Benzene
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Draw Kekulé’s structure of benzene.
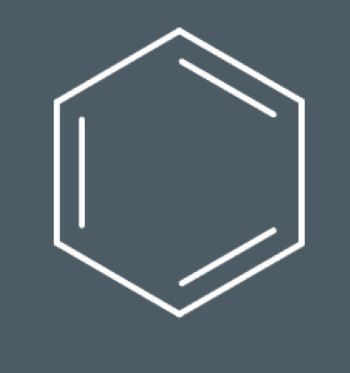
Draw the product that forms when this compound reacts with bromine:
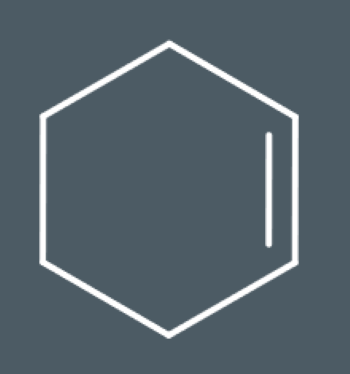
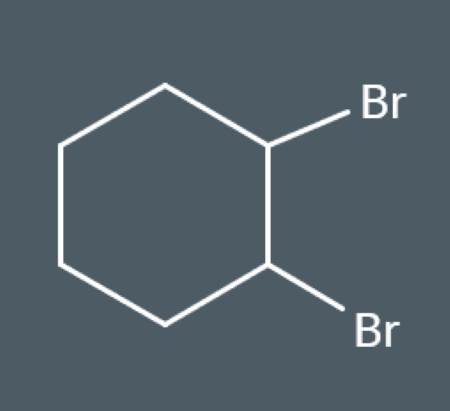
Draw the product that forms when this compound reacts with bromine:
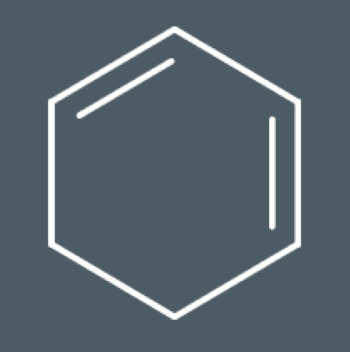
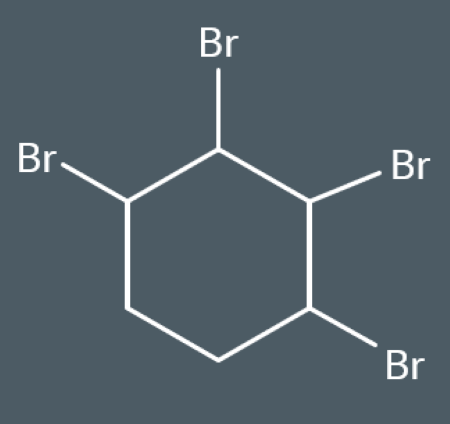
Problems with kekule’s model of benzene? (3)
1) it suggests that benzene should be able to undergo addition reactions with bromine. But, it doesn’t! because it has lower electron density than alkenes.
2) it suggests that benzene should have 2 different carbon-carbon bond lengths.
However, experimental evidence has shown that these bond lengths are the same because each p-orbital overlaps both of its neighbouring p-orbitals by the same amount above and below the ring.
3)it suggests that benzene’s enthalpy of hydrogenation should be approximately -360 kJ mol−1.However, experimental evidence has found that it’s less exothermic than expected! because benzene’s delocalised electrons increase its stability.
What causes carbon to form 4 bonds?
it promotes an electron from a 2s orbital to a 2p orbital.
When two orbitals overlap ‘end-on’, we say they form which type of bonds?
sigma bonds.
When two orbitals overlap ‘side-on’, we say they form which type of bonds?
pi bonds
If Kekulé’s model of benzene is correct, then each carbon atom would promote an electron from its….
2s orbital to a 2p orbital.
If Kekulé’s model of benzene is correct how many sigma and pi bonds would benzene form?
Each carbon atom would then form 3 sigma
bonds and one pi bond.
Because of how the p orbitals in benzene overlap, the electrons in these orbitals are…
delocalised.
Structure in benzene? (3)
each carbon forms 3 sigma bonds.
a p orbital from each carbon overlaps with two neighbouring p orbitals to form a pi system.
the electrons are delocalised across the ring.
How do we often draw benzene?

Benzene’s delocalised electrons means that its electron density …
is lower electron density than alkenes.
Bonding in Benzene
You should say that each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds.
You should say that the remaining p orbitals overlap above and below the ring to form a pi system.
You should say that the electrons in these p orbitals are delocalised.
The Shape of Benzene
You should say that benzene is planar.
You should say that the bond angles in benzene are 120°.
You should say that the C-C bonds are equal in length
Which of the following statements are true for Kekulé’s model of benzene and the delocalisation model?(2)
p orbitals overlap sideways
Electrons can be found above and below the ring
Explain why the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is less exothermic than expected.
Benzene has a pi system of electrons which are delocalised across the ring. These delocalised electrons stabilise the molecule. This makes the enthalpy of hydrogenation less exothermic than expected due to the extra energy needed to disrupt the pi system.