lab practical 4
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/49
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
1
New cards
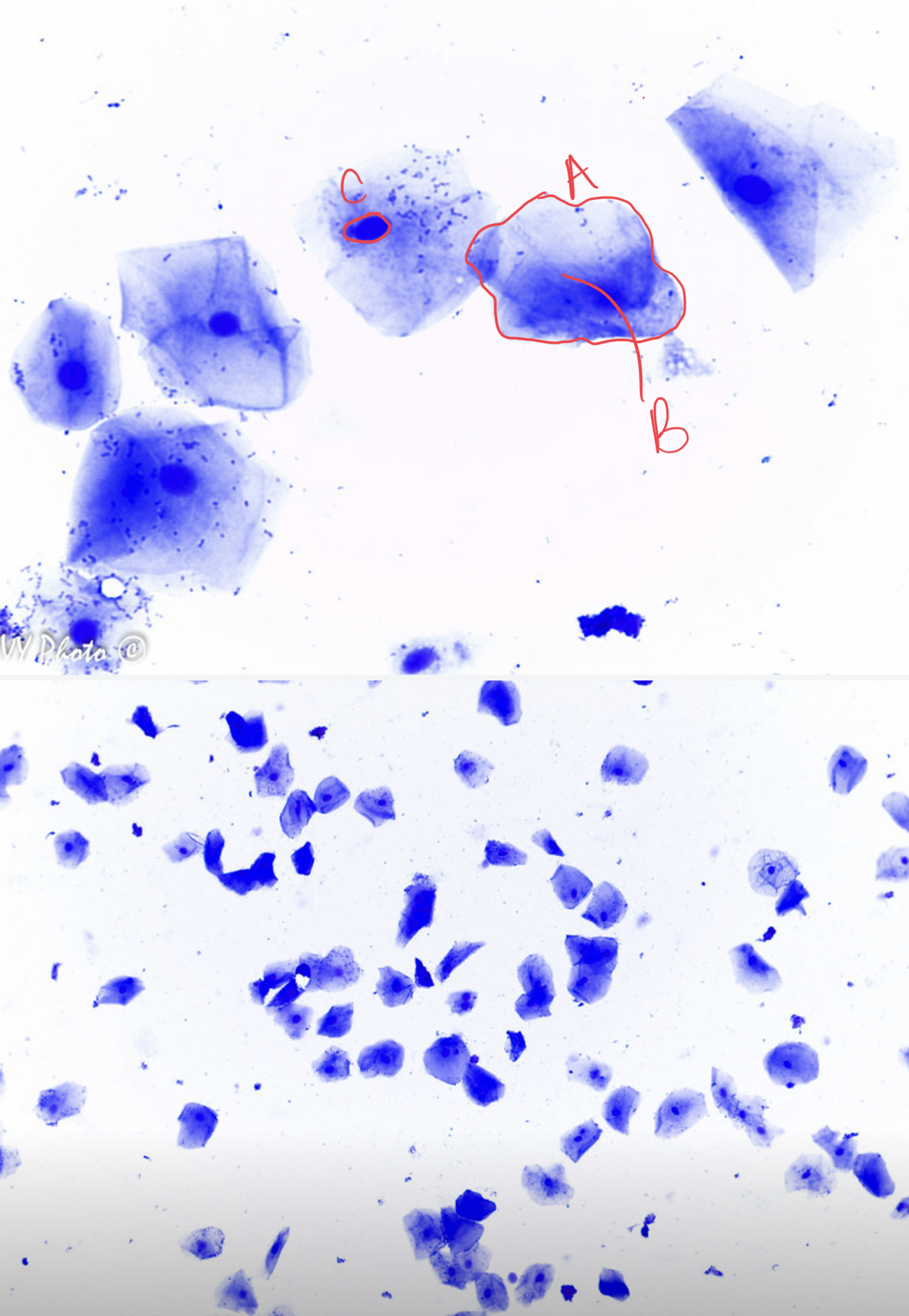
* tissue type
* location
* label
* location
* label
simple squamous epithelial tissue, mouth lining, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus
2
New cards
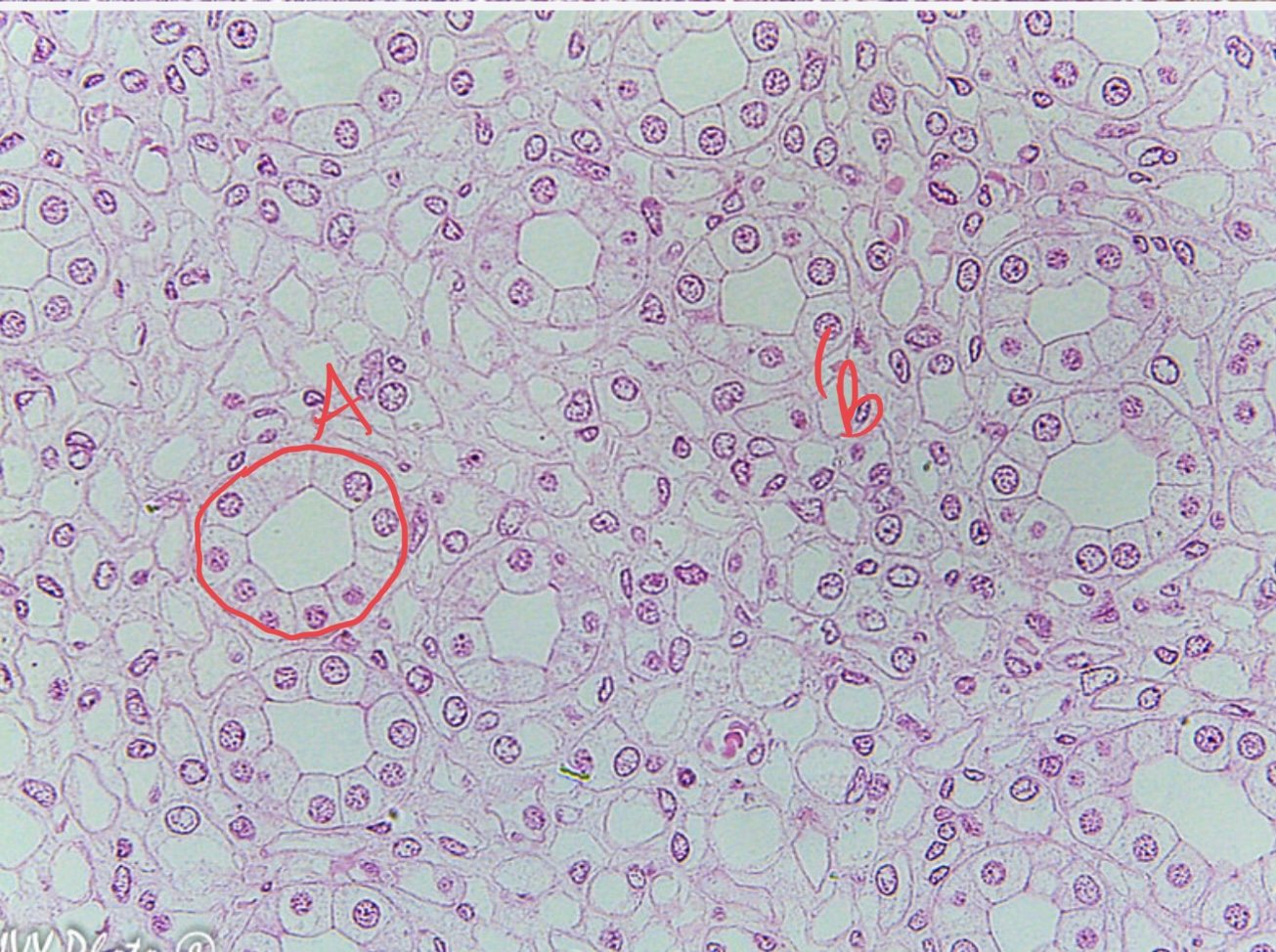
* tissue type
* location
* label
* location
* label
simple cuboidal epithelial tissue, kidney tubule lining, cell membrane, nucleus
3
New cards
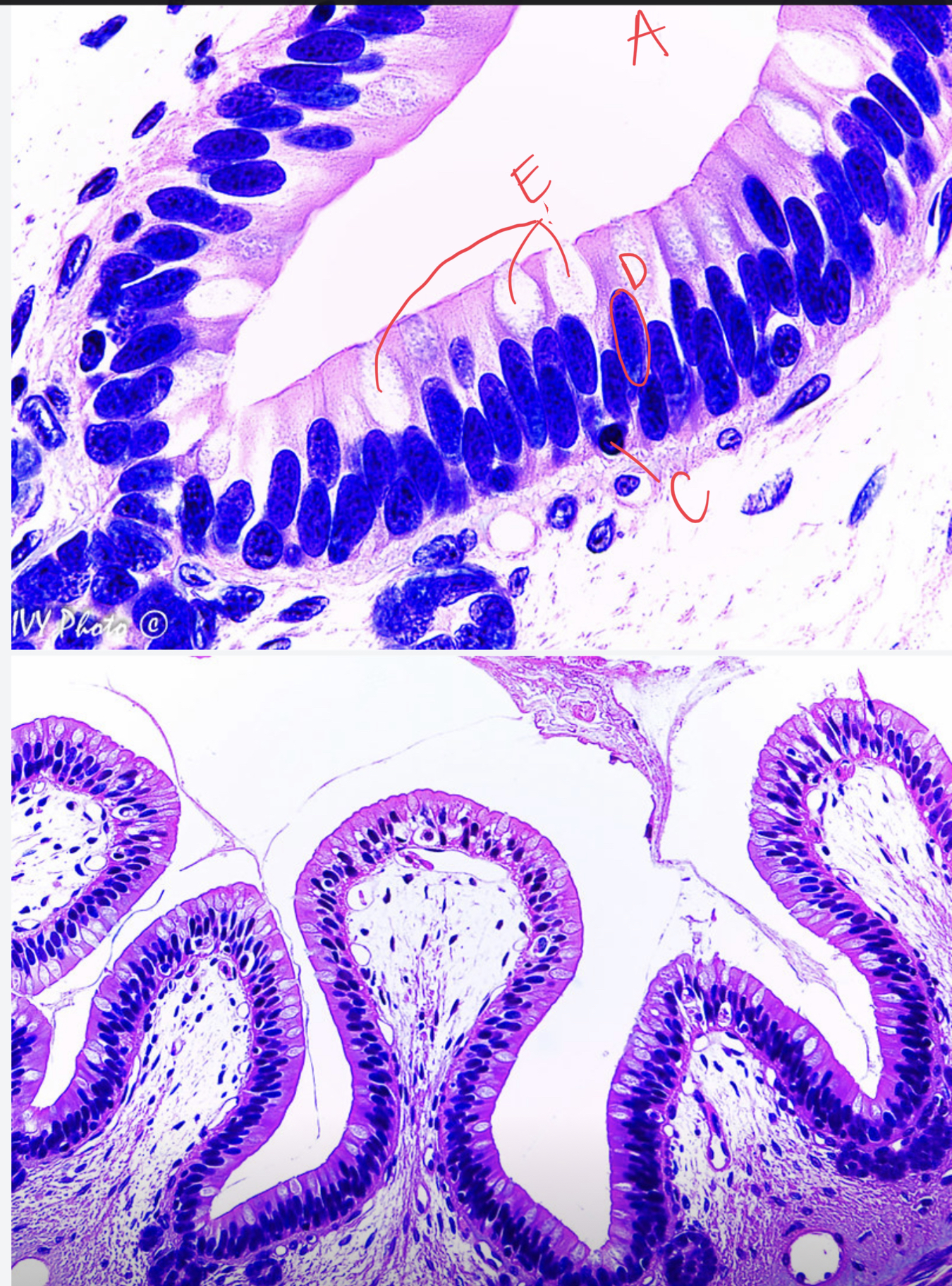
* tissue type
* location
* label
* function of goblet cells?
* location
* label
* function of goblet cells?
simple columnar epithelial, stomach lining, lumen of intestine, nucleus, cell membrane, goblet cell, contains and secretes mucus
4
New cards
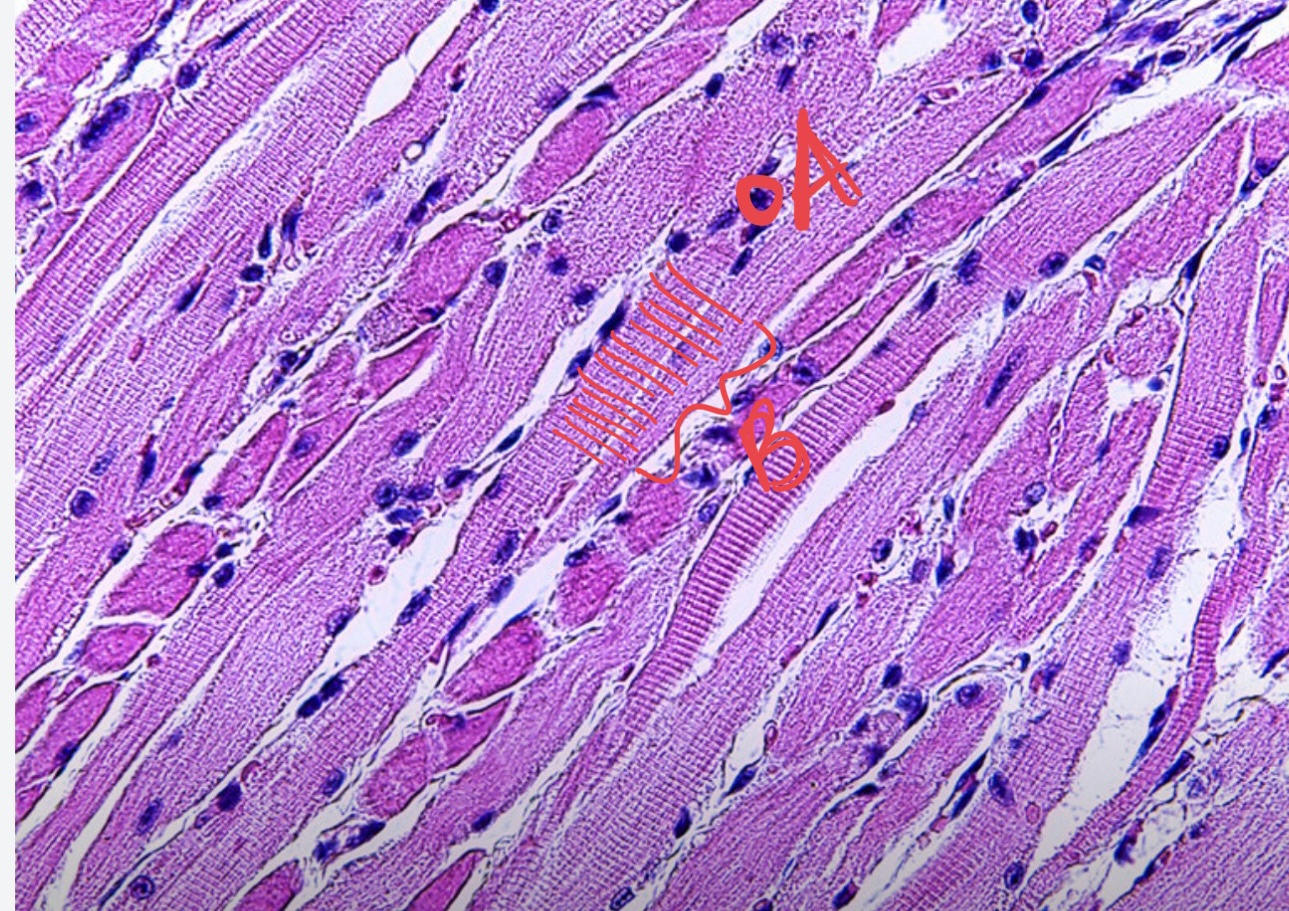
* tissue type
* label
* does it have striations?
* voluntary or involuntary?
* label
* does it have striations?
* voluntary or involuntary?
skeletal muscle, nucleus, striations, yes, voluntary
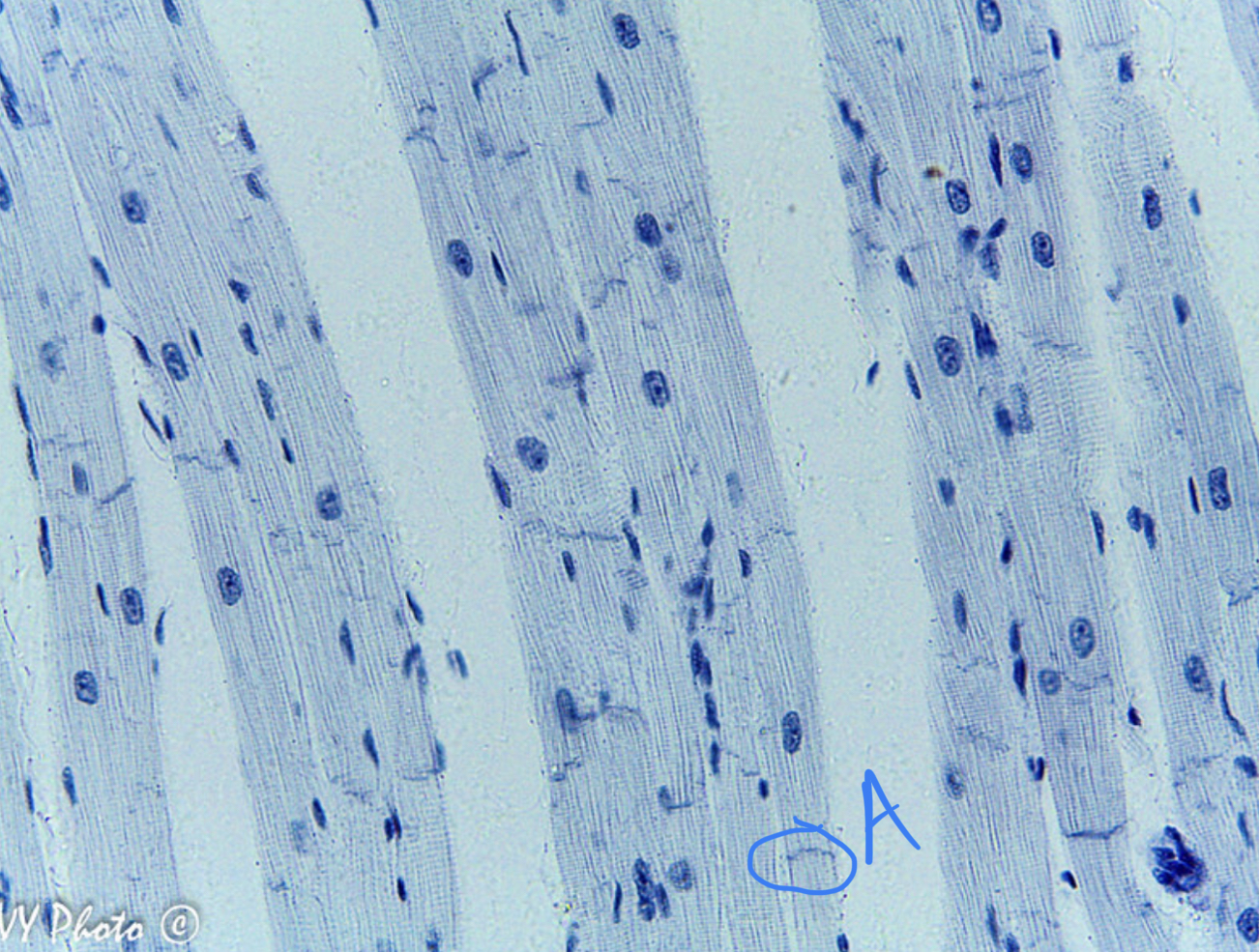
5
New cards
* tissue type
* label
* does it have striations?
* voluntary or involuntary?
* label
* does it have striations?
* voluntary or involuntary?
smooth muscle, nucleus, muscle fibers, no, involuntary
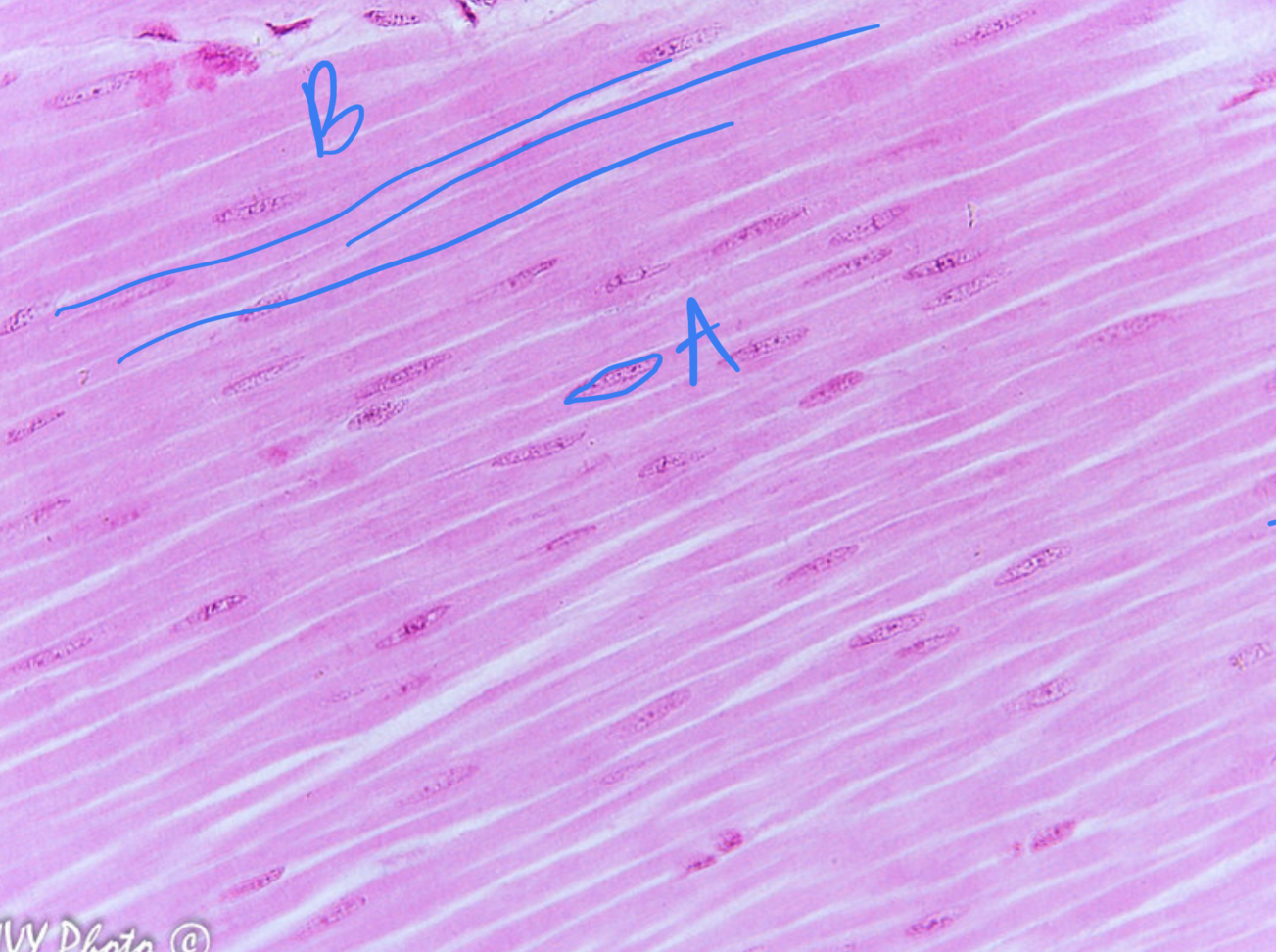
6
New cards
* tissue type
* label
* voluntary or involuntary?
* nucleate or ennucleate?
* label
* voluntary or involuntary?
* nucleate or ennucleate?
cardiac muscle, intercalated disks, no, involuntary, nucleate
7
New cards
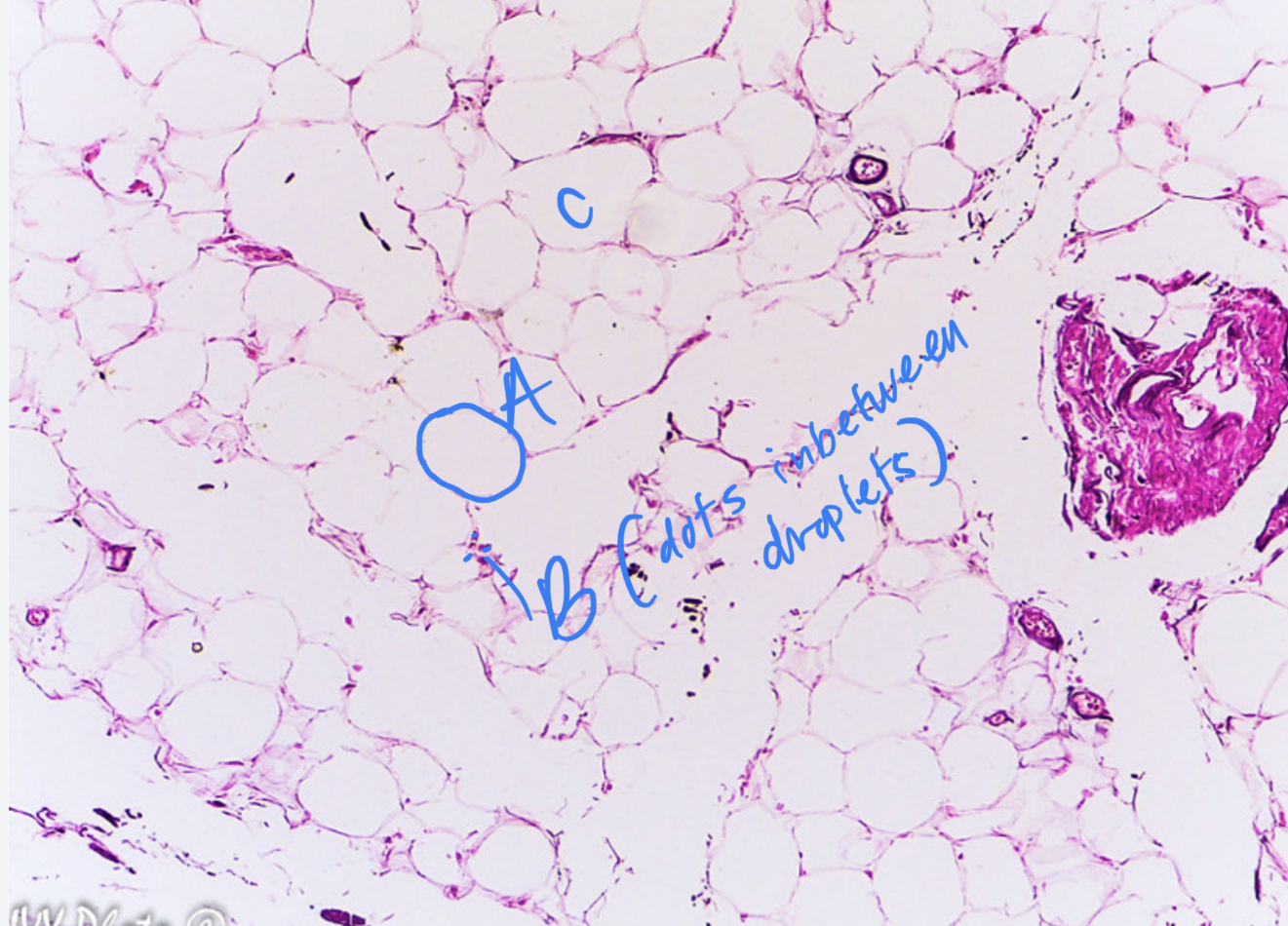
* tissue type
* label
* label
connective adipose, cell membrane, nucleus, fat droplet
8
New cards
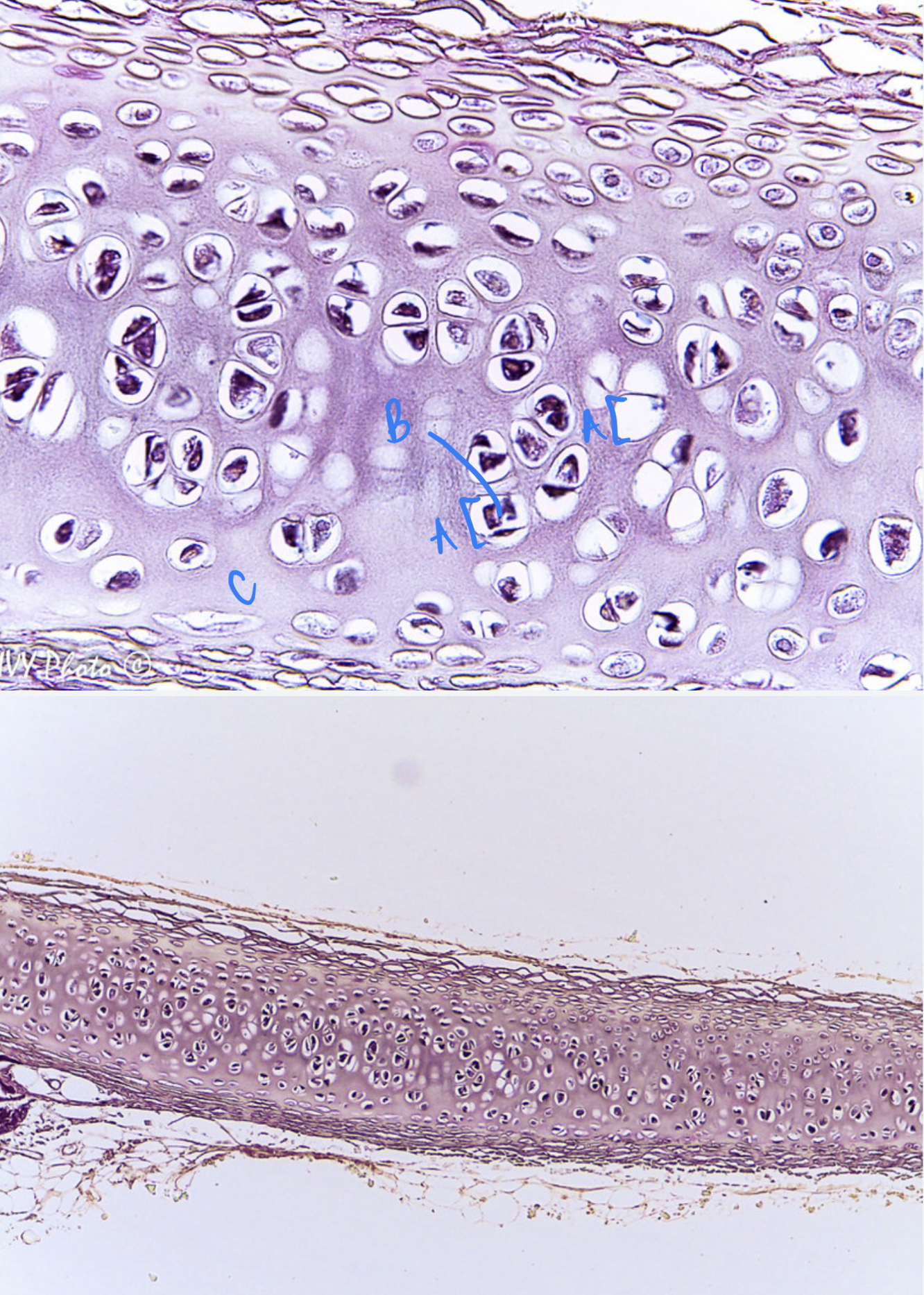
* tissue type
* label
* label
cartilage connective, lacunae, chondrocyte in lacuna, matrix
9
New cards
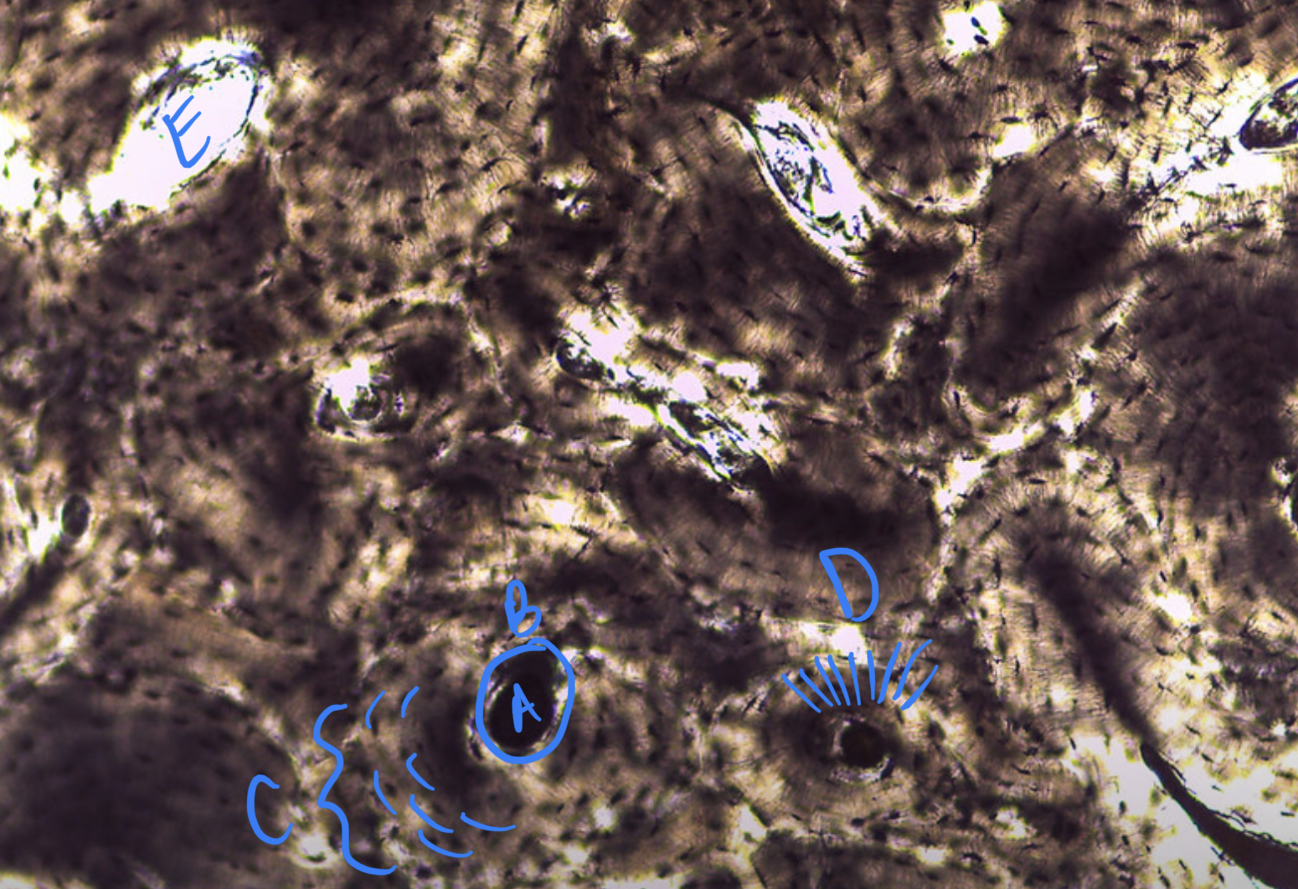
* tissue type
* label
* label
bone connective, central canal, osteon, osteocyte in lacuna, canaliculi, matrix
10
New cards
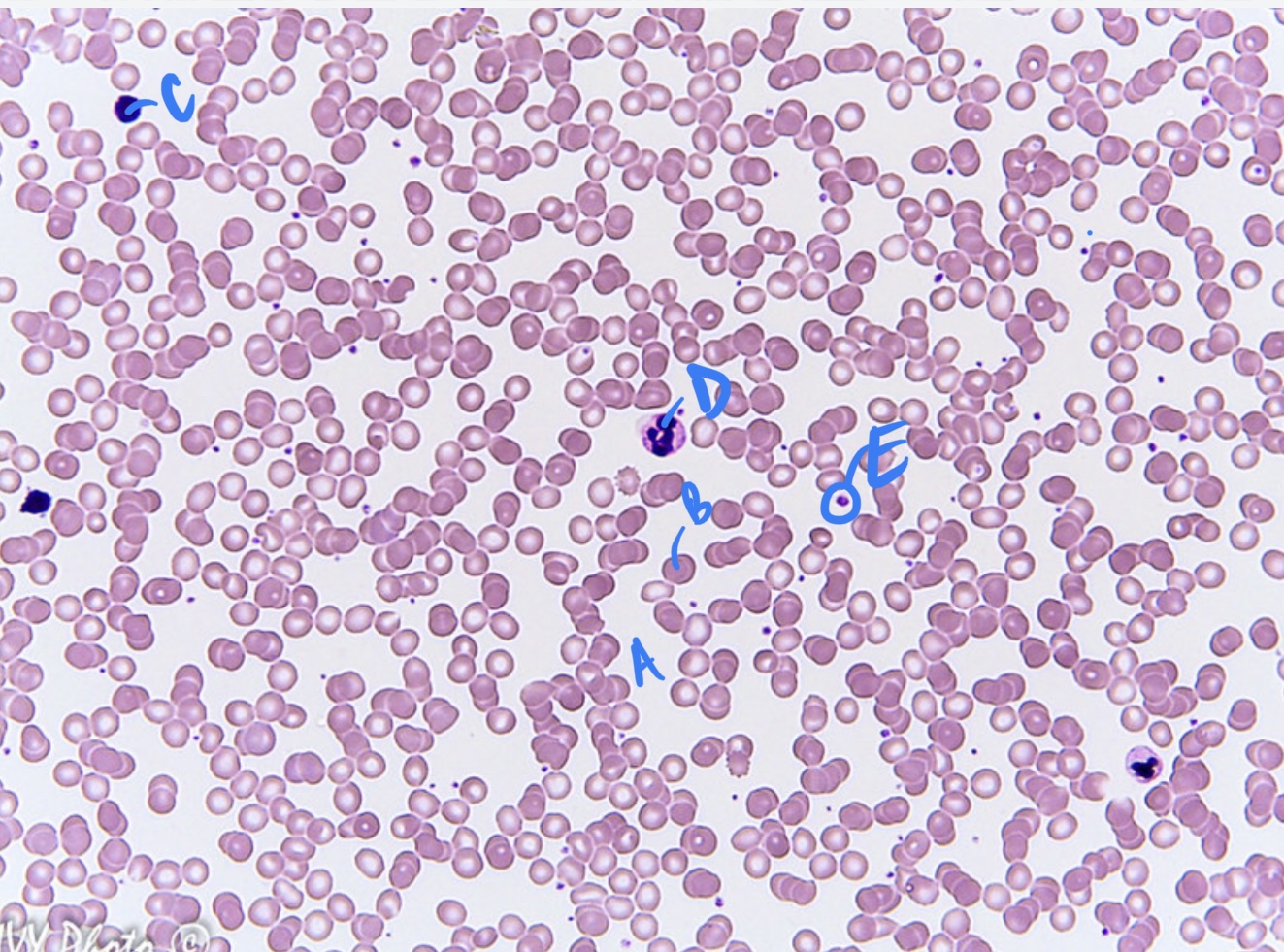
* tissue type
* label
* label
blood connective, plasma, erythrocyte, lymphocyte, neutrophil, platelet
11
New cards
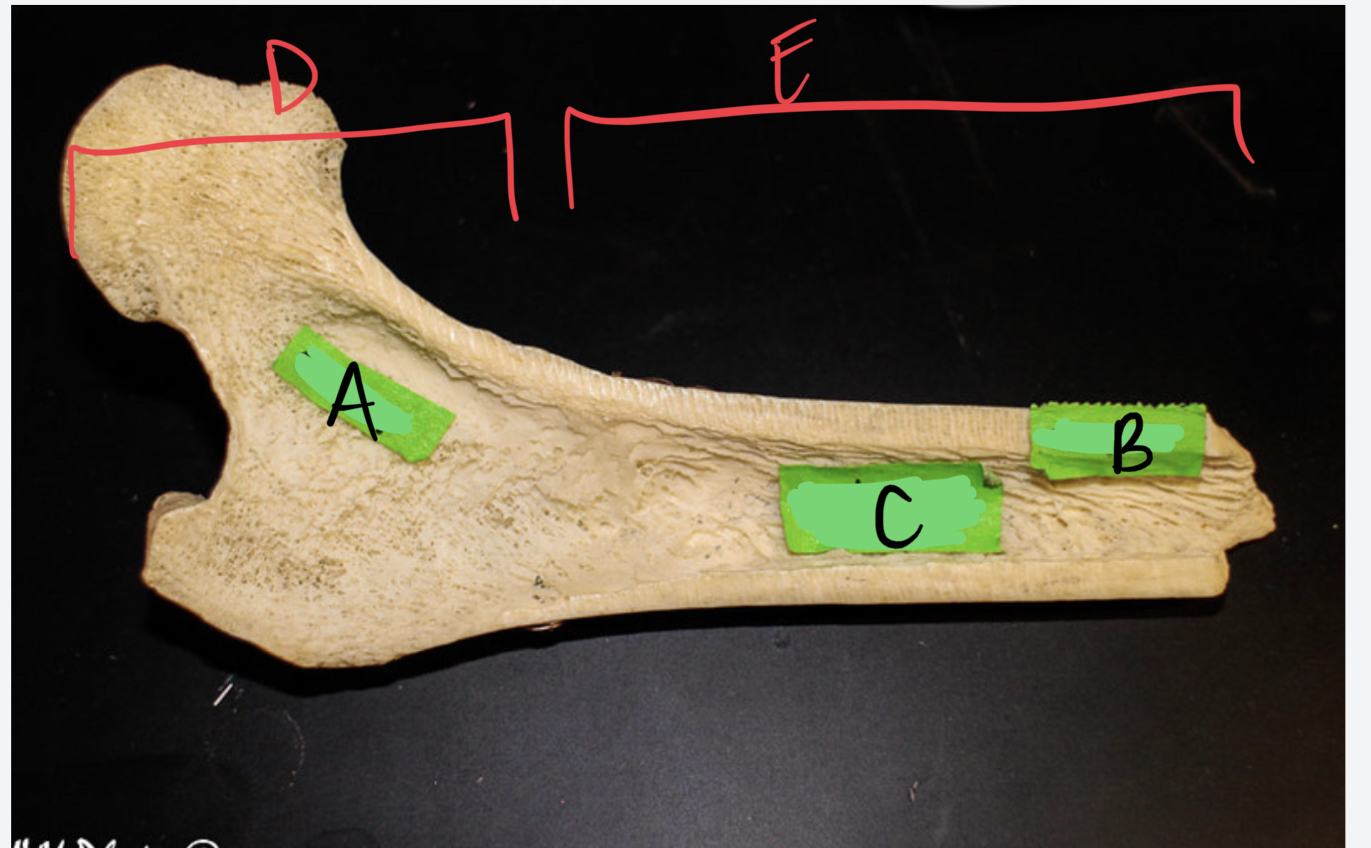
* bone name
* label
* ____: active; produces stem cells for blood cells
* ____: inactive; stores blood stem cells, cartilage, fat
* label
* ____: active; produces stem cells for blood cells
* ____: inactive; stores blood stem cells, cartilage, fat
long bone, spongy bone, compact bone, medullary cavity, red bone marrow region, yellow bone marrow region, red bone marrow region, yellow bone marrow region
12
New cards
* what bones make up axial skeleton?
* what bones make up appendicular skeleton?
* what bones make up pectoral girdle?
* what bones make up pelvic girdle?
* what bones make up appendicular skeleton?
* what bones make up pectoral girdle?
* what bones make up pelvic girdle?
skull, vertebral column, rib cage, sternum, arms, legs, pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle, clavicle, scapula, ilium, ischium, pubic bone, sacrum, coccyx
13
New cards
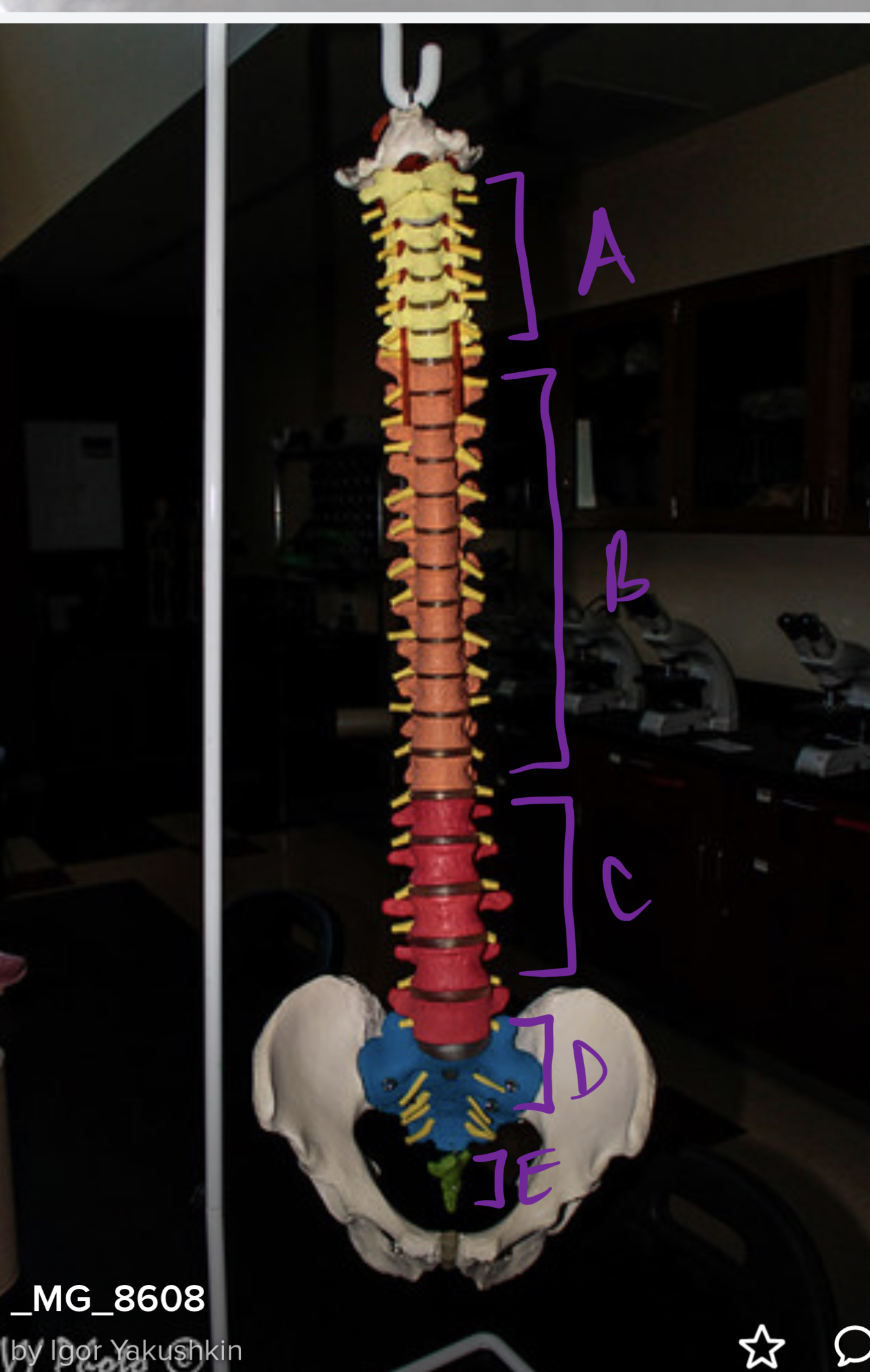
* label
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccyx
14
New cards
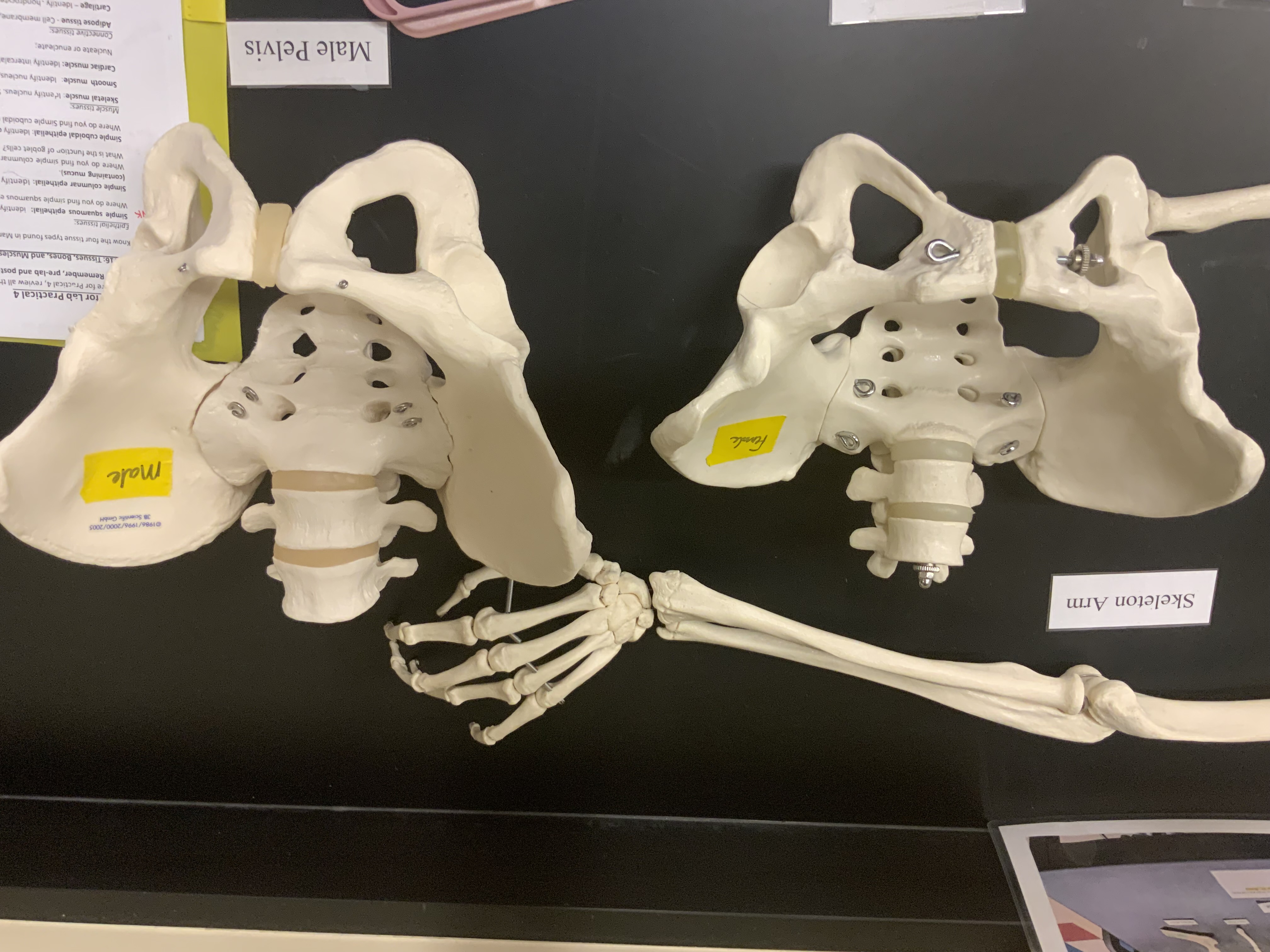
* which pelvis is male (left or right)
right
15
New cards
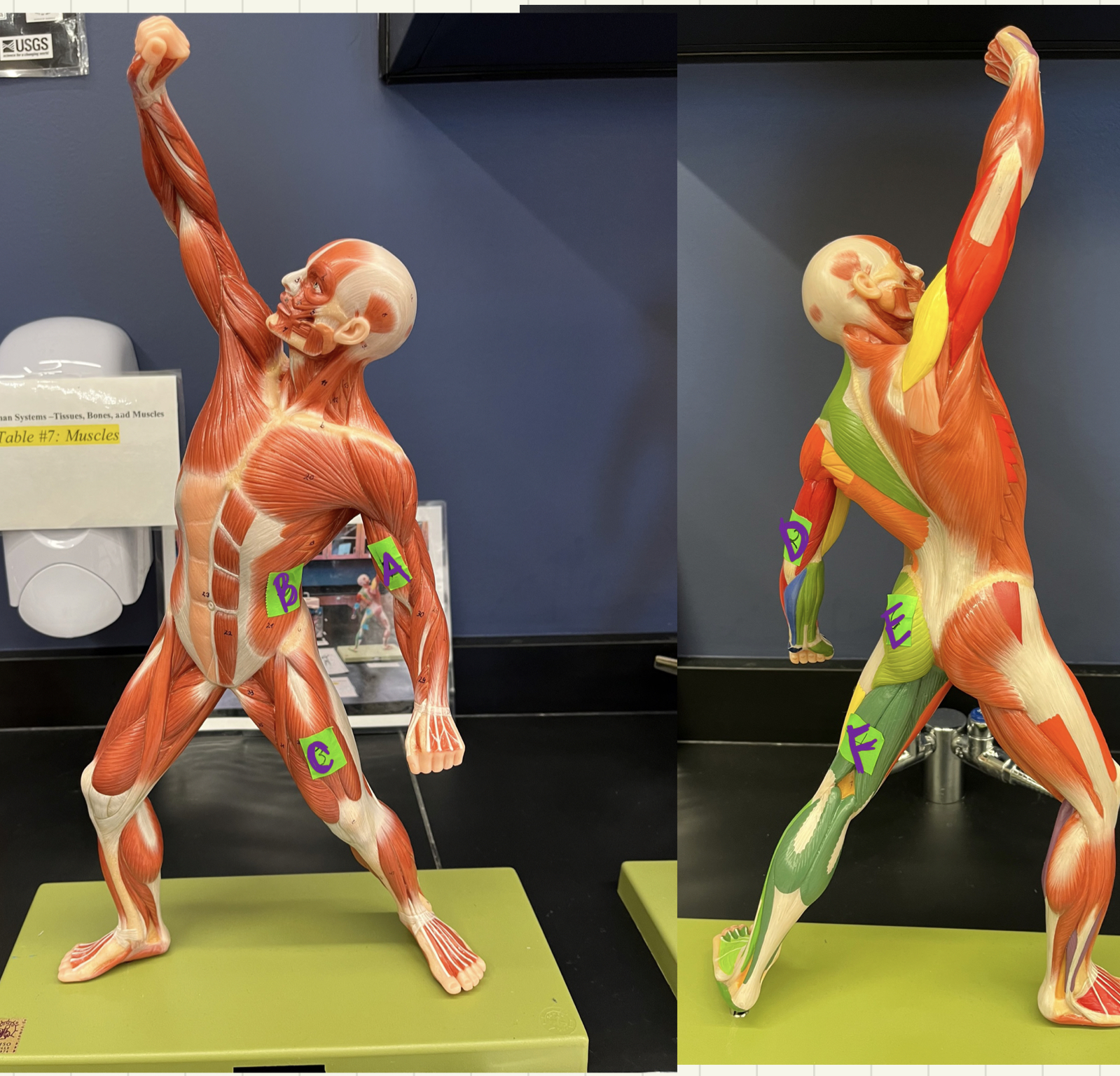
* label
biceps brachii, external oblique, quadriceps femoris, triceps brachii, gluteus maximus, hamstring group
16
New cards
* 3 digestive systems?
intracellular, gastrovascular cavity, gi tract
17
New cards
MAMMALIAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
_____: mastication + bolus formation
_____: transports bolus to stomach
_____: mechanically breaks apart bolus + HCL and enzymes + makes chyme
_____: absorption and digestion + works with accessory organs
a. 3 parts?
_____: secretes pancreatic juice + neutralizing alkaline solution, everything into → duodenum
_____: produces bile + converts glucose into glycogen + detoxification of harmful substances
_____: stores/releases bile into duodenum to emulsify fats
_____: absorbs water/vitamins + prepares feces for excretion
a. 3 parts?
_____: mastication + bolus formation
_____: transports bolus to stomach
_____: mechanically breaks apart bolus + HCL and enzymes + makes chyme
_____: absorption and digestion + works with accessory organs
a. 3 parts?
_____: secretes pancreatic juice + neutralizing alkaline solution, everything into → duodenum
_____: produces bile + converts glucose into glycogen + detoxification of harmful substances
_____: stores/releases bile into duodenum to emulsify fats
_____: absorbs water/vitamins + prepares feces for excretion
a. 3 parts?
mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, duodenum, ileum, jejunum, pancreas, liver, gallbladder, large intestine, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon
18
New cards
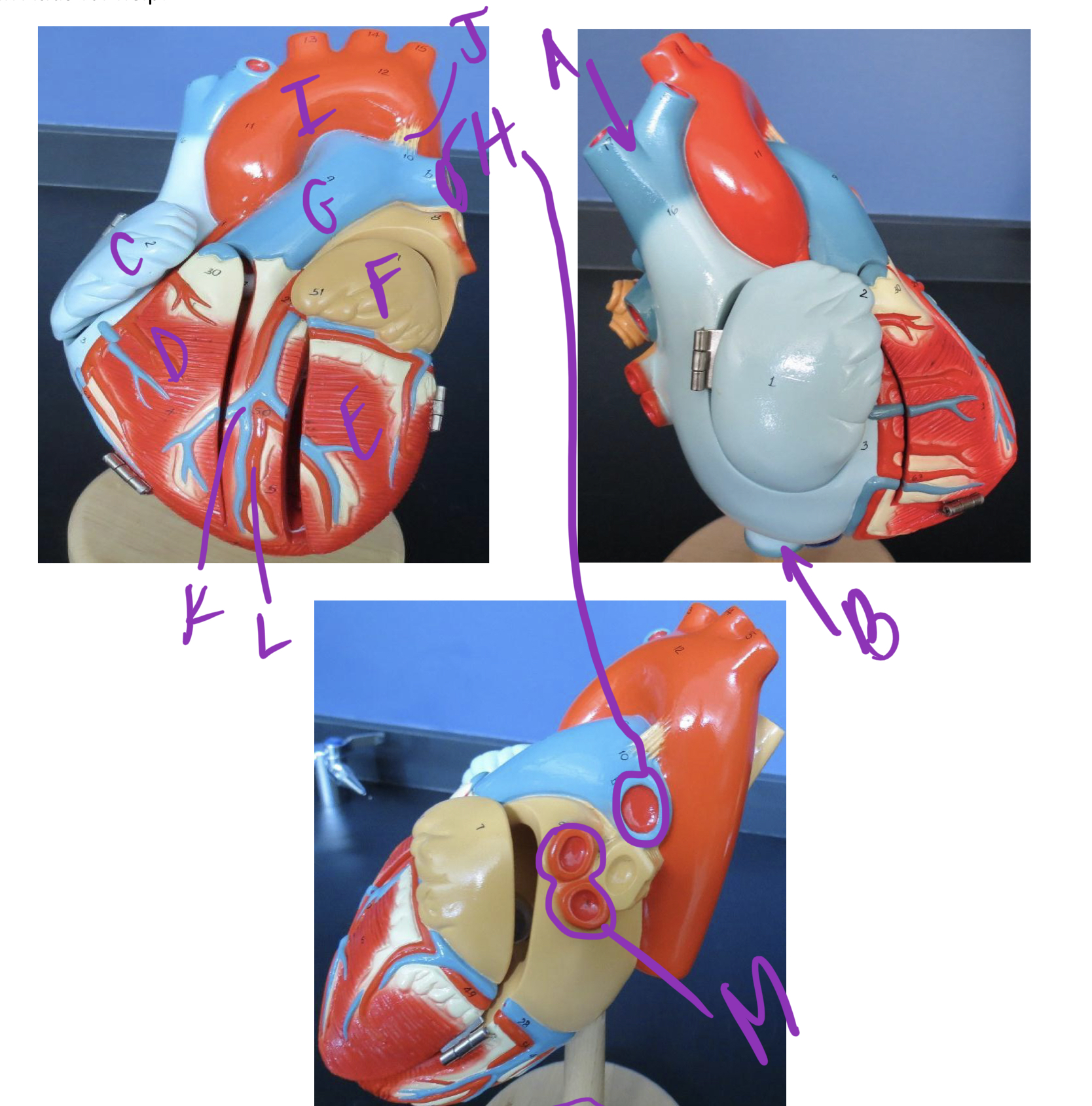
* label
* what is function of coronary arteries and veins
* what is function of coronary arteries and veins
superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, right atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, left atrium, pulmonary trunk, pulmonary artery, aorta, ductus arteriosis, coronary vein, coronary artery, pulmonary vein, supply heart with blood
19
New cards
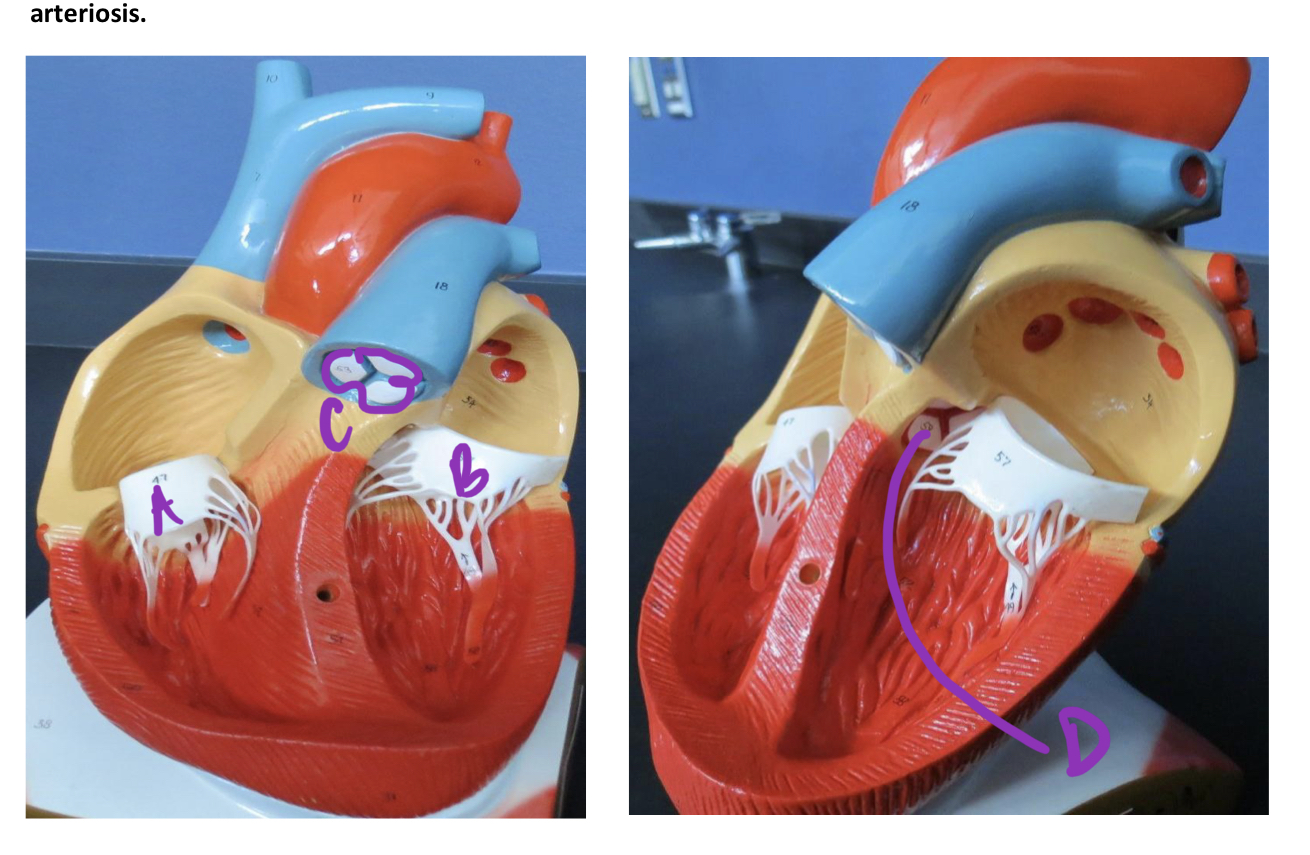
* label
tricuspid valve, bicuspid valve, pulmonary semilunar valve, aortic semilunar valve
20
New cards
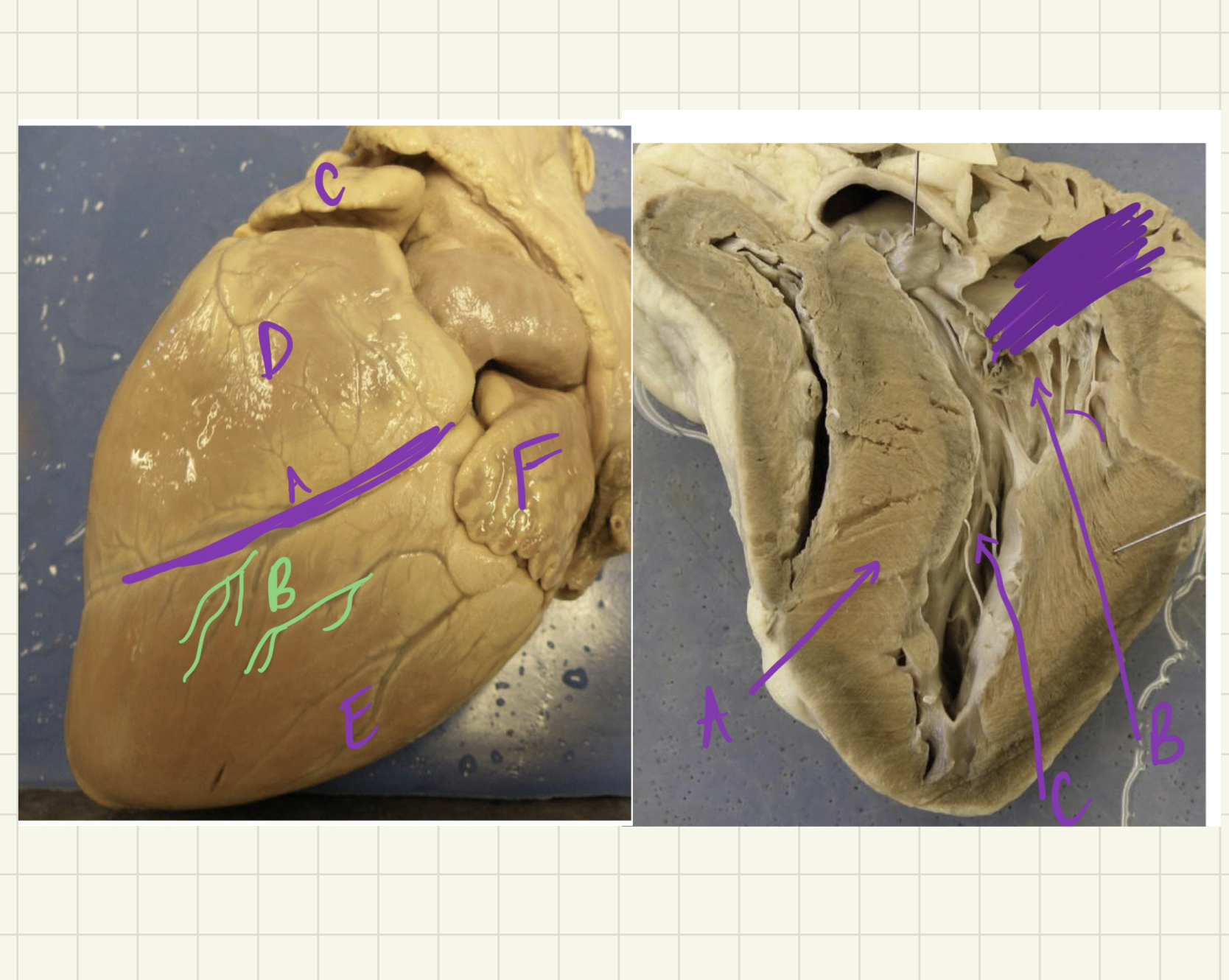
* label
interventricular groove, coronary vessels, right atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, left atrium, interventricular septum, chordae tendinae, papillary muscles
21
New cards
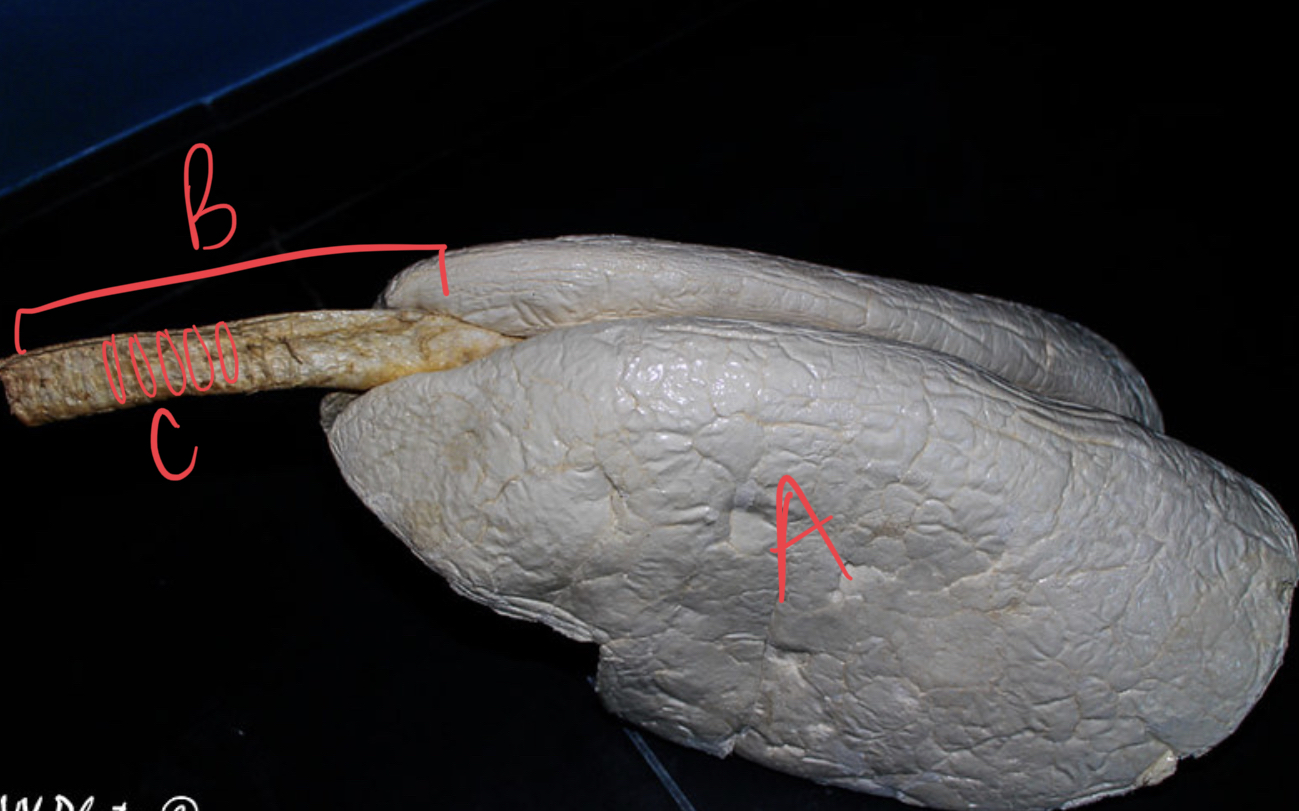
* label
lungs, trachea, cartilaginous rings
22
New cards
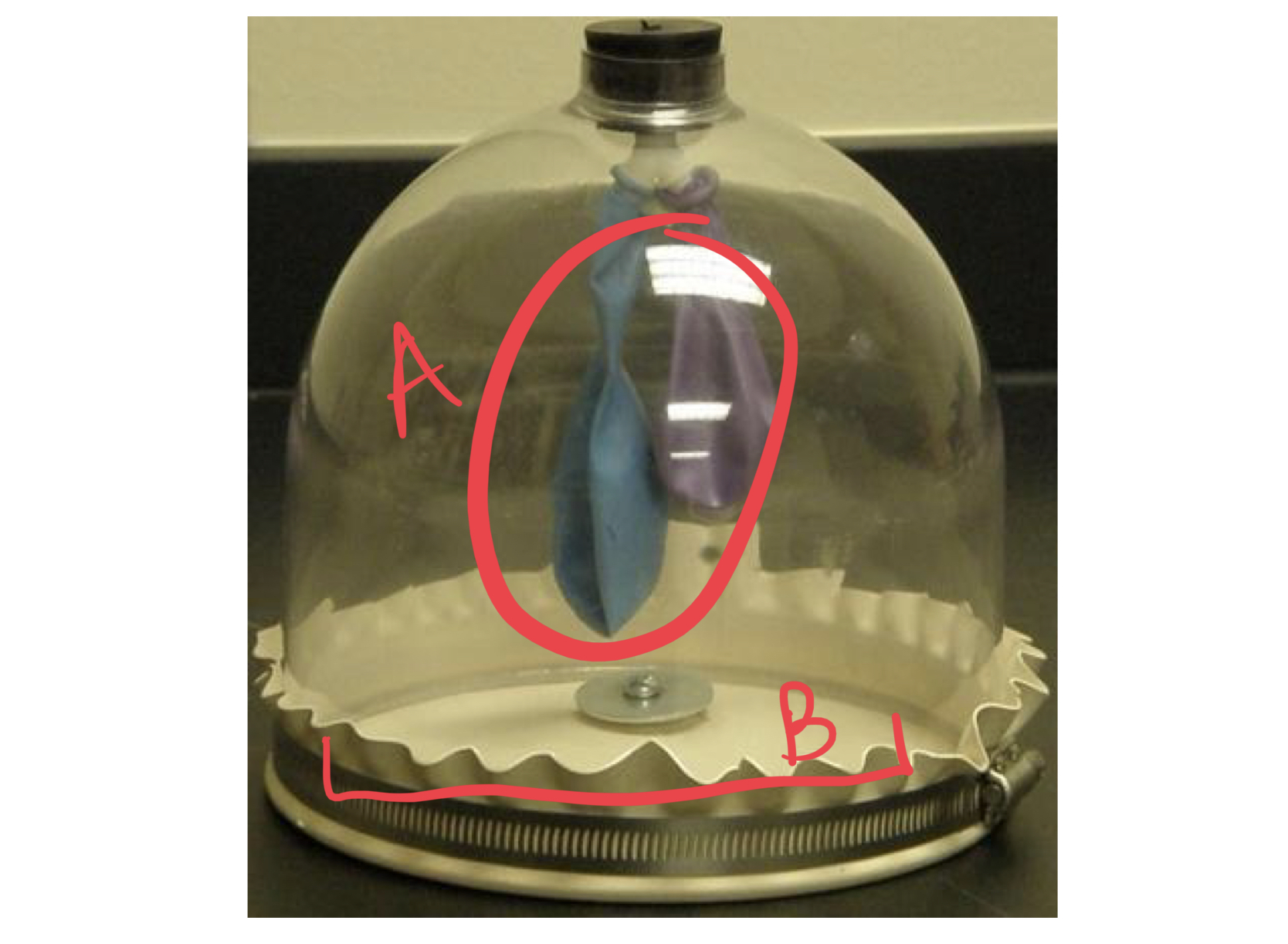

* label
lungs, diaphragm
23
New cards
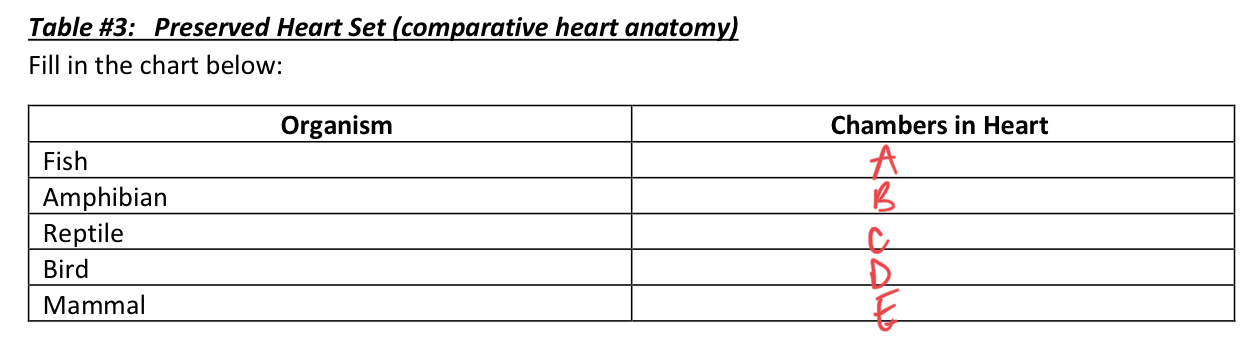
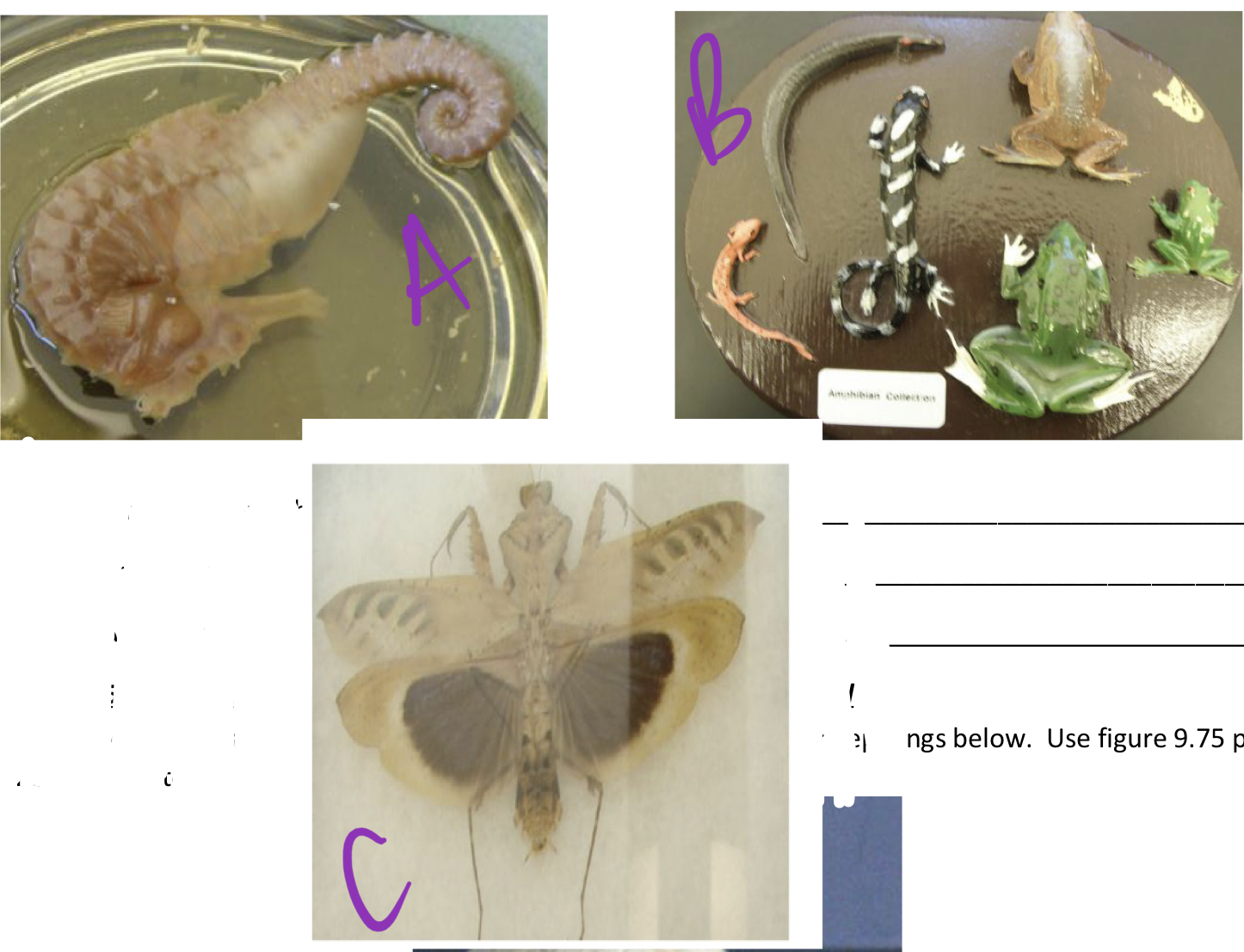
* fill in
2, 3, 3, 4, 4
24
New cards

* open or closed circulatory system?
closed, closed, open
25
New cards
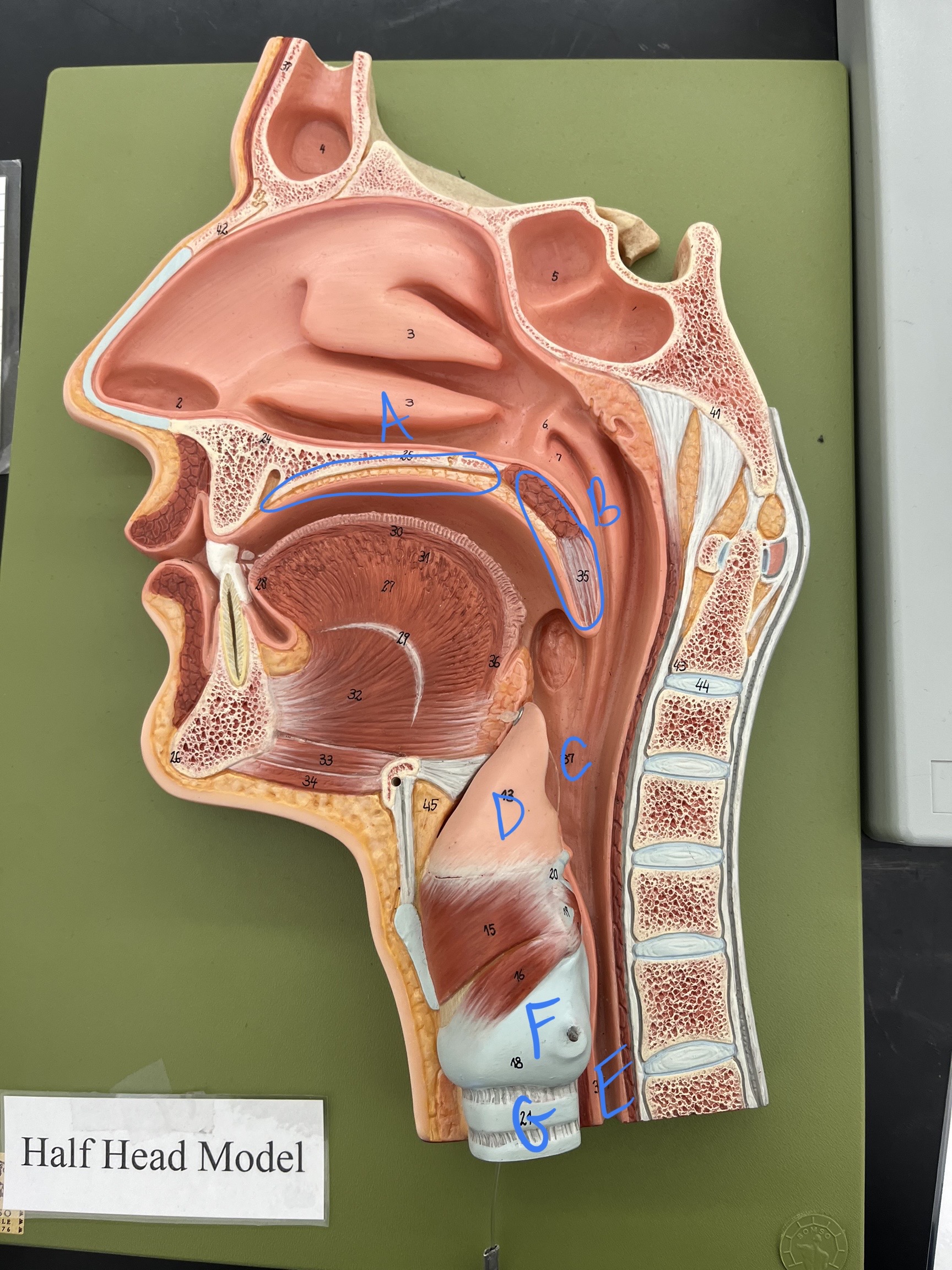
* label
* epiglottis function?
* epiglottis function?
hard palate, soft palate, pharynx, epiglottis, esophagus, larynx, trachea, prevents food from entering trachea
26
New cards
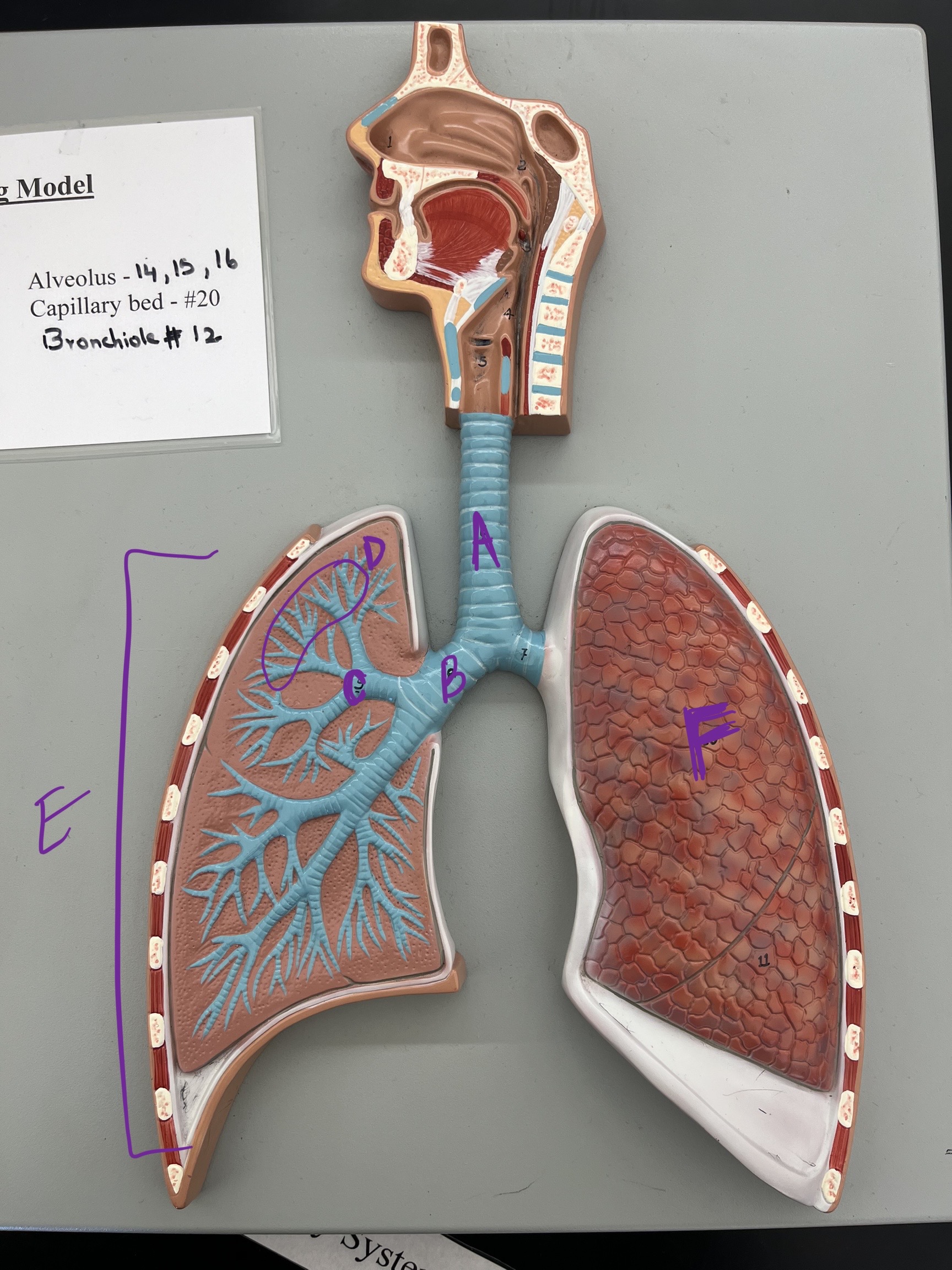
* label
trachea, primary bronchi, secondary bronchi, tertiary bronchi, lungs, diaphragm
27
New cards
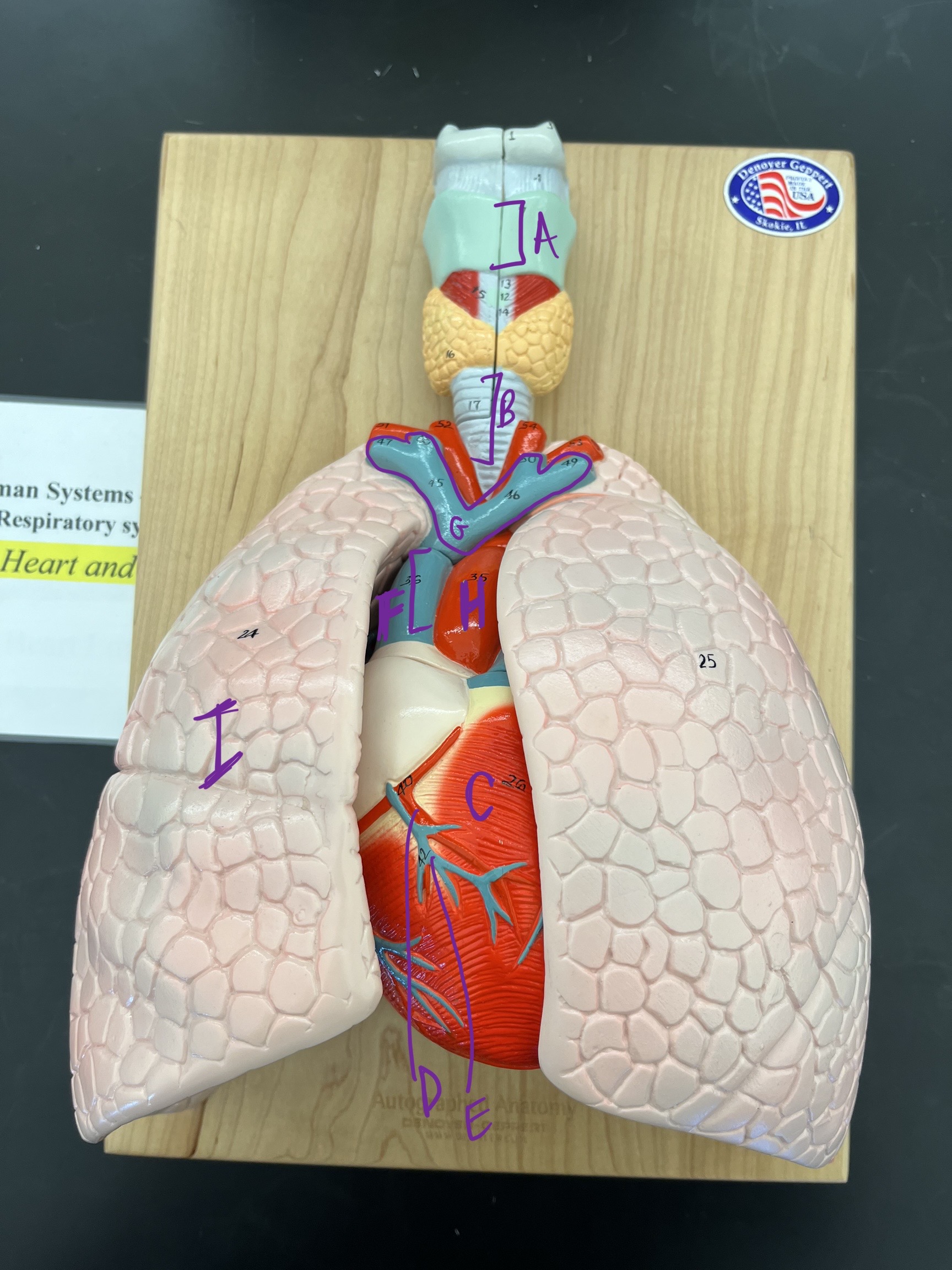
* label
* function of larynx?
* function of larynx?
* larynx, trachea, heart, coronary artery, coronary vein, pulmonary trunk, pulmonary arteries, aorta, lungs, speaking, breathing, swallowing
28
New cards
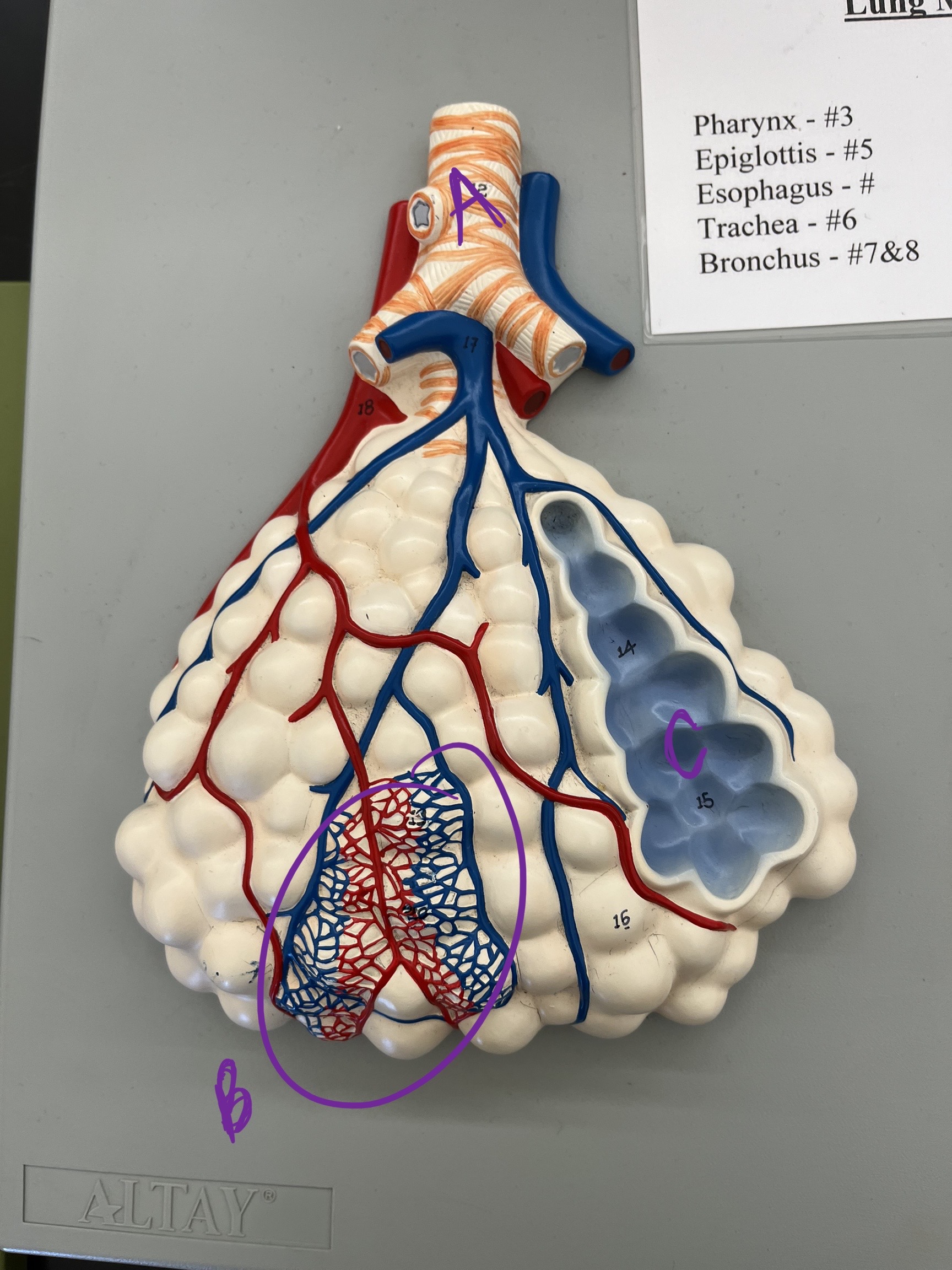
* label
* is this pulmonary circulation (blood exchange w/lungs) or systematic circulation (blood exchange to entire body)?
* is this pulmonary circulation (blood exchange w/lungs) or systematic circulation (blood exchange to entire body)?
bronchiole, capillary beds, alveoli, pulmonary
29
New cards
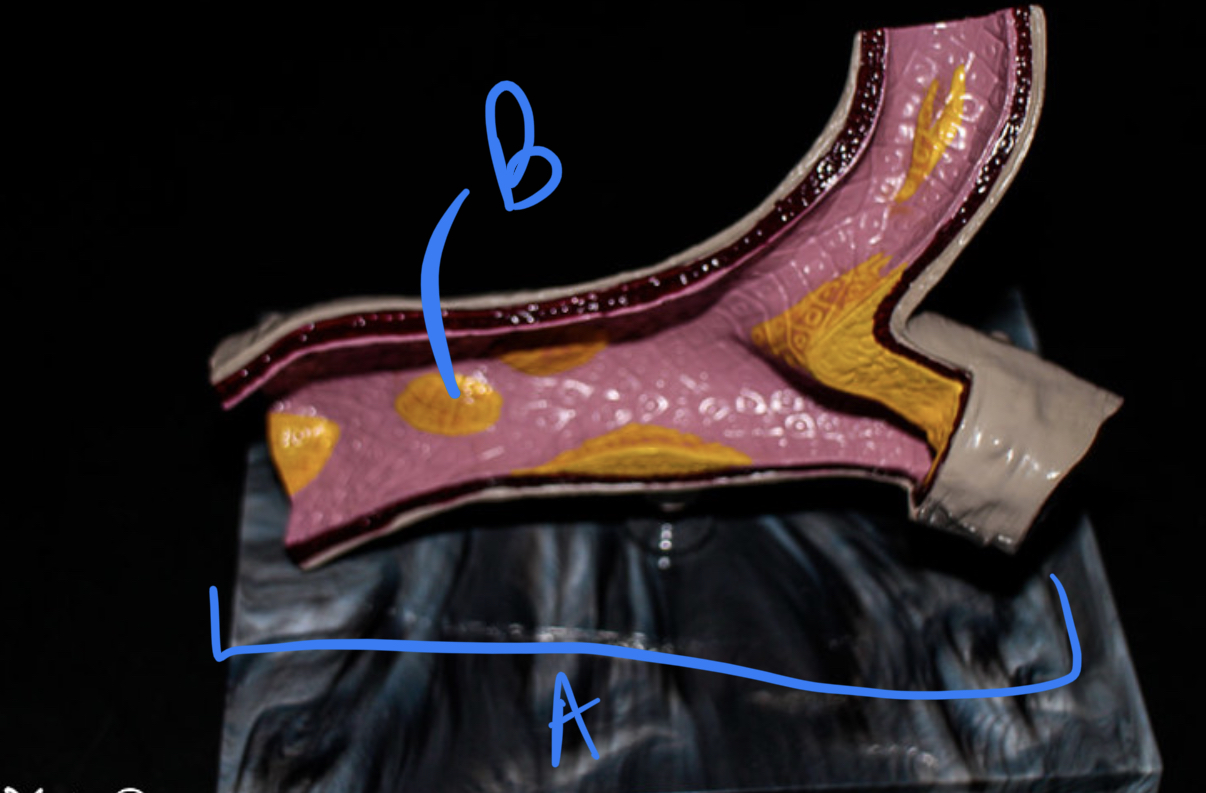
* label
* what disease condition does plaque accumulation in arteries cause?
* what disease condition does plaque accumulation in arteries cause?
artery, plaque, atherosclerosis
30
New cards
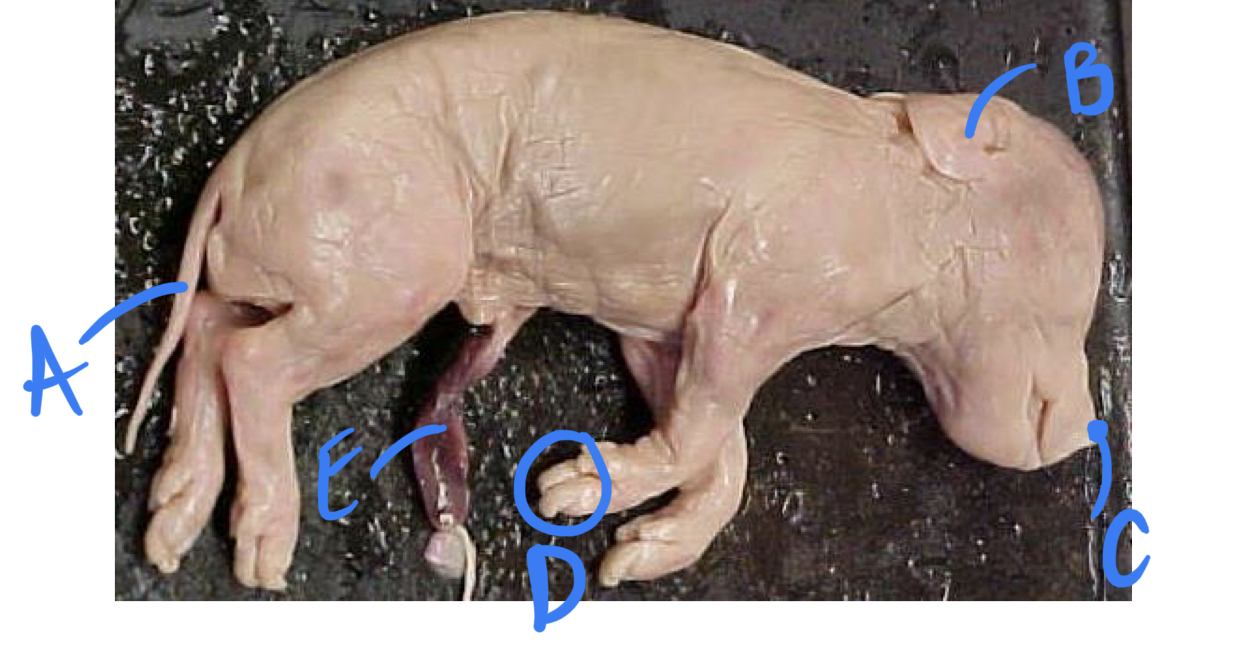

* label
* how to tell if its male or female
a. male: has scrotum sac + urogenital opening near umbilical cord
b. female: urogenital opening near anus
* how to tell if its male or female
a. male: has scrotum sac + urogenital opening near umbilical cord
b. female: urogenital opening near anus
tail, pinna, naris, hoof, umbilical cord
31
New cards
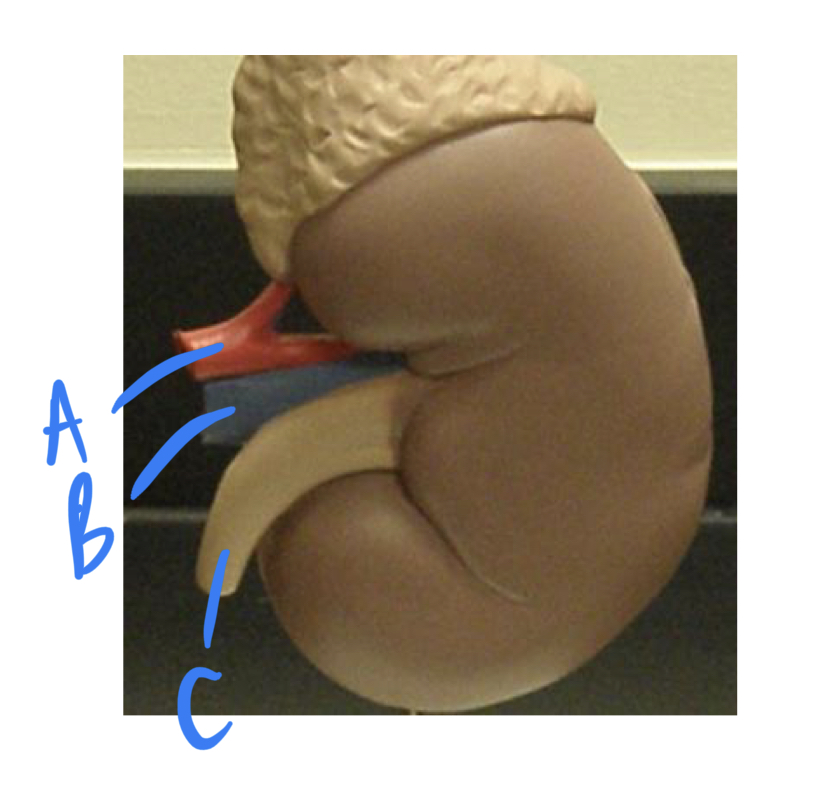
* what organ is this
* label
* label
kidney, renal artery, renal vein, ureter
32
New cards
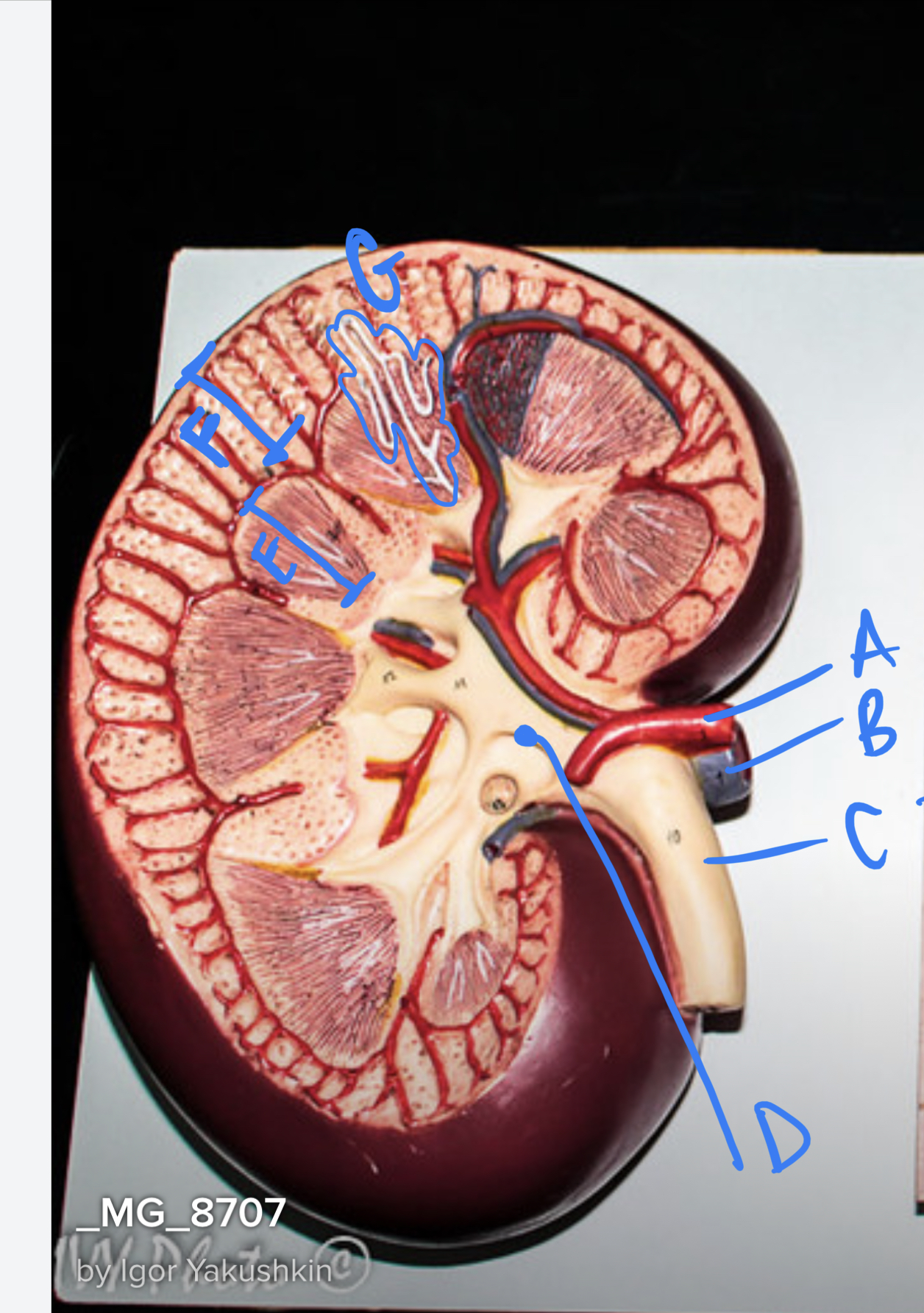
* label
renal artery, renal vein, ureter, renal pelvis, renal medulla, renal cortex, nephron
33
New cards
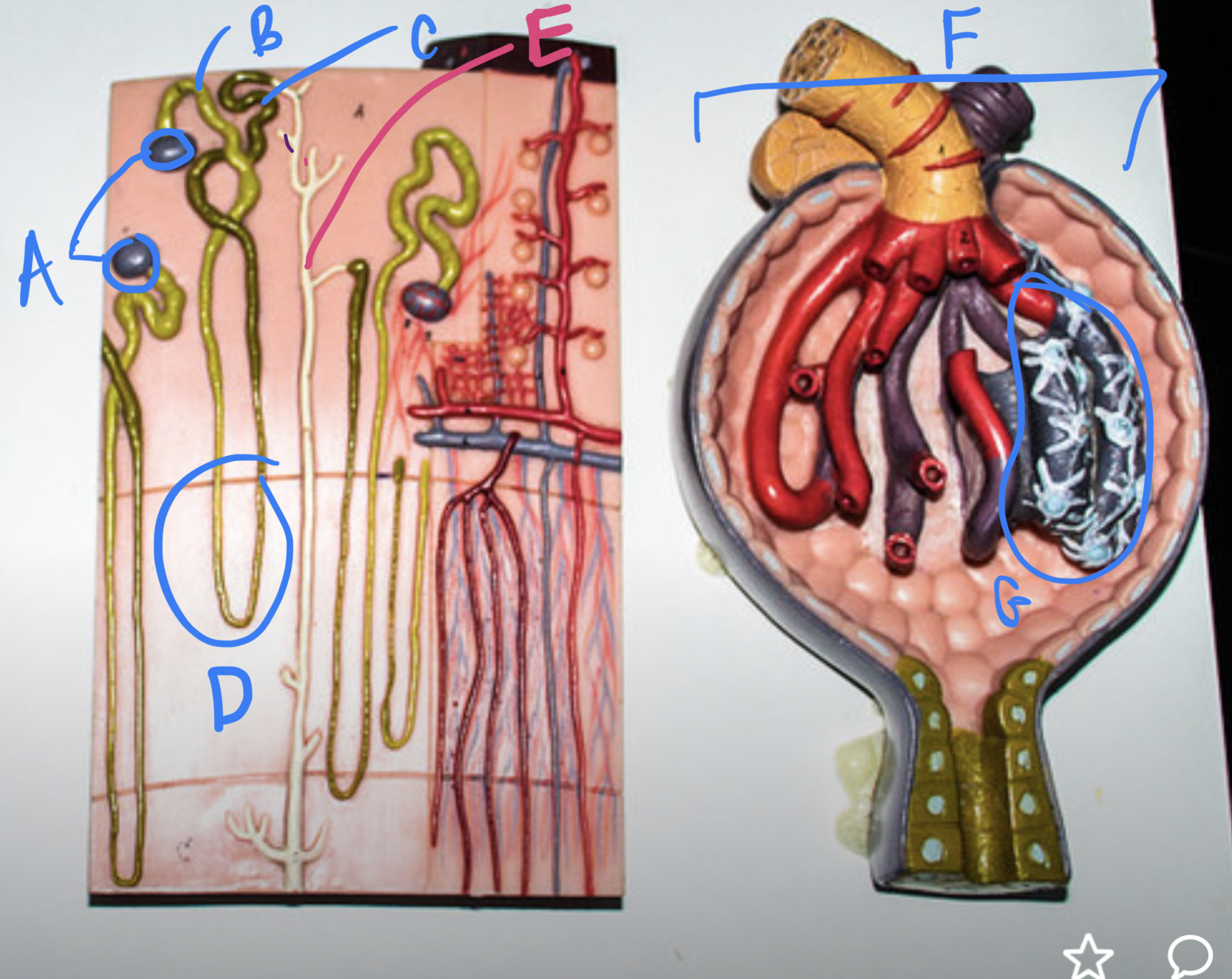
(closer look inside kidney)
* label
* what kind of tissue lines the kidney tubules
* label
* what kind of tissue lines the kidney tubules
bowmans capsule, proximal convoluted tube, distal convoluted tube, loop of henle, collecting duct, bowmans capsiule, glomecular capillaries, cuboidal epithelial
34
New cards
special types of asexual reproduction:
* ____: pinches off from parent
a. example?
* ____: birth from unfertilized eggs (single mothaaa)
a. example?
* ____: part of an organism can grow into entirely new individual
a. example?
* ____: pinches off from parent
a. example?
* ____: birth from unfertilized eggs (single mothaaa)
a. example?
* ____: part of an organism can grow into entirely new individual
a. example?
budding, hydra, parthenogenesis, honeybee drones, regeneration, sea stars
35
New cards
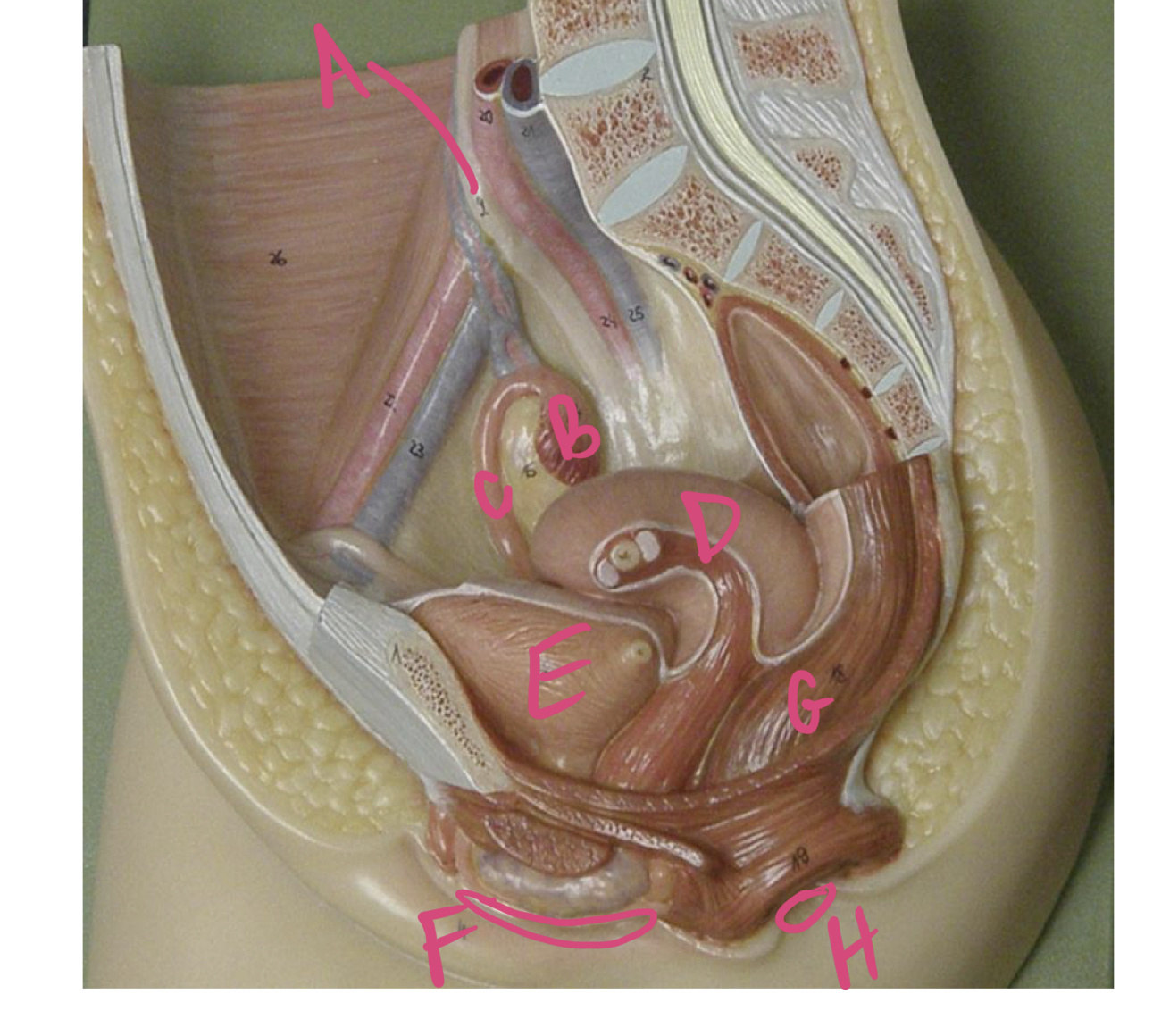
* label
* female organ for copulation?
* structure holding growing fetus?
* function of corpus luteum?
* female organ for copulation?
* structure holding growing fetus?
* function of corpus luteum?
ureter, ovary, oviduct, uterus, urinary bladder, vagina, rectum, anus, vagina, uterus, produce estrogen and progesterone
36
New cards
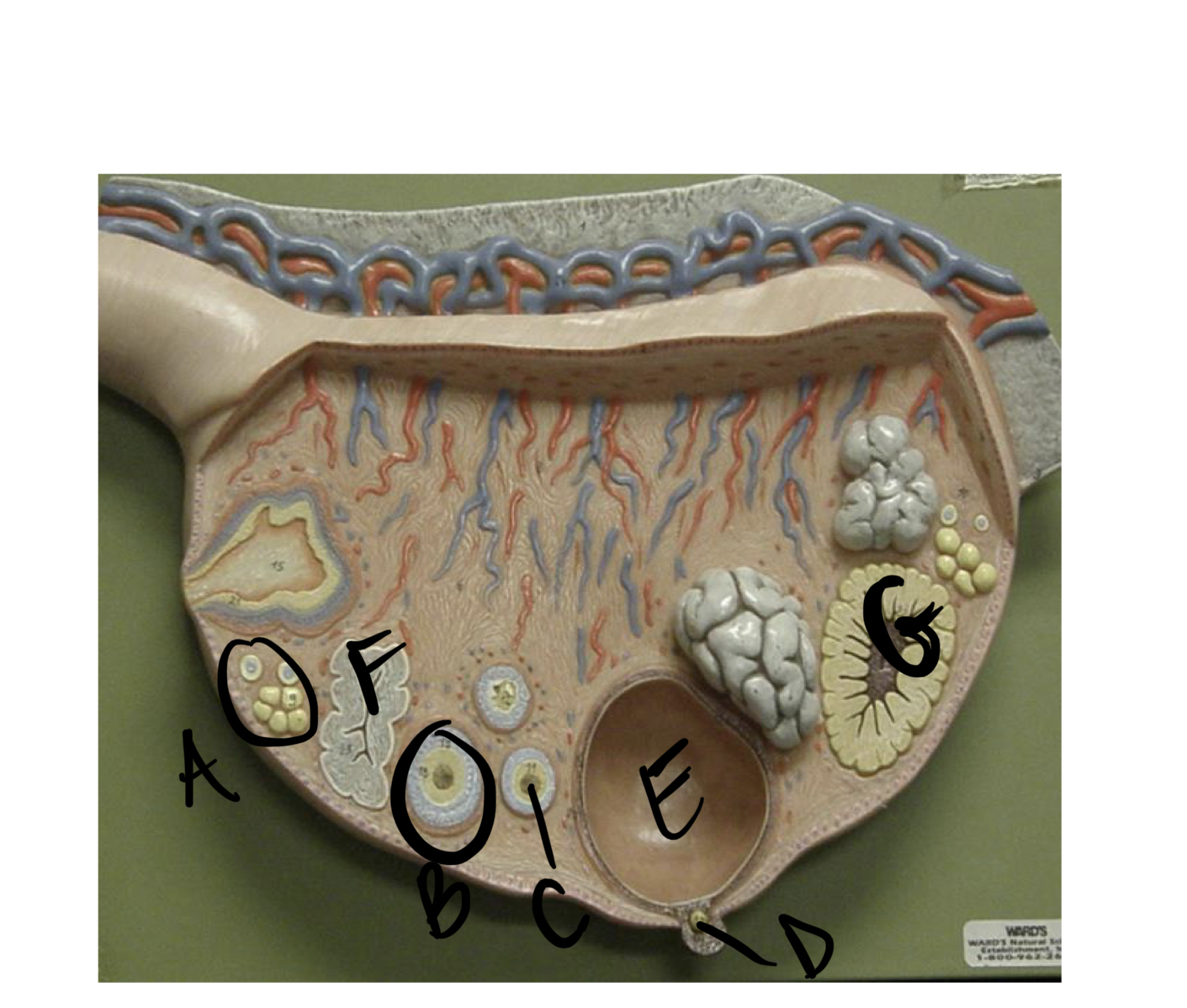
* label
primary follicle, secondary follicle, primary oocyte, secondary oocyte, graafian follicle, corpus albicans, corpus luteum
37
New cards
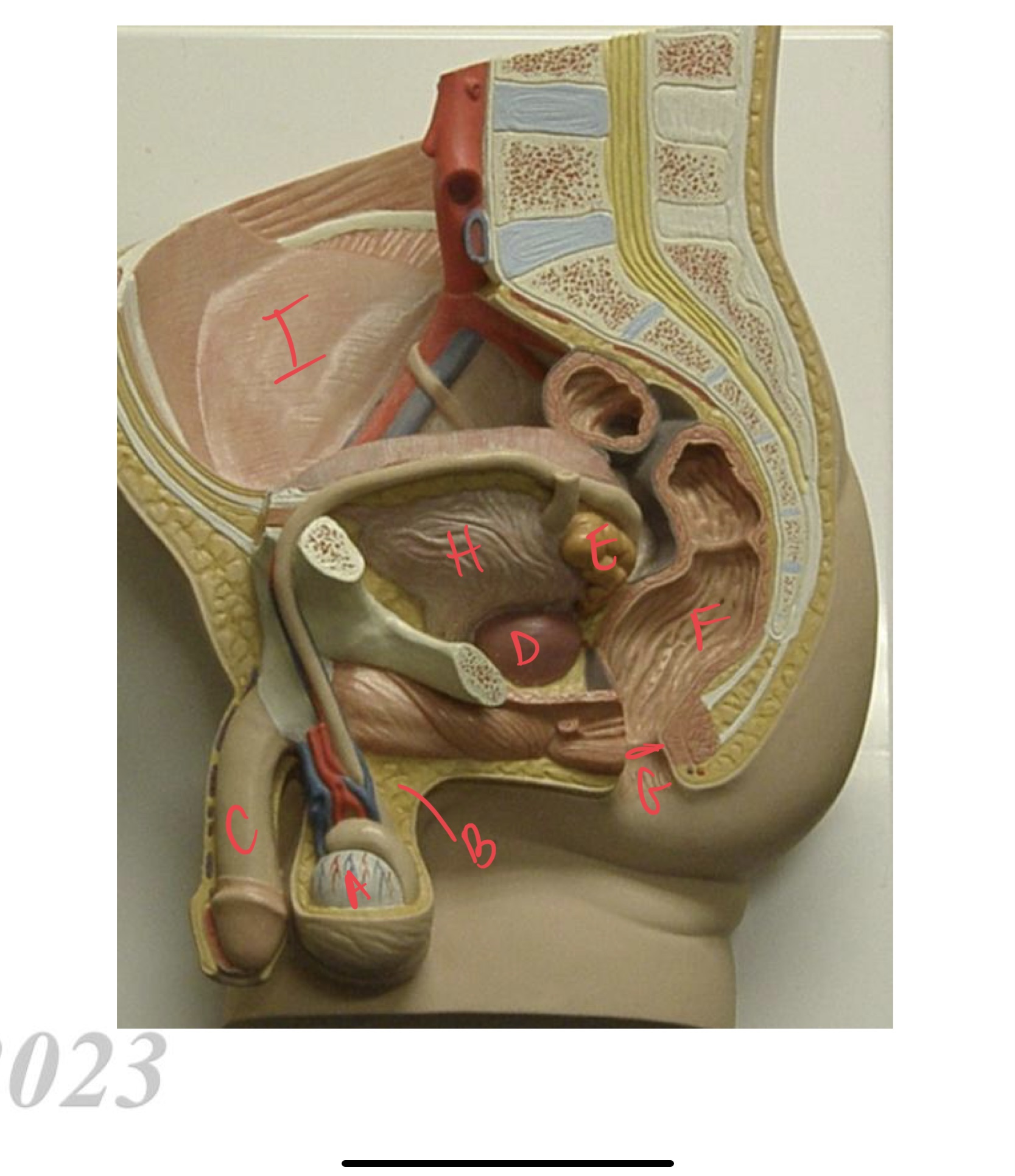
* label
* male organ for copulation?
* male organ for copulation?
testis, epididymis, penis, prostate, seminal vesicle, rectum, anus, urinary bladder, vas deferens, penis
38
New cards
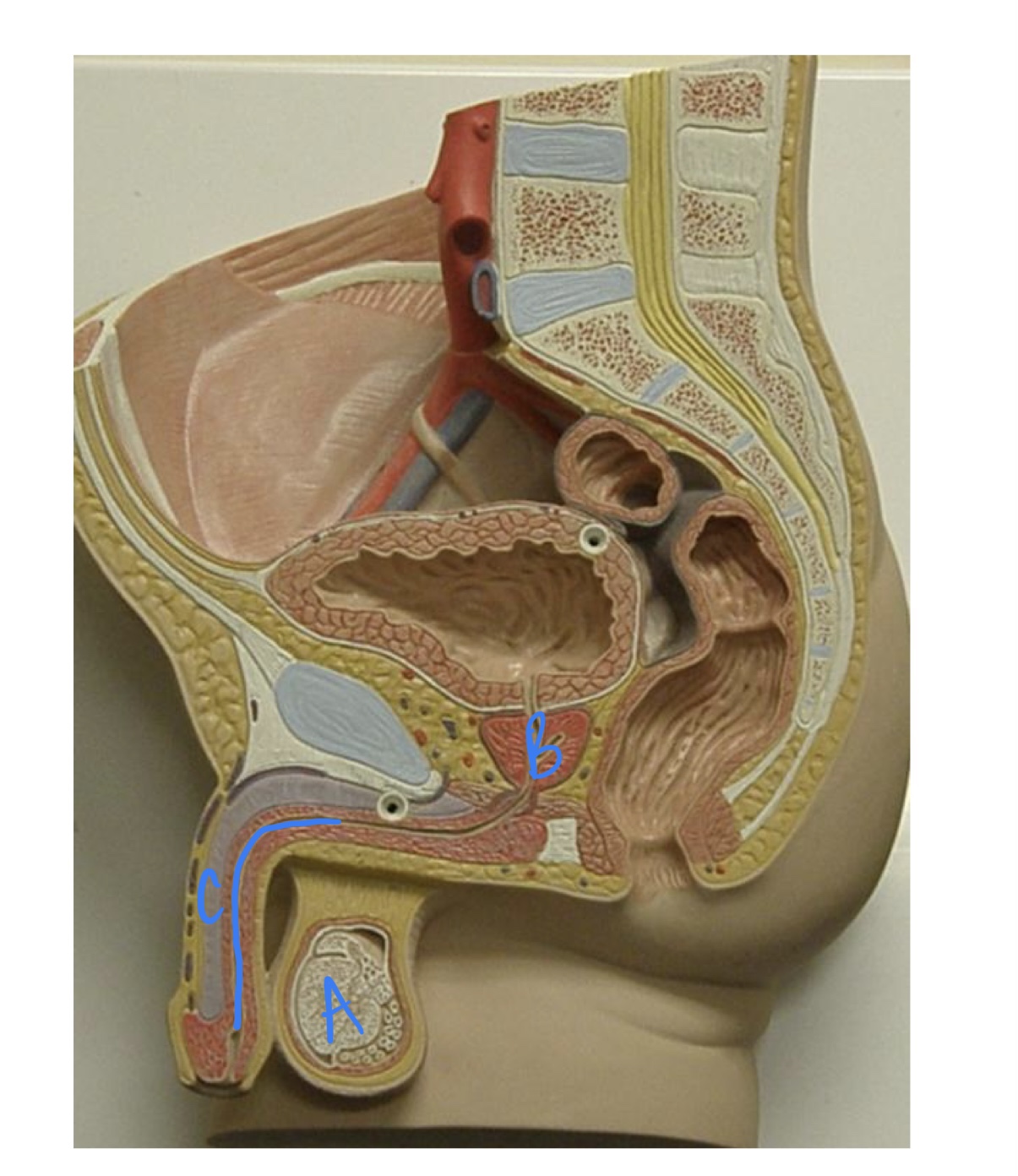
* label
seminiferous tubules, prostate gland, urethra
39
New cards
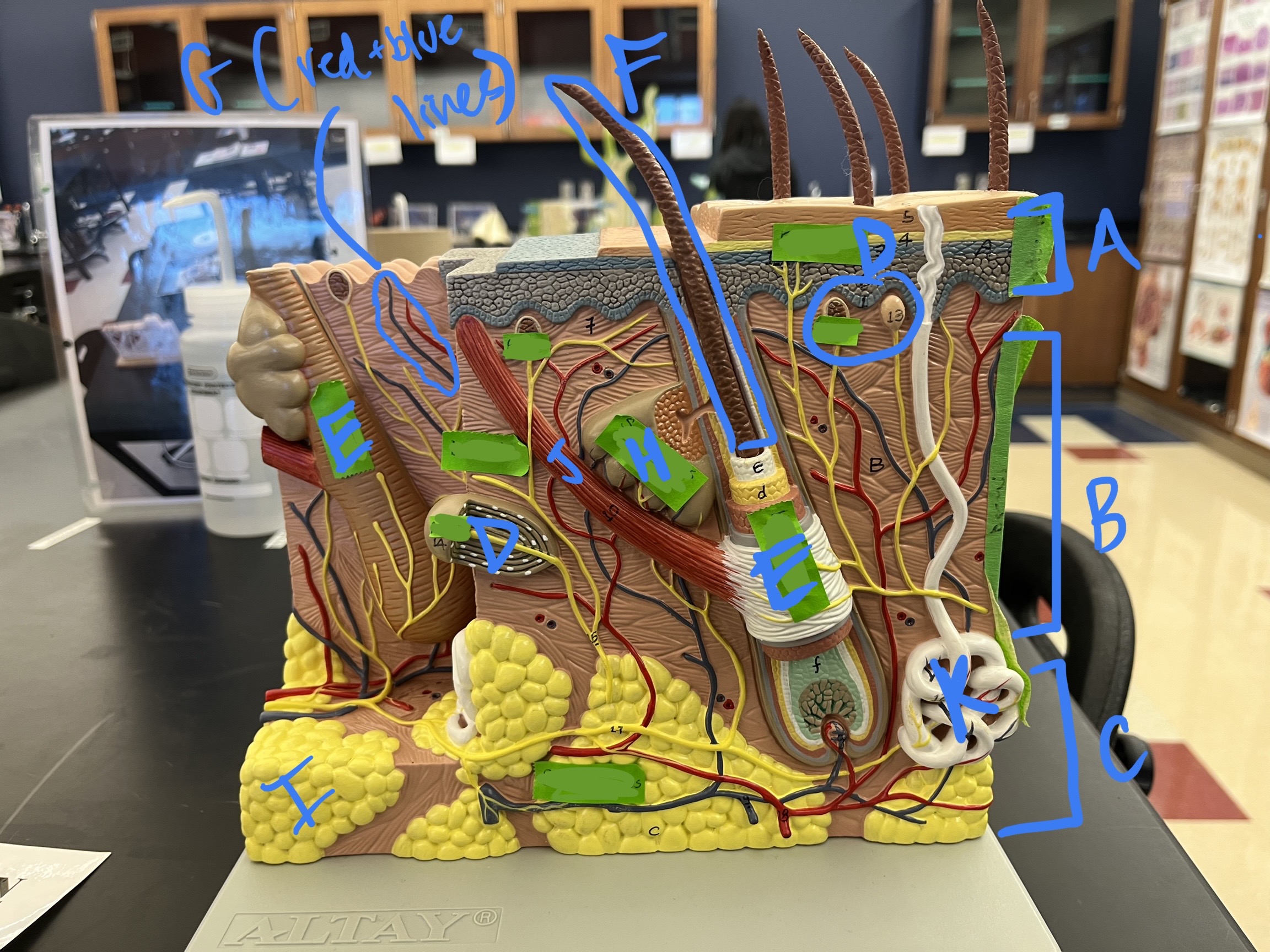

* label
* function of arrector pili muscle?
* function of sebaceous gland?
* location of receptors of pain, temp, and pressure?
* function of arrector pili muscle?
* function of sebaceous gland?
* location of receptors of pain, temp, and pressure?
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis, sensory receptors, hair follicle, hair shaft, blood vessels, sebaceous gland, adipose tissue, arrector pili muscle, sweat gland, makes hair stand up for thermoregulation or fear, makes skin water resistant and moist, epidermis
40
New cards
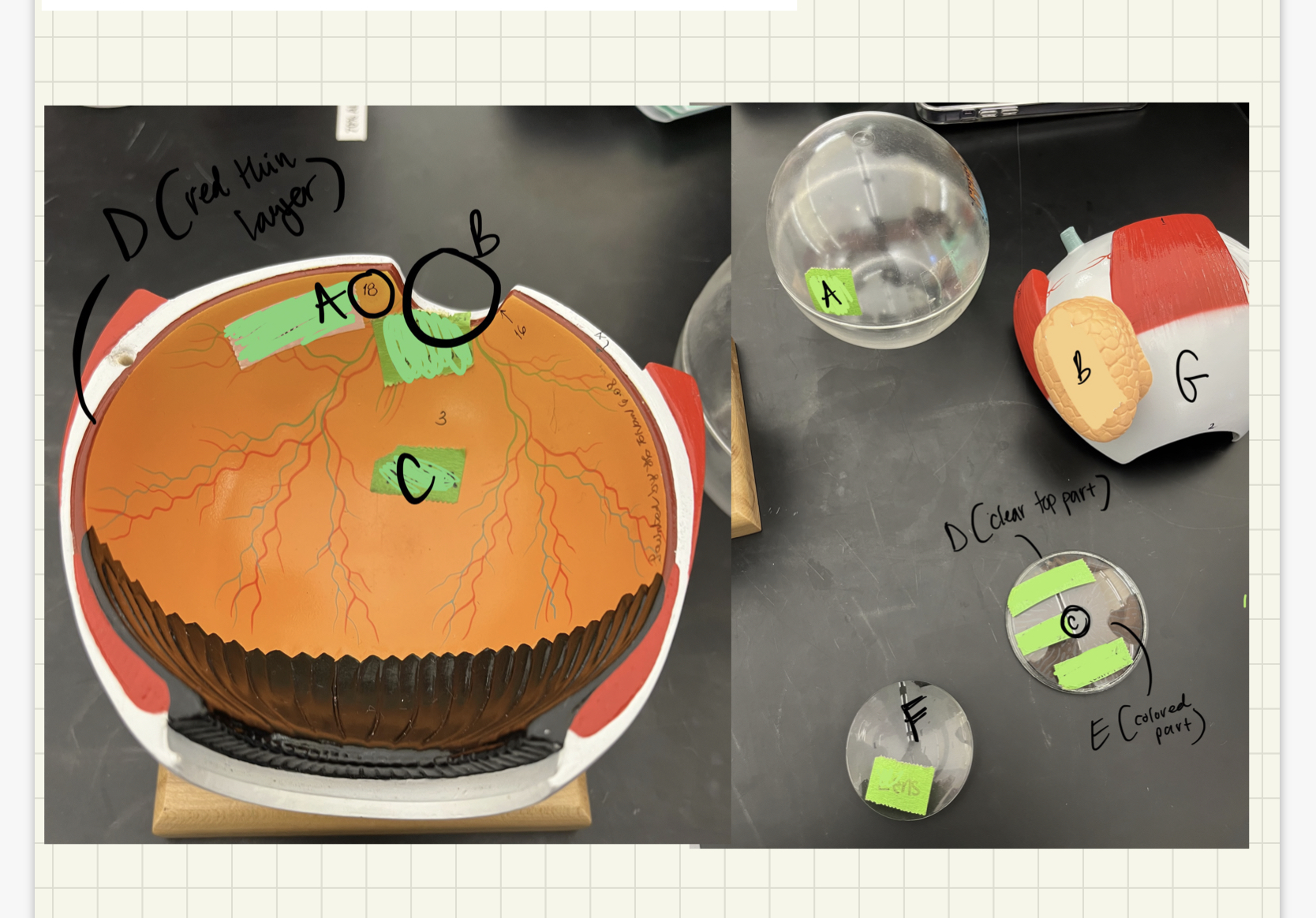
* label
* which eye layer contains photoreceptors?
* where is the blind spot in the eye?
* which eye layer contains photoreceptors?
* where is the blind spot in the eye?
macula lutea, blind spot, retina, choroid, vitreous humor, lacrimal gland, pupil, cornea, iris, lens, sclera, retina, region of retina with no photoreceptors
41
New cards
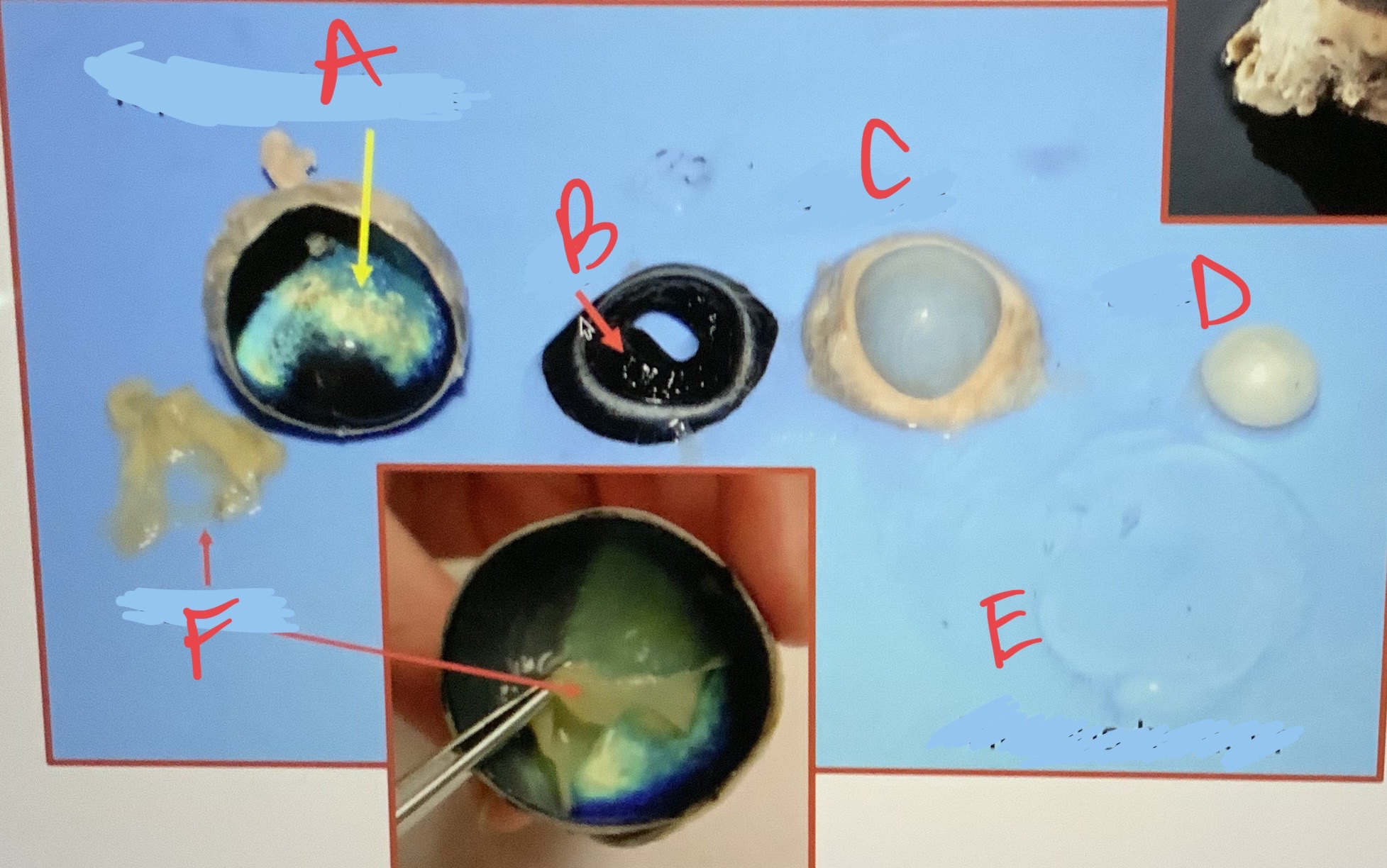
* label
* function of tapetum lucidum?
a. do humans have this?
* function of tapetum lucidum?
a. do humans have this?
tapetum lucidum, iris, cornea, lens, vitreous humor, retina, reflect light to enhance vision, no
42
New cards
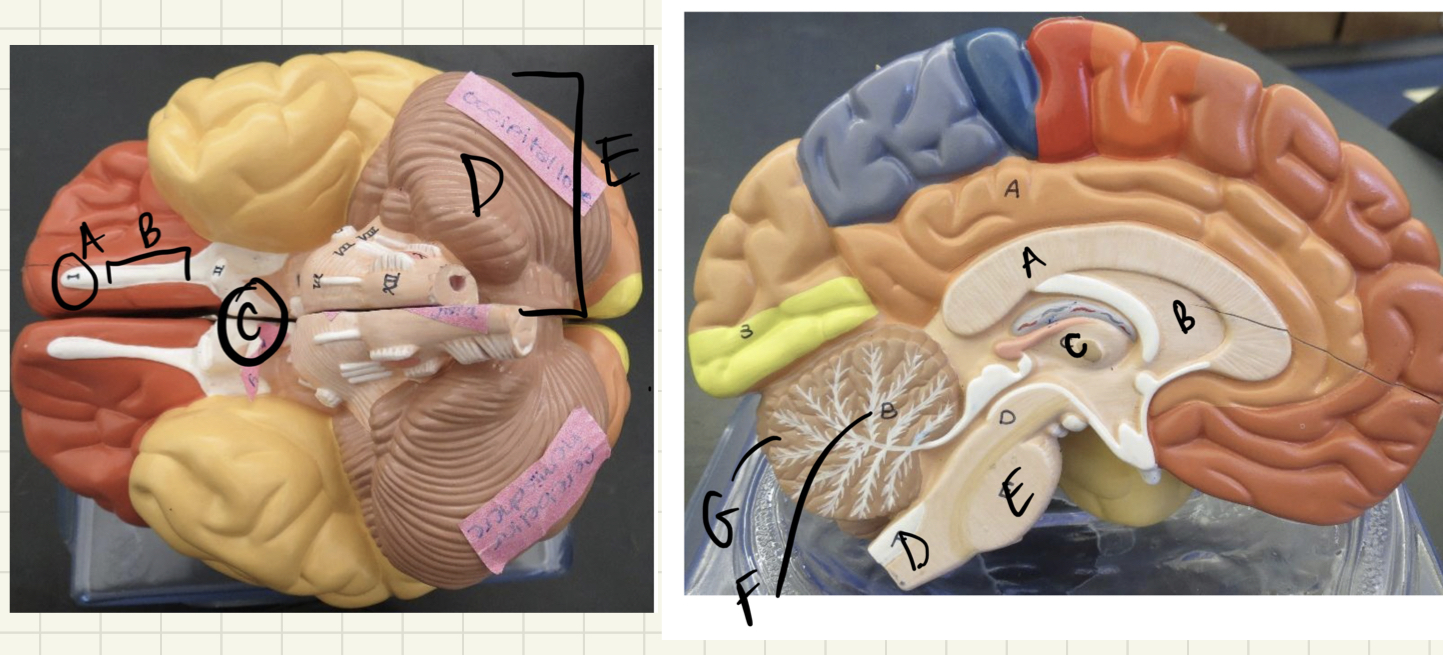
* label
* which part of the brain processes info collected by sensory organs?
* which part of the brain controls high function thoughts?
* which part of the brain maintains basic homeostasis?
* which part of the brain processes info collected by sensory organs?
* which part of the brain controls high function thoughts?
* which part of the brain maintains basic homeostasis?
olfactory bulb, optic nerve, optic chiasma, cerebellum, cerebral hemisphere, corpus callosum, lateral ventricle, thalamus, medulla, pons, white matter, grey matter, midbrain, forebrain, hindbrain
43
New cards
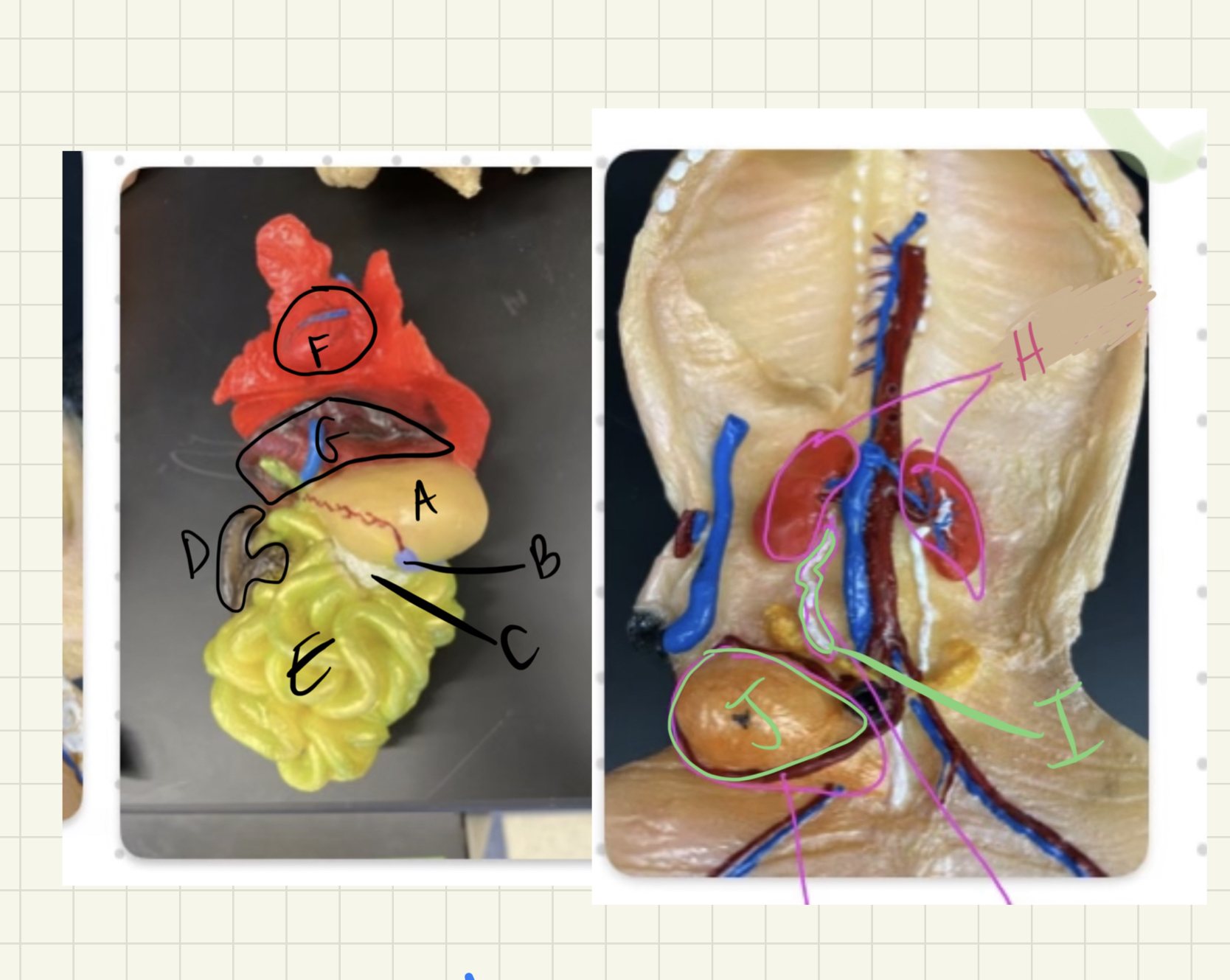
* label
stomach, spleen, pancreas, large intestine, small intestine, heart, liver, kidneys, ureter, urinary bladder
44
New cards
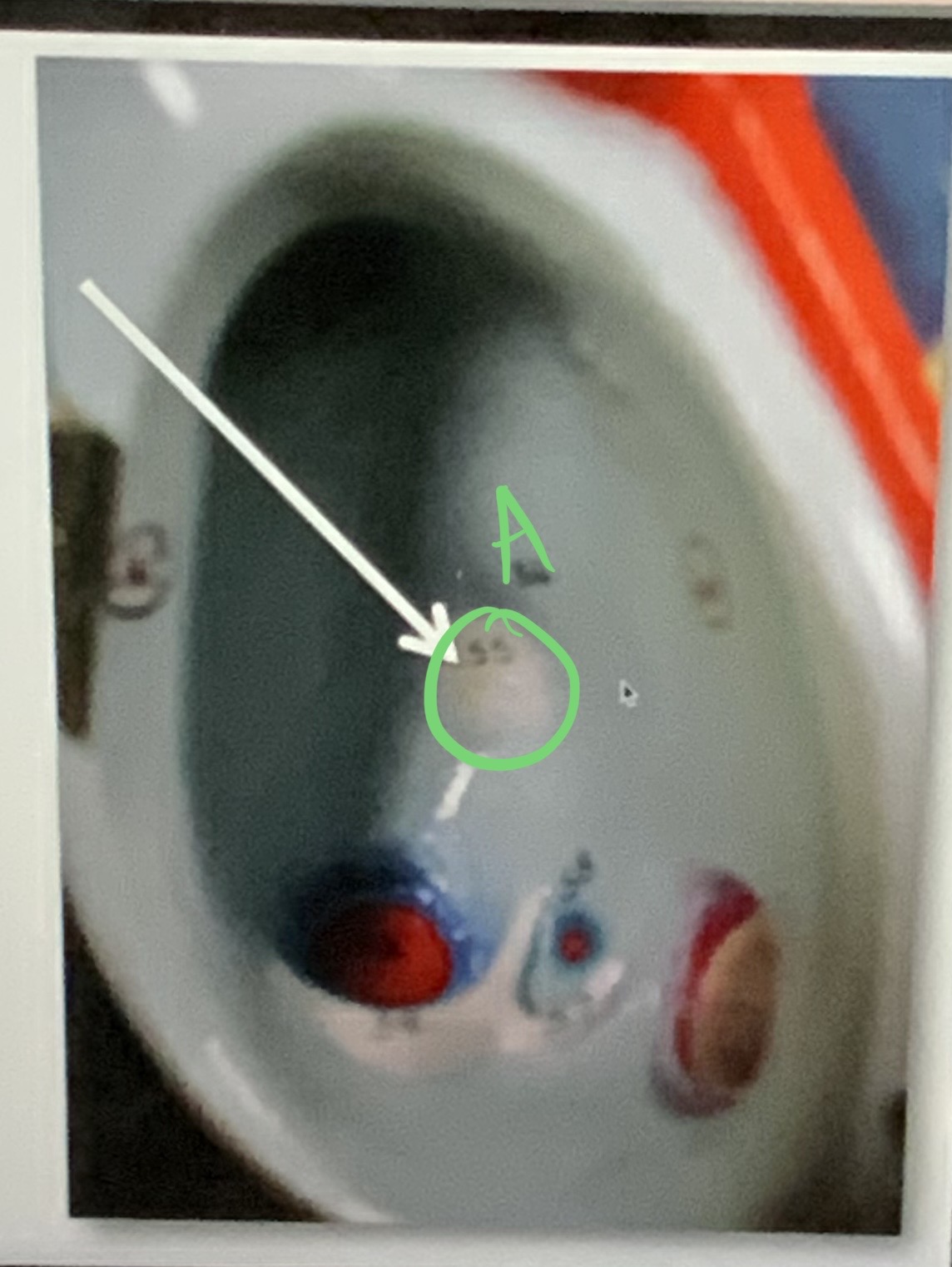

* label
(note: this is located inside right atrium)
(note: this is located inside right atrium)
fossa ovalis
45
New cards
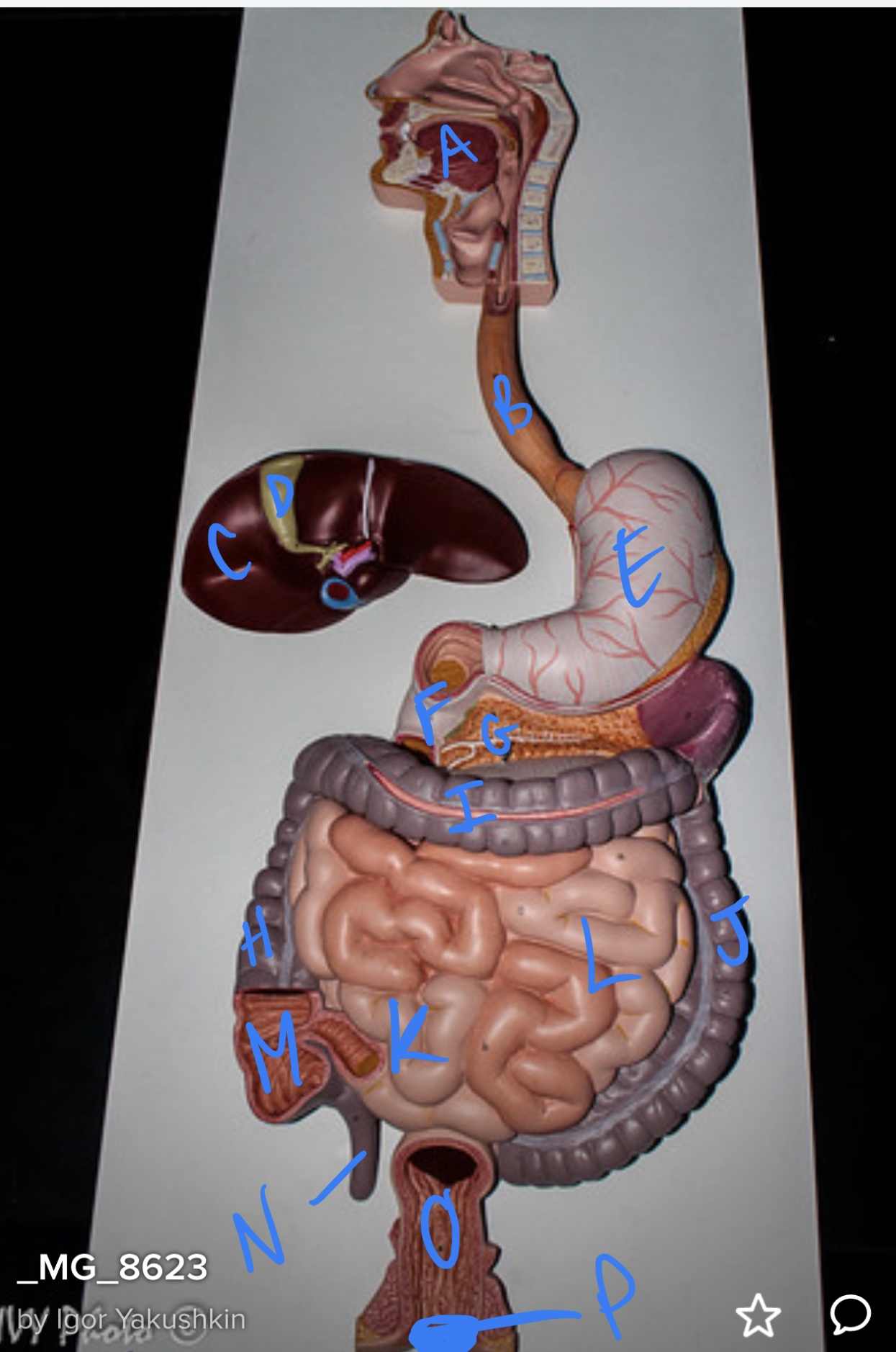
* label
oral cavity, esophagus, liver, gallbladder, stomach, duodenum, pancreas, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, ileum, jejunum, cecum, appendix, rectum, anus
46
New cards
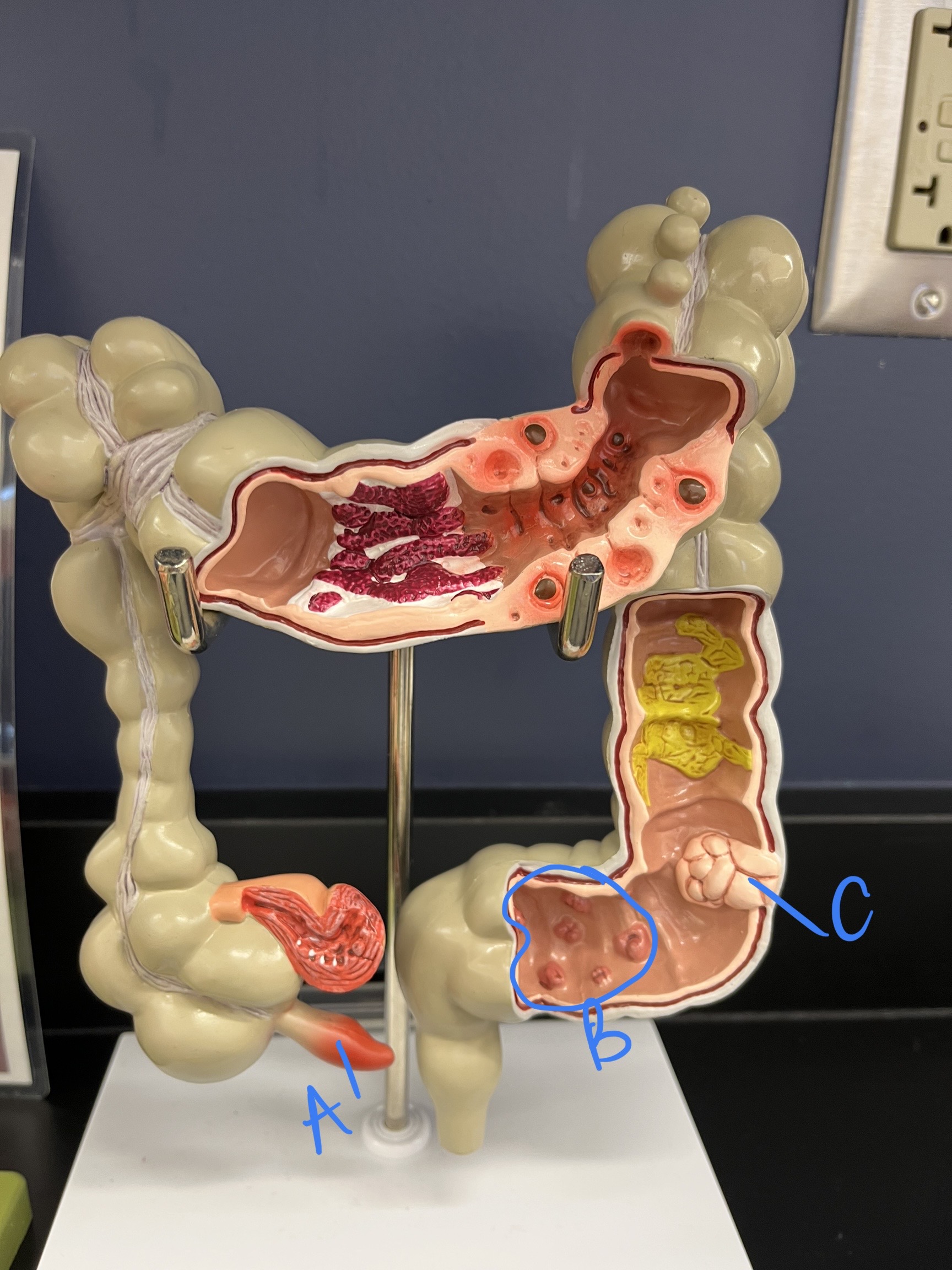
* label
* reccomended age for cancer screening?
* reccomended age for cancer screening?
appendicitis, polyps, cancer, 45-55
47
New cards
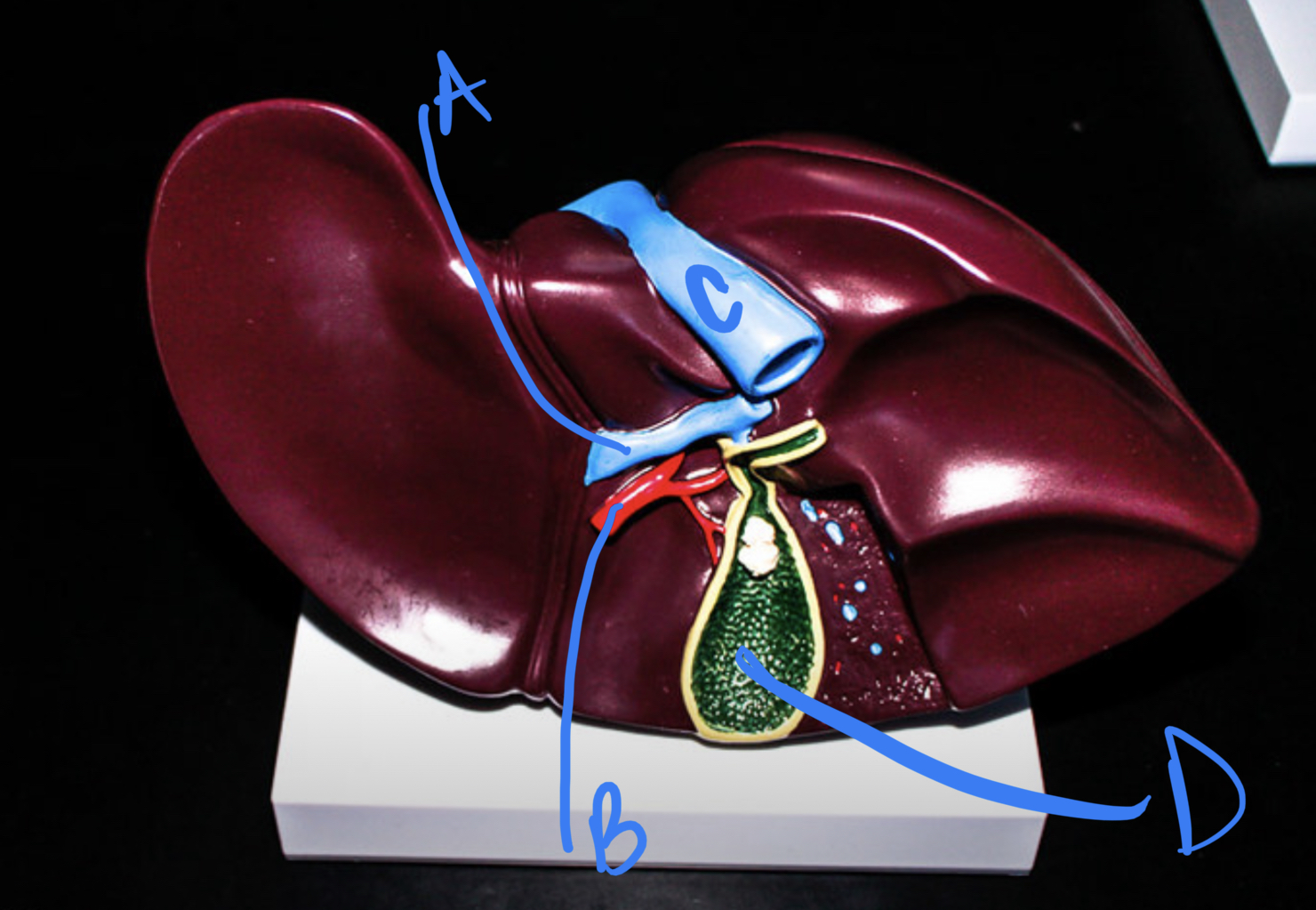
* label
hepatic portal vein, hepatic artery, inferior vena cava, gallbladder
48
New cards
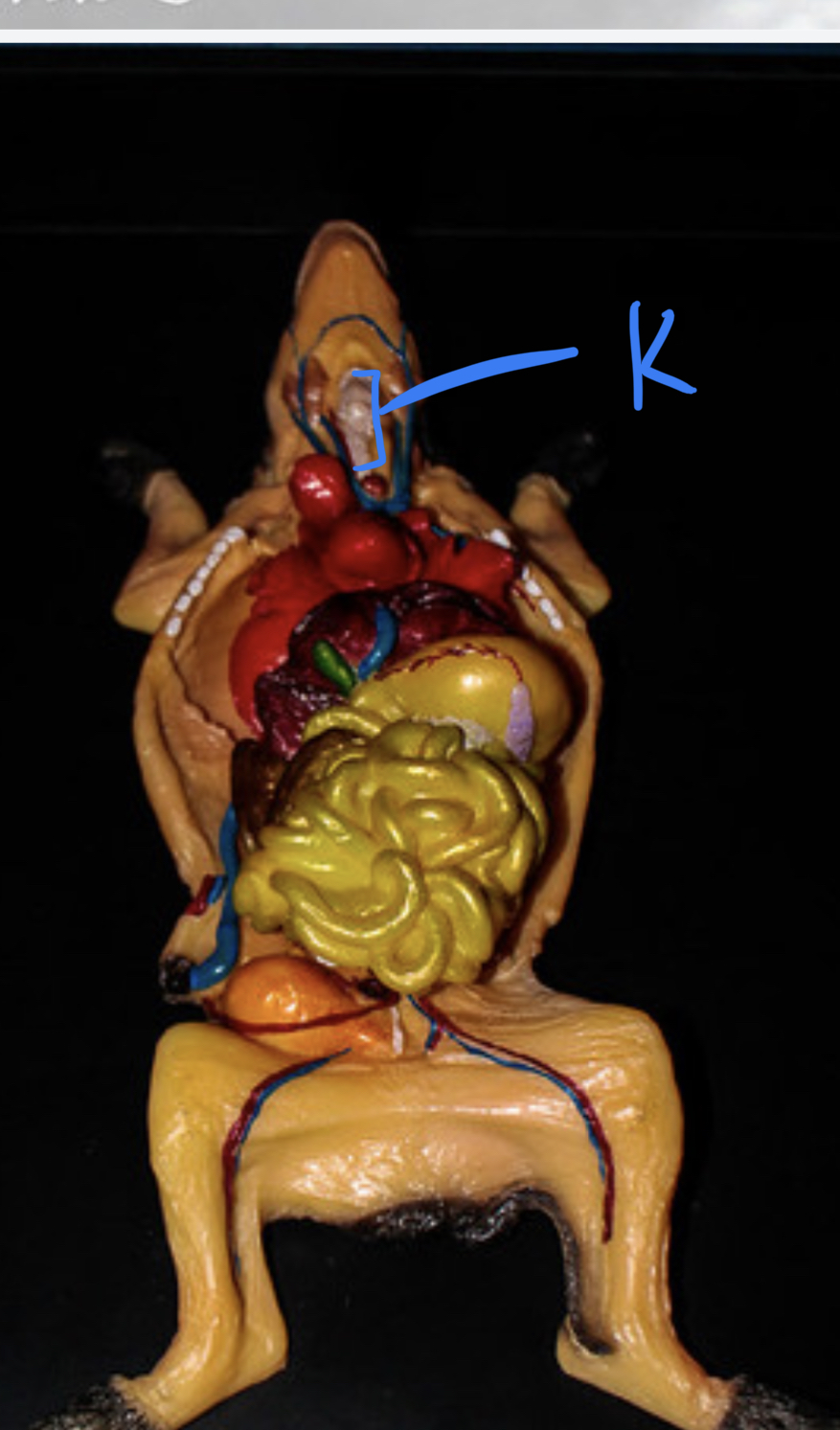
Label
Larynx
49
New cards
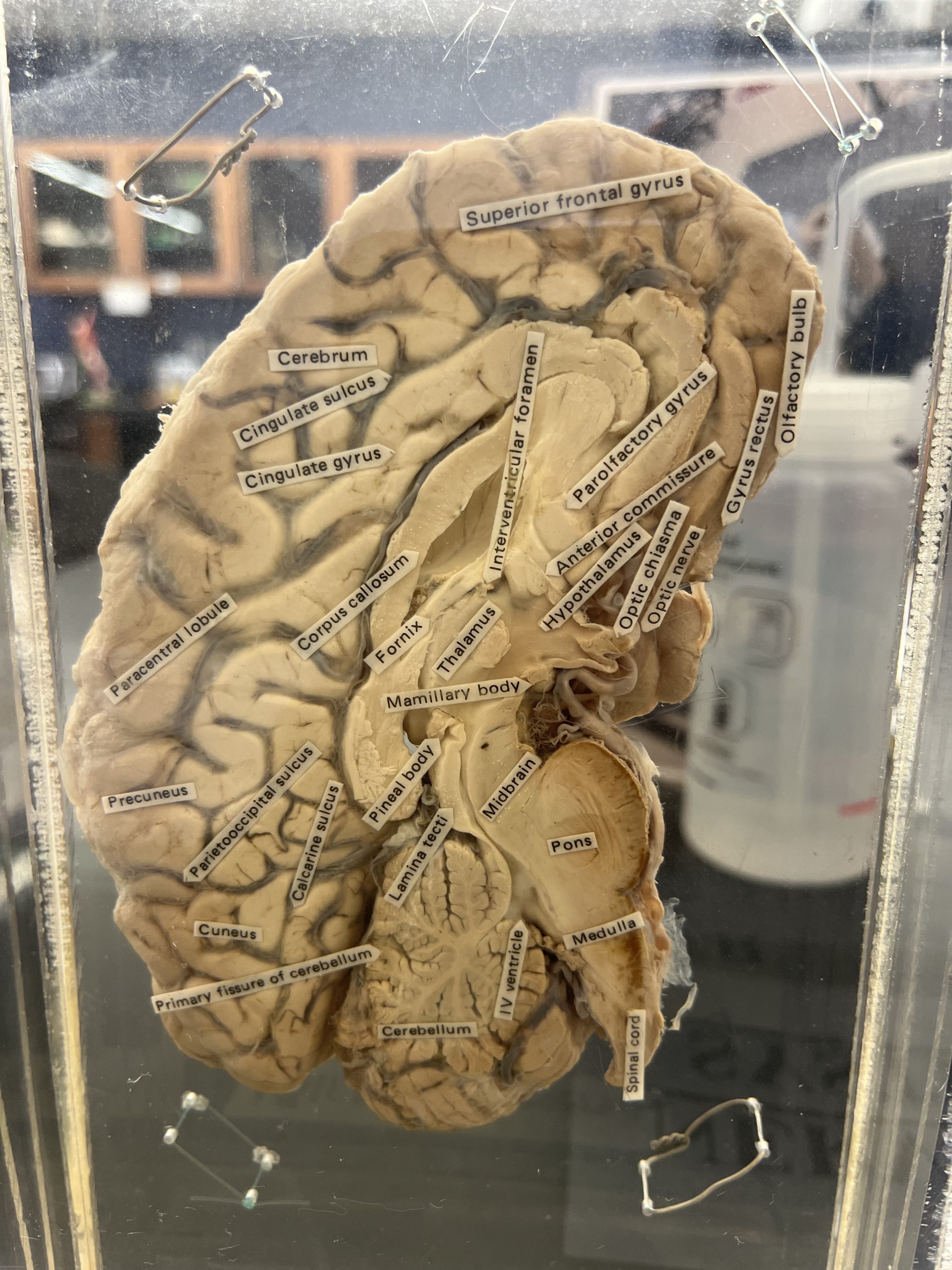
Study this lol
50
New cards
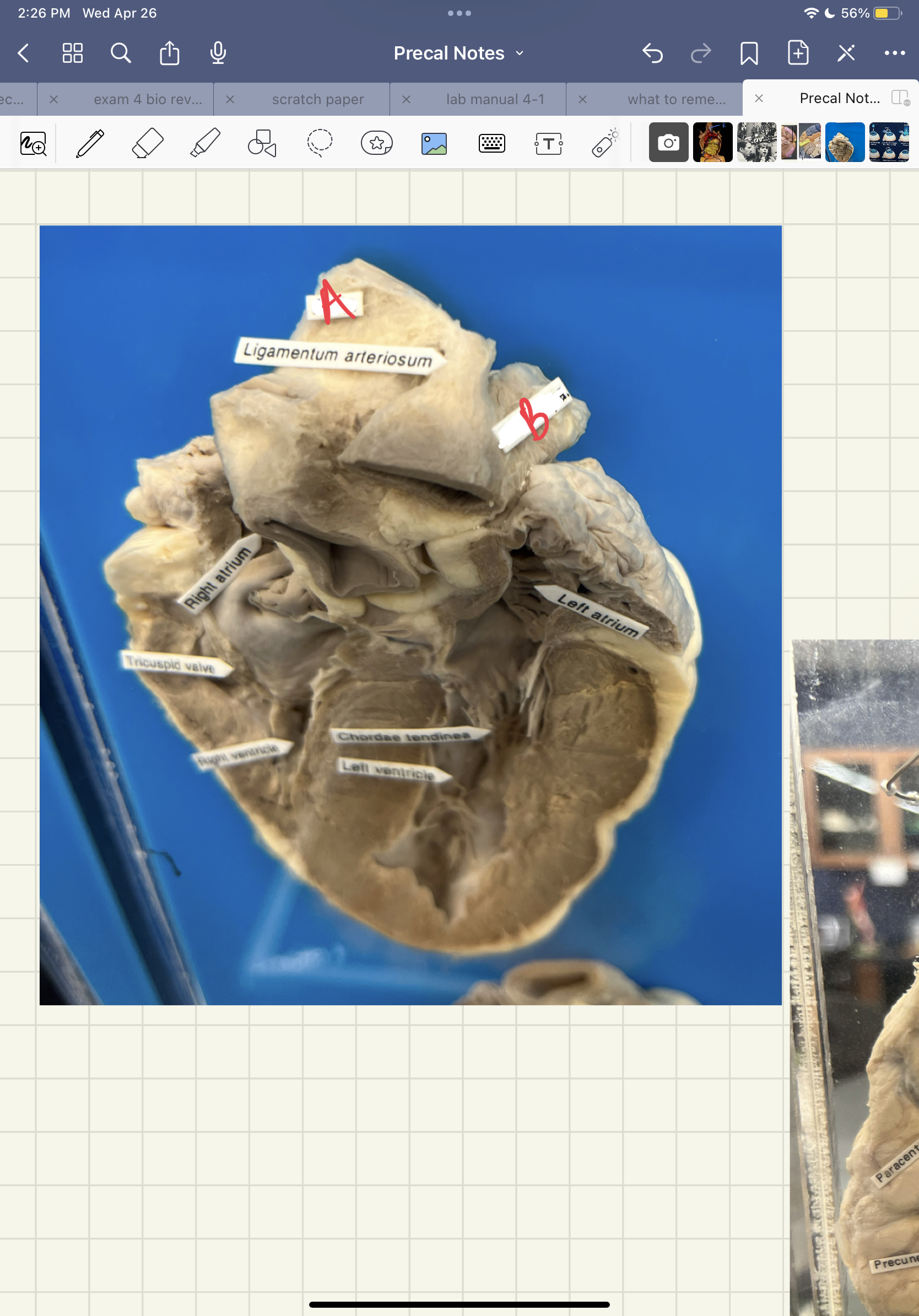
* label
Aorta, pulmonary artery