Lecture 4 Innate Immunity pt 2
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
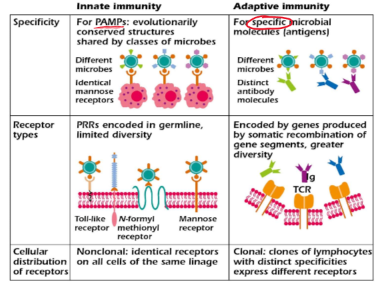
What are PAMPS?
PAMPS (Pathogen-associated molecular patterns)
Specific molecular structures commonly found on the surface of pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites
What are DAMPs?
DAMPs (Damaged-associated molecules patterns)
Molecular motifs expressed on infected or damaged host cells
What are PRRs?
PRRs (Pattern recognition receptors)
Class of receptors that recognize common pathogen and damaged cell surface structures.
Where are PRRs found?
Found on and in innate immune cells
Macrophages and Dendritic cells
EXPRESSED on neutrophils, NK cells
What are the common PRR families?
TLRs (Toll like receptors)
CLRs (C-type lectin receptors)
FPRs (F-met-leu-phe receptors)
NLRs (NOD-like receptors)
RLRs (RIG-I-like receptors)
What are TLRs? (Toll-like receptors)
Expressed by macrophages, dendritic cells, and nonimmune cells like fibroblasts
Classified based on their cell localization
In humans, TLR family has 10 members (TLR 1-10)
Activated TLRs facilitate the initiation of adaptive immunity through pro-inflammatory cytokines
Protects the host from microbial infection
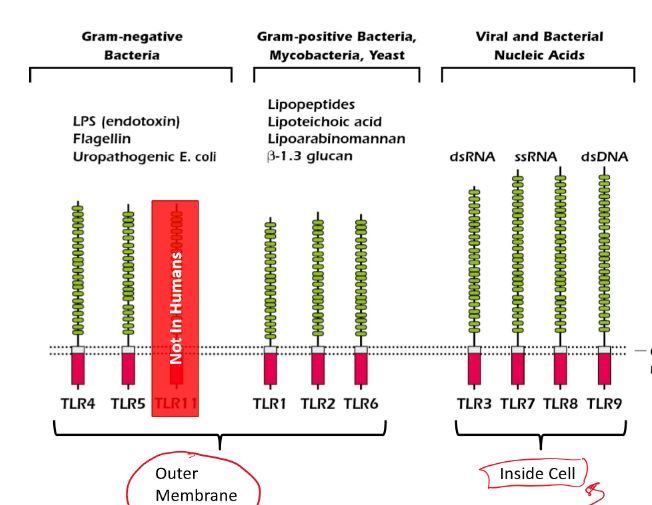
What TLRs are on the outer membrane?
T1, T2, T4, T5, T6
What TLRs are inside the cell?
T3, T7, T8, T9
What does TLR 10 do?
Contains an inhibitory function at the start of innate immune responses
What are CLRs? (C-Type Lectin receptors)
Membrane-bound receptors
Bind to carbohydrates in a calcium-dependent manner
involved in BACTERIAL and FUNGAL recognition
Modulate (adjust) the innate immune response
What are NLRs? (NOD-like receptors)
Intercellular PRRs
Detect intracellular PAMPs (Pathogen-associated molecular patterns), and danger signals
FORM inflammasomes
Inflammasomes help resolve infections
Contributes to cytokine-driven inflammation
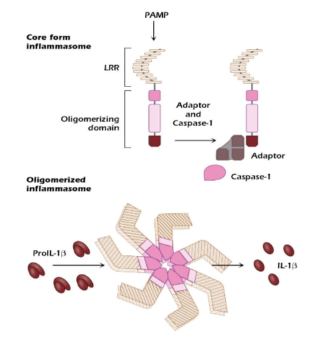
What happens if NLRs are left behind?
Leads to chronic inflammation
What are RLRs? (RIG-I-Like Receptors)
Family of three cytoplasmic RNA helicases
Search for DOUBLE STRANDED RNA
Produce type 1 interferons in infected cells
Essential for host ANTIVIRAL responses
What are F-Met-Leu-Phe Receptors?
Mononuclear and PMN phagocytes
fMet is exclusively used by bacteria for protein synthesis initiation
Formylated peptides attract phagocytes to migrate to their position (chemotaxis)
What is important about f-Met?
Body will target f-Met due to only being used by bacteria for protein synthesis