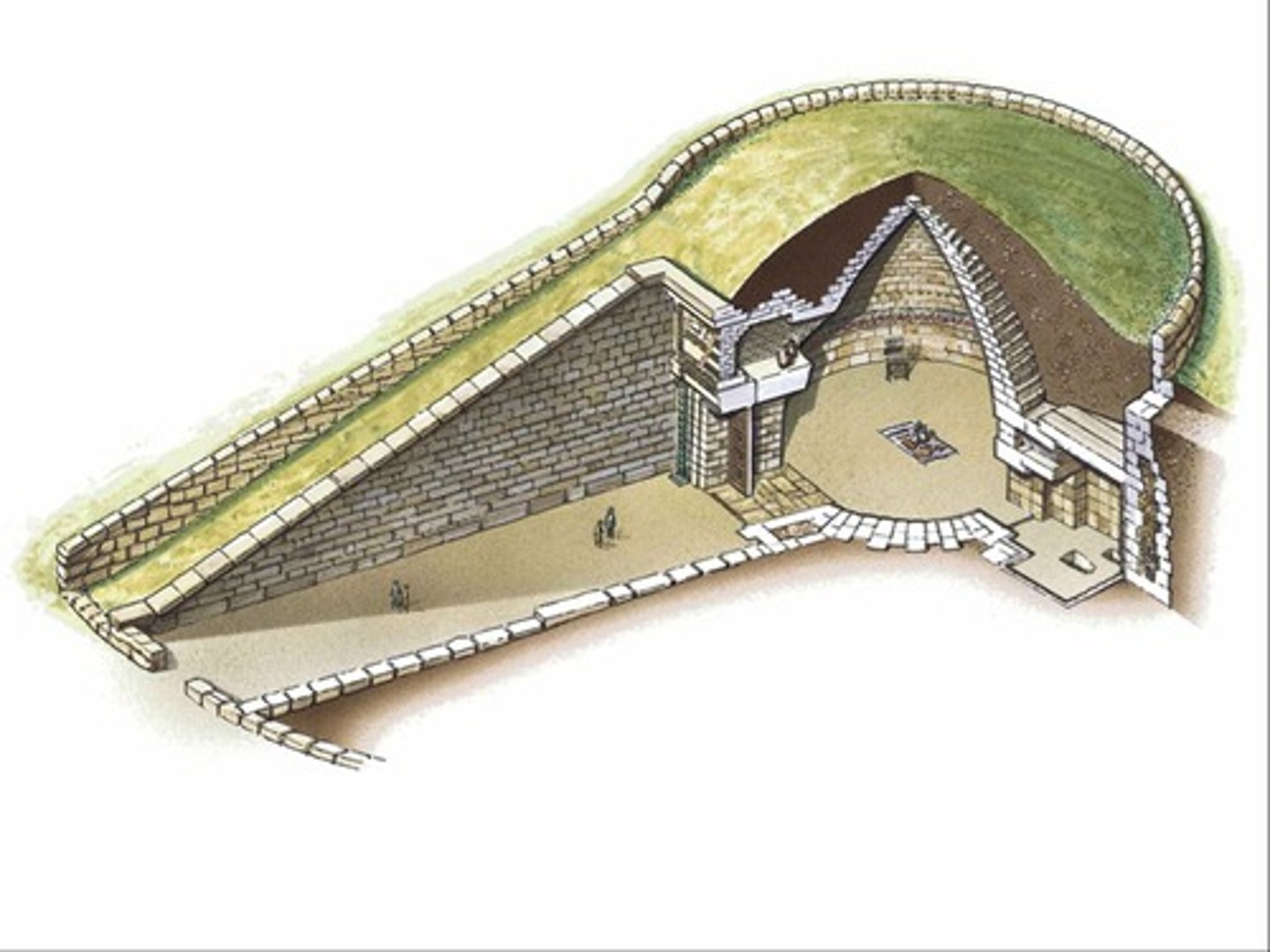
"Treasury of Atreus," Mycenae, Greece, c. 1250 BCE, Mycenaean
• Circular form; long passage (like the dromos/avenue at Newgrange)
• Avenue/passage with monumental entry; relieving arch in triangular form over portal
City Plan, Paestum (Poseidinia), Paestum (southern) Italy, eighth century BCE, Archaic Greek
Per Strigas - ("by bands") a gridding system of land division using a small number of east-west avenues to divide a site into long bands, which were then subdivided using narrow north-south streets

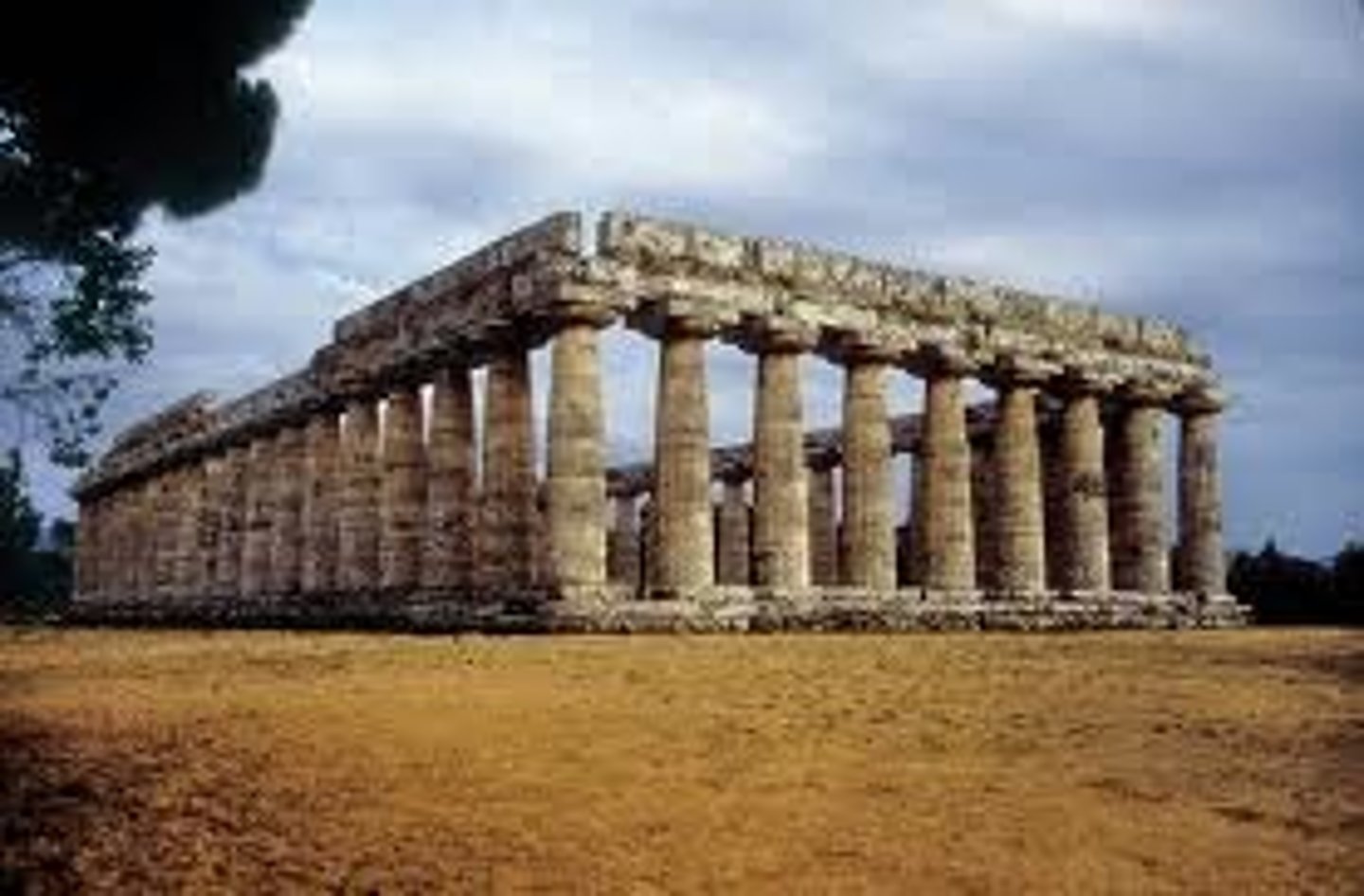
Temple of Hera, Paestum, Italy. c. 550-540 BCE, Archaic Greece
• Possible origins: Megaron at Mycenae / Temple of Amun-Ra at Karnak/Luxor, Egypt
• This is a Doric temple.

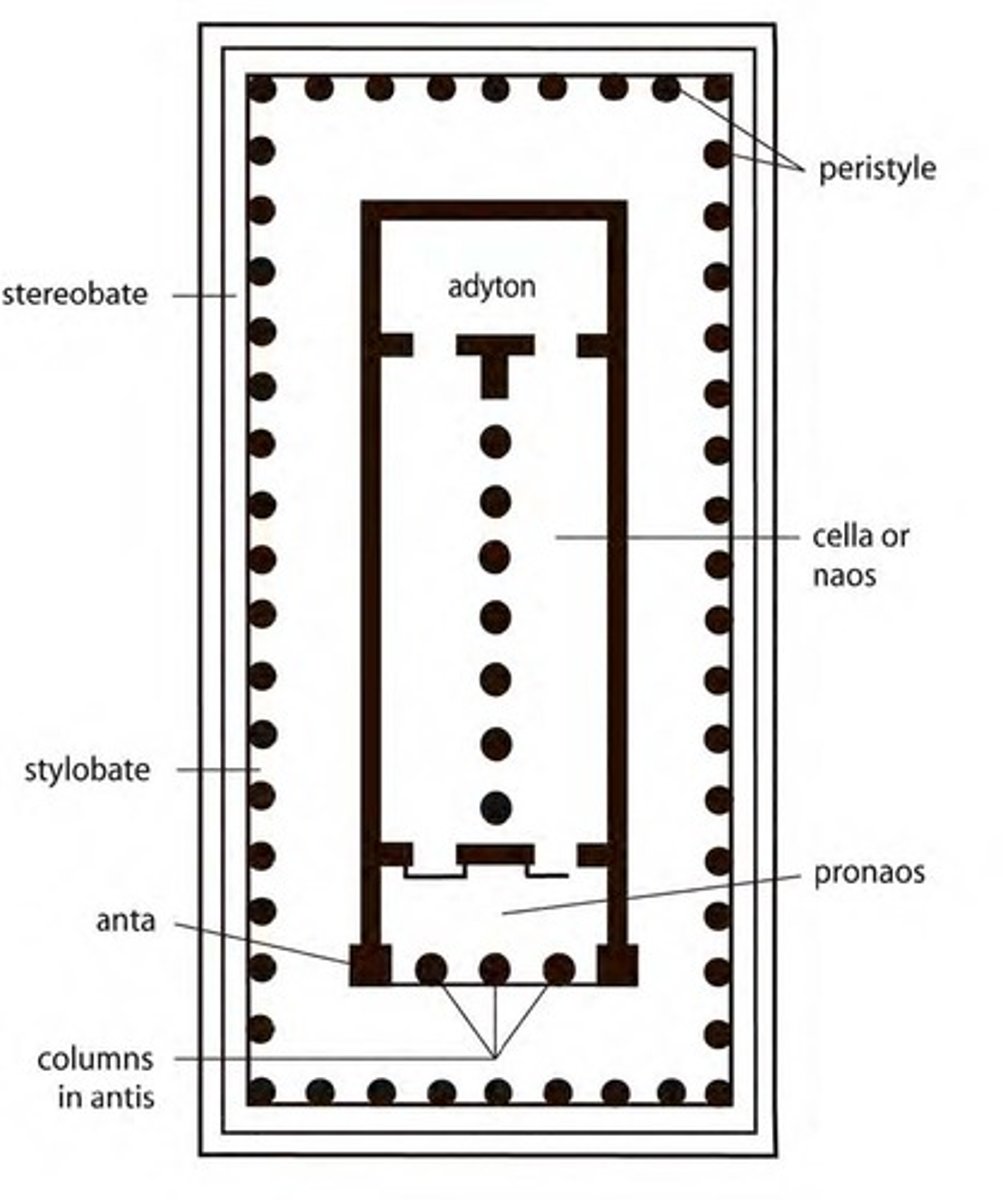
**PARTS OF GREEK TEMPLES
CELLA or NAOS
PRONAOS
PERISTYLE
STYLOBATE (top step)/
STEREOBATE (lower steps)
**The Classical Orders & building parts in Greek Architecture
• For Doric order,
Column = Shaft + Capital
Frieze = triglyphs + metopes
• For Ionic order and Corinthian order
Column = Base + Shaft + Capital
• Entablature = architrave + frieze + cornice
• Pediment and gable

The path of the Panathenaic Procession through Athens, Greece, Classical Period
Dipylon Gate - Agora - Acropolis
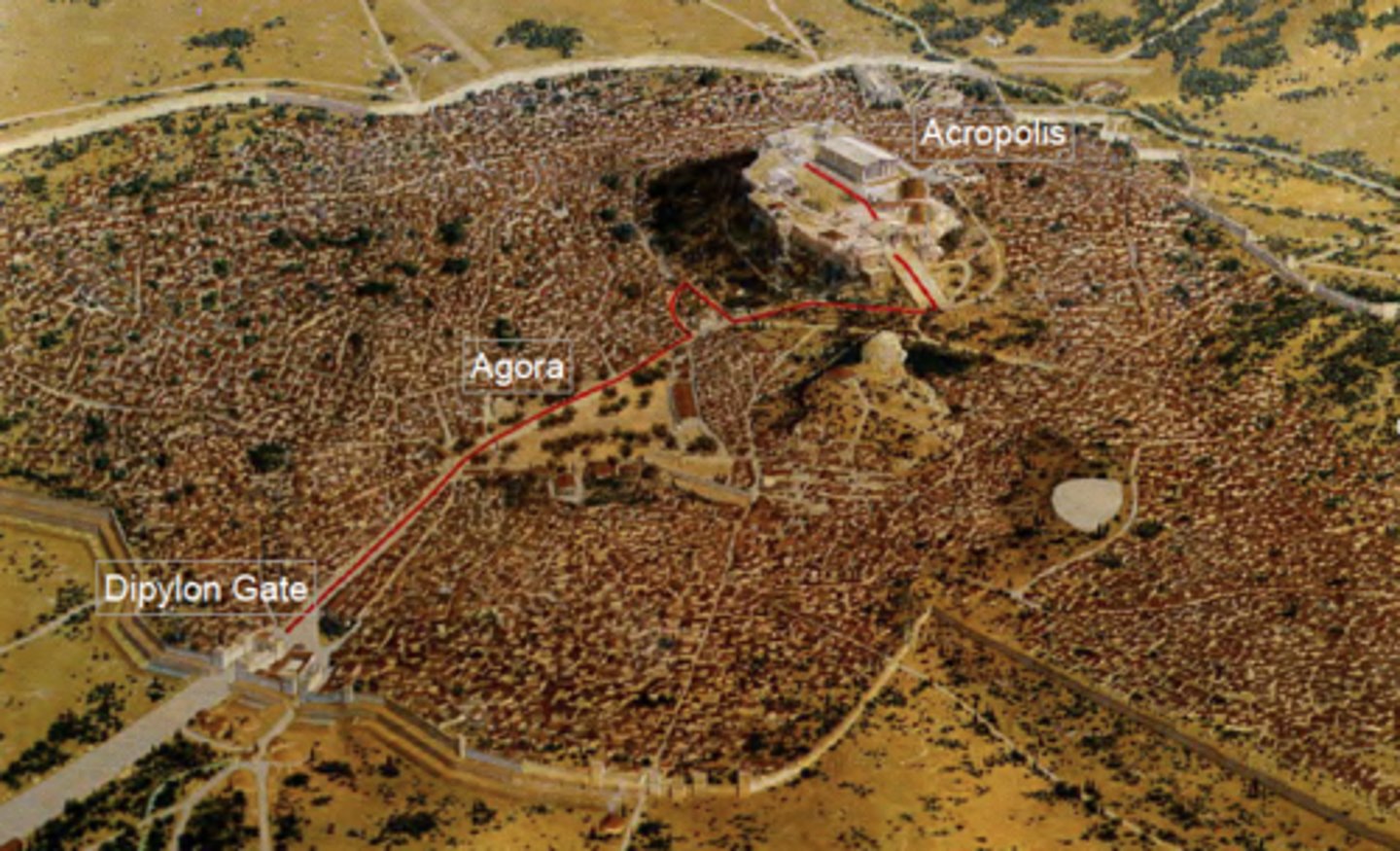
Athenian Acropolis: Sanctuary of Athena Acropolis
• The Acropolis as a site of memory for Athenians: Events that happened on the Acropolis hill in Greek mythology: the birth of Athena & Athena defeats Poseidon
• Main Altar outside Parthenon

Propylaia, Athens, Greece, 437-432 BCE, Classical
Greek (designed by Mnesikles)
通廊
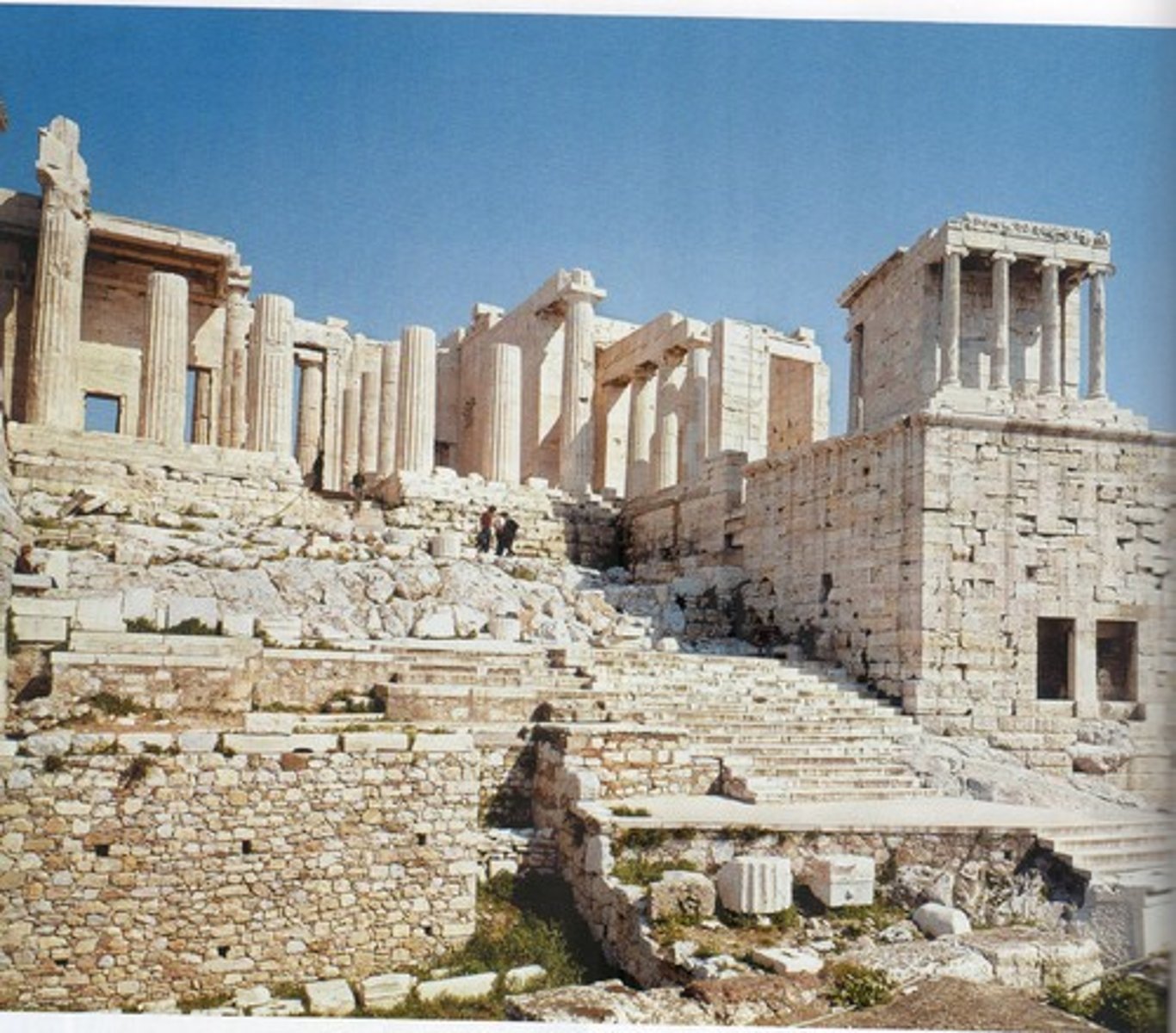

The Parthenon, Athens, Greece, 447-432 BC, Classical Greek
• This is a Doric temple.
• Plan of the Parthenon differs from the plan of the temples at Paestum or Delphi in the internal
walls/rooms.
• The Entablature: Metopes, including Lapith and Centaur, BM 27, has visual metaphor for Athenians' (lapiths, men) war and victory over the Persians (shown as the "Other," foreign, centaurs)
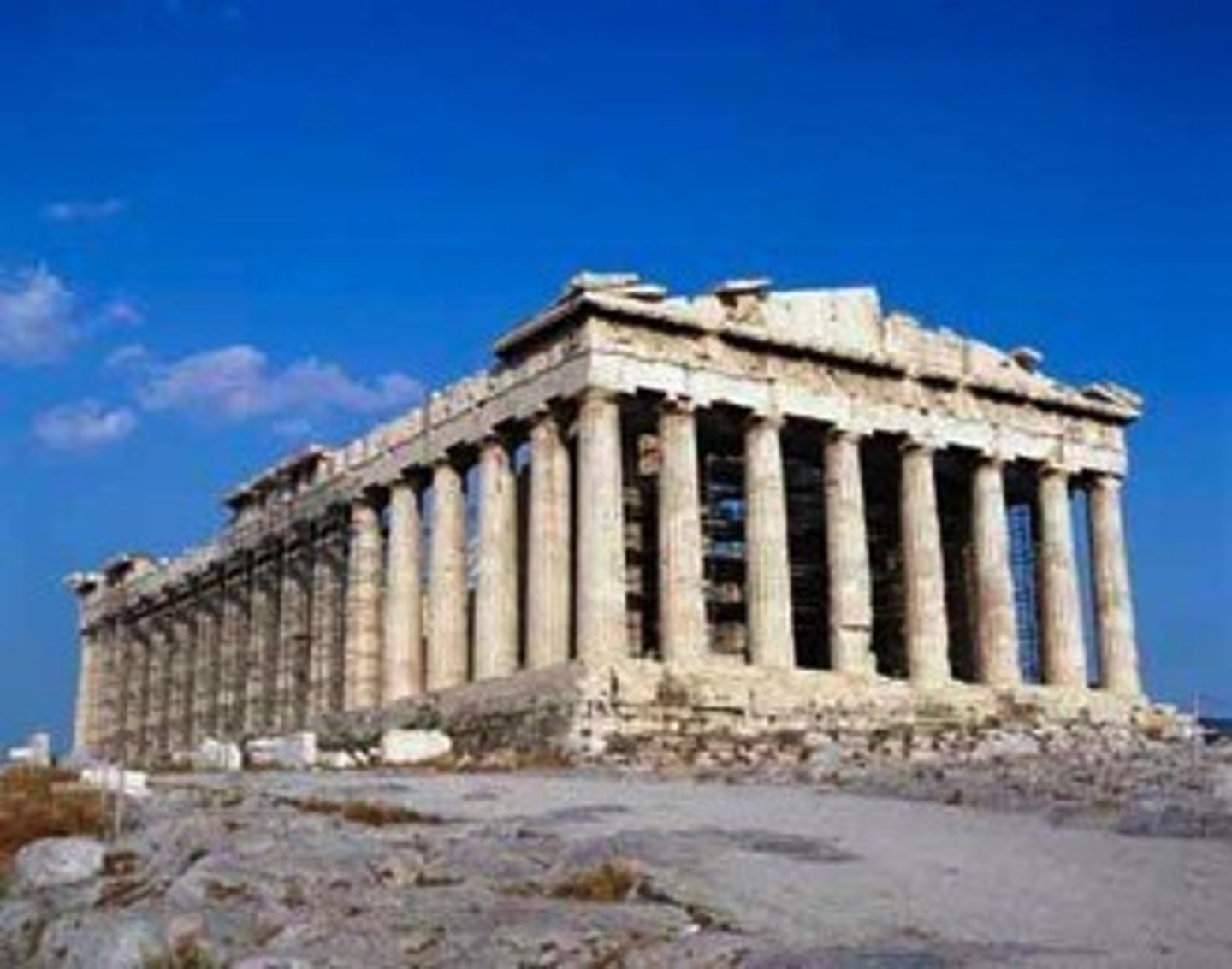

Parthenon's Pedimental Sculpture
• West Pediment: The Contest Between Athena and Poseidon for Rule over the Athenians
• East Pediment: The Birth of Athena
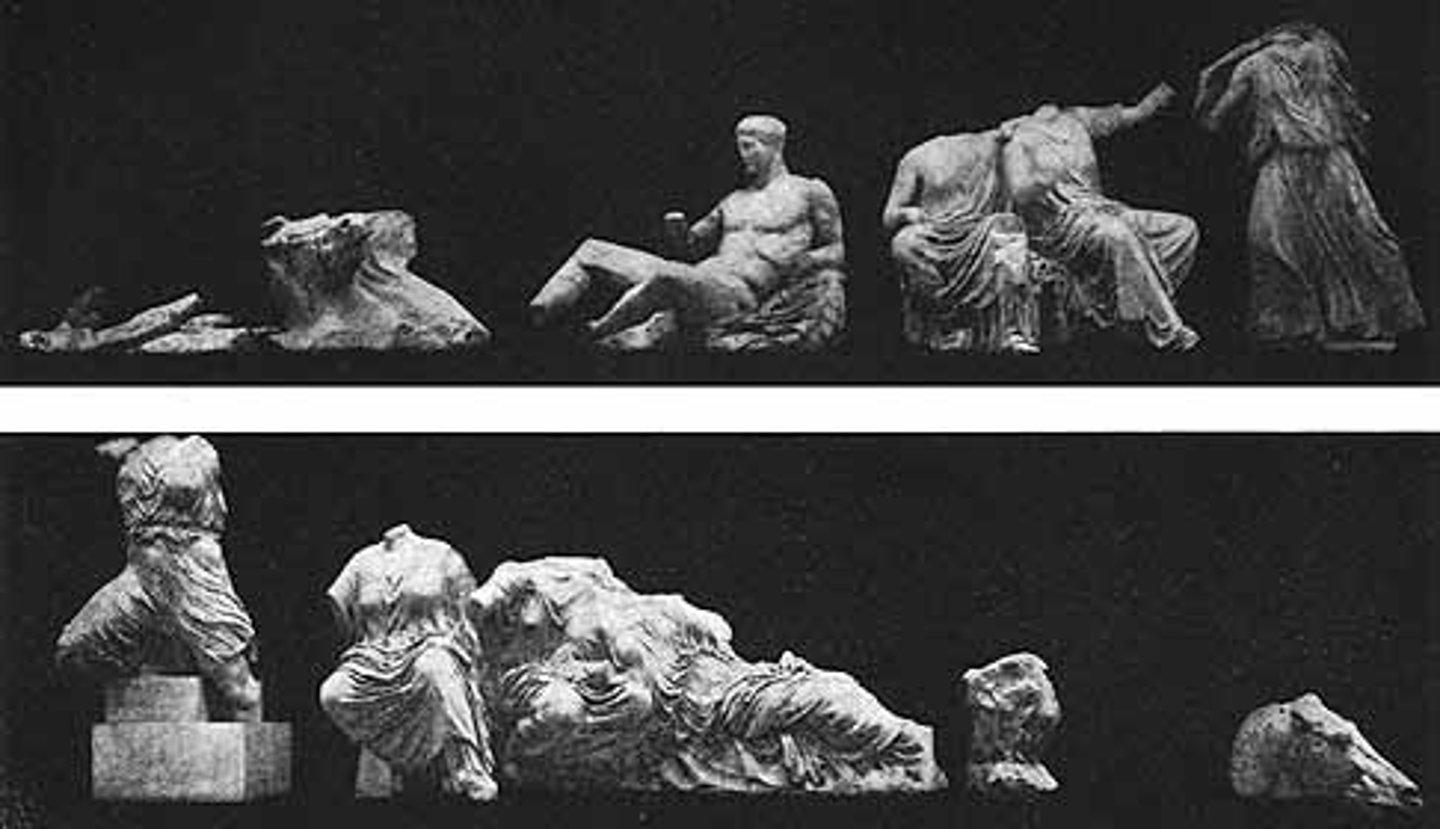

Parthenon Frieze: Panathenaic Procession
• Painted in antiquity
• Riders and cattle for sacrifice
• folding the peplos and seated gods; women
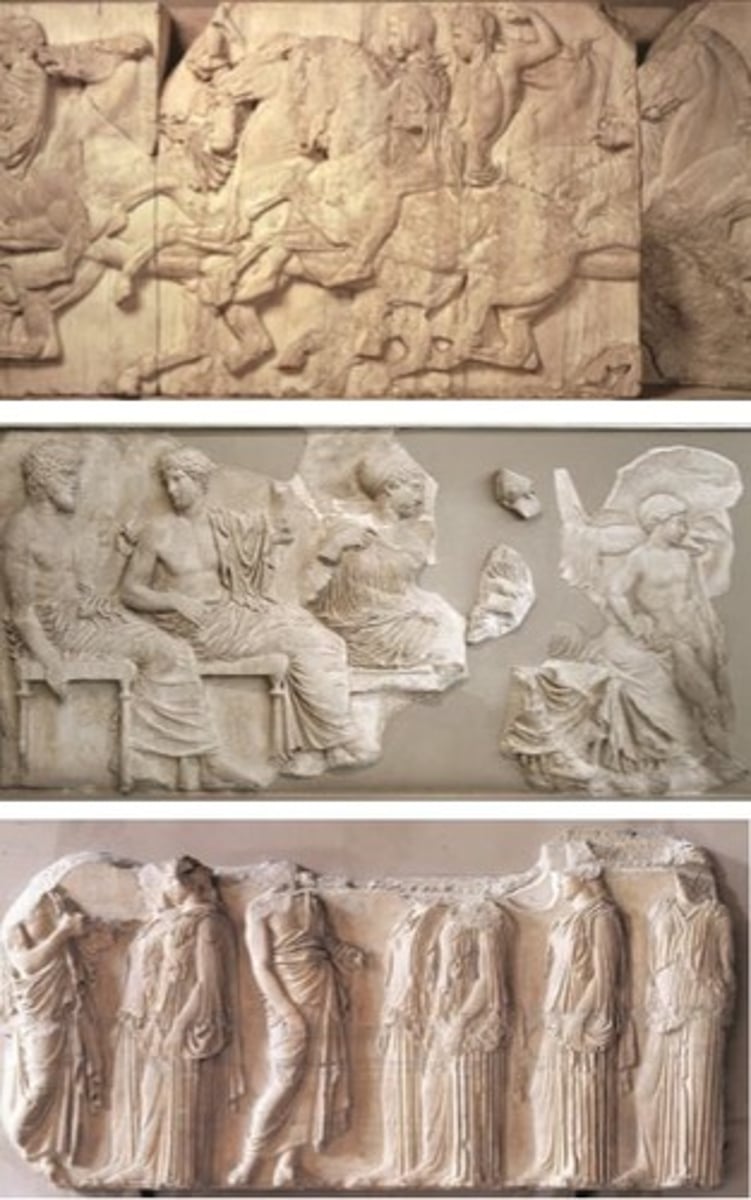

The Erechtheion (on Acropolis), Athens, Greece, 421-405 BCE , High Classical Greece
Cella of Athena + Caryatid Porch - 伊瑞克提翁神殿

Maison Carré, Nîmes, France, c 20 BCE, Roman Imperial
• Roman Forum, temple with external altar built into staircase; Roman relief of ox being ritually slaughtered at a temple.
• Like the Greeks, the Romans' main liturgical acts (religious rituals, such as sacrificing animals and roasting their meat) happen at OUTDOOR altars
• Example of a TEMPLE/Religious Structure

Roman city "kit"
• building blocks used to house necessary institutions throughout the cities of the provinces.
• This regularity also gave a familiar feel - spreading "Romaness" - to many Roman cities throughout the vast territory the empire controlled.
• forum, (civic) basilica, commemorative monument, temple/religious space, bath, market. Often arranged around two streets: cardo and decumanus

Forum of Trajan, Rome, Italy as in the second century CE, Imperial Rome

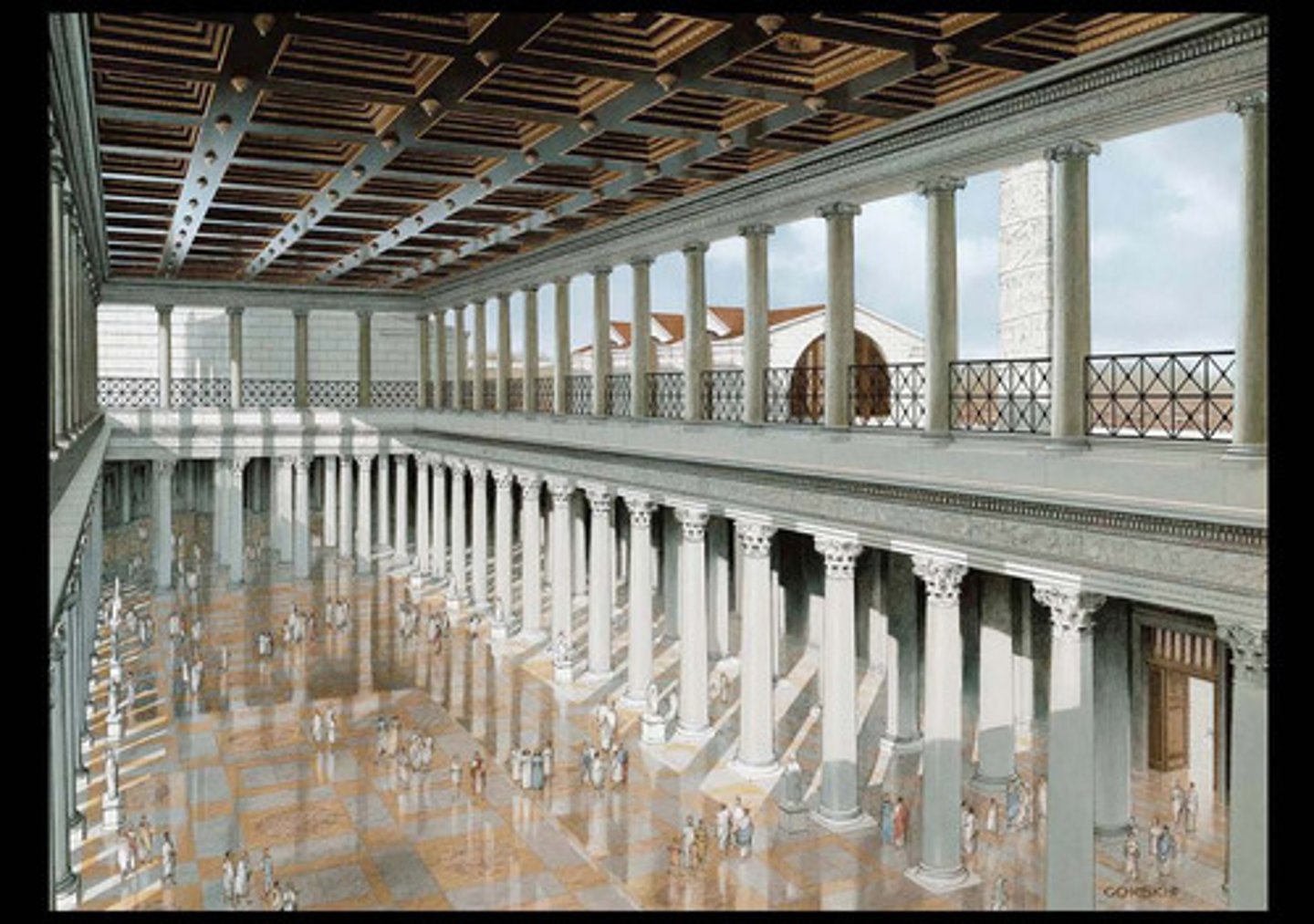
Basilica Ulpia, Rome, Italy (in the Forum of Trajan), 98-117 CE, Imperial Roman, Patron: Emperor Trajan
example of a civic basilica, for law courts and administration

Column of Trajan, Rome, Italy, 113 CE, Patron: Emperor Trajan. Imperial Roman.
example of a triumphal/commemorative monument

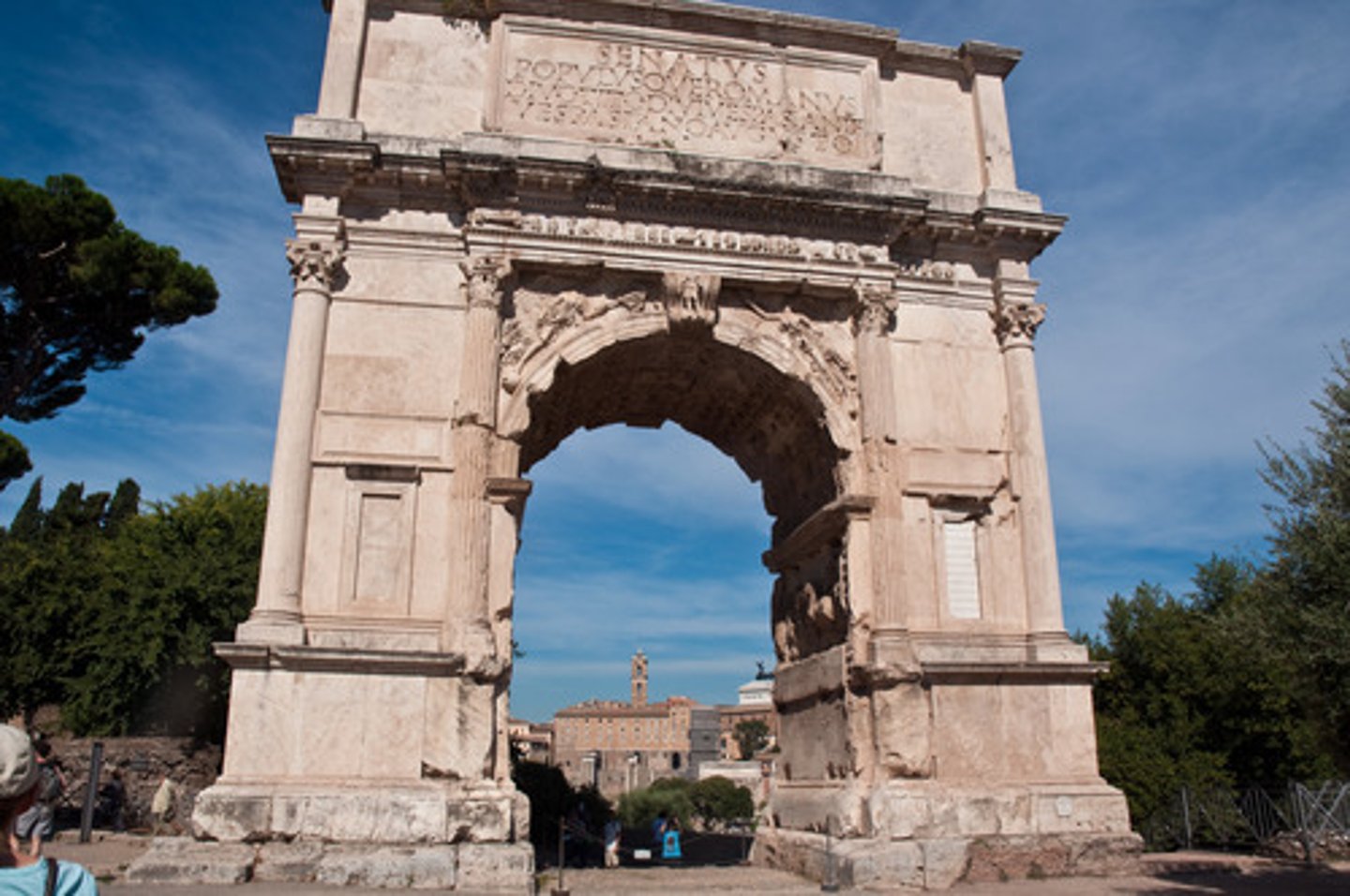
Arch of Titus, Rome, Italy, 81 CE, Patron: : Emperor Titus, Imperial Roman
example of a triumphal/commemorative monument

Markets of Trajan, Rome, Italy (in the Forum of Trajan), 98-117 CE, Imperial Roman, Patron: Emperor Trajan
example of MARKET

Pantheon, Rome, Italy, 118-28 CE, patron: Emperor Hadrian, Imperial Roman
• Geometric sophistication
• Spherical form in a square
• Circle and square motifs(图案) used repeated in many ways
• the interior revetment in many different marbles

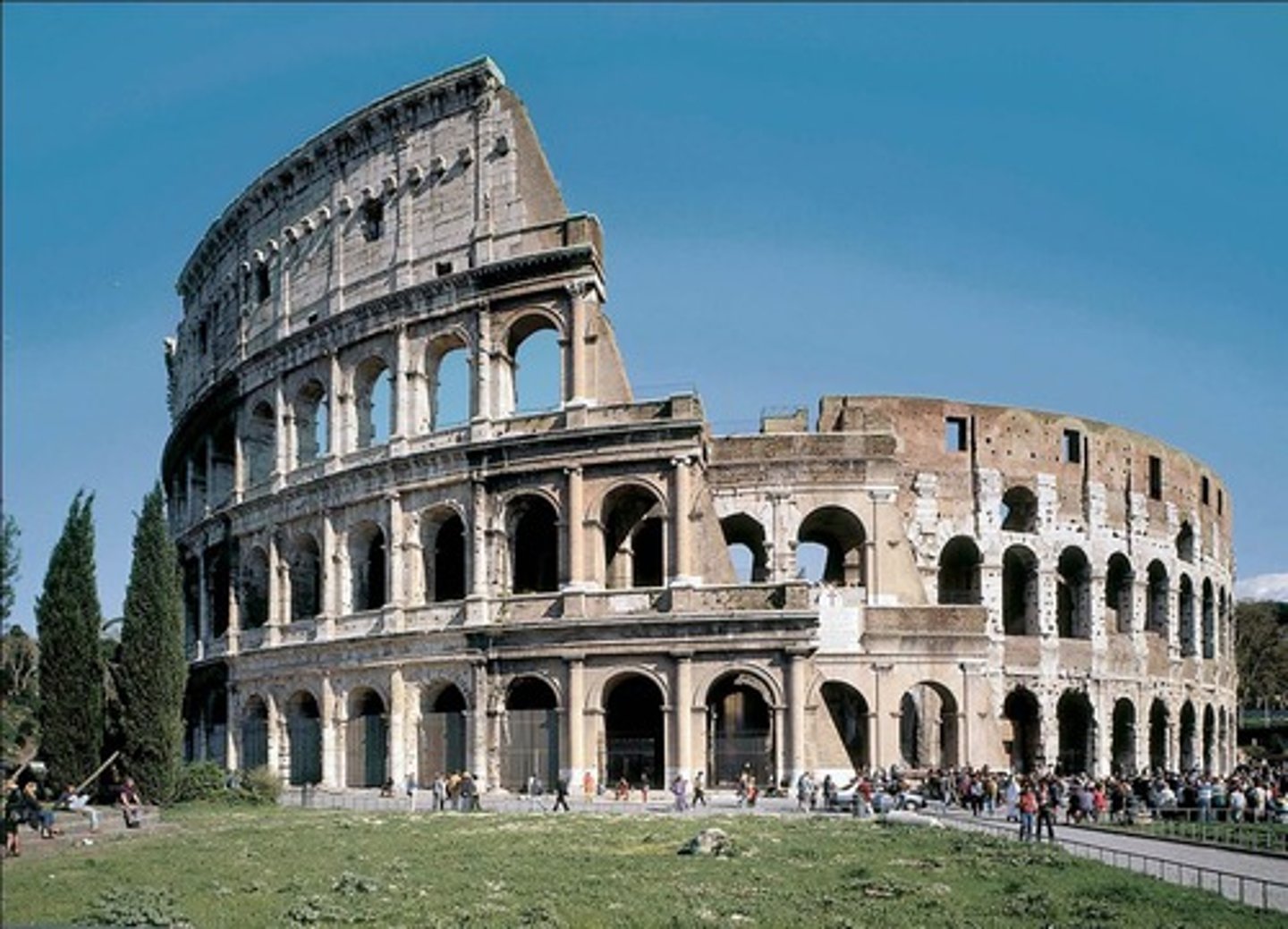
Colosseum, Rome, Italy, c. 70-82 CE, Imperial Roman, patron: Emperor Vespasian
example of a entertainment/sporting venue or theater that could also be used for imperial ceremony

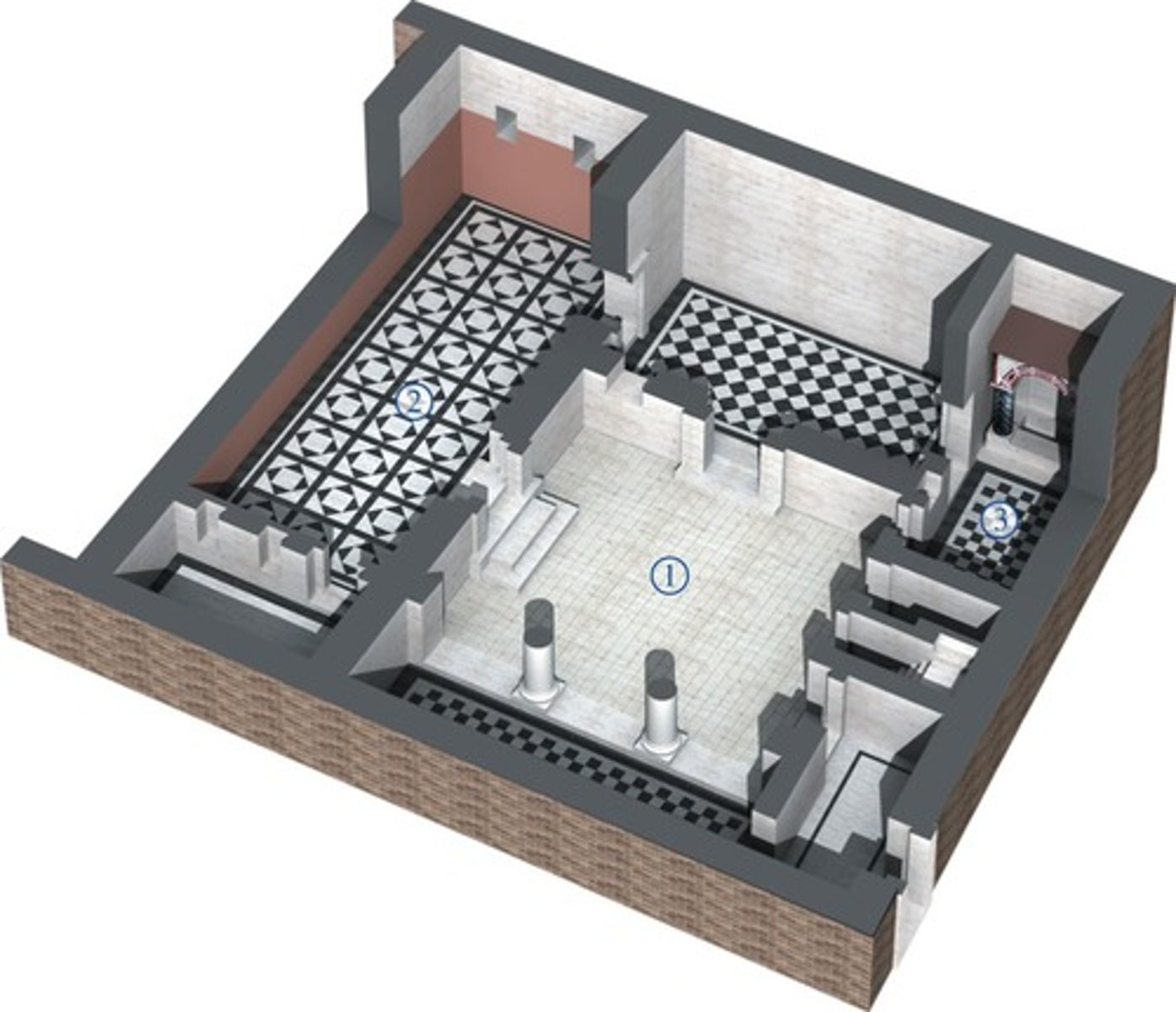
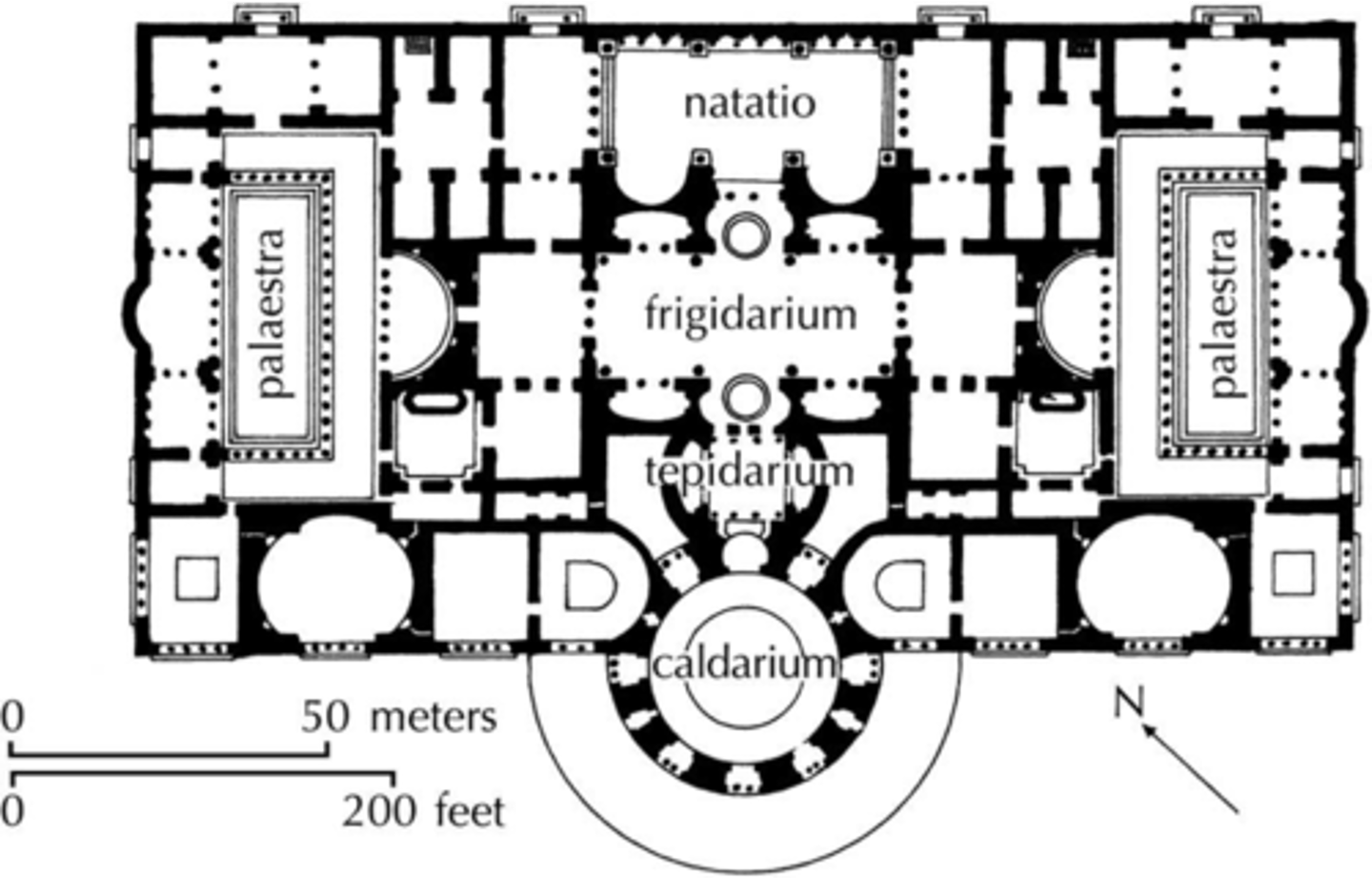
Baths of Caracalla, Rome, Italy, 212-216 CE, Imperial Roman, patron: Emperor Caracalla
• example of a bath complex
• Interior ornamentation including over life-size statuary
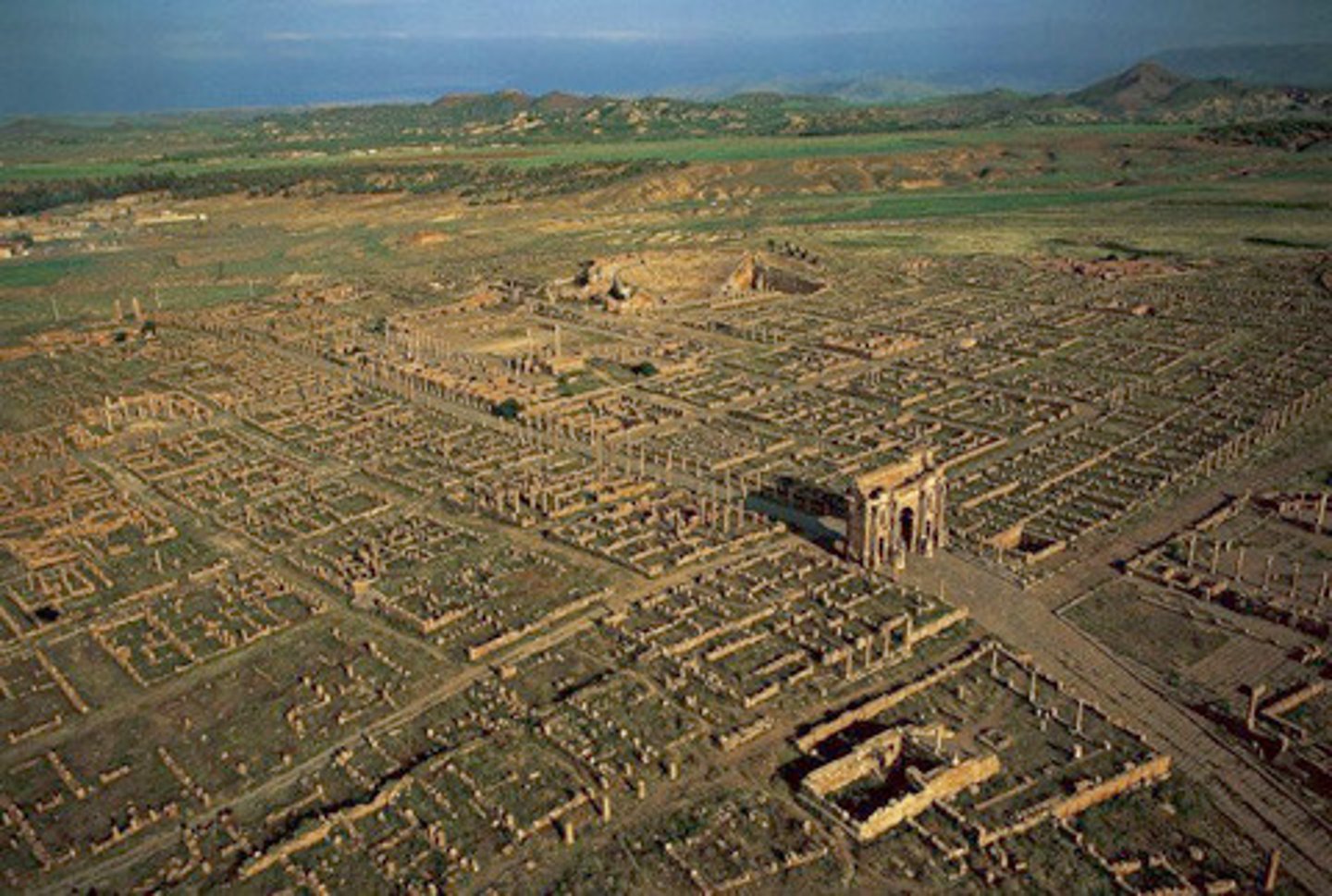
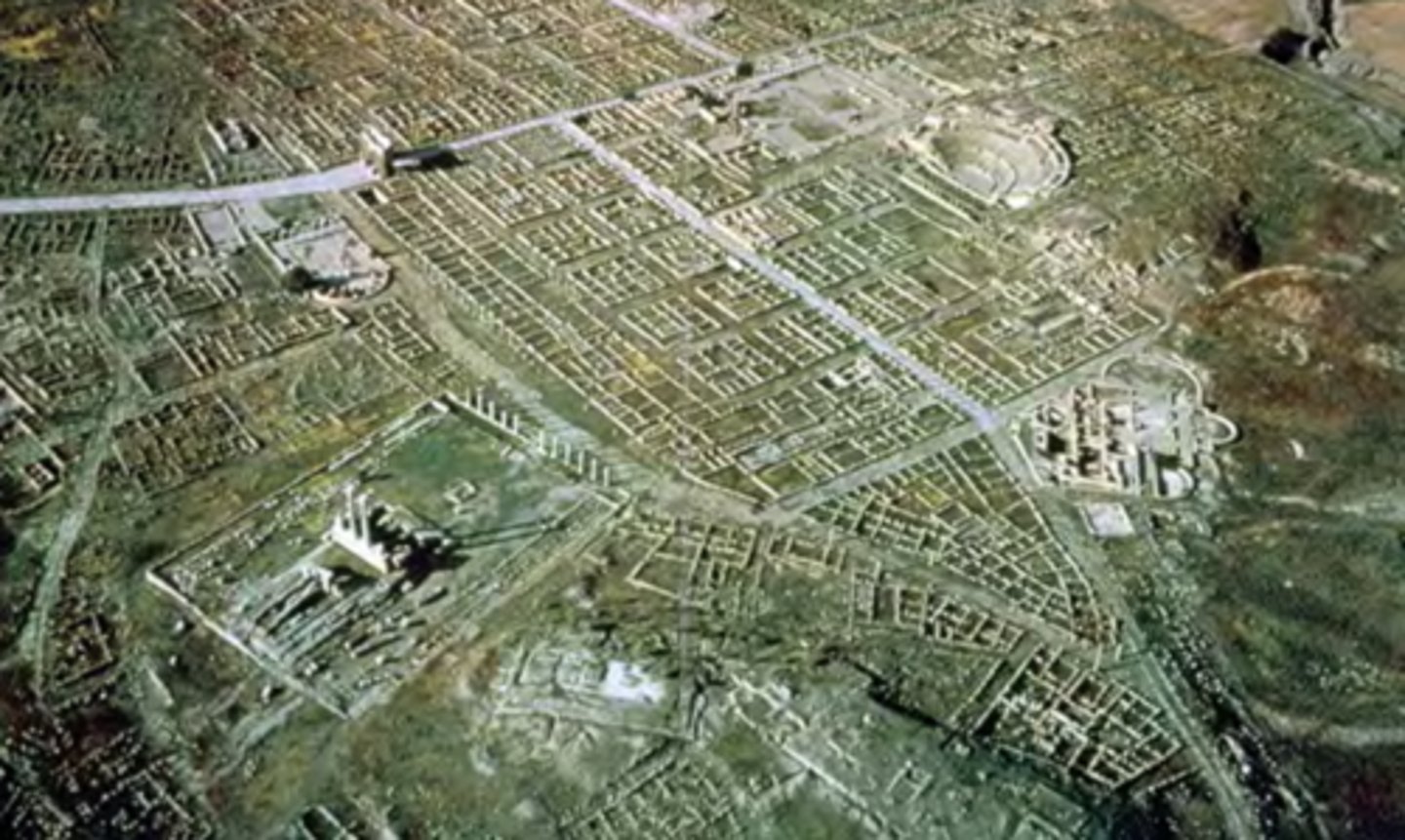
City ruins, Timgad, Algeria, founded 100 CE, Imperial Roman
Know as an example of the Roman urban "kit", with all of its major parts:
• Colonnaded Street, the Decumanus
• Forum and theater
• Theater
• Temple

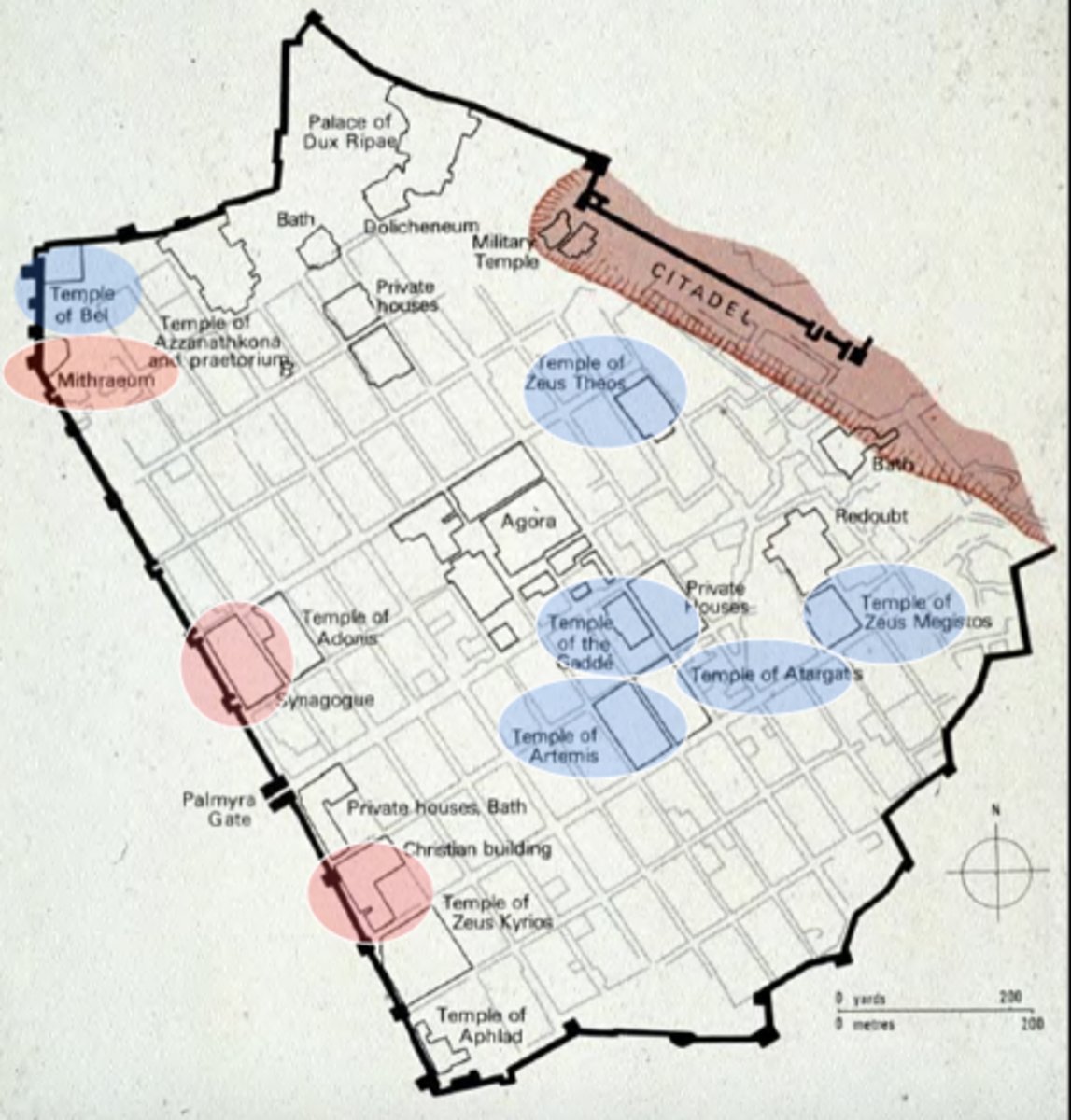
City plan, Dura Europos Syria, mid 3rd century CE, Late Antique (Roman border/provincial city with mixed ethnicities/religions)
• overall Roman grid of the city, based on an earlier Greek grid
• Roman with mixed ethnicities/religions
Dura Europos Synagogue, Dura Europos, Syria, 250 CE, Late Antique (Roman & Jewish)
interior wall with figural fresco ornamentation in registers, stories from the Torah.
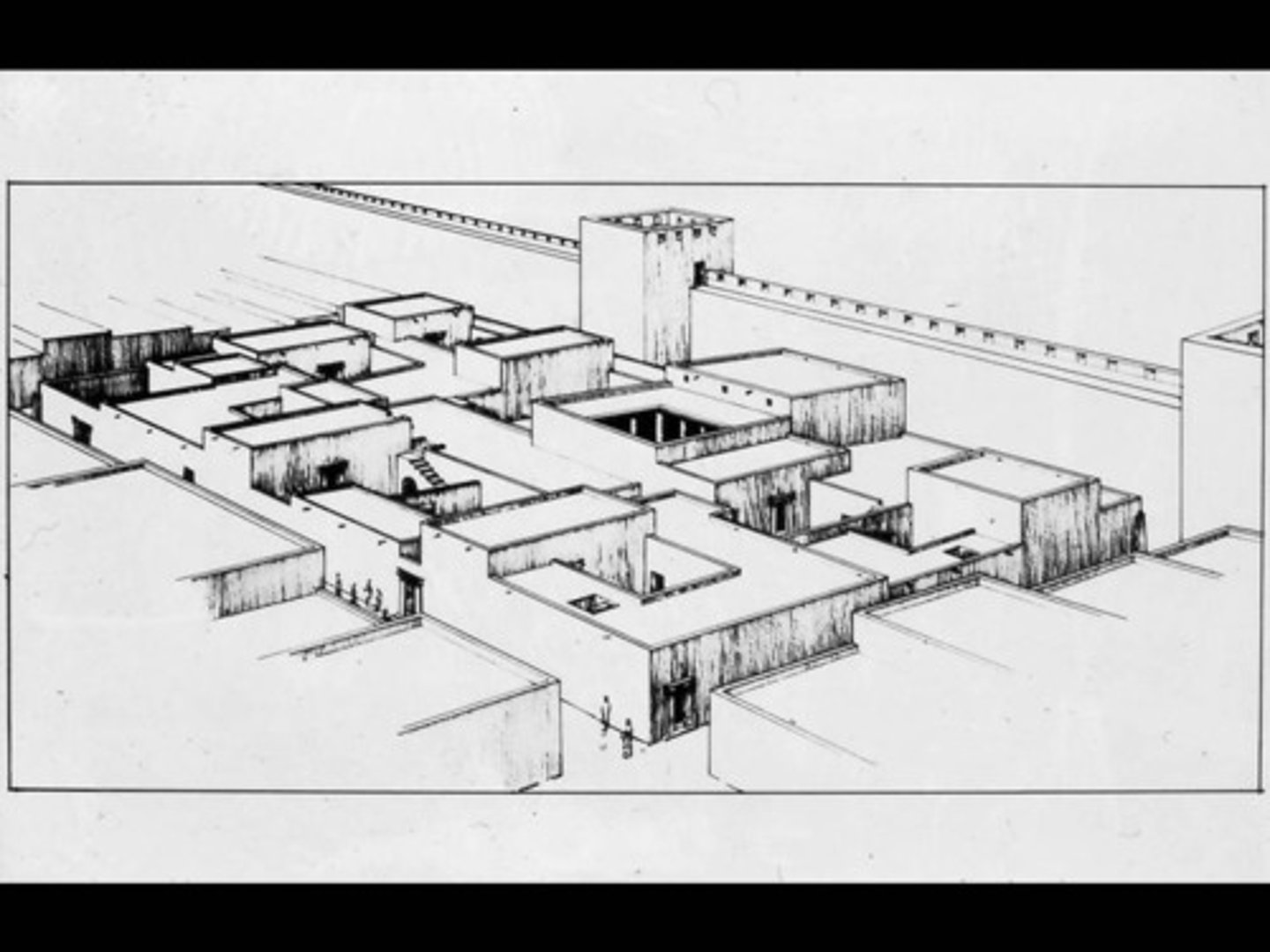
Domus Ecclesiae (Christian house-church), Dura Europos, Syria, c240 CE, Late Antique (Roman & Christian)