Chapter 3 - Kaplan MCAT Gen Chem Review
1/61
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
elements come together to form
molecules
molecules are held together by
chemical bonds
chemical bonds are formed via
valence electrons
atoms usually bond to ___ rule
octet
incomplete octet
elements stable with fewer than 8 in valence
expanded octet
-can hold more than 8 in valence
-any element in period 3 or greater
molecule with an odd number of electrons cannot
distribute to give 8 to each
ionic bond
electrons from an atom with low ionization energy are transferred to an atom with high ionization energy
the ions in an ionic bond are held together by
electrostatic attraction between the opposite charges
__ bonds create a lattice of rows of cations and anions (in solid state)
ionic
in the lattice structure of ionic bonds, the attractive forces between + and - ions are ______
maximized
ionic bonds are usually formed between ___ and ___
metals and nonmetals
EN
electronegativity
covalent bond
electron pair is shared between 2 atoms with similar electronegativities
bond order
number of shared electron pairs between 2 atoms
bond length
avg distance between the 2 nuclei of atoms in a bond
more shared electrons =
-smaller bond length
-more energy needed to break
bond energy
energy required to break a bond by separating its components into their isolated, gaseous, atomic states
greater bond energy =
stronger bond
nonpolar
electron pair shared equally
types of covalent bonds
-nonpolar
-polar
-coordinate covalent
nonpolar bonds occur when the atoms have
nearly identical electronegativities
diatomic molecules
only 2 atoms bonded (H_2, CL_2, N_2)
polar
electron pair shared equally
polar bonds occur when atoms have
-moderately different electronegativities
-one atom partially neg, one partially pos
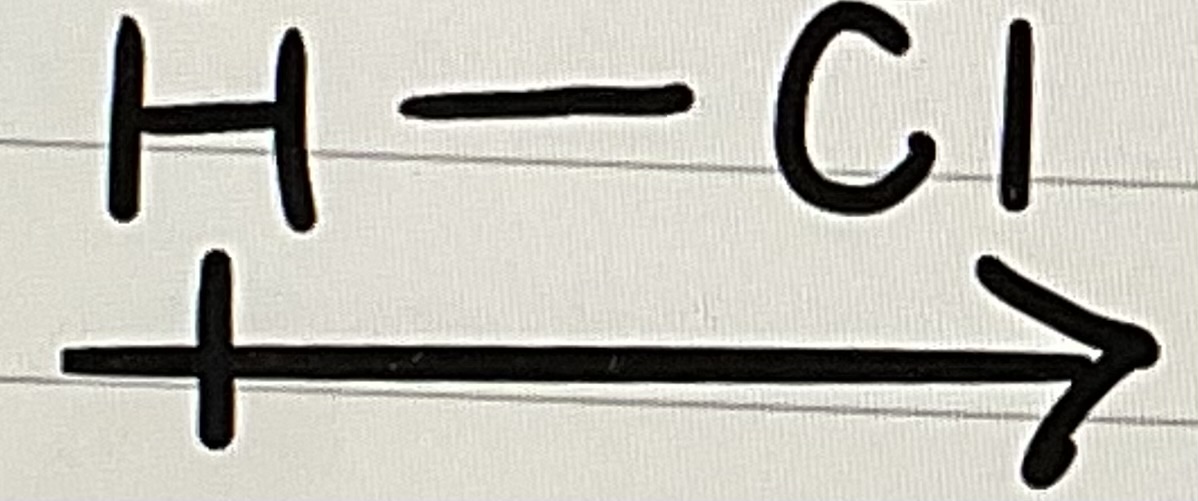
in a digram for a polar bond, arrow points toward
negative end
dipole moment of polar bond formula
p=qd
p=qd meaning
p=dipole moment
q=magnitude of charge
d=displacement vector separating 2 partial charges (in debye units, coulomb-meters)
coordinate covalent
if both electrons are contributed by 1 atom
coordinate covalent bonds are indistinguishable from
other covalent bonds
coordinate covalent bonds are typically found in
lewis acid-base reactions
lewis dot diagram rules
-H always in terminal position
-halogens usually in terminal position
-least electronegative atom central
formal charge
difference between ‘the number of electrons assigned to an atom in a lewis structure’ and ‘the number of electrons normally found in that atoms valence shell’
formal charge formula
V-(N_nonbonding)-(1/2)(N_bonding)
V-(N_nonbonding)-(1/2)(N_bonding) meaning
V = normal # of electrons in atoms valence shell
N_nonbonding = # of nonbonding electrons
N_bonding = # of bonding electrons (double the # of bonds)
charge of an ion/compound
the sum of the formal charges of the atoms comprising it
resonance structures
same arrangement of atoms but different placement of electrons
valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR)
-uses lewis dot structures to predict the molecular geometry of covalently bonded molecules
-arranges electron pairs around central atom
electric geometry
spatial arrangement of all pairs of electrons around the central atom, including the bonding and lone pairs
molecular geometry
the spatial arrangement of only the bonding pairs of electrons
coordination number
the number of atoms that surround and are bonded to a central atom
no net dipole moment=
bond dipoles cancel each other out, nonpolar
net dipole moment=
bond dipoles do not cancel each other out, polar
bonding orbital
forms when the signs of the 2 atomic orbitals are the same
antibonding orbital
forms when the signs of the 2 atomic orbitals are different
sigma bond
when orbitals overlap head-tohead
sigma bonds (do / do not) allow for free rotation
do
pi bond
when orbitals overlap so that there are 2 parallel electrons around cloud densities
π bonds (do / do not) allow for free rotation
do not
london dispersion forces
the attraction or repulsive interactions of the short-lived and rapidly shifting dipoles
if electron density is unequally distributed it causes
formation of short-lived dipoles
london dispersion forces are a type of
van der waals force
weakest intermolecular attraction
london dispersion forces
london dispersion forces are only significant when molecules are ____
in close proximity
if molecule is more easily polarizable, it posesses (larger/smaller) dispersion forces
larger
dipole-dipole interactions
in polar molecules, pos region of one molecule is close to neg region of another
dipole-dipole interaction vs london dispersion forces
duration
dipole-dipole interactions are denoted by
dashed lines, indicating temporary
hydrogen bonds
pos charged hydrogen atom interacts with the partial neg charge of Fluorine, Oxygen, or Nitrogen on nearby molecules
hydrogen bonds are an unusually strong form of
dipole-dipole interaction
hydrogen bonds may be ____ or ____
intra- or intermolecular
strongest intermolecular attraction
hydrogen bond