PSY202 Motivation
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
What is Motivation?
Internal and External Factors that propel one in specific directions, usually toward a goal.
2
New cards
What is Internal “Push“referred to as?
Drive.
3
New cards
What is the Drive Reduction Theory?
* The drive/want to do something (Hunger; wanting to eat when hungry)
* Primary Drive
* Secondary Drive
* Primary Drive
* Secondary Drive
4
New cards
What is __Primary Drive?__
* Not born with this drive
* The psychological state in response to an internal physiological need
* Motivates behaviours that aids survival
* The psychological state in response to an internal physiological need
* Motivates behaviours that aids survival
5
New cards
What is __Secondary Drive?__
* Learned by association with a primary drive.
* With the secondary drive, you can reinforce the primary drives you might have
* With the secondary drive, you can reinforce the primary drives you might have
6
New cards
What is __Homeostasis?__
* The process of the body maintaining a steady state
* Moving from an optimal state to another state activates drives, and the drives will motivate behaviours to return to a steady state again
* Moving from an optimal state to another state activates drives, and the drives will motivate behaviours to return to a steady state again
7
New cards
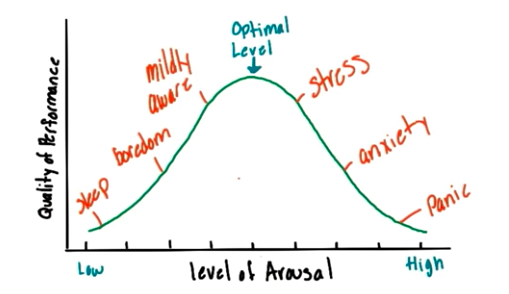
What is Yerkes-Dodson Law?
* States what moderate levels of arousal lead to optimal performance
* Prefer to be in optimal levels of performance, rather than too much or too little
* Performance and Arousal relationship shown in inverted U shape
* Prefer to be in optimal levels of performance, rather than too much or too little
* Performance and Arousal relationship shown in inverted U shape
8
New cards
What are External “Pulls“referred to as?
Incentives.
9
New cards
What are Incentives?
* Environmental (external) factors that exert pulling effects on out actions
* These interact with internal factors
* Drives can motivate these needs
* These interact with internal factors
* Drives can motivate these needs
10
New cards
What did **Maslow** contribute to Motivation?
States that needs are prioritized in a hierarchy, The Hierarchy of Needs.
11
New cards
What is the __Hierarchy of Needs?__
* The order in which needs are prioritized
* __Psychological__ Needs come first
* __Social and Esthetic__ Needs come later
* __Unfilled__ Needs are often the basis for action
* __Psychological__ Needs come first
* __Social and Esthetic__ Needs come later
* __Unfilled__ Needs are often the basis for action
12
New cards
What is the Hunger Drive?
* Mostly associated with eating
* Role of Hypothalamus, Hormones, External Factors
* Role of Hypothalamus, Hormones, External Factors
13
New cards
What is the __Role of the Hypothalamus__?
* When the brain is signalled that we are hungry or not
* **Ventromedial**
* Satiety Center: signal to stop eating
* **Lateral**
* Hunger Center: signal to eat more
* **Ventromedial**
* Satiety Center: signal to stop eating
* **Lateral**
* Hunger Center: signal to eat more
14
New cards
What are Hunger Hormones?
* __Ghrelin__ (stomach) increases hunger
* __Cholecystokinin__ (small intestine) decreases hunger
* __Cholecystokinin__ (small intestine) decreases hunger
15
New cards
What Biologically Influences Weight Gain/Obedity?
* Chemical Messengers
* Set Point
* Fat Cells
* Metabolic Rate
* Set Point
* Fat Cells
* Metabolic Rate
16
New cards
What do __Chemical Messengers__ do to Influence Weight Gain and Obesity?
* __Leptin__ is a hormone produced by fat cells and it tells the body to work off fat
* It reduces appetite and increases the amount of energy used
* Obese people are seemingly less resistant to the effects of Leptin because body may not be signaled leading to them wanting to eat more
* It reduces appetite and increases the amount of energy used
* Obese people are seemingly less resistant to the effects of Leptin because body may not be signaled leading to them wanting to eat more
17
New cards
What does __Set Point__ do to Influence Weight Gain and Obesity?
* Is the Natural body weight that the body seeks to maintain; genetics
* Weight loss below set point is often regained
* Obese people have a higher set point at birth, which makes it harder to lose weight
* Weight loss below set point is often regained
* Obese people have a higher set point at birth, which makes it harder to lose weight
18
New cards
What do __Fat Cells__ do to Influence Weight Gain and Obesity?
* Is determined by genetics and food intake
* Being significantly overweight leads to increase in the number of fat cells
* Changes from early childhood to adulthood cause fat cell number to stabilize
* Being significantly overweight leads to increase in the number of fat cells
* Changes from early childhood to adulthood cause fat cell number to stabilize
19
New cards
What does __Metabolic Rate__ do to Influence Weight Gain and Obesity?
Obese people are born with a low rate that leads them to burn fewer calories.
20
New cards
What Psychologically Influences Weight Gain/Obesity?
* Expectations and External Cues
* Portion Distortion (portion size changes constantly as years pass)
* Unit Bias (cognition that a unit of food is the appropriate and optimal amount; if something is brought in larger size, more eating is required)
* Portion Distortion (portion size changes constantly as years pass)
* Unit Bias (cognition that a unit of food is the appropriate and optimal amount; if something is brought in larger size, more eating is required)
21
New cards
What is Sexual Drive/Desire affected by?
* Sex Hormones
* Neurotransmitters
* Neurotransmitters
22
New cards
How do Sex Hormones affect sexual drive/desires?
__Testosterone__ enhances and increases sexual drive.
23
New cards
How do Neurotransmitters affect sexual drive/desire?
* __Serotonin__ decreases desire
* __Dopamine__ increases desire
* __Dopamine__ increases desire
24
New cards
What is Sexual Orientation?
* A person’s sexual and emotional attraction to members of the same/opposite sex
* Heterosexuality (opposite sex), Homosexuality (same sex), Bisexuality (both sex), Asexuality (neither sex)
* Heterosexuality (opposite sex), Homosexuality (same sex), Bisexuality (both sex), Asexuality (neither sex)
25
New cards
What is involved in the determination ofSexual Orientation?
* Evidence from Twin Studies
* Bem’s “Exotic (familiar) becomes Erotic (attracted)” Theory
* Sex Hormones and Prenatal Influences
* Brain Differences
* Bem’s “Exotic (familiar) becomes Erotic (attracted)” Theory
* Sex Hormones and Prenatal Influences
* Brain Differences
26
New cards
How does __Evidence from Twin Studies__ help determine Sexual Orientation?
* Genetics
* As the __Genetic relatedness__ *increases* → __Concordance rate__ for homosexuality *increases* (if one twin is homosexual, 50% likely for the other to be homosexual as well)
* As the __Genetic relatedness__ *increases* → __Concordance rate__ for homosexuality *increases* (if one twin is homosexual, 50% likely for the other to be homosexual as well)
27
New cards
How does __Bem’s “Exotic becomes Erotic” Theory__ help determine Sexual Orientation?
* Genetics and Environment factors
* Biological Variables cause children to be born with certain temperamental characteristics that will cause them to seek out their interactions with others accordingly
* Being around one specific sex causes the other to appear more exotic to you
* Biological Variables cause children to be born with certain temperamental characteristics that will cause them to seek out their interactions with others accordingly
* Being around one specific sex causes the other to appear more exotic to you
28
New cards
How do __Sex Hormones and Prenatal Influences__ help determine Sexual Orientation?
* Study shows that greater prenatal exposure to __Androgen__ (male hormone) in Lesbians than in Straight women
* “Older Brother Effect“ claims that the more boys brothers a boy has, the more likely they are to be homosexual (likeliness is up 33% for every brother they have due to mothers environment changes)
* “Older Brother Effect“ claims that the more boys brothers a boy has, the more likely they are to be homosexual (likeliness is up 33% for every brother they have due to mothers environment changes)
29
New cards
How do __Brain Differences__ help determine Sexual Orientation?
* Possible influence of regions in the __Hypothalamus__
* Larger __Corpus Callosum__ in gay men
* Connects the two hemispheres is larger in gay men than straight
* Larger __Corpus Callosum__ in gay men
* Connects the two hemispheres is larger in gay men than straight