Plate Tectonics/ Earth's Interior
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
The earliest model of Earth’s Interior was made by who?
Emil Wiechert
What specific thing do geologists study to determine the chemistry deep within the earth?
meteorites
What are S Seismic waves? What is the S short for? In what direction do particles move with the S wave?
What are P Seismic waves? What is the P short for? In what direction do particles move with the P wave?
S Waves:
Slower moving waves that ONLY move through solids.
S stands for Secondary.
Particles move up and down with the wave.
P Waves:
Fast moving waves that can go through solids AND liquids.
P stands for Primary.
Particles move back and forth/ parallel to travel direction.
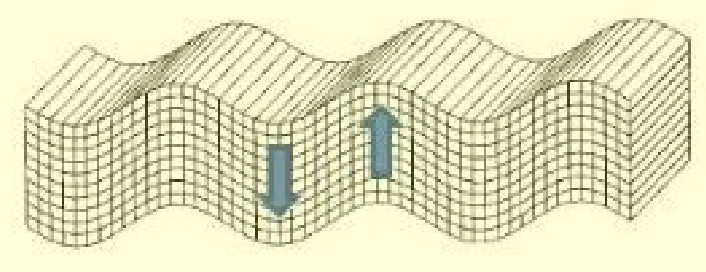
What Seismic wave does this image represent?
S wave
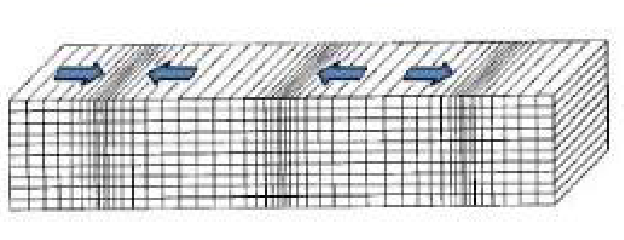
What Seismic wave does this image represent?
P wave
What does the crust of the Earth mostly consist of? What are the 2 different kinds of crust and what are they predominately made of?
Crust consists mostly of minerals with a lot of silica, making it the lease dense layer.
2 different crusts:
continental- silica rich minerals
Oceanic- iron rich minerals
True or false: oceanic crust is thinner than continental crust
True. Oceanic crust is more dense but thinner than continental crust.
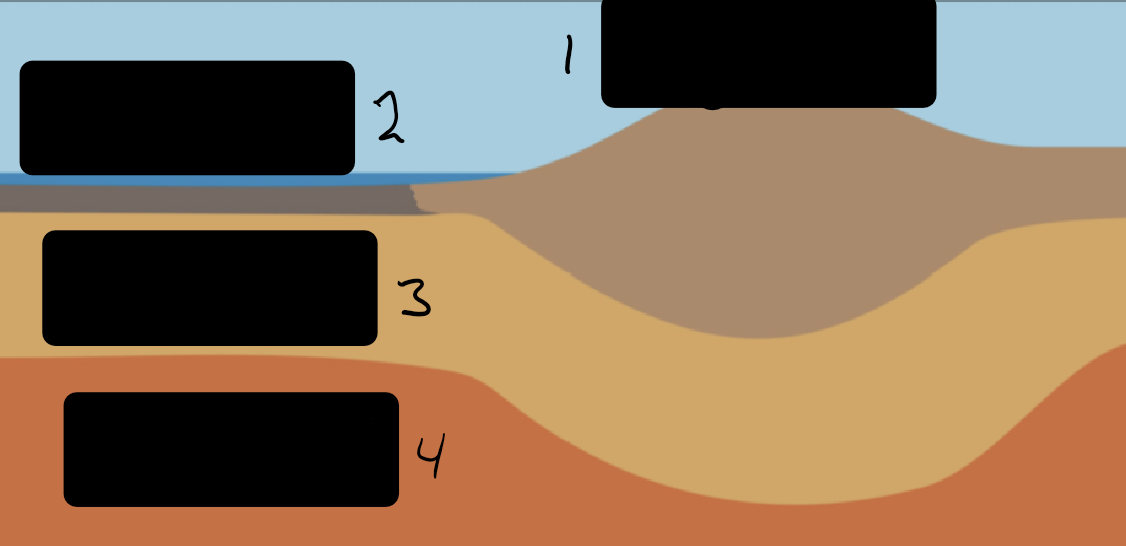
Identify the layers and both crusts
1) Continental Crust
2) Oceanic Crust
3) Lithosphere
4) Asthenosphere
What is the base of the crust called? What happens at this area? What does it separate?
The Moho Zone
P wave velocity changes
Separates the crust from the upper mantle.
What is the Physical Model? What does this model explain?
What is the Chemical Model? What is a very important aspect of this model? What are the layers of the earth (name them from most to least dense)? What are they made out of?
Physical Model:
The Model looks at the divided interior based on the physical properties of the rocks
Explains phenomena like volcanos and earthquakes
Chemical Model:
Model that looks at the structural properties of earth’s interior.
The layers are stratified based on density.
Core (iron/nickel), Mantle(less iron and peridotite), Crust (iron and silica rich minerals)
Name the 5 major divisions by physical properties from least dense to most dense.
1) Lithosphere
2) Asthenosphere
3) Mesosphere
4) Outer Core
5) Inner core
The lithosphere is broken into ____. Each plate is composed of either _____ and/or ______. These ____ float on the _____.
Plates, Oceanic crust, Continental crust.
Plates, Asthenosphere.
Name the 4 major landform features and define them. In which major landform does new oceanic crust form?
1) Mid Ocean Ridge- linear underwater mountain ranges (new oceanic crust forms)
2) Trenches- Lowest areas on the Earth
3) Continental Margins- transition zone where land meets ocean
4) Abyssal plain- broad deep ocean basins
Who proposed the idea of pangea? Which also introduced the modern theory of ____ which explains the idea of why the tectonic plates move.
Alfred, Continental drift
Who proposed the idea of Seafloor spreading?
Harry
What is inclination? What about declination?
Inclination: Curving magnetic flux lines cause a compass needle to tilt toward or away from Earth’s surface.
Declination: measured difference between magnetic north and the true geographic north.
Name the evidence for seafloor spreading and explain/ define each
1) Paleomagnetic data- earth’s magnetic fields preserved in rocks
2) rock ages on seafloor- the farther away from the Mid Ocean ridge, the older the seafloor
3) age and thickness of deep sea sediments- newly created seafloor DOES NOT have sediment on top. The older the seafloor is, the thicker the sediment layer is on top.
4) apparent polar wandering- Each continent has a separate polar wandering path. Hess’s idea was that the continents were moving, NOT THE POLES, because of seafloor spreading.
What are mantle plumes?
True or false: mantle plumes are independent from plates.
areas where heat and or rocks in the mantle are rising towards the surface, burning through plates to get to the surface.
True
What is the difference between active and passive margins? Where are they located?
Active: Convergent, Divergent, Transform. next to subduction zones.
Passive: Not plate boundaries. Next to Mid ocean ridges
What is subduction? Subduction occurs in which plate boundary?
Convergent plate boundaries cause one of the plates to sink under (subduct) another plate boundary.
Convergent
What is an accretionary prism?
Sediment being scraped off the subducting plate and get plastered onto the overriding plate.
What are volcanic arcs? Volcanic arcs mark ____.
Line of volcanos
subduction zones
True or false: volcanic arcs and hot spots are the same thing.
False
Arcs from continental crust are called ____.
Arcs from oceanic crust are called____.
Continental arc
Island arc
Name the 3 main types of convergent plate boundaries. Which one has the most volcanism? What about mountain building?
1) Oceanic-Continental - Most volcanism
2) Oceanic-Oceanic
3) Continental-Continental - Mountain Building
Most transform faults are found at____.
Mid Ocean Ridges
Which plate boundary creates the deepest earthquakes?
Convergent.
Name and explain the 2 main ways that drive plate motions.
1) Ridge Push- Gravity pushes ridge down forcing it to spread outward
2) Slab Pull- Gravity pulls down the subducting plate due to being more dense
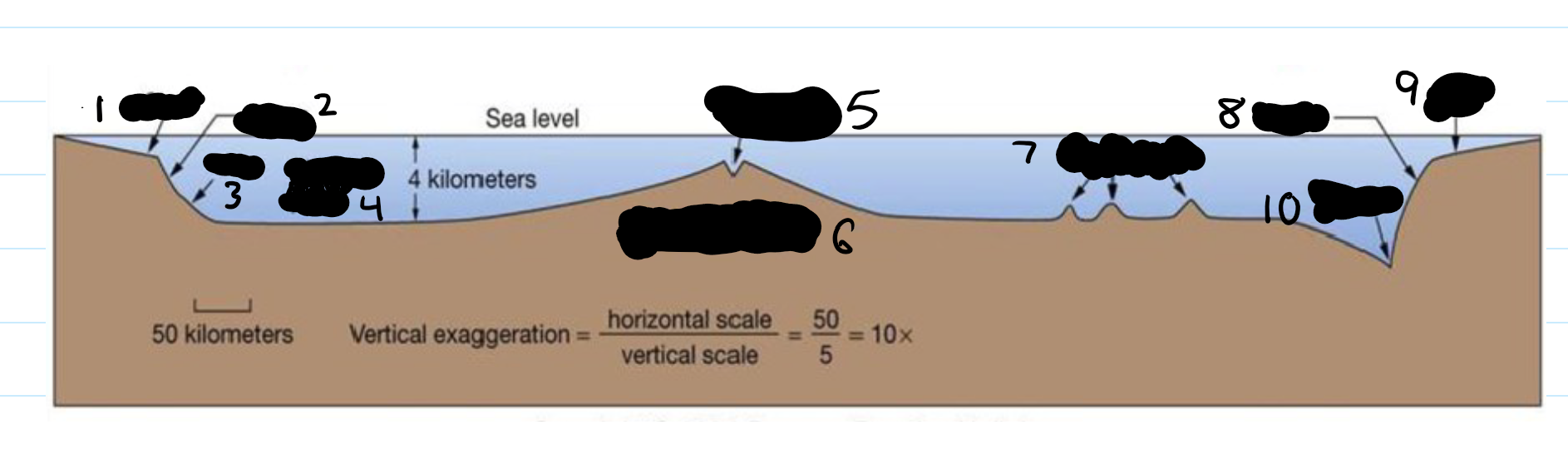
Which continental margin is on the left? The right? Label the picture. Give an example of a location where each of these continental margins would be found.
Left: Passive, Right: Active
1) Continental shelf 2) Continental slope,
3) Continental Rise 4) Abyssal Plain,
5) Rift Valley 6) Mid ocean Ridge,
7) Seamounts 8) Continental Slope,
9) Continental Shelf 10) Trench
Passive: found on east coast (Delaware)
Active: Found on west coast (California)
Where is new seafloor generated? Where is it destroyed?
Generated at divergent plate boundaries at mid ocean ridges. They are destroyed at convergent plate boundaries at subduction zones.
Explain the basic process of paleomagnetism on the seafloor.
Magma rises at mid ocean ridges and cools into basalt which locks the direction of the earth’s magnetic field at the given time. This gets recorded into the rocks itself.
Name and describe the 3 different pieces of evidence Wegner used to support his theory of Pangea and Continental drift?
1) Geographic fit of the continents- continents fit like a puzzle
2) Paleoclimatology- Ancient glacial deposits found in tropical regions
3) Paleontological (fossils)- fossils on different land masses are similar.
Explain the relationship between the depth and age of the seafloor from the Mid-Ocean Ridges to the Continental Margin.
The youngest seafloor is made at mid ocean ridges. As new seafloor is created, this causes seafloor spreading. The new seafloor will push the older surrounding seafloor to the continental margins. The older seafloor will be pushed downwards due to the sediments that build on top of that seafloor.
What features typically define the edges of our Tectonic Plates?
Active continental margins that include Convergent, Divergent, and Transform plate boundaries. This can create feature like trenches, faults, mountains, and volcanoes.